Diagnostic Performance of Automated SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay in Nasal Swab during COVID-19 Vaccination Campaign
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Specimens
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 RT-q PCR
2.3. LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 Ag
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
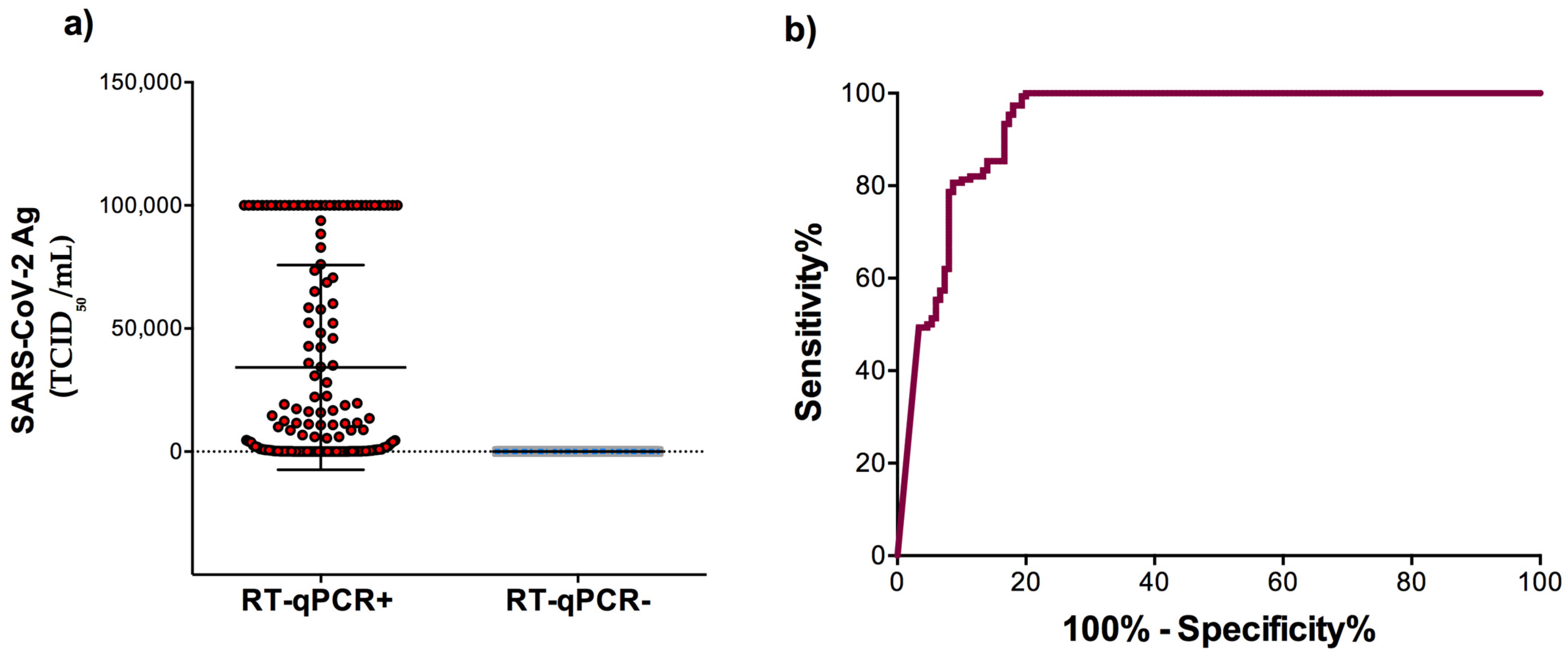
3.1. Sensitivity and Specificity of the Automated LIAISON® SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test
3.2. Antigen Detection According to the RT-qPCR Ct Values
3.3. RT-qPCR, Antigen Detection and COVID-19 Vaccination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kucharski, A.J.; Klepac, P.; Conlan, A.J.K.; Kissler, S.M.; Tang, M.L.; Fry, H.; Gog, J.R.; Edmunds, W.J.; Emery, J.C.; Medley, G.; et al. Effectiveness of isolation, testing, contact tracing, and physical distancing on reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in different settings: A mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, J.; Weng, L.; Ling, L.; Egi, M.; Lim, C.M.; Divatia, J.V.; Shrestha, B.R.; Arabi, Y.M.; Ng, J.; Gomersall, C.D.; et al. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Challenges and recommendations. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Bajwa, N.; Soni, D.; Das, S.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzikouri, S.; Nourlil, J.; Benjelloun, S.; Kohara, M.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K. Coronavirus disease 2019-Historical context, virology, pathogenesis, immunotherapy, and vaccine development. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2020, 16, 2992–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefever, S.; Indevuyst, C.; Cuypers, L.; Dewaele, K.; Yin, N.; Cotton, F.; Padalko, E.; Oyaert, M.; Descy, J.; Cavalier, E.; et al. Comparison of the Quantitative DiaSorin Liaison Antigen Test to Reverse Transcription-PCR for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Outpatients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0037421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haage, V.C.; de Ferreira Oliveira-Filho, E.; Moreira-Soto, A.; Kühne, A.; Fischer, C.; Sacks, J.A.; Corman, V.M.; Müller, M.A.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Impaired performance of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests at elevated and low temperatures. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 138, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, G.C.; Lau, S.S.; Wong, K.K.; Chow, N.L.; Lau, C.S.; Lam, E.T.; Chan, R.C.; Tsang, D.N. Analytical sensitivity and clinical sensitivity of the three rapid antigen detection kits for detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 133, 104684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, A.K.; Nikolai, O.; Kausch, F.; Wintel, M.; Hommes, F.; Gertler, M.; Krüger, L.J.; Gaeddert, M.; Tobian, F.; Lainati, F.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid test with self-collected nasal swab versus professional-collected nasopharyngeal swab. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altawalah, H.; AlHuraish, F.; Alkandari, W.A.; Ezzikouri, S. Saliva specimens for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Kuwait: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 132, 104652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Haage, V.C.; Bleicker, T.; Schmidt, M.L.; Mühlemann, B.; Zuchowski, M.; Jo, W.K.; Tscheak, P.; Möncke-Buchner, E.; Müller, M.A.; et al. Comparison of seven commercial SARS-CoV-2 rapid point-of-care antigen tests: A single-centre laboratory evaluation study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e311–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baro, B.; Rodo, P.; Ouchi, D.; Bordoy, A.E.; Saya Amaro, E.N.; Salsench, S.V.; Molinos, S.; Alemany, A.; Ubals, M.; Corbacho-Monné, M.; et al. Performance characteristics of five antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test (Ag-RDT) for SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic infection: A head-to-head benchmark comparison. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Berhane, S.; Taylor, M.; Adriano, A.; Davenport, C.; Dittrich, S.; Emperador, D.; Takwoingi, Y.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 3, CD013705. [Google Scholar]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergwerk, M.; Gonen, T.; Lustig, Y.; Amit, S.; Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, C.; Mandelboim, M.; Levin, E.G.; Rubin, C.; Indenbaum, V.; et al. Covid-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovida, F.; Cassaniti, I.; Paolucci, S.; Percivalle, E.; Sarasini, A.; Piralla, A.; Giardina, F.; Sammartino, J.C.; Ferrari, A.; Bergami, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine breakthrough infections with the alpha variant are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic among health care workers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.G.; Burgess, J.L.; Naleway, A.L.; Tyner, H.; Yoon, S.K.; Meece, J.; Olsho, L.E.W.; Caban-Martinez, A.J.; Fowlkes, A.L.; Lutrick, K.; et al. Prevention and Attenuation of Covid-19 with the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 Vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine-Tiefenbrun, M.; Yelin, I.; Katz, R.; Herzel, E.; Golan, Z.; Schreiber, L.; Wolf, T.; Nadler, V.; Ben-Tov, A.; Kuint, J.; et al. Initial report of decreased SARS-CoV-2 viral load after inoculation with the BNT162b2 vaccine. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despres, H.W.; Mills, M.G.; Shirley, D.J.; Schmidt, M.M.; Huang, M.L.; Jerome, K.R.; Greninger, A.L.; Bruce, E.A. Quantitative measurement of infectious virus in SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Delta and Epsilon variants reveals higher infectivity (viral titer:RNA ratio) in clinical samples containing the Delta and Epsilon variants. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotsu, Y.; Omata, M. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 lineage rapidly spreads and replaces R.1 lineage in Japan: Serial and stationary observation in a community. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 105088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.C.K.; Lau, S.S.Y.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Chow, N.L.S.; Lau, C.S.; Ng, K.H.L.; Lam, E.T.K.; Chan, R.C.W.; Tsang, D.N.C. Evaluation of automated antigen detection test for detection of SARS-CoV-2. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 101, 115490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gili, A.; Paggi, R.; Russo, C.; Cenci, E.; Pietrella, D.; Graziani, A.; Stracci, F.; Mencacci, A. Evaluation of Lumipulse® G SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay automated test for detecting SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (NP) in nasopharyngeal swabs for community and population screening. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altawalah, H. Antibody Responses to Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection or after COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines 2021, 9, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartard, C.; Berger, S.; Josse, T.; Schvoerer, E.; Jeulin, H. Performance evaluation of an automated SARS-CoV-2 Ag test for the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection on nasopharyngeal swabs. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häuser, F.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Dreis, K.J.; Renzaho, A.; Youhanen, S.; Kremer, W.M.; Podlech, J.; Galle, P.R.; Lackner, K.J.; Rossmann, H.; et al. Evaluation of a laboratory-based high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for non-COVID-19 patient screening at hospital admission. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 210, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Gianfilippi, G.; Fiorio, G.; Pighi, L.; De Nitto, S.; Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G. Clinical Assessment of the DiaSorin LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 Ag Chemiluminescence Immunoassay. EJIFCC Electron. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 32, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Nagasawa, T.; Ishii, Y.; Yagi, S.; Okuma, S.; Kashiwagi, K.; Maeda, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Yoshizawa, S.; Tateda, K. Clinical validation of quantitative SARS-CoV-2 antigen assays to estimate SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in nasopharyngeal swabs. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, B.; Khan, M.; Shah, N.; Dawood, M.M.; Jehanzeb, V.; Shafi, M. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 antigen electrochemiluminescence immunoassay to RT-PCR assay for laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 in Peshawar. Diagnosis 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, N.; Orihara, Y.; Kodana, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Matsuoka, M.; Kawamura, R.; Takeuchi, S.; Imai, K.; Tarumoto, N.; Maesaki, S.; et al. Evaluation of a chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay-based high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for the diagnosis of COVID-19: The VITROS® SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6778–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirotsu, Y.; Sugiura, H.; Maejima, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Tsutsui, T.; Kakizaki, Y.; Miyashita, Y.; Omata, M. Comparison of Roche and Lumipulse quantitative SARS-CoV-2 antigen test performance using automated systems for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favresse, J.; Gillot, C.; Oliveira, M.; Cadrobbi, J.; Elsen, M.; Eucher, C.; Laffineur, K.; Rosseels, C.; Van Eeckhoudt, S.; Nicolas, J.B.; et al. Head-to-Head Comparison of Rapid and Automated Antigen Detection Tests for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sberna, G.; Basile, F.; Guarino, M.L.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Bordi, L.; Parisi, G. Comparison of Allplex™ SARS-CoV-2 Assay, Easy SARS-CoV-2 WE and Lumipulse quantitative SARS-CoV-2 antigen test performance using automated systems for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, S1201-9712, 00781–00785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignier, N.; Bérot, V.; Bonnave, N.; Peugny, S.; Ballet, M.; Jacoud, E.; Michaud, C.; Gaillet, M.; Djossou, F.; Blanchet, D.; et al. Breakthrough Infections of SARS-CoV-2 Gamma Variant in Fully Vaccinated Gold Miners, French Guiana, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2673–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Gupta, A.; Rooge, S.; Gupta, E. Performance evaluation of automated chemiluminescence immunoassay based antigen detection—Moving towards more reliable ways to predict SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 298, 114299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.H.; Morris, C.P.; Sachithanandham, J.; Amadi, A.; Gaston, D.; Li, M.; Swanson, N.J.; Schwartz, M.; Klein, E.Y.; Pekosz, A.; et al. Infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant is Associated with Higher Infectious Virus Loads Compared to the Alpha Variant in both Unvaccinated and Vaccinated Individuals. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, N.V.V.; Ngoc, N.M.; Nguyet, L.A.; Quang, V.M.; Ny, N.T.H.; Khoa, D.B.; Phong, N.T.; Toan, L.M.; Hong, N.T.T.; Tuyen, N.T.K.; et al. An observational study of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant infections among vaccinated healthcare workers in Vietnam. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 41, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, G.C.; Subhadra, S.; Turuk, J.; Parai, D.; Rath, S.; Sabat, J.; Rout, U.K.; Kanungo, S.; Choudhary, H.R.; Nanda, R.R.; et al. Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections among BBV-152 (COVAXIN®) and AZD1222 (COVISHIELDT M ) recipients: Report from eastern state of India. J. Med. Virol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, T.; Yan, Y.; Tabe, Y.; Seyama, K.; Deshpande, G.A. Real-world evidence for the effectiveness and breakthrough of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine at a medical center in Japan. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2021, 17, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinholt, T.; Doddapaneni, H.; Qin, X.; Menon, V.; Meng, Q.; Metcalf, G.; Chao, H.; Gingras, M.C.; Avadhanula, V.; Farinholt, P.; et al. Transmission event of SARS-CoV-2 delta variant reveals multiple vaccine breakthrough infections. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquart, F.; Abad, C.; Ambroise, J.; Bernard, M.; Cosentino, G.; Giannoli, J.M.; Débarre, F. Characterisation of vaccine breakthrough infections of SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Alpha variants and within-host viral load dynamics in the community, France, June to July 2021. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singanayagam, A.; Hakki, S.; Dunning, J.; Madon, J.K.; Crone, M.A.; Koycheva, A.; Derqui-Fernandez, N.; Barnett, L.J.; Whitfield, G.M.; Varro, R.; et al. Community transmission and viral load kinetics of the SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) variant in vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals in the UK: A prospective, longitudinal, cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singanayagam, A.; Patel, M.; Charlett, A.; Lopez Bernal, J.; Saliba, V.; Ellis, J.; Ladhani, S.; Zambon, M.; Gopal, R. Duration of infectiousness and correlation with RT-PCR cycle threshold values in cases of COVID-19, England, January to May 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| RT-qPCR Positive Patients (N = 150) | RT-qPCR Negative Subjects (N = 150) | |
|---|---|---|
| Median age (range), year | 34 (4–74) | 43 (7–79) |
| Sex, no. (%) | ||
| Male | 54 (36) | 84 (56) |
| Female | 96 (64) | 66 (44) |
| Presenting symptoms and signs, no. (%) | ||
| Fever | 12 (8) | 6 (4) |
| Headache | 10 (6.7) | 1 (0.7) |
| Cough | 14 (9.3) | 4 (2.7) |
| Generalised weakness | 12 (8) | 3 (2) |
| Nasal congestion | 9 (6) | - |
| Sore throat | 5 (3.3) | 2 (1.3) |
| Ageusia/Anosmia | 10 (6.7) | 3 (2) |
| Diarrhea | 3 (2) | 2 (1.3) |
| Shortness of breath | 7 (4.7) | 2 (1.3) |
| COVID-19 vaccine, no. (%) | ||
| Pfizer–BioNTech | 30 (20) | 44 (29.3) |
| ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 | 29 (19.3) | 47 (31.3) |
| Value (%) | (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 75.33 | (67.64–82.00) |
| Specificity | 100.00 | (97.57–100.00) |
| Negative likelihood ratio | 0.25 | (0.19–0.3) |
| Positive predictive value | 100 | (92.32–99.13) |
| Negative predictive value | 80.21 | (75.40–84.28) |
| Accuracy | 87.67 | (83.40–91.17) |
| SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral Load | Median Ct Value (Range) | n | Positive | Median SARS-CoV-2 Ag Value TCID50/mL (Range) | Sensitivity |
| High | 15.94 (10.65–18.53) | 58 | 56 | 100,000 (1800–100,000) | 96.55% |
| Medium | 22.29 (18.64–28.52) | 77 | 56 | 5736 (220–100,000) | 72.73% |
| Low | 30.07 (28.79–31.67) | 15 | 1 | 336 | 6.67% |
| All | 19.90 (10.65–31.67) | 150 | 113 | 25,353 (220–100,000) | 75.33% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altawalah, H.; Alfouzan, W.; Al-Fadalah, T.; Ezzikouri, S. Diagnostic Performance of Automated SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay in Nasal Swab during COVID-19 Vaccination Campaign. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112110
Altawalah H, Alfouzan W, Al-Fadalah T, Ezzikouri S. Diagnostic Performance of Automated SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay in Nasal Swab during COVID-19 Vaccination Campaign. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112110
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltawalah, Haya, Wadha Alfouzan, Talal Al-Fadalah, and Sayeh Ezzikouri. 2021. "Diagnostic Performance of Automated SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay in Nasal Swab during COVID-19 Vaccination Campaign" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112110
APA StyleAltawalah, H., Alfouzan, W., Al-Fadalah, T., & Ezzikouri, S. (2021). Diagnostic Performance of Automated SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay in Nasal Swab during COVID-19 Vaccination Campaign. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112110






