Micro-Computed Tomography Whole-Block Imaging Reveals Origin and Path of Rectal Cancer Tumor Deposits: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Selection
2.2. Whole-Slide Imaging Analysis
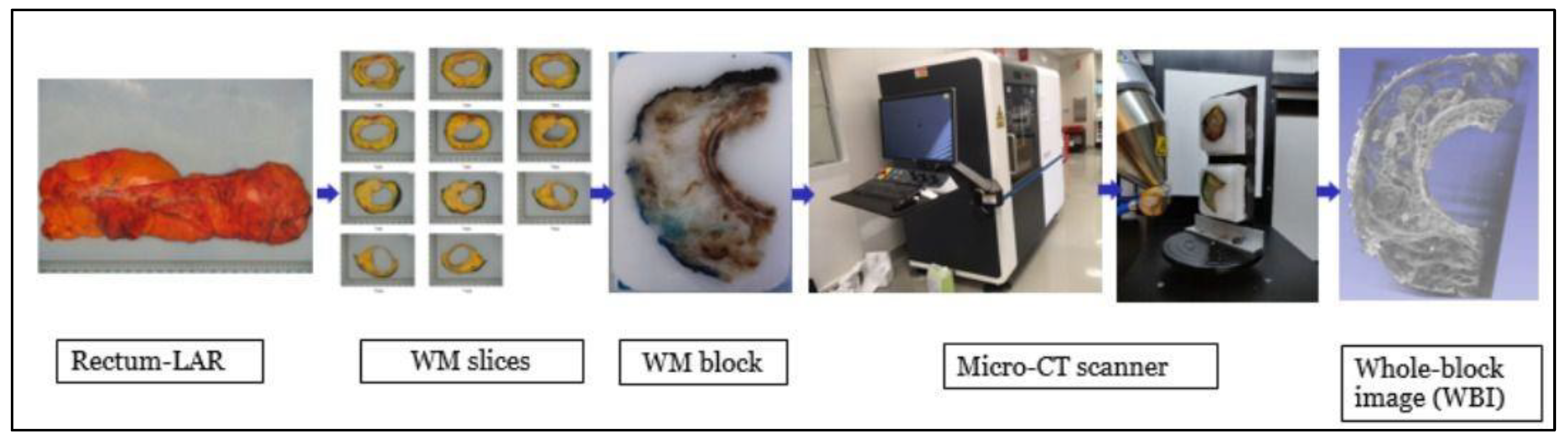
2.3. Whole-Block Imaging Analysis
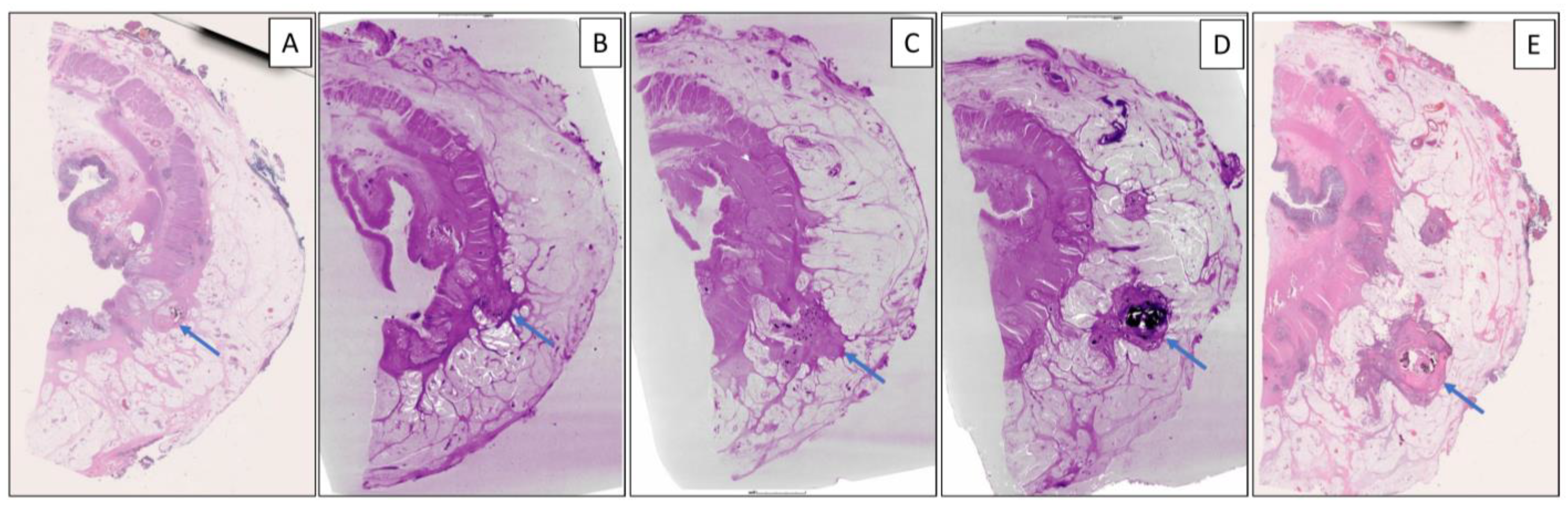
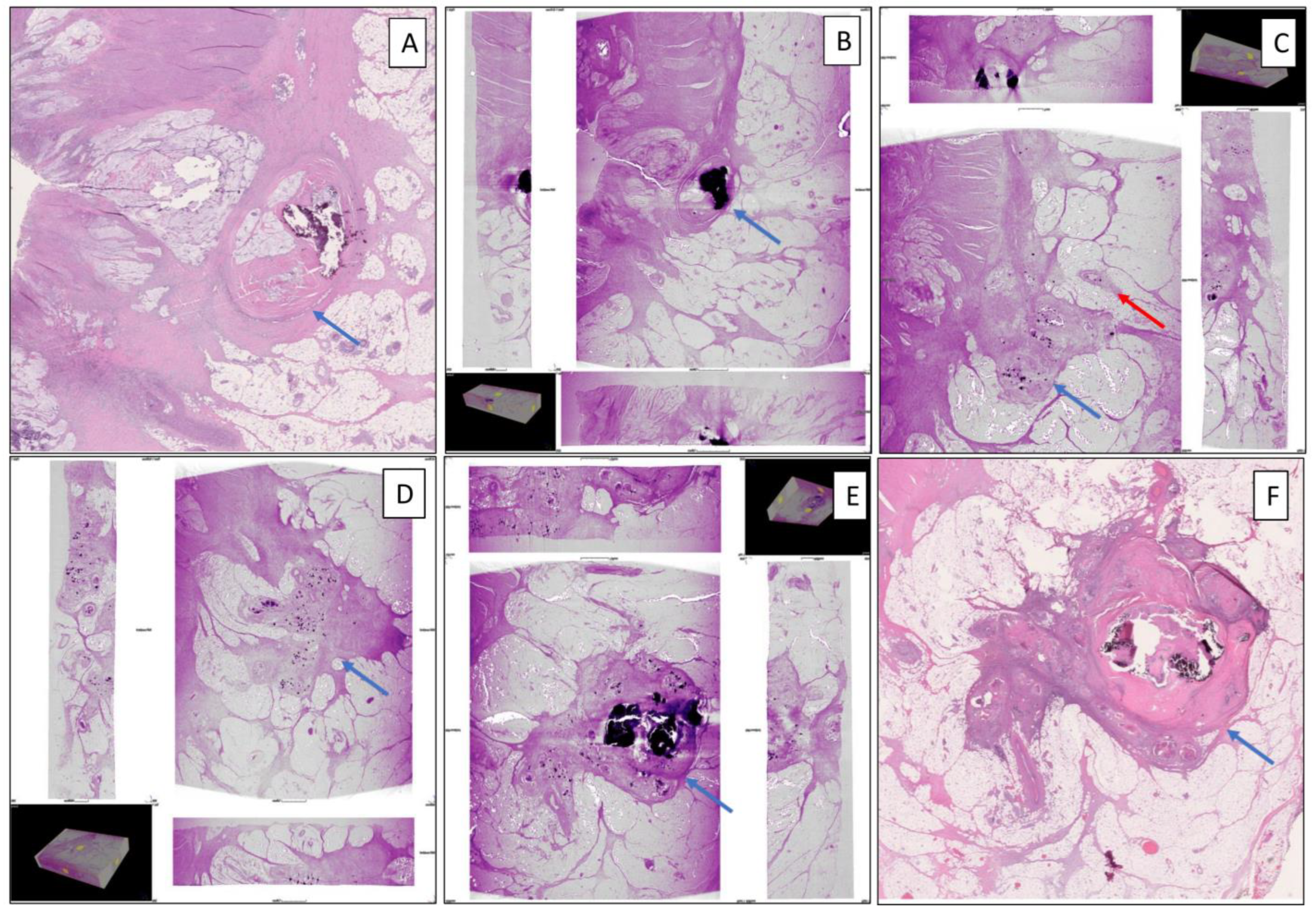
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohnishi, T.; Teplov, A.; Kawata, N.; Ibrahim, K.; Ntiamoah, P.; Firat, C.; Haneishi, H.; Hameed, M.; Shia, J.; Yagi, Y. Three-Dimensional Vessel Segmentation in Whole-Tissue and Whole-Block Imaging Using a Deep Neural Network: Proof-of-Concept Study. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Cesmecioglu, E.; Firat, C.; Sakamoto, H.; Teplov, A.; Kawata, N.; Ntiamoah, P.; Ohnishi, T.; Ibrahim, K.; Vakiani, E.; et al. Pathological Evaluation of Rectal Cancer Specimens Using Micro-Computed Tomography. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Teplov, A.; Ibrahim, K.; Inoue, T.; Stueben, B.; Katabi, N.; Hameed, M.; Yagi, Y.; Ghossein, R. Detection and assessment of capsular invasion, vascular invasion and lymph node metastasis volume in thyroid carcinoma using microCT scanning of paraffin tissue blocks (3D whole block imaging): A proof of concept. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Knijn, N.; Hugen, N.; Marshall, H.C.; Sugihara, K.; Tot, T.; Ueno, H.; Quirke, P. Tumor Deposits in Colorectal Cancer: Improving the Value of Modern Staging—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, A.; Martínez, C.G.; D’Souza, N.; Pucher, P.; Brown, G.; Nagtegaal, I. The significance of tumour deposits in rectal cancer after neoadjuvant therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Q.; Gu, L. Clinical and Pathologic Predictors of Tumor Deposits in Colorectal Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2023, 55, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Shi, Q.; Meyers, J.; Jin, Z.; Svrcek, M.; Fuchs, C.; Couture, F.; Kuebler, P.; Ciombor, K.; Bendell, J.; et al. Combining tumor deposits with the number of lymph node metastases to improve the prognostic accuracy in stage III colon cancer: A post hoc analysis of the CALGB/SWOG 80702 phase III study (Alliance)☆. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuval, J.B.; Thompson, H.M.; Firat, C.; Verheij, F.S.; Widmar, M.M.; Wei, I.H.; Pappou, E.M.; Smith, J.J.M.; Weiser, M.R.; Paty, P.B.; et al. MRI at Restaging After Neoadjuvant Therapy for Rectal Cancer Overestimates Circumferential Resection Margin Proximity as Determined by Comparison with Whole-Mount Pathology. Dis. Colon Rectum 2022, 65, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-H.; Firat, C.; Thompson, H.M.; Gangai, N.; Zheng, J.; Capanu, M.; Bates, D.D.B.; Paroder, V.; García-Aguilar, J.; Shia, J.; et al. Extramural Venous Invasion and Tumor Deposit at Diffusion-weighted MRI in Patients after Neoadjuvant Treatment for Rectal Cancer. Radiology 2023, 308, e230079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Teplov, A.; Rekhtman, N.; Travis, W.; Yagi, Y. The Roles of Whole Block Imaging with Micro-Computed Tomography in Lung Adenocarcinoma. In Laboratory Investigation; Nature Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, A.L.; Buckley, J.; Tang, R.; Brachtel, E.; Rai, U.; Michaelson, J.; Ly, A.; Specht, M.C.; Yagi, Y.; Smith, B.L. A Study of the Growth Patterns of Breast Carcinoma Using 3D Reconstruction: A Pilot Study. Breast J. 2017, 23, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firat, C.; Teplov, A.; Kawata, N.; Ibrahim, K.; Ntiamoah, P.; Hameed, M.; Vakiani, E.; Garcia-Aguilar, J.; Yagi, Y.; Shia, J. Whole Block Imaging (WBI) Utilizing Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) Reveals Pathological Information Not Detected on Regular Histology: A Pilot Study of Rectal Cancer Resection Specimens. In Laboratory Investigation; Nature Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.J.; Wan, X.B.; Yang, Z.L.; Fu, X.H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, D.K.; Song, S.X.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, H.Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Snail promotes lymph node metastasis and Twist enhances tumor deposit formation through epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarioglu, S. Tumor Deposits Mechanism, Morphology and Prognostic Implications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wünsch, K.; Müller, J.; Jähnig, H.; Herrmann, R.A.; Arnholdt, H.M.; Märkl, B. Shape is not associated with the origin of pericolonic tumor deposits. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 133, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Firat, C.; Urganci, N.; Teplov, A.; Cesmecioglu, E.; Bakoglu, N.; Vakiani, E.; Ntiamoah, P.; Weiser, M.R.; Garcia-Aguilar, J.; Hameed, M.; et al. Micro-Computed Tomography Whole-Block Imaging Reveals Origin and Path of Rectal Cancer Tumor Deposits: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161704
Firat C, Urganci N, Teplov A, Cesmecioglu E, Bakoglu N, Vakiani E, Ntiamoah P, Weiser MR, Garcia-Aguilar J, Hameed M, et al. Micro-Computed Tomography Whole-Block Imaging Reveals Origin and Path of Rectal Cancer Tumor Deposits: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(16):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161704
Chicago/Turabian StyleFirat, Canan, Nil Urganci, Alexei Teplov, Emine Cesmecioglu, Nilay Bakoglu, Efsevia Vakiani, Peter Ntiamoah, Martin R. Weiser, Julio Garcia-Aguilar, Meera Hameed, and et al. 2024. "Micro-Computed Tomography Whole-Block Imaging Reveals Origin and Path of Rectal Cancer Tumor Deposits: A Pilot Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 16: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161704
APA StyleFirat, C., Urganci, N., Teplov, A., Cesmecioglu, E., Bakoglu, N., Vakiani, E., Ntiamoah, P., Weiser, M. R., Garcia-Aguilar, J., Hameed, M., Yagi, Y., & Shia, J. (2024). Micro-Computed Tomography Whole-Block Imaging Reveals Origin and Path of Rectal Cancer Tumor Deposits: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 14(16), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161704






