Diagnostic Potential of Two Novel Biomarkers for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Quantitative CSF Proteomics Analysis Using TMT Technology
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparing the Clinical Traits of Patients and Controls
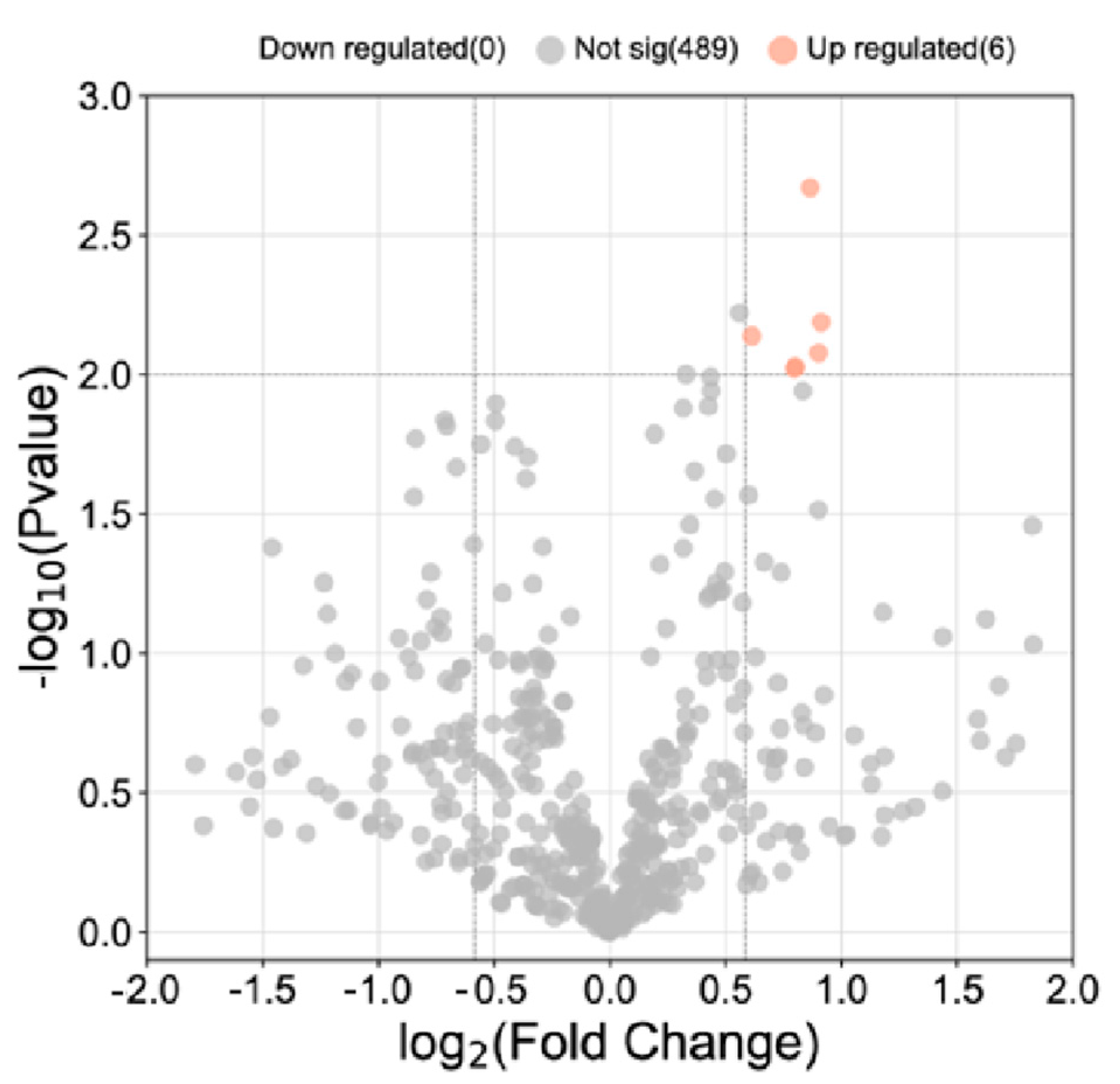
3.2. Proteomic Analysis of CSF from MS and NMOSD Patients
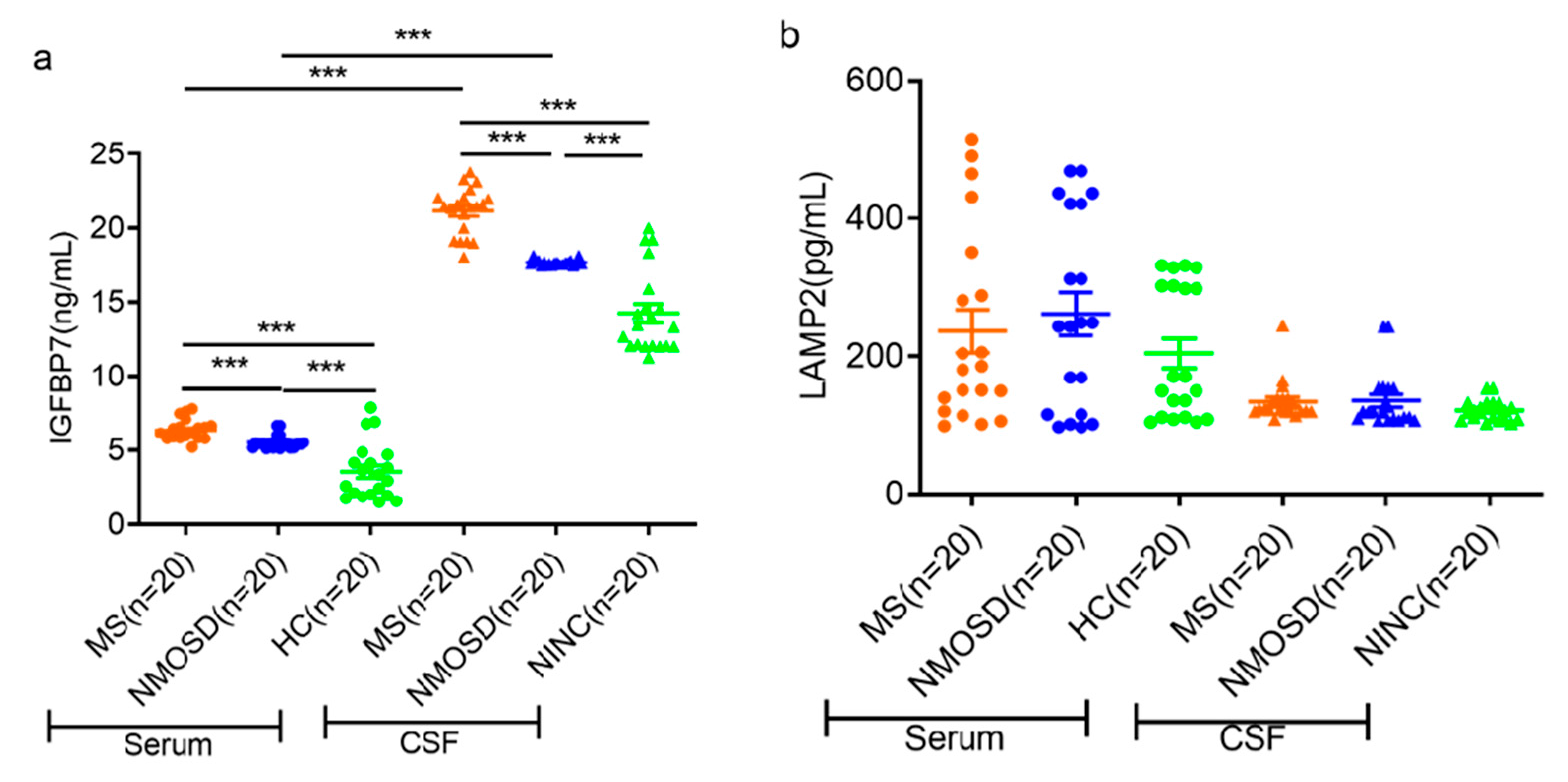
3.3. ELISA Validation of Candidate Proteins
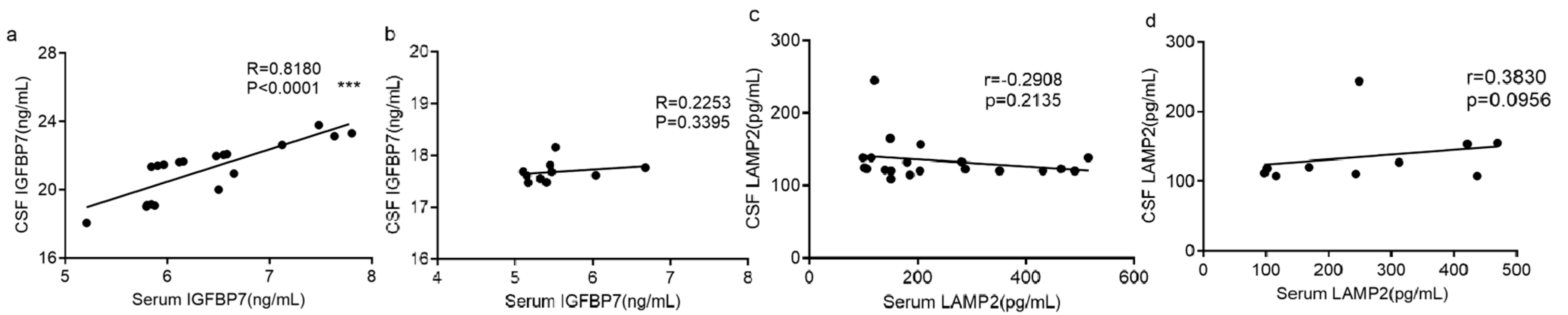
3.4. Correlation between Serum and CSF Measurements of Each Protein
3.5. Evaluating the Efficacy of IGFBP7 and LAMP2 in the Diagnosis of MS and NMOSD
3.6. Effectiveness of IGFBP7 and LAMP2 in Differentiating NMOSD from MS
3.7. Assessment of the Predictive Capability of IGFBP7 and LAMP2 for SPMS
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filippi, M.; Bar-Or, A.; Piehl, F.; Preziosa, P.; Solari, A.; Vukusic, S.; Rocca, M.A. Multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, S.; Nicholas, R.; Reynolds, R.; Magliozzi, R. Intrathecal Inflammation in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toczylowska, B.; Zieminska, E.; Podlecka-Pietowska, A.; Ruszczynska, A.; Chalimoniuk, M. Serum metabolic profiles and metal levels of patients with multiple sclerosis and patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders—NMR spectroscopy and ICP-MS studies. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 60, 103672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; de Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.; Li, X.F.; Jung, I.J.; Kim, H.J. Does interferon beta treatment exacerbate neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder? Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica: State-of-the-art and emerging therapies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.R.; Tanner, M. The latest diagnostic criteria and treatment options for neuromyelitis optica. JAAPA J. Am. Acad. Physician Assist. 2019, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A. Applying the 2017 McDonald diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciak, K.; Pietrasik, S.; Dziedzic, A.; Redlicka, J.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M.; Wlodarczyk, T.; Miller, E. Th17-Related Cytokines as Potential Discriminatory Markers between Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic’s Disease) and Multiple Sclerosis—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Malekzadeh, A.; Leurs, C.; Bridel, C.; Killestein, J. Body fluid biomarkers for multiple sclerosis—The long road to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandi, D.; Kokas, Z.; Biernacki, T.; Bencsik, K.; Klivenyi, P.; Vecsei, L. Proteomics in Multiple Sclerosis: The Perspective of the Clinician. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoman, M.E.; McKarns, S.C. Metabolomic Profiling in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Biomarker Discovery. Metabolites 2020, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowarik, M.C.