A Left and Right Truncated Schechter Luminosity Function for Quasars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Flat Cosmology
3. The Adopted LFs
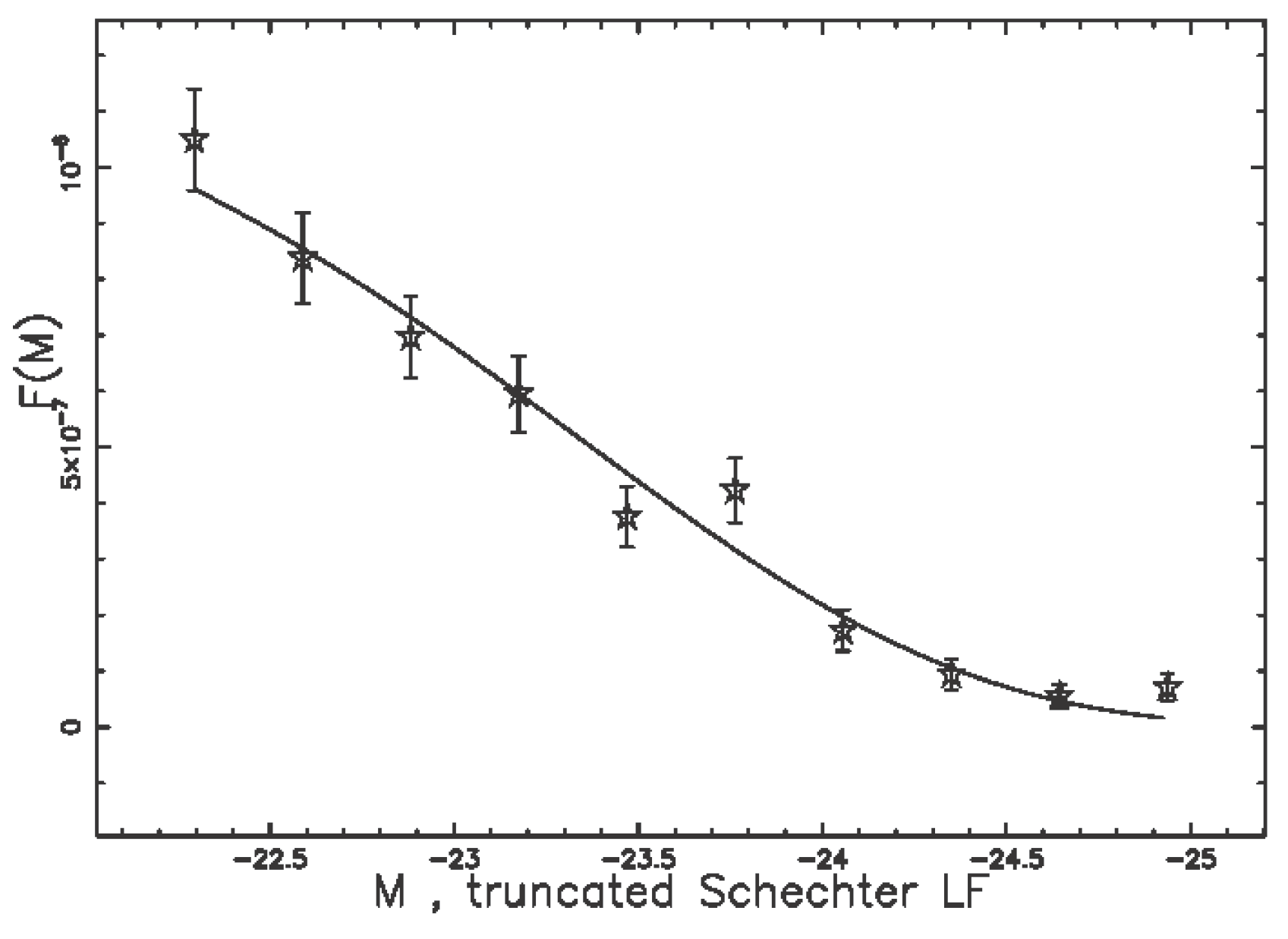
3.1. The Schechter LF
3.2. The Truncated Schechter LF
3.3. The Double Power Law
3.4. The Pei Function
4. The Astrophysical Applications
4.1. K-Correction
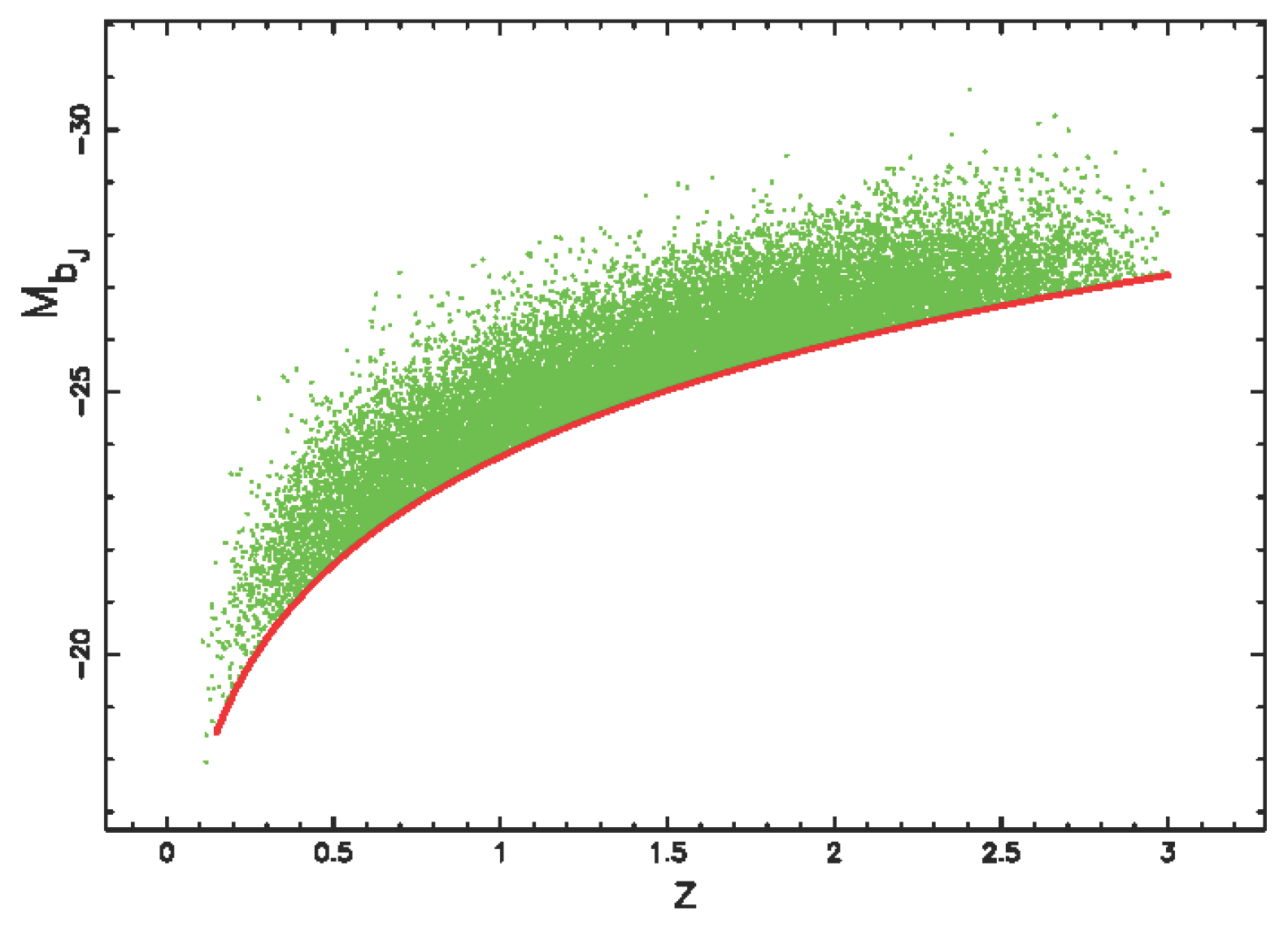
4.2. The Sample of QSO
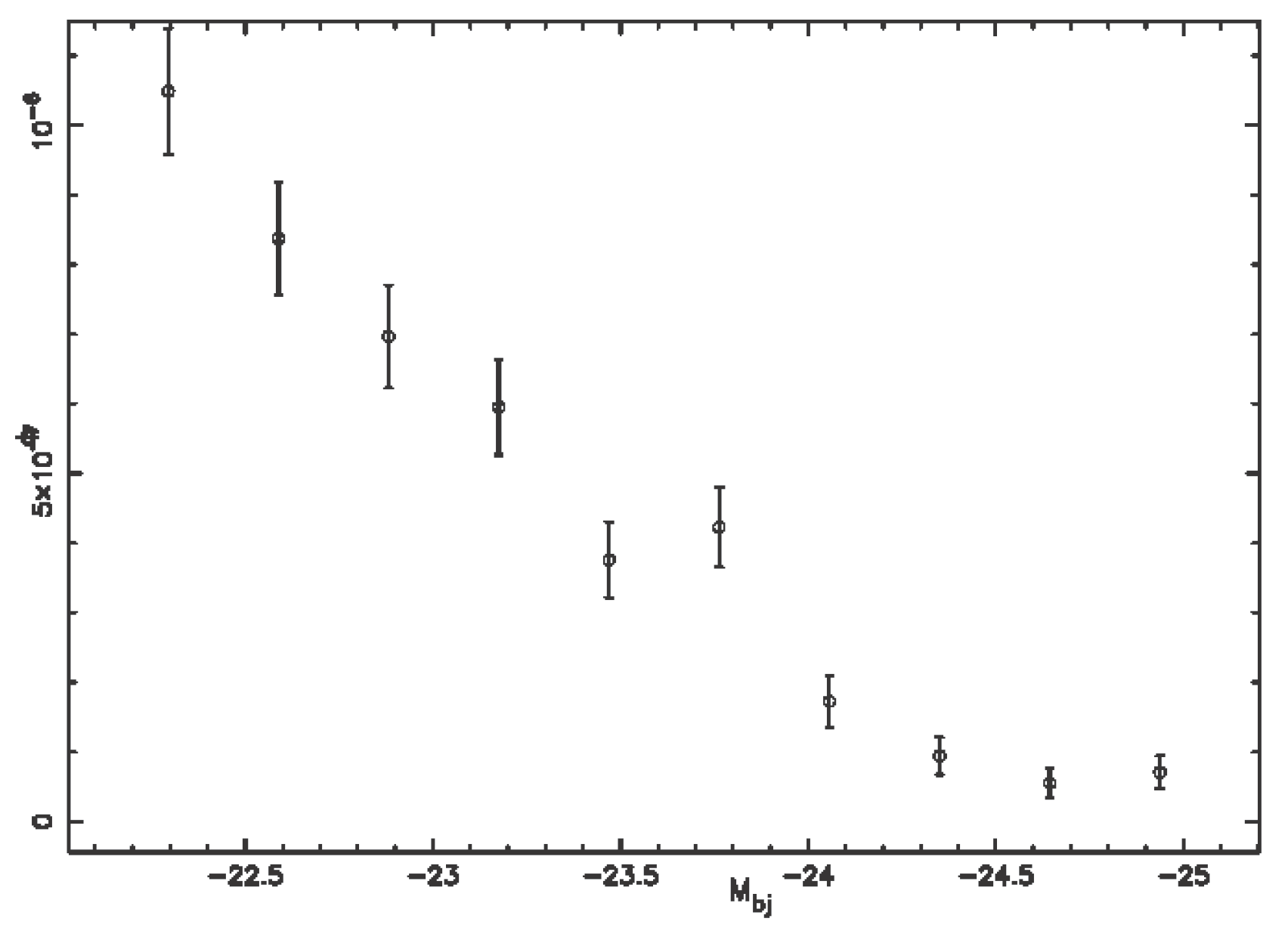
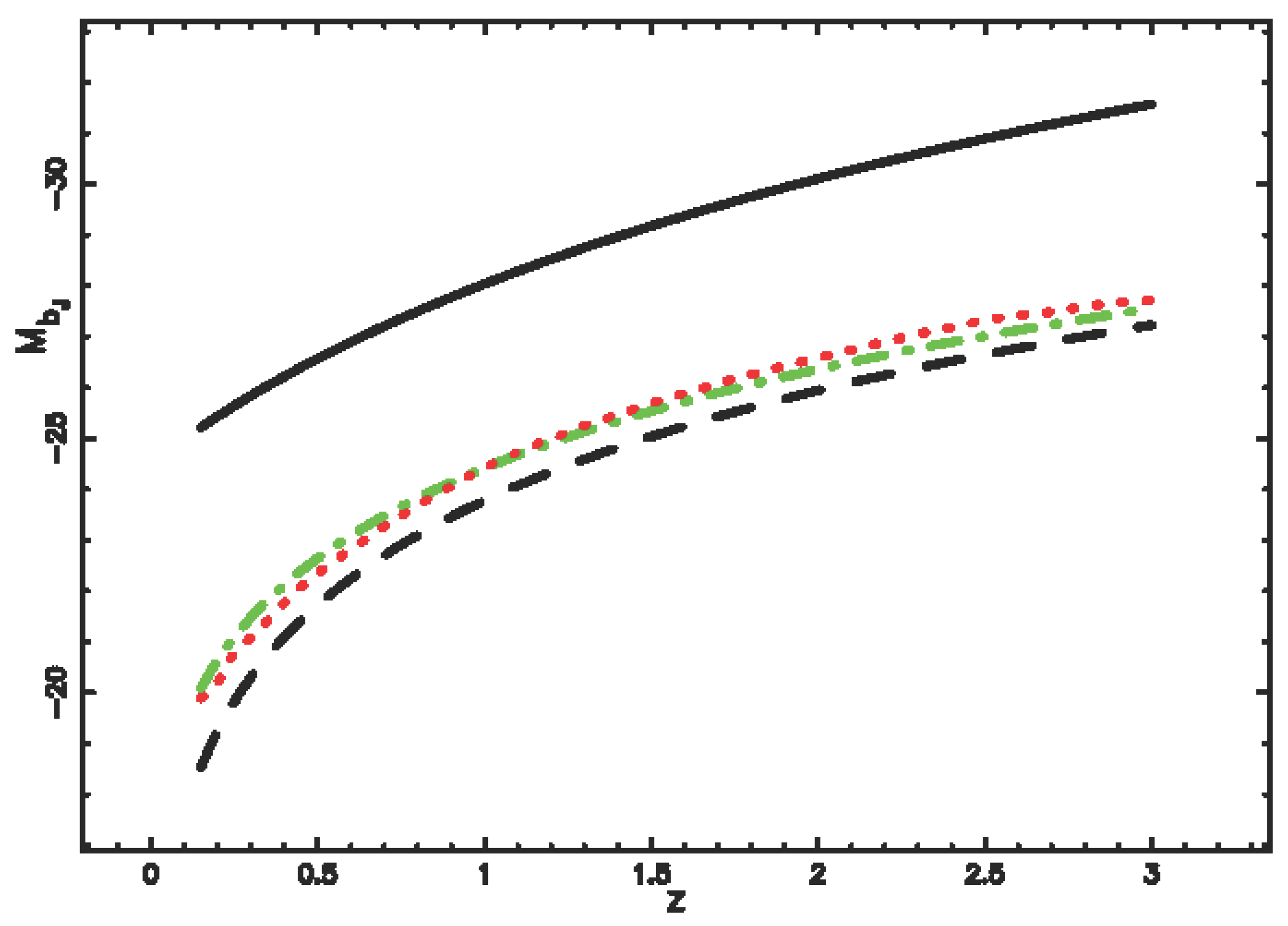
4.3. The Luminosity Function for QSOs
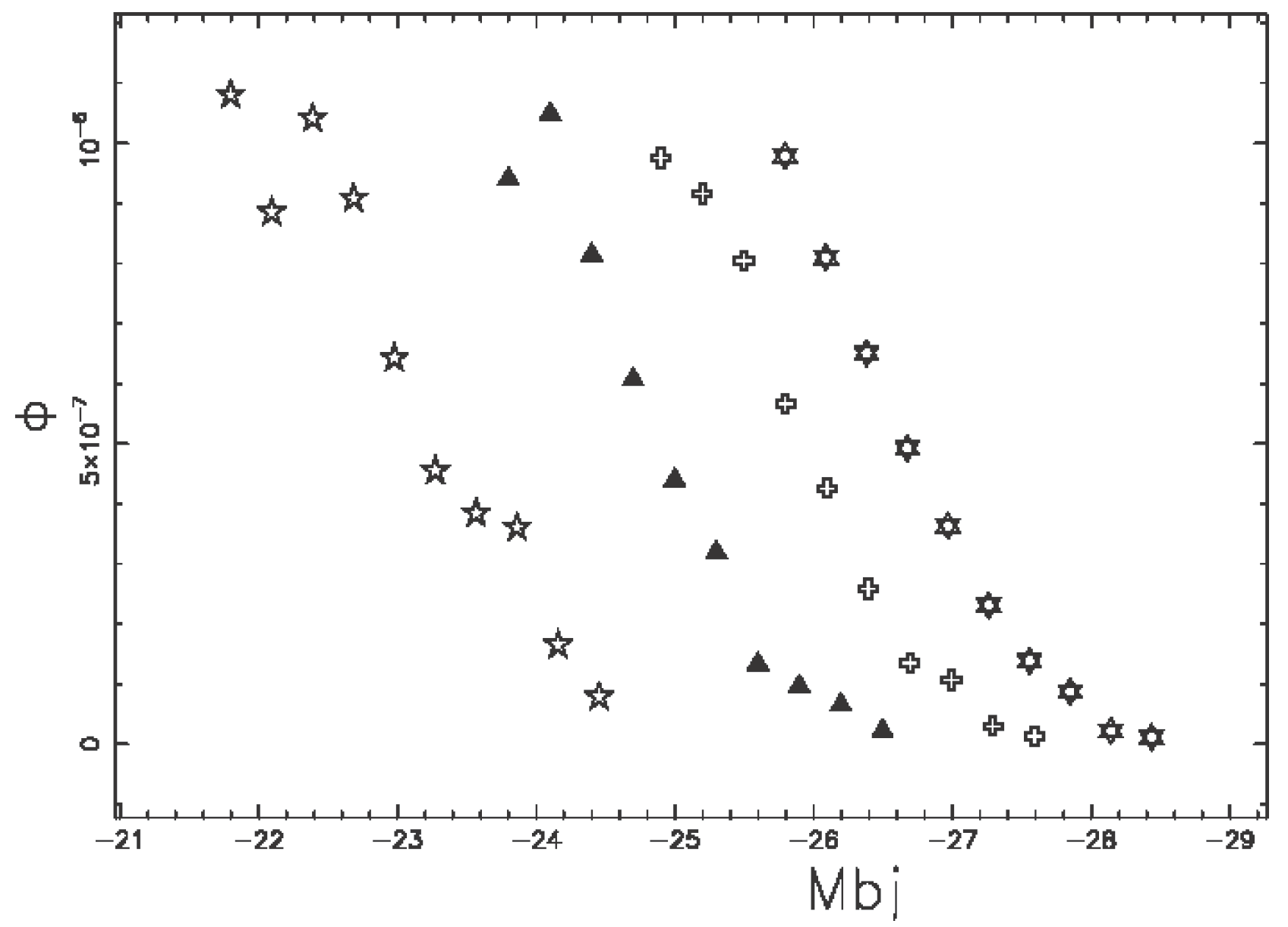
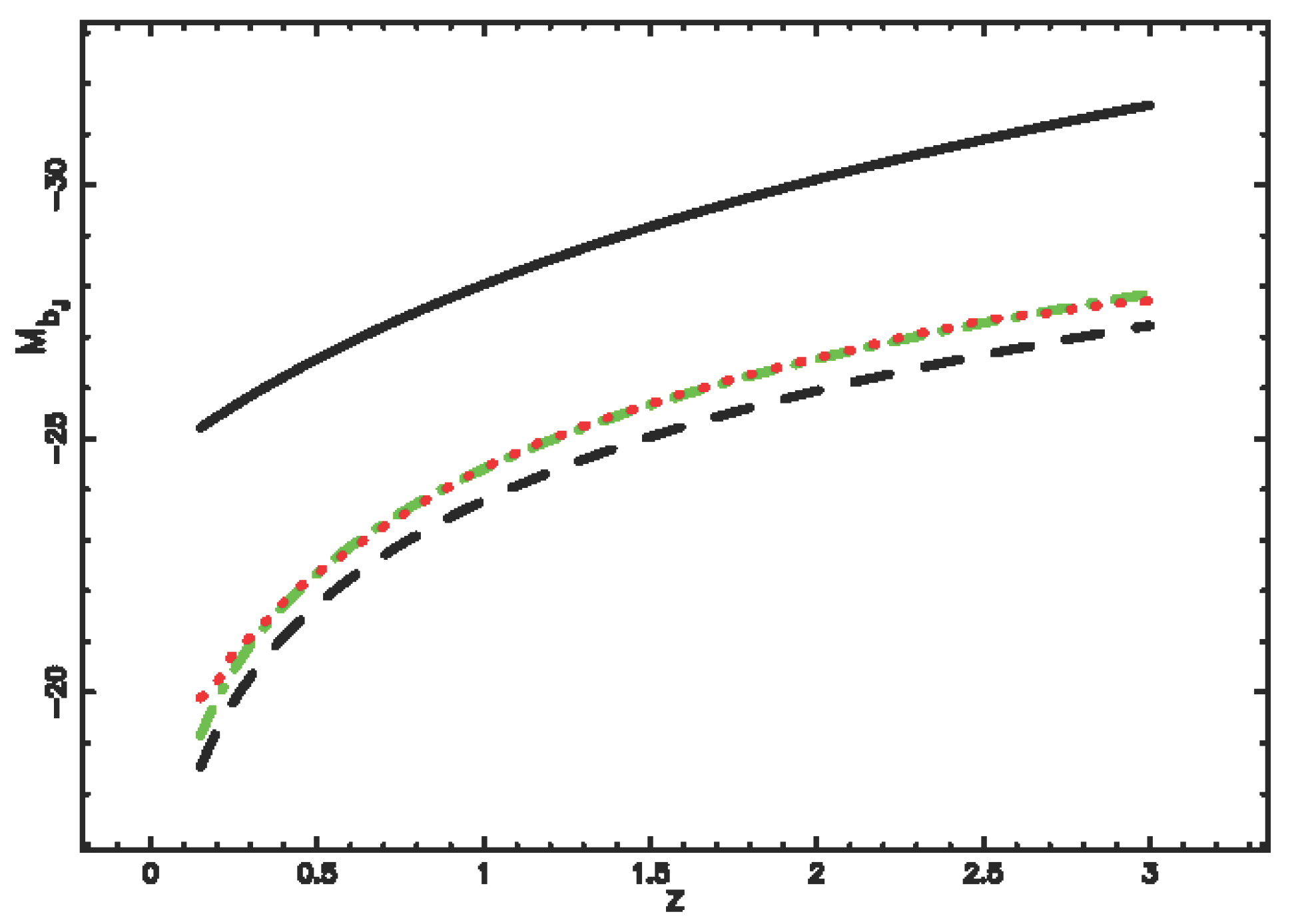
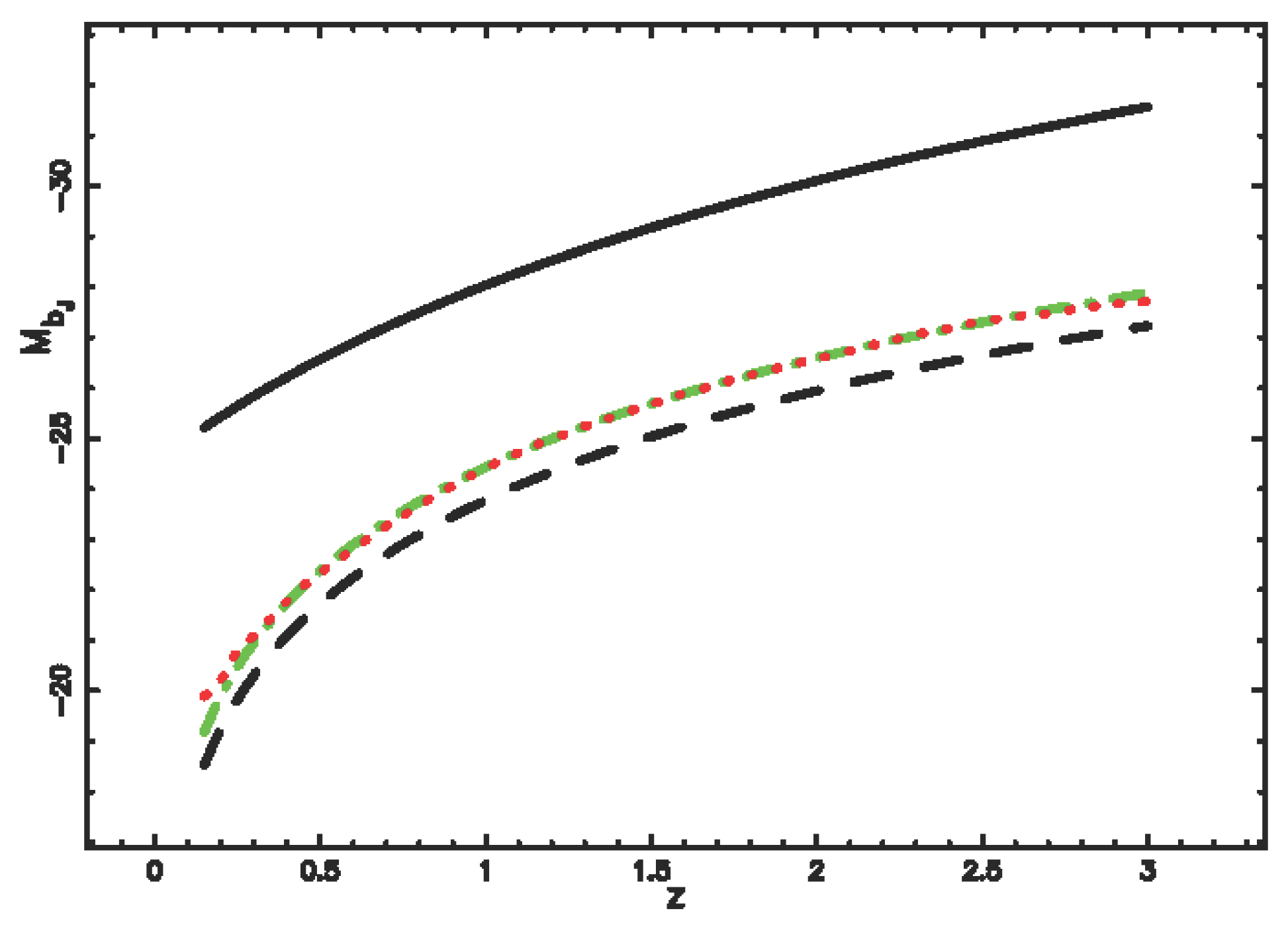
4.4. Evolutionary Effects
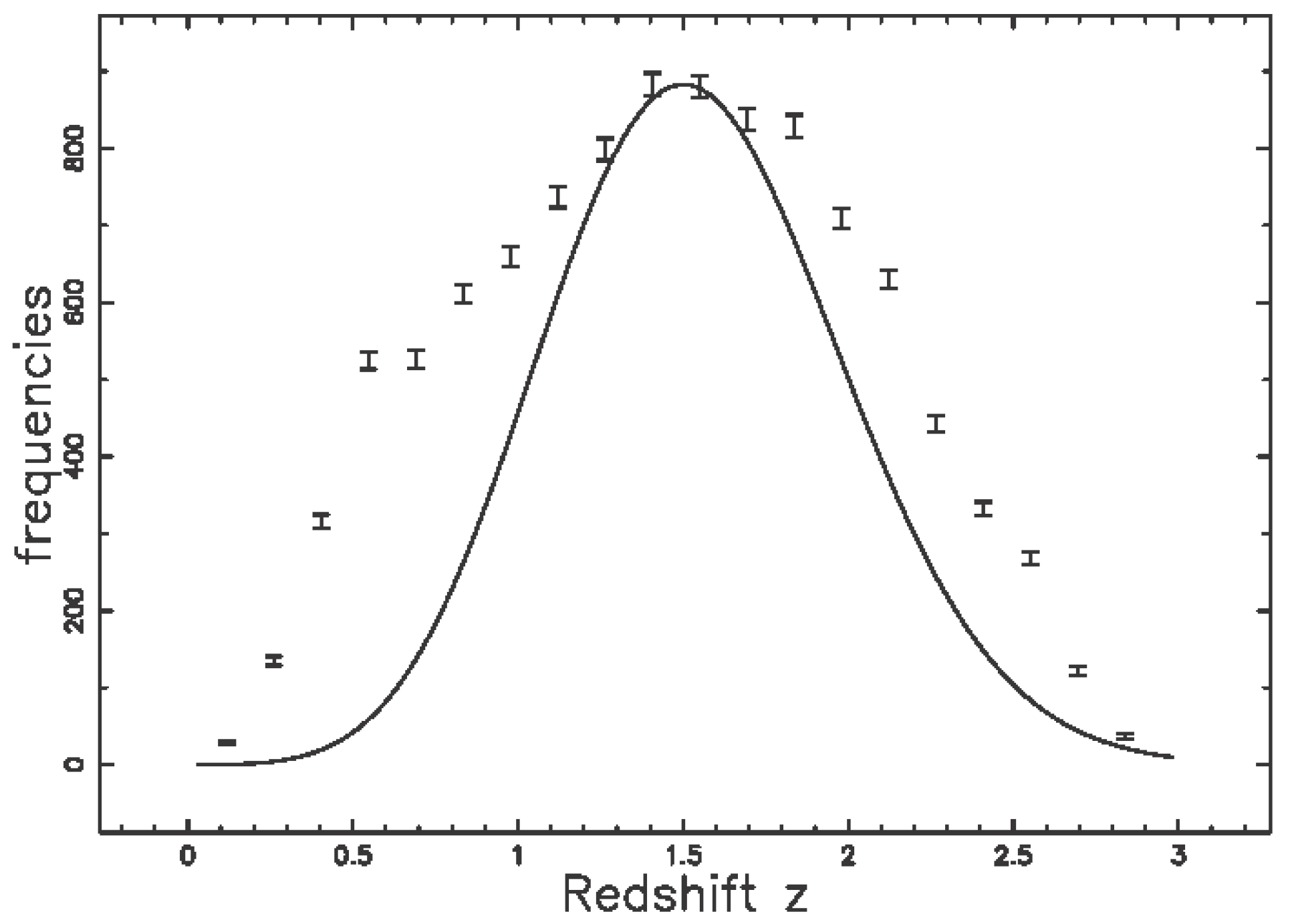
4.5. The Photometric Maximum
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schechter, P. An analytic expression for the luminosity function for galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1976, 203, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.J.; Hewett, P.C.; Osmer, P.S. A wide-field multicolor survey for high-redshift quasars, Z greater than or equal to 2.2. 