Exploring the Biology of Quasi-Social Idiobiont Parasitoids in the Genus Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Analysis
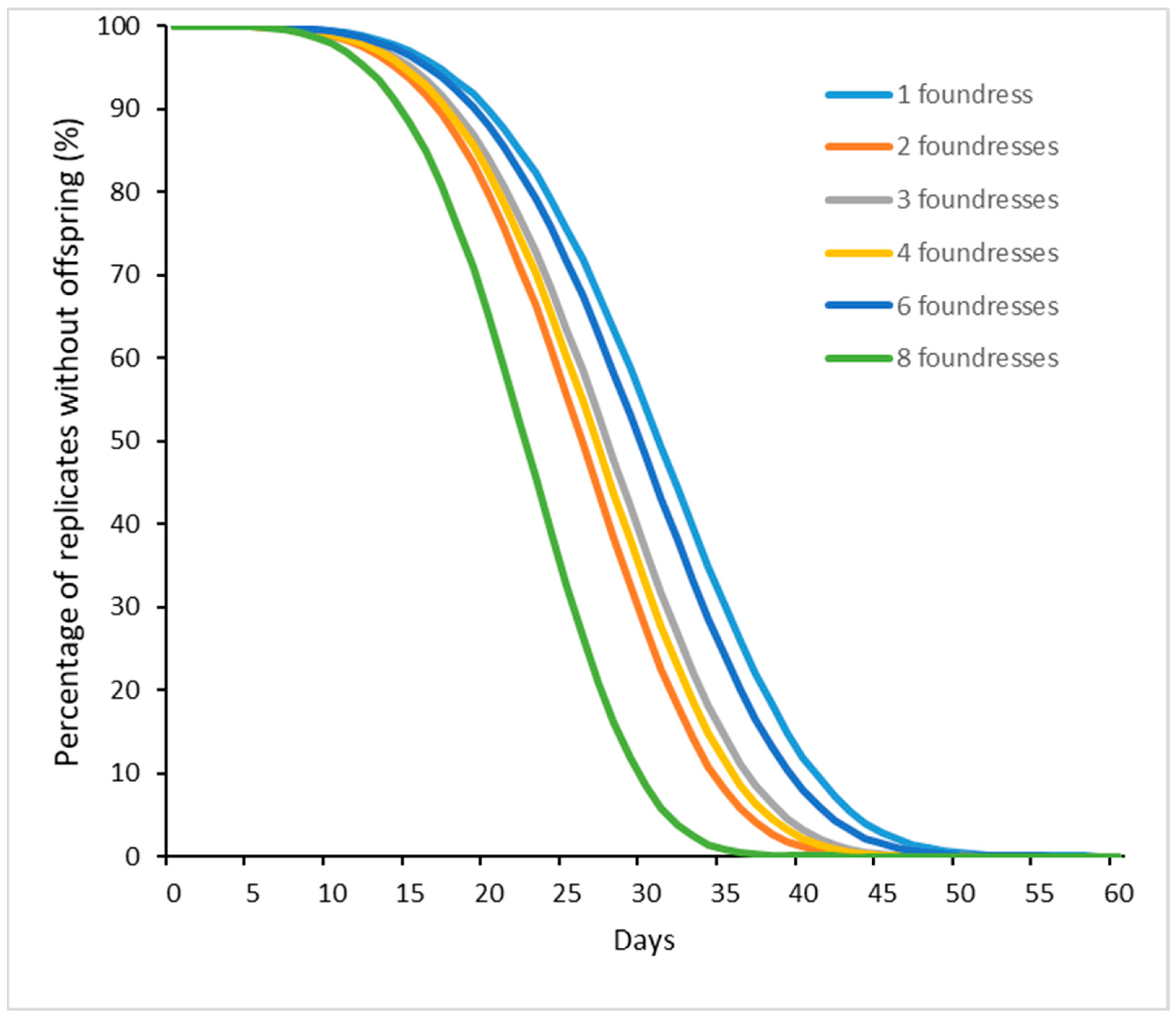
3.2. Offspring Production
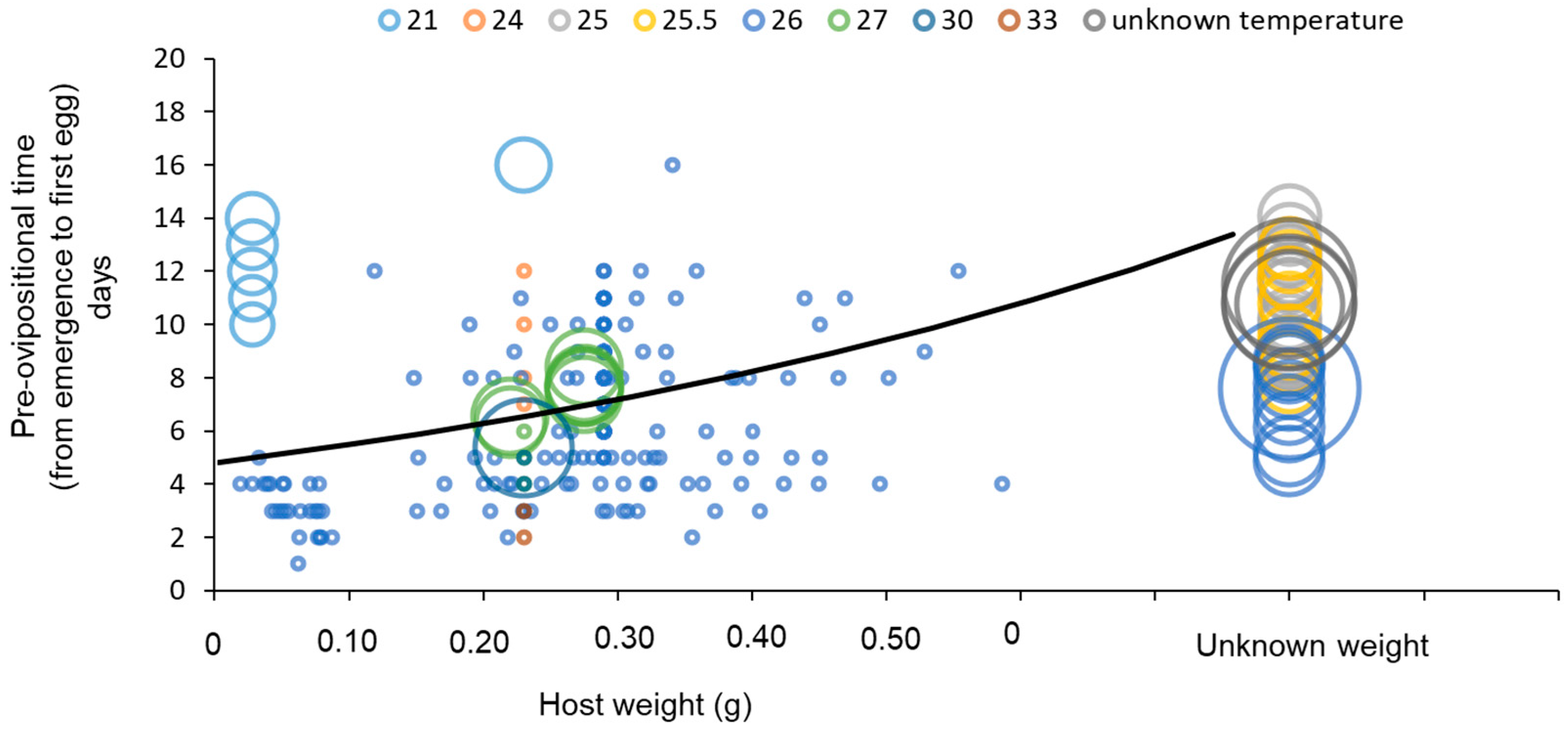
3.3. Developmental Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordh, G.; Móczár, L. A catalog of the world Bethylidae (Hymenoptera, Aculeata). Mem. Am. Entomol. Inst. 1990, 46, 1–364. [Google Scholar]
- Lanes, G.; Gobbi, F.T.; Azevedo, C.O. Report on a collection of Bethylidae (Hymenoptera) from Central Florida, USA, with description of a new species of Lepidosternopsis ogloblin. J. Hym. Res. 2004, 13, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, C.O. Insecta, Hymenoptera, Bethylidae: Range extension and filling gaps in Australia. Check List 2006, 2, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, C.O.; Alencar, I.D.; Ramos, M.S.; Barbosa, D.N.; Colombo, W.D.; Vargas, J.M.; Lim, J. Global guide of the flat wasps (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae). Zootaxa 2018, 4489, 1–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, C.O.; Colombo, W.D. Synopsis of the Neotropical Sclerodermus Latreille (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae) with description of a new species attacking human beings. Zootaxa 2022, 5124, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugrabi, D.; Azevedo, C. Insecta, Hymenoptera, Bethylidae: Range extension and filling gaps in Madagascar. Check List 2010, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brothers, D.J.; Carpenter, J.M. Phylogeny of Aculeata: Chrysidoidea and Vespoidea. J. Hym. Res. 1993, 2, 227–302. [Google Scholar]
- Clausen, C.P. Entomophagous Insects; McGraw-Hill Book Company: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, J.A. The Bethyline species (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae: Bethylinae) imported into New Zealand for biological control of pest leafrollers. N. Z. J. Zool. 1998, 25, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kieffer, J.J. Bethylidae. Das Tierreich. 1914, 41, 1–595. [Google Scholar]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Meng, L.; Kapranas, A.; Xu, F.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Li, B. Mutually beneficial host exploitation and ultra-biased sex ratios in quasisocial parasitoids. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.K.; Lupi, D.; Jucker, C.; Hardy, I.C.W. Kinship effects in quasi-social parasitoids I: Co-foundress number and relatedness affect suppression of dangerous hosts. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 130, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.K.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Jucker, C.; Lupi, D. Kinship effects in quasi-social parasitoids II: Co-foundress relatedness and host dangerousness interactively affect host exploitation. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 130, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.K.; Jucker, C.; De Marchi, B.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Lupi, D. Performance of Sclerodermus brevicornis, a parasitoid of invasive longhorn beetles, when reared on rice moth larvae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2021, 169, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanes, G.; Azevedo, C. Phylogeny and taxonomy of Sclerodermini (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae, Epyrinae). Insect Syst. Evol. 2008, 39, 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.Y.; Li, B.P.; Lin, F.; Meng, L. Influence of host body size on potential reproductive capability of Sclerodermus guani (Hymenoptera: Bethiylidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2016, 59, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Cao, L.M.; Yang, Z.Q. The developmental strategies and related profitability of an idiobiont ectoparasitoid Sclerodermus pupariae vary with host size. Ecol. Entomol. 