Numerical Responses of Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on a Diet of Liposcelis decolor (Pearman) (Psocodea: Liposcelididae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rearing of Liposcelis decolor
2.2. Rearing of Xylocoris flavipes
2.3. Experimental Arenas
2.4. Numerical Responses of Adult♀ X. flavipes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Number of Eggs Laid by Adult♀ Xylocoris flavipes
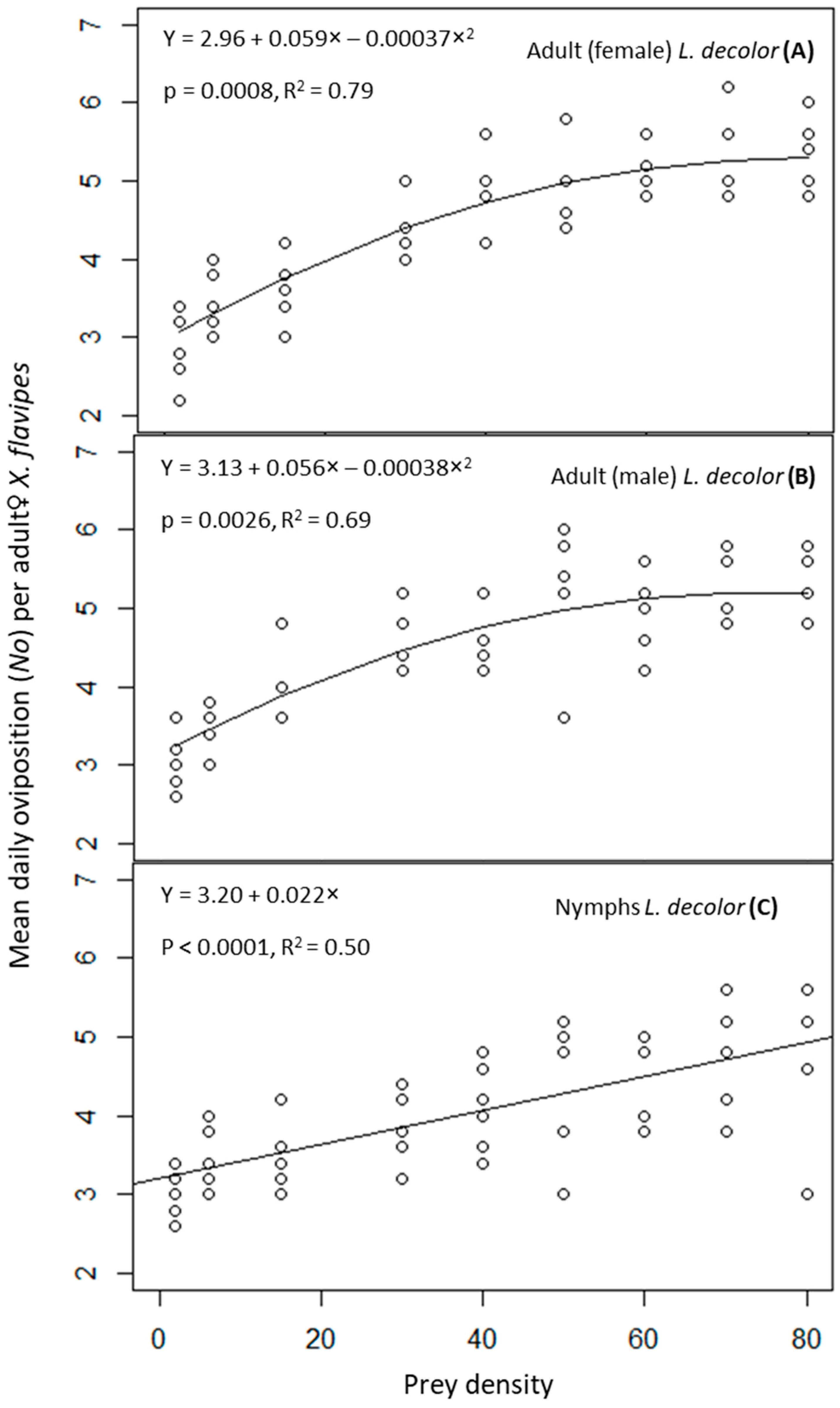
3.2. Oviposition Efficiency of Adult♀ Xylocoris flavipes on a Diet of Liposcelis decolor at Different Developmental Stages and Densities
3.3. Efficiency of Conversion of Ingested Food Resources (ECI) of Adult♀ Xylocoris flavipes on a Diet of Liposcelis decolor at Different Developmental Stages and Densities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phillips, T.W.; Throne, J.E. Biorational approaches to managing stored product insects. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, M.K.; Collins, P.J.; Throne, J.E.; Wang, J.J. Biology and management of psocids infesting stored products. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucerova, Z. Weight loss of wheat grains caused by psocid infestation (Liposcelis bostrychophila: Liposcelididae: Psocoptera). Plant Proctect. Sci. 2002, 38, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.G.; Opit, G.P.; Giles, K.L.; Adam, B. Weight loss and germination failure caused by psocids in different wheat varieties. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, C.G.; Rumbos, C.I. Emerging pests in durable stored products. In Recent Advances in Stored Product Protection; Athanassiou, C.G., Arthur, F.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, J.K.; Opit, G.P.; Noden, B.H.; Giles, K.L. Estimating discriminating doses of phosphine for adults of eight species of psocids of genera Liposcelis (Psocodea: Liposcelididae) and Lepinotus (Psocodea: Trogiidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2022, 99, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbogast, R.T. Cannibalism in Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae), a predator of stored-product insects. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1979, 25, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöller, M.E.; Flinn, P.W.; Grieshop, M.J.; Zd’árková, E. Biological control of stored product pests. In Insect Management for Food Storage and Processing Second Edition; Heaps, J.W., Ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemistry International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2006; pp. 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosomtwe, A.; Opit, G.; Giles, K.; Kard, B.; Goad, C. Functional responses of the warehouse pirate bug Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on a diet of Liposcelis decolor (Pearman) (Psocodea: Liposcelididae). Insects 2025, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrum, D.W.; Subramanyam, B. Fundamentals of Stored-Product Entomology; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Loko, Y.L.; Dansi, A.; Tamo, M.; Bokonon-Gantaa, H.; Assogba, P.; Dansi, M.; Vodouhe’, R.; Akoegninou, A.; Sanni, A. Storage insects on yam chips and their traditional management in Northern Benin. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 484536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basumatary, M.M.; Patgiri, P.; Handique, G. First report of warehouse pirate bug (Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on stored paddy from north-east India. Insect Environ. 2013, 19, 94–95. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, M.E. The natural control of animal populations. J. Anim. Ecol. 1949, 18, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, P.J.; Harmsen, R. Functional and numerical responses do not always indicate the most effective predator for biological control: An analysis of two predators in a two-prey system. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 39, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, V.J.; Babu, A.; Roobakkumar, A.; Perumalsamy, K. Functional and numerical responses of the predatory mite, Neoseiulus longispinosus to the red spider mites, Oligonychus coffeae, infesting tea. J. Insect Sci. 2012, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danso, J.K.; Opit, G.P.; Giles, K.L.; Noden, B.H. Numerical responses of the predatory mites, Cheyletus eruditus (Trombidiformes: Cheyletidae) and Cheyletus malaccensis to Liposcelis decolor (Psocodea: Liposcelididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawley, M.J. The numerical responses of insect predators to changes in prey density. J. Anim. Ecol. 1975, 44, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffaker, C.B.; Shea, K.P.; Herman, S.G. Experimental studies on predator: Complex dispersion and levels of food in an acarine predator-prey interaction. Hilgardia 1963, 34, 305–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omkar, O.; Pervez, A. Functional and numerical responses of Propylea dissecta (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Appl. Ento. 2004, 128, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madahi, K.; Sahragard, A.; Hosseini, R. Predation rate and numerical response of Aphidoletes aphidimyza feeding on different densities of Aphis craccivora. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedola, C.V.; Sanchez, N.L.; Lijesthrom, G. Effect of tomato leaf hairiness on functional and numerical response of Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2001, 25, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C. Growth and development of coccinellid larvae on dry foods (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Can. Entomol. 1965, 97, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.F.; Truzi, C.C.; Veiga, A.C.P.; Sipriano-Nascimento, T.P.; Vacari, A.M.; De Bortoli, S.A. Life table of Xylocoris afer (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) feeding on eggs of Corcyra cephalonica (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J. Asi. Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockford, E.L. North American Psocoptera (Insecta); CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, J.; Howard, R.W. A proposed role for the cuticular fatty amides of Liposcelis bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelidae) in preventing adhesion of entomopathogenic fungi with dry-conidia. Mycopathologia 2004, 158, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, M.K. Psocid and mite pests of stored commodities: Small but formidable enemies. In Proceedings of the 9th International Working Conference on Stored Product Protection, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 15–18 October 2006; Volume 15, pp. 1061–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Danso, J.K.; Opit, G.P.; Goad, C.L.; Noden, B.H.; Giles, K.L. Functional responses of predatory mites, Cheyletus eruditus (Schrank) and Cheyletus malaccensis Oudemans (Trombidiformes: Cheyletidae) to Liposcelis decolor (Pearman) (Psocodea: Liposcelididae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2023, 103, 102–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathipour, Y.; Maleknia, B. Functional response and predation rate of Agistemus pistaciae (Acari: Stigmaeidae) on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) at different temperatures. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 21, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Opit, G.P.; Throne, J.E. Population growth and development of the psocid Lepinotus reticulatus at constant temperatures and relative humidities. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opit, G.P.; Roitberg, B.; Gillespie, D.R. The functional response and prey preference of Feltiella acarisuga (Vollot) (Diptera: Cecidomiidae) for two of its prey: Male and female two-spotted spider mites, Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychiidae). Can. Entomol. 