Gene Expression Profiling Indicated Diverse Functions and Characteristics of Core Genes in Pea Aphid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Data Preprocessing
2.2. Identifying Specifically Expressed Genes
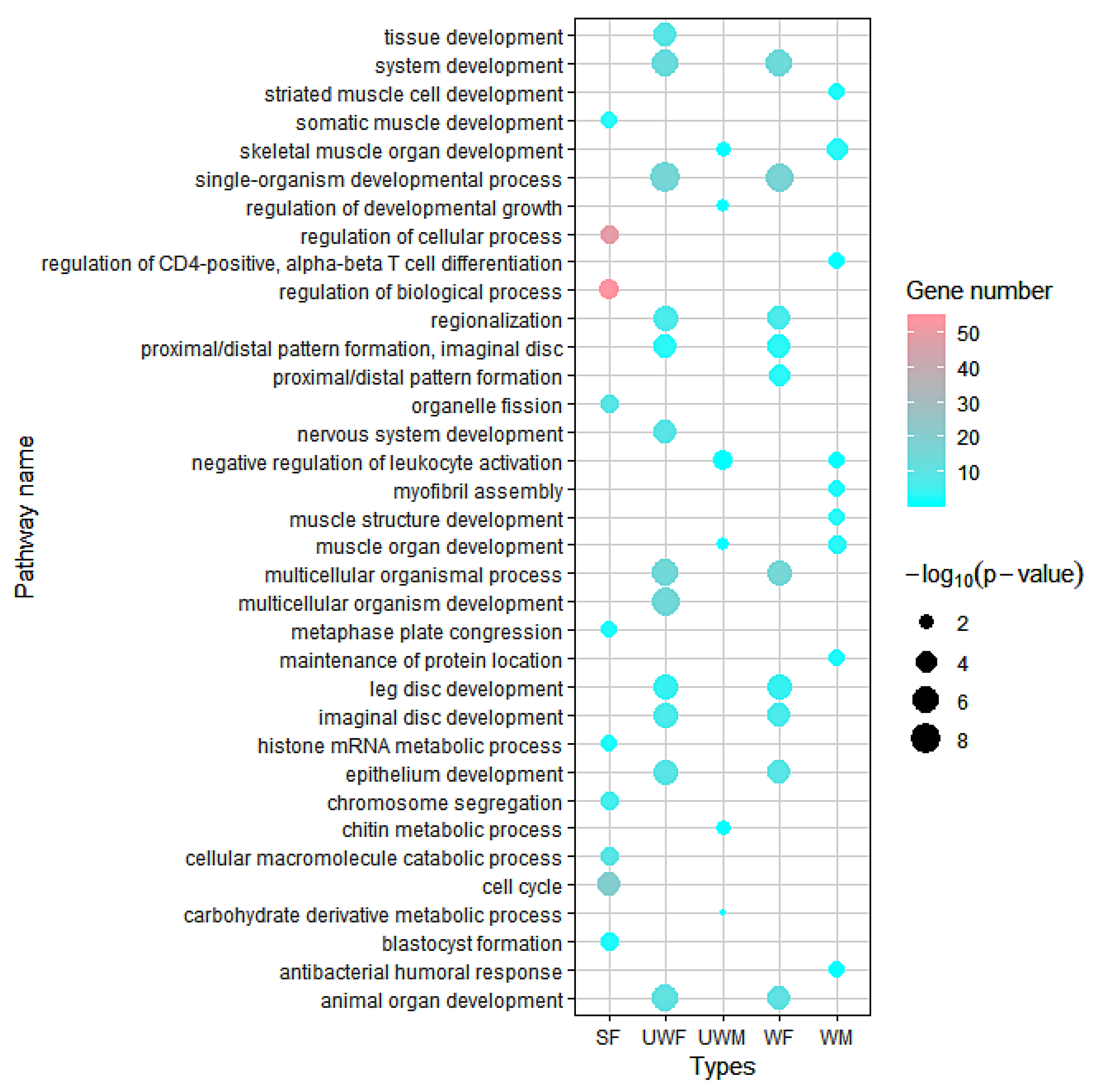
2.3. Data Analysis and Gene Function Annotation
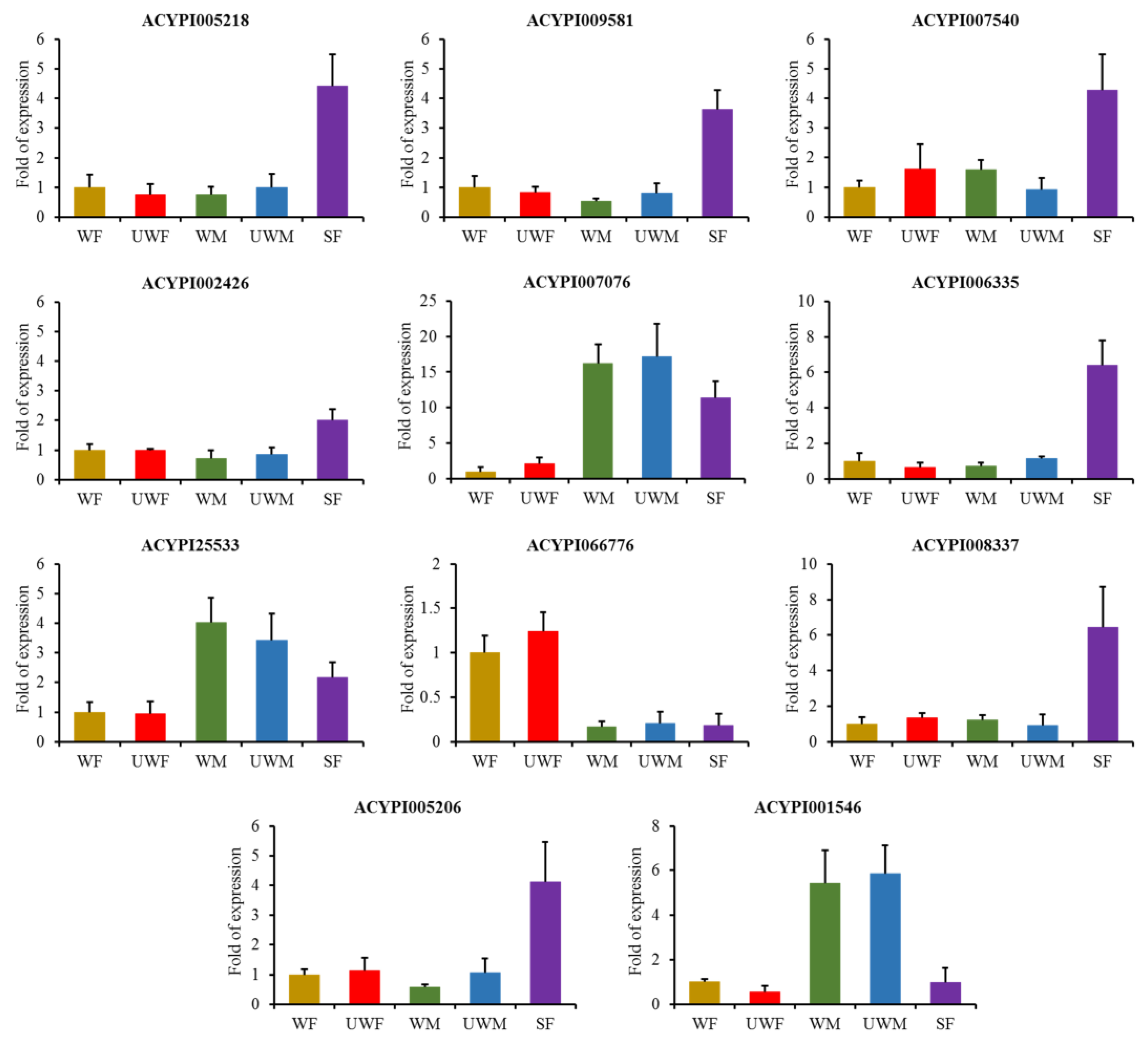
2.4. Insect Materials and Quantitative Real-Time Pcr (Qrt-Pcr)
2.5. Gene Expression Patterns and Potential Transcription Factors
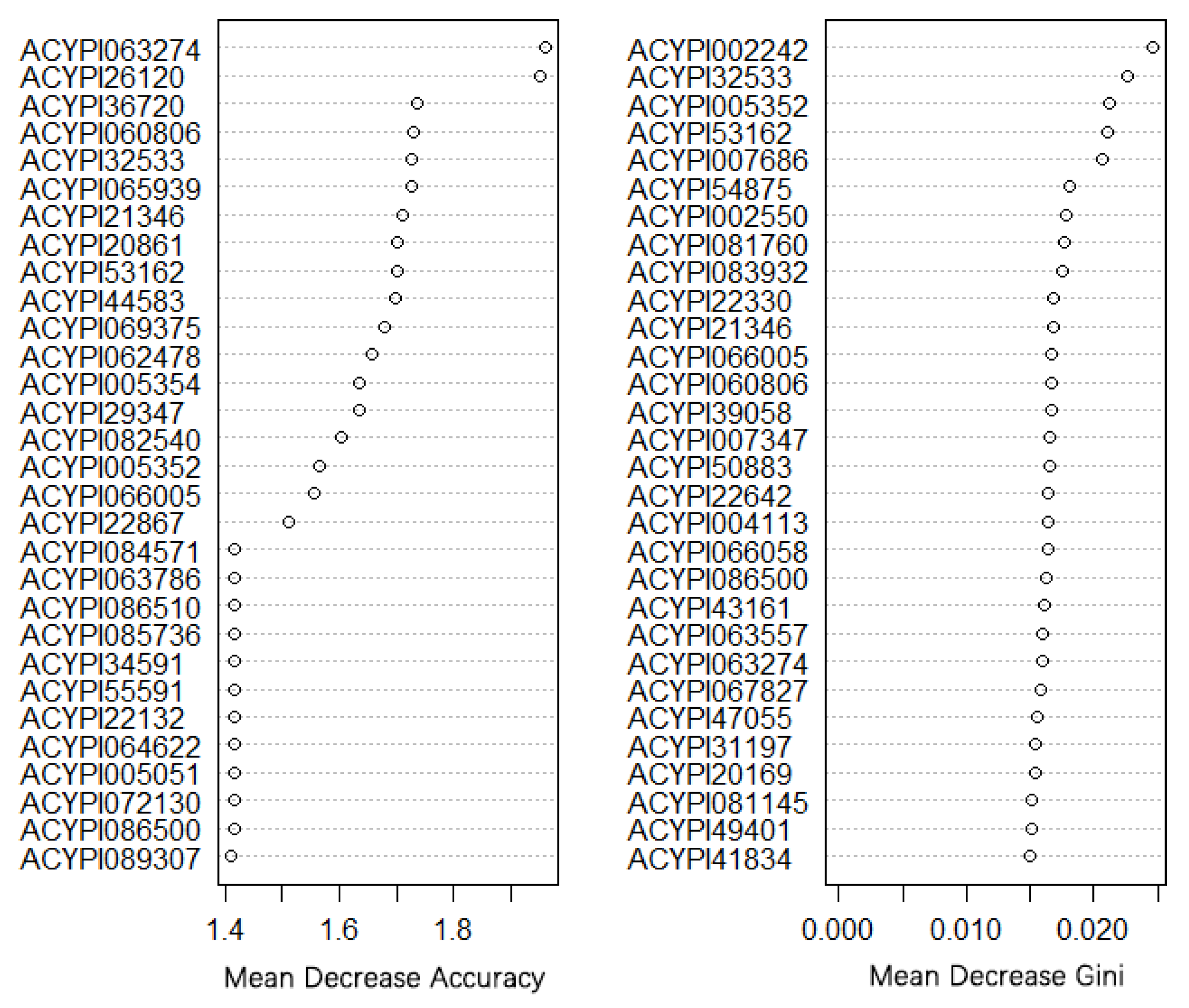
2.6. Random Forest Method to Find Morph-Biased Markers
3. Results
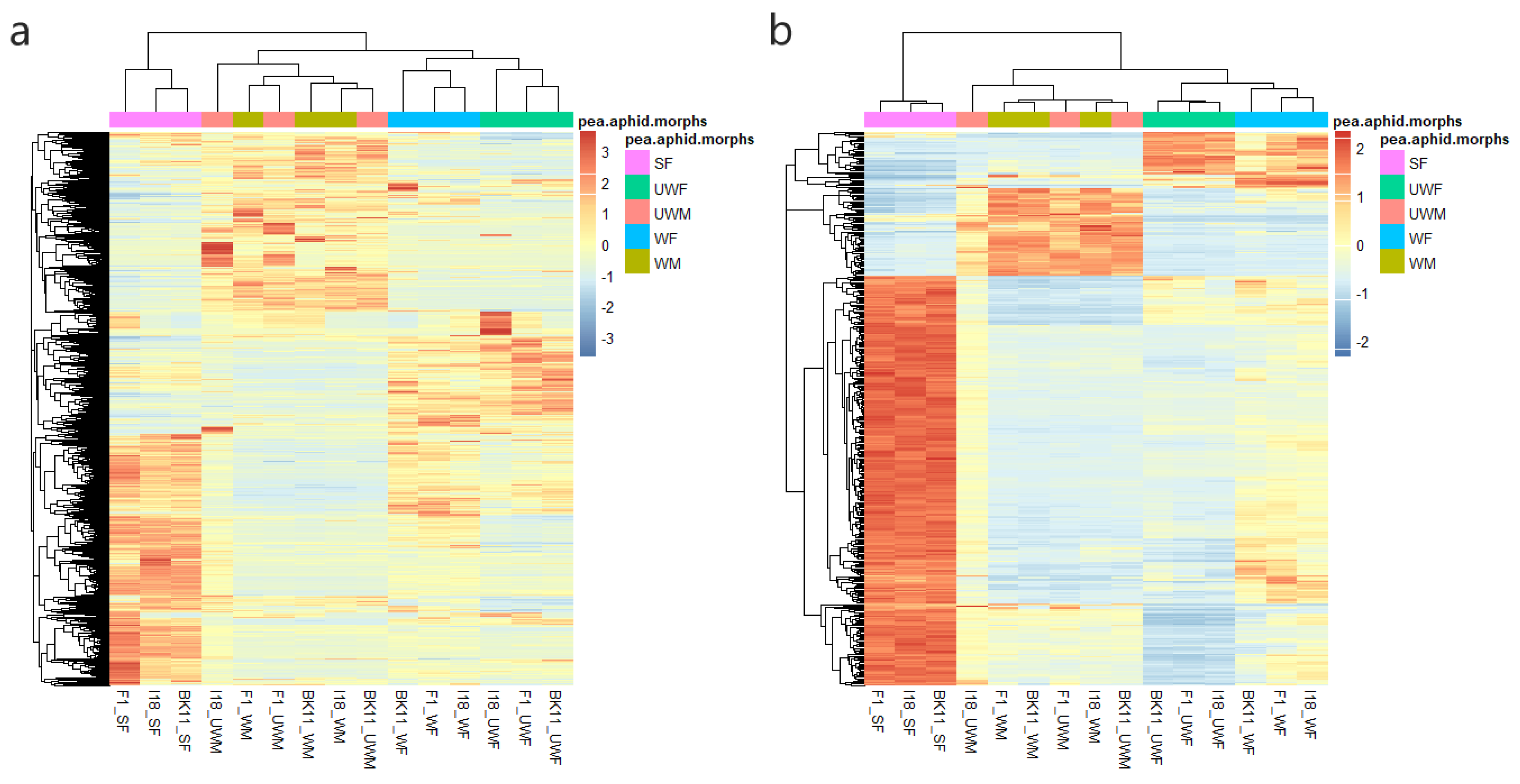
3.1. Transcriptome Profiling of 15 Types of Pea Aphids
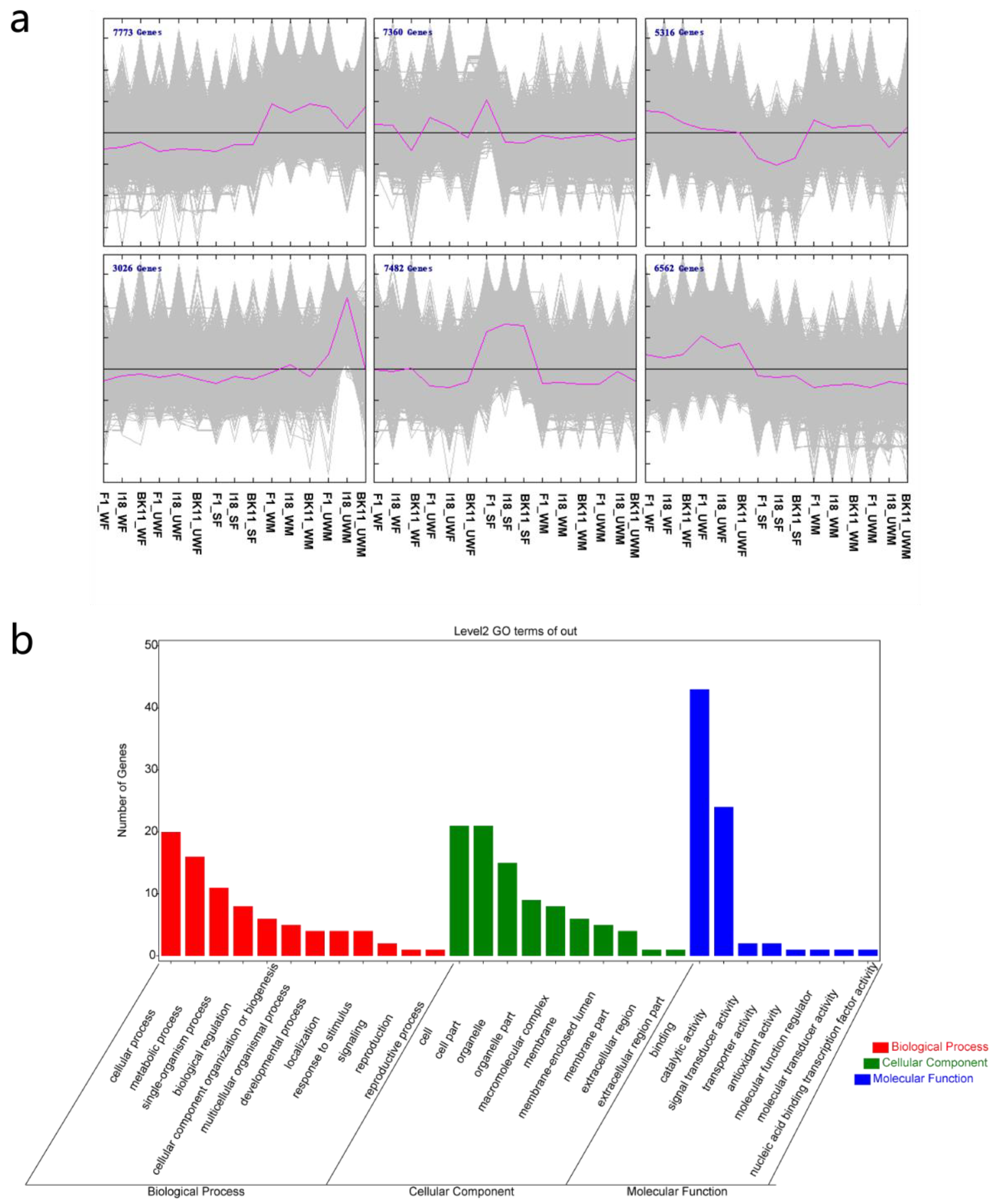
3.2. Gene Expression Patterns and Potential Transcription Factors
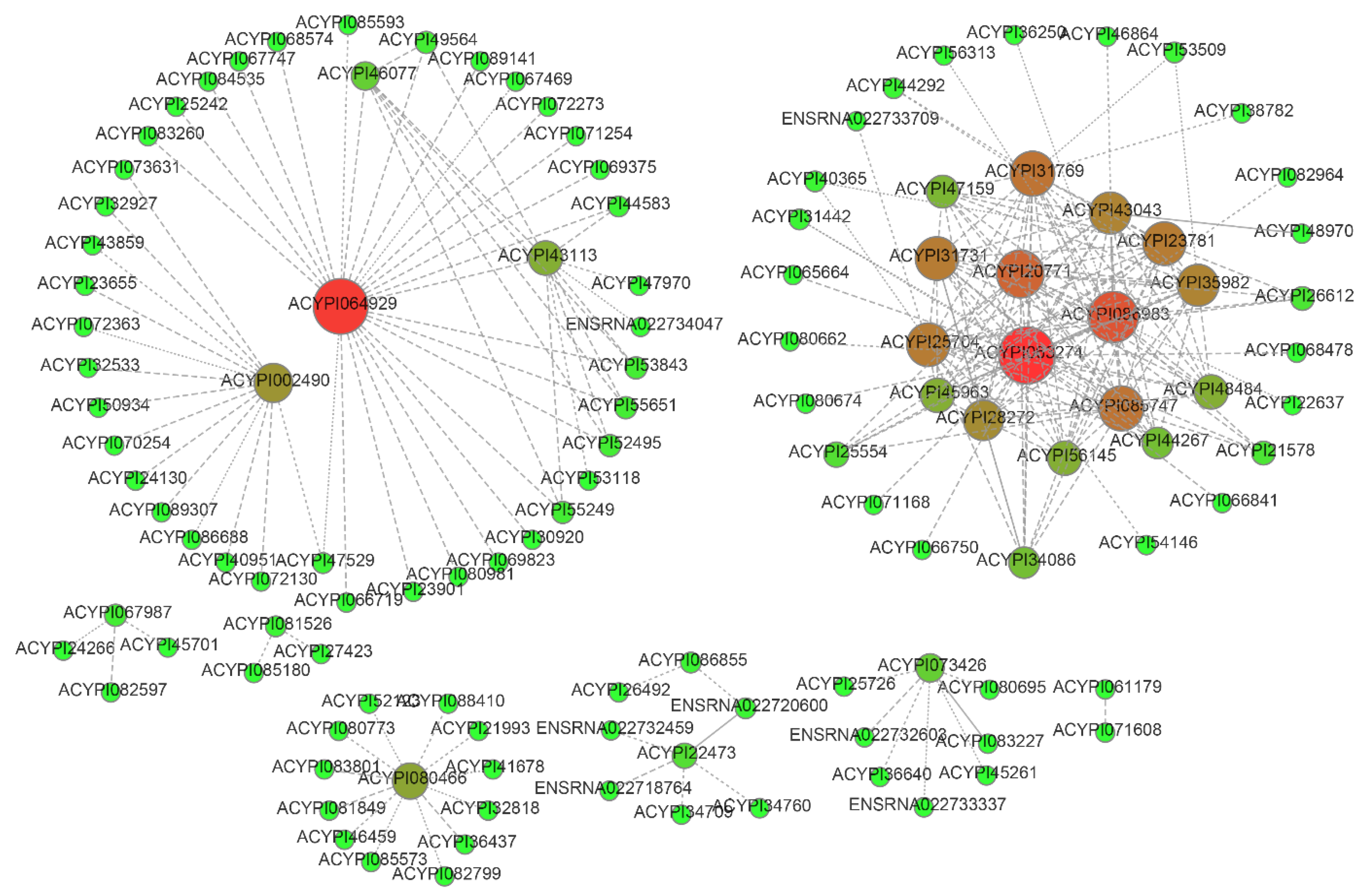
3.3. Gene Co-Expression Network and Morph-Biased Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilabert, A.; Simon, J.C.; Mieuzet, L.; Halkett, F.; Stoeckel, S.; Plantegenest, M.; Dedryver, C.A. Climate and agricultural context shape reproductive mode variation in an aphid crop pest. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 3050–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.; Bechinski, E.J.; Stokes, B.S.; Pappu, H.R.; Eigenbrode, S.D. Deriving economic models for pea aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) as a direct-pest and a virus-vector on commercial lentils. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, M.L.; Laughton, A.M.; Parker, B.J.; Wichmann, H.; Fan, M.; Sok, D.; Hrček, J.; Acevedo, T.; Gerardo, N.M. The influence of symbiotic bacteria on reproductive strategies and wing polyphenism in pea aphids responding to stress. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purandare, S.R.; Bickel, R.D.; Julie, J.; Claude, R.; Brisson, J.A. Accelerated evolution of morph-biased genes in pea aphids. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 8, 2073–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, B.K. Phenotypic plasticity in aphids (Homoptera: Insecta): Components of variation and causative factors. Curr. Sci. 2006, 93, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, K.; Baudach, A.F. Epigenetic control of polyphenism in aphids. In Biology and Ecology of Aphids; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Chapter 4; pp. 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Dedryver, C.A.; Le Gallic, J.F.; Mahéo, F.; Simon, J.C.; Dedryver, F. The genetics of obligate parthenogenesis in an aphid species and its consequences for the maintenance of alternative reproductive modes. Heredity 2013, 110, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grantham, M.E. The Evolutionary and Molecular Basis of the Pea Aphid Wing Polyphenism. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rochester, New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trionnaire, G.L.L.; Jaubert-Possamai, S.; Bonhomme, J.L.; Gauthier, J.P.; Guernec, G.; Le Cam, A.; Legeai, F.; Monfort, J.M.; Tagu, D. Transcriptomic profiling of the reproductive mode switch in the pea aphid in response to natural autumnal photoperiod. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, M.E.; Antonio, C.J.; O’Neil, B.R.; Zhan, Y.X.; Brisson, J.A. A case for a joint strategy of diversified bet hedging and plasticity in the pea aphid wing polyphenism. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, J.; Visser, J.H.; Piron, P.G.M. Peripheral odour perception by adult aphid forms with the same genotype but different host-plant preferences. J. Insect Physiol. 1995, 41, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Braendle, C.; Friebe, I.; Caillaud, M.C.; Stern, D.L. Genetic variation for an aphid wing polyphenism is genetically linked to a naturally occurring wing polymorphism, Proceedings. Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, M.E.; Shingleton, A.W.; Dudley, E.; Brisson, J.A. Expression profiling of winged-and wingless-destined pea aphid embryos implicates insulin/insulin growth factor signaling in morph differences. Evol. Dev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulain, H.; Legeai, F.; Guy, E.; Morliere, S.; Douglas, N.E.; Oh, J.; Murugan, M.; Smith, M.; Jaquiéry, J.; Peccoud, J.; et al. Fast evolution and lineage-specific gene family expansions of aphid salivary effectors driven by interactions with host-plants. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1554–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, I.; Benjamin, H.; Shmoish, M.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Shklar, M.; Ophir, R.; Bar-Even, A.; Horn-Saban, S.; Safran, M.; Domany, E. Genome-wide midrange transcription profiles reveal expression level relationships in human tissue specification. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatamian, A.; Paull, E.O.; Califano, A.; Yu, J. SJARACNe: A scalable software tool for gene network reverse engineering from big data. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2165–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apweiler, R.; Bairoch, A.; Wu, C.H.; Barker, W.C.; Boeckmann, B.; Ferro, S.; Gasteiger, E.; Huang, H.; Lopez, R.; Magrane, M.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Uriarte, R.; Alvarez de Andrés, S. Gene selection and classification of microarray data using random forest. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chan, C.K.K. Analysis of RNA-Seq data using TopHat and Cufflinks. Plant Bioinform. 2016, 1374, 339–361. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.K.; Lubinsky, B.; Bansode, V.B.; Moinz, M.B.J.; McCormack, G.P.; Travers, S.A. QTrim: A novel tool for the quality trimming of sequence reads generated using the Roche/454 sequencing platform. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Miura, T. Two developmental switch points for the wing polymorphisms in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon Pisum. Evodevo 2013, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriventseva, E.V.; Tegenfeldt, F.; Petty, T.J.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Simão, F.A.; Pozdnyakov, I.A.; Ioannidis, P.; Zdobnov, E.M. OrthoDB v8: Update of the hierarchical catalog of orthologs and the underlying free software. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Miao, Y.R.; Jia, L.H.; Yu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, A.Y. AnimalTFDB 3.0: A comprehensive resource for annotation and prediction of animal transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.C.; Stoeckel, S.; Tagu, D. Evolutionary and functional insights into reproductive strategies of aphids. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2010, 333, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, M.; Libbrecht, R.; Wheeler, D.E. Molecular mechanisms of phenotypic plasticity in social insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 13, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.L.; Lagos, D.M.; Mitchell, R.F.; Hartman, G.L.; Voegtlin, D.J. Life history and morphological plasticity of the soybean aphid, Aphis Glycines. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2011, 140, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennacchio, F.; MAncini, D. Aphid parasitoid venom and its role in host regulation. In Parasitoid Viruses: Symbionts Pathogens; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Chapter 20; pp. 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hazell, S.P.; Groutides, C.; Neve, B.P.; Blackburn, T.M.; Bale, J.S. A comparison of low temperature tolerance traits between closely related aphids from the tropics, temperate zone, and Arctic. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, A.; Plantegenest, M.; Simon, J.C. Host races of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum differ in male wing phenotypes. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintjens, R.; Rooman, M. Structural classification of HTH DNA-binding domains and protein-DNA interaction modes. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 262, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakirova, Z.; Fanutza, T.; Bonet, J.; Readhead, B.; Zhang, W.; Yi, Z.; Beauvais, G.; Zwaka, T.P.; Ozelius, L.J.; Blitzer, R.D.; et al. Mutations in THAP1/DYT6 reveal that diverse dystonia genes disrupt similar neuronal pathways and functions. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.F.; Zhang, Y.P.; Sun, S.M.; Gong, Y.S.; Xiong, Y.W.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Jin, S.B.; Fu, H.T. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression analysis of a Broad-Complex homolog during development in the oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 5141–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajgo, S.; Ali, S.; Popescu, O.; Badea, T.C. Dynamic expression of transcription factor Brn3b during mouse cranial nerve development. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1033–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total Reads | Mapped Reads | Mapping Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1_WF | 93097593 | 79389596 | 85.30% |
| F1_UWF | 101313506 | 88512217 | 87.40% |
| F1_SF | 91946734 | 82783997 | 90.00% |
| I18_WF | 109616712 | 80872988 | 73.80% |
| I18_UWF | 82776192 | 59534227 | 71.90% |
| BK11_WF | 102979257 | 97275709 | 94.50% |
| BK11_UWF | 106808567 | 96654529 | 90.50% |
| F1_WM | 80133908 | 67200794 | 83.90% |
| F1_UWM | 68817463 | 62643966 | 91.00% |
| I18_WM | 100710783 | 63792363 | 63.30% |
| I18_UWM | 94077934 | 63733175 | 67.70% |
| I18_SF | 106615474 | 92694245 | 86.90% |
| BK11_WM | 82734259 | 70391904 | 85.10% |
| BK11_UWM | 71796221 | 66195361 | 92.20% |
| BK11_SF | 90793111 | 87397909 | 96.30% |
| Gene ID | Family | Full Sequence e-Value | Best Domain e-Value | Domain Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACYPI006621 | HTH | 1.70 × 10−10 | 4.00 × 10−10 | 1 |
| ACYPI010241 | HTH | 4.70 × 10−07 | 1.10 × 10−06 | 1 |
