Assessment of the Biological Control Potential of Common Carabid Beetle Species for Autumn- and Winter-Active Pests (Gastropoda, Lepidoptera, Diptera: Tipulidae) in Annual Ryegrass in Western Oregon
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sampling
2.2. Statistical Analyses
2.3. Molecular Gut Content Analysis
3. Results
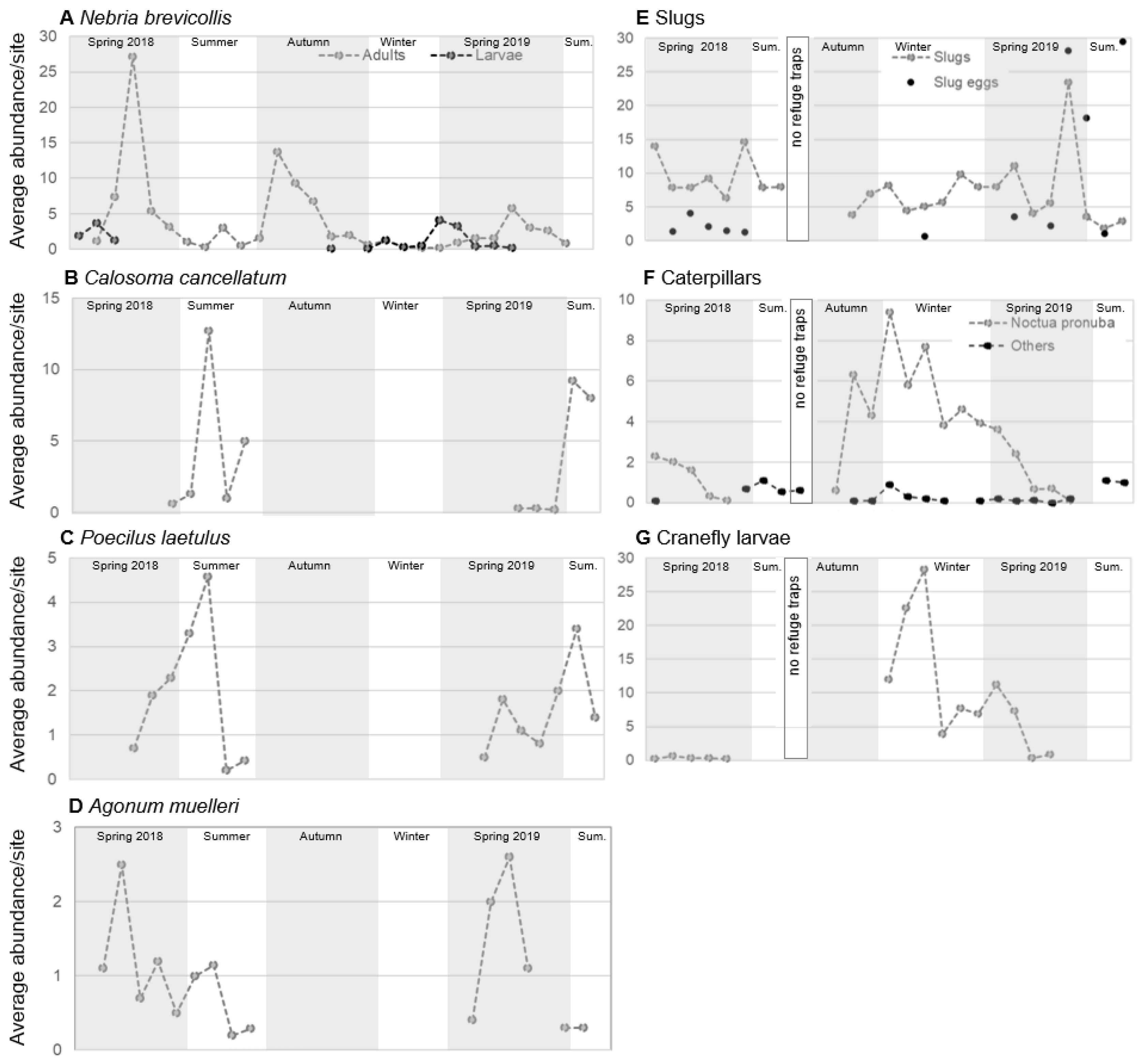
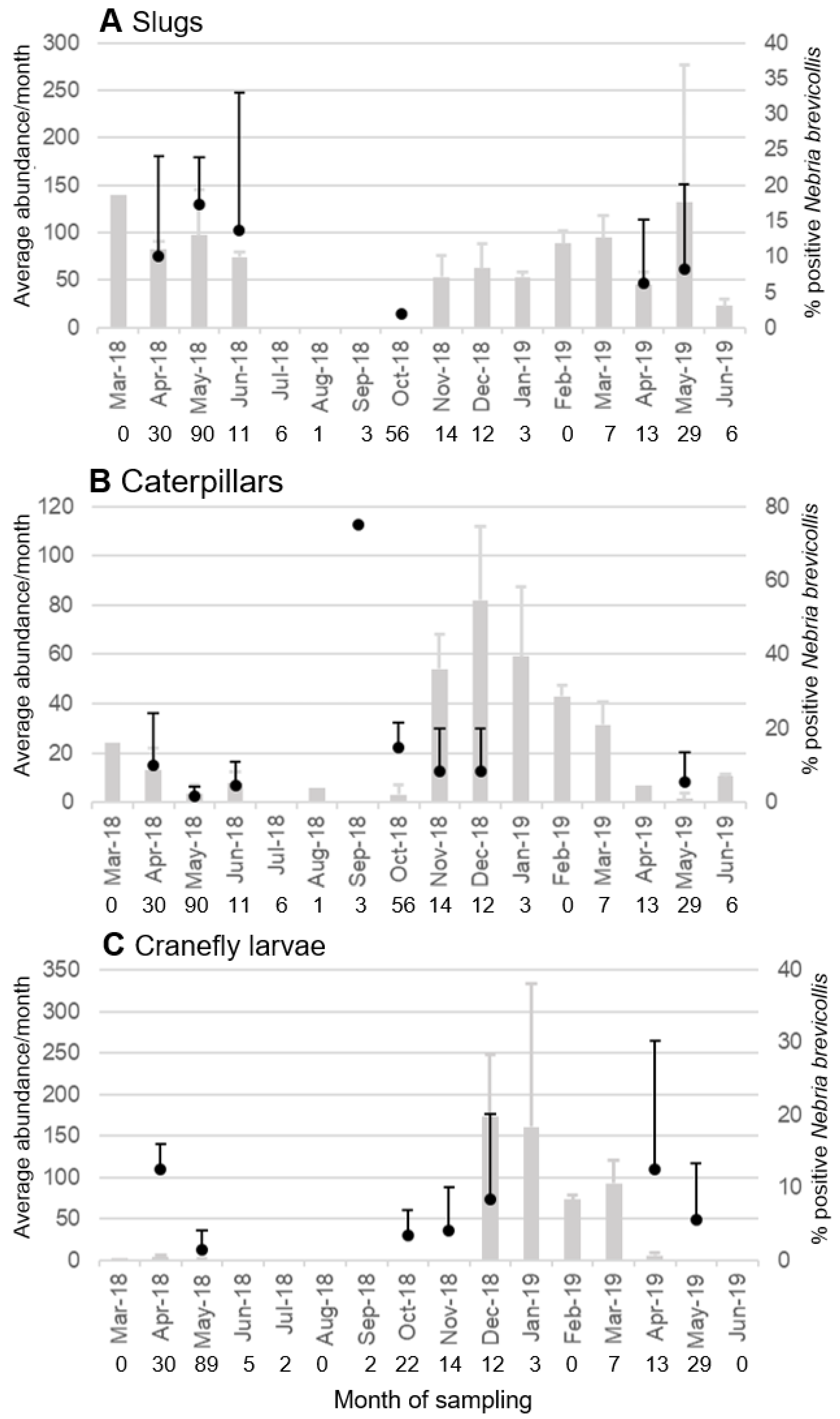
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Overlap of Carabids and Annual Ryegrass Pests
3.2. Impact of Field Margin and Disk Tilling on Carabid Species Distributions
3.3. Identification of Pest DNA in Carabid Gut Contents by qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Feeding Trials
| Replicates | 31 May 2019 | 1 June 2019 | 3 June 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | |||
| 6 | |||
| 7 | |||
| 8 | Eggs disturbed | ||
| 9 | |||
| 10 | |||
| 11 | |||
| 12 | |||
| 13 | Eggs disturbed | Eggs disturbed | |
| 14 | |||
| 15 | |||
| 16 | |||
| 17 | Carabid dead | trial ended | |
| 18 | |||
| 19 | |||
| 20 |
| Replicates | 10 June 2019 | 11 June 2019 | 13 June 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | 1 slug hatched | ||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | 1 slug hatched | ||
| 6 | |||
| 7 | Eggs disturbed | ||
| 8 | |||
| 9 | |||
| 10 | 1 slug hatched | ||
| 11 | Eggs disturbed | ||
| 12 | Eggs disturbed | ||
| 13 | |||
| 14 | Eggs disturbed | ||
| 15 | |||
| 16 | Slug dead | ||
| 17 | |||
| 18 | |||
| 19 | |||
| 20 | 1 slug hatched |
Appendix B. DNA Detection
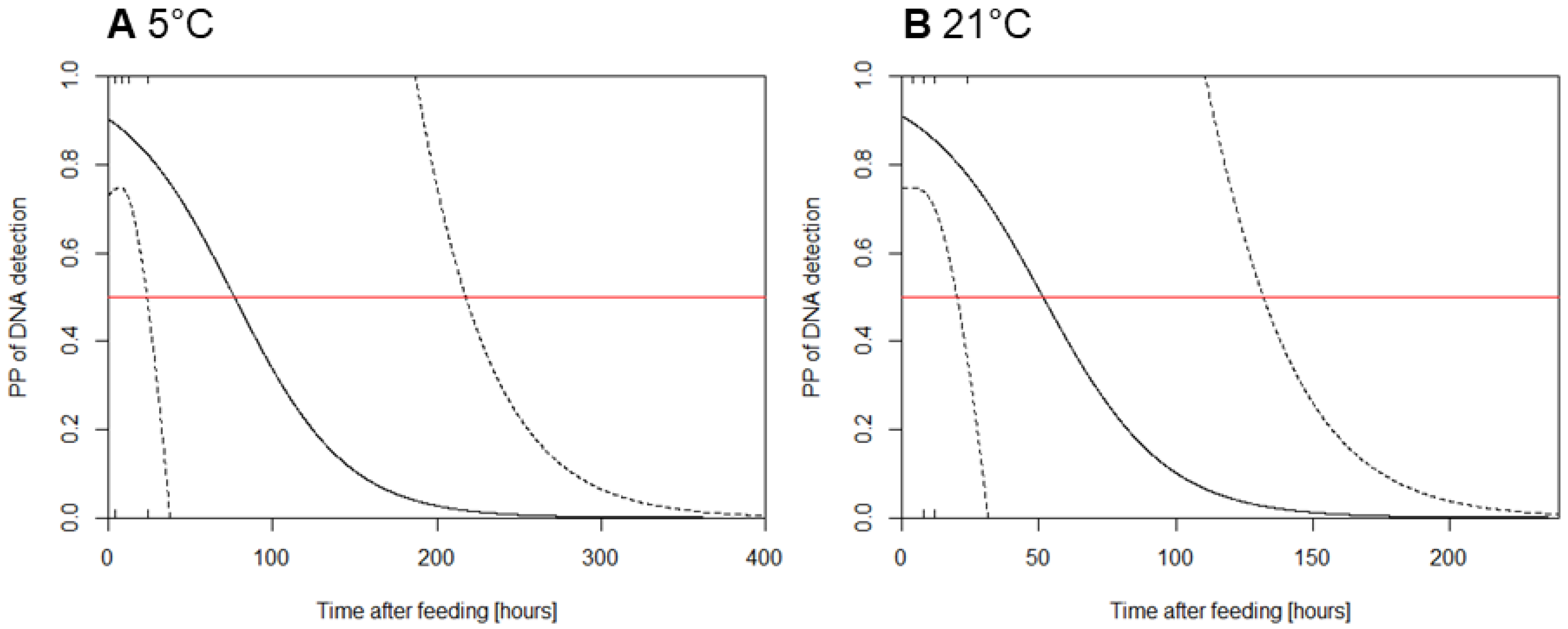
References
- Bohan, D.A.; Bohan, A.C.; Glen, D.M.; Symondson, W.O.; Wiltshire, C.W.; Hughes, L. Spatial dynamics of predation by carabid beetles on slugs. J. Anim. Ecol. 2000, 69, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayre, K. Effect of predator size and temperature on the predation of Deroceras reticulatum (Mϋller) (Mollusca) by carabid beetles. J. Appl. Entomol. 2001, 125, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, J.; Port, G.R. Predation by the carabid beetles Pterostichus madidus and Nebria brevicollis is affected by size and condition of the prey slug Deroceras reticulatum. Agric. For. Entomol. 2001, 3, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, J.; Port, G.R. Predation on the slug Deroceras reticulatum by the carabid beetles Pterostichus madidus and Nebria brevicollis in the presence of alternative prey. Agric. For. Entomol. 2001, 3, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberholzer, F.; Frank, T. Predation by the carabid beetles Pterostichus melanarius and Poecilus cupreus on slugs and slug eggs. Biocontrol. Sci. Technol. 2003, 13, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberholzer, F.; Escher, N.; Frank, T. The potential of carabid beetles (Coleoptera) to reduce slug damage to oilseed rape in the laboratory. Eur. J. Entomol. 2003, 100, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laub, C.A.; Luna, J.M. Winter cover crop suppression practices and natural enemies of armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in no-till corn. Environ. Entomol. 