Brown Rice Vinegar as an Olfactory Field Attractant for Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) and Zaprionus indianus Gupta (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Cherimoya in Maui, Hawaii, with Implications for Attractant Specificity between Species and Estimation of Relative Abundance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trap Assembly
2.2. Attractant Solutions
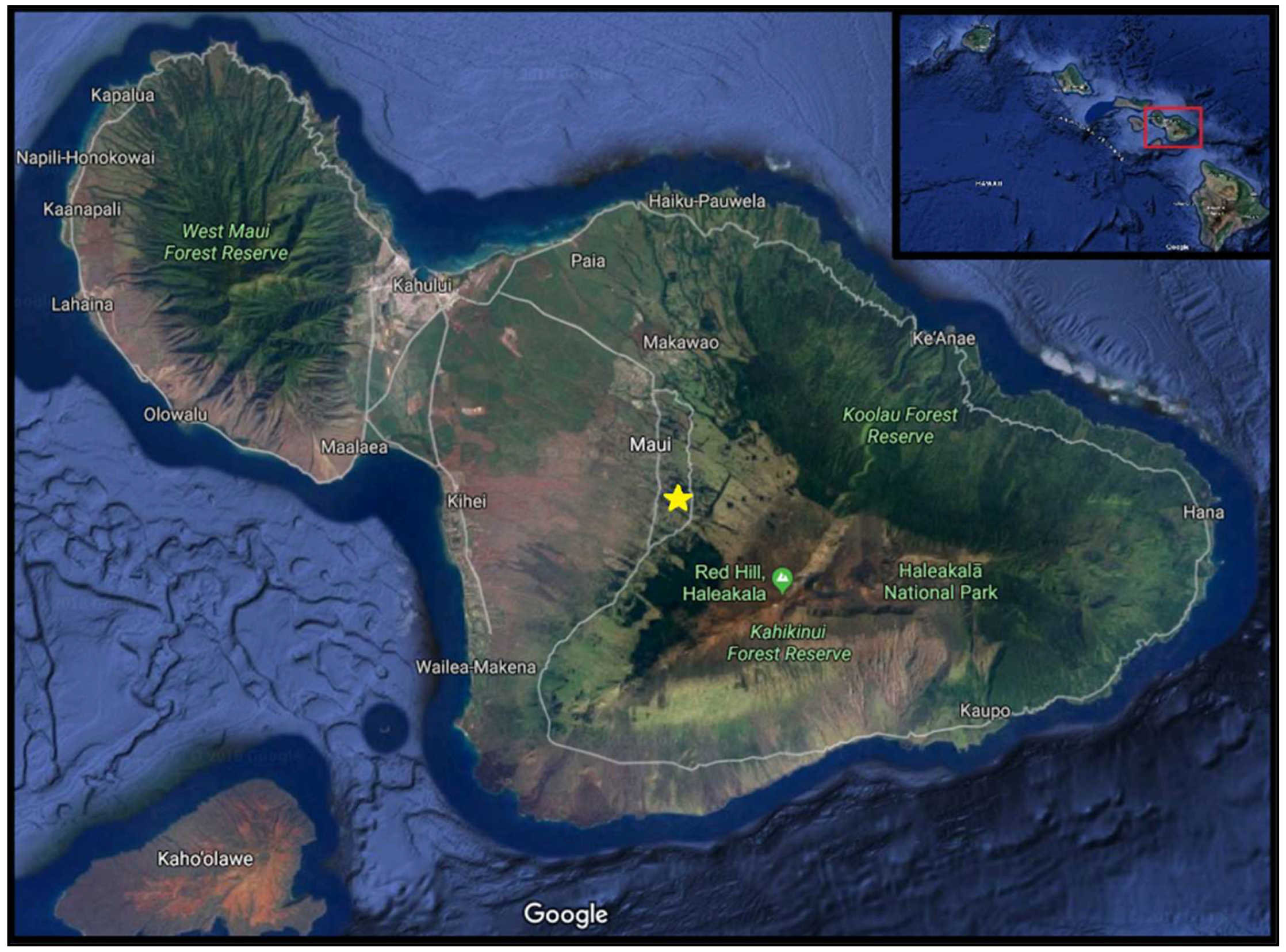
2.3. Trap Installation and Maintenance
2.4. Species Identification
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Drosophila suzukii: Mean Captures and Attractant Specificity
3.2. Zaprionus indianus: Mean Captures and Attractant Specificity
3.3. Non-Target Drosophilid: Mean Captures and Attractant Specificity
3.4. Estimated Relative Abundance of D. suzukii, Z. indianus, and Non-Target Drosophilids in Cherimoya
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauser, M. A historic account of the invasion of Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in the continental United States, with remarks on their identification. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasa, R.; Tadeo, E. Invasive drosophilid pests Drosophila suzukii and Zaprionus indianus (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Veracruz, Mexico. Fla. Entomol. 2015, 98, 987–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprá, M.; Poppe, J.L.; Schmitz, H.J.; Cristina De Toni, D.; Valente, V.L.S. The first records of the invasive pest Drosophila suzukii in the South American continent. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süss, L.; Costanzi, M. Presence of Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura, 1931) (Diptera Drosophilidae) in Liguria (Italy). J. Entomol. Acarol. Res. Ser. II 2010, 42, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, G.; Maca, J.; Bächli, G.; Serra, L.; Pascual, M. First records of the potential pest species Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Europe. J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 136, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toševski, I.; Milenković, S.; Krstić, O.; Kosovac, A.; Jakovljević, M.; Mitrović, M.; Cvrković, T.; Jović, J. Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura, 1931) (Diptera: Drosophilidae), a new invasive pest in Serbia. Plant Prot. 2014, 65, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneshiro, K.Y. Drosophila (Sophophora) suzukii (Matsumura). Notes and exhibitions. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1983, 24, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Asplen, M.K.; Anfora, G.; Biondi, A.; Choi, D.; Chu, D.; Daane, K.M.; Gilbert, P.; Gutierrez, A.P.; Hoelmer, K.A.; Hutchison, W.D.; et al. Invasion biology of spotted wing Drosophila (Drosophila suzukii): A global perspective and future priorities. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 469–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.I.; Browne, M.; MacKinnon, K.; Noble, I. The link between international trade and the global distribution of invasive alien species. Biol. Invasions 2008, 10, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, transport, and trouble: Managing invasive species pathways in an era of globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiman, N.G.; Walton, V.M.; Dalton, D.T.; Anfora, G.; Burrack, H.J.; Chiu, J.C.; Daane, K.M.; Grassi, A.; Miller, B.; Tochen, S.; et al. Integrating temperature-dependent life table data into a matrix projection model for Drosophila suzukii population estimation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Mata, R.A.; Tidon, R.; Côrtes, L.G.; De Marco, P., Jr.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F. Invasive and flexible: Niche shift in the drosophilid Zaprionus indianus (Insecta, Diptera). Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Soares, N.F.; Nogueira-Alves, A.; Mirth, C.K. Adaption to new nutritional environments: Larval performance, foraging decisions, and adult oviposition choices in Drosophila suzukii. BMC Ecol. 2017, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, D.E.; Nascimento, A.M.; Stein, C.P.; Haddad, M.L.; Bento, J.M.S.; Parra, J.R.P. Biology, thermal requirements, and estimation of the number of generations of Zaprionus indianus (Diptera: Drosophilidae) for the main fig producing regions of Brazil. Fla. Entomol. 2007, 90, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revadi, S.; Lebreton, S.; Witzgall, P.; Anfora, G.; Dekker, T.; Becher, P. Sexual behavior of Drosophila suzukii. Insects 2015, 6, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnsworth, D.; Hamby, K.A.; Bolda, M.; Goodhue, R.E.; Williams, J.C.; Zalom, F.G. Economic analysis of revenue losses and control costs associated with the spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura), in the California raspberry industry. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 73, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzi, D.; Bravin, E.; Meraner, M.; Finger, R.; Kuske, S. Economic impact of the introduction and establishment of Drosophila suzukii on sweet cherry production in Switzerland. Insects 2017, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, D.B.; Bolda, M.P.; Goodhue, R.E.; Dreves, A.J.; Lee, J.; Bruck, D.J.; Walton, V.M.; O’Neal, S.D.; Zalom, F.G. Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae): Invasive pest of ripening soft fruit expanding its geographic range and damage potential. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2011, 2, G1–G7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, J.A.; Yang, L.H.; Morales, V.M.; Boundy-Mills, K.L. Drosophila regulate yeast density and increase yeast community similarity in a natural substrate. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, S.L.; Mehlferber, E.; Moore, P.J. Life-history trade-offs under different larval diets in Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Physiol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrack, H.J.; Fernandez, G.E.; Spivey, T.; Kraus, D.A. Variation in selection and utilization of host crops in the field and laboratory by Drosophila suzukii Matsumura (Diptera: Drosophilidae), an invasive frugivore. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgi, M.; Bräcker, L.B.; Lebreton, S.; Kadow, I.C.G.; Gompel, N.; Prud’homme, B. Evolution of multiple sensory systems drives novel egg-laying behavior in the fruit pest Drosophila suzukii. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matavelli, C.; Carvalho, M.A.; Martins, N.E.; Mirth, C.K. Differences in larval nutritional requirements and female oviposition preference reflect the order of fruit colonization of Zaprionus indianus and Drosophila simulans. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 82, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, D.; Andreazza, F.; Botton, M.; Baronio, C.A.; Nava, D.E. Susceptibility and interactions of Drosophila suzukii and Zaprionus indianus (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in damaging strawberry. Neotrop. Entomol. 2017, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Camejo, L.A.; Maldonado-Morales, G.; Bayman, P. Differential microbial diversity in Drosophila melanogaster: Are fruit flies potential vectors of opportunistic pathogens? Int. J. Microbiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioriatti, C.; Guzzon, R.; Anfora, G.; Ghidoni, F.; Mazzoni, V.; Villegas, T.R.; Dalton, D.T.; Walton, V.M. Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) contributes to the development of sour rot in grape. