DKK1 and Its Receptors in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Promising Molecular Target
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. DKK and EAC
2.1. DKK Proteins Expression Levels in EAC
2.2. DKK Proteins Function in EAC
2.3. DKK Proteins as Serum Biomarkers in EAC
3. DKK Proteins in Correlation with Other Receptors Studied in EAC
3.1. EGFR—Her2
3.2. VEGF—VEGFR-2
3.3. c-MET
4. DKK as Immunomodulator
5. Clinical Trials of DKK1 in EAC
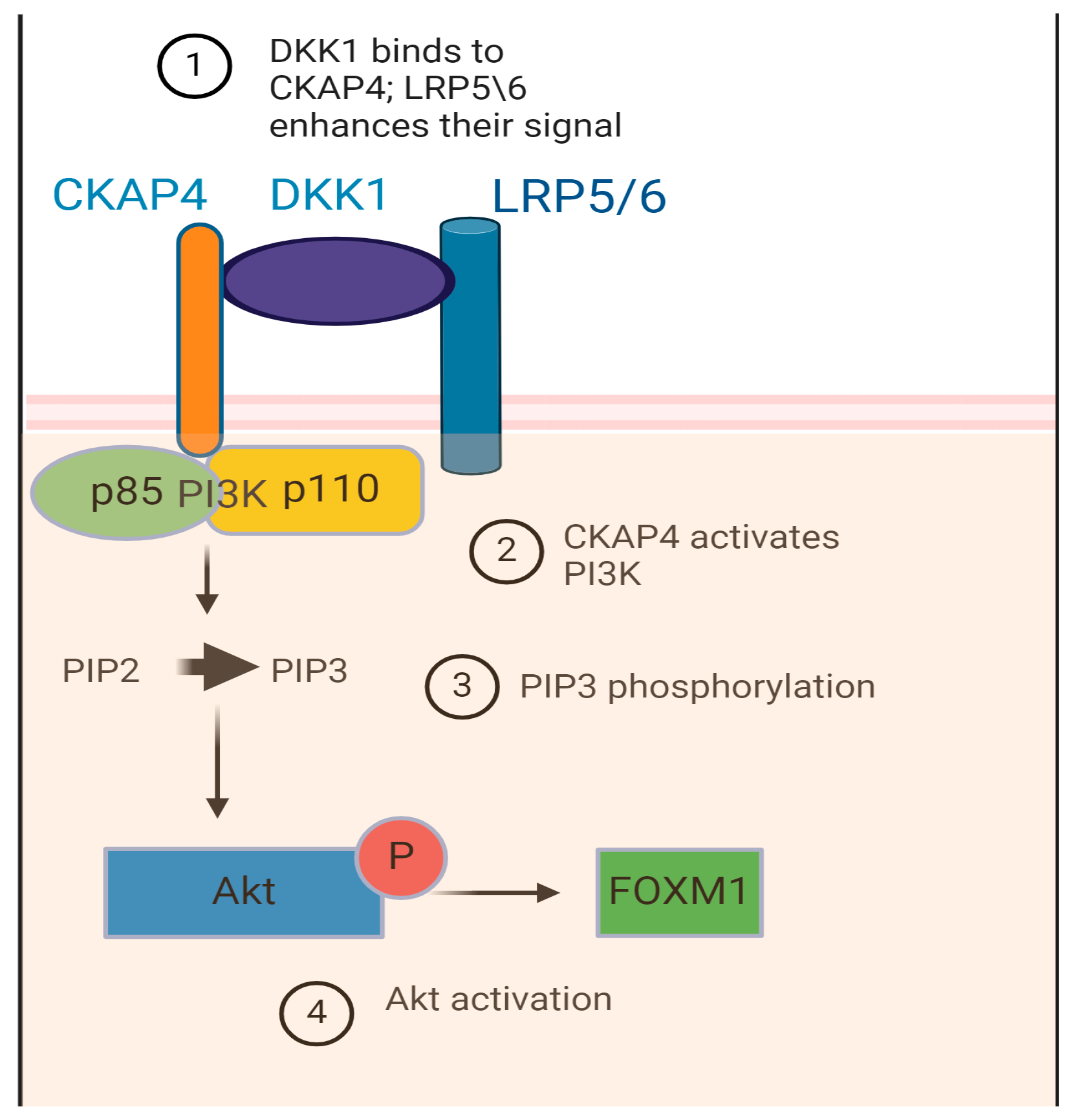
6. Potential Receptors for DKK-Mediated Function in EAC: A Novel Interpretation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, M.; Roshandel, G.; McCormack, V.; Malekzadeh, R. Current Status and Future Prospects for Esophageal Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- SEER; National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, M.D. Cancer Stat Facts: Esophageal Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/esoph.html (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Lyros, O.; Lamprecht, A.K.; Nie, L.; Thieme, R.; Götzel, K.; Gasparri, M.; Haasler, G.; Rafiee, P.; Shaker, R.; Gockel, I. Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) promotes tumor growth via Akt-phosphorylation and independently of Wnt-axis in Barrett’s associated esophageal adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 330–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Niehrs, C. Function and biological roles of the Dickkopf family of Wnt modulators. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7469–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Fumoto, K.; Shojima, K.; Nojima, S.; Osugi, Y.; Tomihara, H.; Eguchi, H.; Shintani, Y.; Endo, H.; Inoue, M.; et al. CKAP4 is a Dickkopf1 receptor and is involved in tumor progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2689–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Chu, H.Y.; Yu, S.; Yao, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.T. Drug Discovery of DKK1 Inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 847387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mazon, M.; Masi, D.; Carreau, M. Modulating Dickkopf-1: A Strategy to Monitor or Treat Cancer? Cancers 2016, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Xie, L.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhai, L.; Li, S.; Qin, X. Prognostic significance of dickkopf-1 overexpression in solid tumors: A meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 3145–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Qi, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y. Dickkopf-1 expression is down-regulated during the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence and correlates with reduced microvessel density and VEGF expression. Histopathology 2015, 67, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Gao, J.; Leng, X. Dickkopf-1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colon cancer cells and contributes to colon cancer suppression. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aguilera, Ó.; González-Sancho, J.M.; Zazo, S.; Rincón, R.; Fernández, A.F.; Tapia, O.; Canals, F.; Morte, B.; Calvanese, V.; Orgaz, J.L.; et al. Nuclear DICKKOPF-1 as a biomarker of chemoresistance and poor clinical outcome in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5903–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gurluler, E.; Tumay, L.V.; Guner, O.S.; Kucukmetin, N.T.; Hizli, B.; Zorluoglu, A. The role of preoperative serum levels for Dickkopf-related protein 1 as a potential marker of tumor invasion in patients with stage II and III colon cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yao, G.; Shu, H.; Lin, B.; Hood, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Gu, J.; et al. Elevated expression of DKK1 is associated with cytoplasmic/nuclear beta-catenin accumulation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinomas. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, G.D.; Fang, F.; Liu, Z.; Lau, S.H.; Zhang, J.F.; Lau, W.Y.; Yang, L.Y. Dickkopf-1: As a diagnostic and prognostic serum marker for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2013, 28, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, E.K.; Mak, C.K.; Fatima, S.; Lo, R.C.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Dai, H.; Poon, R.T.; Yuen, M.F.; Lai, C.L.; et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of serum and tissue dickkopf-1 levels in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.L. Dickkopf-1 (dkk1) promotes invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. J. Ital. Soc. Gastroenterol. Ital. Assoc. Study Liver 2013, 45, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, H.E.; Park, D.J.