Multi-TeV Gamma Rays from GRB 221009A: Challenges for Emission Mechanisms, EBL Opacity, and Fundamental Physics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observational Overview of GRB 221009A
2.1. Prompt Gamma-Ray Emission
2.2. Multi-Wavelength Afterglow
2.3. Very-High-Energy Gamma-Ray Emission
3. The Multi-TeV Emission Puzzle: EBL Attenuation and Afterglow Models
3.1. Extragalactic Background Light and Gamma-Ray Attenuation
3.2. Standard Afterglow Models and Their Limitations
4. Theoretical Explanations
4.1. Challenge I: Production of Multi-TeV Gamma Rays
4.1.1. Limitations of Standard Emission Models
4.1.2. Multi-Zone Synchrotron Self-Compton Emission
- A compact, highly magnetized zone that produces the observed X-ray emission via synchrotron radiation
- A larger, less magnetized zone where electrons upscatter their own synchrotron photons to TeV energies via the SSC process
- Two distinct regions with typical sizes of and separated by distance
- Two converging shells of radius and
- Multiple compact regions (of typical size ) with strong magnetic field embedded within a larger zone of size
4.1.3. Reverse Shock Emission
- Episode I: Where external inverse-Compton (EIC) dominates due to strong prompt emission
- Episode II: Where proton synchrotron becomes more prominent as prompt emission fades
4.1.4. Pair-Balance Synchrotron Self-Compton Emission
4.1.5. Stochastic Turbulent Acceleration and a Second Electron Component
4.2. Challenge II: Propagation of Multi-TeV Gamma Rays
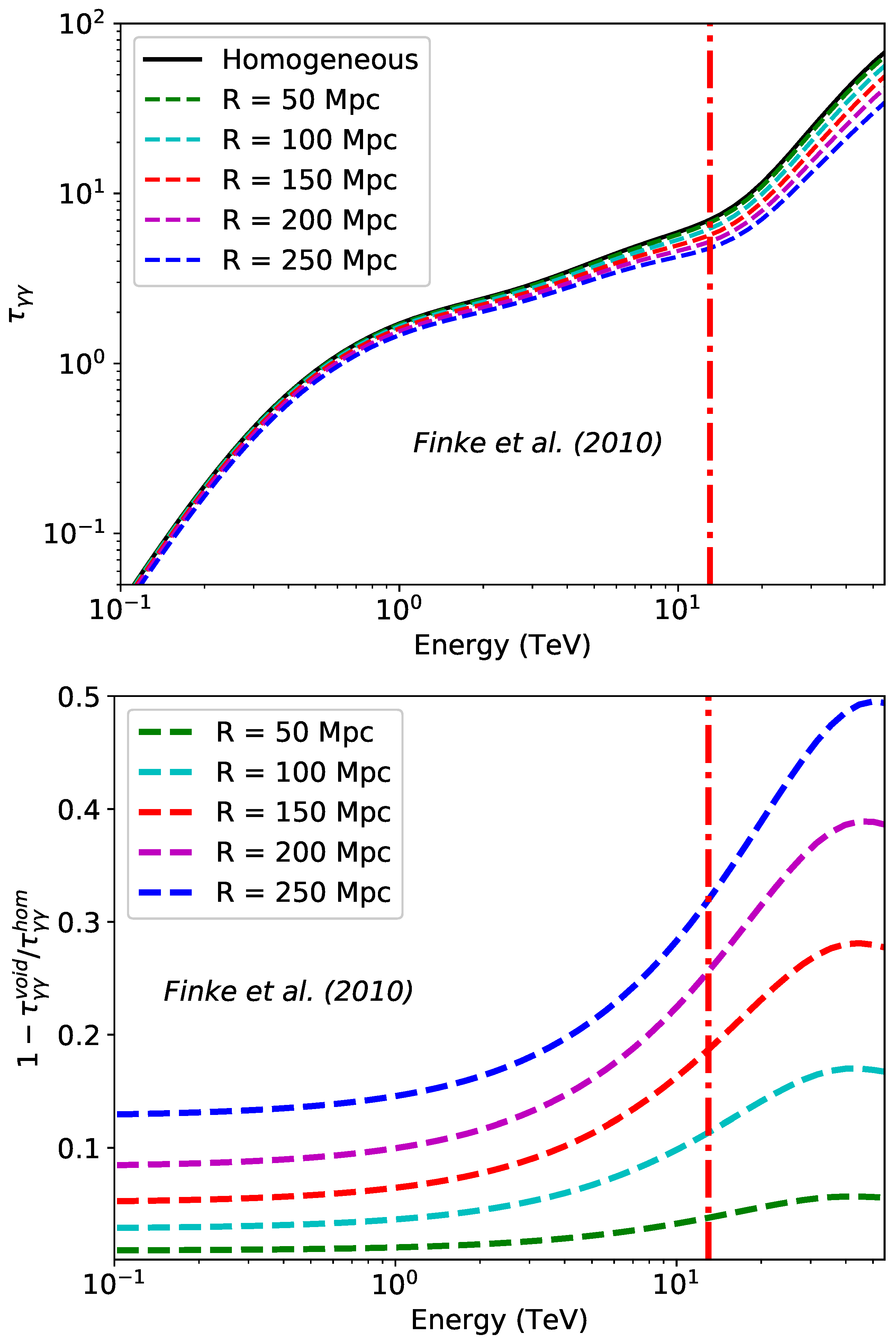
4.2.1. Reduced EBL Density Due to Cosmic Voids
4.2.2. New Physics: Axion-Like Particles
4.2.3. New Physics: Lorentz Invariance Violation
4.2.4. New Physics: Heavy Sterile Neutrino Decay
4.2.5. Ultrahigh-Energy Cosmic Ray Cascades
- UHECR Acceleration: Protons are accelerated to energies of – eV in the GRB jet, particularly at the energy dissipation radius during the prompt emission phase. The energy dissipation radius of GRB 221009A is estimated to be [19]:where the variability timescale is measured as s [19], is the bulk Lorentz factor, and c is the speed of light.
- Maximum Energy of Accelerated Protons: By comparing the dynamic timescale , the proton synchrotron cooling timescale , and the photomeson production timescale with the proton acceleration timescale , He et al. [19] derived the maximum energy of accelerated protons as:where is the acceleration efficiency, is the gamma-ray luminosity in units of erg/s, and are the energy fractions in electrons and magnetic fields in units of and , respectively, and is the variability timescale in units of s.
- UHECR Propagation: These UHECRs propagate through intergalactic space, where they interact with background photon fields—primarily the cosmic microwave background (CMB) and the EBL—through two dominant processes [17]:
- Bethe-Heitler pair production:
- Photopion production: or
- Electromagnetic Cascade Development: The secondary particles produced in these interactions initiate electromagnetic cascades. High-energy photons from decay undergo pair production on the EBL (), while the resulting electrons and positrons upscatter background photons through inverse Compton scattering (). This cascade process continues until photon energies fall below the pair-production threshold [17].
5. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burns, E.; Svinkin, D.; Fenimore, E.; Kann, D.A.; Fernández, J.F.A.; Frederiks, D.; Hamburg, R.; Lesage, S.; Temiraev, Y.; Tsvetkova, A. GRB 221009A: The BOAT. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 946, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, B.; Troja, E.; Ryan, G.; Beniamini, P.; van Eerten, H.; Granot, J.; Dichiara, A.; Ricci, R.; Lipunov, V.; Gill, R.; et al. A Structured Jet Explains the Extreme GRB 221009A. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z. et al. [LHAASO Collaboration] A tera–electron volt afterglow from a narrow jet in an extremely bright gamma-ray burst. Science 2023, 380, adg9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The LHAASO Collaboration. Very High-Energy Gamma-Ray Emission Beyond 10 TeV from GRB 221009A. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malesani, D.B.; Levan, A.J.; Izzo, L.; de Ugarte Postigo, A.; Ghirlanda, G.; Heintz, K.E.; Kann, D.A.; Lamb, G.P.; Palmerio, J.; Salafia, O.S.; et al. The Brightest GRB Ever Detected: GRB 221009A as a Highly Luminous Event at z = 0.151. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 670, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; van der Horst, A.J.; Bright, J.S.; Leung, J.K.; Anderson, G.E.; Fender, R.; Fernandez, J.F.A.; Bremer, M.; Chandra, P.; Dobie, D.; et al. Rocking the BOAT: The Ups and Downs of the Long-Term Radio Light Curve for GRB 221009A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 533, 4435–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ramírez, R.; Lang, R.G.; Pozanenko, A.; Martínez-Huerta, H.; Hu, Y.-D.; Pandey, S.B.; Gupta, R.; Ror, A.K.; Zhang, B.-B.; Caballero-García, M.D.; et al. Early photometric and spectroscopic observations of the extraordinarily bright INTEGRAL-detected GRB 221009A. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 692, A3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, H.; Nakajima, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Soejima, Y.; Mihara, T.; Kawamuro, T.; Yamada, S.; Ueda, Y.; Shidatsu, M.; et al. MAXI/GSC Detection of the new X-ray transient Swift J1913.1+1946. Astron. Telegr. 2022, 15651. Available online: https://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?read=15651 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Franceschini, A.; Rodighiero, G.; Vaccari, M. The Extragalactic Optical-IR Background and its Evolution. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 487, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.D.; Razzaque, S.; Dermer, C.D. Modeling the Extragalactic Background Light from Stars and Dust. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Primack, J.R.; Rosario, D.J.; Prada, F.; Gilmore, R.C.; Faber, S.M.; Koo, D.C.; Somerville, R.S.; Pérez-Torres, M.A.; Pérez-González, P.; et al. Extragalactic Background Light Inferred from AEGIS Galaxy SED-type Fractions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 2556–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.D.; Razzaque, S. Possible Evidence for Lorentz Invariance Violation in Gamma-Ray Burst 221009A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 942, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakar, E.; Ando, S.; Sari, R. Klein-Nishina Effects on Optically Thin Synchrotron and Synchrotron Self-Compton Spectrum. Astrophys. J. 2009, 703, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Razzaque, S.; Böttcher, M.; Finke, J.D.; Domínguez, A. Influence of Cosmic Voids on the Propagation of TeV Gamma-Rays and the Puzzle of GRB 221009A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 532, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangulyan, D.; Taylor, A.M.; Aharonian, F. The Formation of Hard Very High Energy Spectra from Gamma-ray Burst Afterglows via Two-zone Synchrotron Self-Compton Emission. Astrophys. J. 2023, 947, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Murase, K.; Mészáros, P. External Inverse-Compton and Proton Synchrotron Emission from the Reverse Shock as the Origin of VHE Gamma Rays from the Hyper-bright GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 947, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Razzaque, S. Ultrahigh-Energy Cosmic-Ray Signature in GRB 221009A. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 670, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Razzaque, S.; Mirabal, N.; Omodei, N.; Murase, K.; Martinez-Castellanos, I. Tracing the Imprints of Large-Scale Magnetized Structure on γ Rays from GRB 221009A. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.15890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.-N.; Zhang, B.-T.; Fan, Y.-Z. A Detectable Ultra-high-energy Cosmic-Ray Outburst from GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. 2023, 963, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Galanti, G.; Roncadelli, M. Relevance of axionlike particles for very-high-energy astrophysics. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 105030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirizzi, A.; Raffelt, G.G.; Serpico, P.D. Signatures of axionlike particles in the spectra of TeV gamma-ray sources. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanti, G.; Nava, L.; Roncadelli, M.; Tavecchio, F.; Bonnoli, G. Observability of the Very-High-Energy Emission from GRB 221009A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 251001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troitsky, S.V. Parameters of axion-like particles required to explain high-energy photons from GRB 221009A. JETP Lett. 2022, 116, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baktash, A.; Horns, D.; Meyer, M. Interpretation of multi-TeV photons from GRB221009A. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2210.07172. [Google Scholar]
- Brdar, V.; Li, Y.-F. Neutrino origin of LHAASO’s 18 TeV GRB221009A photon. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 839, 137763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.Y.; Trautner, A. GRB 221009A Gamma Rays from the Radiative Decay of Heavy Neutrinos? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiks, D.; Svinkin, D.; Lysenko, A.L.; Molkov, S.; Tsvetkova, A.; Ulanov, M.; Ridnaia, A.; Lutovinov, A.A.; Lapshov, I.; Tkachenko, A.; et al. Properties of the Extremely Energetic GRB 221009A from Konus-WIND and SRG/ART-XC Observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 949, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, S.; Veres, P.; Briggs, M.S.; Goldstein, A.; Kocevski, D.; Burns, E.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Bhat, P.N.; Huppenkothen, D.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. INTEGRAL Observations of GRB 221009A. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 684, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration. Absence of High-Energy Neutrinos Associated with GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 954, L16. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, S.; Albert, A.; Alshamsi, M.; Garre, S.A.; Ambrosone, A.; Ameli, F.; Andre, M.; Androutsou, E.; Anguita, M.; Aphecetche, L.; et al. Search for Neutrinos from GRB 221009A with KM3NeT/ARCA & ORCA. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 3, 011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres, P.; Burns, E.; Bissaldi, E.; Lesage, S.; Roberts, O.; Fermi GBM Team. GRB 221009A: Fermi GBM Detection of an Extraordinarily Bright GRB. GRB Coordinates Network, Circular 32636. 2022. Available online: https://gcn.nasa.gov/circulars/32636 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Lesage, S.; Veres, P.; Briggs, M.S.; Goldstein, A.; Kocevski, D.; Burns, E.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Bhat, P.N.; Huppenkothen, D.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. Fermi-GBM Discovery of GRB 221009A: An Extraordinarily Bright GRB from Onset to Afterglow. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 952, L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Kennea, J.A.; Dichiara, S.; Kobayashi, K.I.; Iwakiri, W.B.; Beardmore, A.P.; Evans, P.A.; Heinz, S.; Lien, A.; Oates, S.R.; et al. GRB 221009A: Discovery of an Exceptionally Rare Nearby and Energetic Gamma-Ray Burst. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 946, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.J.; Ren, J.; He, H.N.; Yang, Y.P.; Wei, D.M.; Dai, Z.G.; Zhang, B.T. A Novel Model for the MeV Emission Line in GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 953, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Feng, H.; Liu, T. A Neutron Capture Explanation for the 10 MeV Emission Line Seen in GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2025, 983, L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipunov, V.; Gorbovskoy, E.; Zhirkov, K.; Tyurina, N.; Balanutsa, P.; Kuznetsov, A.; Vlasenko, D.; Antipov, G.; Zimnukhov, D.; Senik, V.; et al. GRB 221009A: Global MASTER-Net OT Detection. GRB Coordinates Network, Circular 32634. 2022. Available online: https://gcn.nasa.gov/circulars/32634 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Xiong, S.-L.; Li, C.-K.; Gao, H.; Xue, W.-C.; Liu, J.-C.; Wang, C.-W.; Tan, W.-J.; Peng, W.-X.; et al. Observation of GRB 221009A Early Afterglow in X-Ray/Gamma-Ray Energy Bands. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 962, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, R.Y.; Wang, X.Y. GRB 221009A: Revealing a Hidden Afterglow during the Prompt Emission Phase with Fermi-GBM Observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 956, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Z.P.; Liu, R.Y.; Zou, Y.C.; Li, Z.; Dai, Z.G. Implication from GRB 221009A: Can TeV emission come from the GRB prompt phase? Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2023, 66, 129511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarratana, S.; Salafia, O.S.; Giroletti, M.; Ghirlanda, G.; Rhodes, L.; Atri, P.; Marcote, B.; Yang, J.; An, T.; Anderson, G.; et al. The expansion of the GRB 221009A afterglow. Astronomy Astrophys. 2024, 690, A74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Gao, H.-X.; Xu, F.; Li, B.; Sun, T.-R.; Wang, A.-L.; Xu, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Yang, J.; et al. Spreading and multi-wavelength emissions of an ultra-narrow relativistic jet from GRB 221009A. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.17765. [Google Scholar]
- Tak, D.; Uhm, Z.L.; Paek, G.S.H.; Im, M.; Arimoto, M.; Choi, H.; Kim, S.; Omodei, N.; Racusin, J.; Urata, Y.; et al. Multiwavelength Afterglow Analysis of GRB 221009A: Unveiling the Evolution of a Cooling Break in a Wind-like Medium. Astrophysical J. 2025, 978, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, T.; Alexander, K.D.; Margutti, R.; Eftekhari, T.; Chornoc, R.; Berger, E.; Cendes, Y.; Duerr, A.; Perley, D.A.; Ravasio, M.E.; et al. Radio GeV Afterglow GRB 221009A. Astrophysical J. Lett. 2023, 946, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Observation of Inverse Compton Emission from a Long Gamma-Ray Burst. Nature 2019, 575, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangulyan, D.; Aharonian, F.; Taylor, A.M. Naked Forward Shock Seen in the TeV Afterglow Data of GRB 221009As. Astrophys. J. 2024, 966, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Benkhali, F.A.; Aschersleben, J.; Ashkar, H.; Backes, M.; Baktash, A.; Martins, V.B.; Batzofin, R.; Becherini, Y.; Berge, D.; et al. H.E.S.S. Follow-up Observations of GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 946, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, O. et al. [CTA–LST Collaboration] GRB 221009A Observations with LST-1 at VHE Gamma Rays. POS Proc. Sci. 2024, 464, 58. Available online: https://air.uniud.it/handle/11390/1289305 (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Dzhappuev, D.D.; Afashokov, Y.Z.; Dzaparova, I.M.; Dzhatdoev, T.A.; Gorbacheva, E.A.; Karpikov, I.S.; Khadzhiev, M.M.; Klimenko, N.F.; Kudzhaev, A.U.; Kurenya, A.N.; et al. Swift J1913.1+1946/GRB 221009A: Detection of a 250-TeV photon-like air shower by Carpet-2. Astron. Telegr. 