Extrinsic and Intrinsic Competition between Chouioa cunea Yang and Tetrastichus septentrionalis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Two Pupal Parasitoids of the Fall Webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Extrinsic Competition: The Order of and Time Intervals between Parasitism by Two Pupal Parasitoids
2.3. Intrinsic Competition: The Order of and Time Intervals between Parasitism by Two Pupal Parasitoids
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
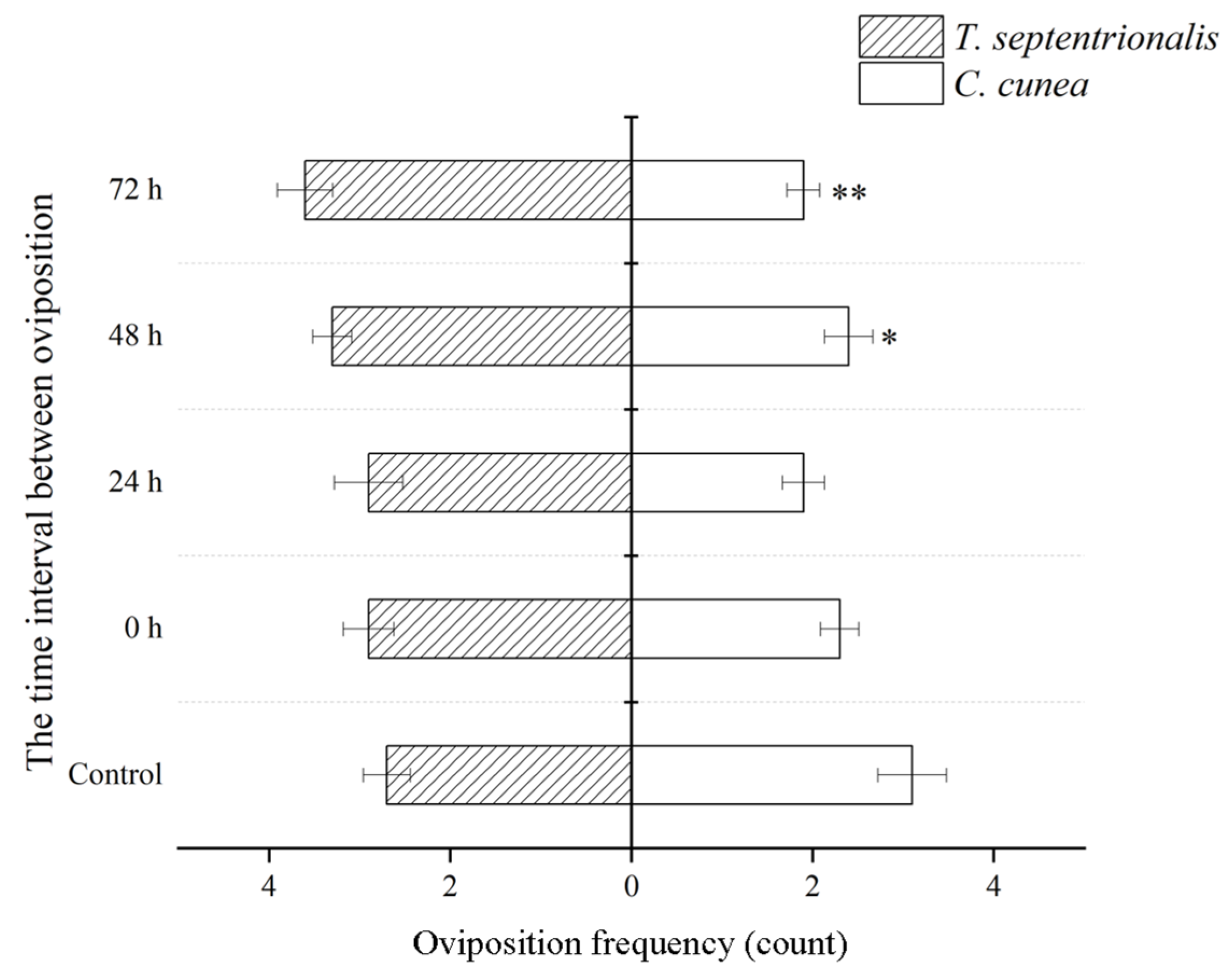
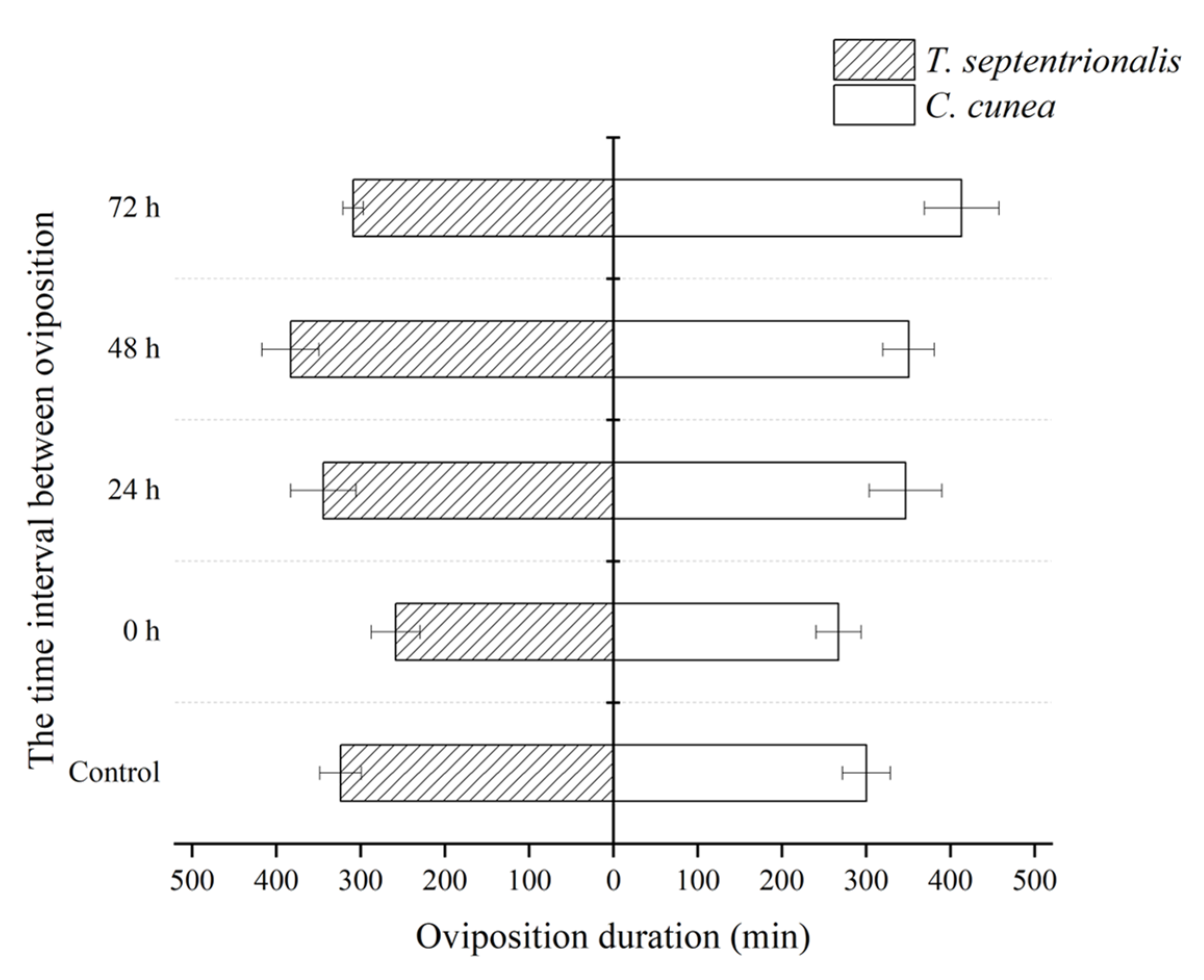
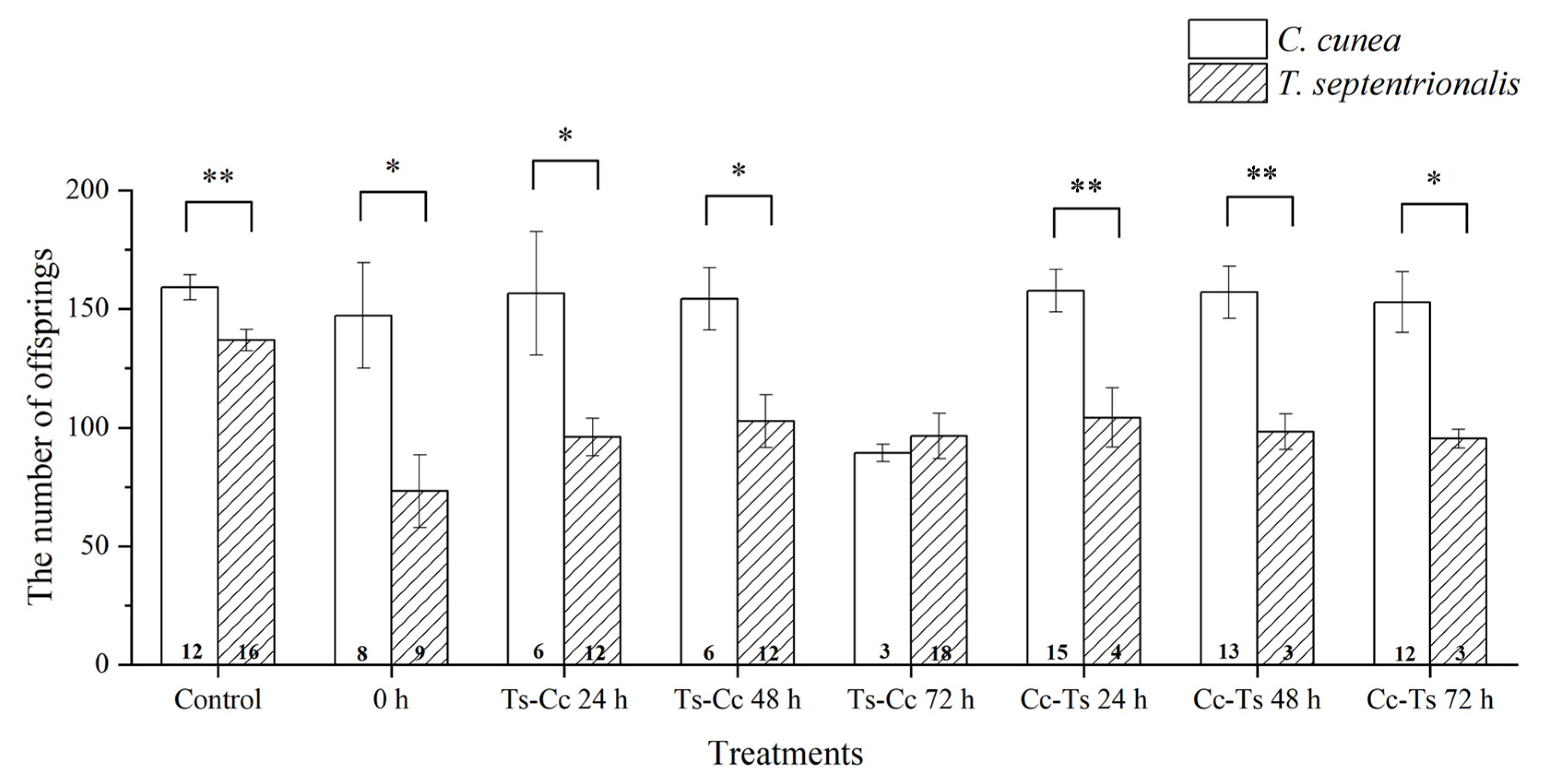
3.1. Results of Extrinsic Competition: The Order of and Time Intervals between Parasitism by Two Pupal Parasitoids
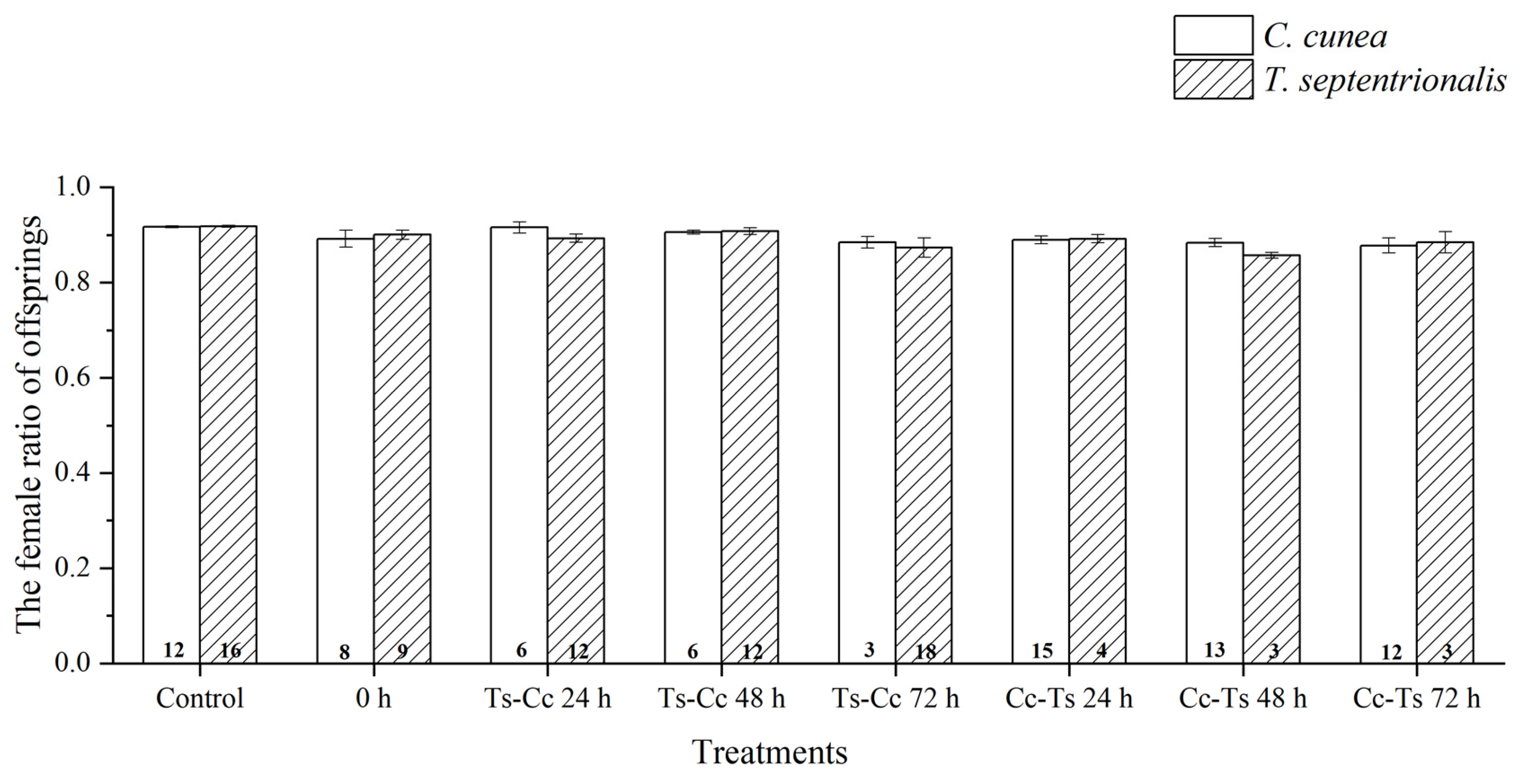
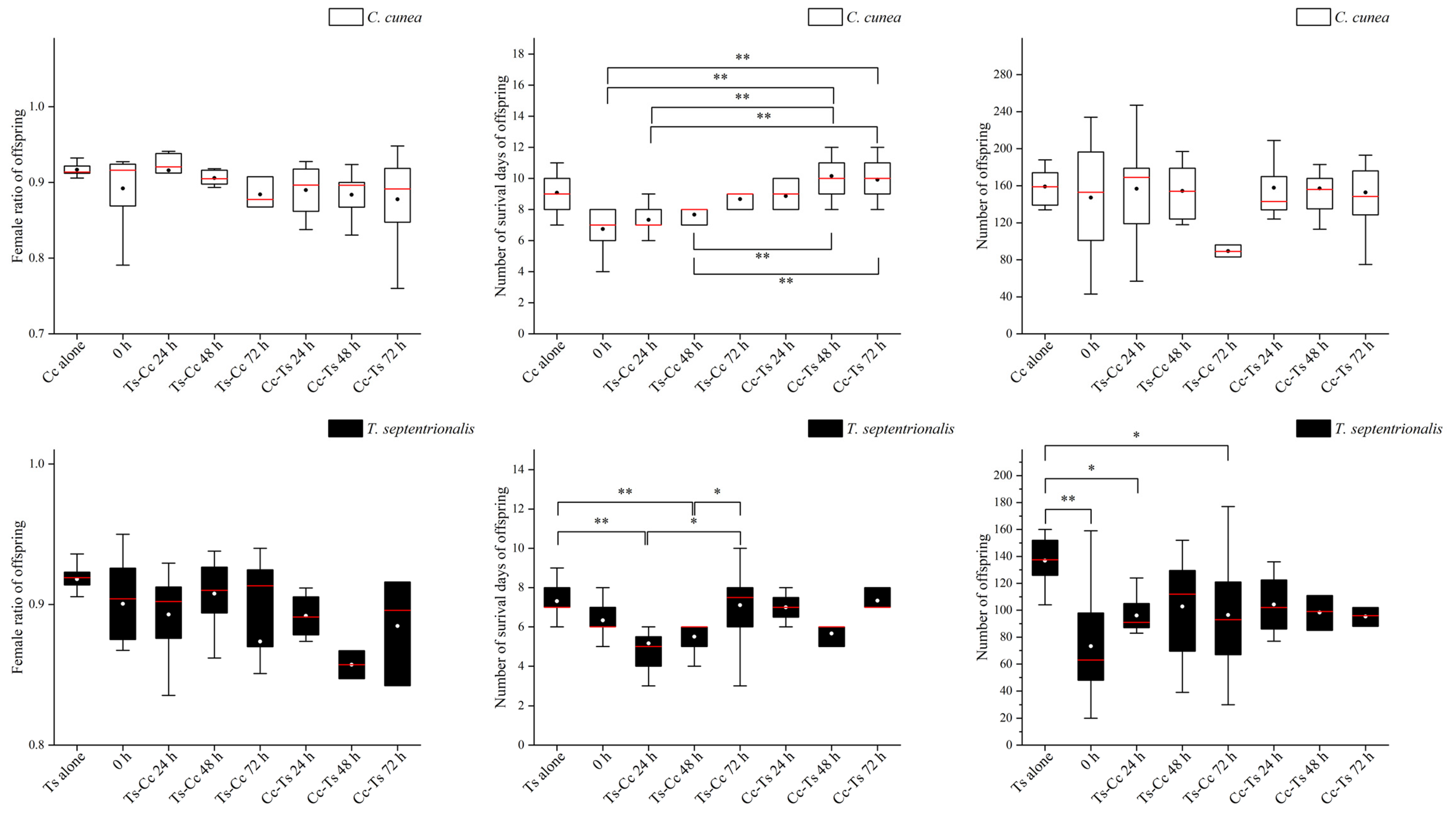
3.2. Results of Intrinsic Competition: The Order of and Time Intervals between Parasitism by Two Pupal Parasitoids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, N.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Hu, X.; Zhou, X.J.; et al. Fall webworm genomes yield insights into rapid adaptation of invasive species. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.F. Synonymy and Color Variation in the Fall Webworm, Hyphantria cunea Drury (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Can. Entomol. 1963, 95, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.L.; Wang, H.K.; Jiang, F.Y. Reproduction and biological characteristic of Chouioia cunea. J. For. Res. 2002, 13, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Cao, L.M.; Sun, S.H.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.L. Research Progress on the Utilization of Natural Enemy Insects of Hyphantria cunea (Drury). Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.N. Recent advances in biological control of important native and invasive forest pests in China. Biol. Control 2014, 68, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.M.; Ma, Q.H.; Meng, Z.J.; Yan, S.C. Progress in the sustainable control of Hyphantria cunea. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2023, 60, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi, D.; Engel, M.S. Insects Take to the Skies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Quicke, D.L.J. Parasitic Wasps; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jervis, M.A. Insects as Natural Enemies: A Practical Perspective; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.A. Researches on techniques for biocontrol of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea, a severe invasive insect pest to China. J. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2007, 44, 465–471. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Daane, K.M.; Zheng, Y. Research and application of Chouioia cunea Yang (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in China. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, B.; Yuan, R.; Lu, Z.; Shu, X.; Fang, Y.; Tian, S.; Qu, Q.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Chouioia cunea Yang, the parasitic wasp of the fall webworm. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wei, J. A new species of Eulophidae (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) parasitizing fall weborm in China and Korea. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2001, 01, 98–102+132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Lu, S.L.; Liu, W.X.; Wang, W.X.; Wang, W.; Wan, F.H. Comparing immature development and life history traits in two coexisting host-feeding parasitoids, Diglyphus isaea and Neochrysocharis formosa (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiling, P.; Cornelissen, T.J.B.C. What makes a successful biocontrol agent? A meta-analysis of biological control agent performance. Biol. Control 2005, 34, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoth, M.; Frid, L.; Myers, J.H. Multiple agents in biological control: Improving the odds? J. Biol. Control 2002, 24, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.J. Competition among parasitoid species on a stage-structured host and its effect on host suppression. Am. Nat. 1993, 141, 372–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.A.; Poelman, E.H.; Tanaka, T. Intrinsic inter- and intraspecific competition in parasitoid wasps. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, A.; Peri, E.; Vinson, S.B.; Colazza, S. Intraguild interactions between two egg parasitoids exploring host patches. BioControl 2011, 56, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, P.; Messing, R.; Jones, V. Parasitoid drift after biological control introductiqns: Re-examining pandora’s box. Am. Entomol. 2000, 46, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.-L.; Liu, W.-X.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Cheng, X.-Q.; Guo, J.-Y.; Wan, F.-H. Interactions between Diglyphus isaea and Neochrysocharis formosa (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), two parasitoids of agromyzid leafminers. Biol. Control. 2018, 126, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcez, A.M.; Krüger, A.P.; Nava, D.E. Intrinsic competition between 2 pupal parasitoids of Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2023, 116, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.R.; Shao, L.S.; Feng, H.C.; Nie, L.; Yang, J.; Tan, H.L. Threshold temperature and effective accumulated temperature of Tetrastichus septentrionalis. J. For. Pest Dis. 2007, 4, 9–10+47. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.Y.; Bin, C.; Zhang, H.Y.; Dong, H.; Cui, L. Relationship between female fecundity, developing time and female body size of Chouioia cunea yang (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2010, 26, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.C. A study in insect multiparasitism: II. The mechanism and control of competition for possession of the host. J. Exp. Biol. 1961, 38, 605–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Duan, J.J.; Lelito, J.; Driesche, R.V. Multiparasitism by Tetrastichus planipennisi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) and Spathius agrili (Hymenoptera: Braconidae): Implication for biological control of the emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Biol. Control 2013, 65, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marktl, R.C.; Stauffer, C.; Schopf, A. Interspecific competition between the braconid endoparasitoids Glyptapanteles porthetriae and Glyptapanteles liparidis in Lymantria dispar larvae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 105, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboka, K.; Schulthess, F.; Chabi-Olaye, A.; Labo, I.; Gounou, S.; Smith, H. Self-, intra-, and interspecific host discrimination in Telenomus busseolae Gahan and T. isis Polaszek (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), Sympatric Egg Parasitoids of the African Cereal Stem Borer Sesamia calamistis Hampson (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Insect Behav. 2002, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.P.; Zhang, F.; Wu, K. Interspecific competition between Peristenus spretus and Peristenus relictus (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), larval parasitoids of Apolygus lucorum (Hemiptera: Miridae). Biol. Control 2018, 117, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, R.; Wajnberg, E.; Monge, J.-P.; Goubault, M. The effect of direct interspecific competition on patch exploitation strategies in parasitoid wasps. Oecologia 2015, 177, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, A.; Kapranas, A.; Garcia-Marí, F.; Luck, R.F. Host discrimination, superparasitism and infanticide by a gregarious endoparasitoid. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, Q.; Dorn, S.J.E.E. Superparasitism in Cotesia glomerata: Response of hosts and consequences for parasitoids. Ecol. Entomol. 2010, 28, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, A.; Peri, E.; Bradleigh Vinson, S.; Colazza, S. Interspecific extrinsic and intrinsic competitive interactions in egg parasitoids. BioControl 2012, 57, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlings, T.C.J.; McCall, P.J.; Alborn, H.T.; Tumlinson, J.H. An elicitor in caterpillar oral secretions that induces corn seedlings to emit chemical signals attractive to parasitic wasps. J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Torres, C.S.A.; Matthews, R.W. Development of Melittobia australica Girault and M. digitata Dahms (Parker) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) parasitizing Neobellieria bullata (Parker) (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) puparia. J. Neotrop. Entomol. 2003, 32, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids:Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 67. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, C.M.D.; Mescher, M.C. Intrinsic competition between larval parasitoids with different degrees of host specificity. Ecol. Entomol. 2005, 30, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, C.M.D.; Cortesero, A.M.; Stapel, J.O.; Lewis, W.J. Intrinsic and extrinsic competitive interactions between two larval parasitoids of Heliothis virescens. Ecol. Entomol. 1999, 24, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, L.; Sabbatini-Peverieri, G.; Simoni, S.; Cervo, R.; Hoelmer, K.A.; Roversi, P.F. Interspecific competition between Trissolcus japonicus and Trissolcus mitsukurii, two promising candidates for biocontrol of Halyomorpha halys. Biol. Control 2022, 176, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.D. Extraordinary sex ratios. Science 1967, 156, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Harvey, J.A.; Biere, A.; Gols, R. Rain downpours affect survival and development of insect herbivores: The specter of climate change? J. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2019, 100, e02819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, H. Oviposition and survival of the European parasite Microctonus bicolor (hymenoptera: Braconidae) in crucifer-infesting flea beetles (coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in manitoba. Can. Entomol. 1983, 115, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.A.; Gols, R.; Strand, M.R. Intrinsic competition and its effects on the survival and development of three species of endoparasitoid wasps. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2009, 130, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louise, E.M.V.; Datema, A.; Janssen, A.; Snellen, H. Clutch size in a larval-pupal endoparasitoid: Consequences for fitness. J. Anim. Ecol. 1994, 63, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Ma, B.; Yan, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R. The hyperparasitoid Marietta picta (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) mediates competitive interactions between two parasitoids of Paratrioza sinica (Hemiptera: Psyllidae): Tamarixia lyciumi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) and Psyllaephagus arenarius (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae). Biol. Control 2018, 126, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | n | Mortality (%) | Parasitism (%) | Host Emergence (%) | Percentage of Adult Emergence (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. cunea | T. septentrionalis | |||||
| Only Cc | 25 | 20 | 48 | 32 | 100 | - |
| Only Ts | 25 | 20 | 64 | 16 | - | 100 |
| Ts-Cc 0 h | 25 | 12 | 68 | 20 | 47.06 | 52.94 |
