A Literature Review of Host Feeding Patterns of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes in Europe
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
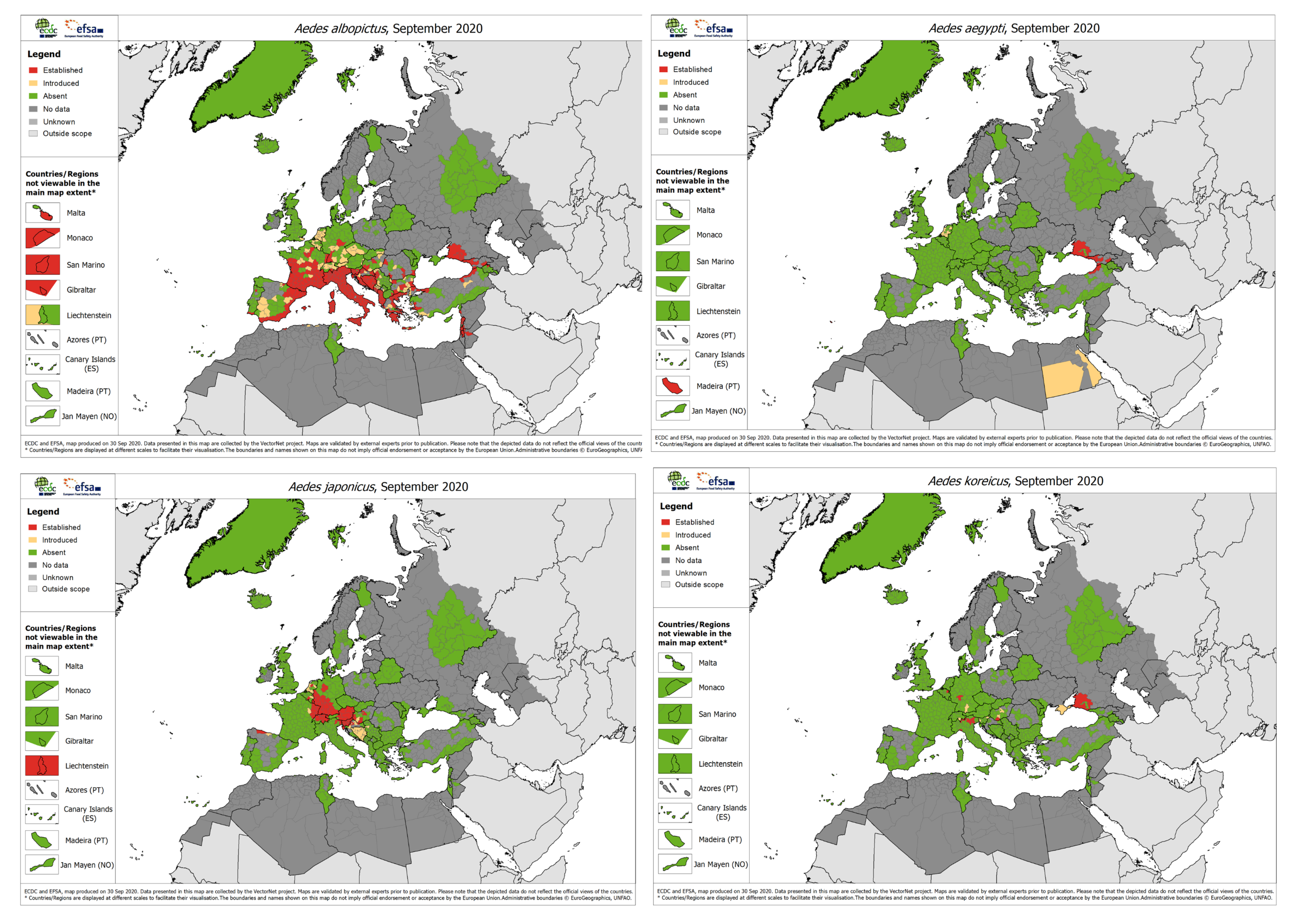
2. Aedes Invasive Mosquitoes in Europe
3. Methods Used for the Identification of Vertebrate Hosts of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes
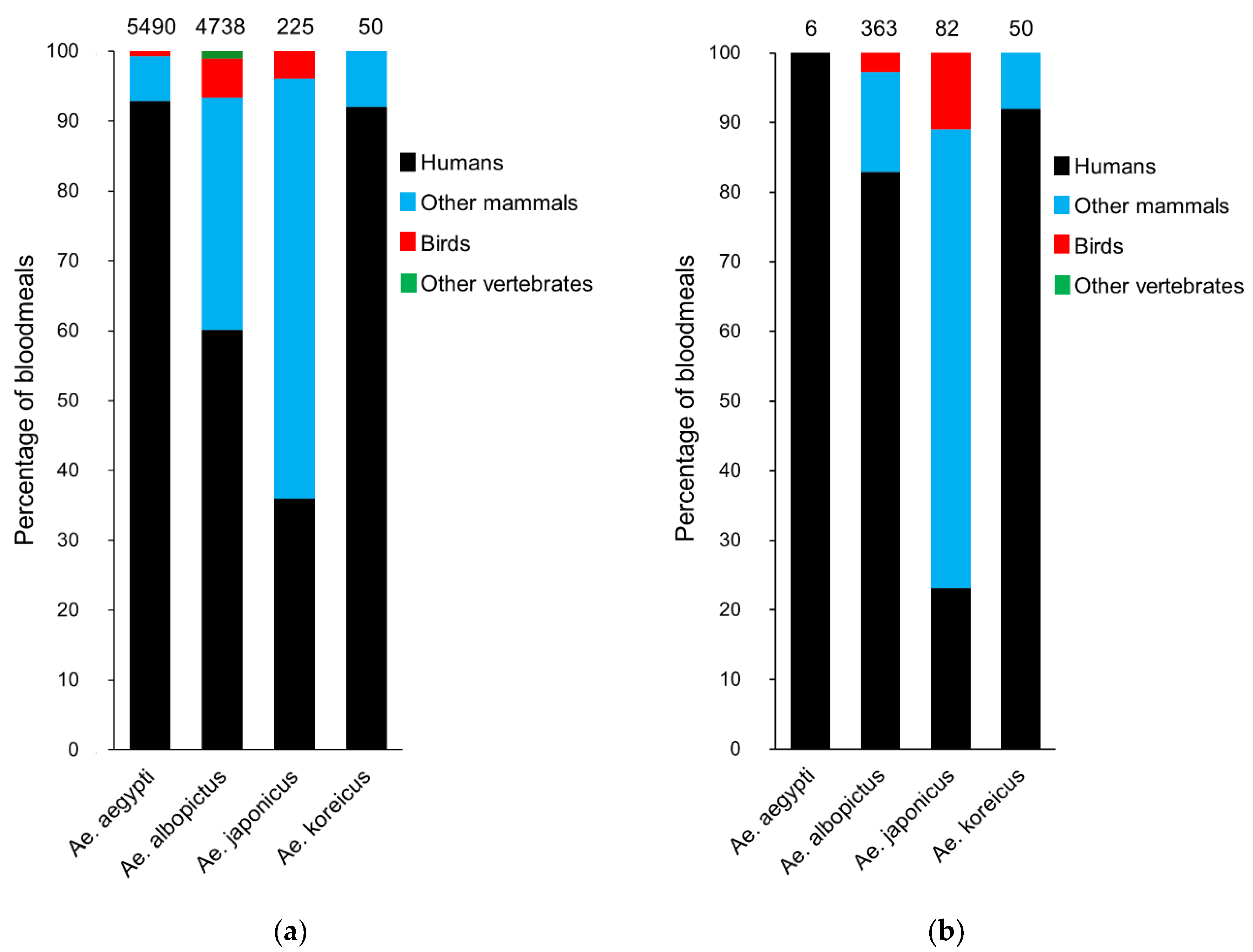
4. Blood Feeding Patterns of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Service, M. Mosquitoes (Culicidae). In Medical Insects and Arachnids; Lane, R.P., Crosskey, R.W., Eds.; Chapman Hall: London, UK, 1993; pp. 120–122. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, N.; Petrić, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Madon, M.; Dahl, C.; Kaiser, A. Mosquitoes and Their Control, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tolle, M. Mosquito-borne Diseases. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2009, 39, 97–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, H.; Kronefeld, M.; Werner, D. Culicid Mosquitoes as Vectors of Disease Agents in Europe. In Arthropods as Vectors of Emerging Diseases; Mehlhorn, H., Ed.; Springer: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-92-4-156572-1. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D. Emergence and re-emergence of mosquito-borne arboviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklinos, L.H.V.; Jones, K.E.; Redding, D.W.; Abubakar, I. The effect of global change on mosquito-borne disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugueras, S.; Fernández-Martínez, B.; Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Figuerola, J.; Montalvo Porro, T.; Rius, C.; Larrauri, A.; Gómez-Barroso, D. Environmental drivers, climate change and emergent diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and their vectors in southern Europe: A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlock, J.M.; Hansford, K.M.; Versteirt, V.; Cull, B.; Kampen, H.; Fontenille, D.; Hendrickx, G.; Zeller, H.; Van Bortel, W.; Schaffner, F. An entomological review of invasive mosquitoes in Europe. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2015, 105, 637–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, N. Critical review of the vector status of Aedes albopictus. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2004, 18, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Neto, J.; Powell, J.; Bonizzoni, M. Aedes aegypti vector competence studies: A review. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 67, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-López, R.; Bialosuknia, S.; Ciota, A.; Montalvo, T.; Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Gangoso, L.; Figueroa, J.; Kramer, L.D. Vector Competence of Aedes caspius and Ae. albopictus Mosquitoes for Zika Virus, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Rúa, A.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R.; Mousson, L.; Vazeille, M.; Fuchs, S.; Yébakima, A.; Gustave, J.; Girod, R.; Dusfour, I.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; et al. Chikungunya Virus Transmission Potential by Local Aedes Mosquitoes in the Americas and Europe. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Ruche, G.; Souarès, Y.; Armengaud, A.; Peloux-Petiot, F.; Delaunay, P.; Desprès, P.; Lenglet, A.; Jourdain, F.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Charlet, F.; et al. First two autochthonous dengue virus infections in metropolitan France, September. Eur. Surveill. 2010, 15, 19676. [Google Scholar]
- Monge, S.; García-Ortúzar, V.; López Hernández, B.; Lopaz Pérez, M.; Delacour-Estrella, S.; Sánchez-Seco, M.; Fernández Martínez, B.; García San Miguel, L.; García-Fulgueiras, A.; Sierra Moros, M.J. Characterization of the first autochthonous dengue outbreak in Spain (August–September 2018). Acta Trop. 2020, 205, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarini, L.; Barzon, L.; Foglia, F.; Manfrin, V.; Pacenti, M.; Pavan, G.; Rassu, M.; Capelli, G.; Montarsi, F.; Martini, S.; et al. First autochthonous dengue outbreak in Italy, August 2020. Eur. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2001606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilauri, P.; Bellini, R.; Calzolari, M.; Angelini, R.; Venturi, L.; Fallacara, F.; Cordioli, P.; Angelini, P.; Venturelli, C.; Merialdi, G.; et al. Chikungunya Virus in Aedes albopictus, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giron, S.; Franke, F.; Decoppet, A.; Cadiou, B.; Travaglini, T.; Thirion, L.; Durand, G.; Jeannin, C.; L’Ambert, G.; Grard, G.; et al. Vector-borne transmission of Zika virus in Europe, southern France, August. Eur. Surveill. 