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Wemlinger, S.; Ritchie, A.M.; Hemmer, B.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L. The cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin transcriptome and proteome in neuromyelitis optica reveals central nervous system-specific B cell populations. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.L.; Owens, G.P. Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics: A new window for understanding human demyelinating disorders? Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, M.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nirasawa, T.; Thiele, H.; Becker, M.; Alexandrov, T.; Saida, T.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuo, H.; Tomimoto, H.; et al. Proteomic pattern analysis discriminates among multiple sclerosis-related disorders. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.F.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.R.; Ding, Y.; Ding, M.P. Proteomic analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; McKinney, K.Q.; Pavlopoulos, A.J.; Han, M.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, S. Exosomal proteome analysis of cerebrospinal fluid detects biosignatures of neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 462, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.F.; Lu, Q.Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Yang, Y.; Ding, M.P. Proteomics comparison of the sera from multiple sclerosis patients and neuromyelitis optica patients. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 9292–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.H.; Beck, H.C.; Kristensen, L.P.; Burton, M.; Csepany, T.; Simo, M.; Dioszeghy, P.; Sejbaek, T.; Grebing, M.; Heegaard, N.H.; et al. The Urine Proteome Profile Is Different in Neuromyelitis Optica Compared to Multiple Sclerosis: A Clinical Proteome Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R.; Schroll, M.M.; Hummon, A.B. Comparison of In-Solution, FASP, and S-Trap Based Digestion Methods for Bottom-Up Proteomic Studies. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2480–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Osman, R.A.; Sun, J.; Qian, L.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, G. Discovery of Novel Biomarkers for Diagnosing and Predicting the Progression of Multiple Sclerosis Using TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomics. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 700031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowska, L.; Koziarska, D.; Karakiewicz, B.; Kotwas, A.; Knyszynska, A.; Folwarski, M.; Dec, K.; Stachowska, E.; Hawrylkowicz, V.; Kulaszynska, M.; et al. Hepcidin (rs10421768), Transferrin (rs3811647, rs1049296) and Transferrin Receptor 2 (rs7385804) Gene Polymorphism Might Be Associated with the Origin of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chu, Y.; Ma, R.; Dou, M.; Li, S.; Song, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, L. Ferroptosis as a mechanism of oligodendrocyte loss and demyelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 