1997, 129, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, J.A.J.; Sabelis, M.W.; Kuchlein, J.H. Sources of variation in predation rate at high prey densities: An analytic model and a mite example. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1988, 5, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, B.E.; Phillips, T.W. Functional response of Xylocoris flavipes (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) effects of prey species and habitat. Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabelis, M.W.; Janssen, A. Evolution of life-history patterns in the Phytoseiidae. In Mites: Ecological and Evolutionary Analyses of Life-History Patterns; Houck, M.A., Ed.; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1944; pp. 70–99. [Google Scholar]
- Milonas, P.G.; Partsinevelos, G.; Martinou, A.F. Patch assessment for oviposition by a predator: The effect of prey density and prey oviposition period. J. Insect Behav. 2015, 28, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubl, P.; Blackmore, V.; Johnson, J.C. Wasteful killing in urban black widows: Gluttony in response to food abundance. Ethology 2011, 117, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounibos, L.P.; Makhni, S.; Alto, B.W.; Kesavaraju, B. Surplus killing by predatory larvae of Corethrella appendiculata: Prepupal timing and site-specific attack on mosquito prey. J. Insect Behav. 2008, 21, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lecato, G.L.; Collins, H.L. Laboratory rearing of Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on a diet of Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) eggs. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1976, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, J.H.; Press, J.W. Suppression of residual populations of stored-product pests in empty corn bins by releasing the predator Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter). Biocontrol 1992, 2, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarkwah, C.; Obeng-Ofori, D.; Opuni-Frimpong, E.; Ulrichs, C.; Schöller, M. Predator-parasitoid-host interaction: Biological control of Rhyzopertha dominica and Sitophilus oryzae by a combination of Xylocoris flavipes and Theocolax elegans in stored cereals. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2018, 167, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Zhang, Z.Q. Prey preference and reproduction of predatory mites, Amblybromalus limonicus and Neoseiulus cucumeris, on eggs of and 1st instar nymphs of the Tomato/Potato Psyllid. Int. J. Acarol. 2017, 43, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddick, E.W.; Dindo, M.L.; Grodowitz, M.J.; Cottrell, T.E. Oviposition strategies in beneficial insects. Int. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 10, 1179543318787160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Fan, Y.; Mo, W.; Xin, T.; Xia, B.; Zou, Z. Functional response of adult Cheyletus malaccensis (Acari: Cheyletidae) to different developmental stages of Aleuroglyphus ovatus (Acari: Acaridae). J. Stored Prod. 2019, 84, 101–525. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jee/article/116/4/1447/7205414 (accessed on 23 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Shannag, H.K.; Obeidat, W.M. Interaction between plant resistance and predation of Aphis fabae (Homoptera: Aphididae) by Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2008, 152, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loko, Y.L.E.; Toffa, J.; Gavoedo, D.M. Effect of population density on oviposition, development, and survival of Alloeocranum biannulipes (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) preying on Dinoderus porcellus (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae). J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2022, 83, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Predator | Variable | Source | Df | F | p–Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult♀ X. flavipes | No | PS | 2, 135 | 0.60 | 0.5492 |
