Exploration of Candidate Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis, Regulation and Recognition of the Male-Produced Aggregation Pheromone of Halyomorpha halys
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
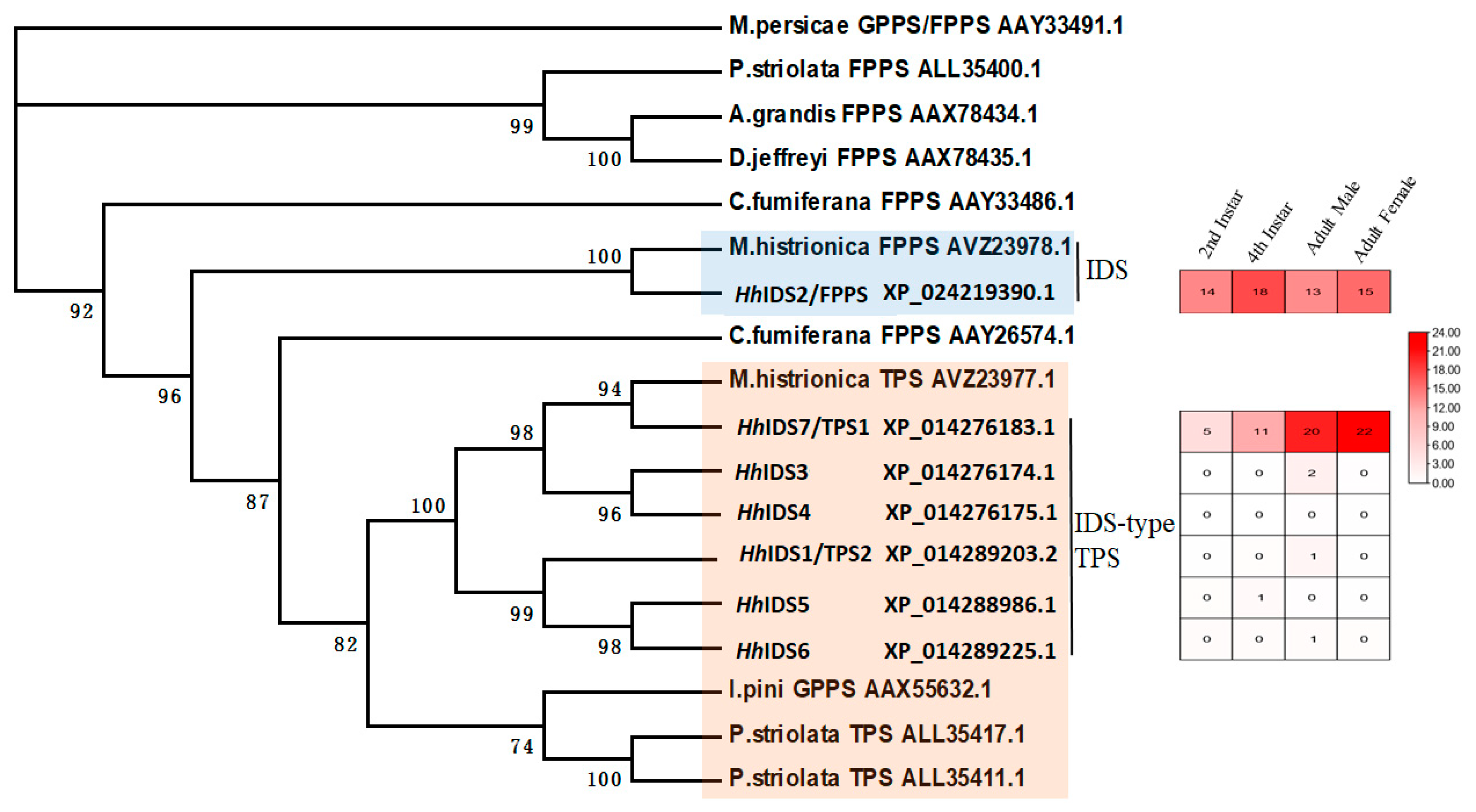
2.1. Identification of Farnesyl Diphosphate (FDP) and Terpene Synthase (TPS) Genes in H. halys
2.2. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
2.3. Molecular Docking of HhTPS1 and HhCSP 5 in H. halys
3. Results
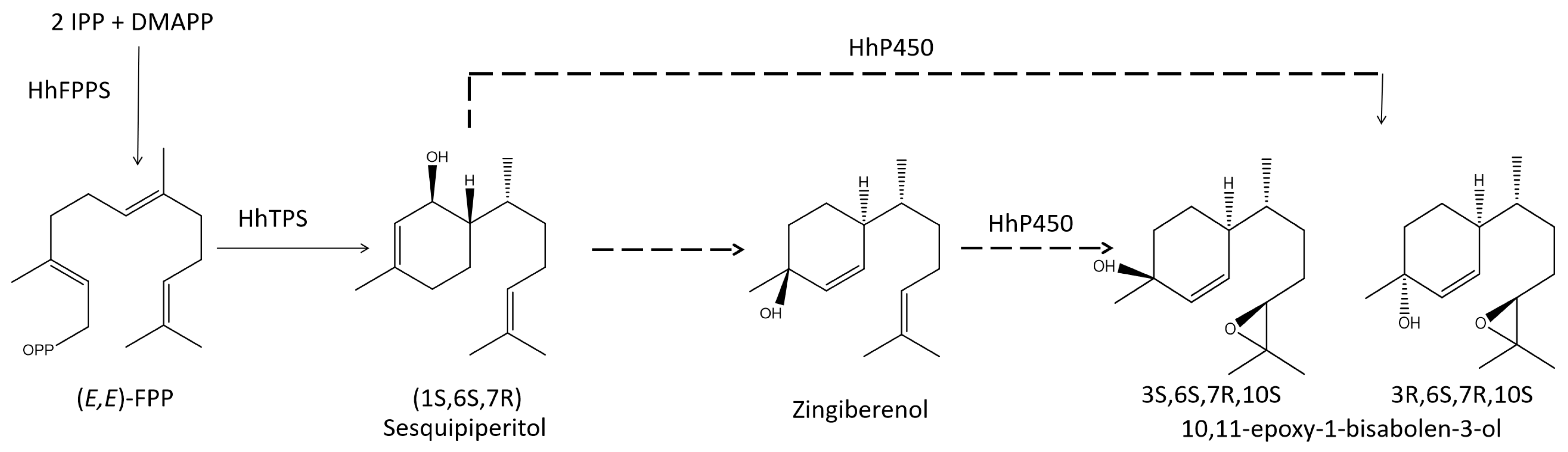
3.1. Identification of Key FDP and TPS Genes in the Aggregation Pheromone Biosynthesis Pathway
3.2. Co-Expression Network Analysis to Identify the HhTPS1 Co-Expressed Genes
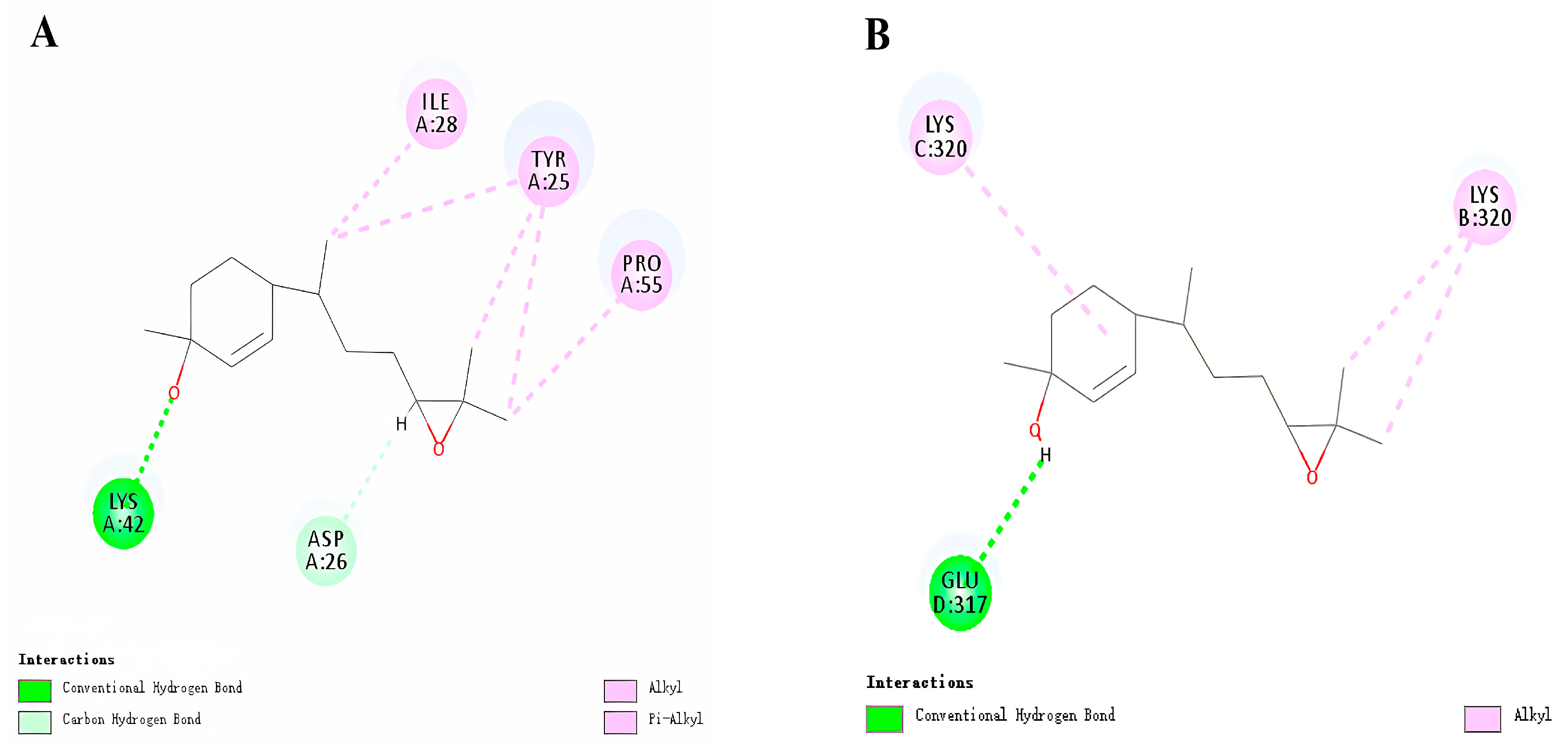
3.3. Molecular Docking of HhTPS1 and HhCSP5
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, D.H.; Short, B.D.; Joseph, S.V.; Bergh, J.C.; Leskey, T.C. Review of the biology, ecology, and management of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskey, T.C.; Nielsen, A.L. Impact of the Invasive Brown Marmorated Stink Bug in North America and Europe: History, Biology, Ecology, and Management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 599–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Gariepy, T.; Mason, P.; Gillespie, D.; Talamas, E.; Haye, T. Seasonal parasitism and host specificity of Trissolcus japonicus in northern China. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, M.E.; Bansal, R.; Benoit, J.B.; Blackburn, M.B.; Chao, H.; Chen, M.; Cheng, S.; Childers, C.; Dinh, H.; Doddapaneni, H.V.; et al. Brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), genome: Putative underpinnings of polyphagy, insecticide resistance potential and biology of a top worldwide pest. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.C.; Morrison, W.R.; Khrimian, A.; Rice, K.B.; Leskey, T.C.; Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Nielsen, A.L.; Blaauw, B.R. Chemical ecology of Halyomorpha halys: Discoveries and applications. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 989–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrimian, A.; Zhang, A.; Weber, D.C.; Ho, H.Y.; Aldrich, J.R.; Vermillion, K.E.; Siegler, M.A.; Shirali, S.; Guzman, F.; Leskey, T.C. Discovery of the aggregation pheromone of the brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys) through the creation of stereoisomeric libraries of 1-bisabolen-3-ols. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acebes-Doria, A.L.; Agnello, A.M.; Alston, D.G.; Andrews, H.; Beers, E.H.; Bergh, J.C.; Bessin, R.; Blaauw, B.R.; Buntin, G.D.; Burkness, E.C.; et al. Season-Long Monitoring of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Throughout the United States Using Commercially Available Traps and Lures. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 113, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, B.D.; Khrimian, A.; Leskey, T.C. Pheromone-based decision support tools for management of Halyomorpha halys in apple orchards: Development of a trap-based treatment threshold. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoni, G.; Bertoldi, V.; Malek, R.; Foti, M.C.; Peri, E.; Maistrello, L.; Haye, T.; Conti, E. Native egg parasitoids recorded from the invasive Halyomorpha halys successfully exploit volatiles emitted by the plant–herbivore complex. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Abubeker, S.; Yu, M.; Leskey, T.; Zhang, A. Semiochemical Production and Laboratory Behavior Response of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug, Halyomorpha Halys. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0140876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, E.J.N.; Lin, G.M.; Voigt, C.A.; Clardy, J. Bacterial terpene biosynthesis: Challenges and opportunities for pathway engineering. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2889–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholl, D. Biosynthesis of terpene pheromones in hemiptera/stink bugs. In Insect Pheromone Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Dannert, C. Biosynthesis of terpenoid natural products in fungi. Adv. Biochem. Eng./Biotechnol. 2015, 148, 19–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, C.I.; Weisshaar, S.; Lin, R.P.; Bohlmann, J. Functional plasticity of paralogous diterpene synthases involved in conifer defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Lin, Y.J.; Pickett, J.A.; Birkett, M.A.; Wu, K.; Wang, G.; Zhou, J.J. Expression of lima bean terpene synthases in rice enhances recruitment of a beneficial enemy of a major rice pest. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Fu, N.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Functional characterization of (E)-β-caryophyllene synthase from lima bean and its up-regulation by spider mites and alamethicin. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilg, A.B.; Bearfield, J.C.; Tittiger, C.; Welch, W.H.; Blomquist, G.J. Isolation and functional expression of an animal geranyl diphosphate synthase and its role in bark beetle pheromone biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9760–9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.; Lehner, B.; Khrimian, A.; Muchlinski, A.; Luck, K.; Köllner, T.G.; Weber, D.C.