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellutti, N.; Gallmetzer, A.; Innerebner, G.; Schmidt, S.; Zelger, R.; Koschier, E.H. Dietary yeast affects preference and performance in Drosophila suzukii. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Bruck, D.J.; Dreves, A.J.; Loriatti, C.; Vogt, H.; Baufeld, P. In focus: Spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii, across perspectives. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1349–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Burrack, H.J.; Barrantes, L.D.; Beers, E.H.; Dreves, A.J.; Hamby, K.A.; Haviland, D.R.; Isaacs, R.; Richardson, T.A.; Shearer, P.W.; et al. Evaluation of monitoring traps for Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in North America. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epsky, N.D.; Gill, M.A.; Cha, D.H.; Landolt, P.J. Trapping the African fig fly (Diptera: Drosophilidae) with combinations of vinegar and wine. Fla. Entomol. 2014, 97, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, D.M.; McGhee, P.S.; Hermann, S.L.; Gut, L.J.; Miller, J.R. Alignment of spotted wing drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae) on odorless disks varying in color. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landolt, P.J.; Adams, T.; Rogg, H. Trapping spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) (Diptera: Drosophilidae) with combinations of vinegar and wine, and acetic acid and ethanol. J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 136, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiber, J.R.; Unelius, C.R.; Lee, J.C.; Suckling, D.M.; Qian, M.C.; Bruck, D.J. Attractiveness of fermentation and related products to spotted wing drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Chem. Ecol. 2014, 43, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stensmyr, M.C.; Giordano, E.; Balloi, A.; Angioy, A.; Hansson, B.S. Novel natural ligands for Drosophila olfactory receptor neurons. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stökyl, J.; Strutz, A.; Dafni, A.; Svatos, A.; Doubsky, J.; Knaden, M.; Sachse, S.; Hansson, B.S.; Stensmyr, M.C. A deceptive pollination system targeting drosophilids through olfactory mimicry of yeast. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucher, C.P.; Hilker, M.; de Bruyne, M. Interactions of carbon dioxide and food odours in Drosophila: Olfactory hedonics and sensory neuron properties. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidler, N.H.; Liu, C.; Hamby, K.A.; Zalom, F.G.; Syed, Z. Volatile codes: Correlation of olfactory signals and reception in Drosophila-yeast chemical communication. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.; Kim, A.Y.; Jung, J.K.; Donahue, K.M.; Jung, C.; Choi, M.Y.; Koh, Y.H. The biochemical adaptations of spotted wing drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae) to fresh fruits reduced fructose concentrations and glutathione-S transferase activities. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambysellis, M.P.; Ho, K.; Craddock, E.M.; Piano, F.; Parisi, M.; Cohen, J. Pattern of ecological shifts in the diversification of Hawaiian Drosophila inferred from a molecular phylogeny. Curr. Biol. 1995, 5, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, P.M.; Lapoint, R.T.; Bonacum, J.; Lasola, J.; Owen, E.; Wu, Y.; DeSalle, R. Phylogenetic and ecological relationships of the Hawaiian Drosophila inferred by mitochondrial DNA analysis. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 58, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnacca, K.N.; Price, D.K. Rapid adaptive radiation and host plant conservation in the Hawaiian picture wing Drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 92, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesey, I.W.; Knaden, M.; Hansson, B.S. Olfactory specialization in Drosophila suzukii supports an ecological shift in host preference from rotten to fresh fruit. J. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 41, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, Y.; Buchiewicz, N.; Long, T.A.F. Nutritional geometry and fitness consequences in Drosophila suzukii, the Spotted-Wing Drosophila. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 2842–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasa, R.; Tadeo, E.; Toledo-Hérnandez, R.A.; Carmona, L.; Lima, I.; Williams, T. Improved capture of Drosophila suzukii by a trap baited with two attractants in the same device. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.H.; Adams, T.; Rogg, H.; Landolt, P.J. Identification and field evaluation of fermentation volatiles from wine and vinegar that mediate attraction of spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, Y.; Akasaka, N.; Goda, I.; Sakoda, H.; Fujiwara, S. Effective trapping of fruit flies with cultures of metabolically modified acetic acid bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2265–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.H.; Adams, T.; Werle, C.T.; Sampson, B.J.; Adamczyk, J.J., Jr.; Rogg, H.; Landolt, P.J. A four-component synthetic attractant for Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) isolated from fermented bait headspace. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnici, F.; Guerrero, E.D.; Sonni, F.; Natali, N.; Marín, R.N.; Riponi, C. Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) characterization of volatile compounds in quality vinegars with protected European geographical indication. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4784–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Shearer, P.W.; Barrantes, L.D.; Beers, E.H.; Burrack, H.J.; Dalton, D.T.; Dreves, A.J.; Gut, L.J.; Hamby, K.A.; Haviland, D.R.; et al. Trap designs for monitoring Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Stewart, T.J.; Biondi, A.; Chavez, B.A.; Ingels, C.; Caprile, J.; Grant, J.A.; Walton, V.M.; Daane, K.M. Population dynamics and ecology of Drosophila suzukii in Central California. J. Pest Sci. 2016, 89, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremmer, L.; David, J.; Borowiec, N.; Thaon, M.; Ris, N.; Poirié, M.; Gatti, J. The African fig fly Zaprionus indianus: A new invasive pest in France? Bull. Insectol. 2017, 70, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Akasaka, N.; Higashikubo, H.; Ishii, Y.; Sakoda, H.; Fujiwara, S. Polyamines in brown rice vinegar function as potent attractants for the spotted wing drosophila. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willbrand, B.W.; Pfeiffer, D.; Leblanc, L.; Yassin, A. First report of African fig fly, Zaprionus indianus Gupta (Diptera: Drosophilidae), on the island of Maui, Hawaii, USA, in 2017 and potential impacts to the Hawaiian entomofauna. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 2018, 50, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, D.H.; Gill, M.A.; Epsky, N.D.; Werle, C.T.; Adamczyk, J.J.; Landolt, P.J. From a non-target to a target: Identification of a fermentation volatile blend attractive to Zaprionus indianus. J. Appl. Entomol. 2015, 139, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.B.; Jones, S.K.; Morrison, W., III; Leskey, T.C. Spotted wing drosophila prefer low hanging fruit: Insights into foraging behavior and management strategies. J. Insect Behav. 2017, 30, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vloch, J. Identifying Drosophila suzukii. Oregon Department of Agriculture 2013. Available online: http://www.oregon.gov/oda/shared/documents/publications/ippm/spottedwingdrosophilaidkey.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2017).
