Buzzing Homes: Using Citizen Science Data to Explore the Effects of Urbanization on Indoor Mosquito Communities
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Citizen Science Dataset
2.2. Classification of Urbanization Level by Indicator Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
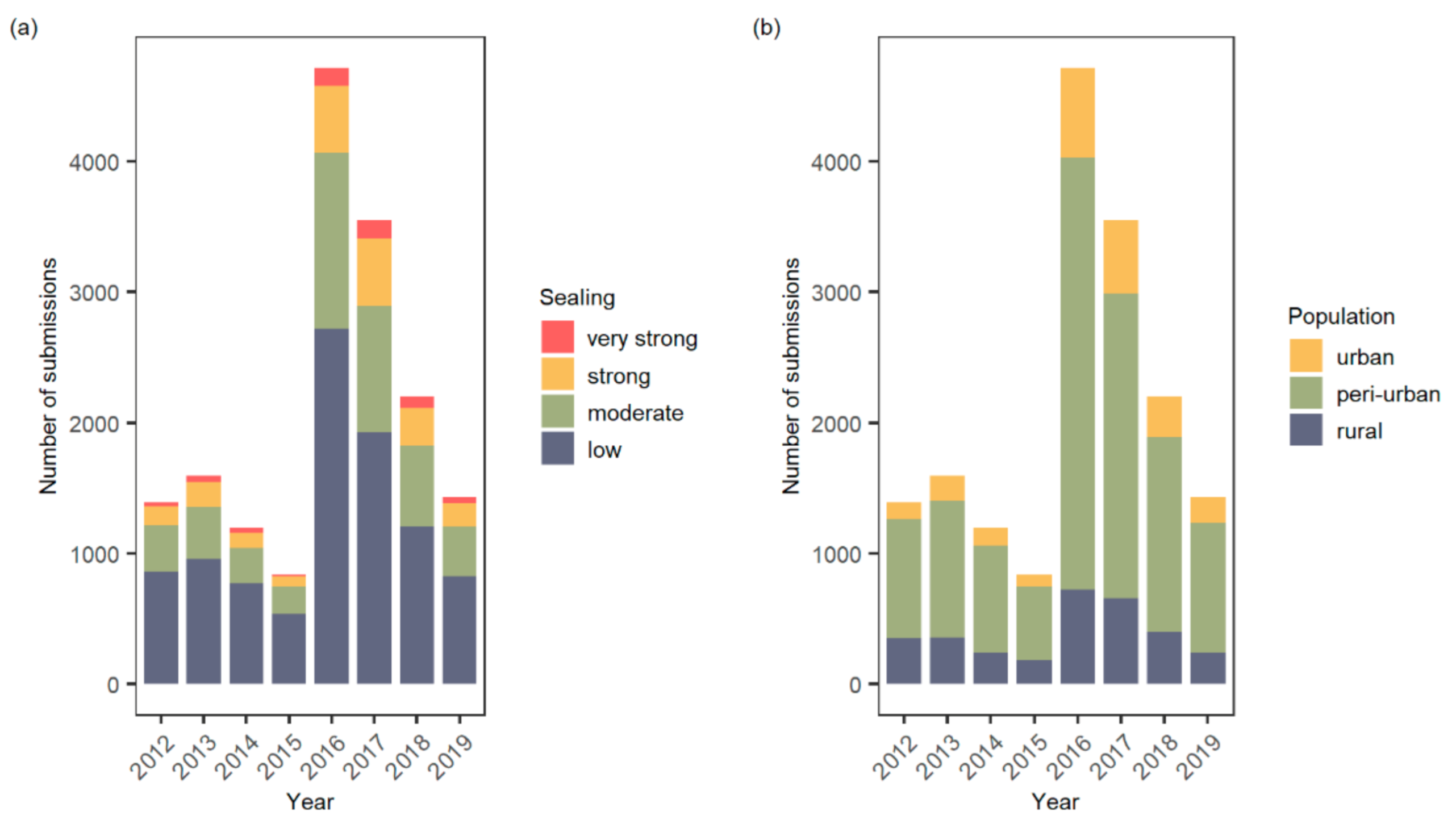
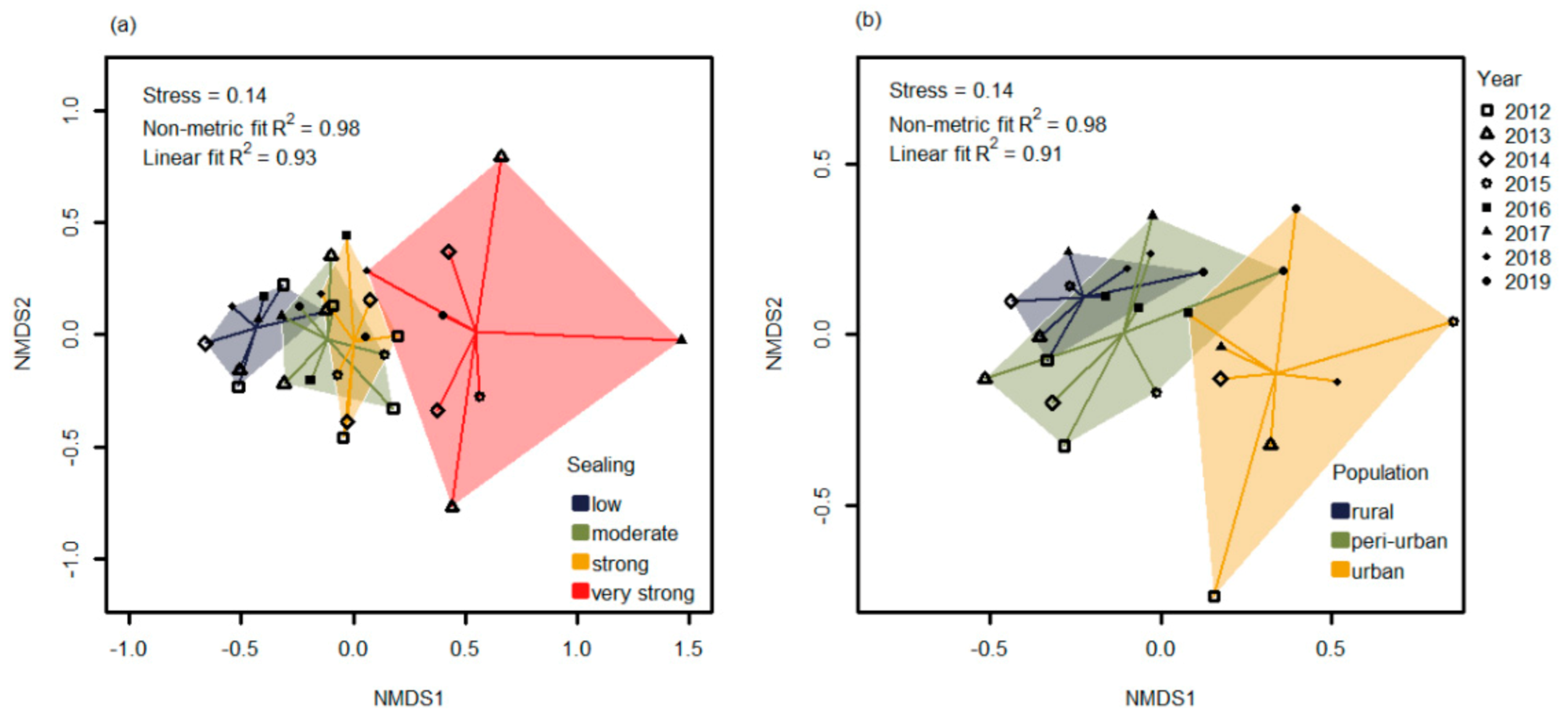
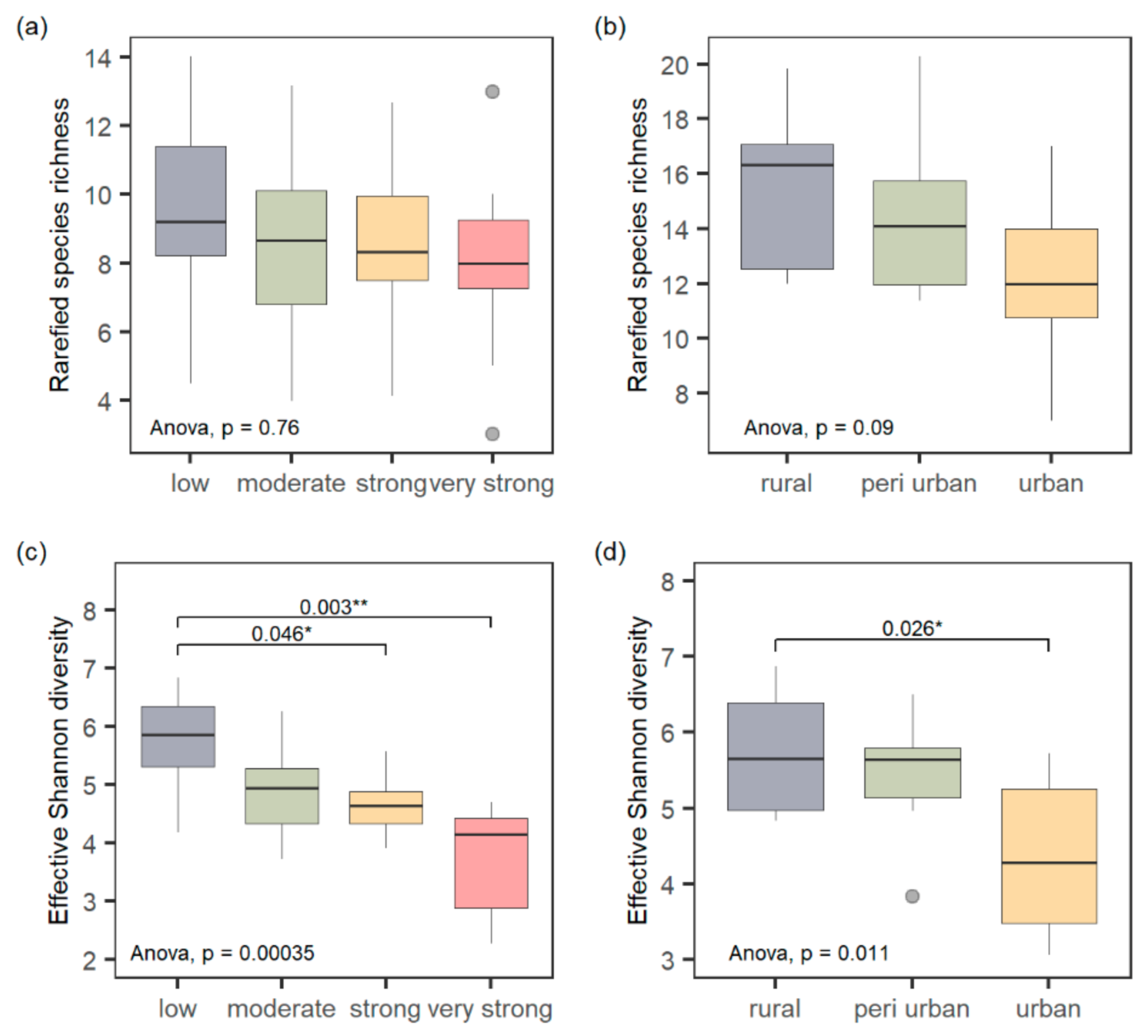
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gossner, C.M.; Ducheyne, E.; Schaffner, F. Increased risk for autochthonous vector-borne infections transmitted by Aedes albopictus in continental Europe. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlock, J.M.; Hansford, K.M.; Versteirt, V.; Cull, B.; Kampen, H.; Fontenille, D.; Hendrickx, G.; Zeller, H.; Van Bortel, W.; Schaffner, F. An entomological review of invasive mosquitoes in Europe. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2015, 105, 637–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, H.; Walther, D. Vector potential of mosquito species (Diptera: Culicidae) occurring in Central Europe. In Mosquito-Borne Diseases: Implications for Public Health; Benelli, G., Mehlhorn, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 10, pp. 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlin, I.; Faraji, A.; Ninivaggi, D.V.; Barker, C.M.; Kilpatrick, A.M. Anthropogenic impacts on mosquito populations in North America over the past century. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, D.E. Mosquito-borne diseases as a consequence of land use change. EcoHealth 2004, 1, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, E.N.; Tokarz, R.E.; Smith, R.C. Satellite imaging and long-term mosquito surveillance implicate the influence of rapid urbanization on Culex vector populations. Insects 2019, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, A.B.B.; Beier, J.C.; Benelli, G. Complexity of the relationship between global warming and urbanization–an obscure future for predicting increases in vector-borne infectious diseases. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, A.B.B.; Benelli, G.; Beier, J.C. Beyond frontiers: On invasive alien mosquito species in America and Europe. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.; Borstler, J.; Badusche, M.; Luhken, R.; Garms, R.; Tannich, E. Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) of metropolitan Hamburg, Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honnen, A.C.; Monaghan, M.T.; Sharakhov, I. City-dwellers and country folks: Lack of population differentiation along an urban-rural gradient in the mosquito Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townroe, S.; Callaghan, A. British container breeding mosquitoes: The impact of urbanisation and climate change on community composition and phenology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manica, M.; Filipponi, F.; D’Alessandro, A.; Screti, A.; Neteler, M.; Rosa, R.; Solimini, A.; Della Torre, A.; Caputo, B. Spatial and temporal hot spots of Aedes albopictus abundance inside and outside a South European metropolitan area. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebl, K.; Zittra, C.; Silbermayr, K.; Obwaller, A.; Berer, D.; Brugger, K.; Walter, M.; Pinior, B.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Rubel, F. Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) and their relevance as disease vectors in the city of Vienna, Austria. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobucar, A.; Benic, N.; Krajcar, D.; Kosanovic-Licina, M.L.; Tesic, V.; Merdic, E.; Vrucina, I.; Savic, V.; Barbic, L.; Stevanovic, V.; et al. An overview of mosquitoes and emerging arboviral infections in the Zagreb area, Croatia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraguti, M.; Martinez-de la Puente, J.; Roiz, D.; Ruiz, S.; Soriguer, R.; Figuerola, J. Effects of landscape anthropization on mosquito community composition and abundance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzidová, M.; Čabanová, V.; Stloukal, E.; Miterpáková, M. Fluctuation of mosquito species in capital city of Slovakia in years 2015 and 2016. Folia Faun. Slov. 2016, 21, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Spence Beaulieu, M.R.; Hopperstad, K.; Dunn, R.R.; Reiskind, M.H. Simplification of vector communities during suburban succession. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardo, M.V.; Rubio, A.; Junges, M.T.; Vezzani, D.; Carbajo, A.E. Heterogeneous distribution of Culex pipiens, Culex quinquefasciatus and their hybrids along the urbanisation gradient. Acta Trop. 2018, 178, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsripong, P.; Green, A.; Kittayapong, P.; Kapan, D.; Wilcox, B.; Bennett, S. Mosquito vector diversity across habitats in central Thailand endemic for dengue and other arthropod-borne diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, M.; Armbruster, P.A.; Tuno, N. Differences in responses to urbanization between invasive mosquitoes, Aedes japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) and Aedes albopictus, in their native range, Japan. J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer Steiger, D.B.; Ritchie, S.A.; Laurance, S.G. Mosquito communities and disease risk influenced by land use change and seasonality in the Australian tropics. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayi, M.P.A.; Bamou, R.; Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Fontaine, A.; Jeffries, C.L.; Walker, T.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Cornel, A.J.; Tchuinkam, T. Habitat and seasonality affect mosquito community composition in the west region of Cameroon. Insects 2020, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.; Martins, E.A.C.; de Oliveira, O.; de Oliveira, V.; de Oliveira Neto, B.P.; de Oliveira, J.E. Dispersion of Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus, 1762) and Aedes albopictus (Skuse, 1894) in the rural zone of North Paraná state. Brazil. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2004, 47, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; Engeler, L.; Vavassori, L.; Suter, T.; Guidi, V.; Gschwind, M.; Tonolla, M.; Flacio, E. Surveillance of invasive Aedes mosquitoes along Swiss traffic axes reveals different dispersal modes for Aedes albopictus and Ae. japonicus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullenberg, C.; Kasperowski, D. What is citizen science? A scientometric meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, R.; Strezov, V. An analysis of citizen science based research: Usage and publication patterns. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Puig, N.; De Filippo, D.; Mauleón, E.; Sanz-Casado, E. Scientific landscape of citizen science publications: Dynamics, content and presence in social media. Publications 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, J.L.; Zuckerberg, B.; Bonter, D.N. Citizen science as an ecological research tool: Challenges and benefits. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 41, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiago, P.; Ceia-Hasse, A.; Marques, T.A.; Capinha, C.; Pereira, H.M. Spatial distribution of citizen science casuistic observations for different taxonomic groups. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernat, N.; Kampen, H.; Ruland, F.; Jeschke, J.M.; Werner, D. Drivers of spatio-temporal variation in mosquito submissions to the citizen science project ‘Mückenatlas’. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldmann, J.; Heilmann-Clausen, J.; Holm, T.E.; Levinsky, I.; Markussen, B.; Olsen, K.; Rahbek, C.; Tøttrup, A.P.; Leung, B. What determines spatial bias in citizen science? Exploring four recording schemes with different proficiency requirements. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.F. Understanding sampling and taxonomic biases recorded by citizen scientists. J. Insect Conserv. 2014, 18, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, L.; Ruete, A. Explaining spatial variation in the recording effort of citizen science data across multiple taxa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelling, S.; Fink, D.; La Sorte, F.A.; Johnston, A.; Bruns, N.E.; Hochachka, W.M. Taking a ‘Big Data’ approach to data quality in a citizen science project. Ambio 2015, 44 (Suppl. 4), 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, E.; Specht, H. Influence of volunteer and project characteristics on data quality of biological surveys. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelling, S.; Johnston, A.; Bonn, A.; Fink, D.