| N | 8, 135 | 2.29 | 0.0247 | ||
| PS*N | 16, 135 | 0.05 | 1.0000 | ||
| No/N | PS | 2, 135 | 0.15 | 0.8630 | |
| N | 8, 135 | 20.72 | <0.0001 | ||
| PS*N | 16, 135 | 0.01 | 1.0000 | ||
| ECI | PS | 2, 135 | 0.02 | 0.9782 | |
| N | 8, 135 | 14.42 | <0.0001 | ||
| PS*N | 16, 135 | 0.01 | 1.0000 |
| Predator | Prey Density (N) | Eggs Laid per Predator (No) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prey Stage | ||||
| Female | Male | Nymph | ||
| Adult♀ X. flavipes | 2 | 2.93 ± 0.67 B | 3.07 ± 0.72 B | 3.07 ± 0.71 B |
| 6 | 3.53 ± 0.77 AB | 3.50 ± 0.76 AB | 3.53 ± 0.77 AB | |
| 15 | 3.63 ± 0.78 AB | 4.00 ± 0.82 AB | 3.50 ± 0.76 AB | |
| 30 | 4.40 ± 0.86 A | 4.70 ± 0.89 A | 3.80 ± 0.80 AB | |
| 40 | 4.90 ± 0.90 A | 4.67 ± 0.88 A | 4.10 ± 0.83 AB | |
| 50 | 4.83 ± 0.90 A | 4.93 ± 0.91 A | 4.43 ± 0.86 A | |
| 60 | 5.10 ± 0.92 A | 4.97 ± 0.91 A | 4.37 ± 0.85 A | |
| 70 | 5.33 ± 0.94 A | 5.20 ± 0.93 A | 4.80 ± 0.89 A | |
| 80 | 5.30 ± 0.94 A | 5.30 ± 0.94 A | 4.87 ± 0.90 A | |
| Predator | Prey Density (N) | Oviposition Efficiency (No/N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prey Stage | ||||
| Female | Male | Nymph | ||
| Adult♀ X. flavipes | 2 | 1.47 ± 0.60 A | 1.53 ± 0.63 A | 1.53 ± 0.63 A |
| 6 | 0.59 ± 0.24 B | 0.58 ± 0.24 B | 0.59 ± 0.24 B | |
| 15 | 0.24 ± 0.10 C | 0.27 ± 0.11 BC | 0.23 ± 0.10 C | |
| 30 | 0.15 ± 0.06 C | 0.16 ± 0.06 C | 0.13 ± 0.05 C | |
| 40 | 0.12 ± 0.05 C | 0.12 ± 0.05 C | 0.10 ± 0.04 C | |
| 50 | 0.10 ± 0.04 C | 0.10 ± 0.04 C | 0.09 ± 0.04 C | |
| 60 | 0.09 ± 0.03 C | 0.08 ± 0.03 C | 0.07 ± 0.03 C | |
| 70 | 0.08 ± 0.03 C | 0.07 ± 0.03 C | 0.07 ± 0.03 C | |
| 80 | 0.07 ± 0.03 C | 0.07 ± 0.03 C | 0.06 ± 0.02 C | |
| Predator | Prey Density (N) | Efficiency of Conversion of Ingested Food Resources (ECI)% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prey Stage | ||||
| Female | Male | Nymph | ||
| Adult♀ X. flavipes | 2 | 149.07 ± 60.86 A | 153.33 ± 62.60 A | 156.11 ± 63.73 A |
| 6 | 59.79 ± 24.41 B | 59.01 ± 24.09 B | 60.93 ± 24.87 B | |
| 15 | 27.43 ± 11.20 BC | 28.76 ± 11.74 BC | 26.49 ± 10.81 BC | |
| 30 | 19.15 ± 7.82 C | 18.72 ± 7.64 C | 16.42 ± 6.71 C | |
| 40 | 16.11 ± 6.58 C | 14.51 ± 5.92 C | 14.76 ± 6.03 C | |
| 50 | 12.63 ± 5.16 C | 13.60 ± 5.55 C | 12.40 ± 5.06 C | |
| 60 | 12.34 ± 5.04 C | 11.12 ± 4.54 C | 11.31 ± 4.62 C | |
| 70 | 12.50 ± 5.10 C | 11.37 ± 4.64 C | 12.22 ± 4.99 C | |
| 80 | 12.45 ± 5.08 C | 11.61 ± 4.74 C | 12.31 ± 5.02 C | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bosomtwe, A.; Opit, G.; Goad, C.; Giles, K.; Kard, B. Numerical Responses of Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on a Diet of Liposcelis decolor (Pearman) (Psocodea: Liposcelididae). Insects 2025, 16, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030296
Bosomtwe A, Opit G, Goad C, Giles K, Kard B. Numerical Responses of Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on a Diet of Liposcelis decolor (Pearman) (Psocodea: Liposcelididae). Insects. 2025; 16(3):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030296
Chicago/Turabian StyleBosomtwe, Augustine, George Opit, Carla Goad, Kristopher Giles, and Brad Kard. 2025. "Numerical Responses of Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on a Diet of Liposcelis decolor (Pearman) (Psocodea: Liposcelididae)" Insects 16, no. 3: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030296
APA StyleBosomtwe, A., Opit, G., Goad, C., Giles, K., & Kard, B. (2025). Numerical Responses of Xylocoris flavipes (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) on a Diet of Liposcelis decolor (Pearman) (Psocodea: Liposcelididae). Insects, 16(3), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030296