2014, 39, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, L.; Sun, J. Host-Size mediated Trade-Off in a parasitoid Sclerodermus harmandi. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Tang, Y.; Wei, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Relationships between body size and parasitic fitness and offspring performance of Sclerodermus pupariae Yang et Yao (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackauer, M.; Sequeira, R.; Otto, M. Growth and development in parasitoid wasps: Adaptation to variable host resources. Vertical Food Web Interactions. In Evolutionary Patterns and Driving Forces; Dettner, K., Bauer, G., Volkl, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997; pp. 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, J.A.; Jervis, M.A.; Gols, R.; Jiang, N.Q.; Vet, L.E.M. Development of the parasitoid, Cotesia rubecula (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) in Pieris rapae and Pieris brassicae (Lepidoptera: Pieridae): Evidence for host regulation. J. Insect Physiol. 1999, 45, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, M.R. Developmental traits and life-history evolution in parasitoids. In Parasitoid Population Biology; Hochberg, M.E., Ives, A.R., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 139–162. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, J.A.; Strand, M.R. The developmental strategies of endoparasitoid wasps vary with host feeding ecology. Ecology 2002, 83, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, K.; Yang, Z.; Jennings, D.E.; Duan, J.J. Effects of biotic and abiotic factors on phenotypic partitioning of wing morphology and development in Sclerodermus pupariae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skvarla, M.J. A review of Sclerodermus Latreille, 1809 (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) Infestations and report of the first case in North America North of Mexico. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, M.K.; Lupi, D.; Hardy, I.C.W. Co-foundress confinement elicits kinship effects in a naturally sub-social parasitoid. J. Evol. Biol. 2020, 33, 1068–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jucker, C.; Hardy IC, W.; Malabusini, S.; de Milato, S.; Zen, G.; Savoldelli, S.; Lupi, D. Factors affecting the reproduction and mass-rearing of Sclerodermus brevicornis (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), a natural enemy of exotic flat-faced longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae: Lamiinae). Insects 2020, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.H.; Lu, J. Alternative hosts of Sclerodermus pupariae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), a larval parasitoid of the longhorn beetle Massicus raddei (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2012, 55, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Lyu, D.; Jeong, Y.J.; Shin, S.C.; Lee, S. A Taxonomic Note on Sclerodermus harmandi, Ectoparasite of Stem and Wood Boring Insect Larvae (Hymenoptera: Chrysidoidea’-Bethylidae) in South Korea. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2006, 9, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Gao, S.K.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.Q. Determination of the optimal parasitoid-to-host ratio for efficient mass-rearing of the parasitoid, Sclerodermus pupariae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roff, D.A. The evolution of wing dimorphism in insects. Evolution 1986, 40, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Favaro, R.; Jucker, C.; Azevedo, C.O.