U-Net and Its Variants Based Automatic Tracking of Radial Artery in Ultrasonic Short-Axis Views: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Enrollment and Datasets Formulation
2.2. Data Preprocessing and Augmentation
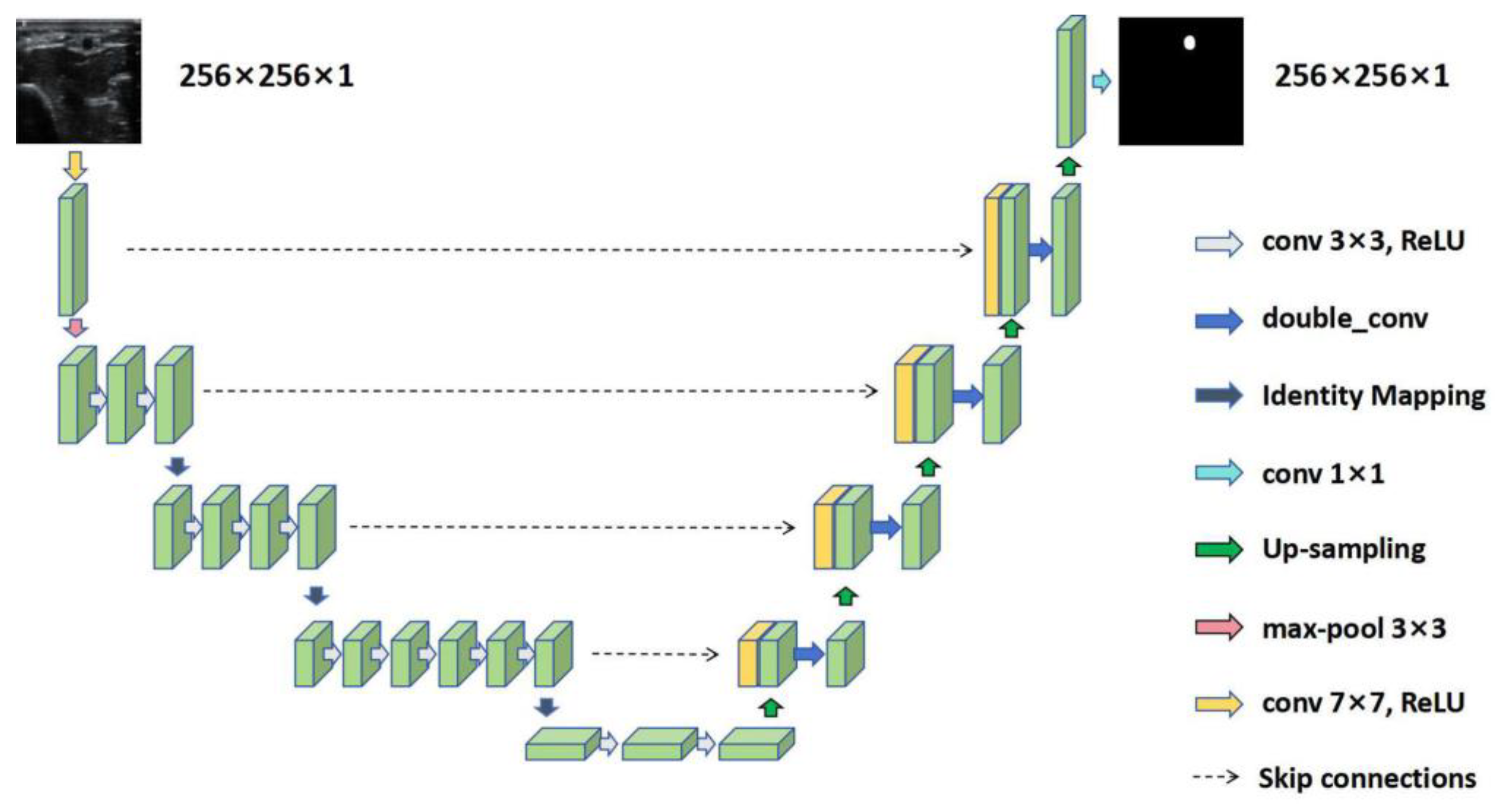
2.3. RAT Using U-Net and Its Variants
2.4. Experimental Setup and Statistical Analysis
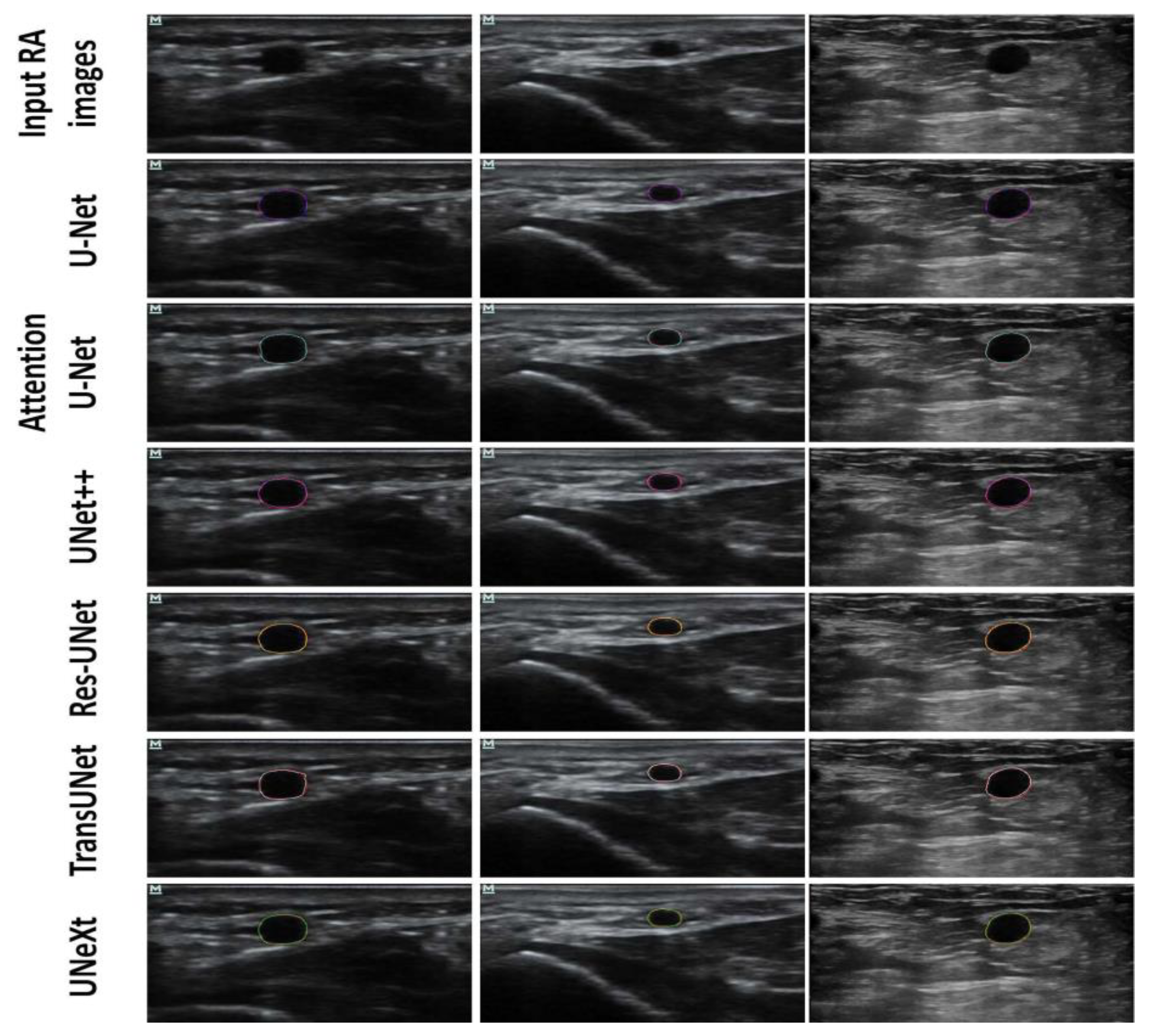
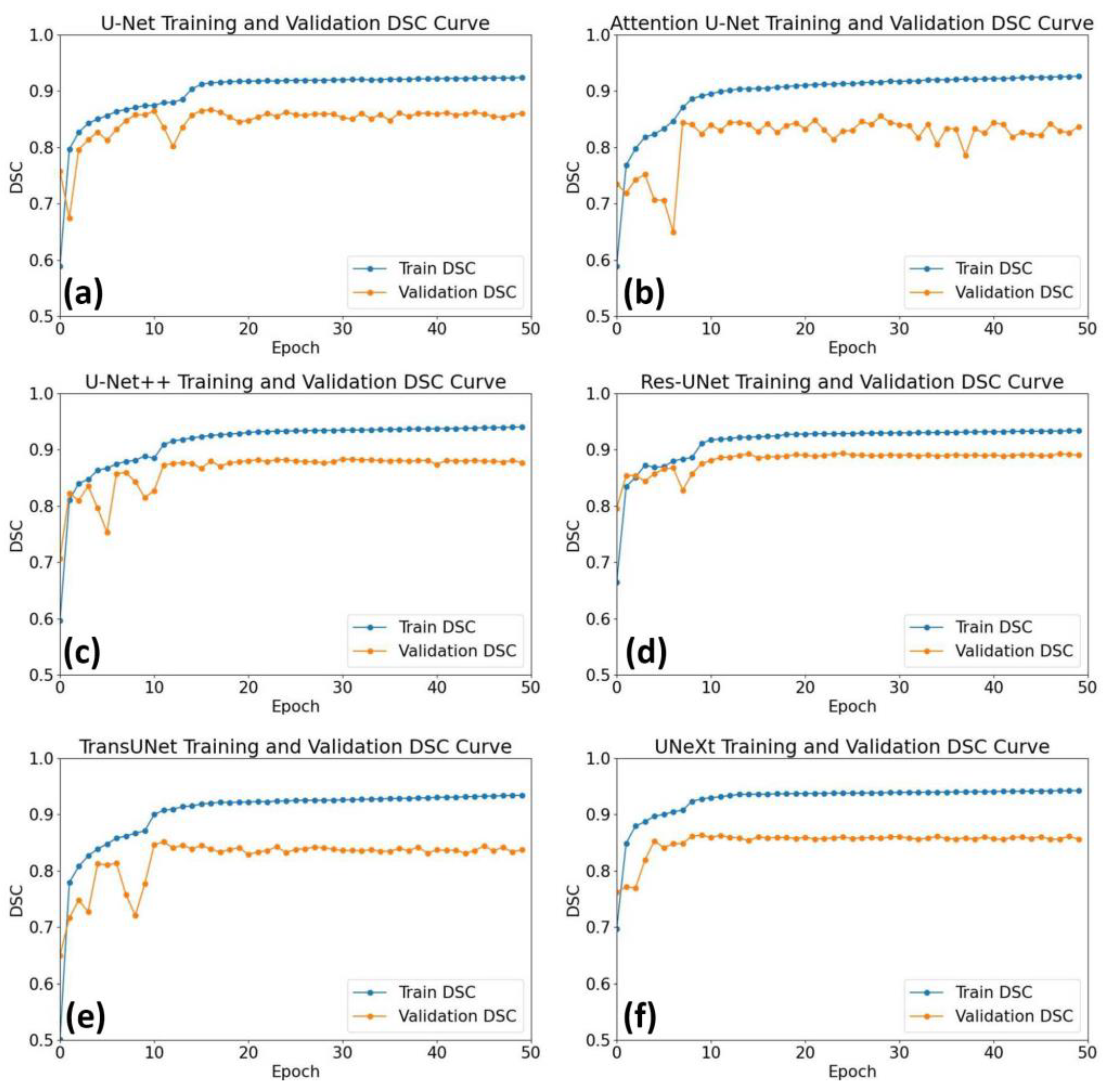
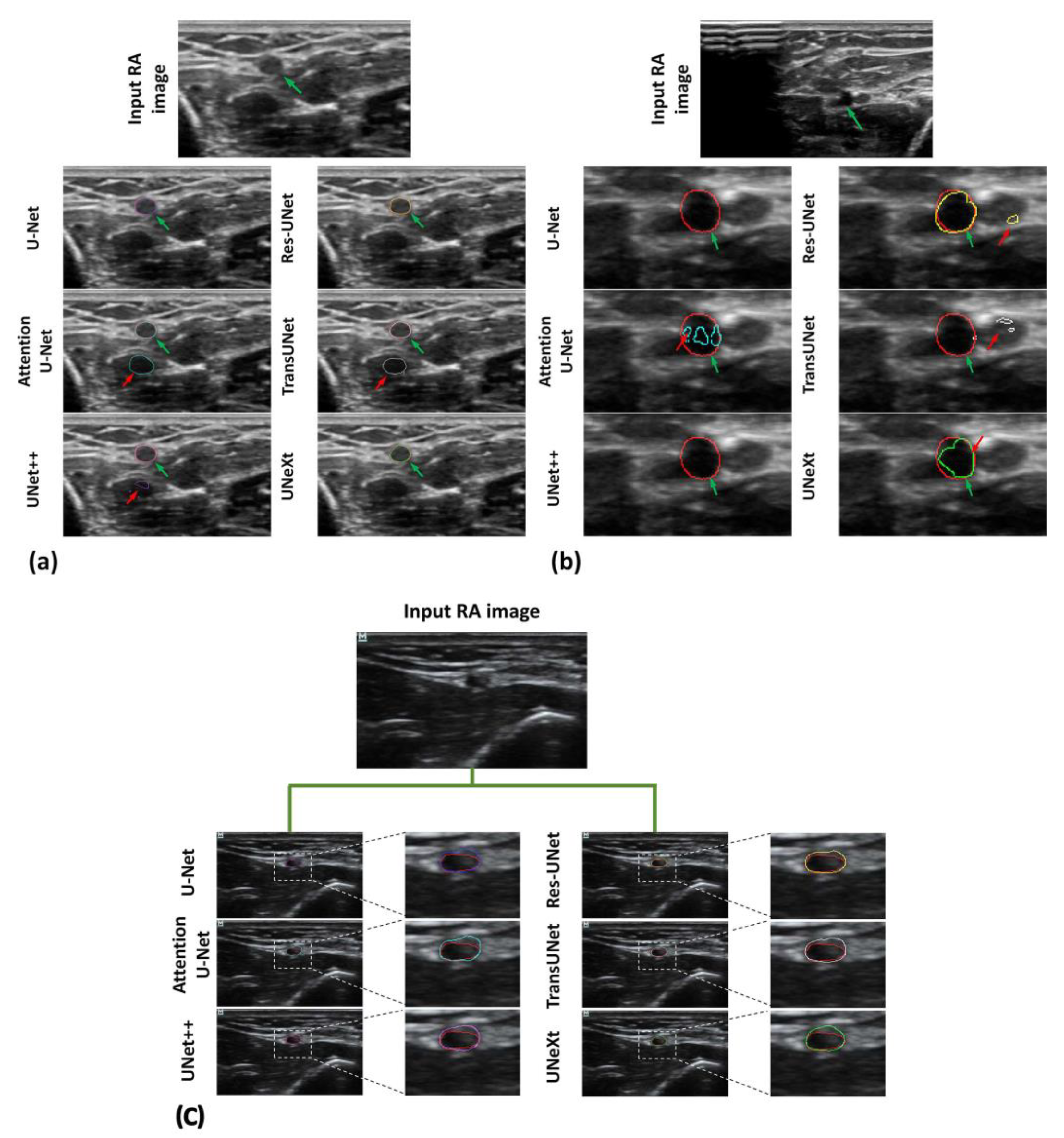
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliver, L.-A.; Oliver, J.-A.; Ohanyan, S.; Park, W.; Benelyahoo, A.; Vadivelu, N. Ultrasound for Peripheral and Arterial Access. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 33, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, G.A.; Blaivas, M.; Conrad, S.A.; Corradi, F.; Koenig, S.; Lamperti, M.; Saugel, B.; Schummer, W.; Slama, M. Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Access in Critical Illness. Intens. Care Med. 2019, 45, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamperti, M.; Biasucci, D.G.; Disma, N.; Pittiruti, M.; Breschan, C.; Vailati, D.; Subert, M.; Traškaitė, V.; Macas, A.; Estebe, J.-P.; et al. European Society of Anaesthesiology Guidelines on Peri-Operative Use of Ultrasound-Guided for Vascular Access (PERSEUS Vascular Access). Eur. J. Anaesth. 2020, 37, 344–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Sadud, R.; Schnobrich, D.; Mathews, B.K.; Candotti, C.; Abdel-Ghani, S.; Perez, M.G.; Rodgers, S.C.; Mader, M.J.; Haro, E.K.; Dancel, R.; et al. Recommendations on the Use of Ultrasound Guidance for Central and Peripheral Vascular Access in Adults: A Position Statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 14, E1–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa Pacha, H.; Alahdab, F.; Al-khadra, Y.; Idris, A.; Rabbat, F.; Darmoch, F.; Soud, M.; Zaitoun, A.; Kaki, A.; Rao, S.V.; et al. Ultrasound-Guided