Life History and the Relation Between Population Dynamics and Meteorological Factors of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiidae) in Shanghai, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigation on the Biology of H. cunea in Shanghai
2.2. Monitoring of H. cunea Population Dynamics in Shanghai
2.3. Meteorological Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
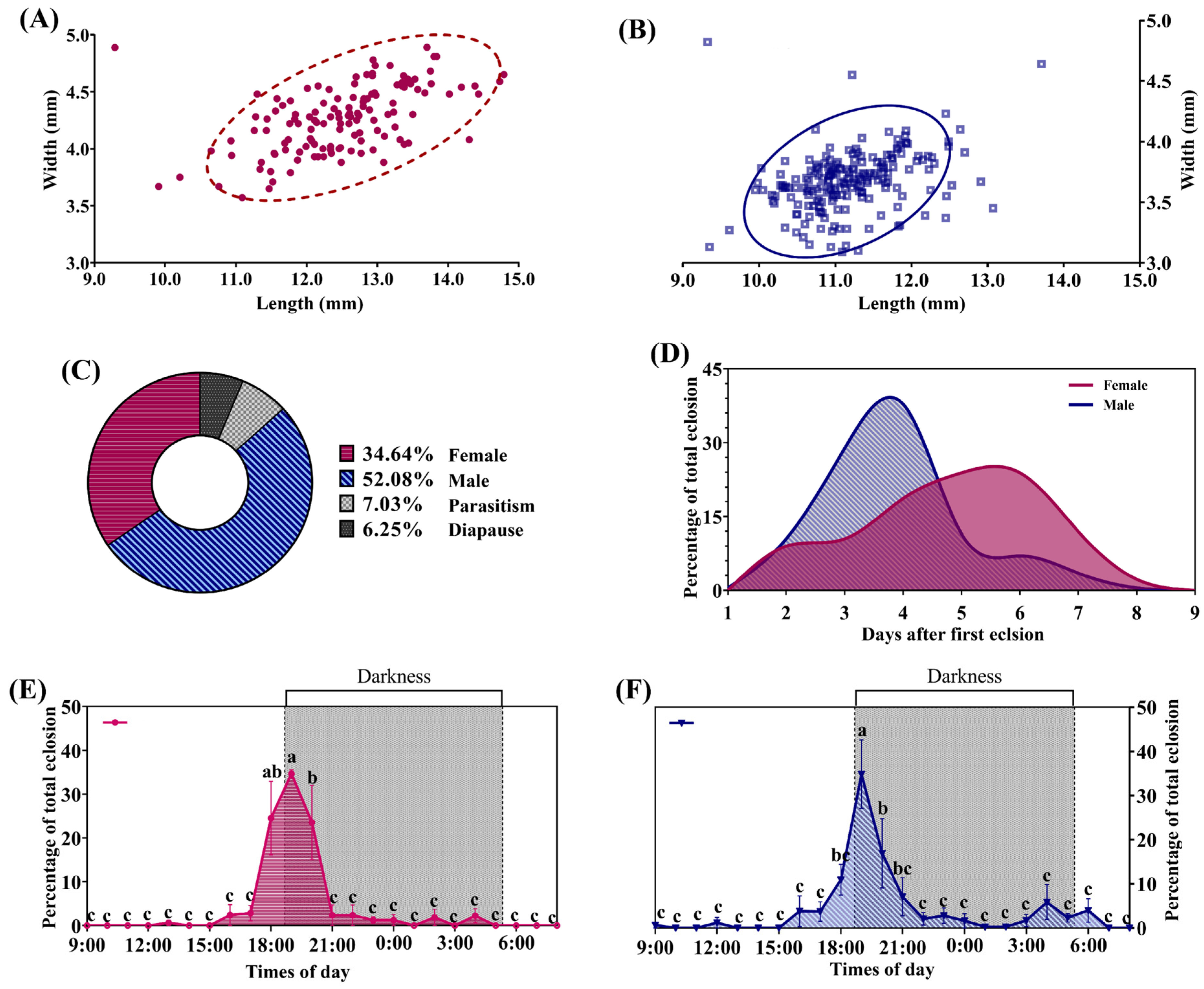
3.1. Biology of H. cunea in Shanghai
3.2. Population Dynamics of H. cunea in Shanghai
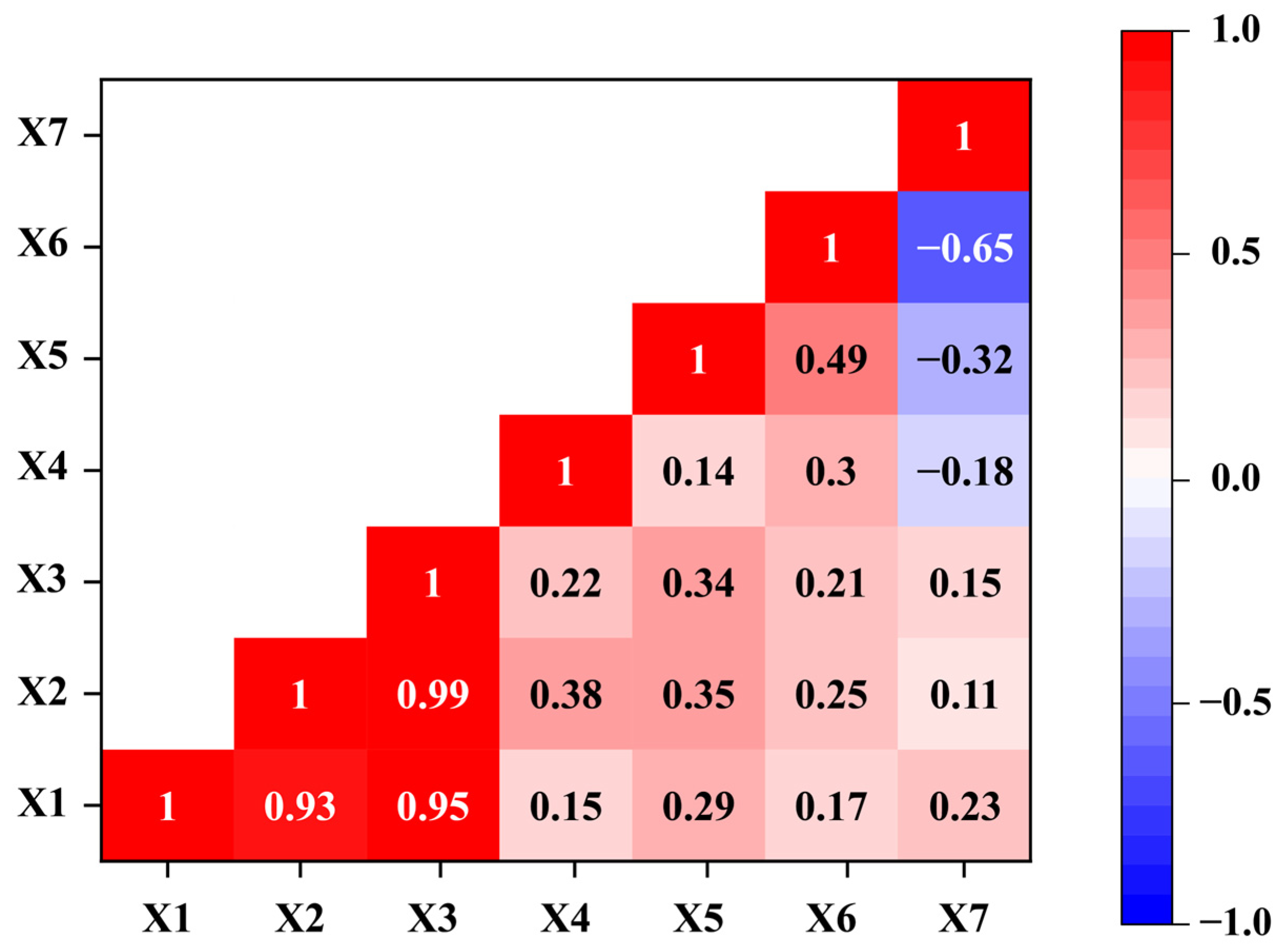
3.3. Principal Component Analysis of Meteorological Factors
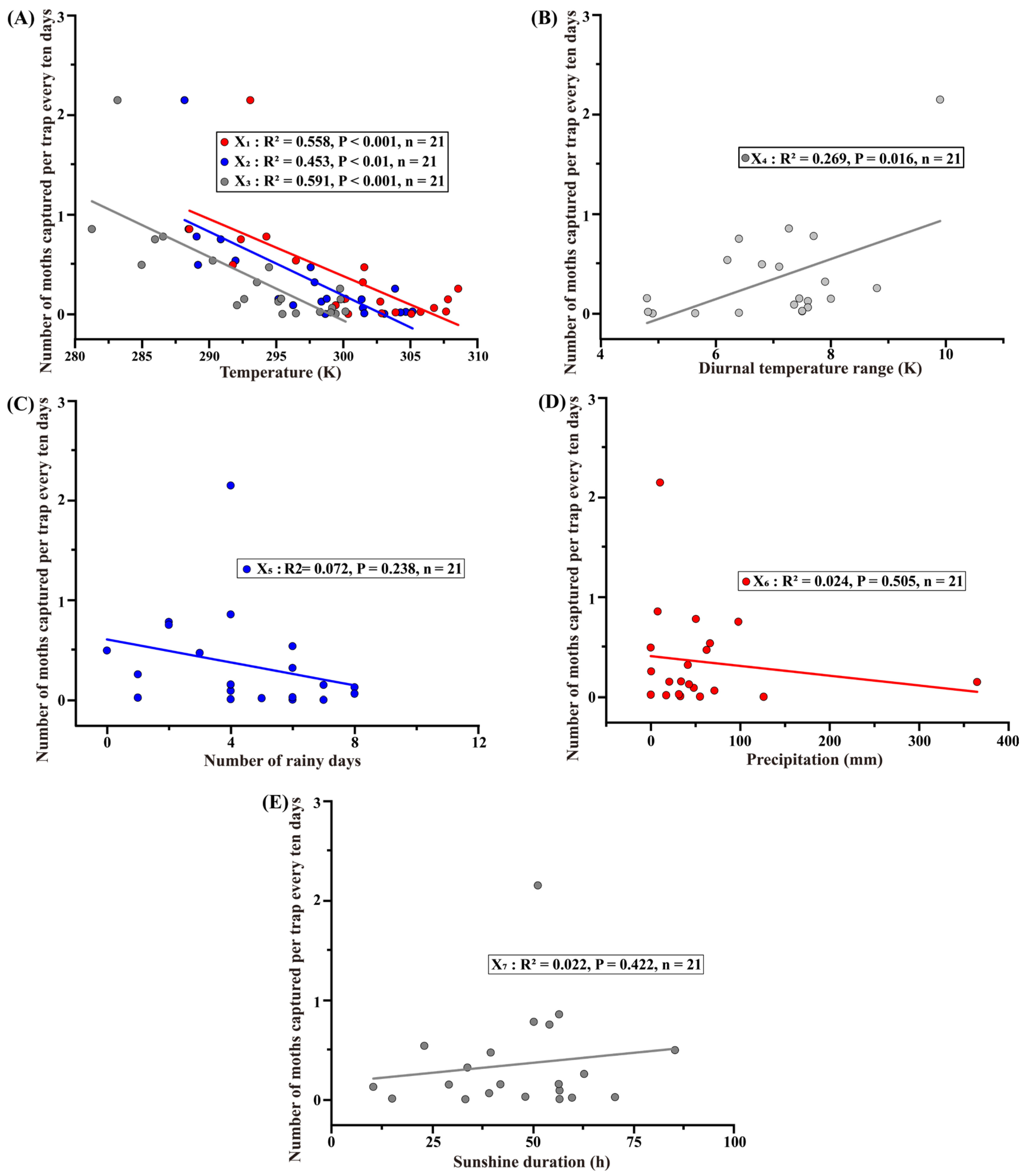
3.4. Correlation Between Meteorological Factors and Population Dynamics of H. cunea in Shanghai
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schowalter, T.D.; Ring, D.R. Biology and Management of the Fall Webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2017, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Geng, Y.; Hao, D.; Dai, L.; Sun, S. Research Progress and Prospect of the Control Technology of Hyphantria cunea. For. Pest Dis. 2022, 41, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, F.; Arbetman, M.; Toth, A.L. A Potential Role for Phenotypic Plasticity in Invasions and Declines of Social Insects. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, K.; Tollrian, R. Inducible Defences as Key Adaptations for the Successful Invasion of Daphnia lumholtzi in North America? Proc. R. Soc. B 2009, 276, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glon, M.G.; Reisinger, L.S.; Pintor, L.M. Biogeographic Differences between Native and Non-Native Populations of Crayfish Alter Species Coexistence and Trophic Interactions in Mesocosms. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 3475–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Q. Occurrence, Forest Control Status and Prospect of Fall-Webworm (Hyphantria cunea Drury) in China. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2022, 53, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G. Occurrence Regularity of Hyphantria cunea in Jinshan District of Shanghai. For. Pest Dis. 2022, 41, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; He, S.; Zhu, C.; Wang, T.; Xu, Z.; Zong, S. Projecting the Current and Future Potential Global Distribution of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae) Using CLIMEX. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, T.D. Temporal and Spatial Foraging Behavior of the Larvae of the Fall Webworm Hyphantria cunea. Psyche 2015, 2015, 359765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Hyphantria cunea (Drury) in Beijing and Its Influencing Factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 5480–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wei, X.; Xiao, H.; He, H.; Xia, Q.; Xue, F. Diapause Induction and Termination in Hyphantria cunea (Drury) (Lepidoptera: Arctiinae). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Nagasaka, M.; Fukuda, T.; Hagihara, H. Shifting of the Life Cycle and Life-history Traits of the Fall Webworm in Relation to Climate Change. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2007, 125, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xu, M.; Zhao, L. Plasticity of Life-History Traits and Adult Fitness of Fall Webworm in Relation to Climate Change. Insects 2024, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Yang, L.; Han, S.; Cao, B. Effects of High Temperature on the Growth and Development of Hyphantria cunea. Shandong For. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Bangay, R.; Tuno, N. Mild Winter Causes Increased Mortality in the Fall Webworm Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Insects 2023, 14, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.F.; Fulton, W.C. Models for the Development and Survival of Hyphantria cunea in Relation to Temperature and Humidity: Introduction. Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 1970, 102, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothill, J.D. The Natural Control of the Fall Web Worm (Hyphantria cunea, Drury) in Canada, Together with an Account of Its Several Parasites; Canada’s Department of Agriculture: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1922; pp. 5–34. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, R.F. The Value of Historical Data in Population Research, with Particular Reference to Hyphantria cunea Drury. The Can. Entomol. 1964, 96, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Zhao, V.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Hao, D. Trapping Activity of Sex Pheromone Lure Synthesized Independently of Hyphantria cunea in Forest and Its Application. For. Pest Dis. 2022, 41, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L. Insect-Plant Correlation Under Environmental Stress. Chin. J. Ecol. 1995, 14, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczek, A.P. Phenotypic Plasticity and Diversity in Insects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyche, L. Fall Webworm: A Guide to Recognition and Habits in Alabama; Alabama Agricultural Experiment Station: Auburn, AL, USA, 1999; Circular 324; pp. 1–9. Available online: https://aurora.auburn.edu/handle/11200/2104 (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Lees, A.D. The Physiology and Biochemistry of Diapause. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1956, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L. Difference in Nutrient Accumulation Patterns between Diapause-destined and Non-diapause-destined Larvae of Hyphantria cunea. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2023, 171, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Takeda, S. The Adult Eclosion Rhythm in Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae): Endogenous and Exogenous Light Effects. Biol. Rhythm Res. 1994, 25, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Cao, M. Research Progress in the Management of Fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Drury) (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). J. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 40, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandehson, D.E. The Relation of Temperature to the Growth of Insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 1910, 3, 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Régnière, J.; Powell, J.; Bentz, B.; Nealis, V. Effects of Temperature on Development, Survival and Reproduction of Insects: Experimental Design, Data Analysis and Modeling. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissold, F.J.; Simpson, S.J. Temperature, Food Quality and Life History Traits of Herbivorous Insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zuo, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Teng, F.; Hao, D. A Description of Temperature-Dependent Development to Infer Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae) and Its Application to Predict the Species Voltinism in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2025, 118, 1762–1771, Erratum in J. Econ. Entomol. 2025, 118, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Teng, F.; Zhong, G.; Xue, M.; Li, H.; Hao, D. Effects of Long-Term Thermal Stress on Population Dynamics and HSP70 Expression of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2025, 118, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Cui, D. The Involvement of Human Factors Brings New Findings for Predicting Global Suitability Habitat for Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e71421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fleischer, S.J.; Saunders, M.C.; Thomas, M.B. The Influence of Diurnal Temperature Variation on Degree-Day Accumulation and Insect Life History. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriber, J.M.; Sonke, B. Effects of Diurnal Temperature Range on Adult Size and Emergence Times from Diapausing Pupae in Papilio glaucus and P. canadensis (Papilionidae). Insect Sci. 2011, 18, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Zhao, F.; Ma, C.-S. Wide Diurnal Temperature Variation Inhibits Larval Development and Adult Reproduction in the Diamondback Moth. J. Therm. Biol. 2019, 84, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terblanche, J.S.; Nyamukondiwa, C.; Kleynhans, E. Thermal Variability Alters Climatic Stress Resistance and Plastic Responses in a Globally Invasive Pest, the Mediterranean Fruit Fly (Ceratitis capitata). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 137, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dooremalen, C.; Suring, W.; Ellers, J. Fatty Acid Composition and Extreme Temperature Tolerance Following Exposure to Fluctuating Temperatures in a Soil Arthropod. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, F.T.; Stanewsky, R. Temperature Synchronization of the Drosophila Circadian Clock. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; An, H.; King-Jones, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, W. Noncanonical Action of Circadian Clock Genes Controls Winter Diapause Entry via the NuA4/TIP60 Complex in Harmonia axyridis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2510550122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensing, L.; Ruoff, P. Temperature Effect on Entrainment, Phase Shifting, and Amplitude of Circadian Clocks and Its Molecular Bases. Chronobiol. Int. 2002, 19, 807–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horák, J.; Rada, P.; Lettenmaiera, L.; Andreasa, M.; Boguscha, P.; Jaworskic, T. Importance of meteorological and land use parameters for insect diversity in agricultural landscapes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Initial Eigenvalues | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Eigenvalues | Percentage of Variance (%) | Cumulative (%) | Factor | Eigenvalues | Percentage of Variance (%) | Cumulative (%) |
| F1 | 3.294 | 47.060 | 47.060 | F1 | 3.095 | 44.208 | 44.208 |
| F2 | 1.953 | 27.900 | 74.960 | F2 | 1.988 | 28.395 | 72.602 |
| F3 | 0.895 | 12.780 | 87.740 | F3 | 1.060 | 15.138 | 87.740 |
| F4 | 0.532 | 7.603 | 95.343 | ||||