3: The luminosity function. Astrophys. J. 1994, 421, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, P.; Miller, L. The UVX quasar optical luminosity function and its evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 293, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, S.P.; Phillipps, S. Is the Luminosity Distribution of Field Galaxies Really Flat? Astrophys. J. 1996, 469, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.F.; McIntosh, D.H.; Katz, N.; Weinberg, M.D. The Optical and Near-Infrared Properties of Galaxies. I. Luminosity and Stellar Mass Functions. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2003, 149, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, M.R.; Lupton, R.H.; Schlegel, D.J.; Strauss, M.A.; Brinkmann, J.; Fukugita, M.; Loveday, J. The Properties and Luminosity Function of Extremely Low Luminosity Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2005, 631, 208–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaniz, J.S.; Lima, J.A.S. Galaxy Luminosity Function: A New Analytic Expression. Braz. J. Phys. 2004, 34, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croom, S.M.; Smith, R.J.; Boyle, B.J.; Shanks, T.; Miller, L.; Outram, P.J.; Loaring, N.S. The 2dF QSO Redshift Survey—XII. The spectroscopic catalogue and luminosity function. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 349, 1397–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, C.S.; Muller, K.E. Properties of doubly-truncated gamma variables. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2000, 29, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaninetti, L. The Luminosity Function of Galaxies as Modeled by a Left Truncated Beta Distribution. Int. J. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 4, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaninetti, L. On the Number of Galaxies at High Redshift. Galaxies 2015, 3, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaninetti, L. Pade Approximant and Minimax Rational Approximation in Standard Cosmology. Galaxies 2016, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, B.J.; Shanks, T.; Peterson, B.A. The evolution of optically selected QSOs. II. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1988, 235, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.C. The luminosity function of quasars. Astrophys. J. 1995, 438, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Kasai, M. An