versus Palpation-Guided Radial Artery Catheterization in Adult Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. Heart J. 2019, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Maitra, S.; Baidya, D.K. Comparison between Ultrasound Guided Technique and Digital Palpation Technique for Radial Artery Cannulation in Adult Patients: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Anesth. 2018, 47, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.-K.; Zhao, G.-F.; Deng, J.-H.; Li, D.-W. Oblique versus Longitudinal Axis/in-Plane Approaches for Ultrasound-Guided Radial Arterial Cannulation: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Anaesth. 2020, 37, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, S.; Tian, J. “Modified Dynamic Needle Tip Positioning” Short-Axis, Out-of-Plane, Ultrasound-Guided Radial Artery Cannulation in Neonates: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Shi, S.; Xu, Y.; Ye, M.; Bai, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Long-Axis in-Plane Combined with Short-Axis out-of-Plane Technique in Ultrasound-Guided Arterial Catheterization in Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Anesth. 2023, 85, 111038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbriaco, G.; Monesi, A.; Giugni, A.; Cilloni, N. Radial Artery Cannulation in Intensive Care Unit Patients: Does Distance from Wrist Joint Increase Catheter Durability and Functionality? J. Vasc. Access 2021, 22, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrìaco, G.; Monesi, A.; Spencer, T.R. Preventing Radial Arterial Catheter Failure in Critical Care—Factoring Updated Clinical Strategies and Techniques. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2022, 41, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Gao, F. Exploring Hemodynamic Mechanisms and Re-intervention Strategies for Partial False Lumen Thrombosis in Stanford Type B Aortic Dissection after Thoracic Aortic Endovascular Repair. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 417, 132494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolfaghari, H.; Andiapen, M.; Baumbach, A.; Mathur, A.; Kerswell, R.R. Wall Shear Stress and Pressure Patterns in Aortic Stenosis Patients with and without Aortic Dilation Captured by High-performance Image-based Computational Fluid Dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1011479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaru, A.J.; Abdulkadir, M.; Kovo, A.S.; Corfield, M.R.; Tanko, N.; Odey, O.A.; Aroke, U.O. Three-dimensional High-resolution Image Inversion and Pore Level CFD Characterisation of Effective Thermal Conductivity of Replicated Microcellular Structures. Int. J. Thermofluids 2022, 14, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saruwatari, M.S.; Nguyen, T.N.; Talari, H.F.; Matisoff, A.J.; Sharma, K.V.; Donoho, K.G.; Basu, S.; Dwivedi, P.; Bost, J.E.; Shekhar, R. Assessing the Effect of Augmented Reality on Procedural Outcomes during Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Access. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2023, 49, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topol, E.J. High-Performance Medicine: The Convergence of Human and Artificial Intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.D.M.; Remeseiro, B.; Grau, M.; Elosua, R.; Betriu, À.; Fernandez-Giraldez, E.; Igual, L. Semantic Segmentation with DenseNets for Carotid Artery Ultrasound Plaque Segmentation and CIMT Estimation. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 103, 101784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarski, M.; Chauhan, S. Improved Real-Time Segmentation of Intravascular Ultrasound Images Using Coordinate-Aware Fully Convolutional Networks. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 91, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.Y.; Changaai Mangalote, I.A.; Meher, P.K.; Aboumarzouk, O.; Al-Ansari, A.; Halabi, O.; Dakua, S.P. Advancements in Deep Learning for B-Mode Ultrasound Segmentation: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 8, 2126–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Stoyanov, D., Taylor, Z., Carneiro, G., Syeda-Mahmood, T., Martel, A., Maier-Hein, L., Tavares, J.M.R.S., Bradley, A., Papa, J.P., Belagiannis, V., et al., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11045, pp. 3–11. ISBN 978-3-030-00888-8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, K.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Heidari, A.A.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Algarni, A.D.; Elmannai, H. Eres-UNet++: Liver CT Image Segmentation Based on High-Efficiency Channel Attention and Res-UNet++. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 158, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Mei, J.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wei, Q.; Luo, X.; Xie, Y.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; et al. TransUNet: Rethinking the U-Net Architecture Design for Medical Image Segmentation through the Lens of Transformers. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, F.; Wen, J.; He, F.; Xia, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. SC-Unext: A Lightweight Image Segmentation Model with Cellular Mechanism for Breast Ultrasound Tumor Diagnosis. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 37, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzopardi, C.; Camilleri, K.P.; Hicks, Y.A. Bimodal Automated Carotid Ultrasound Segmentation Using Geometrically Constrained Deep Neural Networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health. Inf. 2020, 24, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Chen, J.; Gu, Y.; Liu, J. MFA-UNet: A Vessel Segmentation Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Attention Module. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1249331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagan, J.H.; Shirsat, H.S.; Mathias, G.P.; Mallya, B.V.; Andrade, J.; Rajagopal, K.V.; Kumar, J.R.H. Automated Segmentation of Common Carotid Artery in Ultrasound Images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 58419–58430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, L. Uncertainty Aware Temporal-Ensembling Model for Semi-Supervised ABUS Mass Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkani Chenarlogh, V.; Shabanzadeh, A.; Ghelich Oghli, M.; Sirjani, N.; Farzin Moghadam, S.; Akhavan, A.; Arabi, H.; Shiri, I.; Shabanzadeh, Z.; Sanei Taheri, M.; et al. Clinical Target Segmentation Using a Novel Deep Neural Network: Double Attention Res-U-Net. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Cheema, M.N.; Sheng, B.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Yang, P.; Jung, Y.; Qin, J.; Kim, J.; Feng, D.D. OFF-eNET: An Optimally Fused Fully End-to-End Network for Automatic Dense Volumetric 3D Intracranial Blood Vessels Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7192–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, G.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Kong, Y.; Wu, J.; Tang, L.; Zhu, X.; Dillenseger, J.-L.; Shao, P.; et al. Dense Biased Networks with Deep Priori Anatomy and Hard Region Adaptation: Semi-Supervised Learning for Fine Renal Artery Segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Zong, X.; Hung, S.-C.; Lin, W.; Shen, D. Multi-Channel Multi-Scale Fully Convolutional Network for 3D Perivascular Spaces Segmentation in 7T MR Images. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 46, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, S.; Chang, C.; Shi, J. Joint Localization and Classification of Breast Cancer in B-mode Ultrasound Imaging Via Collaborative Learning with Elastography. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 4474–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Fang, Z.; Gu, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J. High-resolution Image Reconstruction for Portable Ultrasound Imaging Devices. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2019, 2019, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number of Parameters | Training Time | Inference Time for Each Image | |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 7,851,969 | 19,715.48 s | 0.387 s |
| Attention U-Net | 34,877,421 | 25,938.19 s | 0.459 s |
| UNet++ | 9,162,753 | 24,757.11 s | 0.376 s |
| Res-UNet | 24,449,857 | 13,242.36 s | 0.410 s |
| TransUNet | 104,097,149 | 24,313.91 s | 1.868 s |
| UNeXt | 1,471,633 | 17,396.22 s | 0.565 s |
| DSC (%) | JSC (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Res-UNet | 93.14 ± 3.58 | 87.93 ± 5.57 |
| U-Net++ | 91.98 ± 6.31 | 86.08 ± 8.88 |
| U-Net | 91.79 ± 8.51 | 86.19 ± 10.02 |
| UNeXt | 91.33 ± 5.16 | 84.94 ± 7.93 |
| Attention U-Net | 91.20 ± 7.49 | 85.02 ± 10.17 |
| TransUNet | 91.08 ± 7.02 | 84.88 ± 9.48 |
| U-Net | Attention U-Net | U-Net++ | Res-UNet | TransUNet | UNeXt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 1 | 1.57 × 10−1 | 5.36 × 10−1 | 5.76 × 10−3 * | 4.77 × 10−8 * | 2.24 × 10−5 * |
| Attention U-Net | 1.57 × 10−1 | 1 | 5.33 × 10−2 | 3.76 × 10−5 * | 5.20 × 10−4 * | 1.23 × 10−2 * |
| U-Net++ | 5.36 × 10−1 | 5.33 × 10−2 | 1 | 4.32 × 10−2 * | 4.91 × 10−10 * | 2.08 × 10−6 * |
| Res-UNet | 5.76 × 10−3 * | 3.76 × 10−5 * | 4.32 × 10−2 * | 1 | 8.31 × 10−18 * | 6.53 × 10−13 * |
| TransUNet | 4.77 × 10−8 * | 5.20 × 10−4 * | 4.91 × 10−10 * | 8.31 × 10−18 * | 1 | 2.90 × 10−1 |
| UNeXt | 2.24 × 10−5 * | 1.23 × 10−2 * | 2.08 × 10−6 * | 6.53 × 10−13 * | 2.90 × 10−1 | 1 |
| U-Net | Attention U-Net | U-Net++ | Res-UNet | TransUNet | UNeXt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 1 | 6.39 × 10−2 | 8.35 × 10−1 | 6.74 × 10−3 | 4.49 × 10−7 * | 1.64 × 10−6 * |
