New Molecular Phylogenetic Evidence Confirms Independent Origin of Coxal Combs in the Families of the ‘Cydnoid’ Complex (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomoidea)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Taxa
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. PCR Amplification, Purification, and Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Photographic Documentation
2.6. Morphological Data
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Alignment
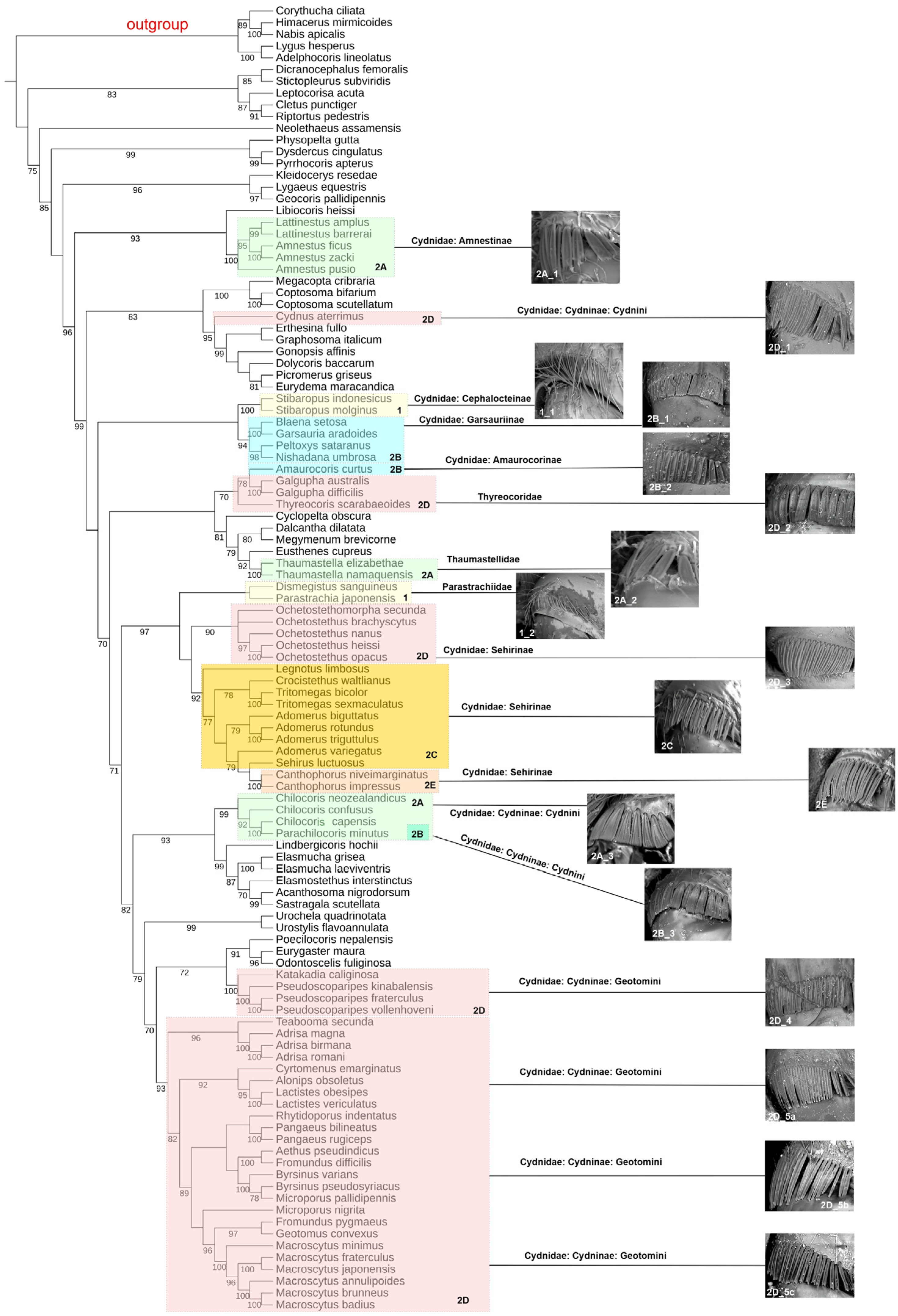
3.2. Tree Topology
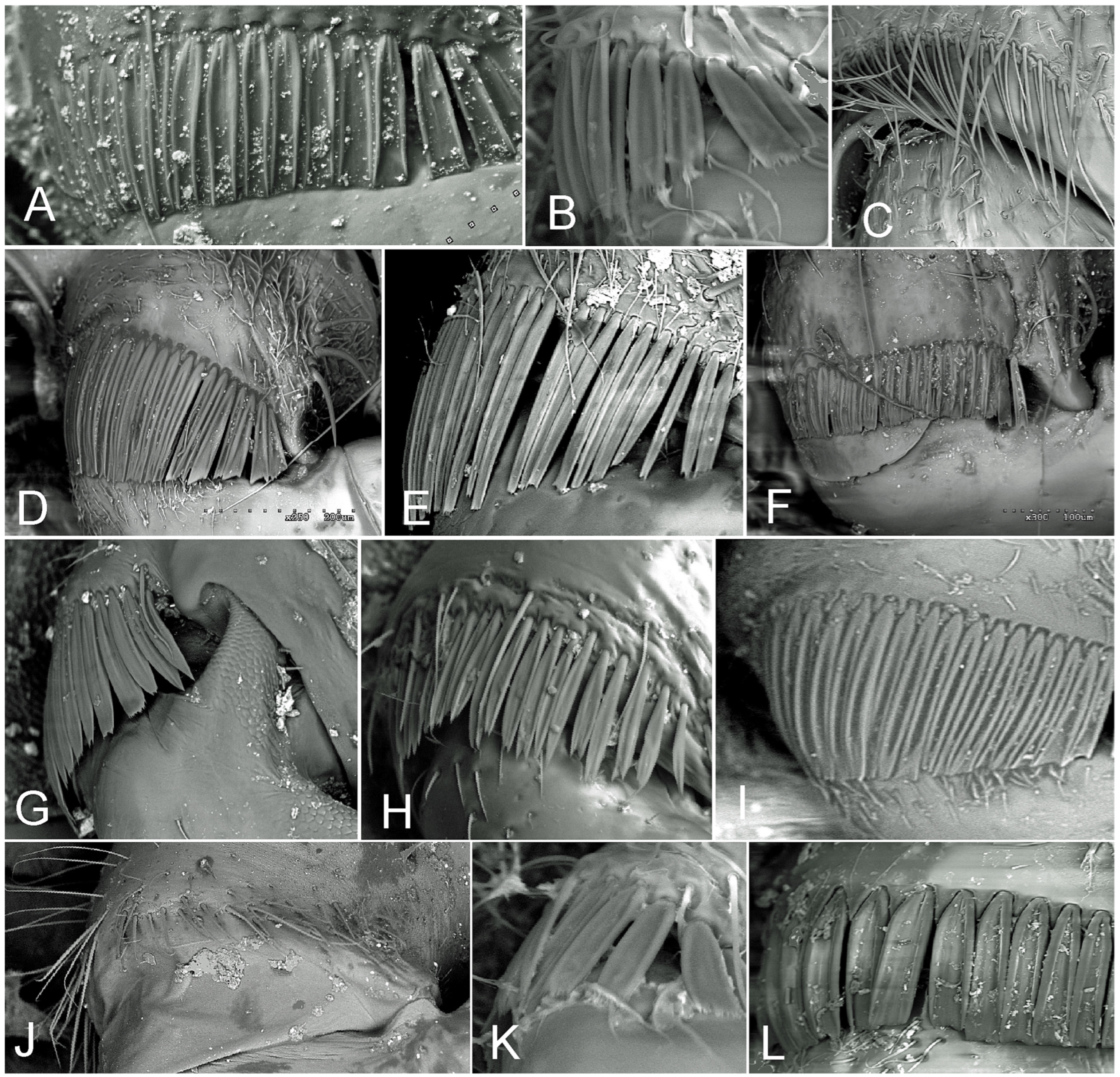
3.3. Types of Coxal Combs versus Classification of the Family Cydnidae
4. Discussion
4.1. Natural History of the Broadly Defined Cydnidae versus the Presence of Coxal Combs
4.2. Polyphyly of the Broadly Defined Cydnidae (Sensu Schuh & Weirauch, 2020)
4.3. Polyphyly of the Family Cydnidae Sensu Pluot-Sigwalt & Lis, 2008
4.4. Monophyly of Sehirinae + Parastrachiidae
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, G.K. Legs and locomotion. In The Insects: Structure and Function, 5th ed.; Simpson, S.J., Douglas, A.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 157–192. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, H.V.; Doyen, J.T.; Purcel III, A.H. Introduction to Insect Biology and Diversity, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. x + 564. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi, D.; Engel, M.S. Evolution of the Insects; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 755. [Google Scholar]
- Beutel, R.G.; Friedrich, F.; Yang, X.-K.; Ge, S.-Q. Insect Morphology and Phylogeny: A Textbook for Students of Entomology; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2014; p. 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertner, C.F.; Nardi, C. Burrower bugs (Cydnidae). In True Bugs (Heteroptera) of the Neotropics; Panizzi, A.R., Grazia, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2015; pp. 639–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, R.T.; Weirauch, C.H. True Bugs of the World (Hemiptera: Heteroptera). Classification and Natural History, 2nd ed.; Monograph Series; Siri Scientific Press: Manchester, UK, 2020; Volume 8, p. 767, 32 plates. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A.; Pluot-Sigwalt, D. Nymphal and adult cephalic chaetotaxy of the Cydnidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera), and its adaptive, taxonomic and phylogenetic significance. Eur. J. Entomol. 2002, 99, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterton, S.L. Scales and setae. In Encyclopedia of Insects; Resh, V.H., Carde, R.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 901–904. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A. Coxal combs in the Cydnidae sensu lato and three other related “cydnoid” families—Parastrachiidae, Thaumastellidae, Thyreocoridae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera): Functional, taxonomic, and phylogenetic significance. Zootaxa 2010, 2476, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.H. Evolution of Cicadomorpha (Insecta, Hemiptera). Biol. Environ. Sci. 2002, 176, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.J.; Hasiotis, S.T. Traces and burrowing behaviors of the cicada nymph cicadetta calliope: Neoichnology and paleoecological significance of extant soil-dwelling insects. Palaios 2008, 23, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, N.; Midgley, J.M.; Timm, A.E.; Villet, M.H. Successful identification of the final instar nymph of Quintilia carinata (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) by DNA extraction from the exuvium. J. Nat. Hist. 2014, 48, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, R.D. Cicadas of Southern Africa. An Illustrated Guide to Known Species; SANBI Publishing: Pretoria, South Africa, 2021; Volume 7, pp. 1–207. [Google Scholar]