1992, 21, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Luna, J.M.; Stone, N.D.; Youngman, R.R. Generalist predator consumption of armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and effect of predator removal on damage in no-till corn. Environ. Entomol. 1994, 23, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.G. Relationships of Natural Enemies and Non-Prey Foods; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Polo, P.; Alomar, O.; Castañé, C.; Lundgren, J.G.; Piñol, J.; Agustí, N. Molecular assessment of predation by hoverflies (Diptera: Syrphidae) in Mediterranean lettuce crops. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.L.; King, R.A.; Dodd, C.S.; Harwood, J.D.; Glen, D.M.; Bruford, M.W.; Symondson, W.O.C. Rapid screening of invertebrate predators for multiple prey DNA targets. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelson, M.J.; Chapman, E.G.; Archbold, D.D.; Obrycki, J.J.; Harwood, J.D. Molecular identification of predation by carabid beetles on exotic and native slugs in a strawberry agroecosystem. Biol. Control. 2011, 56, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firlej, A.; Doyon, J.; Harwood, J.D.; Brodeur, J. A multi-approach study to delineate interactions between carabid beetles and soybean aphids. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Landis, D.A.; Van der Werf, W. Early-season predation impacts the establishment of aphids and spread of beet yellows virus in sugar beet. Entomophaga 1997, 42, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.B.; Landis, D.A.; Cardoso, F.F.; Difonzo, C.D. Impact of predation on establishment of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines in soybean, Glycine max. Biocontrol 2005, 50, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiverton, P.A. Predation of Rhopalosiphum padi (Homoptera: Aphididae) by polyphagous predatory arthropods during the aphids’ pre-peak period in spring barley. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1987, 111, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövei, G.L.; Sunderland, K.D. Ecology and behavior of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, K.D.; Harwood, J.D. Temporal dynamics of natural enemy–pest interactions in a changing environment. Biol. Control. 2014, 75, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, K.J.; Dreyer, J.; Kowles, K.A.; Penn, H.J.; Sitvarin, M.I.; Harwood, J.D. Spring forward: Molecular detection of early season predation in agroecosystems. Food Webs 2016, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.T. The occurrence and importance of ground beetles in agricultural and surrounding habitats. In Carabid beEtles; Erwin, T.L., Ball, G.E., Whitehead, D.R., Halpern, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 485–505. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.E.G.; Forsythe, T.G. Feeding mechanisms, and their variation in form, of some adult ground-beetles (Coleoptera: Caraboidea). J. Zool. 1985, 206, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, M.; Desender, K. Feeding ecology of grassland-inhabiting carabid beetles (Carabidae, Coleoptera) in relation to the availability of some prey groups. Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 1987, 22, 223–246. [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, J.D.; Sunderland, K.D.; Symondson, W.O. Prey selection by linyphiid spiders: Molecular tracking of the effects of alternative prey on rates of aphid consumption in the field. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 3549–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, J.D.; Desneux, N.; Yoo, H.J.S.; Rowley, D.L.; Greenstone, M.H.; Obrycki, J.J.; O’Neil, R.J. Tracking the role of alternative prey in soybean aphid predation by Orius insidiosus: A molecular approach. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 4390–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, J.D.; Yoo, H.J.S.; Greenstone, M.H.; Rowley, D.L.; O’Neil, R.J. Differential impact of adults and nymphs of a generalist predator on an exotic invasive pest demonstrated by molecular gut-content analysis. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.G.; Schmidt, J.M.; Welch, K.D.; Harwood, J.D. Molecular evidence for dietary selectivity and pest suppression potential in an epigeal spider community in winter wheat. Biol. Control 2013, 65, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromp, B. Carabid beetles in sustainable agriculture: A review on pest control efficacy, cultivation impacts and enhancement. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 74, 187–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinner, B.R.; House, G.J. Arthropods and other invertebrates in conservation-tillage agriculture. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1990, 35, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.F.; Connery, J.; Fortune, T.; Forristal, D.; Grant, J. A comparison of the effects of minimum-till and conventional-till methods, with and without straw incorporation, on slugs, slug damage, earthworms and carabid beetles in autumn-sown cereals. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 151, 605–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuke, F.O.; Kihara, J.; Ayaga, G.; Micheni, A.N. Conservation agriculture enhances soil fauna richness and abundance in low input systems: Examples from Kenya. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovskaya, N.A. Field carabid beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) of Byelorussia. Entomol. Rev. 1970, 49, 476–483. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, W.D. Vergleich der epigäischen Bodenfauna bei wendender bzw. nichtwendender Grundbodenbearbeitung. Mitteilungen aus der Biologischen Bundesanstalt für Land-und Forstwirtschaft 1986, 232, 290. [Google Scholar]