Analytical Approximation of the Luminosity Distance in Flat Cosmologies with a Cosmological Constant. Prog. Theor. Phys. 2012, 127, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, A.; Řípa, J. A curious relation between the flat cosmological model and the elliptic integral of the first kind. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 556, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etherington, I.M.H. On the Definition of Distance in General Relativity. Philos. Mag. 1933, 15, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN. The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, A.R. How many cosmological parameters? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 351, L49–L53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlowski, W.; Szydowski, M. Constraints on Dark Energy Models from Supernovae. In 1604-2004: Supernovae as Cosmological Lighthouses; Turatto, M., Benetti, S., Zampieri, L., Shea, W., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 342, pp. 508–516. [Google Scholar]
- Olver, F.W.J.; Lozier, D.W.; Boisvert, R.F.; Clark, C.W. NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, B.J.; Shanks, T.; Croom, S.M.; Smith, R.J.; Miller, L.; Loaring, N.; Heymans, C. The 2dF QSO Redshift Survey—I. The optical luminosity function of quasi-stellar objects. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 317, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G.T.; Strauss, M.A.; Fan, X.; Hall, P.B.; Jester, S.; Schneider, D.P.; Vanden Berk, D.E.; Stoughton, C.; Anderson, S.F.; Brunner, R.J.; et al. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Quasar Survey: Quasar Luminosity Function from Data Release 3. Astron. J. 2006, 131, 2766–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, N.P.; McGreer, I.D.; White, M.; Richards, G.T.; Myers, A.D.; Palanque-Delabrouille, N.; Strauss, M.A.; Anderson, S.F.; Shen, Y.; Brandt, W.N.; et al. The SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: The Quasar Luminosity Function from Data Release Nine. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.A. Optical Luminosity Function of Quasi Stellar Objects. Am. J. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisotzki, L. Quasar spectra and the K correction. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 353, 861–866. [Google Scholar]
