Bacterial Communities of Ixodes scapularis from Central Pennsylvania, USA
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collections
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Sample Preparation for Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of Microbiome Sequence Data
2.5. Taxon-Specific Amplification and Sequence Confirmation
2.6. Assays for Tick-Borne Pathogens
2.6.1. Borrelia burgdorferi Infection Frequency
2.6.2. Taqman PCR Assay for Anaplasma phagocytophilum
2.7. Taxon-Specific Quantitative PCR of Nonpathogenic Symbiotic Bacteria
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing of Individual and Pooled Tick DNA Using V6 Hypervariable Region
3.2. Bacterial Community Composition of Pooled Tick DNA Using the V4 Hypervariable Region
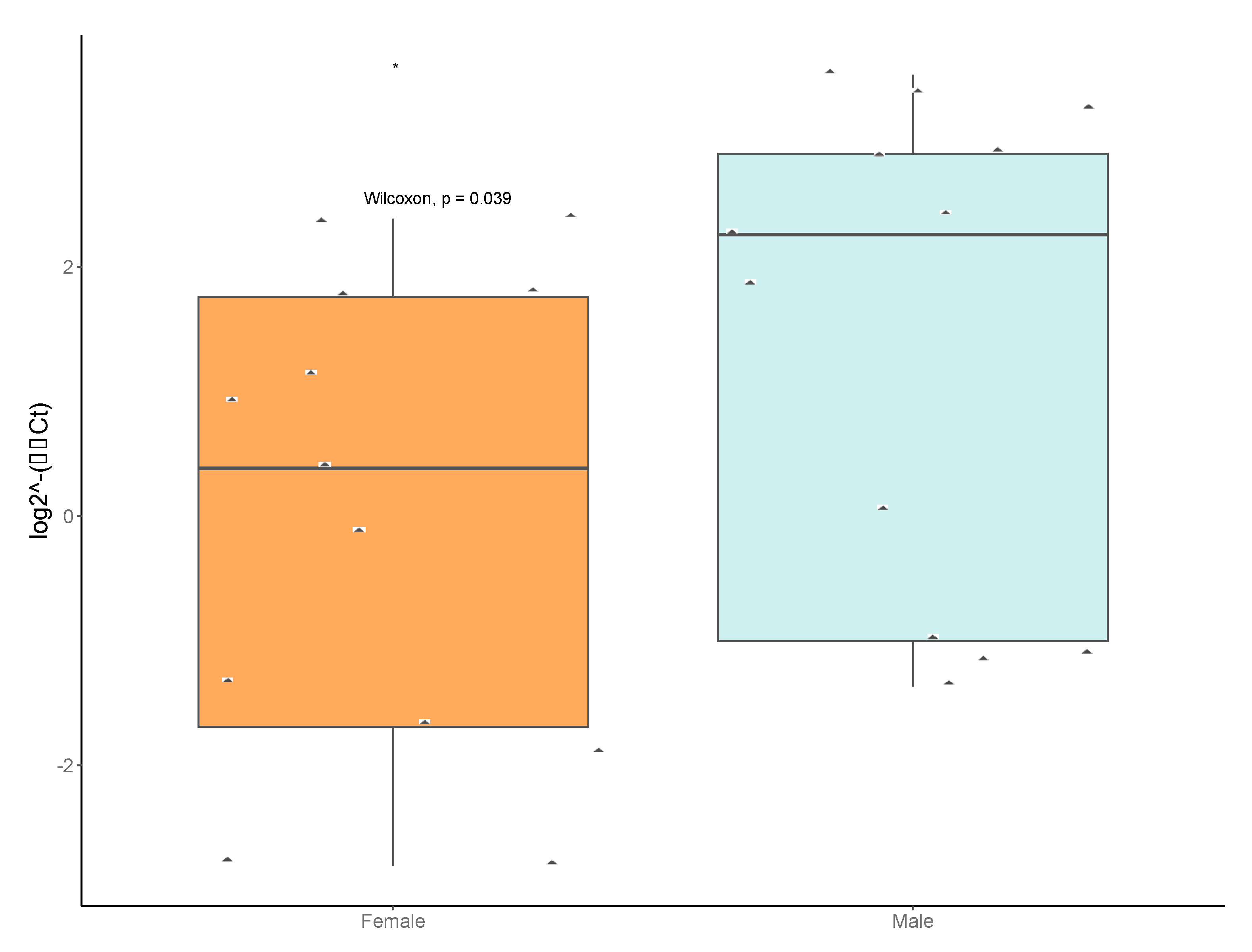
3.3. Sex- and Location-Specific Differences in Microbial Diversity
3.4. Confirmation by Gene-Specific Amplification and Sequencing
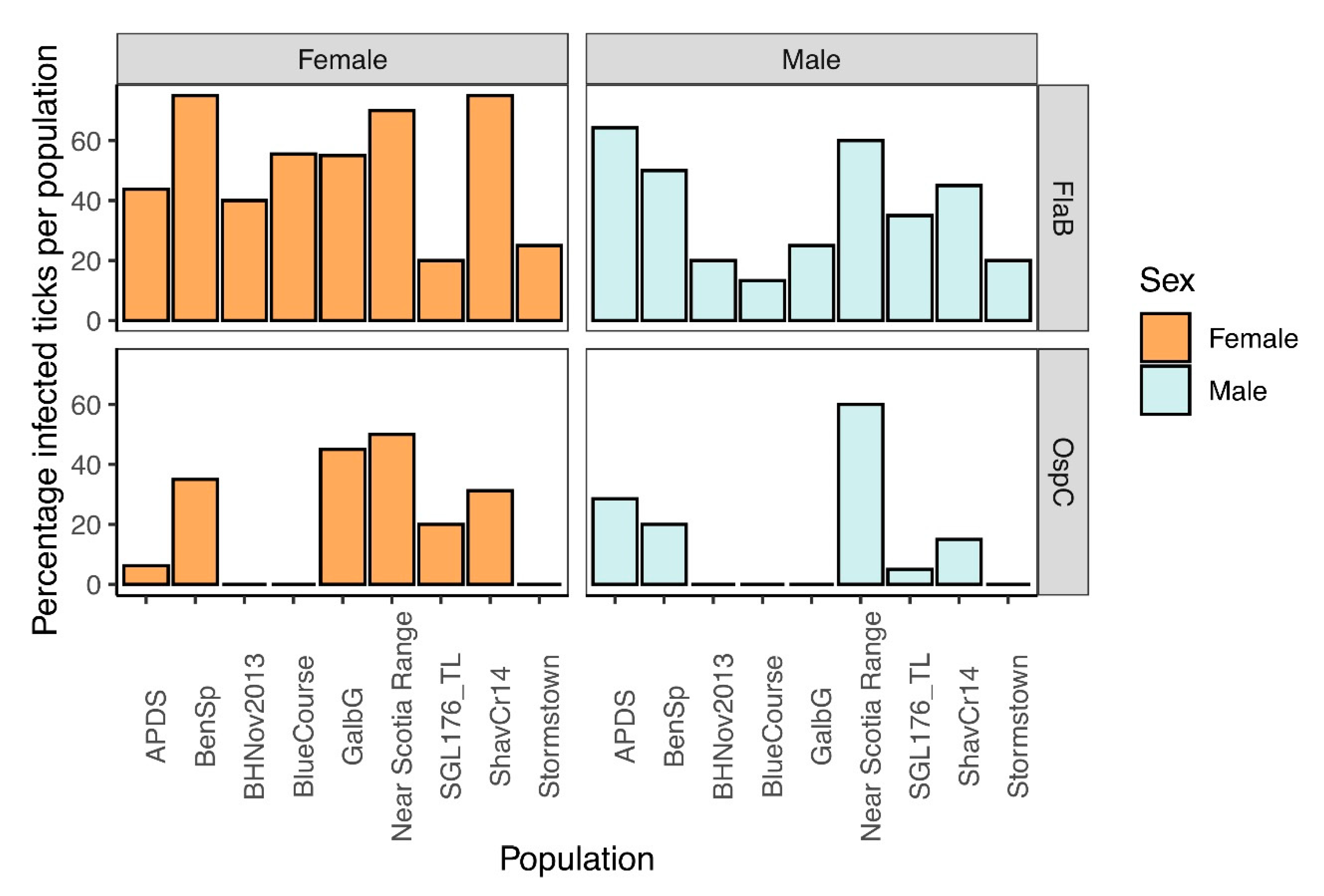
3.5. Confirmation of Borrelia burgdorferi Identification and Frequency in Ticks Tested
3.6. Taxon-Specific Quantitative PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sonenshine, D.E. Range Expansion of Tick Disease Vectors in North America: Implications for Spread of Tick-Borne Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpi, G.; Cagnacci, F.; Wittekindt, N.E.; Zhao, F.; Qi, J.; Tomsho, L.P.; Drautz, D.I.; Rizzoli, A.; Schuster, S.C. Metagenomic Profile of the Bacterial Communities Associated with Ixodes ricinus Ticks. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Treuren, W.; Ponnusamy, L.; Brinkerhoff, R.J.; Gonzalez, A.; Parobek, C.M.; Juliano, J.J.; Andreadis, T.G.; Falco, R.C.; Ziegler, L.B.; Hathaway, N.; et al. Variation in the Microbiota of Ixodes Ticks with Regard to Geography, Species, and Sex. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6200–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, I.; Fieck, A.; Read, A.; Hillesland, H.; Klein, N.; Kang, A.; Durvasula, R. Paratransgenic Control of Vector Borne Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Rasgon, J.L.; Hughes, G.L. The microbiome modulates arbovirus transmission in mosquitoes. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, C.A.; Reif, K.E.; Scoles, G.A.; Mason, K.L.; Mousel, M.; Noh, S.M.; Brayton, K.A. The bacterial microbiome of Dermacentor andersoni ticks influences pathogen susceptibility. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duron, O.; Morel, O.; Noël, V.; Buysse, M.; Binetruy, F.; Lancelot, R.; Loire, E.; Ménard, C.; Bouchez, O.; Vavre, F.; et al. Tick-Bacteria Mutualism Depends on B Vitamin Synthesis Pathways. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1896–1902.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Jasinskas, A.; Barbour, A.G. Antibiotic Treatment of the Tick Vector Amblyomma americanum Reduced Reproductive Fitness. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-Y.; Zhang, K.-J.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Ge, C.; Gotoh, T.; Hong, X.-Y. Wolbachia Strengthens Cardinium-Induced Cytoplasmic Incompatibility in the Spider Mite Tetranychus piercei McGregor. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.J.; Gawronski, J.D.; Eveleigh, D.E.; Benson, D.R. Intracellular Symbionts and Other Bacteria Associated with Deer Ticks (Ixodes scapularis) from Nantucket and Wellfleet, Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.X.; Moy, F.; Daniels, T.J.; Godfrey, H.P.; Cabello, F.C. Molecular analysis of microbial communities identified in different developmental stages of Ixodes scapularis ticks from Westchester and Dutchess Counties, New York. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, S.; Zhang, Y.; Allen, M.S. Bacterial microbiomes of Ixodes scapularis ticks collected from Massachusetts and Texas, USA. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolnik, C.P.; Falco, R.C.; Daniels, T.J.; Kolokotronis, S.-O. Transient influence of blood meal and natural environment on blacklegged tick bacterial communities. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicana, B.; Couper, L.I.; Kwan, J.Y.; Tahiraj, E.; Swei, A. Comparative Microbiome Profiles of Sympatric Tick Species from the Far-Western United States. Insects 2019, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirans, J.E.; Clifford, C.M. The Genus Ixodes in the United States: A Scanning Electron Microscope Study and Key to the Adults. J. Med. Entomol. 1978, 15, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, J.M.; Goddard, J.; Rasgon, J.L. Population and demographic structure of Ixodes scapularis Say in the eastern United States. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S. Tools for Microbiome Analysis in R. Version 2.1.24. 2017. Available online: http://microbiome.github.com/microbiome (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr, Version 0.3.0; 2020. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/ggpubr/ (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, J.W.; Kostelnik, L.M.; Zeidner, N.S.; Massung, R.F. Multiplex real-time PCR for detection of anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3164–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmeister, E.K.; Glass, G.E.; Childs, J.E.; Persing, D.H. Population Dynamics of a Naturally Occurring Heterogeneous Mixture of Borrelia burgdorferi Clones. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 5709–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Muellegger, R.R.; Stockenhuber, C.; Soyer, H.P.; Hoedl, S.; Luger, A.; Kerl, H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi-specific DNA in urine specimens from patients with erythema migrans before and after antibiotic therapy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, A.R.; Velten, R.; Stouthamer, R. Incidence of a new sex-ratio-distorting endosymbiotic bacterium among arthropods. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, S.J.; Grissell, E.E. Tracing the geographical origin of Megastigmus transvaalensis (Hymenoptera: Torymidae): An African wasp feeding on a South American plant in North America. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantard, O.; Bouju-Albert, A.; Malard, M.-A.; Hermouet, A.; Capron, G.; Verheyden, H. Detection of Wolbachia in the tick Ixodes ricinus is due to the presence of the Hymenoptera Endoparasitoid Ixodiphagus hookeri. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediannikov, O.; Sekeyová, Z.; Birg, M.-L.; Raoult, D. A Novel Obligate Intracellular Gamma-Proteobacterium Associated with Ixodid Ticks, Diplorickettsia massiliensis, Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, M.; Bain, O.; Guerrero, R.; Martin, C.; Pocacqua, V.; Gardner, S.L.; Franceschi, A.; Bandi, C. Mapping the presence of Wolbachia pipientis on the phylogeny of filarial nematodes: Evidence for symbiont loss during evolution. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilker, T.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; LiPuma, J.J. PCR-Based Assay for Differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Other Pseudomonas Species Recovered from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2074–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.-E.; Roux, V.; Raoult, D. Phylogenetic analysis of spotted fever group rickettsiae by study of the outer surface protein rOmpA. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braig, H.R.; Zhou, W.; Dobson, S.L.; O’Neill, S.L. Cloning and Characterization of a Gene Encoding the Major Surface Protein of the Bacterial Endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-19-513584-8. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgdorfer, W.; Hayes, S.F.; Mavros, A.J. Nonpathogenic rickettsiae in Dermacentor andersoni: A limiting factor for the distribution of Rickettsia ricketsii. In Rickettsiae and Rickettsial Diseases; Burgdorfer, W., Anacker, R.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981; p. 650. ISBN 0-12-143150-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtti, T.J.; Simser, J.A.; Baldridge, G.D.; Palmer, A.T.; Munderloh, U.G. Factors influencing in vitro infectivity and growth of Rickettsia peacockii (Rickettsiales: Rickettsiaceae), an endosymbiont of the Rocky Mountain wood tick, Dermacentor andersoni (Acari, Ixodidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 90, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simser, J.A.; Palmer, A.T.; Munderloh, U.G.; Kurtti, T.J. Isolation of a Spotted Fever Group Rickettsia, Rickettsia peacockii, in a Rocky Mountain Wood Tick, Dermacentor andersoni, Cell Line. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Kocan, K.M. Infection Exclusion of the Rickettsial Pathogen Anaplasma marginale in the Tick Vector Dermacentor variabilis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaluso, K.R.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Ceraul, S.M.; Azad, A.F. Rickettsial infection in Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae) inhibits transovarial transmission of a second Rickettsia. J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia-Nuss, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Meyer, J.M.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Sattelle, D.B.; De La Fuente, J.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Megy, K.; et al. Genomic insights into the Ixodes scapularis tick vector of Lyme disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtti, T.J.; Palmer, A.T.; Oliver, J.H. Rickettsiella-like Bacteria in Ixodes woodi (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchon, D.; Cordaux, R.; Greve, P. Rickettsiella, intracellular pathogens of arthropods. In Manipulative Tenants: Bacteria Associated with Arthropods; Zchori-Fein, E., Bourtzis, K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 127–148. ISBN 978-1-4398-2749-9. [Google Scholar]
- Leclerque, A.; Kleespies, R.G. A Rickettsiella bacterium from the Hard Tick, Ixodes woodi: Molecular Taxonomy Combining Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) with Significance Testing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, J.; Bouchon, D. Feminizing Wolbachia influence microbiota composition in the terrestrial isopod Armadillidium vulgare. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, A.R.; Breeuwer, J.A. Wolbachia-induced parthenogenesis in a genus of phytophagous mites. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 2245–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasgon, J.L.; Scott, T.W. Wolbachia and cytoplasmic incompatibility in the California Culex pipiens mosquito species complex: Parameter estimates and infection dynamics in natural populations. Genetics 2003, 165, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar]
- Crowder, C.D.; Carolan, H.E.; Rounds, M.A.; Honig, V.; Mothes, B.; Haag, H.; Nolte, O.; Luft, B.J.; Grubhoffer, L.; Ecker, D.J.; et al. Prevalence of Borrelia miyamotoi in Ixodes ticks in Europe and the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1678–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, S.; Kurtti, T.J.; Noda, H. In Vitro Cultivation and Antibiotic Susceptibility of a Cytophaga-Like Intracellular Symbiote Isolated from the Tick Ixodes scapularis. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeuwer, H.; Ros, V.I.D.; Groot, T.V.M. Cardinium: The next addition to the family of reproductive parasites. In Manipulative Tenants: Bacteria Associated with Arthropods; Zchori-Fein, E., Bourtzis, K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 207–224. ISBN 978-1-4398-2749-9. [Google Scholar]
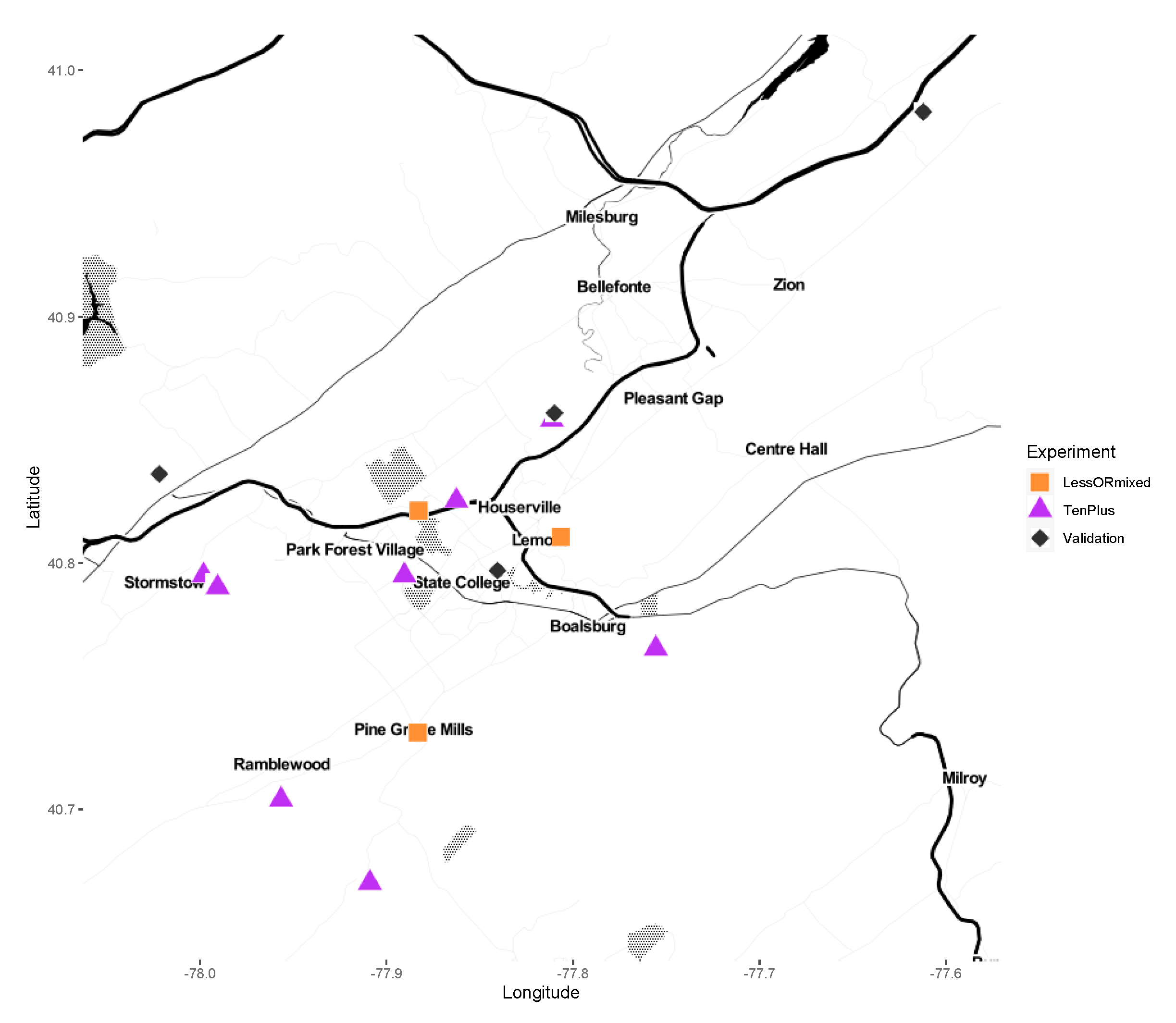
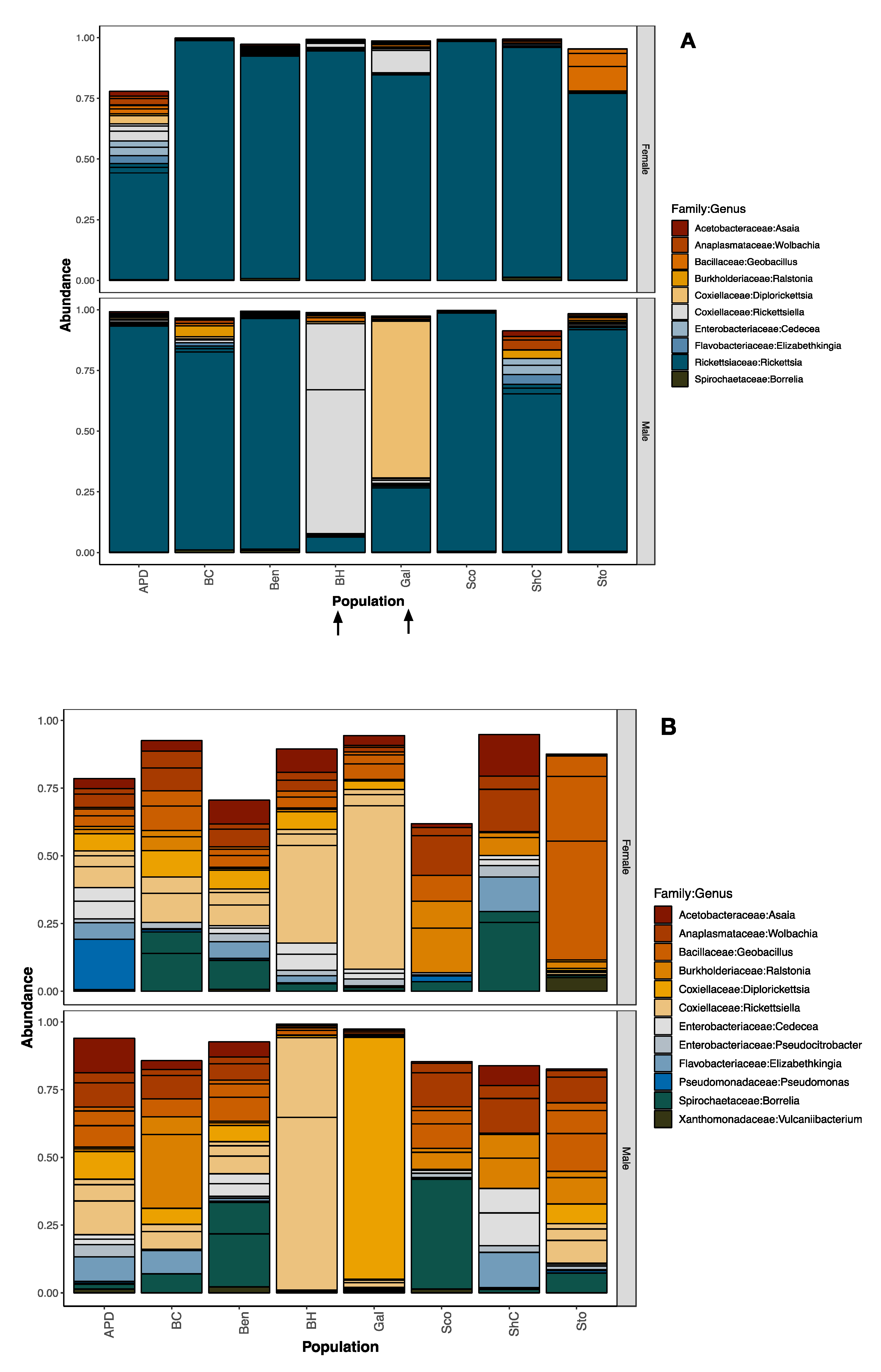
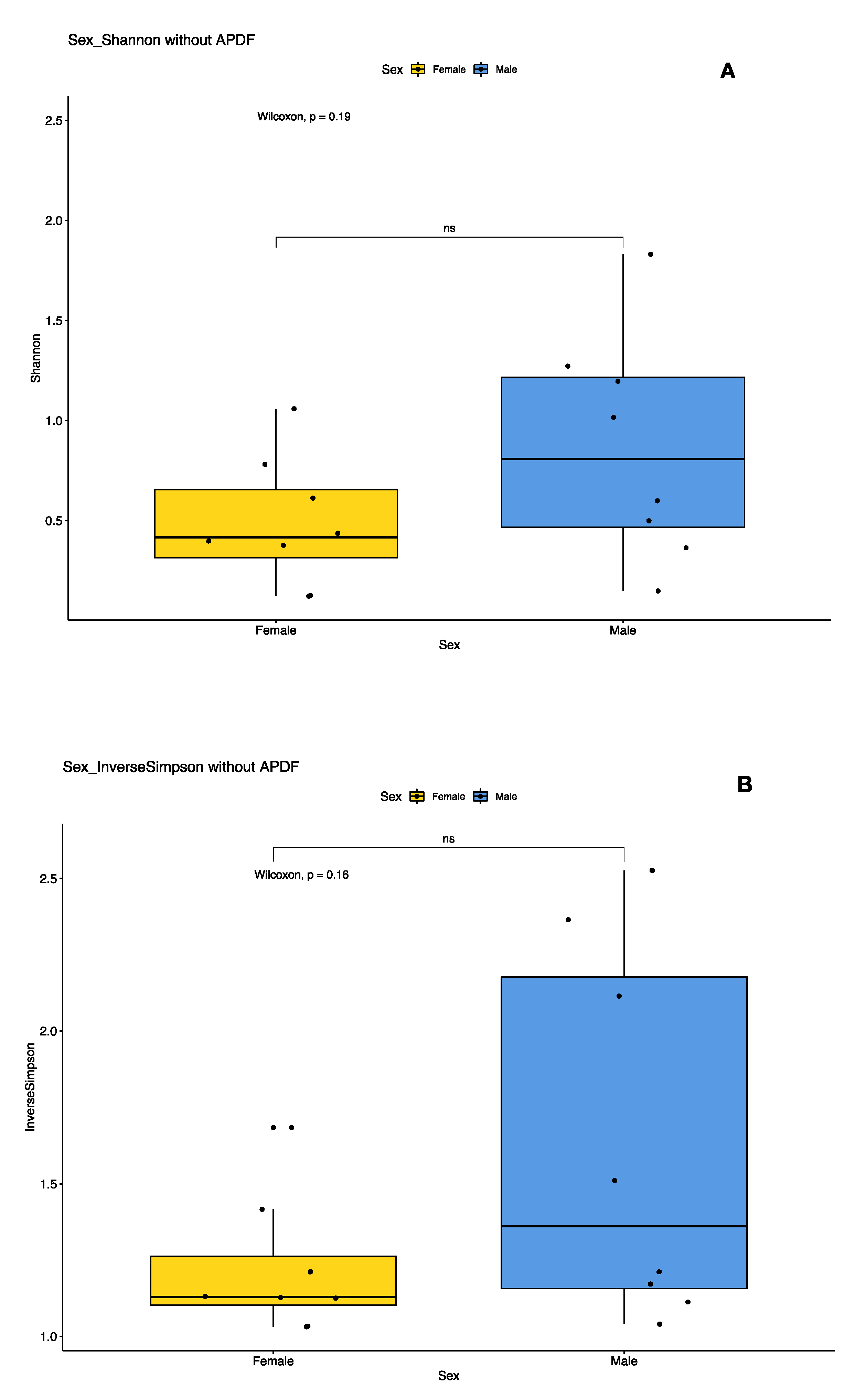
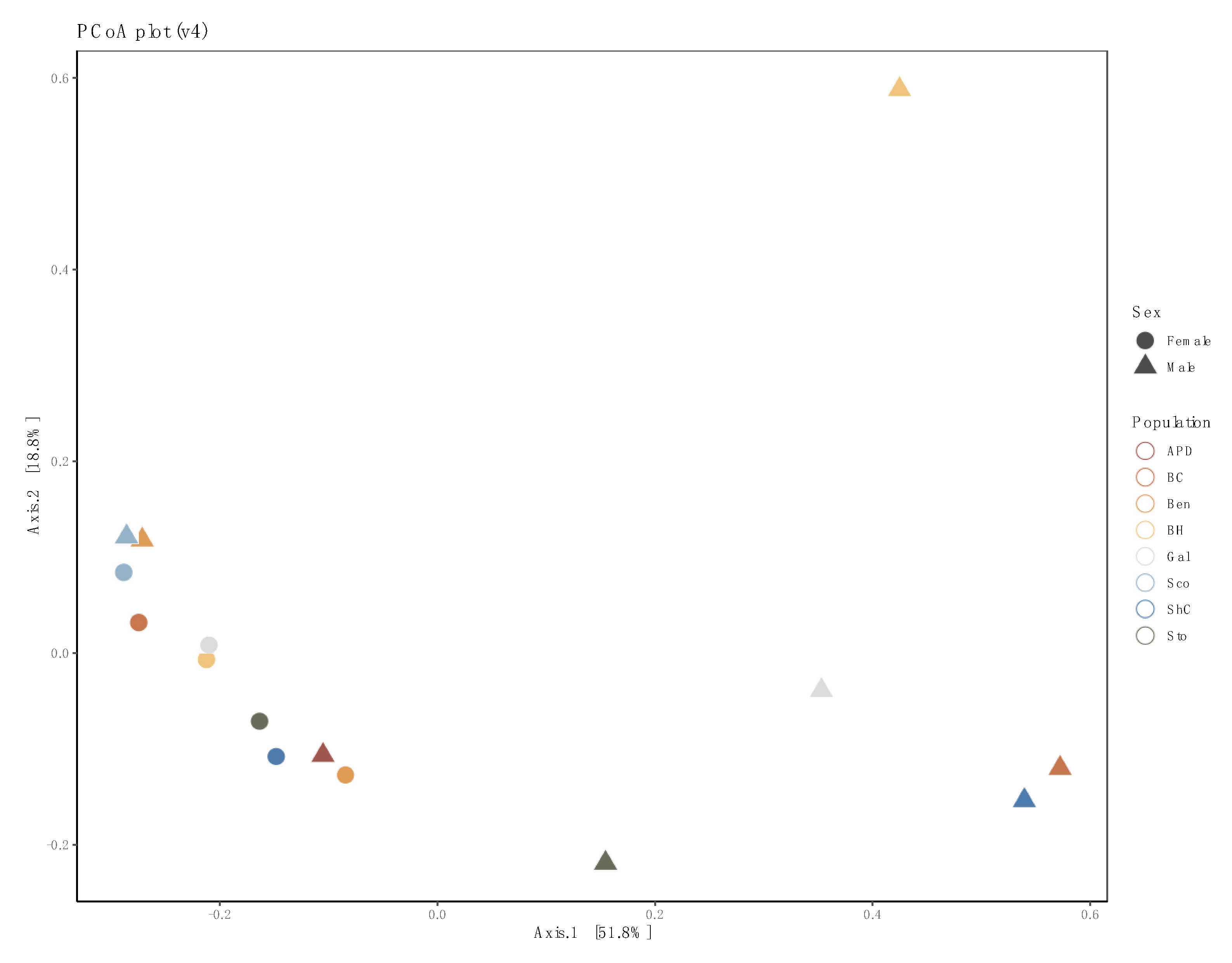

| Collection Year | Sample ID | Population | Sex | Individuals or Pools Sequenced (N) | Region Sequenced (V4 or V6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | BHF01-F10 | Big Hollow (BH) | Females | Individuals (10) | V6 |
| 2012 | BHM01-M10 | Big Hollow (BH) | Males | Individuals (10) | V6 |
| 2012 | SCF01-F10 | Shaver’s Creek (ShCr) ª | Females | Individuals (10) | V6 |
| 2013 | MB001 | Stormstown (Sto) | Females | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB002 | Stormstown (Sto) | Males | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB004 | Blue Course (BC) | Females | Pooled (18) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB003 | Blue Course (BC) | Males | Pooled (15) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB006 | AgProgressDays (APD) | Females | Pooled (16) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB005 | AgProgressDays (APD) | Males | Pooled (14) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB008 | Big Hollow (BH) | Females | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB007 | Big Hollow (BH) | Males | Pooled (15) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB009 | Galbraith (Gal) | Females | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB010 | Galbraith (Gal) | Males | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB012 | Benner Springs (Ben) | Females | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB011 | Benner Springs (Ben | Males | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB013 | State Gameland 176 (SGL176/Sco) | Females | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2013 | MB014 | State Gameland 176 (SGL176/Sco) | Males | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2014 | MB015 | Shaver’s Creek (ShCr) | Females | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2014 | MB016 | Shaver’s Creek (ShCr) | Males | Pooled (20) | V4/V6 |
| 2014 | Lem | Lemont b | Females | Pooled (3F) | V4/V6 |
| 2014 | PGM | Pine Grove Mills b | Mixed | Pooled (4F, 4M) | V4/V6 |
| 2014 | Toft | Toftrees b | Mixed | Pooled (11F, 9M) | V4/V6 |
| 2009 | MS1 | Mississippi clade 1 (F3, F5, G4, G6) c | Females | Pooled (4) | V4/V6 |
| 2009 | MS2 | Mississippi clade 2 (F6, F8, G11) d | Females | Pooled (3) | V4/V6 |
| Taxon | Primer Name | Target Gene | Size (bp) | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaplasma phagocytophilum | ApMSP2f | Msp2 (major surface protein 2) | 77 | ATGGAAGGTAGTGTTGGTTATGGTATT | [23] |
| ApMSP2r | TTGGTCTTGAAGCGCTCGTA | ||||
| Ap Taqman probe | ApMSP2p | /HEX/TGGTGCCAG/ZEN/GGTTGAGCTTGAGATTG/IABkFQ | |||
| Borrelia burgdorferi | PC-1s | OspC | 632 | AATGAAAAAGAATACATTAAGTGCA | [24] |
| PC-2a | OspC | TTAAGGTTTTTTTGGACTTTCTGC | |||
| Borrelia burgdorferi | BBSCH31 | FlaB (outer) | 437 | CACACCAGCATCACTTTCAGGGTCT | [25] |
| BBSCH42 | FlaB (outer) | CAACCTCATCTGTCATTGTAGCATCTTTTATTT | |||
| Borrelia burgdorferi | FL59 | FlaB (inner) | 277 | GCATTTTCAATTTTAGCAAGTGATG | [25] |
| FL7 | FlaB (inner) | TTTCAGGGTCTCAGGCGTCTT | |||
| Candidatus Cardinium | CLOf | 16S rRNA | 1100 | GCGGTGTAAAATGAGCGTG | [26] |
| CLOr2 | 16S rRNA | ACCTMTTCTTAACTCAAGCCT | |||
| Chalcidoideae | 1775-COIF | COI | 1047 | CGA- ATAAATAATATAAGATTTTG | [27] |
| 2773-COI-R | COI | GGATAATCTCTATATCGACGAGGTAT | |||
| Flavobacterium | qFlav16SF | 16S rRNA | 142 | CGATGGATACTAGCTGTTGGG | This study |
| qFlav16SR | 16S rRNA | CGAATTAAACCACATGCTCCAC | |||
| Ixodes scapularis | IsActin2F | Actin | 271 | GACCTGACCGACTACCTGATGAAG | This study |
| IsActin2R | Actin | ATGCCGCACGATTCCATACC | |||
| Ixodiphagus hookeri | 401-F | COI | 268 | TTTAGAATATTTATTGATTCAGGGACT | [28] |
| 44-R | CTCCTGCTAAAACTGGTAAAGATAAT | ||||
| Legionellales | RLrpoB6f | rpoB | 729 | AGATGGTACGCSGGTTGATATCGT | [29] |
