Exposure to Non-Native Tropical Milkweed Promotes Reproductive Development in Migratory Monarch Butterflies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monarch Migration and Reproductive Diapause
2.2. Experiment 1: Does Larval Diet Influence Adult Reproductive Status?
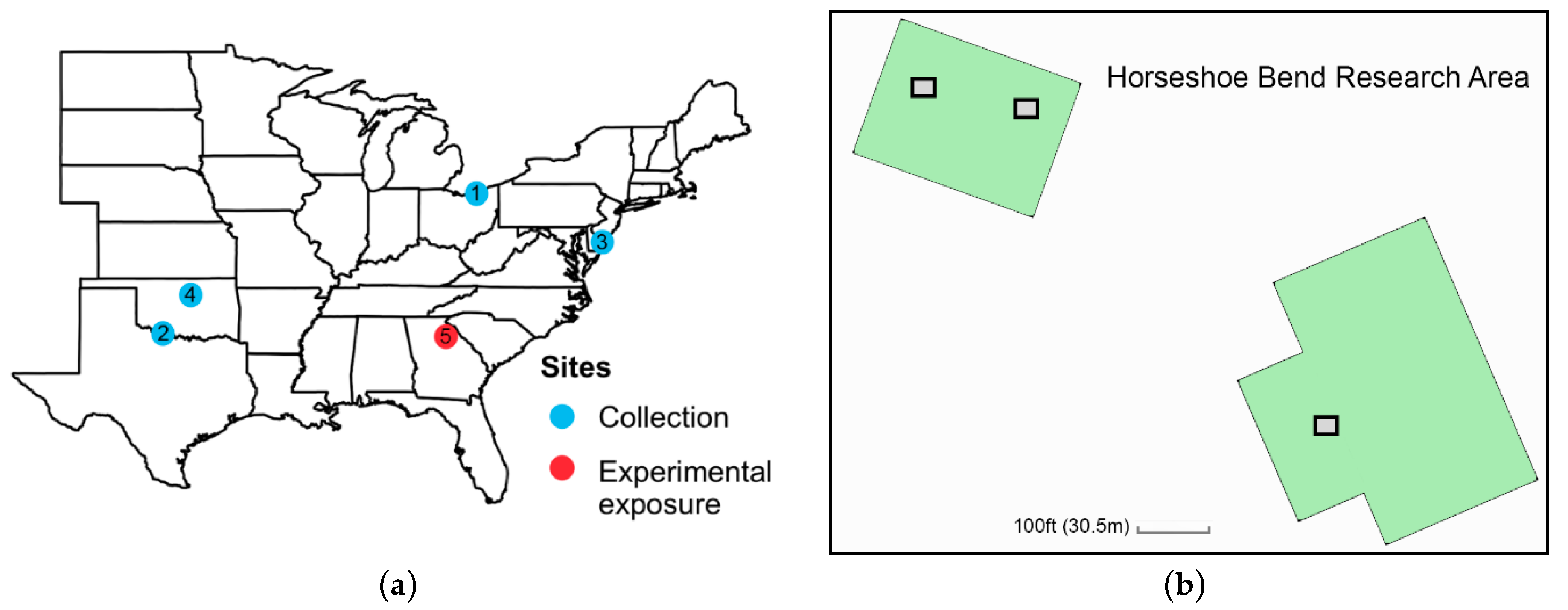
2.3. Experiment 2: Does Adult Milkweed Exposure Affect the Reproductive Status of Wild-Caught Migratory Monarchs?
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Experiment 1: Larval Diet and Reproductive Status
2.4.2. Experiment 2: Adult Migrant Milkweed Exposure
3. Results
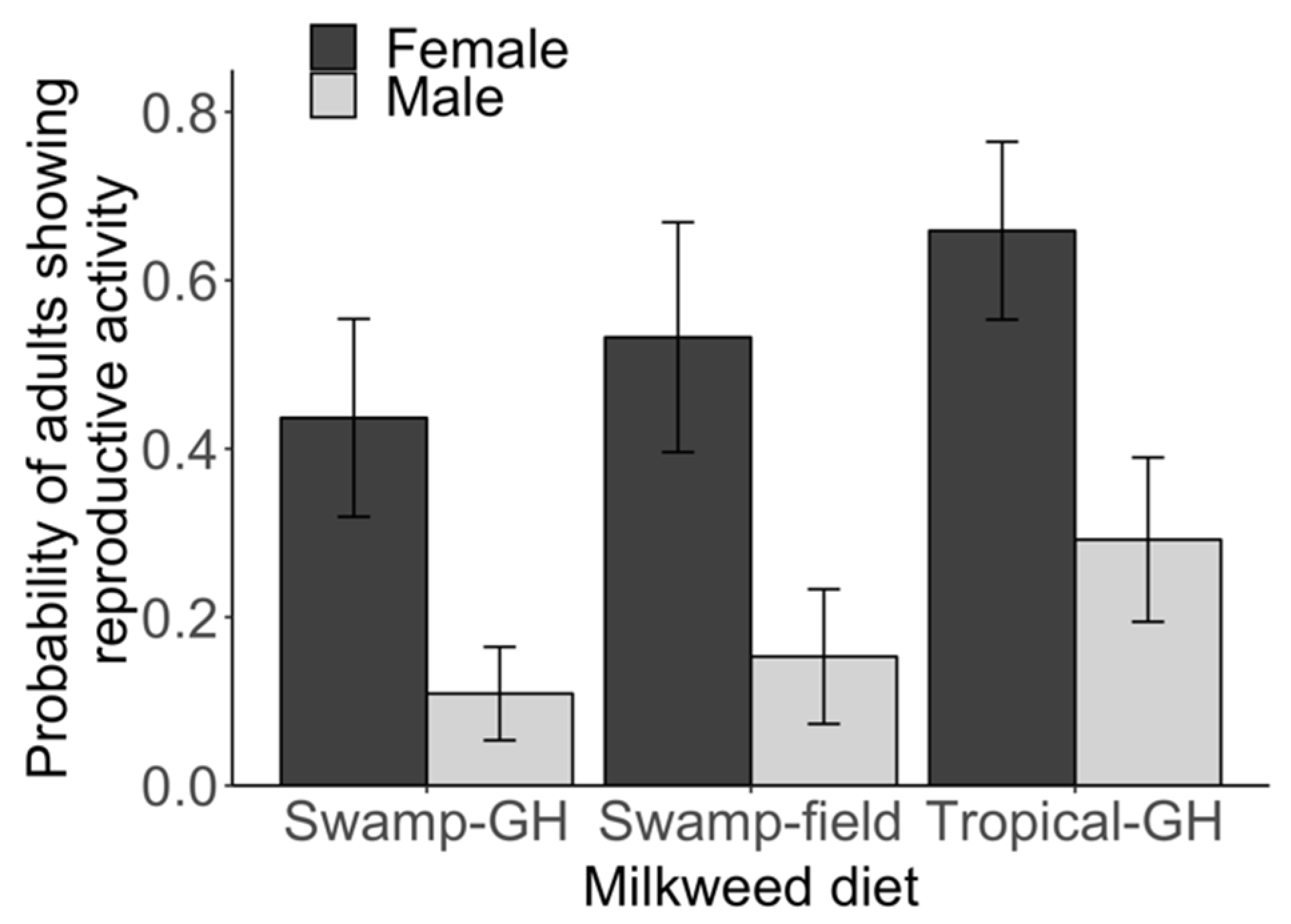
3.1. Experiment 1: Larval Diet and Reproductive Status
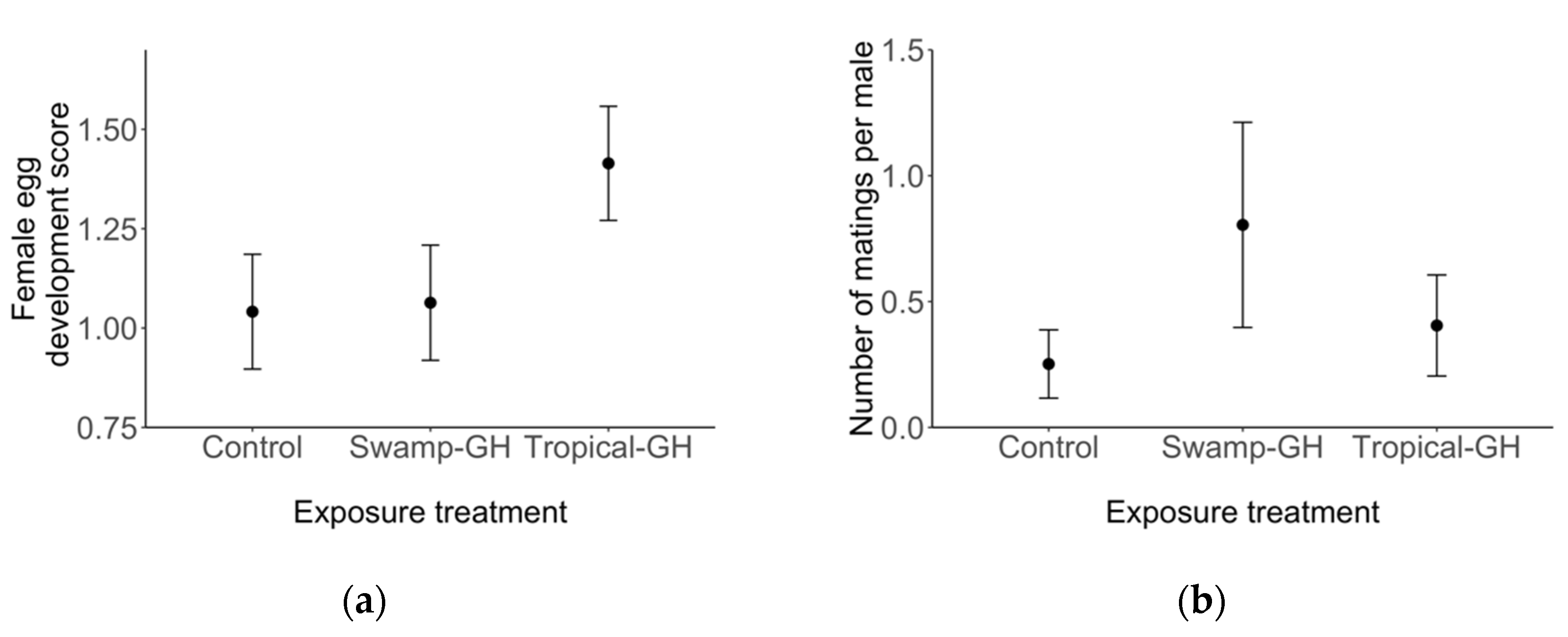
3.2. Experiment 2: Adult Migrant Milkweed Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gatehouse, A.; Zhang, X. Migratory potential in insects: Variation in an uncertain environment. In Insect Migration Tracking Resources through Space and Time; Drake, V., Gatehouse, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 193–245. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Lim, K.S.; Horvitz, N.; Clark, S.J.; Reynolds, D.R.; Sapir, N.; Chapman, J.W. Mass seasonal bioflows of high-flying insect migrants. Science 2016, 354, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, R.A.; Wikelski, M.; Wilcove, D.S. How and Why Do Insects Migrate? Science 2006, 313, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenger-Trolander, A.; Lu, W.; Noyes, M.; Kronforst, M.R. Contemporary loss of migration in monarch butterflies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 201904690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantola, T.; Tracy, J.L.; Baum, K.A.; Quinn, M.A.; Coulson, R.N. Spatial risk assessment of eastern monarch butterfly road mortality during autumn migration within the southern corridor. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 231, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, D.D.; McKenna, K.M.; Malcom, S.B.; Bebenbaum, M. Mortality of Lepidoptera along roadways in central Illinois. J. Lepid. Soc. 2001, 55, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, A.K. Drivers of animal migration and implications in changing environments. Evol. Ecol. 2016, 30, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, T.; Butchart, S.H.; Phillimore, A.B. Temporal shifts and temperature sensitivity of avian spring migratory phenology: A phylogenetic meta-analysis. J. Anim. Ecol. 2017, 86, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassall, C.; Thompson, D.J.; French, G.C.; Harvey, I.F. Historical changes in the phenology of British Odonata are related to climate. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterfield, D.A.; Maerz, J.C.; Altizer, S. Loss of migratory behaviour increases infection risk for a butterfly host. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20141734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.W.; Reynolds, D.R.; Wilson, K. Long-range seasonal migration in insects: Mechanisms, evolutionary drivers and ecological consequences. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altizer, S.; Bartel, R.; Han, B.A. Animal migration and infectious disease risk. Science 2011, 331, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goehring, L.; Oberhauser, K.S. Effects of photoperiod, temperature, and host plant age on induction of reproductive diapause and development time in Danaus plexippus. Ecol. Entomol. 2002, 27, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, H. Migration strategies of insects. Science 1972, 175, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullan, P.J.; Cranston, P.S. The Insects: An Outline of Entomology, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, H.K.; Goyal, G.; Chahil, G. Insect diapause: A review. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 454–473. [Google Scholar]