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Faccoli, M. Reproductive biology of Sclerodermus brevicornis, a European parasitoid developing on three species of invasive longhorn beetles. Biol. Control 2017, 105, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, J. Host suitability of a gregarious parasitoid on beetle hosts: Flexibility between fitness of adult and offspring. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Maternal Care in the Parasitoid Sclerodermus harmandi (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, V.J.M. Abondance de Hypothenemus hampei Ferr., scolyte des graines de cafe, en fonction de sa plante-hote et deson parasite Cephalonomia stephanoderis Betrem, en Cote d-Ivoire. In Mededelingen Landbouwhogeschool Wageningen (Paıses Bajos); Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1973; Volume 73, pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Miller, D.R.; Sun, J. The influence of prior experience on preference and performance of a cryptoparasitoid Scleroderma guani (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) on beetle hosts. Ecol. Entomol. 2009, 34, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, W.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J. Host adaptation of a gregarious parasitoid Sclerodermus harmandi in artificial rearing. BioControl 2010, 55, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühne, H.V.; Becker, C. Zur Biologie und Ökologie von Sclerodema domesticum Latreille (Bethylidae, Hymenoptera), einem Parasiten holzzerstörender Insektenlarven. Z. Angew. Entomol. 1974, 76, 278–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Cao, L.M.; Yao, Y.X.; Tang, Y.L. Re-description of Sclerodermus guani and revision of the genus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) in China. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2014, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kapranas, A.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Tang, X.; Gardner, A.; Li, B. Sex ratios, virginity, and local resource enhancement in a quasisocial parasitoid. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2016, 159, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, Y.X.; Gould, J.R.; Cao, L.M. A new species of Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) parasitising Agrilus planipenns (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) from China, with a key to chinese species in the genus. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2012, 105, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, W.M. The Social Insects: Their Origin and Evolution; Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner: London, UK, 1928. [Google Scholar]
- Malabusini, S.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Jucker, C.; Guanzani, G.; Savoldelli, S.; Lupi, D. Reproductive performance effects of rearing the quasi-social parasitoid, Sclerodermus brevicornis (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), on a factitious host. J. Insect Sci. 2023, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Xu, F.Y.; Li, B.P.; Meng, L. Initiation and rhytm of larva-traslocation behavior during maternal care in an ectoparasitoid Sclerodermus guani (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2013, 56, 392–397. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, J.S. Relational Analysis: The Study of Social Organizations with Survey Methods. Hum. Organ. 1959, 17, 428–436. [Google Scholar]