| RLrpoB2r | rpoB | TTCCATTTGGTGATCGCCATC | |||
| Nematode | Nema12SF | 12S | 450 | GTT CCA GAA TAA TCG GCT A | [30] |
| Nema12SR | ATT GAC GGA TG(AG) TTT GTA CC | ||||
| Pseudomonas | PA-GS-F | 16S rRNA | 618 | GACGGGTGAGTAATGCCTA | [31] |
| PA-GS-R | 16S rRNA | CACTGGTGTTCCTTCCTATA | |||
| Pseudomonas | 16S qPCR_F | 16S rRNA | 143 | TTGTCCTTAGTTACCAGCACG | This study |
| 16S qPCR_R | 16S rRNA | ACCCTTTGTACCGACCATTG | |||
| Rickettsia | r190.7 | RompA | 632 | ATGGCGAATATTTCTCCAAAA | [32] |
| r190.701 | RompA | GTTCCGTTAATGGCAGCATCT | |||
| Rrgap2F | RompA | 1664 | CTACCTTGTACCTTGCTGAGCGAAA | This study | |
| Rrgap2R | AGCTTTGCAGCTAACGGCGCT | ||||
| Rickettsia | qRi16SF | 16S rRNA | 124 | ACCTTACCAACCCTTGACATG | This study |
| qRi16SR | GGACTTAACCCAACATCTCACG | ||||
| Rickettsiella | qRkla6F | 16S rRNA | 135 | AAAGGAATTGACGGGGGCC | This study |
| qRkla6F | CCTGTCTCTTGGTTCCTTTCGG | ||||
| Wolbachia | wsp 81F | wsp | 610 | TGG TCC AAT AAG TGA TGA AGA AAC | [33] |
| wsp 691R | wsp | AAA AAT TAA ACG CTA CTC CA | |||
| qPCR | PCR | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | Sex | I/P (N) | Ap MSP2 | qRi | qRk5 | qRk6 | qPs | qFl | FlaB | OspC | RompA | RLrpo | CLO | Nema | Chal |
| Stormstown | Female | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Stormstown | Males | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| BlueCourse | Males | P (15) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| BlueCourse | Female | P (18) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| APDS | Males | P (14) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| APDS | Female | P (16) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Big Hollow | Males | P/I (15) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| I (20) | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||||||||
| Big Hollow | Female | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Galbraith | Female | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Galbraith | Males | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| I (20) | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||||||||
| Benner Springs | Males | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Benner Springs | Female | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| SGL176 | Female | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| SGL176 | Males | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Shaver’s Creek | Female | P/I (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| I (20) | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||||||||