- Barney, R.J.; Pass, B.C. Ground beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) populations in Kentucky alfalfa and influence of tillage. J. Econ. Entomol. 1986, 79, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo, H.A.; Niemalä, J.K.; Spence, J.R. Farming and ground beetles: Effects of agronomic practice on populations and community structure. Can. Entomol. 1995, 127, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguette, M.; Hance, T.H. Carabid beetles and agricultural practices: Influence of soil ploughing. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 1997, 15, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, H.; Järveläinen, K.; Pakkala, T.; Tiainen, J. The effect of isolation on the occurrence of farmland carabids in a fragmented landscape. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1996, 33, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen, H.; Tiainen, J.; Tukia, H. Farmland carabid beetle communities at multiple levels of spatial scale. Ecography 2001, 24, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Usher, M.B. Biodiversity in agricultural landscapes: The ground beetle communities of woody uncultivated habitats. Biodivers. Conserv. 1998, 7, 1549–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviron, S.; Burel, F.; Baudry, J.; Schermann, N. Carabid assemblages in agricultural landscapes: Impacts of habitat features, landscape context at different spatial scales and farming intensity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 108, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.J.; Winder, L.; Holland, J.M.; Thomas, C.G.; Williams, E. The representation and functional composition of carabid and staphylinid beetles in different field boundary types at a farm-scale. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 135, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, F.; Maelfait, J.P.; Van Wingerden, W.; Schweiger, O.; Speelmans, M.; Aviron, S.; Augenstein, I.; Billeter, R.; Bailey, D.; Bukacek, R.; et al. How landscape structure, land-use intensity and habitat diversity affect components of total arthropod diversity in agricultural landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saska, P.; Vodde, M.; Heijerman, T.; Westerman, P.; van der Werf, W. The significance of a grassy field boundary for the spatial distribution of carabids within two cereal fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 122, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfiffner, L.; Luka, H. Overwintering of arthropods in soils of arable fields and adjacent semi-natural habitats. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 78, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.J.; Booij, C.J.H.; Tscharntke, T. Sustainable pest regulation in agricultural landscapes: A review on landscape composition, biodiversity and natural pest control. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, K.L.; Boatman, N.D.; Wilcox, A.; Holland, J.M.; Chaney, K. Influence of beetle banks on cereal aphid predation in winter wheat. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschumi, M.; Albrecht, M.; Entling, M.H.; Jacot, K. High effectiveness of tailored flower strips in reducing pests and crop plant damage. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, S.E.; Anderson, N.P. Grass Seed Pests. In Legume, Grass, and Field Seed Crops, PNW. Insect Management Handbook; Pacific Northwest Extension Publication: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2020; pp. D15–D26. [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury, S. The cost of slugs to the grass seed industry in the Willamette Valley. In Proceedings of the House Agriculture and Natural Resources Committee Chairman at Oregon Capital in Salem, Salem, OR, USA, May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Slug-Portal. Available online: http://agsci.oregonstate.edu/slug-portal (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Mc Donnell, R.; Anderson, N.; Sullivan, C.; Dreves, A. Slug control. In Integrated Pest Management, PNW Insect Management Handbook; Pacific Northwest Extension Publication: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2019; pp. N14–N16. [Google Scholar]
- Green, J.; Dreves, A.; McDonald, B.; Peachey, R. Winter Cutworm: A New Pest Threat in Oregon; EM 9139; Oregon State University, Extension Service: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.M.; Perry, J.N.; Winder, L. The within-field spatial and temporal distribution of arthropods in winter wheat. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1999, 89, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.F.G.; Parkinson, L.; Marshall, E.J.P. Isolating the components of activity-density for the carabid beetle Pterostichus melanarius in farmland. Oecologia 1998, 116, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroth, C.H. The Ground-Beetles (Carabidae, Excl. Cicindelinae) of Canada and Alaska; Parts 1–6; Entomologiska Salhskapet: London, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.H.; Bohan, D.A.; Powers, S.J.; Wiltshire, C.W.; Glen, D.M.; Semenov, M.A. Modelling Deroceras. reticulatum. (Gastropoda) population dynamics based on daily temperature and rainfall. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 103, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Bohan, D.A.; Potting, R.P.J.; Semenov, M.A.; Glen, D.M. Individual based model of slug population and spatial dynamics. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schley, D.; Bees, M.A. Delay dynamics of the slug Deroceras reticulatum, an agricultural pest. Ecol. Model. 2003, 162, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.5823. [Google Scholar]
- Halekoh, U.; Højsgaard, S. A kenward-roger approximation and parametric bootstrap methods for tests in linear mixed models–the R package pbkrtest. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 59, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. rsq: R-Squared and Related Measures. R Package Version 2.0. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rsq (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Jarman, S.N.; Redd, K.S.; Gales, N.J. Group-specific primers for amplifying DNA sequences that identify Amphipoda, Cephalopoda, Echinodermata, Gastropoda, Isopoda, Ostracoda and Thoracica. Mol. Ecol. Notes. 2006, 6, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sint, D.; Niederklapfer, B.; Kaufmann, R.; Traugott, M. Group-specific multiplex PCR detection systems for the identification of flying insect prey. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, G.M. Molluscs as Crop Pests; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, O. The life history patterns of Nebria degenerata Schaufuss and N. brevicollis Fabricius (Coleoptera, Carabidae). J. Soc. Br. Entomol. 1958, 6, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lindroth, C.H. Die Fennoskandischen Carabidae, 1. Spezieller Teil; Elanders Boktryckeri Aktiebolag: Göteborg, Sweden, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Young, A.G.; Port, G.R. The effect of microclimate on slug activity in the field. In Slugs and Snails in World Agriculture British Crop Protection Council Monograph No. 41; Henderson, I.F., Ed.; British Crop Protection Council: Thornton Heath, UK, 1989; pp. 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Hommay, G.; Kienlen, J.C.; Jacky, F.; Gertz, C. Daily variation in the number of slugs under refuge traps. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2003, 142, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.G.; Port, G.R.; Emmett, B.J.; Green, D.I. Development of a forecast of slug activity: Models to relate slug activity to meteorological conditions. J. Crop. Prot. 1991, 10, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, I.; Mc Donnell, R.; Mc Inerney, C.; Callanan, S.; Gormally, M. EU-protected slug Geomalacus maculosus and sympatric Lehmannia marginata in conifer plantations: What does mark-recapture method reveal about population densities? J. Molluscan Stud. 2017, 83, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.J. Studies on slugs of arable ground. I. Sampling methods. Malacologia 1986, 6, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, B.P.; Byers, R.A.; Bierlein, O.L. Comparison of slug (Mollusca: Pulmonata) trapping in no-till alfalfa. J. Econ. Entomol. 1993, 86, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, R.O.; Murray, P.J. Comparison between defined-area slug traps and other methods of trapping slugs in cereal fields. J. Crop. Prot. 1991, 10, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Warrant, G.W.; Anderson, N.P.; Sullivan, C.S.; Whittaker, G.W.; Trippe, K.M. Can knowledge of spatial variability in slug populations help improve stand establishment? Seed Prod. Res. Or. State Univ. 2014, 151, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, A.K.; Douglas, M.R.; Malcolm, G.M.; Karsten, H.D.; Tooker, J.F. A high-diversity/IPM cropping system fosters beneficial arthropod populations, limits invertebrate pests, and produces competitive maize yields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 292, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowen, E.; Tooker, J.F. Fertilizing corn with manure decreases caterpillar performance but increases slug damage. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Bonte, J.R. Nebria brevicollis (Fabricius, 1792) in North America, benign or malign? (Coleoptera, Carabidae, Nebriini). ZooKeys 2011, 147, 527–543. [Google Scholar]