| F5 | 0.270 | 3.861 | 99.205 | ||||
| F6 | 0.056 | 0.795 | 100.000 | ||||
| F7 | 3.423 × 10−8 | 4.889 × 10−7 | 100.000 | ||||
| Factor Matrix | Rotated Factor Matrix | Factor Score Coefficient Matrix | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F3 |
| X1 | 0.910 | 0.330 | −0.106 | 0.974 | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.330 | −0.035 | −0.094 |
| X2 | 0.969 | 0.196 | 0.074 | 0.960 | 0.095 | 0.229 | 0.298 | −0.026 | 0.117 |
| X3 | 0.949 | 0.259 | −0.071 | 0.981 | 0.074 | 0.073 | 0.324 | −0.010 | −0.045 |
| X4 | 0.401 | −0.296 | 0.836 | 0.167 | 0.147 | 0.948 | −0.053 | −0.097 | 0.949 |
| X5 | 0.528 | −0.480 | −0.409 | 0.371 | 0.715 | −0.165 | 0.118 | 0.405 | −0.343 |
| X6 | 0.434 | −0.784 | −0.061 | 0.136 | 0.860 | 0.217 | −0.010 | 0.424 | 0.057 |
| X7 | −0.028 | 0.898 | 0.047 | 0.283 | −0.837 | −0.170 | 0.147 | −0.435 | −0.059 |
| Dependent Variable | Meteorological Factors | Regression Equation | Coefficient of Determination | ANOVA | VIF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | The numbers of moths captured per trap every 10 days | X3 | 10-day average minimum temperature | Y = −0.057X3 − 0.144X4 + 16.154 | R2 = 0.723 | F = 23.547 p < 0.001 | 1.048 |
| X4 | 10-day average diurnal temperature range | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Li, Z.; Huang, G.; Han, Y.; Hao, D. Life History and the Relation Between Population Dynamics and Meteorological Factors of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiidae) in Shanghai, China. Insects 2025, 16, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111136
Tang S, Li Z, Huang G, Han Y, Hao D. Life History and the Relation Between Population Dynamics and Meteorological Factors of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiidae) in Shanghai, China. Insects. 2025; 16(11):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111136
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Siqi, Zichun Li, Guangyu Huang, Yangyang Han, and Dejun Hao. 2025. "Life History and the Relation Between Population Dynamics and Meteorological Factors of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiidae) in Shanghai, China" Insects 16, no. 11: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111136
APA StyleTang, S., Li, Z., Huang, G., Han, Y., & Hao, D. (2025). Life History and the Relation Between Population Dynamics and Meteorological Factors of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiidae) in Shanghai, China. Insects, 16(11), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111136