| Shaver’s Creek | Males | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Julian, PA 2015 | Females | P (16) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Julian, PA 2015 | Males | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| SGL333_2017 | Females | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| SGL333_2017 | Males | P (20) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| SGL333_2018 | Females | P (50) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| SGL333_2018 | Males | P (40) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Howard, PA | Females | P (9) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Howard, PA | Males | P (15) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Lederer Park, State College | Females | P (21) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Lederer Park, State College | Males | P (21) | ☑ | ☑ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Taxon | Gene | Genbank Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| Rickettsia | RompA | JFKF01000169.1, LN794217.1, CP003340.1, CP047359.1, CP003375.1, CP040325.1, CP001612.1, CP003308.1, CP001227.1, CP012420.1, CP000683.1, CP003342.1 |
| Rickettsiella | rpoB | KP985349.1, KP985348.1, KP985347.1, KP985346.1, KP985354.1, KP985353.1, EF694042.1, JF288929.1, KP985351.1, KP985350.1, AP018005.1, KP985357.1, KP985356.1, KP985355.1 |
| Cardinium | 16S rRNA | AB241135.1, AB241129.1, GU731426.1, AB241131.1, AB241130.1, AY753169.1, MH057615.1, AY635291.1, AB001518.1, LN829689.2, JN204482.1, LC159289.1, AB241132.1, AF350221.1, AB116514.1, KX022134.1, AB506775.1, AB506773.1, AB506774.1, GQ206320.1, CP022339.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakamoto, J.M.; Silva Diaz, G.E.; Wagner, E.A. Bacterial Communities of Ixodes scapularis from Central Pennsylvania, USA. Insects 2020, 11, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100718
Sakamoto JM, Silva Diaz GE, Wagner EA. Bacterial Communities of Ixodes scapularis from Central Pennsylvania, USA. Insects. 2020; 11(10):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100718
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakamoto, Joyce Megumi, Gabriel Enrique Silva Diaz, and Elizabeth Anne Wagner. 2020. "Bacterial Communities of Ixodes scapularis from Central Pennsylvania, USA" Insects 11, no. 10: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100718
APA StyleSakamoto, J. M., Silva Diaz, G. E., & Wagner, E. A. (2020). Bacterial Communities of Ixodes scapularis from Central Pennsylvania, USA. Insects, 11(10), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100718





