Homogeneous Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Diverse Recurrent Possibilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
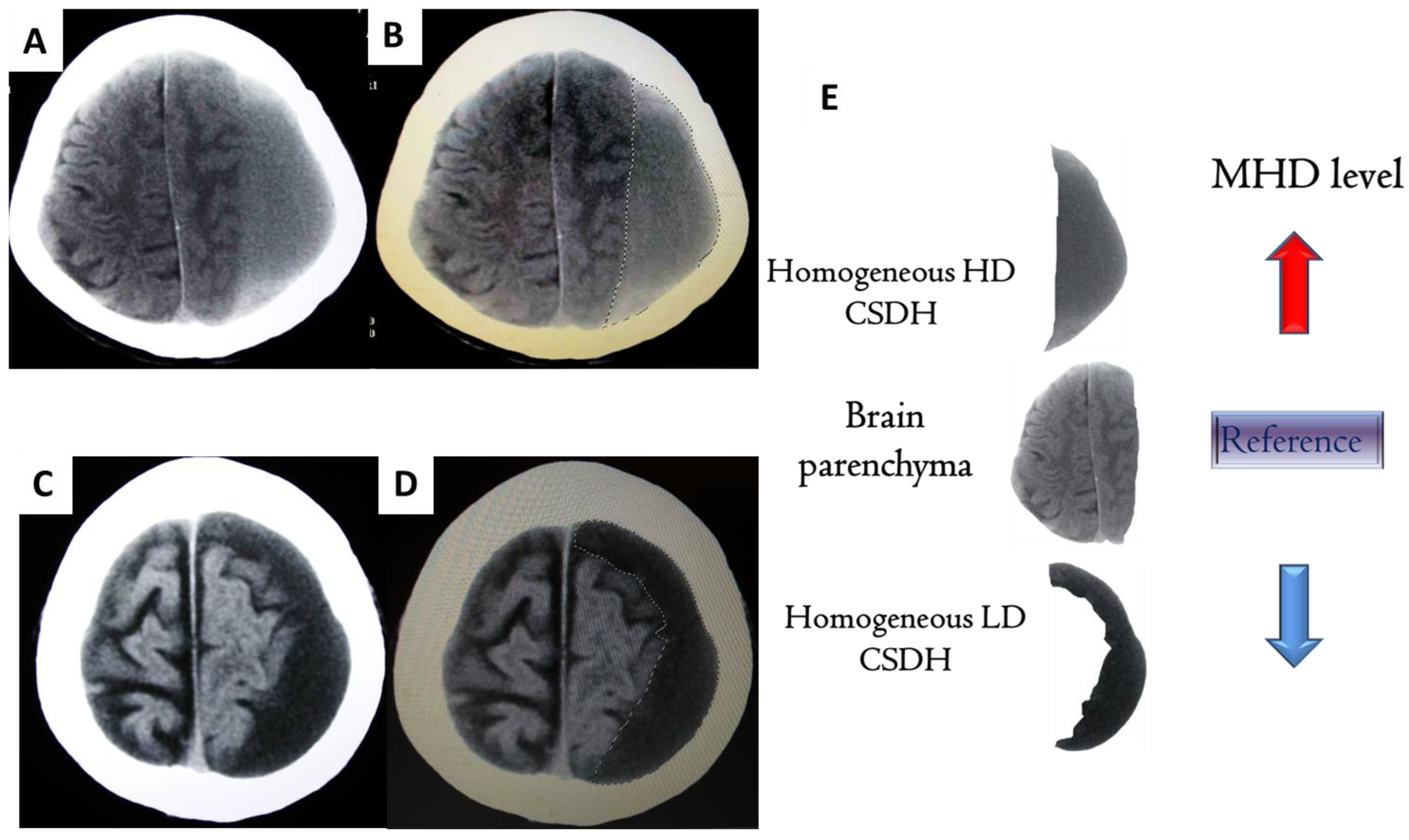
2.2. Clinical Classification of CSDH
2.3. Computer-Assisted Quantitative Analysis of CSDHs
2.4. MHD Quantification for CSDHs [16]
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. MHD Quantitations in Four Types
3.3. MHD Quantitations in Five Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ernestus, R.I.; Beldzinski, P.; Lanfermann, H.; Klug, N. Chronic subdural hematoma: Surgical treatment and outcome in 104 patients. Surg. Neurol. 1997, 48, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellergård, P.; Wisten, O. Operations and re-operations for chronic subdural haematomas during a 25-year period in a well defined population. Acta Neurochir. 1996, 138, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambasivan, M. An overview of chronic subdural hematoma: Experience with 2300 cases. Surg. Neurol. 1997, 47, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Doh, J.W.; Bae, H.G.; Yun, I.G. Relations among traumatic subdural lesions. J. Korean Med. Sci. 1996, 11, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaguchi, H.; Tanishima, T.; Yoshimasu, N. Factors in the natural history of chronic subdural hematomas that influence their postoperative recurrence. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 95, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.R.; Lee, K.S.; Shim, J.J.; Yoon, S.M.; Bae, H.G.; Doh, J.W. Multiple Densities of the Chronic Subdural Hematoma in CT Scans. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2013, 54, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pallero, M.; Pulido-Rivas, P.; Pascual-Garvi, J.M.; Sola, R.G. Chronic subdural haematomas. The internal architecture of the haematoma as a predictor of recurrence. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 59, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, B.S.; Lee, J.K.; Seo, B.R.; Moon, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H. Clinical analysis of risk factors related to recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2008, 43, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.-K.; Kim, B.-C.; Cho, K.-T.; Hong, S.-K. Factors Affecting Postoperative Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2012, 8, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.; Tregubow, A.; Kerry, G.; Schrey, M.; Hammer, C.; Steiner, H.H. Predictors for Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Turk. Neurosurg. 2017, 27, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stanišic, M.; Pripp, A.H. A Reliable Grading System for Prediction of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Recurrence Requiring Reoperation After Initial Burr-Hole Surgery. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanišić, M.; Hald, J.; Rasmussen, I.A.; Pripp, A.H.; Ivanović, J.; Kolstad, F.; Sundseth, J.; Züchner, M.; Lindegaard, K.F. Volume and densities of chronic subdural haematoma obtained from CT imaging as predictors of postoperative recurrence: A prospective study of 107 operated patients. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 323–333; discussion 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, M.; Toyama, M.; Tamatani, S.; Kitazawa, T.; Saito, M. Clinical factors of recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2001, 41, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlmann, E.; Giorgi-Coll, S.; Whitfield, P.C.; Carpenter, K.L.H.; Hutchinson, P.J. Pathophysiology of chronic subdural haematoma: Inflammation, angiogenesis and implications for pharmacotherapy. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisic, M.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Mahesparan, R. Treatment of chronic subdural hematoma by burr-hole craniostomy in adults: Influence of some factors on postoperative recurrence. Acta Neurochir. 