2019, 24, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancrini, G.; Frangipane di Regalbono, A.; Ricci, I.; Tessarin, C.; Gabrielli, S.; Pietrobelli, M. Aedes albopictus is a natural vector of Dirofilaria immitis in Italy. Vet Parasitol. 2003, 118, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, C.T.; Woods, K.; Dusek, R.J.; Sileo, L.S.; Iko, W.M. Wildlife disease and conservation in Hawaii: Pathogenicity of avian malaria (Plasmodium relictum) in experimentally infected Iiwi (Vestiaria coccinea). Ecol. Wildl. Host-Parasite Interact. 1995, 111, S59–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, R. The Role of Introduced Diseases in the extinction of the endemic Hawaiian avifauna. Condor 1968, 70, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.; Mousson, L.; Vazeille, M.; Chamat, S.; Tayeh, J.; Osta, M.; Failloux, A. Aedes albopictus in Lebanon, a potential risk of arboviruses outbreak. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Ferraguti, M.; Ruiz, S.; Montalvo, T.; Casimiro Soriguer, R.; Figuerola, J. Tracing pathogen transmission by mosquitoes under a global change perspective: On the role of the identification of mosquito bloodmeals. In Enciclopedy of Life Science (eLS); John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, R. Molecular methods for arthropod bloodmeal identification and applications to ecological and vector-borne disease studies. Mol. Ecol. Resoures 2009, 2009 9, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesterbeek, J. A brief history of R0 and a receip for its calculation. Acta Biotheor. 2002, 50, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delatte, H.; Desvars, A.; Bouétard, A.; Bord, S.; Gimonneau, G.; Vourc’h, G.; Fontenille, D. Blood-feeding behavior of Aedes albopictus, a vector of Chikungunya on La Réunion. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, M.U.; Sinka, M.E.; Duda, K.A.; Mylne, A.Q.; Shearer, F.M.; Barker, C.M.; Moore, C.G.; Carvalho, R.G.; Coelho, G.E.; Van Bortel, W.; et al. The global distribution of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus. eLife 2015, 4, e08347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romi, R.; Sabatinelli, G.; Savelli, L.; Raris, M.; Zago, M.; Malatesta, R. Identification of a North American mosquito species, Aedes atropalpus (Diptera:Culicidae), in Italy. J. Am. Control Assoc. 1997, 13, 245–246. [Google Scholar]
- Lounibos, L. Ivasions by insect vectors of human diseases. Annu. Rev. 2002, 44, 233–266. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez-Justicia, A.; Smitz, N.; den Hartog, W.; van de Vossenberg, B.; De Wolf, K.; Deblauwe, I.; Van Bortel, W.; Jacobs, F.; Vauz, A.G.C.; Medlock, J.M.; et al. Detection of exotic mosquito species (Diptera: Culicidae) at international airports in Europe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Aedes albopictus—Current Known Distribution: September 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/aedes-albopictus-current-known-distribution-september-2020 (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Aedes aegypti—Current Known Distribution: September 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/aedes-aegypti-current-known-distribution-september-2020 (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Aedes japonicus—Current Known Distribution: September 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/aedes-japonicus-current-known-distribution-september-2020 (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Aedes koreicus—Current Known Distribution: September 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/aedes-koreicus-current-known-distribution-september-2020 (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Aedes atropalpus—Current Known Distribution: September 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/aedes-atropalpus-current-known-distribution-september-2020 (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Izri, A.; Bitam, I.; Charrel, R. First entomological documentation of Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Skuse, 1894) in Algeria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, P.; Sprenger, D. The used tire trade: A mechanism for the worldwide dispersal of container breeding mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1987, 3, 494–501. [Google Scholar]