- Dingle, H. Diapause in a migrant insect, the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae). Oecologia 1974, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, H. Migration and diapause in tropical, temperate, and island milkweed bugs. In Evolution of Insect Migration and Diapause; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 254–276. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, T.; Roy, D.; Dennis, R. The influence of temperature on migration of Lepidoptera into Britain. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, M. Successful overwintering by Clouded Yellow Colias croceus in southern England. Atropos 1999, 8, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, E. Increased abundance of the red admiral butterfly Vanessa atalanta in Britain: The roles of immigration, overwintering and breeding within the country. Ecol. Lett. 1998, 1, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W. Studies on the adult reproductive diapause of the monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus. Biol. Bull. 1981, 160, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W.; Tatar, M. Juvenile hormone regulation of longevity in the migratory monarch butterfly. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, L.P.; Calvert, W.; Hedrick, L.; Christian, J. Biological observations on an overwintering colony of monarch butterflies (Danaus plexippus, Danaidae) in Mexico. J. Lepid. Soc. 1977, 31, 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm, S.B.; Cockrell, B.J.; Brower, L.P. Spring recolonization of eastern North America by the monarch butterfly: Successive brood or single sweep migration. In Biology and Conservation of the Monarch Butterfly; Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 38, pp. 253–267. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, E.; Aschen, H.; Davis, A.K. Citizen science observations of monarch butterfly overwintering in the southern United States. Psyche J. Entom. 