| ACYPI088029 | THAP | 2.90 × 10−19 | 4.10 × 10−19 | 1 |
| ACYPI089479 | THAP | 2.00 × 10−05 | 5.00 × 10−05 | 1 |
| ACYPI28272 | zf-H2C2_2 | 1.80 × 10−112 | 2.60 × 10−10 | 16 |
| ACYPI23901 | zf-H2C2_2 | 6.50 × 10−92 | 3.90 × 10−11 | 14 |
| ACYPI29290 | zf-H2C2_2 | 1.10 × 10−32 | 3.30 × 10−10 | 6 |
| ACYPI080640 | CSRNP_N | 9.40 × 10−06 | 1.00 × 10−05 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, R.; Huang, Y.; Balakrishnan, B.; Chen, M. Gene Expression Profiling Indicated Diverse Functions and Characteristics of Core Genes in Pea Aphid. Insects 2020, 11, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030186
Tian R, Huang Y, Balakrishnan B, Chen M. Gene Expression Profiling Indicated Diverse Functions and Characteristics of Core Genes in Pea Aphid. Insects. 2020; 11(3):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030186
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Ruizheng, Yixiao Huang, Balachandar Balakrishnan, and Maohua Chen. 2020. "Gene Expression Profiling Indicated Diverse Functions and Characteristics of Core Genes in Pea Aphid" Insects 11, no. 3: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030186
APA StyleTian, R., Huang, Y., Balakrishnan, B., & Chen, M. (2020). Gene Expression Profiling Indicated Diverse Functions and Characteristics of Core Genes in Pea Aphid. Insects, 11(3), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030186