- Van der Linde, K. Zaprionus indianus: Species identification and taxonomic position. Drosoph. Inf. Serv. 2010, 93, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yassin, A.; David, J.R. Revision of the Afrotropical species of Zaprionus (Diptera, Drosophilidae) with descriptions of two new species and notes on internal reproductive structures and immature stages. ZooKeys 2010, 51, 33–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oregon State University. Common Adult Features of Family Drosophilidae—Pomace/Vinegar Flies. 2013. Available online: http://uspest.org/swd/pubs/Drosophila_ID_Key_10-14-2014.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Bolker, B.M.; Brooks, M.E.; Clark, C.J.; Geange, S.W.; Poulson, J.R.; Stevens, M.H.H.; White, J.S. Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, R.C.; Milliken, G.A.; Stroup, W.W.; Wolfinger, R.D.; Schabenberger, O. SAS for Mixed Models, 2nd ed.; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2006; ISBN 9781590475003. [Google Scholar]
- Gbur, E.; Stroup, W.W.; McCarter, K.S.; Durham, S.; Young, L.J. Analysis of Generalized Linear Mixed Models in the Agricultural and Natural Resources Sciences; ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780891181828. [Google Scholar]
- Revadi, S.; Vitagliano, S.; Stacconi, M.V.R.; Ramasamy, S.; Mansourian, S.; Carlin, S.; Vrhovsek, U.; Becher, P.G.; Mazzoni, V.M.; Rota-Stabelli, O.; Angeli, S.; et al. Olfactory responses to Drosophila suzukii females to host plant volatiles. Physiol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhang, F.; Kenis, M.; Griepink, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Xiao, C. Identification of active components from volatiles of Chinese bayberry, Myrica rubra attractive to Drosophila suzukii. Arthropod Plant Interact. 