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.E.; Tholl, D. An IDS-Type Sesquiterpene Synthase Produces the Pheromone Precursor (Z)-α-Bisabolene in Nezara viridula. J. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 45, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskey, T.C.; Khrimian, A.; Weber, D.C.; Aldrich, J.C.; Short, B.D.; Lee, D.H.; Morrison, W.R., III. Behavioral responses of the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Stål) to traps baited with stereoisomeric mixtures of 10,11-epoxy-1-bisabolen-3-OL. J. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 41, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.; Khrimian, A.; Young, S.; Lehner, B.; Luck, K.; Wallingford, A.; Ghosh, S.K.B.; Zerbe, P.; Muchlinski, A.; Marek, P.E.; et al. De novo formation of an aggregation pheromone precursor by an isoprenyl diphosphate synthase-related terpene synthase in the harlequin bug. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8634–E8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, M.E.; Rhoades, J.H.; Nelson, D.R.; Kuhar, D.; Lancaster, J.; Lehner, B.; Tholl, D.; Weber, D.C.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.E. A Transcriptome Survey Spanning Life Stages and Sexes of the Harlequin Bug, Murgantia histrionica. Insects 2017, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, P.; Lu, Y.; Kumar, N.; Creasy, T.; Daugherty, S.; Chibucos, M.C.; Orvis, J.; Shetty, A.; Ott, S.; Flowers, M.; et al. Rapid transcriptome sequencing of an invasive pest, the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, M.E.; Shelby, K.S.; Kuhar, D.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.E. Transcriptome of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). PloS ONE 2014, 9, e111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Felicioli, A.; Dani, F.R. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: An overview across arthropods. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, M.; Ban, L.; Song, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, G. Niemann-Pick C2 Proteins: A New Function for an Old Family. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, D.P.; Togawa, R.C.; Costa, M.M.; Grynberg, P.; Martins, N.F.; Andow, D.A. Identification and expression profile of odorant-binding proteins in Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Huang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S. Identification of Candidate Olfactory Genes in the Antennal Transcriptome of the Stink Bug Halyomorpha halys. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, Z.; Lancaster, J.; Larose, H.; Khrimian, A.; Luck, K.; Sparks, M.E.; Gendreau, K.L.; Shewade, L.; Köllner, T.G.; Weber, D.C.; et al. Ancient origin and conserved gene function in terpene pheromone and defense evolution of stink bugs and hemipteran insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 152, 103879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dong, Z.; Fang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Y.Q.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Xia, Q.; et al. OrthoVenn2: A web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W52–W58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Luo, H.; Huo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; et al. KOBAS-i: Intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Lindert, S.; Zhu, W.; Wang, K.; McCammon, J.A.; Oldfield, E. Taxodione and arenarone inhibit farnesyl diphosphate synthase by binding to the isopentenyl diphosphate site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2530–E2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaselli, S.; Crescenzi, O.; Sanfelice, D.; Ab, E.; Wechselberger, R.; Angeli, S.; Scaloni, A.; Boelens, R.; Tancredi, T.; Pelosi, P.; et al. Solution structure of a chemosensory protein from the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10606–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of protein structures: Patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, D.; Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U. VERIFY3D: Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 277, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, J.K.; Law, S.M.; Brooks, C.L., III. Flexible CDOCKER: Development and application of a pseudo-explicit structure-based docking method within CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2016, 37, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Xue, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, T.S.; Bai, Z.; Tan, T. Metabolic engineering strategies for sesquiterpene production in microorganism. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Yeo, Y.; Greenhagen, B.T.; McMullin, T.; Song, L.; Maurina-Brunker, J.; Rosson, R.; Noel, J.P.; Chappell, J. Metabolic engineering of sesquiterpene metabolism in yeast. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, Y.M.; Xu, P.; Hwang, J.K.; Zeng, F.; Tan, K.; Bhagavathy, G.; Chauhan, K.R.; Leal, W.S. Reverse chemical ecology approach for the identification of an oviposition attractant for Culex quinquefasciatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Fu, N.; Li, D.; Chang, H.; Qu, C.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; Luo, C. Identification of an Alarm Pheromone-Binding Chemosensory Protein From the Invasive Sycamore Lace Bug Corythucha ciliata (Say). Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, D.; Dewer, Y.; Qu, C.; Yang, Z.; Tian, J.; Luo, C. Discrimination of Oviposition Deterrent Volatile β-Ionone by Odorant-Binding Proteins 1 and 4 in the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, H.; Li, D.; Dewer, Y.; Niu, C.; Li, F.; Luo, C. Identification and functional characterization of odorant-binding proteins 69a and 76a of Drosophila suzukii. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, B.; Grossi, G.; Falabella, P.; Liu, Y.; Yan, S.; Lu, J.; Xi, J.; Wang, G. Molecular Basis of Alarm Pheromone Detection in Aphids. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.Z.; Tang, R.; Zhang, J.P.; Yang, S.Y.; Chen, G.H.; He, K.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, F. Behavioral Evidence and Olfactory Reception of a Single Alarm Pheromone Component in Halyomorpha halys. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Potential Function | Coexpressed Genes | Weight Values | Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synthase genes in aggregation pheromone biosynthesis pathway | XM_024359849.1 | 0.030 | cytochrome P450 6a14 (LOC106686595) |
| XM_014425704.2 | 0.080 | cytochrome P450 6j1 (LOC106683935) | |
| XM_014435358.2 | 0.068 | cytochrome P450 6a2-like (LOC106690077) | |
| XM_024361356.1 | 0.128 | cytochrome P450 6j1-like (LOC106678797) | |
| XM_024361357.1 | 0.184 | cytochrome P450 6j1-like (LOC106678797) | |
| XM_024362540.1 | 0.176 | cytochrome P450 6a2-like (LOC106678035) | |
| XM_014428854.1 | 0.092 | cytochrome P450 4C1 (LOC106685872) | |
| Transcriptional factors in aggregation pheromone biosynthesis pathway | XM_024361675.1 | 0.040 | zinc finger protein 711-like (LOC106678825) |
| XM_024362041.1 | 0.211 | zinc finger MIZ domain-containing protein 1-like (LOC106691938) | |
| XM_024359956.1 | 0.177 | zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 1-like (LOC106682986) | |
| XM_024360254.1 | 0.175 | putative homeodomain transcription factor (LOC106692479) | |