- Croom, S.M.; Richards, G.T.; Shanks, T.; Boyle, B.J.; Strauss, M.A.; Myers, A.D.; Nichol, R.C.; Pimbblet, K.A.; Ross, N.P.; Schneider, D.P.; et al. The 2dF-SDSS LRG and QSO survey: The QSO luminosity function at z between 0.4 and 2.6. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 399, 1755–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmquist, K. A study of the stars of spectral type A. Lund Medd. Ser. II 1920, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Malmquist, K. On some relations in stellar statistics. Lund Medd. Ser. I 1922, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Behr, A. Zur Entfernungsskala der extragalaktischen Nebel. Astron. Nachr. 1951, 279, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Carrera, F.J. An improved method of constructing binned luminosity functions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 311, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, Y.; Bahcall, J.N. On the simultaneous analysis of several complete samples—The V/Vmax and Ve/Va variables, with applications to quasars. Astrophys. J. 1980, 235, 694–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eales, S. Direct construction of the galaxy luminosity function as a function of redshift. Astrophys. J. 1993, 404, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.S.; Colless, M.; Broadhurst, T.; Heyl, J.; Glazebrook, K. Autofib Redshift Survey—I. Evolution of the galaxy luminosity function. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 280, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, J. A graphical analysis of the systematic error of classical binned methods in constructing luminosity functions. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2013, 345, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.; Percival, W.J.; Peacock, J.A.; Norberg, P.; Baugh, C.M.; Frenk, C.S.; Baldry, I.; Bland-Hawthorn, J.; Bridges, T.; Cannon, R.; et al. The 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey: power-spectrum analysis of the final data set and cosmological implications. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 362, 505–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. |
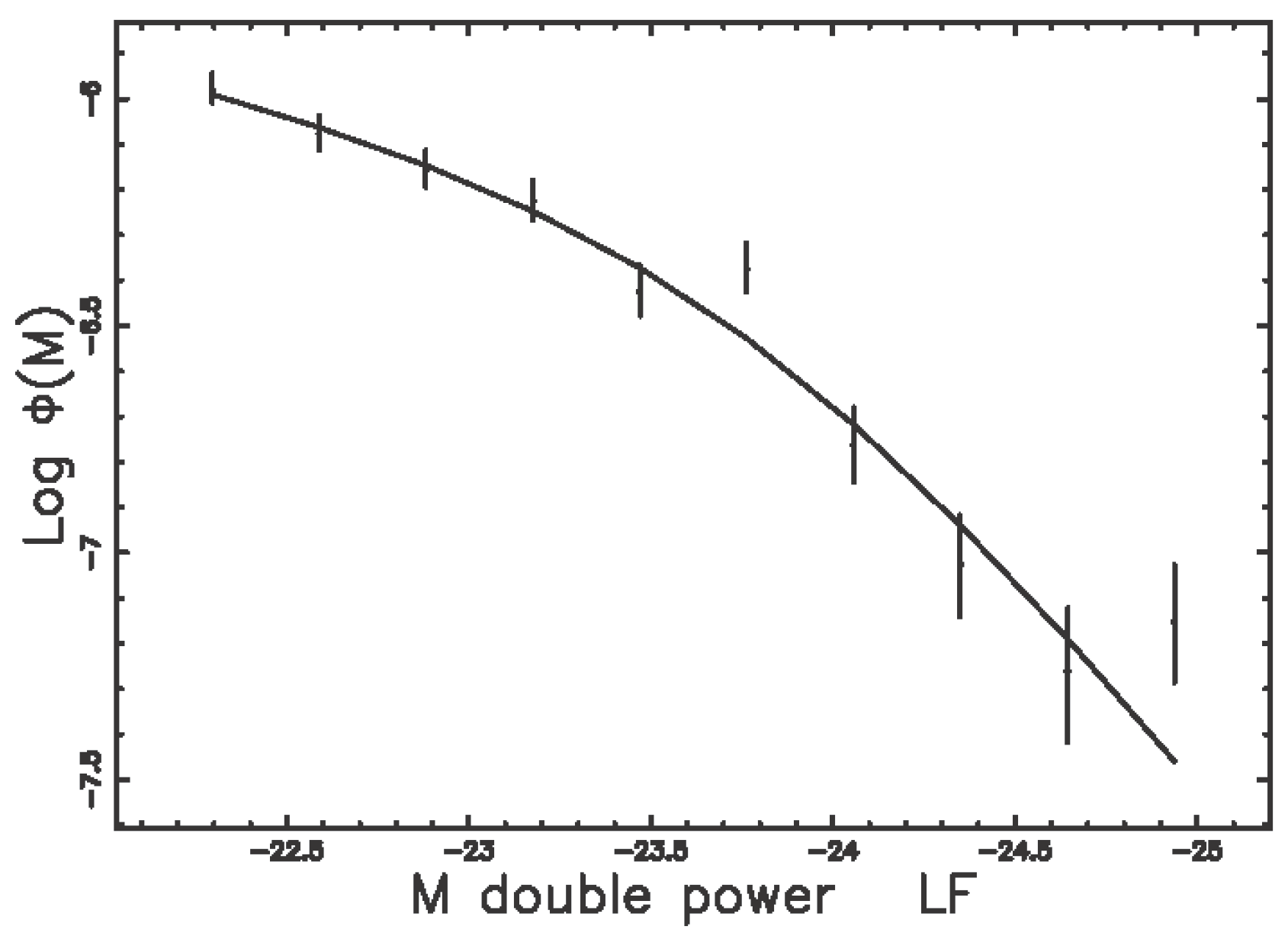
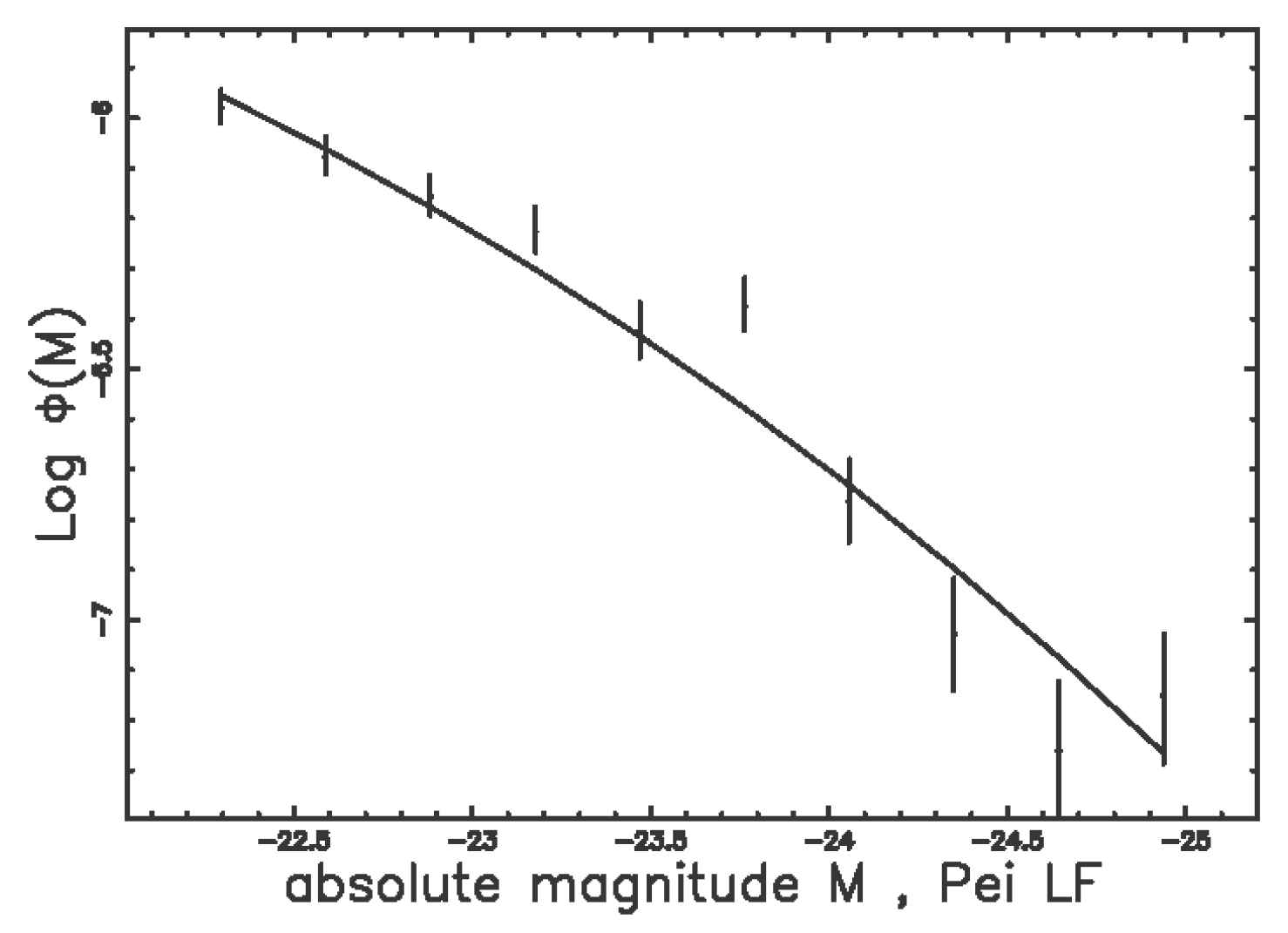
| Q | AIC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –24.93 | –23.28 | –22.29 | 3.38 × | –0.97 | 12.89 | 2.57 | 0.024 | 22.89 |
| Q | AIC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –23.75 | 8.85 × | –1.37 | –10.49 | 1.49 | 0.162 | 16049 |
| Q | AIC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –23.82 | 5.44 × | –3.57 | –1.48 | 9.44 | 1.57 | 0.15 | 17.44 |
| Q | AIC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –16.47 | 3.68 × | 0.924 | 14.4 | 2.05 | 0.044 | 20.40 |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaninetti, L. A Left and Right Truncated Schechter Luminosity Function for Quasars. Galaxies 2017, 5, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5020025
Zaninetti L. A Left and Right Truncated Schechter Luminosity Function for Quasars. Galaxies. 2017; 5(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaninetti, Lorenzo. 2017. "A Left and Right Truncated Schechter Luminosity Function for Quasars" Galaxies 5, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5020025
APA StyleZaninetti, L. (2017). A Left and Right Truncated Schechter Luminosity Function for Quasars. Galaxies, 5(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5020025