2022, 15669. Available online: https://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?read=15669 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Dzhappuev, D.D.; Dzaparova, I.M.; Dzhatdoev, T.A.; Gorbacheva, E.A.; Karpikov, I.S.; Khadzhiev, M.M.; Klimenko, N.F.; Kudzhaev, A.U.; Kurenya, A.N.; Lidvansky, A.S.; et al. Carpet–3 detection of a photonlike air shower with estimated primary energy above 100 TeV in a spatial and temporal coincidence with GRB 221009A. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 111, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana-Lopez, A.; Domínguez, A.; Pérez-González, P.G.; Finke, J.D.; Ajello, M.; Primack, J.R.; Paliya, V.S.; Desai, A. An observational determination of the evolving extragalactic background light from the multiwavelength HST/CANDELS survey in the Fermi and CTA era. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 507, 5144–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biteau, J.; Prandini, E.; Costamante, L.; Lemoine, M.; Padovani, P.; Pueschel, E.; Resconi, E.; Tavecchio, F.; Taylor, A.; Zech, A. Progress in Unveiling Extreme Particle Acceleration in Persistent Astrophysical Jets. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, P.; Rees, M.J. Gamma-Ray Bursts: Multiwaveband Spectral Predictions for Blast Wave Models. Astrophys. J. 1994, 430, L93–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kumar, P. Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts and Relativistic Jets. Phys. Rep. 2015, 561, 1–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M.; Pelletier, G. On the origin of very-high-energy photons in astrophysics: A short introduction to acceleration and radiation physics. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2015, 16, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M.; Rax, J.M.; Pelletier, G. On the origin of the Crab Nebula’s gamma-ray flares: A short overview. J. Plasma Phys. 2019, 85, 175850301. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.-H.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, R.-Y.; Zhang, B. A Narrow Uniform Core with a Wide Structured Wing: Modeling the TeV and Multi-wavelength Afterglows of GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. 2024, 966, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derishev, E.; Piran, T. The contemporaneous phase of GRB afterglows—application to GRB 221009A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 530, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.W.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Asano, K.; Lemoine, M. Interpreting the multi-TeV emission from GRB 221009A with a second electron component accelerated by turbulence in the jet. Astrophys. J. 2025, 989, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Böttcher, M. EBL Inhomogeneity and Hard-Spectrum Gamma-Ray Sources. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudoda, A.M.; Faltenbacher, A. Effects of spatial fluctuations in the extragalactic background light on hard gamma-ray spectra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 2896–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furniss, A.; Amador, J.N.; Hervet, O.; Jackson, O.; Williams, D.A. A Study on the Line of Sight to Galaxies Detected at Gamma-Ray Energies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2025, 980, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, B.-Q. Axion-photon conversion of GRB221009A. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Takahashi, F.; Yamada, M.; Yin, W. Axion dark matter from first-order phase transition, and very high energy photons from GRB 221009A. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 839, 137824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, D.A.; Hernández-Cadena, S.; González, M.M.; Pratts, A.; Alfaro, R.; Serna-Franco, J. GRB 221009A: Spectral Signatures Based on ALPs Candidates. Astrophys. J. 2024, 966, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitsky, S. Towards a model of photon-axion conversion in the host galaxy of GRB 221009A. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhatdoev, T.A.; Khalikov, E.V.; Kircheva, A.P.; Lyukshin, A.A. Electromagnetic cascade masquerade: A way to mimic γ-axion-like particle mixing effects in blazar spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenmüller, K. et al. [CAST Collaboration] A New Up. Limit Axion–photon Coupling Ext. CAST Run A Xe-Based Micromegas Detect. Physical Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 221005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisk Reynes, J.; Matthews, J.H.; Reynolds, C.S.; Russell, H.R.; Smith, R.N.; Marsh, M.C.D. New Constraints Light Axion-Like Part. Using Chandra Transm. Grating Spectrosc. Powerful Clust.-Hosted Quasar H1821+643. Monthly Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 510, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.; Glashow, S.L. High-Energy Tests of Lorentz Invariance. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 59, 116008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LHAASO Collaboration. Stringent Tests of Lorentz Invariance Violation from LHAASO Observations of GRB 221009A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 071501 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-M.; Bi, X.-J.; Yin, P.-F. Constraints on Lorentz invariance violation from the LHAASO observation of GRB 221009A. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 2024, 060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Böttcher, M. Lorentz Invariance Violation Effects on Gamma-Gamma Absorption and Compton Scattering. Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Cotter, G.; Backes, M.; Kasai, E.; Böttcher, M. Investigating the Lorentz invariance violation effect using different cosmological backgrounds. Class. Quantum Gravity 2024, 41, 015022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Asano, K.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Baring, M.G.; et al. A Limit on the Variation of the Speed of Light Arising from Quantum Gravity Effects. Nature 2009, 462, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-J.; Liao, W.; Liu, Z.-K.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhou, S. Invisible neutrino decays as origin of TeV gamma rays from GRB221009. JCAP 2023, 2023, 056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Spectral | Decay | Max E | Fit Remarks | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | Slope | (TeV) | |||
| LHAASO (obs.) | –2 | 13 | Baseline for comparison | [3,4] | |
| Two-zone SSC/stochastic accel. | –2 | 1– | Hardens late; better fit than one-zone SSC, underpredicts TeV; no published | [15,58] | |
| Reverse-shock proton synchrotron | Adds hard component; fit improves (KS test better than SSC-only) | [16,57] | |||
| UHECR cascade | – | — | Reproduces TeV tail, but requires extreme ; no formal fit | [17,19] | |
| Axion–photon reconversion | –2 (int.) | Suppresses EBL; improves by vs. SSC | [22,64] | ||
| Lorentz invariance violation (LIV) | –2 (int.) | Increases transparency; improves by ; | [12,71] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdalla, H. Multi-TeV Gamma Rays from GRB 221009A: Challenges for Emission Mechanisms, EBL Opacity, and Fundamental Physics. Galaxies 2025, 13, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13040095
Abdalla H. Multi-TeV Gamma Rays from GRB 221009A: Challenges for Emission Mechanisms, EBL Opacity, and Fundamental Physics. Galaxies. 2025; 13(4):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdalla, Hassan. 2025. "Multi-TeV Gamma Rays from GRB 221009A: Challenges for Emission Mechanisms, EBL Opacity, and Fundamental Physics" Galaxies 13, no. 4: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13040095
APA StyleAbdalla, H. (2025). Multi-TeV Gamma Rays from GRB 221009A: Challenges for Emission Mechanisms, EBL Opacity, and Fundamental Physics. Galaxies, 13(4), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13040095