2010, 2010, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodson, R.E. The North American species of Asclepias L. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1954, 41, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalden, R.V.; Oberhauser, K.S. Potential changes in eastern North American monarch migration in response to an introduced milkweed, Asclepias curassavica. In Monarchs in a Changing World: Biology and Conservation of an Iconic Butterfly; Oberhauser, K., Nail, K., Altizer, S., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, L.G.; Doll, E.; Holm, E.; Pancho, J.V.; Herberger, J.P. World Weeds: Natural Histories and Distribution; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Satterfield, D.A.; Maerz, J.C.; Hunter, M.D.; Flockhart, D.T.; Hobson, K.A.; Norris, D.R.; Streit, H.; de Roode, J.C.; Altizer, S. Migratory monarchs that encounter resident monarchs show life-history differences and higher rates of parasite infection. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Mahon, B. The American Gardener’s Calendar; Adapted to the Climates and Seasons of the United States; B. Graves: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1806. [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine, N.P. Climate change may alter breeding ground distributions of eastern migratory monarchs (Danaus plexippus) via range expansion of Asclepias host plants. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- iNaturalist. Research-grade Observations. Occurrence Dataset. Available online: https://www.inaturalist.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- Asclepias curassavica L. in GBIF Secretariat (2017). GBIF Backbone Taxonomy. Checklist dataset. Available online: https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei; https://www.gbif.org/ (accessed on 14 May 2019).