2018, 12, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidon, R.; Leite, D.F.; Leão, B.F.D. Impact of the colonisation of Zaprionus (Diptera, Drosophilidae) in different ecosystems of the Neotropical Region: 2 years after the invasion. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 112, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrader, M.E. Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) (Diptera: Drosophilidae): Risk Assessment for an Invasive Vinegar Fly in Virginia Vineyards. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2017; 141p. [Google Scholar]

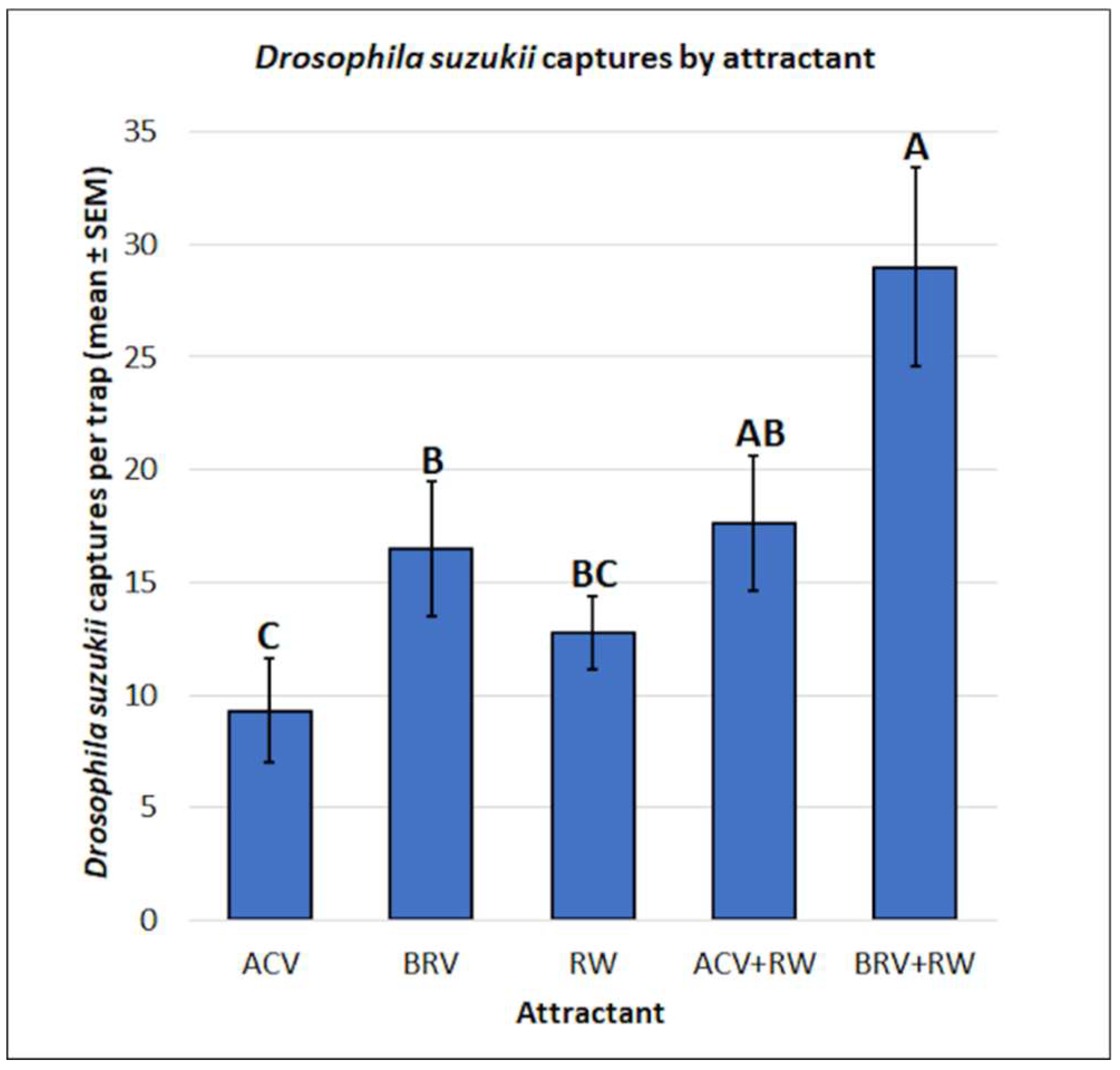
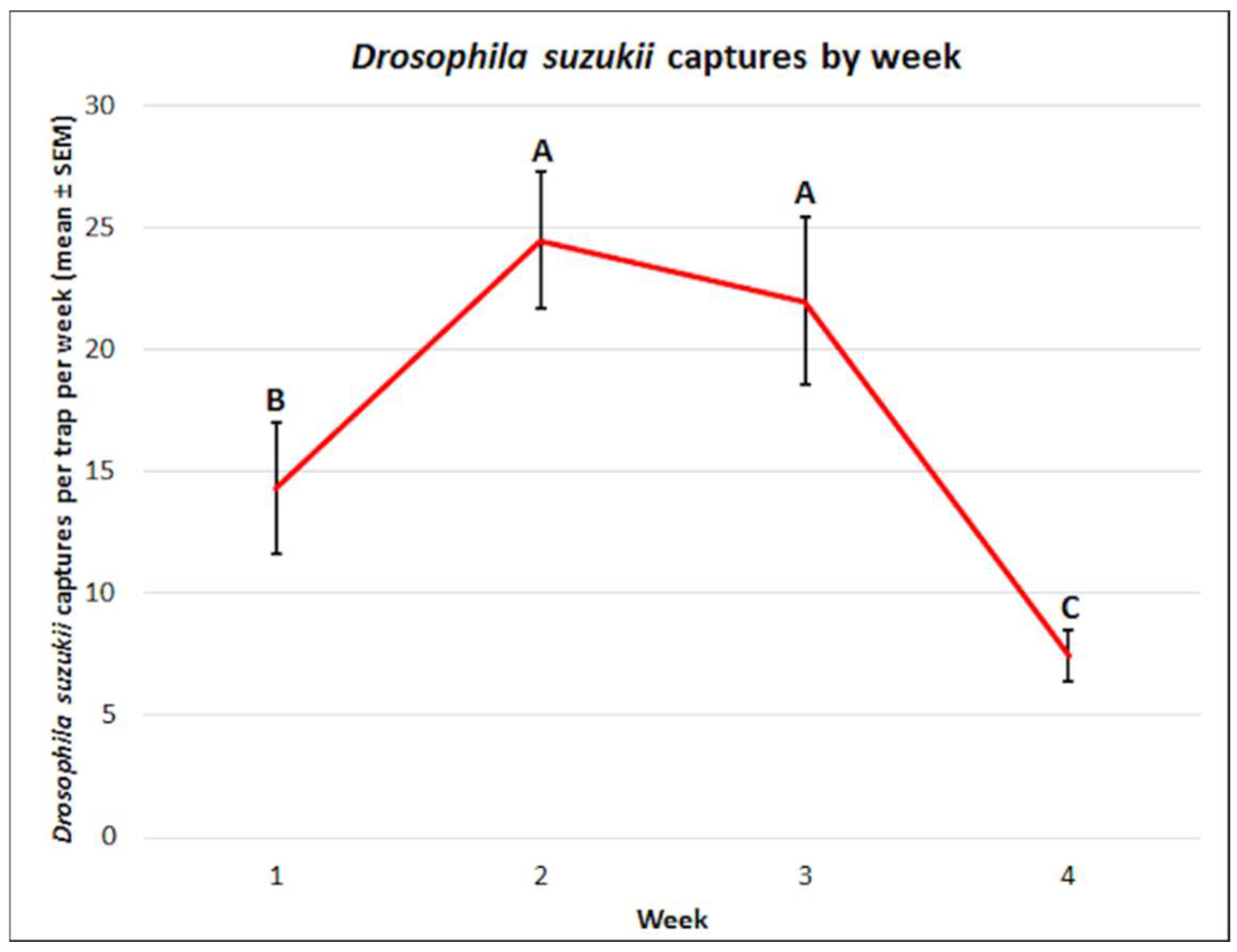
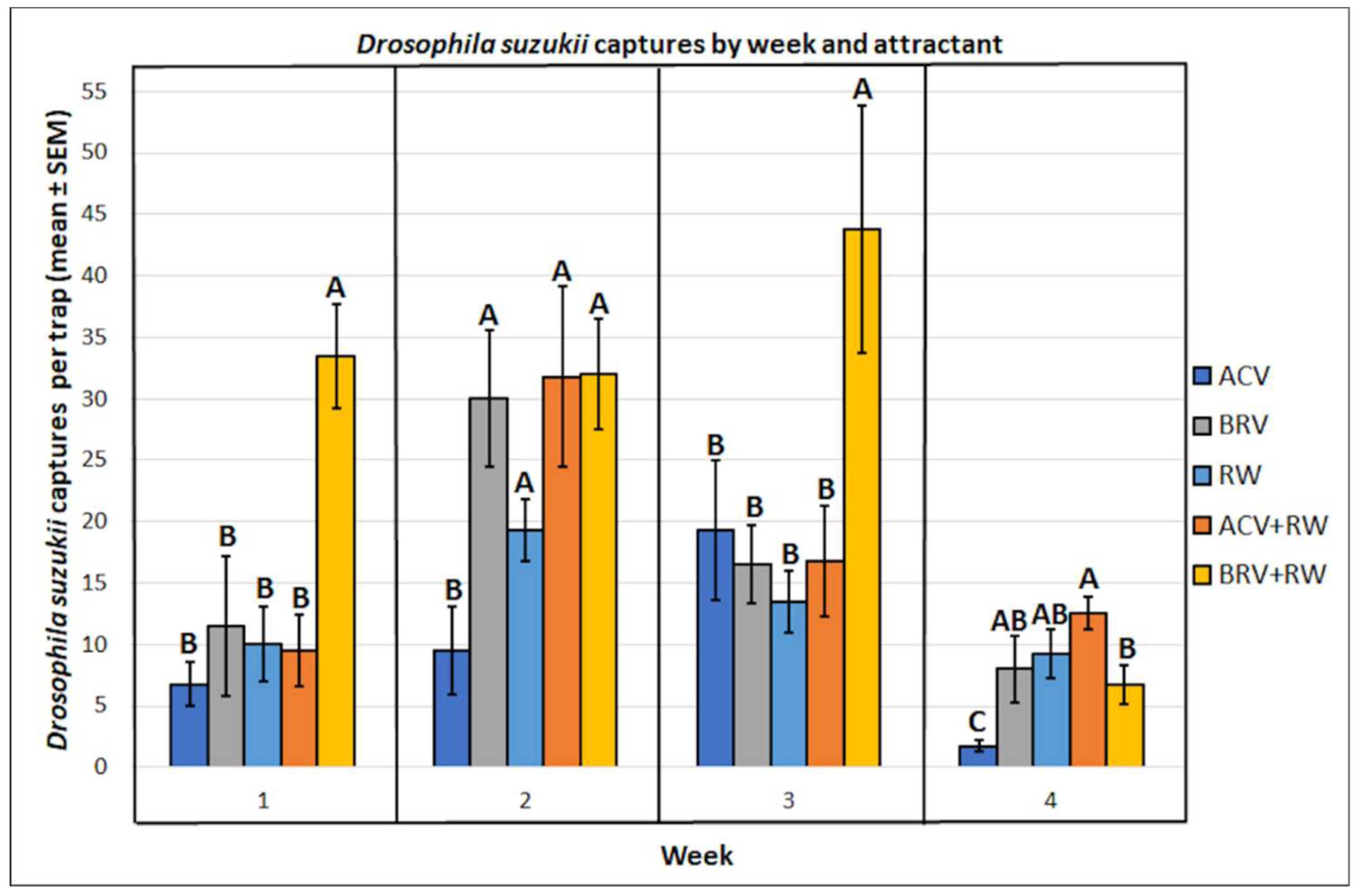
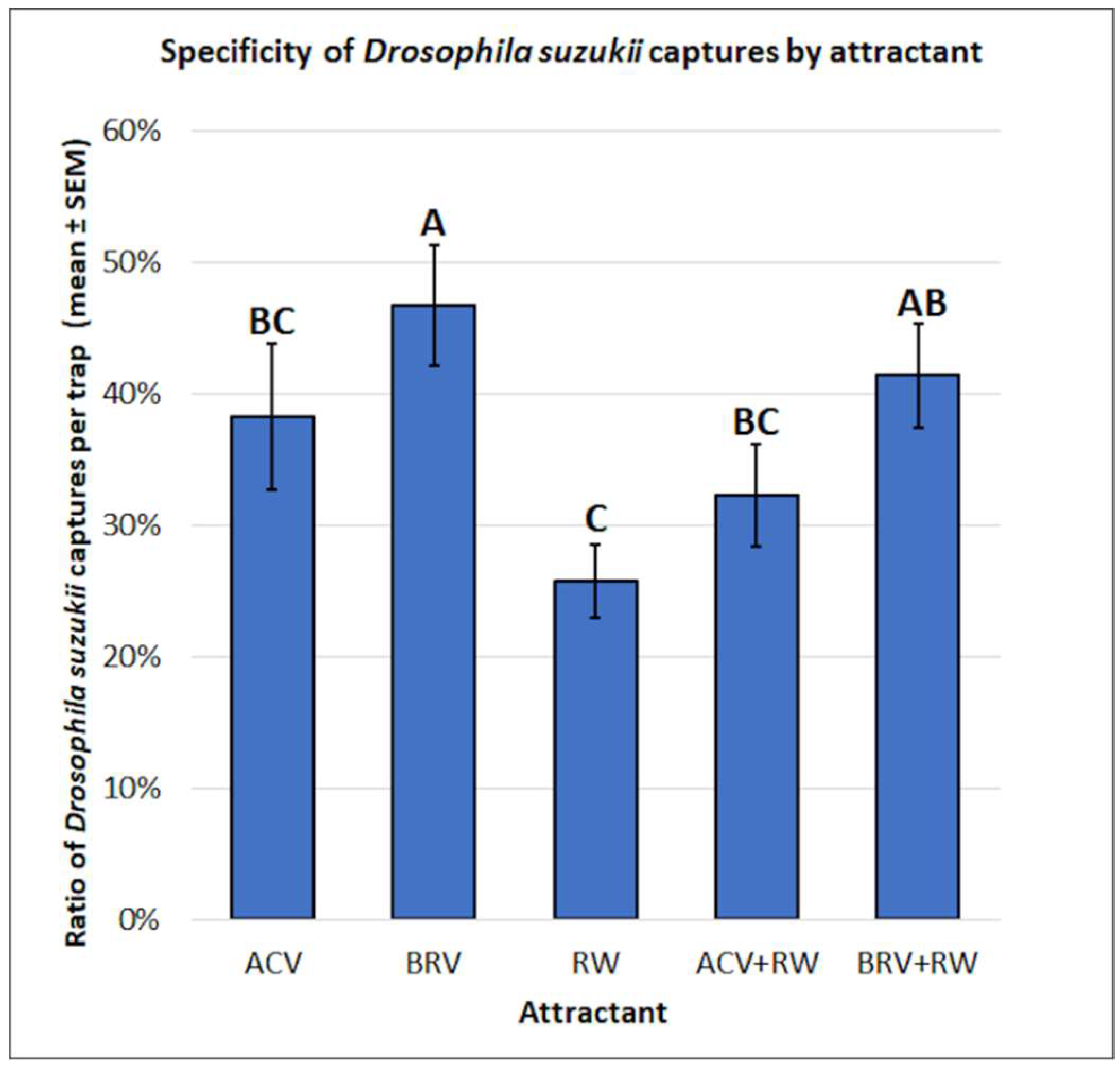
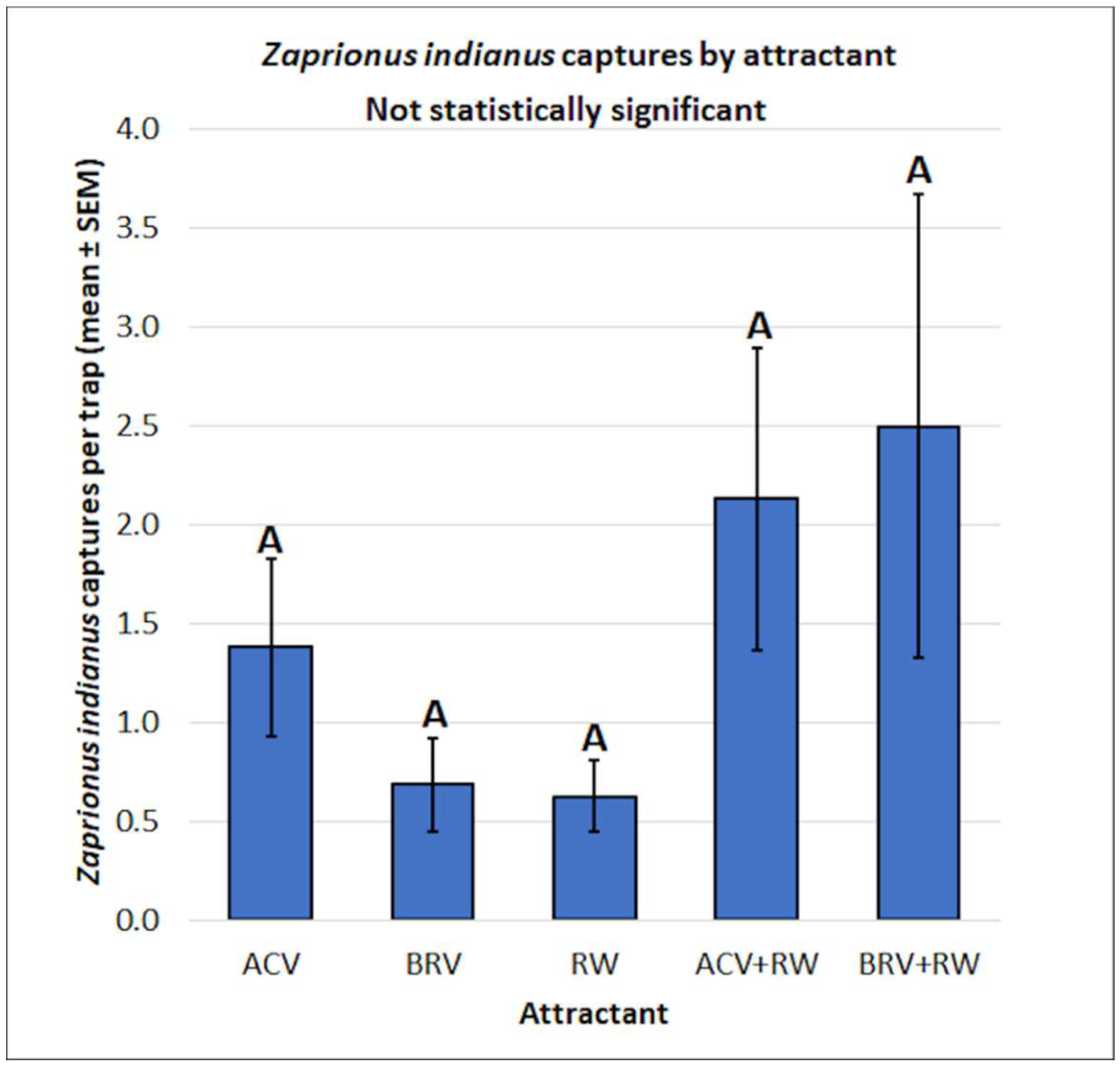
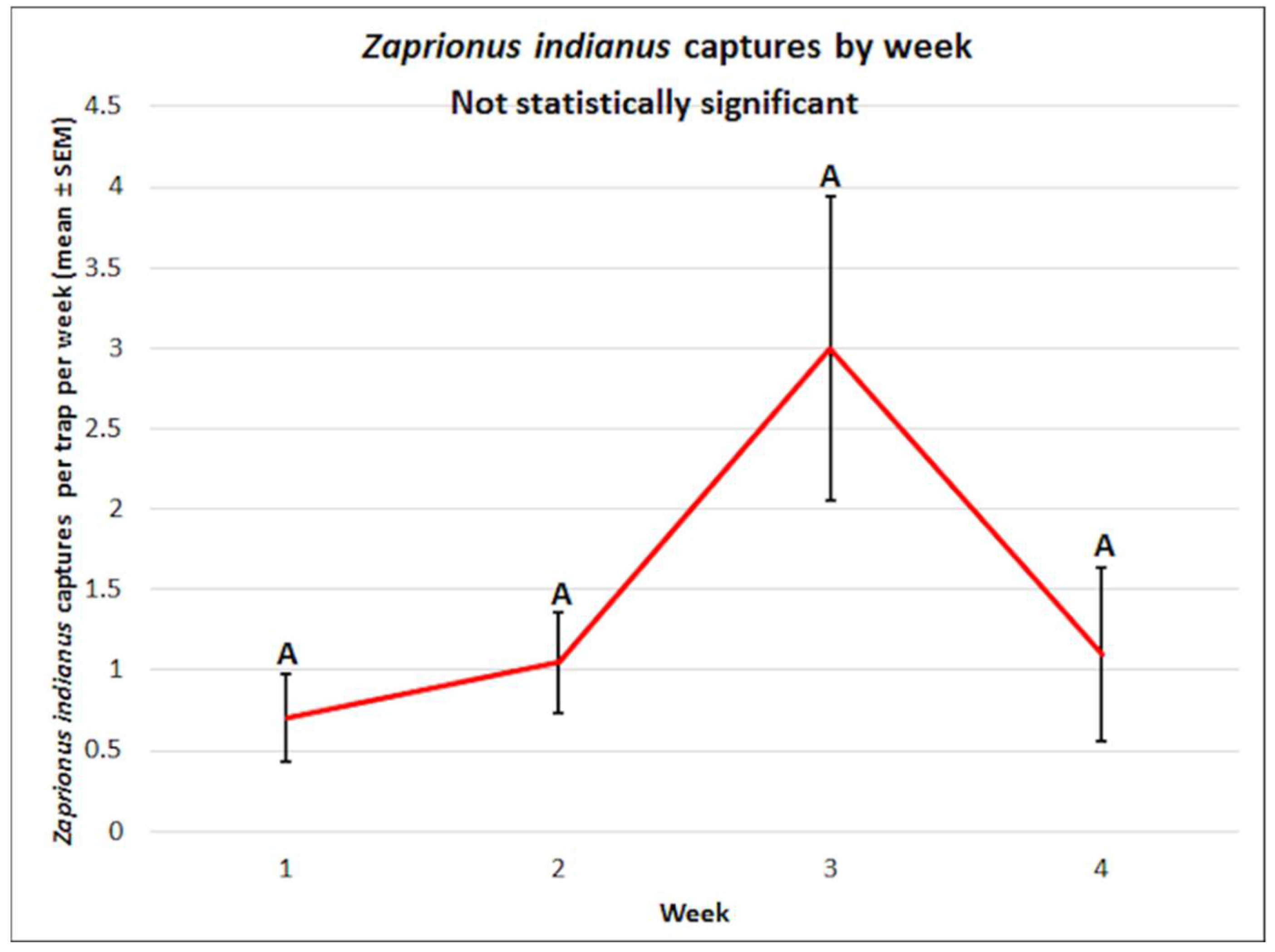