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Bonney, R.; Fernandez, M.; Hochachka, W.M.; Julliard, R.; Kraemer, R.; et al. Using semistructured surveys to improve citizen science data for monitoring biodiversity. Bioscience 2019, 69, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wäldchen, J.; Mäder, P.; Cooper, N. Machine learning for image based species identification. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 2216–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.P.; Boger, R.; Dexter, S.; Low, R. Mosquitoes and public health: Improving data validation of citizen science contributions using computer vision. In Delivering Superior Health and Wellness Management with IoT and Analytics. Healthcare Delivery in the Information Age; Wickramasinghe, N., Bodendorf, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Part 1; pp. 469–493. [Google Scholar]
- Bradter, U.; Mair, L.; Jönsson, M.; Knape, J.; Singer, A.; Snäll, T.; Anderson, B. Can opportunistically collected citizen science data fill a data gap for habitat suitability models of less common species? Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henckel, L.; Bradter, U.; Jönsson, M.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Snäll, T.; Real, R. Assessing the usefulness of citizen science data for habitat suitability modelling: Opportunistic reporting versus sampling based on a systematic protocol. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, N.J.B.; van Strien, A.J.; August, T.A.; de Zeeuw, M.P.; Roy, D.B.; Anderson, B. Statistics for citizen science: Extracting signals of change from noisy ecological data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.; Moran, N.; Musgrove, A.; Fink, D.; Baillie, S.R. Estimating species distributions from spatially biased citizen science data. Ecol. Model. 2020, 422, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, N.J.B.; Jarzyna, M.A.; Keil, P.; Dambly, L.I.; Boersch-Supan, P.H.; Browning, E.; Freeman, S.N.; Golding, N.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Henrys, P.A.; et al. Data integration for large-scale models of species distributions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, C.T.; Martin, J.M.; Major, R.E.; Kingsford, R.T. Avian monitoring–comparing structured and unstructured citizen science. Wildl. Res. 2018, 45, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.V.; Hartop, E.A. Big data from tiny flies: Patterns revealed from over 42,000 phorid flies (Insecta: Diptera: Phoridae) collected over one year in Los Angeles, California, USA. Urban Ecosyst. 2016, 20, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladonja, B.; Poljuha, B. Citizen science as a tool in biological recording–A case study of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle. Forests 2018, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, D.M.; Pauly, G.B.; Kaiser, K. Citizen science as a tool for augmenting museum collection data from urban areas. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, B.; Manica, M.; Filipponi, F.; Blangiardo, M.; Cobre, P.; Delucchi, L.; De Marco, C.M.; Iesu, L.; Morano, P.; Petrella, V.; et al. ZanzaMapp: A scalable citizen science tool to monitor perception of mosquito abundance and nuisance in Italy and beyond. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.R.B.; Oltra, A.; Collantes, F.; Delgado, J.A.; Lucientes, J.; Delacour, S.; Bengoa, M.; Eritja, R.; Bartumeus, F. Citizen science provides a reliable and scalable tool to track disease-carrying mosquitoes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NESCent Working Group on the Evolutionary Biology of the Built Environment; Martin, L.J.; Adams, R.I.; Bateman, A.; Bik, H.M.; Hawks, J.; Hird, S.M.; Hughes, D.; Kembel, S.W.; Kinney, K.; et al. Evolution of the indoor biome. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, D.; Kampen, H. The citizen science project ‘Mueckenatlas’ helps monitor the distribution and spread of invasive mosquito species in Germany. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1790–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Petric, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Madon, M.B.; Dahl, C.; Kaiser, A. Mosquitoes and Their Control, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner, F.; Angel, G.; Geoffroy, B.; Hervy, J.; Rhaiem, A.; Brunhes, J. The Mosquitoes of Europe. An Identification and Training Programme (CD-Rom); IRD Éditions & EID: Méditerrannée, Montpellier, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Heym, E.C.; Kampen, H.; Walther, D. Mosquito species composition and phenology (Diptera, Culicidae) in two German zoological gardens imply different risks of mosquito-borne pathogen transmission. J. Vector. Ecol. 2018, 43, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcker, R. Bodenversiegelung–Verlust vegetationsbedeckter Flächen in Ballungsräumen am Beispiel von Berlin (West). Landsch. Stadt 1985, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Copernicus Land Monitoring Service, European Environment Agency (EEA) (2012). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Dijkstra, L.; Poelmann, H. A Harmonised Definition of Cities and Rural Areas: The New Degree of Urbanisation. European Commission Urban and Re-gional Policy. Working Paper 1. 2014. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/sources/docgener/work/2014_01_new_urban.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Statistisches Bundesamt, Wiesbaden. 2015. Available online: https://ergebnisse.zensus2011.de/ (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Romain, F.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R Package Version 0.8.5. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Hijmans, R.J. raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. R Package Version 2.8-19. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Bivand, R.; Keitt, T.; Rowlingson, B. rgdal: Bindings for the ‘Geospatial’ Data Abstraction Library. R Package Version 1.4-3. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rgdal (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Gotelli, N.J.; Colwell, R.K. Quantifying biodiversity: Procedures and pitfalls in the measurement and comparison of species richness. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Entropy and diversity. Oikos 2006, 113, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, A.J.; Lakeman Fraser, P.; Robinson, L.; Tweddle, J.C.; Sadler, J.P.; West, S.E.; Norman, S.; Batson, M.; Davies, L. The OPAL bugs count survey: Exploring the effects of urbanisation and habitat characteristics using citizen science. Urban Ecosyst. 2015, 18, 1477–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simspon, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-4. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: ‘ggplot2’ based Publication Ready Plots. R Package Version 0.4.0. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pernat, N.; Kampen, H.; Jeschke, J.M.; Werner, D. Citizen science versus professional data collection: Comparison of approaches to mosquito monitoring in Germany. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 58, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, M.A.; Leong, M.; Bayless, K.M.; Malow, T.L.; Dunn, R.R.; Trautwein, M.D. Arthropods of the great indoors: Characterizing diversity inside urban and suburban homes. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberan, A.; Dunn, R.R.; Reich, B.J.; Pacifici, K.; Laber, E.B.; Menninger, H.L.; Morton, J.M.; Henley, J.B.; Leff, J.W.; Miller, S.L.; et al. The ecology of microscopic life in household dust. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, G.; De Laet, J.; Vangestel, C.; Adriaensen, F.; Lens, L. Citizen science in action–Evidence for long-term, region-wide house sparrow declines in Flanders, Belgium. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, J.R.; Armstrong, P.M.; Andreadis, T.G. Patterns of mosquito and arbovirus community composition and ecological indexes of arboviral risk in the northeast United States. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, L.F.; Hamer, G.L.; Walker, E.D.; Brown, W.M.; Ruiz, M.O.; Kitron, U.D. Climatic variability and landscape heterogeneity impact urban mosquito diversity and vector abundance and infection. Ecosphere 2011, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, D.A.; Cobbold, C.A.; Purse, B.V.; Nunn, M.A.; White, S.M. Modelling the effect of temperature on the seasonal population dynamics of temperate mosquitoes. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 400, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, A.B.B.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Ceretti-Junior, W.; Marrelli, M.T. Mosquito populations dynamics associated with climate variations. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, H.E.; Rorke, S.L.; Beckmann, B.; Booy, O.; Botham, M.S.; Brown, P.M.J.; Harrower, C.; Noble, D.; Sewell, J.; Walker, K. The contribution of volunteer recorders to our understanding of biological invasions. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 115, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaux, A.G.C.; Medlock, J.M. Current status of invasive mosquito surveillance in the UK. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, C.T.; Roberts, J.D.; Poore, A.G.B.; Alford, R.A.; Cogger, H.; Rowley, J.J.L. Citizen science data accurately predicts expert-derived species richness at a continental scale when sampling thresholds are met. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroye, P.; Ahmed, N.; Kerr, J.T. Opportunistic citizen science data transform understanding of species distributions, phenology, and diversity gradients for global change research. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5281–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio, M.S.; Rossetti, M.R.; Videla, M.; Baselga, A. Negative effects of urbanization on terrestrial arthropod communities: A meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1412–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, H.L.; Day, H.L.; Reineke, R.; Stevens, N.; Withey, J.C.; Marzluff, J.M.; Meschke, J.S. Climatic and landscape correlates for potential West Nile virus mosquito vectors in the Seattle region. J. Vector Ecol. 2007, 32, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, A.B.B.; Caban-Martinez, A.J.; Ajelli, M.; Vasquez, C.; Petrie, W.; Beier, J.C. Mosquito adaptation to the extreme habitats of urban construction sites. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Früh, L.; Kampen, H.; Koban, M.B.; Pernat, N.; Schaub, G.A.; Werner, D. Oviposition of Aedes japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) and associated native species in relation to season, temperature and land use in western Germany. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlock, J.M.; Vaux, A.G. Impacts of the creation, expansion and management of English wetlands on mosquito presence and abundance–developing strategies for future disease mitigation. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittra, C.; Vitecek, S.; Obwaller, A.G.; Rossiter, H.; Eigner, B.; Zechmeister, T.; Waringer, J.; Fuehrer, H.P. Landscape structure affects distribution of potential disease vectors (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, D. Artificial container-breeding mosquitoes and cemeteries: A perfect match. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2007, 12, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, N.H.; Sylla, M.; Badolo, A.; Lutomiah, J.; Ayala, D.; Aribodor, O.B.; Ibe, N.; Akorli, J.; Otoo, S.; Mutebi, J.P.; et al. Climate and urbanization drive mosquito preference for humans. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 3570–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekoninck, W.; Hendrickx, F.; Vasn Bortel, W.; Versteirt, V.; Coosemans, M.; Damiens, D.; Hance, T.; De Clercq, E.M.; Hendrickx, G.; Schaffner, F.; et al. Human-induced expanded distribution of Anopheles plumbeus, experimental vector of West Nile virus and a potential vector of human malaria in Belgium. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, F.; Thiery, I.; Kaufmann, C.; Zettor, A.; Lengeler, C.; Mathis, A.; Bourgouin, C. Anopheles plumbeus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Europe: A mere nuisance mosquito or potential malaria vector? Malar. J. 2012, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.R.; Beasley, D.E. Democratizing evolutionary biology, lessons from insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 18, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genus | Observed Counts | Weighted Expected Counts | χ2 | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sealing | Low | Moderate | Strong | Very Strong | Low | Moderate | Strong | Very Strong | ||
| Aedes | 2386 | 1064 | 427 | 86 | 2268 | 1063 | 489 | 143 | 36.61 | <0.001 |
| Anopheles | 464 | 149 | 65 | 12 | 397 | 187 | 83 | 23 | 28.23 | <0.001 |
| Coquillettidia | 238 | 79 | 31 | 12 | 208 | 97 | 43 | 12 | 11.21 | <0.011 |
| Culex | 4424 | 2150 | 1023 | 300 | 4706 | 2092 | 877 | 222 | 70.40 | <0.001 |
| Culiseta | 2297 | 1102 | 480 | 144 | 2341 | 1073 | 482 | 128 | 3.70 | ns |
| Population | Rural | Peri-Urban | Urban | Rural | Peri-Urban | Urban | ||||
| Aedes | 645 | 2830 | 488 | 738 | 2683 | 543 | 4.18 | <0.001 | ||
| Anopheles | 233 | 413 | 44 | 128 | 467 | 94 | 131.24 | <0.001 | ||
| Coquillettidia | 80 | 239 | 41 | 67 | 244 | 49 | 41.81 | ns | ||
| Culex | 1462 | 5311 | 1124 | 1470 | 5346 | 1081 | 71.62 | <0.028 | ||
| Culiseta | 732 | 2670 | 621 | 749 | 2723 | 551 | 8.51 | <0.001 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pernat, N.; Kampen, H.; Jeschke, J.M.; Werner, D. Buzzing Homes: Using Citizen Science Data to Explore the Effects of Urbanization on Indoor Mosquito Communities. Insects 2021, 12, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050374
Pernat N, Kampen H, Jeschke JM, Werner D. Buzzing Homes: Using Citizen Science Data to Explore the Effects of Urbanization on Indoor Mosquito Communities. Insects. 2021; 12(5):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050374
Chicago/Turabian StylePernat, Nadja, Helge Kampen, Jonathan M. Jeschke, and Doreen Werner. 2021. "Buzzing Homes: Using Citizen Science Data to Explore the Effects of Urbanization on Indoor Mosquito Communities" Insects 12, no. 5: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050374
APA StylePernat, N., Kampen, H., Jeschke, J. M., & Werner, D. (2021). Buzzing Homes: Using Citizen Science Data to Explore the Effects of Urbanization on Indoor Mosquito Communities. Insects, 12(5), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050374