- Forattini, O. Identificação de Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Skuse) no Brasil. Rev. Saúde Pública 1986, 20, 244–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornel, A.J.; Hunt, R.H. Aedes albopictus in Africa? First records of live specimens in imported tires in Cape Town. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1991, 7, 107–108. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, P. Aedes albopictus and the world trade in used tires, 1988–1995: The shape of things to come? J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1998, 14, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Grist, N.R. Aedes albopictus: The tyre-travelling tiger. J. Infect. 1993, 27, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, E.J.; Dijkstra, E.; Blok, H.; De Vries, A.; Takken, W.; Hofhuis, A.; Koopmans, M.; De Boer, A.; Reusken, C.B.E.M. Accidental importation of the mosquito Aedes albopictus into the Netherlands: A survey of mosquito distribution and the presence of dengue virus. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2008, 22, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeulemeester, J.; Deblauwe, I.; De Witte, J.; Jansen, J.; Hendy, A.; Madder, M. First interception of Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus in Lucky bamboo shipments in Belgium. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2014, 32, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Eritja, R.; Palmer, J.; Roiz, D.; Sanpera-Calbet, I.; Bartumeus, F. Direct Evidence of Adult Aedes albopictus Dispersal by Car. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, C.; Eritja, R.; Roiz, D. First record and establishment of the mosquito Aedes albopictus in Spain. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2006, 20, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, F.; Karch, S. Première observation Aedes albopictus (Skuse, 1894) en France métropolitaine. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. III Sci. Vie 2000, 323, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romi, R.; Di Luca, M.; Majori, G. Current status of Aedes albopictus and Aedes atropalpus in Italy. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1999, 15, 425–427. [Google Scholar]
- Gatt, P.; Deeming, J.; Schaffner, F. First record of Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Skuse) (Diptera: Culicidae) in Malta. Zur. Open Repos. Arch. Univ. Zur. 2009, 27, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatt, P.; Schaffner, F.; Cassar, L. Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Skuse) (Diptera: Culicidae) in Malta—The first winter. Zur. Open Repos. Arch. Univ. Zur. 2010, 28, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, M.Q.; Levine, R.S.; Hawley, W.A.; Lounibos, L.P. Spread of The Tiger: Global Risk of Invasion by The Mosquito Aedes albopictus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petric, D.; Pajovic, I.; Ignjatovic Cupina, A.; Zgomba, M. Aedes albopictus (Skuse, 1894) new mosquito species (Diptera, Culicidae) in entomofauna of Yugoslavia. In Proceedings of the Symposia of the entomologists of Serbia, Belgrade, Serbia, 26–29 September 2001; pp. 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Soghigian, J.; Gloria-Soria, A.; Robert, V.; Le Goff, G.; Failloux, A.; Powell, J.R. Genetic evidence for the origin of Aedes aegypti, the yellow fever mosquito, in the southwestern Indian Ocean. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 3593–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.R. Mosquito-borne human viral diseases: Why Aedes aegypti? Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, I.M.; Kreß, A.; Klingelhöfer, D.; Scherer, C.; Phuyal, P.; Kuch, U.; Ahrens, B.; Groneberg, D.A.; Dhimal, M.; Müller, R. Does winter cold really limit the dengue vector Aedes aegypti in Europe? Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstein, M. Dynamics of Aedes aegypti Distribution, density and seasonal prevalence in the Mediterranean area. Bull. World Health Organ. 1967, 36, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaffner, F.; Mathis, A. Dengue and dengue vectors in the WHO European region: Past, present and scenarios for the future. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiner, M.M.; Demirci, B.; Babuadze, G.; Robert, V.; Schaffner, F. Spread of the invasive mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in the Black Sea region increases risk of Chikungunya, dengue, and Zika outbreaks in Europe. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, F.; Ries, C. First evidence and distribution of the invasive alien mosquito Aedes japonicus (Theobald, 1901) in Luxembourg. Bull. Soc. Nat. luxemb. 2019, 121, 169–183. [Google Scholar]