| Ts-Cc 24 h | 25 | 12 | 72 | 16 | 33.33 | 66.67 |
| Ts-Cc 48 h | 25 | 12 | 72 | 16 | 33.33 | 66.67 |
| Ts-Cc 72 h | 25 | 16 | 84 | 0 | 14.3 | 85.7 |
| Cc-Ts 24 h | 25 | 8 | 76 | 16 | 78.95 | 21.05 |
| Cc-Ts 48 h | 25 | 24 | 64 | 12 | 81.25 | 18.75 |
| Cc-Ts 72 h | 25 | 28 | 60 | 12 | 80 | 20 |
| Ts and Cc | 175 | 16 | 70.96 | 13.14 | 50.81 | 49.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, S. Extrinsic and Intrinsic Competition between Chouioa cunea Yang and Tetrastichus septentrionalis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Two Pupal Parasitoids of the Fall Webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Insects 2024, 15, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080617
Li Z, Yang L, Ma X, Liu X, Cheng Y, Sun S. Extrinsic and Intrinsic Competition between Chouioa cunea Yang and Tetrastichus septentrionalis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Two Pupal Parasitoids of the Fall Webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Insects. 2024; 15(8):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080617
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhixin, Liyuan Yang, Xi Ma, Xudan Liu, Yiran Cheng, and Shouhui Sun. 2024. "Extrinsic and Intrinsic Competition between Chouioa cunea Yang and Tetrastichus septentrionalis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Two Pupal Parasitoids of the Fall Webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae)" Insects 15, no. 8: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080617
APA StyleLi, Z., Yang, L., Ma, X., Liu, X., Cheng, Y., & Sun, S. (2024). Extrinsic and Intrinsic Competition between Chouioa cunea Yang and Tetrastichus septentrionalis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Two Pupal Parasitoids of the Fall Webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Insects, 15(8), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080617