- Majewska, A.A.; Sims, S.; Wenger, S.J.; Davis, A.K.; Altizer, S. Do characteristics of pollinator-friendly gardens predict the diversity, abundance, and reproduction of butterflies? Insect Conserv. Divers. 2018, 11, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nail, K.R.; Stenoien, C.; Oberhauser, K. Immature monarch survival: Effects of site characteristics, density, and time. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2015, 108, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Ali, J.; Rasmann, S.; Fishbein, M. Macroevolutionary trends in the defense of milkweeds against monarchs: Latex, cardenolides, and tolerance of herbivory. In Monarchs in a Changing World: Biology and Conservation of an Iconic Butterfly; Oberhauser, K., Nail, K., Altizer, S., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm, S.; Brower, L. Evolutionary and ecological implications of cardenolide sequestration in the monarch butterfly. Experientia 1989, 45, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, T.; Chiang, A.; Kelavkar, M.; Li, H.; Li, J.; de Castillejo, C.L.F.; Oliver, L.; Potini, Y.; Hunter, M.D.; de Roode, J. Behavioural resistance against a protozoan parasite in the monarch butterfly. J. Anim. Ecol. 2012, 81, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roode, J.C.; Pedersen, A.B.; Hunter, M.D.; Altizer, S. Host plant species affects virulence in monarch butterfly parasites. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goehring, L.; Oberhauser, K.S. Environmental factors influencing postdiapause reproductive development in monarch butterflies. In The Monarch Butterfly. Biology and Conservation; Oberhauser, K.S., Solensky, M., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.A.; Fishbein, M.; Jetter, R.; Salminen, J.P.; Goldstein, J.B.; Freitag, A.E.; Sparks, J.P. Phylogenetic ecology of leaf surface traits in the milkweeds (Asclepias spp.): Chemistry, ecophysiology, and insect behavior. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 848–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, F.; Urquhart, N. Autumnal migration routes of the eastern population of the monarch butterfly (Danaus p. plexippus L.; Danaidae; Lepidoptera) in North America to the overwintering site in the Neovolcanic Plateau of Mexico. Can. J. Zool. 1978, 56, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W. The endocrine basis of reproductive inactivity in monarch butterflies overwintering in central California. J. Insect Physiol. 1973, 19, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W.; Brower, L.; Calvert, W. Reproductive tract development in monarch butterflies overwintering in California and Mexico. J. Lepid. Soc. 1989, 43, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Borland, J.; Johnson, C.C.; Crumpton, T.W., III; Thomas, M.; Altizer, S.M.; Oberhauser, K.S. Characteristics of fall migratory monarch butterflies, Danaus plexippus, in Minnesota and Texas. In The Monarch Butterfly. Biology and Conservation; Oberhauser, K.S., Solensky, M., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, L.P.; Fink, L.S.; Walford, P. Fueling the fall migration of the monarch butterfly. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2006, 46, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beall, G. The fat content of a butterfly, Danaus plexippus Linn., as affected by migration. Ecology 1948, 29, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Chippendale, G. Migration of the monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus: Energy sources. J. Insect. Physiol. 1974, 20, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibo, D.L.; McCurdy, J.A. Lipid accumulation by migrating monarch butterflies (Danaus plexippus L.). Can. J. Zool. 1993, 71, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche McKay, A.; Ezenwa, V.O.; Altizer, S. Unravelling the costs of flight for immune defenses in the migratory monarch butterfly. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliske, T.E. Courtship behavior of the monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus L. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1975, 68, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, L.P.; Oberhauser, K.S.; Boppré, M.; Brower, A.V.; Vane-Wright, R. Monarch sex: Ancient rites, or recent wrongs. Antenna 2007, 31, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Oberhauser, K.S.; Hampton, R. The relationship between mating and oogenesis in monarch butterflies (Lepidoptera: Danainae). J. Insect. Behav. 1995, 8, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhauser, K.S. Effects of spermatophores on male and female monarch butterfly reproductive success. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1989, 25, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, E.; Davis, A.K. Tracking the fall migration of eastern monarchs with journey north roost sightings. In Monarchs in a Changing World: Biology and Conservation of an Iconic Butterfly; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Journey North: Tracking Migrations and Seasons. Available online: https://journeynorth.org/ (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Cockrell, B.J.; Malcolm, S.B.; Brower, L.P. Time, temperature, and latitudinal constraints on the annual recolonization of eastern North America by the monarch butterfly. In Biology and Conservation of the Monarch Butterfly; Malcolm, S.B., Zalucki, M.P., Eds.; Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 38, pp. 233–251. [Google Scholar]
- Altizer, S.; Oberhauser, K.S.; Brower, L.P. Associations between host migration and the prevalence of a protozoan parasite in natural populations of adult monarch butterflies. Ecol. Entomol. 2000, 25, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team, R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 3.6.0; R Core Team R: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M. R package ‘Coxme’: Mixed effects cox models, version 2.2-10. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, P.E.; Carlisle, D.; Osborne, D.J. Desert locusts: Sexual maturation delayed by feeding on senescent vegetation. Science 1965, 149, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.D.; McNeil, J.N. Host-plant quality influences diapause and voltinism in a polyphagous insect herbivore. Ecology 1997, 78, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Miyashita, T. Host plant quality influences diapause induction of Byasa alcinous (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2008, 101, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koštál, V. Eco-physiological phases of insect diapause. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalucki, M.; Rochester, W. Estimating the effect of climate on the distribution and abundance of Danaus plexippus: A tale of two continents. In Proceedings of the 1997 North American Conference on the Monarch Butterfly, Morelia, Michoacán, Mexico; pp. 151–163.