| XM_014438343.2 | 0.11 | zinc finger BED domain-containing protein 4-like (LOC106692406) | |
| XM_014438440.2 | 0.206 | RING finger protein 37 (LOC106692477) | |
| XM_014438969.1 | 0.039 | transcriptional regulatory protein AlgP (LOC106692793) | |
| XM_014433039.2 | 0.083 | transcription factor kayak (LOC106688534) | |
| XM_014433901.1 | 0.055 | zinc finger autosomal protein-like (LOC106689113) | |
| XM_014435086.2 | 0.108 | zinc finger autosomal protein-like (LOC106689884) | |
| XM_014435137.2 | 0.215 | zinc finger protein 711-like (LOC106689915) | |
| XM_014430570.2 | 0.054 | zinc finger protein 420 (LOC106686950) | |
| XM_014431700.2 | 0.137 | coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 1 (LOC106687684) | |
| XM_014425878.2 | 0.058 | coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 2-like (LOC106684044) | |
| XM_014427582.2 | 0.053 | zinc finger MYM-type protein 1 (LOC106685089) | |
| XM_014428786.2 | 0.077 | zinc finger protein 629-like (LOC106685840) | |
| XM_014432021.2 | 0.222 | transcription factor A, mitochondrial (LOC106687869) | |
| Recognition and transport aggregation pheromones | XM_024358492.1 | 0.178 | odorant receptor 85b-like (LOC106692425) |
| XM_014421632.2 | 0.124 | chemosensory protein 5 [Nezara viridula] (LOC106681357) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Zhang, F.; Dewer, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, F. Exploration of Candidate Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis, Regulation and Recognition of the Male-Produced Aggregation Pheromone of Halyomorpha halys. Insects 2023, 14, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020163
Wu C, Zhang F, Dewer Y, Zhang J, Li F. Exploration of Candidate Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis, Regulation and Recognition of the Male-Produced Aggregation Pheromone of Halyomorpha halys. Insects. 2023; 14(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chunyan, Feng Zhang, Youssef Dewer, Jinping Zhang, and Fengqi Li. 2023. "Exploration of Candidate Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis, Regulation and Recognition of the Male-Produced Aggregation Pheromone of Halyomorpha halys" Insects 14, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020163
APA StyleWu, C., Zhang, F., Dewer, Y., Zhang, J., & Li, F. (2023). Exploration of Candidate Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis, Regulation and Recognition of the Male-Produced Aggregation Pheromone of Halyomorpha halys. Insects, 14(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020163