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, W.H.; Park, K.U. Clinical significance of serum and tissue Dickkopf-1 levels in patients with gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.R.; Li, Y.F.; Deng, Z.Q.; Cao, J.Q. Prognostic Significance of Dickkopf-1 in Gastric Cancer Survival: A Meta-Analysis. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2016, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, S. Dickkopf-1 is frequently overexpressed in ovarian serous carcinoma and involved in tumor invasion. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, D.M.; Link, T.; Goeckenjan, M.; Wimberger, P.; Poetsch, A.R.; Jaschke, N.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Göbel, A.; Rachner, T.D.; Kuhlmann, J.D. Evaluation of circulating Dickkopf-1 as a prognostic biomarker in ovarian cancer patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 60, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shizhuo, W.; Tao, J.; Shulan, Z.; Bing, Z. The expression and significance of Dickkopf-1 in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2009, 24, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.H.; Liu, Z.B.; Yang, C.; Qin, W.; Shao, Z.M. Expression of dickkopf-1 and beta-catenin related to the prognosis of breast cancer patients with triple negative phenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37624, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, S.J.; Zhuo, S.R.; Yang, X.Q.; Qin, C.X.; Wang, Z.L. Serum Dickkopf-1 expression level positively correlates with a poor prognosis in breast cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dong, L.L.; Qu, L.Y.; Chu, L.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Liu, Y.H. Serum level of DKK-1 and its prognostic potential in non-small cell lung cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yamabuki, T.; Takano, A.; Hayama, S.; Ishikawa, N.; Kato, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Ito, T.; Ito, H.; Miyagi, Y.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Dikkopf-1 as a novel serologic and prognostic biomarker for lung and esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, S.L.; Huang, G.; Yu, B.; Qin, W.X. Clinical significance and prognostic value of serum Dickkopf-1 concentrations in patients with lung cancer. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begenik, H.; Kemik, A.S.; Emre, H.; Dulger, A.C.; Demirkiran, D.; Ebinc, S.; Kemik, O. The association between serum Dickkopf-1 levels and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.H.; Xu, Y.W.; Guo, H.; Huang, L.S.; Tan, H.Z.; Hong, C.Q.; Li, S.S.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, E.M. Combined detection of serum Dickkopf-1 and its autoantibodies to diagnose esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Makino, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Takemasa, I.; Takeno, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Miyata, H.; Takiguchi, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Matsuura, N.; Mori, M.; et al. Dickkopf-1 expression as a marker for predicting clinical outcome in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Sada, R.; Takada, N.; Harada, A.; Doki, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Kikuchi, A. The Dickkopf1 and FOXM1 positive feedback loop promotes tumor growth in pancreatic and esophageal cancers. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4486–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, C.-H.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Tung, C.-L.; Wu, J.-D.; Lin, C.-T.; Chan, M.W.-Y.; Hsu, C.-D.; Chang, D. High dickkopf-1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.K.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, P. Serum Dickkopf-1 levels as a clinical and prognostic factor in patients with bladder cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 18181–18187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Fukushima, T.; Yorita, K.; Tanaka, H.; Chijiiwa, K.; Kataoka, H. Dickkopf-1 is overexpressed in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and is involved in invasive growth. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.J.; Xie, Y.X.; Liu, X.X.; Huo, Y.M.; Yang, M.W.; Fu, X.L.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.Y.; Li, J.; Hua, R.; et al. The role of Dickkopf-1 as a potential prognostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Darlavoix, T.; Seelentag, W.; Yan, P.; Bachmann, A.; Bosman, F.T. Altered expression of CD44 and DKK1 in the progression of Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2009, 454, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyros, O.; Rafiee, P.; Nie, L.; Medda, R.; Jovanovic, N.; Otterson, M.F.; Behmaram, B.; Gockel, I.; Mackinnon, A.; Shaker, R. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Activation beyond Robust Nuclear β-Catenin Accumulation in Nondysplastic Barrett’s Esophagus: Regulation via Dickkopf-1. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Song, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Liang, H. miR-33a-5p inhibits the progression of esophageal cancer through the DKK1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 20481–20494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Herbst, A.; Kalinski, T.; Qin, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Benedix, F.; Franke, S.; Wartman, T.; et al. miR-221 Mediates Chemoresistance of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma by Direct Targeting of DKK2 Expression. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffmann, L.M.; Loeser, H.; Jacob, A.S.; Maus, M.; Fuchs, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tharun, L.; Essakly, A.; Iannos Damanakis, A.; Zander, T.; et al. Dickkopf-2 (DKK2) as Context Dependent Factor in Patients with Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, L.; Thomas, D.G.; Nadal, E.; Chang, A.C.; Beer, D.G.; Lin, J. The role of Dickkopf-3 overexpression in esophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 150, 377–385.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Otto, B.; Koenig, A.M.; Tolstonog, G.V.; Jeschke, A.; Klaetschke, K.; Vashist, Y.K.; Wicklein, D.; Wagener, C.; Izbicki, J.R.; Streichert, T. Molecular changes in pre-metastatic lymph nodes of esophageal cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramirez, J.G.; Smit, D.J.; Viol, F.; Schrader, J.; Ghadban, T.; Pantel, K.; Izbicki, J.R.; Reeh, M. High Serum Levels of Wnt Signaling Antagonist Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 Are Associated with Impaired Overall Survival and Recurrence in Esophageal Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Birkman, E.M.; Ålgars, A.; Lintunen, M.; Ristamäki, R.; Sundström, J.; Carpén, O. EGFR gene amplification is relatively common and associates with outcome in intestinal adenocarcinoma of the stomach, gastro-oesophageal junction and distal oesophagus. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hedner, C.; Borg, D.; Nodin, B.; Karnevi, E.; Jirström, K.; Eberhard, J. Expression and Prognostic Significance of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors 1 and 3 in Gastric and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liao, J.B.; Lee, H.P.; Fu, H.T.; Lee, H.S. Assessment of EGFR and ERBB2 (HER2) in Gastric and Gastroesophageal Carcinomas: EGFR Amplification is Associated with a Worse Prognosis in Early Stage and Well to Moderately Differentiated Carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2018, 26, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aratani, K.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Ohashi, T.; Miyamae, M.; Okajima, W.; Imamura, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Nishibeppu, K.; Kosuga, T.; et al. Overexpression of EGFR as an Independent Prognostic Factor in Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagogastric Junction. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, J.; McAdam, E.; Danikas, A.; Tselepis, C.; Griffiths, P.; Baxter, J.; Thomas, L.; Manson, J.; Jenkins, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in high-grade dysplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and may represent a biomarker of histological progression in Barrett’s esophagus (BE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretto, G.; Gurski, R.R.; Binato, M.; Navarini, D.; Aguiar, W.W.; Meurer, L. Increase of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in progression of GERD, Barrett, and adenocarcinoma of esophagus. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malka, D.; François, E.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Castan, F.; Bouché, O.; Bennouna, J.; Ghiringhelli, F.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Borg, C.; Samalin, E.; et al. FOLFOX alone or combined with rilotumumab or panitumumab as first-line treatment for patients with advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma (PRODIGE 17-ACCORD 20-MEGA): A randomised, open-label, three-arm phase II trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 115, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rima, F.A.; Hussain, M.; Haque, N.; Dewan, R.K.; Rahman, N.; Jinnah, M.A.; Jeba, R.; Chowdhury, F. HER2 status in Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma. Mymensingh Med. J. 2017, 26, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almhanna, K.; Rosa, M.; Henderson-Jackson, E.; Jiang, K.; Shamekh, R.; Sayegh, Z.; Malafa, M.P.; Coppola, D. Her-2 Expression in Gastroesophageal Intestinal Metaplasia, Dysplasia, and Adenocarcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2016, 24, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Plum, P.S.; Gebauer, F.; Krämer, M.; Alakus, H.; Berlth, F.; Chon, S.H.; Schiffmann, L.; Zander, T.; Büttner, R.; Hölscher, A.H.; et al. HER2/neu (ERBB2) expression and gene amplification correlates with better survival in esophageal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bang, Y.