- Calvert, W.H. Patterns in the spatial and temporal use of Texas milkweeds (Asclepiadaceae) by the monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus L.) during fall, 1996. J. Lepid. Soc. 1999, 53, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Haribal, M.; Renwick, J.A.A. Identification and distribution of oviposition stimulants for monarch butterflies in hosts and nonhosts. J. Chem. Ecol. 1998, 24, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haribal, M.; Renwick, J.A.A. Oviposition stimulants for the monarch butterfly: Flavonol glycosides from Asclepias curassavica. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, B.B.; Brönmark, C.; Nilsson, J.Å.; Hansson, L.A. Partial migration: An introduction. Oikos 2011, 120, 1761–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, B.B.; Brönmark, C.; Nilsson, J.Å.; Hansson, L.A. The ecology and evolution of partial migration. Oikos 2011, 120, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, K.; Partridge, L. A cost of mating in female fruitflies. Nature 1989, 338, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, T. Survival costs of reproduction in Drosophila. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W. Hormonally mediated events in adult monarch butterflies. In Migration: Mechanisms and Adaptive Significance; Rankin, M.A., Ed.; The University of Texas at Austin Marine Science Institute: Austin, TX, USA, 1985; Volume 27, pp. 799–815. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, L.P. New perspectives on the migration biology of the monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus. In Migration: Mechanisms and Adaptive Significance; Rankin, M.A., Ed.; The University of Texas at Austin Marine Science Institute: Austin, TX, USA, 1985; Volume 27, pp. 749–785. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.K.; Rendón-Salinas, E. Are female monarch butterflies declining in eastern North America? Evidence of a 30-year change in sex ratios at Mexican overwintering sites. Biol. Lett. 2009, 6, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brower, L.P.; Taylor, O.R.; Williams, E.H.; Slayback, D.A.; Zubieta, R.R.; Ramirez, M.I. Decline of monarch butterflies overwintering in Mexico: Is the migratory phenomenon at risk? Insect Conserv. Divers. 2012, 5, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thogmartin, W.E.; Diffendorfer, J.E.; López-Hoffman, L.; Oberhauser, K.; Pleasants, J.; Semmens, B.X.; Semmens, D.; Taylor, O.R.; Wiederholt, R. Density estimates of monarch butterflies overwintering in central Mexico. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterfield, D.A.; Villablanca, F.X.; Maerz, J.C.; Altizer, S. Migratory monarchs wintering in California experience low infection risk compared to monarchs breeding year-round on non-native milkweed. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majewska, A.A.; Altizer, S. Exposure to Non-Native Tropical Milkweed Promotes Reproductive Development in Migratory Monarch Butterflies. Insects 2019, 10, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10080253
Majewska AA, Altizer S. Exposure to Non-Native Tropical Milkweed Promotes Reproductive Development in Migratory Monarch Butterflies. Insects. 2019; 10(8):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10080253
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajewska, Ania A., and Sonia Altizer. 2019. "Exposure to Non-Native Tropical Milkweed Promotes Reproductive Development in Migratory Monarch Butterflies" Insects 10, no. 8: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10080253
APA StyleMajewska, A. A., & Altizer, S. (2019). Exposure to Non-Native Tropical Milkweed Promotes Reproductive Development in Migratory Monarch Butterflies. Insects, 10(8), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10080253