- Heckathorn, D.D. Snowball Versus Respondent-Driven Sampling. Sociol. Methodol. 2011, 41, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlin, C. Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering, London, UK, 13–14 May 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, M.; Muftakhidinov, B.; Winchen, T. Engauge Digitizer Software 2020. Available online: http://markummitchell.github.io/engauge-digitizer (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2023. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Crawley, M.J. GLIM for Ecologists; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, I.C.W.; Smith, D.R. Statistical approaches. In Insects as Natural Enemies: Practical Perspectives; Hardy, I.C.W., Wajnberg, E., Eds.; Jervis’s Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2023; pp. 705–742. [Google Scholar]
- Faraway, J.J. Extending the Linear Model with R: Generalized Linear, Mixed Effects and Nonparametric Regression Models; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Aitkin, M.; Anderson, D.; Francis, B.; Hinde, J. Statistical Modelling in GLIM; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.; Hardy, I.C.W. Statistical analysis of sex ratios: An introduction. In Sex Ratios: Concepts and Research Methods; Hardy, I.C.W., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 48–92. [Google Scholar]
- Westwood, J.O. XXXII: Monograph upon the Hymenopterous Genus Scleroderma. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1839, 2, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, S.S.S. VII: On the habits and affinities of the Hymenopterous genus Scleroderma, with descriptions of new species. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1881, 29, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.O. VIII: Observations on the Hymenopterous genus Scleroderma, Klug, and some allied groups. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1881, 29, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, M. The Insects of Japan. In Bethylidae (Hymenoptera); Touka Shobo: Fukuoka, Japan, 2006; Volume 1, p. 319. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.F.; He, J.H. Revision on the scientific name of the bethylid regarded as Sclerodermus guani which used widely in forest of China. J. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 30, 192–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.I.; Koh, S.H.; Chung, Y.J.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, G.H.; Choi, K.S. Biological characteristics of Sclerodermus harmandi (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) parasitised on cerambycid. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2008, 47, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xie, Y.; Yang, S. Potential non-target effects of Sclerodermus harmandi (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) on Triaspis sp. (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, G.; Wu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, X.; Bao, Q.; Tian, C. Influence of Parasitoid-host Ratio on the Mass Rearing of Sclerodermus guani. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2018, 34, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Men, J.; Zhao, B.; Cao, D.D.; Wang, W.C.; Wei, J.R. Evaluating host location in three native Sclerodermus species and their ability to cause mortality in the wood borer Aromia bungii (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in laboratory. Biol. Control 2019, 134, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Ran, C. Optimal Temperatures for Artificial Rearing of Parasitoid, Sclerodermus pupariae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Chin. J. Biol. Control 2019, 35, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Mesterton-Gibbons, M.; Hardy, I.C.W. Defection on the bounty? Kinship and cooperative exploitation of a rich, essential but dangerous resource. Anim. Behav. 