- Peyton, E.L.; Campbell, S.R.; Candeletti, T.M.; Romanowski, M.; Crans, W.J. Aedes (Finlaya) japonicus japonicus (Theobald), a new introduction into the United States. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1999, 15, 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner, F.; Chouin, S.; Guilloteau, J. First record of Orchlerotatus (Finlaya) japonicus japonicus (Theobald, 1901) in metropolitan France. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2003, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Versteirt, V.; Schaffner, F.; Garros, C.; Dekoninck, W.; Coosemans, M.; Van Bortel, W. Introduction and establishment of the exotic mosquito species Aedes japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Belgium. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, F.; Kaufmann, C.; Hegglin, D.; Mathis, A. The invasive mosquito Aedes japonicusin Central Europe. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2009, 23, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, H.; Werner, D. Out of the bush: The Asian bush mosquito Aedes japonicus japonicus (Theobald, 1901) (Diptera, Culicidae) becomes invasive. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez-Justicia, A.; Kampen, H.; Braks, M.; Schaffner, F.; Steeghs, M.; Werner, D.; Zielke, D.; den Hartog, W.; Brooks, M.; Dik, M.; et al. First report of established population of Aedes japonicus japonicus (Theobald, 1901) (Diptera, Culicidae) in the Netherlands. J. Eur. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2014, 32, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Eritja, R.; Ruiz-Arrondo, I.; Delacour-Estrella, S.; Schaffner, F.; Álvarez-Chachero, J.; Bengoa, M.; Puig, M.-Á.; Melero-Alcíbar, R.; Oltra, A.; Bartumeus, F. First detection of Aedes japonicus in Spain: An unexpected finding triggered by citizen science. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, K.L. Contributions to the mosquito fauna of Southeast Asia—IV. Species of subgroup Chrysolineatus of group D, genus Aedes, subgenus Finlaya (Theobald). Contrib. Amer. Entomol. Inst. 1968, 2, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Versteirt, V.; de Clercq, E.M.; Fonseca, D.M.; Pecor, J.; Schaffner, F.; Coosemans, M.; Bortel, W.V. Bionomics of the established exotic mosquito species Aedes koreicus in Belgium, Europe. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelli, G.; Drago, A.; Martini, S.; Montarsi, F.; Soppelsa, M.; Delai, N.; Ravagnan, S.; Mazzon, L.; Schaffner, F.; Mathis, A.; et al. First report in Italy of the exotic mosquito species Aedes (Finlaya) koreicus, a potential vector of arboviruses and filariae. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalan, K.; Šušnjar, J.; Ivović, V.; Buzan, E. First record of Aedes koreicus (Diptera, Culicidae) in Slovenia. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2355–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, D.; Zielke, D.E.; Kampen, H. First record of Aedes koreicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzhonova, O.V.; Patraman, I.V.; Ganushkina, L.A.; Vyshemirskiĭ, O.I.; Sergiev, V.P. The first finding of invasive species Aedes (Finlaya) koreicus (Edwards, 1917) in European Russia. Med. Parazitol. 2014, 1, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kurucz, K.; Kiss, V.; Zana, B.; Schmieder, V.; Kepner, A.; Jakab, F.; Kemenesi, G. Emergence of Aedes koreicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in an urban area, Hungary, 2016. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4687–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, T.; Flacio, E.; Fariña, B.F.; Engeler, L.; Tonolla, M.; Müller, P. First report of the invasive mosquito species Aedes koreicus in the Swiss-Italian border region. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholte, E.J.; Den Hartog, W.; Braks, M.; Reusken, C.; Dik, M.; Hessels, A. First report of a North American invasive mosquito species Ochlerotatus atropalpus (Coquillett) in The Netherlands, 2009. Eur. Surveill. 2009, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraguti, M.; Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Muñoz, J.; Roiz, D.; Ruiz, S.; Soriguer, R.; Figuerola, J. Avian Plasmodium in Culex and Ochlerotatus mosquitoes from southern Spain: Effects of season and host-feeding source on parasite dynamics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpatrick, A.M.; Kramer, L.D.; Jones, M.J.; Marra, P.P.; Daszak, P. West Nile Virus epidemics in North America are driven by shifts in mosquito feeding behavior. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, B. Identification of blood meals of blood-sucking arthropods. Bull. World Health Org. 1956, 15, 473–490. [Google Scholar]
- Lorosa, E.S.; Faria, M.S.; De Oliveira, L.C.M.; Alencar, J.; Marcondes, C.B. Blood meal identification of selected mosquitoes in Rio De Janeiro, Brazil. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2010, 26, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, W. An agar gel difussion method for the identification of mosquito blood-meals. J. Ser. New Jersey Agric. Exp. Stn. 1969, 29, 563–566. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R.; Panicker, K. Identification of bloodmeals of phlebotomine sandflies using the agarose gel diffusion method. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1992, 23, 486–488. [Google Scholar]