- Luff, M.L. The Carabidae (ground beetles) of Britain and Ireland; Royal Entomological Society: St Albans, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Den Boer, P.J. The individual behaviour and population dynamics of some carabid beetles of forests. In On the Evolution of Behaviour in Carabid Beetles; Den Boer, P.J., Thiele, H.U., Weber, T., Eds.; Miscellaneous Papers 18; Agricultural University Wageningen: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Stockan, J.A.; Baird, J.; Langan, S.J.; Young, M.R.; Iason, G.R. Effects of riparian buffer strips on ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) within an agricultural landscape. Insect Conserv. Diver. 2014, 7, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, G.A.; Lucht, W.H. Die Käfer Mitteleuropas. 1. Supplementband mit Katalogteil; Goecke & Evers: Krefeld, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.M.; Reynolds, C.J. The impact of soil cultivation on arthropod (Coleoptera and Araneae) emergence on arable land. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.M.; Luff, M.L. The effects of agricultural practices on Carabidae in temperate agroecosystems. Integr. Pest Manag. Rev. 2000, 5, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatten, T.D.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; La Bonte, J.R.; Guy, S.O.; Eigenbrode, S.D. Effects of tillage on the activity density and biological diversity of carabid beetles in spring and winter crops. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearin, A.F.; Reberg-Horton, S.C.; Gallandt, E.R. Direct effects of tillage on the activity density of ground beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) weed seed predators. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 36, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareau, T.P.; Voortman, C.; Barbercheck, M. Carabid beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) differentially respond to soil management practices in feed and forage systems in transition to organic management. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.J.; Balsbaugh JR, E.U.; French, E.W.; Ben Hoag, K. Influence of tillage management and cropping system on ground beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) fauna in the northern Great Plains. Environ. Entomol. 1990, 19, 1388–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayre, K. Evaluation of Carabids as Predators of Slugs in Arable Land. Ph.D. Thesis, Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Seric Jelaska, L.; Franjevic, D.; Jelaska, S.D.; Symondson, W.O.C. Prey detection in carabid beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in woodland ecosystems by PCR analysis of gut contents. Eur. J. Entomol. 2014, 111, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larochelle, A.; Larivière, M.C. A Natural History of the Ground-Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) of America North of Mexico; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, A.F.; Collins, C.W. The Genus Calosoma: Including Studies of Seasonal Histories, Habits, and Economic Importance of American Species North of Mexico and of Several Introduced Species; United States Department of Agriculture Bulletin No. 417; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1917.