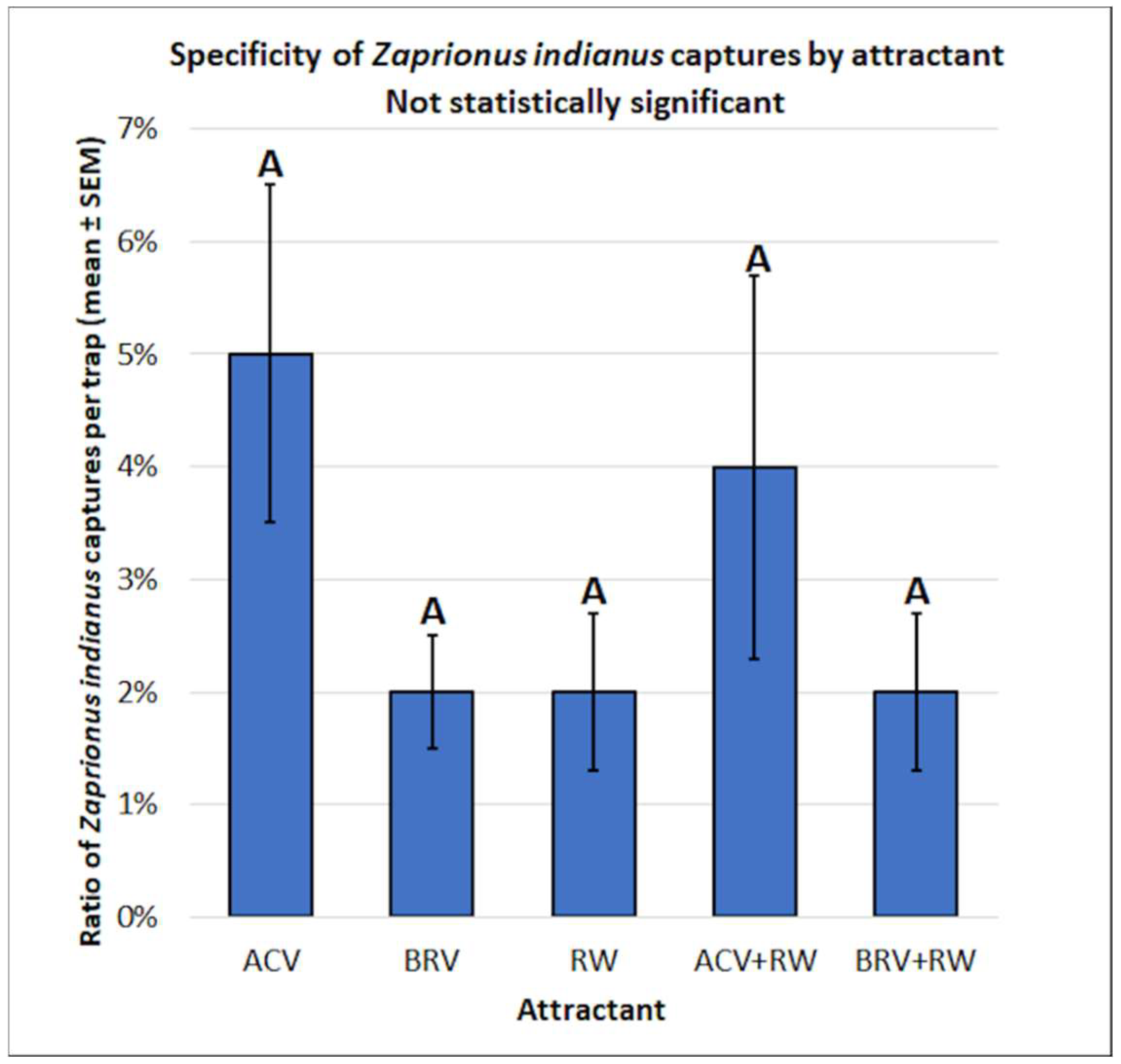
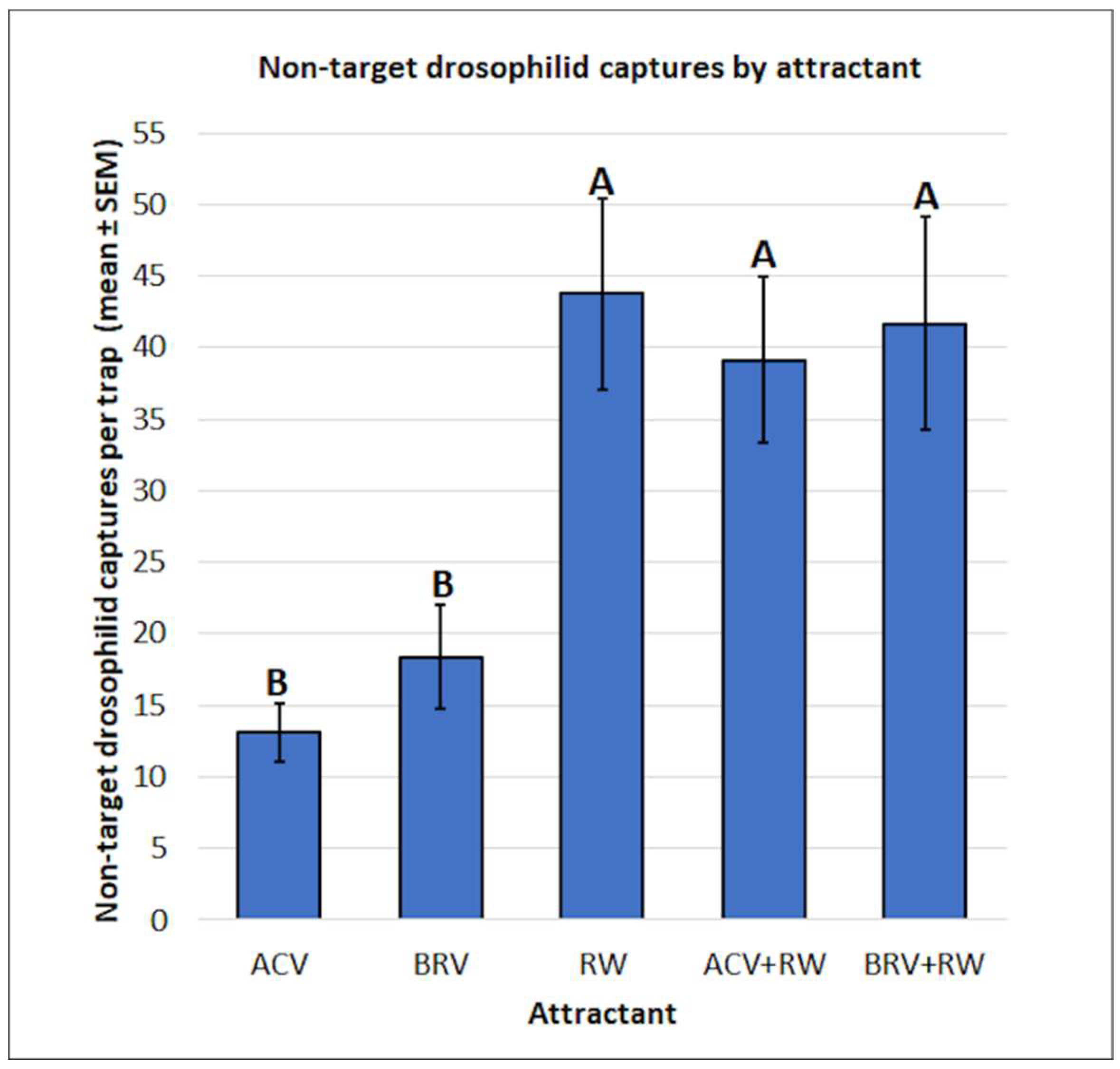
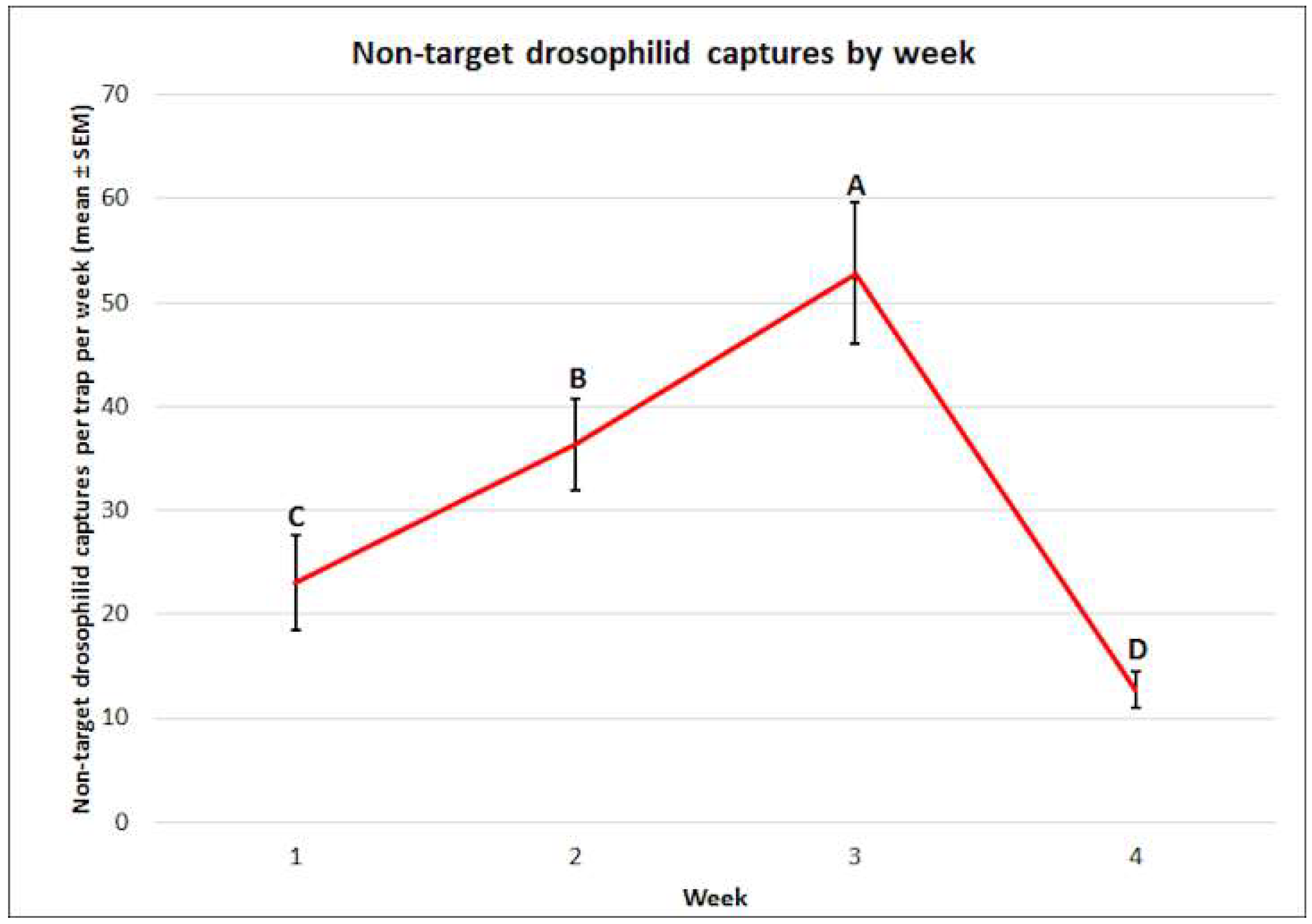
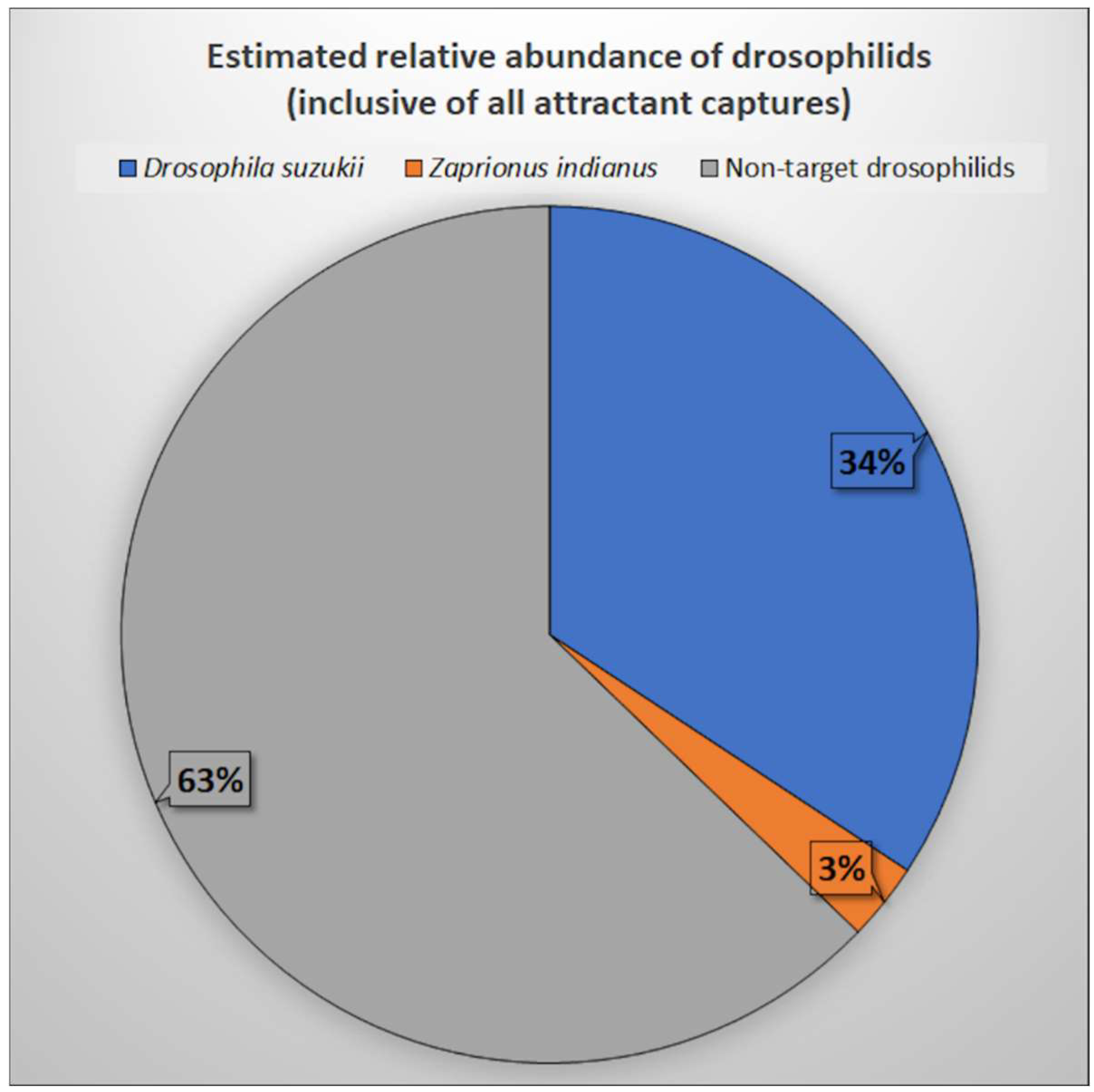
| Attractant Type | Drosophila suzukii Male | Drosophila suzukii Female | Zaprionus indianus Male | Zaprionus indianus Female | Non-Target Drosophilids | Non-Target Other | Total Captures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple cider vinegar | 99 | 50 | 14 | 8 | 210 | 11 | 392 |
| Brown rice vinegar | 173 | 91 | 8 | 3 | 294 | 21 | 590 |
| Red wine | 123 | 81 | 5 | 5 | 700 | 76 | 990 |
| Apple cider vinegar + red wine | 190 | 92 | 12 | 22 | 626 | 59 | 1001 |
| Brown rice vinegar + red wine | 300 | 164 | 21 | 19 | 667 | 51 | 1222 |
| Distilled water | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 9 | 17 |