- Apperson, C.S.; Hassan, H.K.; Harrison, B.A.; Savage, H.M.; Aspen, S.E.; Farajollahi, A.; Crans, W.; Daniels, T.J.; Falco, R.C.; Benedict, M.; et al. Host feeding patterns of established and potential mosquito vectors of West Nile Virus in the eastern United States. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2004, 4, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaklang, S.; Kittayapong, P. Species composition and blood meal analysis of mosquitoes collected from a tourist island, Koh Chang, Thailand. J. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-C.; Teng, H.-J.; Chen, C.-F.; Chen, Y.-C.; Jeng, C.-R. The resting sites and blood-meal sources of Anopheles minimus in Taiwan. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Muñoz, J.; Capelli, G.; Montarsi, F.; Soriguer, R.; Arnoldi, D.; Rizzoli, A.; Figuerola, J. Avian malaria parasites in the last supper: Identifying encounters between parasites and the invasive Asian mosquito tiger and native mosquito species in Italy. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niare, S.; Berenger, J.-M.; Dieme, C.; Doumbo, O.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P.; Almeras, L. Identification of blood meal sources in the main African malaria mosquito vector by MALDI-TOF MS. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandina, F.; Niare, S.; Almeras, L.; Davoust, B.; Doumbo, O.K.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P.; Laroche, M. Identification of mixed and successive blood meals of mosquitoes using MALDI-TOF MS protein profiling. Parasitology 2020, 147, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandina, F.; Niaré, S.; Laroche, M.; Koné, A.K.; Diarra, A.Z.; Ongoiba, A.; Berenger, J.M.; Doumbo, O.K.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Using MALDI-TOF MS to identify mosquitoes collected in Mali and their blood meals. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwanga, E.P.; Mapua, S.A.; Siria, D.J.; Ngowo, H.S.; Nangacha, F.; Mgando, J.; Baldini, F.; González Jiménez, M.; Ferguson, H.M.; Wynne, K.; et al. Using mid-infrared spectroscopy and supervised machine-learning to identify vertebrate blood meals in the malaria vector, Anopheles arabiensis. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, M.F.; Pereira, R.M.; Batich, C.; Koehler, P. Factors Affecting Short-Range Host-Seeking for the Yellow Fever Mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, J.C. Vector incrimination and entomological inoculation rates. In Malaria Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Medicine™; Doolan, D.L., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 72, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-López, L.D.; Pondeville, E.; Kohl, A.; León, R.; Betancourth, M.P.; Almire, F.; Torres-Valencia, S.; Saldarriaga, S.; Mirzai, N.; Ferguson, H.M. The mosquito electrocuting trap as an exposure-free method for measuring human-biting rates by Aedes mosquito vectors. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Zborowski, P.; Graham, G.; Webb, C.; Russell, R.; Craig, S.; Zborowski, P.; Ritchie, S.A.; Russell, R.; van den Hurk, A.F. Blood sources of mosquitoes collected from urban and peri-urban environments in eastern Australia with species-specific molecular analysis of avian blood meals. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Silva, N.; Marques, G.; Brito, M. Host-feeding patterns of potential human disease vectors in the Paraíba Valley Region, State of São Paulo, Brazil. J. Vector Ecol. 2003, 28, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tandom, N.; Ray, S. Host feeding pattern of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in Kolkata, India. Dengue Bull. 2000, 24, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ponlawat, A.; Harrington, L.C. Blood feeding patterns of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in Thailand. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, H.M.; Niebylski, M.; Smith, G.; Mitchell, C.; Craig, J.R.G. Host-feeding patterns of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) at a temperate North American site. J. Med. Entomol. 1993, 30, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.L.; Ponnusamy, L.; Unnasch, T.R.; Hassan, H.K.; Apperson, C.S. Host-feeding patterns of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in relation to availability of human and domestic animals in suburban landscapes of central North Carolina. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niare, S.; Tandina, F.; Davoust, B.; Doumbo, O.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P.; Almeras, L. Accurate identification of Anopheles gambiae Giles trophic preferences by MALDI-TOF MS. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaide, M.; Rico, C.; Ruiz, S.; Soriguer, R.; Muñoz, J.; Figuerola, J. Disentangling vector-borne transmission networks: A universal DNA barcoding method to identify vertebrate hosts from arthropod bloodmeals. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisawat, R.; Sungvornyothin, S.; Jacquet, M.; Komalamisra, N.; Apiwathnasorn, C.; Dujardin, J.; Boyer, S. Preserving blood-fed Aedes albopictus from field to laboratory for blood source determination. JITMM2013 Proc. 2014, 3, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Ruiz, S.; Soriguer, R.; Figuerola, J. Effect of blood meal digestion and DNA extraction protocol on the success of blood meal source determination in the malaria vector Anopheles atroparvus. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egizi, A.; Healy, S.P.; Fonseca, D.M. Rapid blood meal scoring in anthropophilic Aedes albopictus and application of PCR blocking to avoid pseudogenes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 16, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.; Eritja, R.; Alcaide, M.; Montalvo, T.; Soriguer, R.C.; Figuerola, J. Host-feeding patterns of native Culex pipiens and invasive Aedes albopictus mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in urban zones from Barcelona, Spain. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadj-Henni, L.; De Meulemeester, T.; Depaquit, J.; Noël, P.; Germain, A.; Helder, R.; Augot, D. Comparison of vertebrate cytochrome b and prepronociceptin for blood meal analyses in Culicoides. Front. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanigawa, M.; Sato, Y.; Ejiri, H.; Imura, T.; Chiba, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawaguchi, M.; Tsuda, Y.; Murata, K.; Yukawa, M. Molecular identification of avian Haemosporidia in wild birds and mosquitoes on Tsushima Island, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Díez-Fernández, A.; Montalvo, T.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Pangrani, Q.; Soriguer, R.C.; Senar, J.C.; Figuerola, J. Do invasive mosquito and bird species alter avian malaria parasite transmission? Diversity 2020, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yu, H.M.; Lim, H.W.; Yang, S.-C.; Roh, J.Y.; Chang, K.S.; Shin, E.-H.; Ju, Y.R.; Lee, W.-G. Host-feeding pattern and dengue virus detection of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) captured in an urban park in Korea. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennett, J.A.; Bala, A.; Wuithiranyagool, T.; Randle, Y.; Sargent, C.B.; Guzman, H.; Siirin, M.; Hassan, H.K.; Reyna-Nava, M.; Unnasch, T.R.; et al. Associations between two mosquito populations and West Nile Virus in Harris County, Texas, 2003–2006 1. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2007, 23, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, A.; Egizi, A.; Fonseca, D.M.; Unlu, I.; Crepeau, T.; Healy, S.P.; Gaugler, R. Comparative host feeding patterns of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus, in urban and suburban northeastern USA and implications for disease transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-dos Santos, T.; Roiz, D.; Santos de Abreu, F.V.; Luz, S.L.B.; Santalucia, M.; Jiolle, D.; Santos Neves, M.S.A.; Simard, F.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R.; Paupy, C. Potential of Aedes albopictus as a bridge vector for enzootic pathogens at the urban-forest interface in Brazil. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamashiro, M.; Toma, T.; Mannen, K.; Higa, Y.; Miyagi, I. Bloodmeal identification and feeding habits of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) collected at five islands in the Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan. Jap. J. Sanit. Zool. 2011, 62, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Soriguer, R.; Senar, J.; Figuerola, J.; Bueno-Mari, R.; Montalvo, T. Mosquitoes in an urban zoo: Identification of blood meals, flight distances of engorged females, and avian malaria infections. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Tsuda, Y.; Yamada, A. Bloodmeal identification and detection of avian malaria parasite from mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) inhabiting coastal areas of Tokyo Bay, Japan. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kek, R.; Hapuarachchi, H.C.; Chung, C.-Y.; Humaidi, M.B.; Razak, M.A.B.A.; Chiang, S.; Lee, C.; Tan, C.-H.; Yap, G.; Chong, C.-S.; et al. Feeding hostrange of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) demonstrates its opportunistic host-seeking behavior in rural Singapore. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.-X.; Li, C.-X.; Wang, G.; Zheng, Z.; Dong, Y.-D.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Xing, D.; Zhao, T.-Y. Host feeding patterns of mosquitoes in a rural malaria-endemic region in Hainan Island, China. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2014, 30, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenn, T.; Peck, K.J.; Rocha Pereira, G.; Burkett-Cadena, N.D. Vertebrate hosts of Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus, and Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) as potential vectors of Zika Virus in Florida. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, H.; Egizi, A.; Fonseca, D.M.; Leisnham, P.T.; LaDeau, S.L. Primary blood-hosts of mosquitoes are influenced by social and ecological conditions in a complex urban landscape. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriyasatien, P.; Pengsakul, T.; Kittichai, V.; Phumee, A.; Kaewsaitiam, S.; Thavara, U.; Tawatsin, A.; Savadachanukorn, P.A.; Mull, M.S. Identification of blood meal of field caught Aedes aegypti (L.) by multiplex PCR. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2010, 41, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Diallo, D.; Chen, R.; Diagne, C.T.; Ba, Y.; Dia, I.; Sall, A.A.; Weaver, S.C.; Diallo, M. Bloodfeeding patterns of sylvatic arbovirus vectors in southeastern Senegal. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, R.; Bingham, A.M.; Hassan, H.K.; Amador, M.; Mackay, A.J.; Unnasch, T.R. Vertebrate hosts of Aedes aegypti and Aedes mediovittatus (Diptera: Culicidae) in rural Puerto Rico. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, H.C.; Zé-Zé, L.; Alves, M.J. Host-feeding patterns of Culex pipiens and other potential mosquito vectors (Diptera: Culicidae) of West Nile Virus (Flaviviridae) collected in Portugal. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönenberger, A.C.; Wagner, S.; Tuten, H.C.; Schaffner, F.; Torgerson, P.; Furrer, S.; Mathis, A.; Silaghi, C. Host preferences in host-seeking and blood-fed mosquitoes in Switzerland: Host preferences in mosquitoes. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2016, 30, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, G.; Andreadis, T.G.; Armstrong, P.M.; Diuk-Wasser, M. Host-feeding patterns of potential mosquito vectors in Connecticut, USA: Molecular analysis of bloodmeals from 23 species of Aedes, Anopheles, Culex, Coquillettidia, Psorophora, and Uranotaenia. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, G.; Farajollahi, A.; Scott, J.J.; Gaugler, R.; Andreadis, T.G. Human bloodfeeding by the recently introduced mosquito, Aedes japonicus japonicus, and public health implications. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2009, 25, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiens, D.; Ayrinhac, A.; Van Bortel, W.; Versteirt, V.; Dekoninck, W.; Hance, T. Invasive process and repeated cross-sectional surveys of the mosquito Aedes japonicus japonicus establishment in Belgium. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.F.; Armstrong, P.M.; Misencik, M.J.; Bransfield, A.B.; Andreadis, T.G.; Molaei, G. Seasonal distribution, blood-feeding habits, and viruses of mosquitoes in an open-faced quarry in Connecticut, 2010 and 2011. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2018, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montarsi, F.; Drago, A.; Pont, M.D.; Delai, N.; Carlin, S.; Cazzin, S.; Ciocchetta, S.; Arnoldi, D.; Baldacchino, F.; Rizzoli, A.; et al. Current knowledge on the distribution and biology of the recently introduced invasive mosquito Aedes koreicus (Diptera: Culicidae). Atti Accad. Naz. Ital. Entomol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripepi, L. Preferenze Alimentari di Aedes koreicus, una Nuova Zanzara Invasiva e Implicazioni Nella Trasmissione di Patogeni. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Valerio, L.; Marini, F.; Bongiorno, G.; Facchinelli, L.; Pombi, M.; Caputo, B.; Maroli, M.; della Torre, A. Host-feeding patterns of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in urban and rural contexts within Rome province, Italy. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, A.; Shriram, A.N.; Sunish, I.P.; Vidhya, P.T. Host-feeding pattern of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in heterogeneous landscapes of South Andaman, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.E.; Alves, J.M.; Palmer, W.J.; Day, J.P.; Sylla, M.; Ramasamy, R.; Surendran, S.N.; Black, W.C.; Pain, A.; Jiggins, F.M. Population genomics reveals that an anthropophilic population of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes in West Africa recently gave rise to American and Asian populations of this major disease vector. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardelis, M.R.; Turell, M.J. Ochlerotatus j. japonicus in Frederick county, Maryland: Discovery, distribution, and vector competence for West Nile Virus. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2001, 17, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, N.H.; Sylla, M.; Badolo, A.; Lutomiah, J.; Ayala, D.; Aribodor, O.B.; Ibe, N.; Akorli, J.; Otoo, S.; Mutebi, J.-P.; et al. Climate and urbanization drive mosquito preference for humans. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 3570–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Sharma, S.; Krajacich, B.J.; Fakoli III, L.S.; Bolay, F.K.; Diclaro II, J.W.; Johnson, W.E.; Ebel, G.D.; Foy, B.D.; Brackney, D.E. Xenosurveillance: A novel mosquito-based approach for examining the human-pathogen landscape. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomazatos, A.; Jansen, S.; Pfister, S.; Török, E.; Maranda, I.; Horváth, C.; Keresztes, L.; Spînu, M.; Tannich, E.; Jöst, H.; et al. Ecology of West Nile Virus in the Danube Delta, Romania: Phylogeography, xenosurveillance and mosquito host-feeding patterns. Viruses 2019, 11, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Aedes albopictus | Family | Species | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mammals | Hominidae | Homo sapiens | [73,84,97,103,105,106], [107] *, [108,109,110,111,112,113], [114] *, [115], [116] *, [117] |
| Canidae | Canis lupus ** | [97,108,109,110,113], [114] *, [115,117] | |
| Felidae | Felis silvestris ** | [97,105,106], [107] *, [109], [114] *, [117] | |
| Procyonidae | Procyon lotor | [97], [116] * | |
| Muridae | Rattus norvegicus | [110,113], [116] *, [117] | |
| Mus musculus | [105] | ||
| Cricetidae | Peromyscus leucopus | [109] | |
| Sciuridae | Sciurus carolinensis | [111] | |
| Leporidae | Sylvilagus floridanus | [109], [116] * | |
| Suidae | Sus ** | [108,111], [114] *, [115] | |
| Bovidae | Bos taurus | [73] | |
| Cervidae | Odocoileus virginianus | [117] | |
| Equidae | Equus caballus | [97] | |
| Soricidae | Suncus murinus | [111] | |
| Erinaceidae | Erinaceus europaeus | [84] | |
| Dasypopidae | Dasypus novemcintus | [116] * | |
| Phyllostomidae | Tonatia bidens | [110] | |
| Didelphidae | Didelphis virginiana | [97,109] | |
| Birds | |||
| Phasianidae | Gallus domesticus | [97,115] | |
| Turdidae | Turdus merula | [84] | |
| Passeridae | Passer montanus | [84] | |
| Tamnophilide | Taraba major | [110] | |
| Cardinalidae | Cardinalis cardinalis | [97] | |
| Anatidae | Unknown | [115] | |
| Aedes aegypti | |||
| Mammals | Hominidae | Homo sapiens | [92,116,118,119,120,121] |
| Canidae | Canis lupus ** | [92,116,118,120] | |
| Felidae | Felis silvestris ** | [92,120] | |
| Bovidae | Bos taurus | [92,118] | |
| Suidae | Sus scrofa ** | [118] | |
| Equidae | Equus caballus | [120] | |
| Birds | |||
| Phasianidae | Gallus domesticus | [120] | |
| Phasianidae | Francolinus squamatus | [119] | |
| Mimidae | Mimus polyglottos | [116] | |
| Musophagidae | Crinifer piscator | [119] | |
| Aedes japonicus | |||
| Mammals | Hominidae | Homo sapiens | [81,117,122,123,124,125] |
| Canidae | Canis lupus ** | [122] | |
| Canis latrans | [126] | ||
| Felidae | Felis silvestris ** | [117] | |
| Panthera leo persica | [122] | ||
| Procyonidae | Procyon lotor | [126] | |
| Phocidae | Phoca vitulina | [122] | |
| Muridae | Rattus norvegicus | [117] | |
| Sciuridae | Unknown species | [123] | |
| Camelidae | Lama sp. | [122] | |
| Bovidae | Bos taurus | [125] | |
| Boselaphus tragocamelus | [122] | ||
| Ovis sp. | [122] | ||
| Cervidae | Dama dama | [124] | |
| Odocoileus virginianus | [123,124,126] | ||
| Equidae | Equus caballus | [81,124] | |
| Equus asinus | [122] | ||
| Didelphidae | Didelphis virginiana | [124] | |
| Birds | |||
| Phasianidae | Gallus domesticus | [122] | |
| Turdidae | Turdus merula | [122] | |
| Passeridae | Passer domesticus | [122] | |
| Spheniscidae | Spheniscus humboldti | [122] | |
| Rheidae | Rhea pennata | [122] | |
| Aedes koreicus | |||
| Mammals | Hominidae | Homo sapiens | [127,128] |
| Canidae | Canis lupus ** | [127,128] | |
| Bovidae | Bos taurus | [128] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cebrián-Camisón, S.; Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Figuerola, J. A Literature Review of Host Feeding Patterns of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes in Europe. Insects 2020, 11, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120848
Cebrián-Camisón S, Martínez-de la Puente J, Figuerola J. A Literature Review of Host Feeding Patterns of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes in Europe. Insects. 2020; 11(12):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120848
Chicago/Turabian StyleCebrián-Camisón, Sonia, Josué Martínez-de la Puente, and Jordi Figuerola. 2020. "A Literature Review of Host Feeding Patterns of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes in Europe" Insects 11, no. 12: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120848
APA StyleCebrián-Camisón, S., Martínez-de la Puente, J., & Figuerola, J. (2020). A Literature Review of Host Feeding Patterns of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes in Europe. Insects, 11(12), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120848