| Attention U-Net | 6.39 × 10−2 | 1 | 1.07 × 10−1 | 7.34 × 10−6 * | 4.33 × 10−3 * | 6.18 × 10−3 * |
| U-Net++ | 8.35 × 10−1 | 1.07 × 10−1 | 1 | 3.63 × 10−3 * | 1.31 × 10−7 * | 4.49 × 10−6 * |
| Res-UNet | 6.74 × 10−3 * | 7.34 × 10−6 * | 3.63 × 10−3 * | 1 | 2.03 × 10−16 * | 6.61 × 10−15 * |
| TransUNet | 4.49 × 10−7 * | 4.33 × 10−3 | 1.31 × 10−7 * | 2.03 × 10−16 * | 1 | 7.41 × 10−1 |
| UNeXt | 1.64 × 10−6 * | 6.18 × 10−3 | 4.49 × 10−6 * | 6.61 × 10−15 * | 7.41 × 10−1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Gao, R.; Shi, X.; Lang, J.; Xue, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Yu, C.; Zhou, Z. U-Net and Its Variants Based Automatic Tracking of Radial Artery in Ultrasonic Short-Axis Views: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212358
Tian Y, Gao R, Shi X, Lang J, Xue Y, Wang C, Zhang Y, Shen L, Yu C, Zhou Z. U-Net and Its Variants Based Automatic Tracking of Radial Artery in Ultrasonic Short-Axis Views: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(21):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212358
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yuan, Ruiyang Gao, Xinran Shi, Jiaxin Lang, Yang Xue, Chunrong Wang, Yuelun Zhang, Le Shen, Chunhua Yu, and Zhuhuang Zhou. 2024. "U-Net and Its Variants Based Automatic Tracking of Radial Artery in Ultrasonic Short-Axis Views: A Pilot Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 21: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212358
APA StyleTian, Y., Gao, R., Shi, X., Lang, J., Xue, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Shen, L., Yu, C., & Zhou, Z. (2024). U-Net and Its Variants Based Automatic Tracking of Radial Artery in Ultrasonic Short-Axis Views: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 14(21), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212358