| Total | 886 | 480 | 60 | 57 | 2502 | 227 | 4212 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Willbrand, B.N.; Pfeiffer, D.G. Brown Rice Vinegar as an Olfactory Field Attractant for Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) and Zaprionus indianus Gupta (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Cherimoya in Maui, Hawaii, with Implications for Attractant Specificity between Species and Estimation of Relative Abundance. Insects 2019, 10, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030080
Willbrand BN, Pfeiffer DG. Brown Rice Vinegar as an Olfactory Field Attractant for Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) and Zaprionus indianus Gupta (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Cherimoya in Maui, Hawaii, with Implications for Attractant Specificity between Species and Estimation of Relative Abundance. Insects. 2019; 10(3):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030080
Chicago/Turabian StyleWillbrand, Brittany N., and Douglas G. Pfeiffer. 2019. "Brown Rice Vinegar as an Olfactory Field Attractant for Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) and Zaprionus indianus Gupta (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Cherimoya in Maui, Hawaii, with Implications for Attractant Specificity between Species and Estimation of Relative Abundance" Insects 10, no. 3: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030080
APA StyleWillbrand, B. N., & Pfeiffer, D. G. (2019). Brown Rice Vinegar as an Olfactory Field Attractant for Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) and Zaprionus indianus Gupta (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Cherimoya in Maui, Hawaii, with Implications for Attractant Specificity between Species and Estimation of Relative Abundance. Insects, 10(3), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030080