2005, 147, 1249–1256; discussion 1256-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Lu, Y.M.; Chen, T.H.; Wang, S.P.; Hsiao, S.H.; Lin, M.S. Quantitative assessment of post-operative recurrence of chronic subdural haematoma using mean haematoma density. Brain Inj. 2014, 28, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Chang, S.-T.; Lin, M.-S. Statistical relevance of mean hematoma density and it’s internal architecture: Potential clinical application in chronic subdural hematomas. Formos. J. Surg. 2018, 51, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.J.; Lee, K.S.; Shim, J.J.; Yoon, S.M.; Yun, I.G.; Bae, H.G. Postoperative course and recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2010, 48, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, W.M.; Hung, K.S.; Chiu, W.T.; Tsai, S.H.; Lin, J.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, M.S. Quantitative assessment of impaired postevacuation brain re-expansion in bilateral chronic subdural haematoma: Possible mechanism of the higher recurrence rate. Injury 2012, 43, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Kashiwagi, S.; Fujisawa, H.; Ito, H.; Nakamura, K. Characterization of local hyperfibrinolysis in chronic subdural hematomas by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 81, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ohno, K. Chronic subdural hematoma—An up-to-date concept. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2013, 60, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frati, A.; Salvati, M.; Mainiero, F.; Ippoliti, F.; Rocchi, G.; Raco, A.; Caroli, E.; Cantore, G.; Delfini, R. Inflammation markers and risk factors for recurrence in 35 patients with a posttraumatic chronic subdural hematoma: A prospective study. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokmak, M.; Iplikcioglu, A.C.; Bek, S.; Gökduman, C.A.; Erdal, M. The role of exudation in chronic subdural hematomas. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahyouni, R.; Goshtasbi, K.; Mahmoodi, A.; Tran, D.K.; Chen, J.W. Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Perspective on Subdural Membranes and Dementia. World Neurosurg. 2017, 108, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashima, T.; Kubota, T.; Yamamoto, S. Eosinophil degranulation in the capsule of chronic subdural hematomas. J. Neurosurg. 1985, 62, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Shim, J.J.; Yoon, S.M.; Doh, J.W.; Yun, I.G.; Bae, H.G. Acute-on-Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Not Uncommon Events. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2011, 50, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, I.P.; Tank, Y.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Peul, W.C.; Dammers, R.; Lingsma, H.F.; den Hertog, H.M.; Jellema, K.; van der Gaag, N.A. Radiological prognostic factors of chronic subdural hematoma recurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashima, T. The inner membrane of chronic subdural hematomas: Pathology and pathophysiology. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 11, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holl, D.C.; Volovici, V.; Dirven, C.M.F.; Peul, W.C.; van Kooten, F.; Jellema, K.; van der Gaag, N.A.; Miah, I.P.; Kho, K.H.; den Hertog, H.M.; et al. Pathophysiology and Nonsurgical Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: From Past to Present to Future. World Neurosurg. 2018, 116, 402–411.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, H.; Nomura, S.; Tsuchida, E.; Ito, H. Serum protein exudation in chronic subdural haematomas: A mechanism for haematoma enlargement? Acta Neurochir. 1998, 140, 161–165; discussion 165-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaguchi, H.; Tanishima, T.; Yoshimasu, N. Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balevi, M. Organized Chronic Subdural Hematomas Treated by Large Craniotomy with Extended Membranectomy as the Initial Treatment. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2017, 12, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, H.G.; Park, S.H. Craniotomy and Membranectomy for Treatment of Organized Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2018, 14, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kong, M.H.; Song, K.Y. Chronic subdural hematoma treated by small or large craniotomy with membranectomy as the initial treatment. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2011, 50, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, P.; Pant, B.; Shrestha, P.; Rajbhandari, P. Organized subdural hematoma with thick membrane in chronic subdural hematoma. JNMA J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2012, 52, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, D.; Heinze, S.; Riegel, T.; Benes, L. Neuroendoscopic treatment of loculated chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 11, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

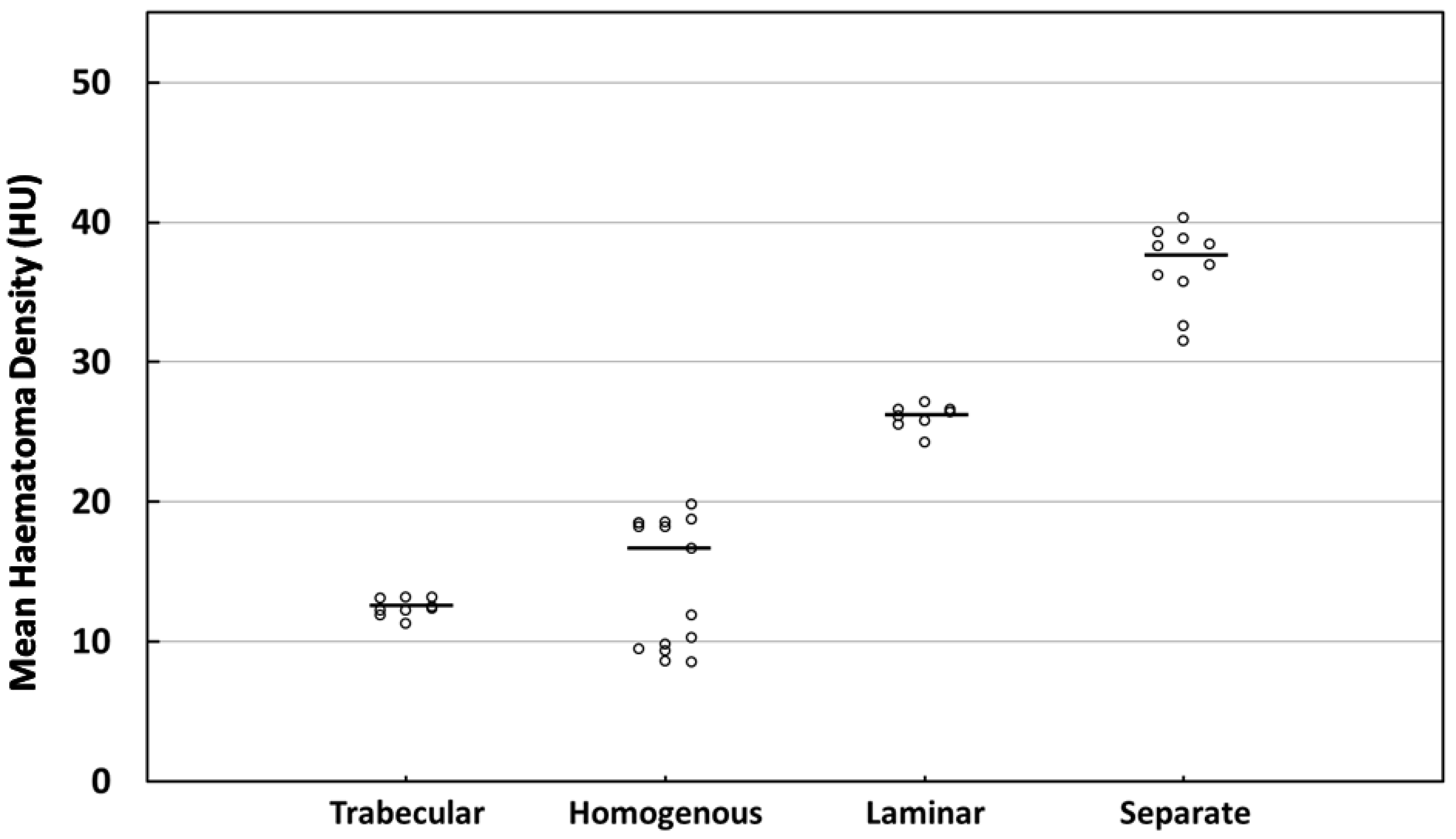
| Trabecular | Homogenous | Laminar | Separate | p-Value a | p-Value b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 9 | 15 | 8 | 10 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD | 12.43 ± 0.63 | 14.34 ± 4.59 | 26.07 ± 0.89 | 36.82 ± 2.89 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 12.33 (1.07) | 16.65 (9.00) | 26.28 (1.01) | 37.65 (3.98) | ||
| 95% CI | 11.95–12.91 | 11.80–16.88 | 25.32–26.81 | 34.76–38.89 | ||
| CV | 5.05% | 32.00% | 3.42% | 7.84% |
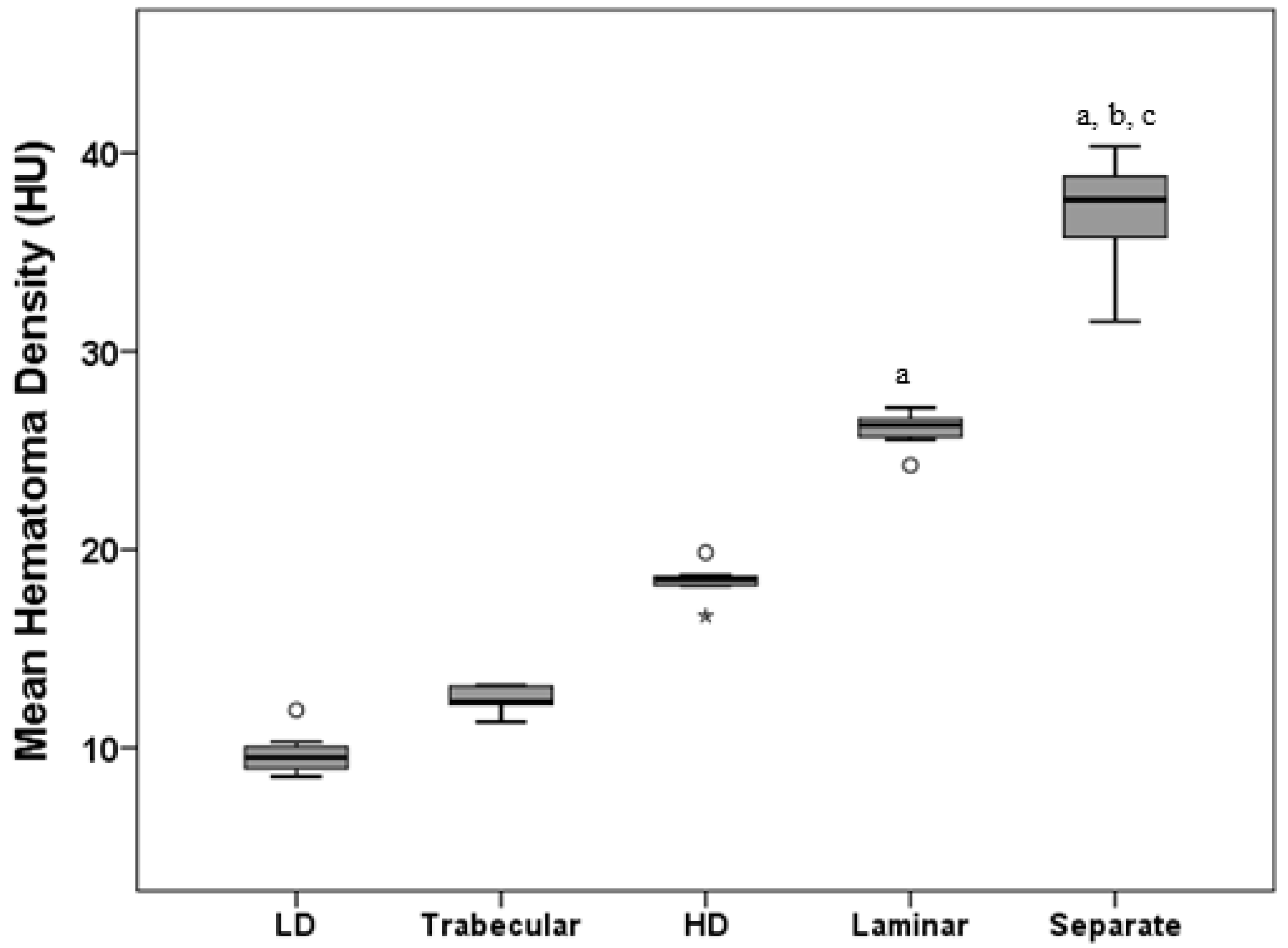
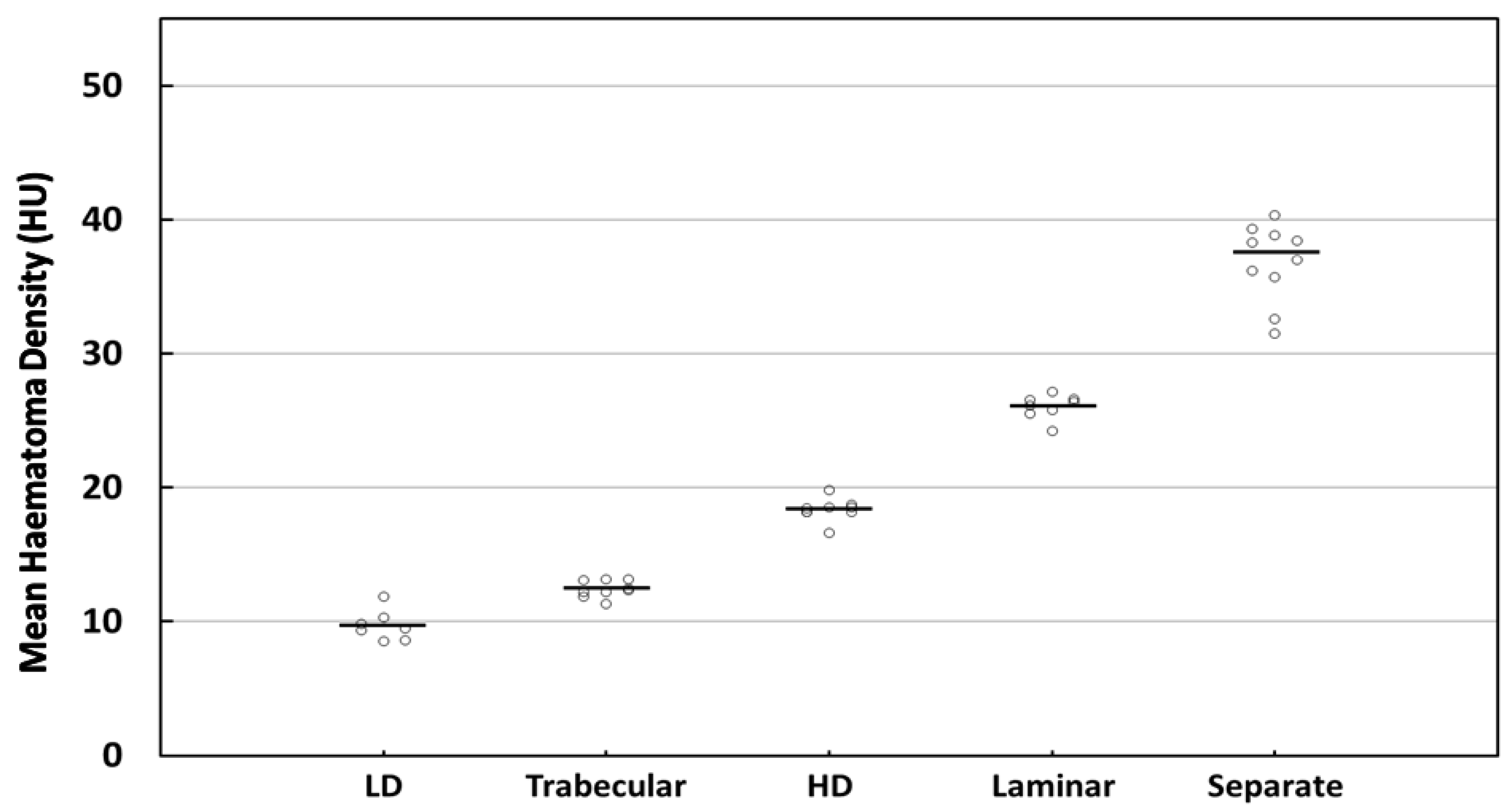
| Homogeneous LD | Trabecular | Homogeneous HD | Laminar | Separate | p-Value a | p-Value b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 7 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 10 | <0.001 | 0.011 |
| Mean ± SD | 9.71 ± 1.15 | 12.43 ± 0.63 | 18.39 ± 0.88 | 26.07 ± 0.89 | 36.82 ± 2.89 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 9.50 (1.72) | 12.33 (1.07) | 18.50 (0.51) | 26.28 (1.01) | 37.65 (3.98) | ||