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697, Erratum in Lancet 2010, 376, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Maron, S.B.; Chatila, W.K.; Millang, B.; Chavan, S.S.; Alterman, C.; Chou, J.F.; Segal, M.F.; Simmons, M.Z.; Momtaz, P.; et al. First-line pembrolizumab and trastuzumab in HER2-positive oesophageal, gastric, or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer: An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rivera, F.; Izquierdo-Manuel, M.; García-Alfonso, P.; Martínez de Castro, E.; Gallego, J.; Limón, M.L.; Alsina, M.; López, L.; Galán, M.; Falcó, E.; et al. Perioperative trastuzumab, capecitabine and oxaliplatin in patients with HER2-positive resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: NEOHX phase II trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 145, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofheinz, R.D.; Hegewisch-Becker, S.; Kunzmann, V.; Thuss-Patience, P.; Fuchs, M.; Homann, N.; Graeven, U.; Schulte, N.; Merx, K.; Pohl, M.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin and docetaxel as perioperative treatment for patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive locally advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma: A phase II trial of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie Gastric Cancer Study Group. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abali, H.; Yalcin, S.; Onal, H.C.; Dane, F.; Oksuzoglu, B.; Ozdemir, N.; Mertsoylu, H.; Artac, M.; Camci, C.; Karabulut, B.; et al. A Phase II Study of the Combination of Oxaliplatin, Capecitabine, and Trastuzumab and Chemoradiotherapy in the Adjuvant Setting in Operated Patients with HER2-positive Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer (TOXAG Study): A Turkish Oncology Group Study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 44, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulendijks, D.; Beerepoot, L.V.; Boot, H.; de Groot, J.W.; Los, M.; Boers, J.E.; Vanhoutvin, S.A.; Polee, M.B.; Beeker, A.; Portielje, J.E.; et al. Trastuzumab and bevacizumab combined with docetaxel, oxaliplatin and capecitabine as first-line treatment of advanced HER2-positive gastric cancer: A multicenter phase II study. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernero, J.; Hoff, P.M.; Shen, L.; Ohtsu, A.; Shah, M.A.; Cheng, K.; Song, C.; Wu, H.; Eng-Wong, J.; Kim, K.; et al. Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive metastatic gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (JACOB): Final analysis of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, J.R.; Bang, Y.J.; Qin, S.K.; Chung, H.C.; Xu, J.M.; Park, J.O.; Jeziorski, K.; Shparyk, Y.; Hoff, P.M.; Sobrero, A.; et al. Lapatinib in Combination with Capecitabine Plus Oxaliplatin in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Advanced or Metastatic Gastric, Esophageal, or Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma: TRIO-013/LOGiC--A Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuss-Patience, P.C.; Shah, M.A.; Ohtsu, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Ajani, J.A.; Castro, H.; Mansoor, W.; Chung, H.C.; Bodoky, G.; Shitara, K.; et al. Trastuzumab emtansine versus taxane use for previously treated HER2-positive locally advanced or metastatic gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GATSBY): An international randomised, open-label, adaptive, phase 2/3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuge, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Dong, W.; Gao, Y. Construction of the model for predicting prognosis by key genes regulating EGFR-TKI resistance. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 968376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moon, S.J.; Choi, H.J.; Kye, Y.H.; Jeong, G.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Myung, J.K.; Kong, G. CTTN Overexpression Confers Cancer Stem Cell-like Properties and Trastuzumab Resistance via DKK-1/WNT Signaling in HER2 Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Angelescu, C.; Burada, F.; Ioana, M.; Angelescu, R.; Moraru, E.; Riza, A.; Marchian, S.; Mixich, F.; Cruce, M.; Săftoiu, A. VEGF-A and VEGF-B mRNA expression in gastro-oesophageal cancers. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 15, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.T.; O’Donnell, M.E.; Maxwell, P.; McGuigan, J.A.; Spence, G.M. Long-term follow-up of immunocytochemical analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and its two receptors, VEGF-R1 (Flt-1) and VEGF-R2 (Flk-1/KDR), in oesophagogastric cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2013, 28, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takala, H.; Saarnio, J.; Wiik, H.; Ohtonen, P.; Soini, Y. HIF-1α and VEGF are associated with disease progression in esophageal carcinoma. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 167, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozłowski, M.; Laudański, W.; Mroczko, B.; Szmitkowski, M.; Milewski, R.; Łapuć, G. Serum tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) are associated with prognosis in esophageal cancer patients. Adv. Med. Sci. 2013, 58, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, G.Y.; Bains, M.S.; Park, D.J.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Rusch, V.W.; Rizk, N.P.; Yoon, S.S.; Millang, B.; Capanu, M.; Goodman, K.A.; et al. Phase II study of bevacizumab and preoperative chemoradiation for esophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cunningham, D.; Stenning, S.P.; Smyth, E.C.; Okines, A.F.; Allum, W.H.; Rowley, S.; Stevenson, L.; Grabsch, H.I.; Alderson, D.; Crosby, T.; et al. Peri-operative chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab in operable oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma (UK Medical Research Council ST03): Primary analysis results of a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 2–3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fuchs, C.S.; Tomasek, J.; Yong, C.J.; Dumitru, F.; Passalacqua, R.; Goswami, C.; Safran, H.; Dos Santos, L.V.; Aprile, G.; Ferry, D.R.; et al. Ramucirumab monotherapy for previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (REGARD): An international, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, H.; Muro, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Oh, S.C.; Bodoky, G.; Shimada, Y.; Hironaka, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Lipatov, O.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): A double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, C.S.; Shitara, K.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Lonardi, S.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Van Cutsem, E.; Ilson, D.H.; Alsina, M.; Chau, I.; Lacy, J.; et al. Ramucirumab with cisplatin and fluoropyrimidine as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic gastric or junctional adenocarcinoma (RAINFALL): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 420–435, Erratum in Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, T.O.; Hofheinz, R.D.; Gaiser, T.; Schmalenberg, H.; Strumberg, D.; Goekkurt, E.; Angermeier, S.; Zander, T.; Kopp, H.G.; Pink, D.; et al. Perioperative FLOT plus ramucirumab for resectable esophagogastric adenocarcinoma: A randomized phase II/III trial of the German AIO and Italian GOIM. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanwei, L.; Feng, H.; Ren, P.; Yue, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, P.; Shang, X.; Pang, Q.; Liu, D.; Chen, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Apatinib Monotherapy for Unresectable, Metastatic Esophageal Cancer: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase II Study. Oncologist 2020, 25, e1464–e1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Seo, S.H.; Cho, K.J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, S.U. Dickkopf-1 promotes angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF receptor 2-mediated mTOR/p70S6K signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 4788–4806. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, R.Y.; Yang, X.R.; Shen, Q.J.; Yang, L.X.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, S.J.; Sun, Y.F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, K.; et al. High expression of Dickkopf-related protein 1 is related to lymphatic metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients after surgery. Cancer 2013, 119, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.L.; Wu, H.F.; Wang, W.J.; Hu, G.M.; Gu, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.X. C-Met as a potential novel prognostic marker in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of esophagus: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Panminerva Med. 2017, 59, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenacci, D.V.; Ang, A.; Liao, W.L.; Shen, J.; O’Day, E.; Loberg, R.D.; Cecchi, F.; Hembrough, T.; Ruzzo, A.; Graziano, F. MET tyrosine kinase receptor expression and amplification as prognostic biomarkers of survival in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2017, 123, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lennerz, J.K.; Kwak, E.L.; Ackerman, A.; Michael, M.; Fox, S.B.; Bergethon, K.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Christensen, J.G.; Wilner, K.D.; Haber, D.A.; et al. MET amplification identifies a small and aggressive subgroup of esophagogastric adenocarcinoma with evidence of responsiveness to crizotinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4803–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aparicio, T.; Cozic, N.