373, 577995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akil, O.; Sun, Y.; Vijayakumar, S.; Zhang, W.; Ku, T.; Lee, C.K.; Jones, S.; Grabowski, G.A.; Lustig, L.R. Spiral ganglion degeneration and hearing loss as a consequence of satellite cell death in saposin B-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 3263–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.C.; Giddens, M.M.; Coleman, B.M.; Hall, R.A. The protective role of prosaposin and its receptors in the nervous system. Brain Res. 2014, 1585, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, R.; Amatya, N.; Majumder, S.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; McGeachy, M.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The RNA-binding protein IMP2 drives a stromal-Th17 cell circuit in autoimmune neuroinflammation. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e152766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Lin, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, K.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; Li, F.; et al. IGF-2 Preprograms Maturing Macrophages to Acquire Oxidative Phosphorylation-Dependent Anti-inflammatory Properties. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1363–1375.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Hu, Y.; Yu, L.; Ke, C.; Vo, C.; Hsu, H.; Li, Z.; Di Donato, A.T.; Chaturbedi, A.; Hwang, J.W.; et al. Weaponizing human EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 (EFEMP1) for 21(st) century cancer therapeutics. Oncoscience 2016, 3, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaki, M.; Ueda, M.; Hoshii, Y.; Mizukami, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yamashita, T.; Ueda, A.; Misumi, Y.; Masuda, T.; et al. A novel age-related venous amyloidosis derived from EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaki, M.; Oishi, T.; Ueda, M. EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 (EFEMP1) amyloid deposits in the lower rectum from aged patient with bloody stools. Pathol. Int. 2022, 72, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Pu, Y.; Shao, Q.; Fang, X.; Han, D.; Zhao, M.; Cao, L. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 is up-regulated during EAE and inhibits the differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, R.L.; De Groot, C.J.; Certa, U.; Ravid, R.; Hoffmann, F.; Kappos, L.; Leppert, D. Multiple sclerosis as a generalized CNS disease—Comparative microarray analysis of normal appearing white matter and lesions in secondary progressive MS. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 152, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, N.; Sormani, M.P. Combining biomarkers to profile multiple sclerosis patients. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Preziosa, P.; Langdon, D.; Lassmann, H.; Paul, F.; Rovira, A.; Schoonheim, M.M.; Solari, A.; Stankoff, B.; Rocca, M.A. Identifying Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: New Perspectives. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.I.; Patrucco, L.; Alonso, R.; Garcea, O.; Deri, N.; Carnero Contentti, E.; Lopez, P.A.; Pettinicchi, J.P.; Caride, A.; Cristiano, E. Diagnostic uncertainty during the transition to secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: Multicenter study in Argentina. Mult. Scler. 2021, 27, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, M.J.; Behringer, R.R.; Brinster, R.L.; McMorris, F.A. Insulin-like growth factor I increases brain growth and central nervous system myelination in transgenic mice. Neuron 1993, 10, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeger, M.; Popken, G.; Zhang, J.; Xuan, S.; Lu, Q.R.; Schwab, M.H.; Nave, K.A.; Rowitch, D.; D’Ercole, A.J.; Ye, P. Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor signaling in the cells of oligodendrocyte lineage is required for normal in vivo oligodendrocyte development and myelination. Glia 2007, 55, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Han, J.; Tang, J.; Ying, Y. IGFBP-7 inhibits the differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells via regulation of Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 4742–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassam, Y.N.; Izzy, S.; Whalen, M.; McGavern, D.B.; El Khoury, J. Neuroimmunology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Time for a Paradigm Shift. Neuron 2017, 95, 1246–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Zhang, J.H.; Obenaus, A. Response of the cerebral vasculature following traumatic brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 2320–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhan, C.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ai, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Wang, D.W. CYP2J2-derived EETs attenuated ethanol-induced myocardial dysfunction through inducing autophagy and reducing apoptosis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 117, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 2007, 447, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.J.; Lu, X.L.; Lv, J.C.; Yang, H.Z.; Qin, L.X.; Zhao, M.H.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.G.; Zhang, H. Genetic association of PRDM1-ATG5 intergenic region and autophagy with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Chinese population. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Fang, F.; Guo, L.; Chen, D.; Chen, J.X.; Stern, D.; Taylor, G.A.; Jiang, H.; Yan, S.S. Genetic deficiency of Irgm1 (LRG-47) suppresses induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by promoting apoptosis of activated CD4+ T cells. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, C.; Jones, J.W.; Hegdekar, N.; Thayer, J.A.; Kumar, A.; Faden, A.I.; Kane, M.A.; Lipinski, M.M. PLA2G4A/cPLA2-mediated lysosomal membrane damage leads to inhibition of autophagy and neurodegeneration after brain trauma. Autophagy 2020, 16, 466–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Packer, M.; Claggett, B.; Liu, J.; Shah, A.M.; Zile, M.R.; Pieske, B.; Voors, A.; Gandhi, P.U.; Prescott, M.F.; et al. IGFBP7 (Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-7) and Neprilysin Inhibition in Patients with Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e005133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Shen, F.; Weinfeld, M.; Sergi, C. Insulin Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP7)-Related Cancer and IGFBP3 and IGFBP7 Crosstalk. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | MS | NMOSD | NINC | HC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRMS (n = 7) | SPMS (n = 13) | ||||
| N (CSF; Serum) | 7;7 | 13;13 | 20;20 | 20;0 | 0;20 |
| Age (year), mean ± SD | 38.7 ± 12.5 | 33.1 ± 11.4 | 36.6 ± 10.0 | 37.2 ± 10.4 | 38.5 ± 8.0 |
| Male (%) | 3(42.9%) | 5(38.5%) | 8(40.0%) | 7(35.0%) | 7(35.0%) |
| Disease duration (year), mean ± SD | 3.1 ± 1.3 | 13.8 ± 5.9 | 10.1 ± 7.1 | - | - |
| EDSS, mean ± SD | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 4.1 ± 1.7 | - | - | - |
| MRI lesion | - | - | - | ||
| 0–8 lesions, n, n% | 9, 45.0% | 8, 40.0% | |||
| ≥9 lesions, n, n% | 11, 55.0% | 12, 60.0% | |||
| Biomarkers | MS vs. Control | NMOSD vs. Control | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cut-off Point | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cut-Off Point | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
| Serum IGFBP7 | 5.0 | 100% | 85% | 5.0 | 100% | 85% |
| CSF IGFBP7 | 17.0 | 100% | 80% | 16.7 | 100% | 80% |
| Serum LAMP2 | 341.5 | 25% | 100% | 376.5 | 30% | 100% |
| CSF LAMP2 | 119.4 | 90% | 50% | 154.4 | 20% | 100% |
| Biomarkers | MS vs. NMOSD | RRMS vs. SPMS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cut-Off Point | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cut-Off Point | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
| Serum IGFBP7 | 4.1 | 100% | 0% | 6.0 | 92.3% | 100% |
| CSF IGFBP7 | 16.5 | 100% | 0% | 21.5 | 76.9% | 100% |
| Serum LAMP2 | 224.5 | 60% | 65% | 165.7 | 69.2% | 71.4% |
| CSF LAMP2 | 146.0 | 30% | 85% | 111.7 | 100% | 14.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, G. Diagnostic Potential of Two Novel Biomarkers for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Multiple Sclerosis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091572
Xu T, Shi Y, Zheng G, Zhang G. Diagnostic Potential of Two Novel Biomarkers for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Multiple Sclerosis. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(9):1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091572
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ting, Yijun Shi, Guanghui Zheng, and Guojun Zhang. 2023. "Diagnostic Potential of Two Novel Biomarkers for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Multiple Sclerosis" Diagnostics 13, no. 9: 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091572
APA StyleXu, T., Shi, Y., Zheng, G., & Zhang, G. (2023). Diagnostic Potential of Two Novel Biomarkers for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Multiple Sclerosis. Diagnostics, 13(9), 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091572