2021, 176, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.F.; Emlen, S.T.; Koenig, W.D.; Rubenstein, D.R. The ecology of cooperative breeding behavior. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfray, H.C.J. The evolution of clutch size in invertebrates. Oxf. Surv. Evol. Biol. 1987, 4, 117–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, I.C.W.; Griffiths, N.T.; Godfray, H.C.J. Clutch size in a parasitoid wasp: A manipulation experiment. J. Anim. Ecol. 1992, 61, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaviezo, T.; Mills, N.J. Factors influencing the evolution of clutch size in a gregarious insect parasitoid. J. Anim. Ecol. 2000, 69, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, J.M.; Crespi, B.J. Cofoundress relatedness and group productivity in colonies of social Dunatothrips (Insecta: Thysanoptera) on Australian acacia. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2008, 62, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Malabusini, S.; Hardy, I.C.; Jucker, C.; Savoldelli, S.; Lupi, D. How many cooperators are too many? Foundress number, reproduction and sex ratio in a quasi-social parasitoid. Ecol. Entomol. 2022, 47, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.D. Extraordinary sex ratios. Science 1967, 156, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, I.C.W. Sex Ratios: Concepts and Research Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- West, S. Sex Allocation; Princeton University Press: Princeton, MJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Iritani, R.; West, S.; Abe, J. Cooperative interactions among females and even more extraordinary sex ratios. Evol. Lett. 2021, 5, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, L.; Hardy, I.C.; Li, B. Reproductive skew in quasisocial parasitoids: How egalitarian is cooperative brooding? Anim. Behav. 2022, 186, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, J.; Malabusini, S.; Guo, X.; Hardy, I.C.W. Individual-and group-level sex ratios under local mate competition: Consequences of infanticide and reproductive dominance. Evol. Lett. 2023, 7, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratte, H.T. Temperature and Insect Development. In Environmental Physiology and Biochemistry of Insects; Hoffmann, K.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Damos, P.; Savopoulou-Soultani, M. Temperature-driven models for insect development and vital thermal requirements. Psyche 2012, 2012, 123405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Luoli, P.; Wang, X. Wing Dimorphism and Sex Ratio Changes in Progeny of Various Sister Broods in Parasitoid Sclerodermus pupariae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). For. Res. 2019, 32, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.L.; Wang, L.N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, S.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.Q. Effect of different parasitoid colonies on the mass rearing of Sclerodermus alternatusi (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Sci. Silvae Sin. 2020, 56, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Dai Huiling, H.E.; Kang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L. Effect of Low Temperature Storage Duration on Breeding of Sclerodermus alternatusi Yang (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Chin. J. Biol. Control 2022, 38, 1361. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Tang, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Effect of Temperature on development and reproduction of Sclerodermus alternatusi. For. Res. 2019, 32, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Semi, K. Evaluation on control efficiency of bethylid parasitoids on pest insects indoor: A case of Sclerodermus sp. (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Tang, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Effects of Larvae Body Size of Thyestilla gebleri on Oviposition Decision of Sclerodermus alternatusi. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2019, 35, 848–854. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, Z.J.; Yang, W.; Hu, J.; Yang, C.P. Screening substitute hosts for mass rearing of Sclerodermus sichuanensis Xiao (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2005, 48, 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.F.; Tang, X.Y.; Meng, L.; Xu, F.Y.; Xie, C.X.; Zheng, H.Y.; Li, B.P. Pre-oviposition and developmental duration in response to host body size and numbers of foundresses in Sclerodermus guani (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). J. Nanjing Agar. Univ. 2015, 38, 584–589. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.K.; Wei, K.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.Q. Effect of parasitoid density on the timing of parasitism and development duration of progeny in Sclerodermus pupariae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Biol. Control. 2016, 97, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, H.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, J. Effects of Low Temperature Storage of Substituted Host on the Reproduction of Sclerodermus guani. Chin. J. Biol. Cont. 2017, 33, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, J.A.; Vet, L.E.M.; Witjes, L.M.A.; Bezemer, T.M. Remarkable similarity in body mass of a secondary hyperparasitoid Lysibia nana and its primary parasitoid host Cotesia glomerata emerging from cocoons of comparable size. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2006, 61, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.G.; Sun, X.G.; Qu, A.J. The oviposition behavior of Scleroderma guani Xiao et Wu. Natl. Enem. Insect. 2004, 26, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.H.; Yan, J.J. Overview of foreign research about Sclerodermus. For. Sci. Technol. 1985, 7, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Meng, L.; Li, B. Cooperatively breeding behavior of Sclerodermus sichuanensis (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) on the host Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2020, 63, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.L.; Wang, L.N.; Jia, J.; Kang, K.; Zeng, B.; Wei, K. Parasitism Rate and Progeny Development of Sclerodermus alternatusi (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) on Different Stage, of Thyestilla gebleri (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). For. Res. 2022, 35, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, K.; Rao, S. Data Extraction from Included Studies. In Principles and Practice of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Biological control of Apriona swainsoni (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) by applying three parasitoid species. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2014, 50, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, J. Control effects of Dastarcus helophoroides and Scleroderma guani against Anoplophora glabripennis. J. Jiangsu For. Sci. Technol. 2014, 41, 6–36. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.; Lan, J.; Xiong, H.; Wan, F.; Xu, H.; Li, C. Controlling effect of the parasitoid Sclerodermus sp. (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) on longhorn beetles attacking plane tree. J. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 40, 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, R.A.; Collins, L.A.; Shuker, D.M. Beyond sex allocation: The role of mating systems in sexual selection in parasitoid wasps. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 599–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabusini, S.; Lupi, D. Hyperparasitic showdown: Sclerodermus cereicollis, a non-aggressive but surprisingly secondary hyperparasitoid. J. Èntomol. Acarol. Res. 2024, 56, 12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, I.C.W.; Dijkstra, L.J.; Gillis, J.E.; Luft, P.A. Patterns of sex ratio, virginity and developmental mortality in gregarious parasitoids. Biol. J. Linn. 1998, 64, 239–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, R.; Meng, L.; Hardy, I.; Li, B. Agonistic responses to potential co-foundresses in a cooperatively brooding quasi-social parasitoid. Ecol. Entomol. 2023, 48, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabusini, S.; Lupi, D.; Mortazavi, N.; Golparvar, Z.; Follador, A.; de Milato, S.; Hardy, I.C.W. Multiple foundresses and multiple hosts: The influences of kinship and host quality on group reproduction in a quasi-social parasitoid. Ecol. Entomol. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba-Aguilar, A.; Munguía-Steyer, R. The sicker sex: Understanding male biases in parasitic infection, resource allocation and fitness. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


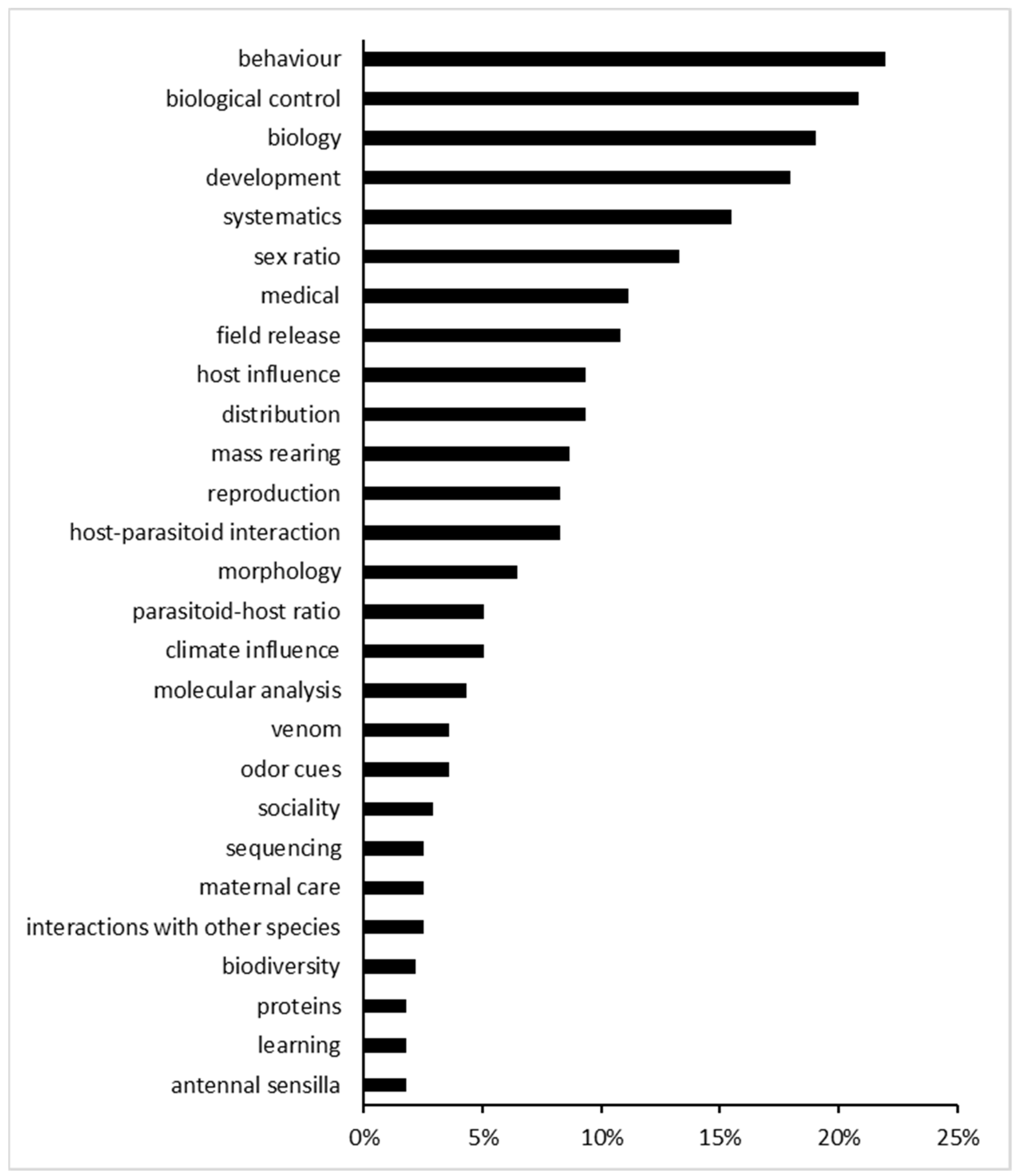






| Main Topics | Additional Topics |
|---|---|
| Behaviour | Antennal sensilla |
| Biological control | Biodiversity |
| Biology | Climate influence |
| Development | Field release |
| Distribution | Host influence |
| Mass-rearing | Host–parasitoid interaction |
| Medical | Interactions with other species |
| Molecular analysis | Learning |
| Systematics | Maternal care |
| Venom | Morphology |
| Odour cues | |
| Parasitism rate | |
| Parasitoid–host ratio | |
| Proteins | |
| Reproduction | |
| Sequencing | |
| Sex ratio | |
| Sociality | |
| Temp. (°C) | Mean Female Developmental Time (from Egg to Adult) ± SE (Days) | Number of Replicates | Sclerodermus Species | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 36.1 ± 1.04 f | 45 | S. puparie; Sclerodermus sp. | [25,86] |
| 21 | 54.5 ± 0.94 g | 55 | S. puparie; S. alternatusi | [65,85] |
| 24 | 39.1 ± 0.90 f | 55 | S. puparie; S. alternatusi | [65,85] |
| 25 | 30.5 ± 0.26 e | 746 | S. puparie; S. brevicornis; S. alternatusi; S. sichuanensis | [20,25,31,33,61,87,88] |
| 25.5 | 28.3 ± 0.55 d | 160 | S. guani | [37] |
| 26 | 26.2 ± 0.33 c | 462 | S. brevicornis; S. harmandi; S. guani | [15,62,63] |
| 27 | 25.4 ± 0.94 bcd | 55 | S. puparie; S. alternatusi | [65,85] |
| 30 | 21.80 ± 0.44 a | 255 | S. puparie; S. alternatusi | [25,65,82,85] |
| 33 | 22.50 ± 0.94 ab | 55 | S. puparie; S. alternatusi | [65,85] |
| Sclerodermus Species | Host Species | N | Weighted Mean Time Development (from Egg to Adult) ± SE (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. alternatusi | Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 277 | 32.30 ± 0.89 cd |
| Thyestilla gebleri (Fald.) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 360 | 34.00 ± 0.74 cd | |
| S. brevicornis | Psacothea hilaris hilaris (Pascoe) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 60 | 21.20 ± 1.80 ab |
| Anoplophora chinensis (Forster) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 32 | 24.00 ± 2.85 abcd | |
| Corcyra cephalonica (Stainton) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) | 195 | 25.80 ± 1.04 ab | |
| Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 60 | 28.50 ± 1.81 abcd | |
| S. guani | Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) | 625 | 26.30 ± 0.64 ab |
| S. harmandi | Triaspis sp. (Hymenoptera:Braconidae) | 15 | 25.40 ± 2.96 abcd |
| Saperda populnea (L.) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 450 | 27.40 ± 1.28 abc | |
| Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 450 | 29.20 ± 1.26 abcd | |