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Meriaux, E.; Plaza, J.; Mineur, L.; Guimbaud, R.; Samalin, E.; Mary, F.; Lecomte, T.; et al. The Activity of Crizotinib in Chemo-Refractory MET-Amplified Esophageal and Gastric Adenocarcinomas: Results from the AcSé-Crizotinib Program. Target Oncol. 2021, 16, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, M.A.; Cho, J.Y.; Tan, I.B.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Yen, C.J.; Kang, A.; Shames, D.S.; Bu, L.; Kang, Y.K. A Randomized Phase II Study of FOLFOX with or Without the MET Inhibitor Onartuzumab in Advanced Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach and Gastroesophageal Junction. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pant, S.; Patel, M.; Kurkjian, C.; Hemphill, B.; Flores, M.; Thompson, D.; Bendell, J. A Phase II Study of the c-Met Inhibitor Tivantinib in Combination with FOLFOX for the Treatment of Patients with Previously Untreated Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Distal Esophagus, Gastroesophageal Junction, or Stomach. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenacci, D.V.T.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Davidenko, I.; Murad, A.M.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Ilson, D.H.; Tjulandin, S.; Gotovkin, E.; Karaszewska, B.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Rilotumumab plus epirubicin, cisplatin, and capecitabine as first-line therapy in advanced MET-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (RILOMET-1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1467–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Lv, C.; Si, J.; Xiong, Y.; Ding, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y. BPI-9016M, a c-Met inhibitor, suppresses tumor cell growth, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via miR203-DKK1. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5890–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chu, H.Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.K.; Tan, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B.T.; Lu, A.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G. Dickkopf-1: A Promising Target for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klempner, S.J.; Bendell, J.C.; Villaflor, V.M.; Tenner, L.L.; Stein, S.M.; Rottman, J.B.; Naik, G.S.; Sirard, C.A.; Kagey, M.H.; Chaney, M.F.; et al. Safety, Efficacy, and Biomarker Results from a Phase Ib Study of the Anti-DKK1 Antibody DKN-01 in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Advanced Esophagogastric Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, R.H.; Qin, J.; Cao, J.L.; Zhang, M.Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; Fang, D.; Xie, S.Q. Dickkopf-1 drives tumor immune evasion by inducing PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 208, 115378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira Farinha, H.; Digklia, A.; Schizas, D.; Demartines, N.; Schäfer, M.; Mantziari, S. Immunotherapy for Esophageal Cancer: State-of-the Art in 2021. Cancers 2022, 14, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yoshida, T.; Ogura, G.; Tanabe, M.; Hayashi, T.; Ohbayashi, C.; Azuma, M.; Kunisaki, C.; Akazawa, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. Clinicopathological features of PD-L1 protein expression, EBV positivity, and MSI status in patients with advanced gastric and esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma in Japan. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dislich, B.; Stein, A.; Seiler, C.A.; Kröll, D.; Berezowska, S.; Zlobec, I.; Galvan, J.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Walch, A.; Langer, R. Expression patterns of programmed death-ligand 1 in esophageal adenocarcinomas: Comparison between primary tumors and metastases. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Knief, J.; Lazar-Karsten, P.; Hummel, R.; Wellner, U.; Thorns, C. PD-L1 expression in carcinoma of the esophagogastric junction is positively correlated with T-cell infiltration and overall survival. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okadome, K.; Baba, Y.; Nomoto, D.; Yagi, T.; Kalikawe, R.; Harada, K.; Hiyoshi, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; et al. Prognostic and clinical impact of PD-L2 and PD-L1 expression in a cohort of 437 oesophageal cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yagi, T.; Baba, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Watanabe, M.; Baba, H. PD-L1 Expression, Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes, and Clinical Outcome in Patients with Surgically Resected Esophageal Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.A.; Kennedy, E.B.; Alarcon-Rozas, A.E.; Alcindor, T.; Bartley, A.N.; Malowany, A.B.; Bhadkamkar, N.A.; Deighton, D.C.; Janjigian, Y.; Karippot, A.; et al. Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy for Advanced Gastroesophageal Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1470–1491, Erratum in J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, JCO2300441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malladi, S.; Macalinao, D.G.; Jin, X.; He, L.; Basnet, H.; Zou, Y.; de Stanchina, E.; Massagué, J. Metastatic Latency and Immune Evasion through Autocrine Inhibition of WNT. Cell 2016, 165, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- D’Amico, L.; Mahajan, S.; Capietto, A.H.; Yang, Z.; Zamani, A.; Ricci, B.; Bumpass, D.B.; Meyer, M.; Su, X.; Wang-Gillam, A.; et al. Dickkopf-related protein 1 (Dkk1) regulates the accumulation and function of myeloid derived suppressor cells in cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klempner, S.J.; Sonbol, B.B.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Uronis, H.E.; Chiu, V.K.; Scott, A.J.; Iqbal, S.; Tejani, M.A.; Stilian, M.C.; Thoma, M.; et al. A phase 2 study (DisTinGuish) of DKN-01 in combination with tislelizumab + chemotherapy as first-line (1L) therapy in patients with advanced gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma (GEA). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempner, S.; Ajani, J.; Chao, J.; Uronis, H.; Sirard, C.; Kagey, M.; Baum, J.; Zhang, L.; Kim, I.H.; Oh, D.Y.; et al. 553 DKN-01 and tislelizumab as a second-line (2L) investigational therapy in advanced DKK1 high gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma (GEA): DisTinGuish Trial. J. ImmunoTher. Cancer 2022, 10 (Suppl. 2), A578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.A.; Klempner, S.J.; Arend, R.C. The anti-DKK1 antibody DKN-01 as an immunomodulatory combination partner for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Dai, H.; Song, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Shi, T.; et al. Combination therapy of DKK1 inhibition and NKG2D chimeric antigen receptor T cells for the treatment of gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2798–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sui, Q.; Liu, D.; Jiang, W.; Tang, J.; Kong, L.; Han, K.; Liao, L.; Li, Y.; Ou, Q.; Xiao, B.; et al. Dickkopf 1 impairs the tumor response to PD-1 blockade by inactivating CD8+ T cells in deficient mismatch repair colorectal cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001498, Erratum in J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Haas, M.S.; Kagey, M.H.; Heath, H.; Schuerpf, F.; Rottman, J.B.; Newman, W. mDKN-01, a Novel Anti-DKK1 mAb, Enhances Innate Immune Responses in the Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtada, J.; Thibaudeau, C.; Wasylyk, B.; Jung, A.C. The Multifaceted Role of Human Dickkopf-3 (DKK-3) in Development, Immune Modulation and Cancer. Cells 2023, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ryan, D.P.; Murphy, J.; Mahalingam, D.; Strickler, J.; Stein, S.; Sirard, C.; Landau, S.; Bendell, J. PD-016: Current results of a phase I study of DKN-01 in combination with paclitaxel (P) in patients (pts) with advanced DKK1+ esophageal cancer (EC) or gastro-esophageal junction tumors (GEJ). Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. 2), ii108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Bhavanasi, D.; Speer, K.F.; Klein, P.S. CKAP4 is identified as a receptor for Dickkopf in cancer cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2419–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kikuchi, A.; Fumoto, K.; Kimura, H. The Dickkopf1-cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 axis creates a novel signalling pathway and may represent a molecular target for cancer therapy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 4651–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kikuchi, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Sada, R. Dickkopf signaling, beyond Wnt-mediated biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 125, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sada, R.; Kimura, H.; Fukata, Y.; Fukata, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Kikuchi, A. Dynamic palmitoylation controls the microdomain localization of the DKK1 receptors CKAP4 and LRP6. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaat9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Shareef, Z.; Ershaid, M.N.A.; Mudhafar, R.; Soliman, S.S.M.; Kypta, R.M. Dickkopf-3: An Update on a Potential Regulator of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iguchi, K.; Sada, R.; Matsumoto, S.; Kimura, H.; Zen, Y.; Akita, M.; Gon, H.; Fukumoto, T.; Kikuchi, A. DKK1-CKAP4 signal axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shinno, N.; Kimura, H.; Sada, R.; Takiguchi, S.; Mori, M.; Fumoto, K.; Doki, Y.; Kikuchi, A. Activation of the Dickkopf1-CKAP4 pathway is associated with poor prognosis of esophageal cancer and anti-CKAP4 antibody may be a new therapeutic drug. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3471–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osugi, Y.; Fumoto, K.; Kikuchi, A. CKAP4 Regulates Cell Migration via the Interaction with and Recycling of Integrin. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 39, e00073-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kajiwara, C.; Fumoto, K.; Kimura, H.; Nojima, S.; Asano, K.; Odagiri, K.; Yamasaki, M.; Hikita, H.; Takehara, T.; Doki, Y.; et al. p63-Dependent Dickkopf3 Expression Promotes Esophageal Cancer Cell Proliferation via CKAP4. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6107–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.X.; Li, J.; Dong, L.W.; Guo, Z.Y. Cytoskeleton-Associated Protein 4, a Promising Biomarker for Tumor Diagnosis and Therapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 7, 552056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sada, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Harada, A.; Kikuchi, A. Newly developed humanized anti-CKAP4 antibody suppresses pancreatic cancer growth by inhibiting DKK1-CKAP4 signaling. Cancer Sci. 2024. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of Tumor | DKK1 Role | Downstream Mechanism | Receptor That Mediates the DKK1 Function | Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | 1. Tumor suppressor 2. Oncogene | 1. Inhibition of expression of VEGF [10], inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway [11] 2. Independent of Wnt [12] | 1. LRP5/6 [11], not defined [10] 2. Not defined | 1. Liu et al. [10], Qi et al. [11] 2. Aguilera et al. [12], Gurluler et al. [13] |
| HCC | Oncogene | Wnt/β-catenin pathway [14] | Not defined | Yu et al. [14], Yang et al. [15], Tung et al. [16], Tao et al. [17] |
| Gastric cancer | Oncogene | Not defined | Not defined | Lee et al. [18], Liu et al. [19] |
| Ovarian cancer | Oncogene | Overexpression/activation of P-JNK1 [20] | Possibly Fzd [20] | Klotz et al. [21], Shizhuo et al. [22], Wang et al. [20] |
| Breast cancer | Oncogene | Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [23] | Not defined | Zhou et al. [24], Xu et al. [23] |
| Lung cancer | Oncogene | Not defined | Not defined | Dong et al. [25], Yamabuki et al. [26], Sheng et al. [27] |
| Esophageal carcinoma | Oncogene | Phosphorylation of Akt | Not defined | Lyros et al. [4], Yamabuki et al. [26], Begenik et al. [28], Peng et al. [29], Makino et al. [30] Kimura et al. [31] |
| Urothelial cancer | Oncogene | Not defined | Not defined | Shen et al. [32], Sun et al. [33] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Oncogene | AKT/MEK-ERK pathway, overexpression of FOXM1 | CKAP4 | Kimura et al. [31], Takahashi et al. [34], Liu et al. [35] |
| Study | Phase | n | Treatment Line | Treatment Arm | 2nd Treatment Arm | OS/PFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02013154 [87,105] | 1b | 22 | ≥2nd line | DKN-01 + paclitaxel [105] | - | 28.9/17.7 (weeks) |
| 63 | ≥2nd line | DKN-01 + pembrolizumab [87] | - | 20.4/6 (weeks) | ||
| DISTINGUISH-PART A [98] | 2 | 25 | 1st line | DKN-01 + tislelizumab + CAPOX | - | 19.5/11.3 (months) |
| DISTINGUISH-PART B [99] | 2 | 52 | 2nd line | DKN-01 + tislelizumab | - | 1.4/-(months) |
| DISTINGUISH-PART C [NCT04363801] | 2 | 160 (1:1) | 1st line | DKN-01 + tislelizumab + CAPOX or FOLFOX6 | Tislelizumab + CAPOX or FOLFOX6 | Ongoing |
| NCT04166721 | 2 | Recruiting | ≥2nd line | DKN-01 + atezolizumab | - | Ongoing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Despotidis, M.; Lyros, O.; Driva, T.S.; Sarantis, P.; Kapetanakis, E.I.; Mylonakis, A.; Mamilos, A.; Sakellariou, S.; Schizas, D. DKK1 and Its Receptors in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Promising Molecular Target. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15010085
Despotidis M, Lyros O, Driva TS, Sarantis P, Kapetanakis EI, Mylonakis A, Mamilos A, Sakellariou S, Schizas D. DKK1 and Its Receptors in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Promising Molecular Target. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleDespotidis, Markos, Orestis Lyros, Tatiana S. Driva, Panagiotis Sarantis, Emmanouil I. Kapetanakis, Adam Mylonakis, Andreas Mamilos, Stratigoula Sakellariou, and Dimitrios Schizas. 2025. "DKK1 and Its Receptors in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Promising Molecular Target" Diagnostics 15, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15010085
APA StyleDespotidis, M., Lyros, O., Driva, T. S., Sarantis, P., Kapetanakis, E. I., Mylonakis, A., Mamilos, A., Sakellariou, S., & Schizas, D. (2025). DKK1 and Its Receptors in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Promising Molecular Target. Diagnostics, 15(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15010085