- Dolling, W.L. A rationalised classification of the burrower bugs (Cydnidae). Syst. Entomol. 1981, 6, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazia, J.; Schuh, R.T.; Wheeler, W.C. Phylogenetic relationships of family groups in Pentatomoidea based on morphology and DNA sequences (Insecta: Heteroptera). Cladistics 2008, 24, 932–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, J.A.; Ziaja, D.; Lis, B.; Gradowska, P.A. Non-monophyly of the “cydnoid” complex within Pentatomoidea (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) revealed by Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of nuclear rDNA sequences. Arthropod Syst. Phylo. 2017, 75, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowińska, A.; Franielczyk-Pietyra, B.; Polhemus, D.A. The leg sensilla of insects from different habitats—Comparison of strictly aquatic and riparian bugs (Corixidae, Ochteridae, Gelastocoridae: Nepomorpha: Insecta: Heteroptera). Insects 2023, 14, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.W. The food plants of some “primitive” Pentatomoidea (Hemiptera: Heteroptera). Phytophaga 1988, 2, 19–45. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, C.W. The Pentatomomorpha (Hemiptera: Heteroptera): An annotated outline of its systematic history. Eur. J. Entomol. 1993, 90, 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, C.W. Prosorrhyncha (Heteroptera and Coleorrhyncha). In Encyclopedia of Insects; Resh, V.H., Carde, R.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 947–965. [Google Scholar]
- Gapud, V.P. A generic revision of the subfamily Asopinae, with consideration of its phylogenetic position in the family Pentatomidae and superfamily Pentatomoidea (Hemiptera-Heteroptera). Philipp. Entomol. 1991, 8, 865–961. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, D.H. A new species of Thaumastella with notes in the morphology, biology and distribution of the two southern African species (Heteroptera: Thaumastellidae). J. Entomol Soc. South. Afr. 1989, 52, 302–316. [Google Scholar]
- Froeschner, R.C. Cydnidae of the Western Hemisphere. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1960, 111, 337–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.H.; Schaefer, C.W. Parastrachiinae (Hemiptera: Cydnidae) raised to family level. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2002, 95, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluot-Sigwalt, D.; Lis, J.A. Morphology of the spermatheca in the Cydnidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera): Bearing of its diversity on classification and phylogeny. Eur. J. Entomol. 2008, 105, 279–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.J. Biodiversity of Heteroptera. In Insect Biodiversity; Footit, R.G., Adler, P.H., Eds.; Science and Society, Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, UK, 2009; pp. 233–263. [Google Scholar]
- Rider, D.A.; Schwertner, C.F.; Vilímová, J.; Rédei, D.; Kment, P.; Thomas, D.B. Higher systematics of the Pentatomoidea. In Invasive Stink Bugs and Related Species (Pentatomoidea): Biology, Higher Systematics, Semiochemistry, and Management; McPherson, J.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 25–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lis, J.A. Molecular apomorphies in the secondary and tertiary structures of length-variable regions (LVRs) of 18S rRNA shed light on the systematic position of the family Thaumastellidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomoidea). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, J.A.; Domagała, P.J. Inconsistencies in the classification of the family Cydnidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomoidea) revealed by molecular apomorphies in the secondary and tertiary structures of 18S rRNA length-variable region L (LVR L). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.W.; Dolling, W.R.; Tachikawa, S. The shieldbug genus Parastrachia and its position within the Pentatomoidea (Insecta: Hemiptera). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1988, 93, 283–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-Z.; Ren, D.; Rider, D.A.; Cai, W.-Z. Phylogeny of the infraorder Pentatomomorpha based on fossil and extant morphology, with description of a new fossil family from China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, J.A.; Heyna, J. Metathoracic wing venation in Cydnidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) and its bearing on the classification of the family. Annal. Zool. 2001, 51, 429–465. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A.; Schaefer, C.W. Tibial combs in the Cydnidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) and their functional, taxonomic and phylogenetic significance. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2005, 43, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Yu, S.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, X.R.; Men, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Rédei, D.; Xie, Q.; Bu, W.J. The evolutionary position of Lestoniidae revealed by molecular autapomorphies in the secondary structure of rRNA besides phylogenetic reconstruction (Insecta: Hemiptera: Heteroptera). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 177, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.M.; Barão, K.R.; Grassi, A.; Ferrari, A. A milestone for Pentatomoidea: Grazia et al. 2008-What do we know and where can we go? Zootaxa 2021, 4958, 406–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Cusachs, M.; Schwertner, C.F.; Kim, J.; Eger, J.; Grazia, J.; Jung, S. Opening Pandora’s box: Molecular phylogeny of the stink bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) reveals great incongruences in the current classification. Syst. Entomol. 2022, 41, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Li, M.; Dong, P.; Cui, Y.; Xie, Q.; Bu, W. Comparative and phylogenomic studies on the mitochondrial genomes of Pentatomomorpha (Insecta: Hemiptera: Heteroptera). BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Duwal, R.K.; Lee, S.W. COI barcoding of true bugs (Insecta, Heteroptera). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, J.A.; Lis, P.; Ziaja, D.J. Comparative studies on 12S and 16S mitochondrial rDNA sequences in pentatomomorphan bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomomorpha). Nat. J. (Opole Sci. Soc.) 2011, 44, 73–91. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A.; Bulińska-Balas, M.; Lis, P.; Ziaja, D.J.; Kocorek, A. Systematic position of Dinidoridae and Tessaratomidae within the superfamily Pentatomoidea (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) based on the analysis of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase II sequences. Nat. J. (Opole Sci. Soc.) 2012, 45, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A.; Kocorek, A.; Ziaja, D.J.; Lis, P. New insight into the systematic position of the endemic Madagascan genus Amberiana (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Dinidoridae) using 12S rDNA sequences. Turk. J. Zool. 2015, 39, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xie, Q.; Li, M.; Gao, C.; Cui, Y.; Xi, L.; Bu, W. Phylogeny of pentatomomorphan bugs (Hemiptera Heteroptera: Pentatomomorpha) based on six Hox gene fragments. Zootaxa 2011, 2888, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Liang, A.P.; Bu, C.P. A molecular phylogeny of Hemiptera inferred from mitochondrial genome sequences. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wei, J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, C.