| Monochamus saltuarius (Gebler) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | - | 26.6 ± 8.04 abcd | |
| Psacothea hilaris (Pascoe) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | - | 28.8 ± 8.04 abcd | |
| S. puparie | Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) | 240 | 25.00 ± 0.74 a |
| Thyestilla gebleri (Fald.) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 334 | 26.80 ± 0.81 ab | |
| Massicus raddei (Blessig) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 343 | 30.30 ± 0.80 bcd | |
| Mesosa myops (Dalman) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 90 | 34.10 ± 1.21 cd | |
| Moechotypa diphysis (Pascoe) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 90 | 34.70 ± 1.21 cd | |
| Lamprodila virgata (Motchulsky) (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) | 60 | 37.50 ± 1.48 d | |
| S. sichuanensis | Sesamia inferens (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) | 15 | 33.50 ± 2.96 abcd |
| Bacchisa dioica (Fairmaire, 1878) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 15 | 33.80 ± 2.96 abcd | |
| Callidium villosulum Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 15 | 34.00 ± 2.96 abcd | |
| Semanotus sinauster Gressitt (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 150 | 34.40 ± 0.94 cd | |
| Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) | 15 | 34.70 ± 2.96 abcd | |
| Dichocrocis punctiferalis Guenée (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) | 15 | 34.70 ± 2.96 abcd | |
| Ostrinia furnacalis Guenée (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) | 15 | 34.90 ± 2.96 abcd | |
| Chinolyda flagellicornis (Smith) (Hymenoptera) | 15 | 34.60 ± 2.96 abcd | |
| Sclerodermus sp. | Monochamus alternatus Hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) | 30 | 32.50 ± 2.10 abcd |
| Temp. (°C) | Mean Male Developmental Time (From Egg To Adult) ± SE (Days) | Number of Replicates | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 61.9 ± 1.82 d | 15 | [65] |
| 24 | 43.0 ± 1.82 c | 15 | [65] |
| 25 | 25.0 ± 0.49 b | 221 | [18,20,61] |
| 25.5 | 23.1 ± 0.79 ab | 80 | [34] |
| 27 | 45.7 ± 1.05 c | 45 | [65,83] |
| 30 | 20.4 ± 0.88 a | 65 | [65,82] |
| 33 | 21.2 ± 1.83 ab | 15 | [65] |
| Temp. (°C) | Weighted Mean Pre-Ovipositional Time ± SE (Days) | Number of Replicates | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 12.67 ± 1.87 ab | 6 | [65] |
| 24 | 9.25 ± 2.29 ab | 4 | [65] |
| 25 | 10.65 ± 0.21 b | 486 | [38,61] |
| 25.5 | 10.36 ± 0.36 b | 160 | [34] |
| 26 | 6.81 ± 0.22 a | 547 | [63,89,95] |
| 27 | 5.00 ± 2.65 ab | 239 | [65,83,96] |
| 30 | 4.00 ± 2.65 ab | 103 | [65,82] |
| 33 | 2.50 ± 3.24 ab | 2 | [65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malabusini, S.; Lupi, D. Exploring the Biology of Quasi-Social Idiobiont Parasitoids in the Genus Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Insects 2024, 15, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110880
Malabusini S, Lupi D. Exploring the Biology of Quasi-Social Idiobiont Parasitoids in the Genus Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Insects. 2024; 15(11):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110880
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalabusini, Serena, and Daniela Lupi. 2024. "Exploring the Biology of Quasi-Social Idiobiont Parasitoids in the Genus Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae)" Insects 15, no. 11: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110880
APA StyleMalabusini, S., & Lupi, D. (2024). Exploring the Biology of Quasi-Social Idiobiont Parasitoids in the Genus Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Insects, 15(11), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110880