| 95% CI | 8.67–10.77 | 11.95–12.91 | 17.66–19.13 | 25.32–26.81 | 34.76–38.89 | ||
| CV | 11.85% | 5.05% | 4.78% | 3.42% | 7.84% |
| Beta | SE | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSDHs | |||
| Trabecular | reference | ||
| Homogenous | 1.90 | 1.37 | 0.174 |
| Laminar | 13.50 | 1.57 | <0.001 |
| Separate | 24.43 | 1.48 | <0.001 |
| Age, years | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.346 |
| Gender (Male vs. Female) | −0.670 | 1.190 | 0.579 |
| Follow-up duration, month | −0.010 | 0.040 | 0.751 |
| Beta | SE | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSDHs | |||
| Homogeneous LD | reference | ||
| Trabecular | 2.64 | 0.84 | 0.004 |
| Homogeneous HD | 8.60 | 0.88 | <0.001 |
| Laminar | 16.20 | 0.88 | <0.001 |
| Separate | 27.03 | 0.83 | <0.001 |
| Age, years | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.539 |
| Gender (Male vs. Female) | −0.10 | 0.62 | 0.867 |
| Follow-up duration, month | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.467 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kung, W.-M.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-J.; Lin, M.-S. Homogeneous Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Diverse Recurrent Possibilities. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112695
Kung W-M, Wang Y-C, Chen W-J, Lin M-S. Homogeneous Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Diverse Recurrent Possibilities. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112695
Chicago/Turabian StyleKung, Woon-Man, Yao-Chin Wang, Wei-Jung Chen, and Muh-Shi Lin. 2022. "Homogeneous Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Diverse Recurrent Possibilities" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112695
APA StyleKung, W.-M., Wang, Y.-C., Chen, W.-J., & Lin, M.-S. (2022). Homogeneous Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Diverse Recurrent Possibilities. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112695