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Q. The complete mitochondrial genome of Pentatoma rufipes (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae) and its phylogenetic implications. ZooKeys 2021, 1042, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, A.C.M.; Lessinger, A.C.; Azeredo-Espin, A.M.L. Methods for recovery of mitochondrial DNA sequences from museum specimens of myiasis-causing flies. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2002, 16, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebsgaard, M.B.; Andersen, N.M.; Damgaard, J. Phylogeny of the true water bugs (Nepomorpha: Hemiptera–Heteroptera) based on 16S and 28S rDNA and morphology. Syst. Entomol. 2004, 29, 488–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.; Hajibabaei, M.; Blackburn, D.C.; Hanken, J.; Cantin, E.; Posfai, J.; Evans, T.C., Jr. DNA damage in preserved specimens and tissue samples: A molecular assassement. Front. Zool. 2008, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Elias, S.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Haile, J.; Munch, K.; Kuzmina, S.; Froese, D.G.; Sher, A.; Holdaway, R.N.; Willerslev, E. Non-Destructive Sampling of Ancient Insect DNA. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, J.A.; Ziaja, D.J.; Lis, P. Recovery of mitochondrial DNA for systematic studies of Pentatomoidea (Hemiptera: Heteroptera): Successful PCR on early 20th century dry museum specimens. Zootaxa 2011, 2748, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Kamiński, M.J.; Kanda, K.; Sweet, A.D.; Betancourt, J.L.; Holmgren, C.A.; Hempel, E.; Alberti, F.; Hofreiter, M. Recovery and analysis of ancient beetle DNA from subfossil packrat middens using high-throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, D.G.; Ibáñez, R.; Jaramillo, C.A.; Crawford, A.J.; Ray, J.M.; Gotte, S.W.; Jacobs, J.F.; Wynn, A.H.; Gonzalez-Porter, G.P.; McDiarmid, R.W.; et al. DNA barcoding of the National Museum of Natural History reptile tissue holdings raises concerns about the use of natural history collections and the responsibilities of scientists in the molecular age. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Frati, F.; Beckenbach, A.; Crespi, B. Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequence and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994, 87, 651–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognato, A.I.; Vogler, A.P. Exploring data interaction and nucleotide alignment in a multiple gene analysis of Ips (Coleoptera: Scolytinae). Syst. Biol. 2001, 50, 758–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new 417 heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Mark, P.V.D.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): New York, NY, USA; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.W.; Wilcox, D.B. A new species of Thaumastellidae (Hemiptera: Pentatomoidea) from southern Africa. J. Entomol. Soc. South. Afr. 1971, 34, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Tachikawa, S.; Schaefer, C.W. The biology of Parastrachia japonensis (Hemiptera: Pentatomoidea: ?-dae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Hironaka, M.; Nomakuchi, S. A review of the ecological parameters and implications of subsociality in Parastrachia japonensis (Hemiptera: Cydnidae), a semelparous species that specializes on a poor resource. Popul. Ecol. 2001, 43, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Nomakuchi, S. The Life History of the Parental Shield Bug, Parastrachia japonensis; Entomology Monographs; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Štys, P.; Davidová, J. Taxonomy of Thyreocoris (Heteroptera, Thyreocoridae). Annot. Zool. Bot. 1979, 134, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bundy, C.S.; McPherson, J.E. Life history and laboratory rearing of Corimelaena incognita (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Thyreocoridae), with descriptions of immature stages. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2009, 102, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matesco, V.C.; Grazia, J. Revision of the genus Alkindus Distant (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Thyreocoridae: Corimelaeninae). Zootaxa 2013, 3750, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josifov, M.V. Fauna Bulgarica 12. Heteroptera, Pentatomoidea; Academia Scientiarum Bulgariae: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1981; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, C.A. The Pentatomoidea of Illinois with keys to the Nearctic genera. Bull. Ill. Nat. Hist. Surv. 1919, 13, 157–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands Teil 54. Wanzen oder Heteropteren. I. Pentatomorpha; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1966; p. 235. [Google Scholar]
- Linnavuori, R.E. Cydnidae of West, Central and North-East Africa (Heteroptera); Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board: Helsinki, Finland, 1993; Volume 192, pp. 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A. A review of the tribe Amaurocorini, E. Wagner, with remarks on its systematic position within the family (Heteroptera: Cydnidae). Ann. Upp. Siles. Mus. Entomol. 1993, 4, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A. A Revision of Oriental Burrower Bugs; Upper Silesian Museum: Bytom, Poland, 1994; p. 349. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell-Lefroy, H. The insect fauna of Tirhut. I. Rhynchota Heteroptera. Rec. Indian Mus. 1909, 3, 301–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, R.F. Some new or little-known Hemiptera from Florida and Georgia. J. N. Y. Entomol. Soc. 1925, 33, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Linnavuori, R. Hemiptera of lsrael. In Annales Zoologici Societatis Zoologicae-Botanicae Fennicae “Vanamo“; Vanamo: Helsinki, Finland, 1960; Volume 22, pp. 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ehanno, B. 1961 Contribution à la connaissance des Hétéroptères Pentatomides armoricaines. Bull. Sot. Sci. Bretagne 1961, 36, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Putshkov, V.G. Fauna of Ukraine 21. Shield-bugs (Hemiptera, Pentatomoidea); Ukrainian Academy of Science: Kiev, Ukrain, 1961; p. 338. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, S. Hemiptera-Heteroptera. In Iconographia Insectorum Japonicorum Colore Naturali Edita, Volumen III; Asashina, S., Ishihara, T., Yasumatsu, K., Eds.; Hokuryukan: Tokyo, Japan, 1965; pp. 1–358. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.W.; Pitts, J.T. Pest status of Pangaeus bilineatus attacking peanuts in Texas. J. Econ. Entomol. 1974, 67, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, J.A.; Becker, M.; Schaefer, C.W. Burrower bugs (Cydnidae). In Heteroptera of Economic Importance; Schaefer, C.W., Panizzi, A.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 405–419. [Google Scholar]
- Riis, L.; Esbjerg, P.; Bellotti, A.C. Influence of temperature and soil moisture on some population growth parameters of Cyrtomenus bergi (Hemiptera: Cydnidae). Fla. Entomol. 2005, 88, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłys, G.; Lis, J.A. First cave records for Palearctic burrower bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Cydnidae) from Tajikistan, with a checklist of the World Cydnidae associated with caves. Zootaxa 2013, 3686, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, J.A.; Lis, B. Chilocoris laevicollis Horváth, 1919, and Ch. umbricola Linnavuori, 1993—Two trogloxenic burrower bugs recorded for the first time in Gabon (Central Africa). Zootaxa 2006, 4061, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breddin, G. Rhynchoten aus Ameisen-und Tennitenbauten. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 1904, 48, 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Froeschner, R. Three new species of burrowing bugs found in association with ants in Brazil (Hemiptera: Cydnidae). J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 1975, 48, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A. Chilocoris quadraticollis Linnavuori, 1993 (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Cydnidae): First records from the Democratic Republic of Congo with first data on its biology. Hetero Pol. Acta Faun. 2015, 9, 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Champion, G.C. A species of Scaptocoris Perty, found at the roots of sugar-cane. Entomol. Mon. Mag. 1900, 36, 235–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbrink, G. De kederische wortelwans. Meded. Proefstn. Java-Suikerind. 1912, 22, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Mouna, M.; Bensusan, K.; Perez, C.; Cortes, J. A review of entomological research on sandy beaches in Morocco, with an emphasis on Coleoptera. In Sandy Beaches and Coastal Zone Management—Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Sandy Beaches, Morocco, Rabat, 19–23 October 2009; Bayed, A., Ed.; Institut Scientifique: Rabat, Morocco, 2011; Volume 6, pp. 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fancello, L.; Cillo, D.; Bazzato, E. Cephalocteinae Mulsant et Rey, 1866 (Hemiptera, Heteroptera), a subfamily of Cydnidae new for the Italian fauna: First record of Cephalocteus scarabaeoides (Fabricius, 1807) from SardiniA. Zootaxa 2016, 4067, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, H. Inventa entomologica itineria Hispanici et Maroccani quod ab 1926 fecerunt Harald et Hakan Lindberg. XIII. Hemiptera Heteroptera (excl. Capsidae et Hydrobiotica). Comment. Biol. 1932, 3, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- de la Fuente, J.A. Revisión de los Pentatómidos ibéricos. Familia Cydnidae Billberg 1820. Bol. R. Soc. Esp. Hist. Nat. Biol. 1972, 70, 33–78. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, J.C.M. A new fossorial bug of the genus Scaptocoris Perty, 1830 (Hemiptera, Cydnidae). Bol. Mus. Nac. Nova Sér. Zool. 1952, 110, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Froeschner, R.C.; Chapman, Q.L. A South American cydnid, Scaptocoris castaneus Perty, established in the United States (Hemiptera: Cydnidae). Entomol. News 1963, 74, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, E.D.M.; Pasini, A.; Fonseca, I.C.B. Association of the soil bug Atarsocoris sp. (Hemiptera: Cydnidae) with the weed Senecio brasiliensis Less. Neotrop. Entomol. 2003, 32, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oliveira, L.J.; Malaguido, A.B. Flutuaçăo populacional dos percevejos castanhos da raiz, Scaptocoris castanea Perty (Hemiptera: Cydnidae), no perfil do solo em áreas produtoras de soja nas regiőes centro-oeste e sudeste do Brasil. Neotrop. Entomol. 2004, 33, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nardi, C.; Fernandes, P.M.; Rodrigues, O.D.; Bento, J.M.S. Flutuaçăo populacional e distribuiçăo vertical de Scaptocoris carvalhoi Becker (Hemiptera: Cydnidae) em área de pastagem. Neotrop. Entomol. 2007, 36, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Medeiros, M.O.; Sales Junior, O.; Amaral, J.L.; Souza, E.A.; Brito, M.N.; Tomazele, R. Dinâmica populacional de adultos de Atarsocoris brachiariae (Hemiptera: Cydnidae) comparados ao volume de precipitação na região de Rondonópolis MT. Rev. Biodivers. 2009, 8, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ávila, C.J.; Xavier, L.M.S.; Santos, V. Fluctuation and vertical distribution of a population of brown root stink bug (Scaptocoris castanea) in the soil profile in Mato Grosso do Sul State, Brazil. (Hemiptera: Cydnidae). Entomotrop 2015, 30, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Otten, E.; Müller, H.J. Heteroptera, Homoptera-Teil 1. In Handbuch Der Pflanzenkrankheiten; Sorauer, P., Ed.; Parey: Hamburg, Germany, 1956; Volume 5, pp. 1–399. [Google Scholar]