- Gidaspow, T. North American caterpillar hunters of the genera Calosoma and Callisthenes (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1959, 116, 225–344. [Google Scholar]
- Foltan, P.; Sheppard, S.; Konvicka, M.; Symondson, W.O. The significance of facultative scavenging in generalist predator nutrition: Detecting decayed prey in the guts of predators using PCR. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 4147–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juen, A.; Traugott, M. Detecting predation and scavenging by DNA gut-content analysis: A case study using a soil insect predator-prey system. Oecologia 2005, 142, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, J.D.; Phillips, S.W.; Sunderland, K.D.; Symondson, W.O. Secondary predation: Quantification of food chain errors in an aphid-spider-carabid system using monoclonal antibodies. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Bell, J.; Sunderland, K.D.; Fenlon, J.; Skervin, D.; Symondson, W.O. Detection of secondary predation by PCR analyses of the gut contents of invertebrate generalist predators. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 4461–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, J.; Port, G.R. The influence of mucus production by the slug, Deroceras reticulatum, on predation by Pterostichus madidus and Nebria brevicollis (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Biocontrol. Sci. Technol. 2002, 12, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatteland, B.A.; Grutle, K.; Mong, C.E.; Skartveit, J.; Symondson, W.O.C.; Solhøy, T. Predation by beetles (Carabidae, Staphylinidae) on eggs and juveniles of the Iberian slug Arion lusitanicus in the laboratory. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, K.D. A review of methods of quantifying invertebrate predation occurring in the field. Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 1987, 22, 13–34. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, R.F.; Shepard, B.M.; Kenmore, P.E. Experimental methods for evaluating arthropod natural enemies. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1988, 33, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianezzola, E.; Roth, S.; Hatteland, B.A. Predation by carabid beetles on the invasive slug Arion vulgaris in an agricultural semi-field experiment. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2013, 103, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Experimental Sites | Control Sites | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site ID | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E5 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
| Tilled 2017 | no | no | no | no | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Tilled 2018 | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Field margin | Gravel | Vegetation | Gravel | Vegetation | ||||||
| Species | Number of Guts |
|---|---|
| Agonum muelleri | 51 |
| Calosoma cancellatum | 68 |
| Nebria brevicollis (adults) | 280 |
| Nebria brevicollis (larvae) | 36 |
| Poecilus laetulus | 99 |
| Total | 534 |
| Species/Pest Group | Best Model | Χ2 | p | R2adj FE | R2adj RE | R2adj F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agonum muelleri | AD = FM + S | 4.662 | 0.031 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.21 |
| Calosoma cancellatum | AD = 1 + S | n/a | n/a | |||
| Nebria brevicollis | AD = FM + S | 9.164 | 0.003 | 0.16 | −0.03 | 0.13 |
| Poecilus laetulus | AD = FM + S | 7.702 | 0.006 | 0.11 | −0.16 | −0.05 |
| Species | Df | F Value | Probability (>F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agonum muelleri | Y | 1 | 0.019 | 0.891 |
| T | 1 | 0.544 | 0.471 | |
| Y:T | 1 | 0.238 | 0.632 | |
| Res. | 16 | |||
| Calosoma cancellatum | Y | 1 | 4.115 | 0.0595 |
| T | 1 | 0.584 | 0.4558 | |
| Y:T | 1 | 0.466 | 0.5044 | |
| Res. | 16 | |||
| Nebria brevicollis | Y | 1 | 1.008 | 0.3303 |
| T | 1 | 2.431 | 0.1399 | |
| Y:T | 1 | 4.394 | 0.0523 | |
| Res. | 16 | |||
| Poecilus laetulus | Y | 1 | 0.280 | 0.604 |
| T | 1 | 0.026 | 0.873 | |
| Y:T | 1 | 0.004 | 0.949 | |
| Res. | 16 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reich, I.; Jessie, C.; Ahn, S.-J.; Choi, M.-Y.; Williams, C.; Gormally, M.; Mc Donnell, R. Assessment of the Biological Control Potential of Common Carabid Beetle Species for Autumn- and Winter-Active Pests (Gastropoda, Lepidoptera, Diptera: Tipulidae) in Annual Ryegrass in Western Oregon. Insects 2020, 11, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110722
Reich I, Jessie C, Ahn S-J, Choi M-Y, Williams C, Gormally M, Mc Donnell R. Assessment of the Biological Control Potential of Common Carabid Beetle Species for Autumn- and Winter-Active Pests (Gastropoda, Lepidoptera, Diptera: Tipulidae) in Annual Ryegrass in Western Oregon. Insects. 2020; 11(11):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110722
Chicago/Turabian StyleReich, Inga, Casi Jessie, Seung-Joon Ahn, Man-Yeon Choi, Christopher Williams, Mike Gormally, and Rory Mc Donnell. 2020. "Assessment of the Biological Control Potential of Common Carabid Beetle Species for Autumn- and Winter-Active Pests (Gastropoda, Lepidoptera, Diptera: Tipulidae) in Annual Ryegrass in Western Oregon" Insects 11, no. 11: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110722
APA StyleReich, I., Jessie, C., Ahn, S.-J., Choi, M.-Y., Williams, C., Gormally, M., & Mc Donnell, R. (2020). Assessment of the Biological Control Potential of Common Carabid Beetle Species for Autumn- and Winter-Active Pests (Gastropoda, Lepidoptera, Diptera: Tipulidae) in Annual Ryegrass in Western Oregon. Insects, 11(11), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110722