- Blatchley, W.S. Heteroptera or True Bugs of Eastern North America, with Especial Reference to the Faunas of Indiana and Florida; Nature Publishing Co.: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1926; p. 1116. [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga, M.C.; Cervantes, L.P. Life cycle and description of a new species of Amnestus Dallas (Hemiptera-Heteroptera: Cydnidae) associated with the fruits of several species of Ficus (Moraceae) in Mexico. J. N. Y. Entomol. Soc. 2001, 109, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, M.C. Revision generica de la familia Cydnidae (Hemiptera-Heteroptera) en México, con un listado de las especies conocidas. An. Inst. Biol. Univ. Nac. Auton. Mex. Zool. 2002, 73, 157–192. [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga, M.C.; Cervantes, L.P. Description of six new species of Amnestus Dallas (Hemiptera-Heteroptera: Cydnidae) from Mexico. J. N. Y. Entomol. Soc. 2005, 113, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, M.C.; Cervantes, L.P. Cydnidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) del centro de investigaciones Costeras La Mancha, Actopan, Veracruz, México. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2006, 77, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga, M.C.; Cervantes, L.P. The genus Amnestus Dallas (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Cydnidae: Amnestinae) in Mexico, with the description of eleven new species from Chiapas. Zootaxa 2014, 3779, 401–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, J.E., Jr. A new genus and three new species of burrowing bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera Cydnidae: Amnestinae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2008, 110, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, A.N. Some insects from the Chilibrillo bat caves of Panama. Insecutor Inscitiae Menstruus 1924, 12, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Tomokuni, M. First record of Garsauria aradoides Walker from Japan (Cydnidae). Rostria 1982, 34, 414. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Froeschner, R.C. The genus Blaena Walker (=Macrymenus Signoret) with the description of four new species and a key to the known forms (Hemiptera: Cydnidae). Rec. S. Aust. Mus. 1960, 13, 453–466. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A.; Heyna, J. 2001. Revision of the Australian genus Blaena (Heteroptera: Cydnidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2001, 98, 321–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, T.R.E.; Hine, D.J. Further notes on the biology of Sehirus bicolor (L.) (Hemiptera, Cydnidae). Entomol. Mon. Mag. 1950, 86, 299–301. [Google Scholar]
- Sites, R.W.; McPherson, J.E. Life history and laboratory rearing of Sehirus cinctus cinctus (Hemiptera: Cydnidae), with descriptions of immature stages. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1982, 75, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.F.; Brodie III, E.D.; Brown, J.H. Parent-offspring coadaptation and the dual genetic control of maternal care. Science 2001, 292, 1710–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.F.; Combs, N.; Brodie III, E.D. Insights into the costs of complex maternal care behavior in the burrower bug (Sehirus cinctus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2005, 57, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerzhner, I. New and little known Heteroptera from Mongolia and adjacent regions of the USSR. III. Ins. Mongol. 1976, 4, 30–86. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rizzotti-Vlach, M. Una nuova specie di Ochetostethus della Sardegna e note sulla distribuzione del genere in Italia (Heteroptera, Cydnidae). Nouv. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 17, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.A.; Lis, B.; Ziaja, D.; Dobosz, R. Description and DNA barcoding of Ochetostethomorpha secunda, a new species of the South African endemic burrower bug genus (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Cydnidae) from Namibia. Zootaxa 2014, 3884, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerca, J. Understanding natural selection and similarity: Convergent, parallel and repeated evolution. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 5451–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, D.H. Order Hemiptera. In Insects of Southern Africa; Scholtz, C.H., Holm, E., Eds.; Butterworths: Durban, South Africa, 1986; pp. 112–175. [Google Scholar]
- Weirauch, C.; Schuh, R.T.; Cassis, G.; Wheeler, W.C. Revisiting habitat and lifestyle transitions in Heteroptera (Insecta: Hemiptera): Insights from a combRocained morphological and molecular phylogeny. Cladistics 2019, 35, 67–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.L.; Zhang, Q.L.; Guo, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.Y. Comparative mitogenomic analysis of the superfamily Pentatomoidea (Insecta: Hemiptera: Heteroptera) and phylogenetic implications. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.L.; Zhang, Q.L.; Guo, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Corizus tetraspilus (Hemiptera: Rhopalidae) and phylogenetic analysis of Pentatomomorpha. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Leavengood, J.M., Jr.; Chapman, E.G.; Burkhardt, D.; Song, F.; Jiang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Cai, W. Mitochondrial phylogenomics of Hemiptera reveals adaptive innovations driving the diversification of true bugs. Proc. Biol. Sci. B 2017, 284, 20171223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic implications for Eurydema maracandica (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Mitochond. DNA B 2017, 2, 550–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raupach, M.J.; Hendrich, L.; Küchler, S.M.; Deister, F.; Morinière, J.; Gossner, M.M. Building-up of a DNA barcode library for true bugs (insecta: Hemiptera: Heteroptera) of Germany reveals taxonomic uncertainties and surprises. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, J.A. The Family Cydnidae—A need for reclassification? In Proceedings of the Abstract of the Second Quadrennial Meeting of the International Heteropterists’ Society, St. Petersburg, Russia, 16–19 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lis, J.A.; Domagała, P.J.; Lis, B. New Molecular Phylogenetic Evidence Confirms Independent Origin of Coxal Combs in the Families of the ‘Cydnoid’ Complex (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomoidea). Insects 2024, 15, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100792
Lis JA, Domagała PJ, Lis B. New Molecular Phylogenetic Evidence Confirms Independent Origin of Coxal Combs in the Families of the ‘Cydnoid’ Complex (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomoidea). Insects. 2024; 15(10):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100792
Chicago/Turabian StyleLis, Jerzy A., Paweł J. Domagała, and Barbara Lis. 2024. "New Molecular Phylogenetic Evidence Confirms Independent Origin of Coxal Combs in the Families of the ‘Cydnoid’ Complex (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomoidea)" Insects 15, no. 10: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100792
APA StyleLis, J. A., Domagała, P. J., & Lis, B. (2024). New Molecular Phylogenetic Evidence Confirms Independent Origin of Coxal Combs in the Families of the ‘Cydnoid’ Complex (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomoidea). Insects, 15(10), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100792






