Vascular Imaging Techniques to Diagnose and Monitor Patients with Takayasu Arteritis: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Pathophysiology of TA
1.2. TA and Stroke Risk
1.3. Importance of Follow-Up Vascular Imaging in TA
2. Conventional Imaging Techniques for Diagnosis and Monitoring of TA
2.1. Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
2.2. Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
2.2.1. Diagnosis
2.2.2. Monitoring
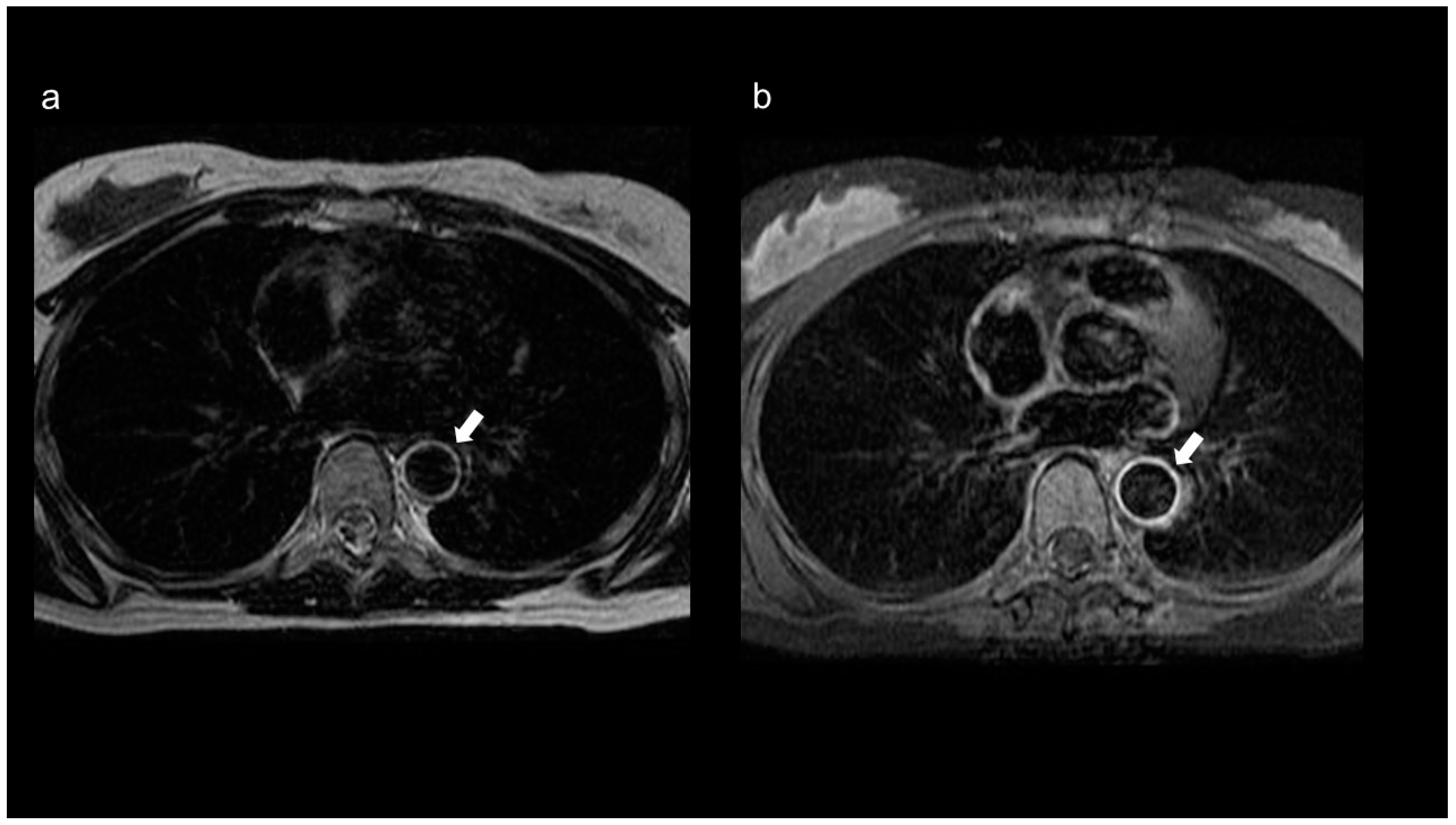
2.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)/Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
2.3.1. Diagnosis
2.3.2. Monitoring
2.4. Duplex Ultrasonography (DUS)
2.4.1. Diagnosis
2.4.2. Monitoring
2.5. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
2.5.1. Diagnosis
2.5.2. Monitoring
3. Comparative Analysis of Available Imaging Techniques
4. Novel Imaging Techniques for TA
4.1. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
4.2. Infrared Thermography
4.3. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography (CEUS)
4.4. Superb Microvascular Imaging (SMI)
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Numano, F. The story of Takayasu arteritis. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keser, G.; Aksu, K.; Direskeneli, H. Takayasu arteritis: An update. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 48, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, J.C. Takayasu arteritis—Advances in diagnosis and management. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschlimann, F.A.; Barra, L.; Alsolaimani, R.; Benseler, S.M.; Hebert, D.; Khalidi, N.; Laxer, R.M.; Noone, D.; Pagnoux, C.; Twilt, M.; et al. Presentation and disease course of childhood-onset versus adult-onset Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.S.; Hallahan, C.W.; Giordano, J.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Fauci, A.S.; Rottem, M.; Hoffman, G.S. Takayasu arteritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyahi, E. Takayasu arteritis: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Santo, M.; Stelmaszewski, E.V.; Villa, A. Takayasu arteritis in paediatrics. Cardiol. Young 2018, 28, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombetti, E.; Mason, J.C. Takayasu arteritis: Advanced understanding is leading to new horizons. Rheumatology 2018, 58, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.; Haroche, J.; Toledano, D.; Cacoub, P.; Mathian, A.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Le Thi Huong-Boutin, D.; Cluzel, P.; Gorochov, G.; Amoura, Z. Cluster analysis of arterial involvement in Takayasu arteritis reveals symmetric extension of the lesions in paired arterial beds. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, S.; Di Renzo, M.; Bova, G.; Auteri, A.; Pasqui, A.L. Takayasu′s arteritis: A review of the literature. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2006, 1, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, R.; Batista, P.; Pedro, L.M.; Fernandes, A.; Melo, T.P. Takayasu arteritis presenting with internal carotid artery dissection. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 33, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.S.; Weyand, C.M.; Langford, C.A.; Goronzy, J.J. Inflammatory Diseases of Blood Vessels; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Numano, F.; Kishi, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Ohkawara, M.; Kakuta, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: Atherosclerotic lesions in Takayasu arteritis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 902, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Xiao, M.; Zhou, L.; Kang, N.; Liang, X.; Li, F. Takayasu′s arteritis presenting with common carotid artery dissection: A rare case report. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 4061–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidhate, M.; Garg, R.K.; Yadav, R.; Kohli, N.; Naphade, P.; Anuradha, H.K. An unusual case of Takayasu′s arteritis: Evaluation by CT angiography. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2011, 14, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.A.; Nerenheim, A.; Seipelt, E.; Poehls, C.; Gromnica-Ihle, E. Diagnosis of early Takayasu arteritis with sonography. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Ikeda, T.; Feigin, V.L. Global, regional and country-specific burden of ischaemic stroke, intracerebral haemorrhage and subarachnoid haemorrhage: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Neuroepidemiology 2020, 54, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.M.; Geraldes, R.; Sousa, R.; Alarcão, J.; Costa, J. Stroke and transient ischemic attack in Takayasu′s arteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjaminsen, E.; Reigstad, A.; Cengija, V.; Lilleby, V.; Carlsson, M. Stroke as the sole manifestation of Takayasu arteritis in a 15-year-old boy with latent tuberculosis. Case Rep. Neurol. Med. 2016, 2016, 8736248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, W.; Alsaqabi, F.; Alkadi, A.; Amr, H.A.E.-A.; Moshrif, A.; Mahdy, M.E. Ischemic stroke as the first presentation of Takayasu′s arteritis in young male. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, K.; Gharzai, L.; Bardeloza, K.; Houghton, B. Takayasu arteritis presenting as embolic stroke. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Águeda, A.F.; Monti, S.; Luqmani, R.A.; Buttgereit, F.; Cid, M.; Dasgupta, B.; Dejaco, C.; Mahr, A.; Ponte, C.; Salvarani, C.; et al. Management of Takayasu arteritis: A systematic literature review informing the 2018 update of the EULAR recommendation for the management of large vessel vasculitis. RMD Open 2019, 5, e001020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Direskeneli, H.; Aydin, Z.S.; Merkel, A.P. Assessment of disease activity and progression in Takayasu′s arteritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, S86–S91. [Google Scholar]
- Oura, K.; Taguchi, K.; Yamaguchi Oura, M.; Itabashi, R.; Maeda, T. A case of Takayasu′s arteritis with a thrombosed aneurysm on the common carotid artery causing ischemic stroke. Intern. Med. 2021. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.H.; Beckman, J. Takayasu arteritis: Challenges in diagnosis and management. Heart 2018, 104, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, D.; Lambert, M.; Mirault, T.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Koskas, F.; Cluzel, P.; Mignot, C.; Schoindre, Y.; Chiche, L.; Hatron, P.-Y.; et al. Retrospective analysis of surgery versus endovascular intervention in Takayasu arteritis. Circulation 2012, 125, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Chung, J.W.; Lee, K.W.; Park, Y.B.; Han, M.C. CT angiography of Takayasu arteritis: Comparison with conventional angiography. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1997, 8, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, N.; Kalra, N.; Garg, M.K.; Kang, M.; Lal, A.; Jain, S.; Suri, S. Multidetector CT angiography in Takayasu arteritis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 77, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, I.; Nakagawa, T.; Himeno, Y.; Numano, F.; Shibuya, H. Takayasu arteritis: Evaluation of the thoracic aorta with CT angiography. Radiology 1998, 209, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Yin, W.; Gao, Y.; Hou, Z.; An, Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, X.; Zhao, S.; Das, P.; et al. Assessment of disease activity in Takayasu arteritis: A quantitative study with computed tomography angiography. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 289, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, N.; Hayashi, K.; Sakamoto, I.; Ogawa, Y.; Matsumoto, T. Takayasu arteritis: Protean radiologic manifestations and diagnosis. Radiographics 1997, 17, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, L.; Kanji, T.; Malette, J.; Pagnoux, C. Imaging modalities for the diagnosis and disease activity assessment of Takayasu′s arteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanninen, R.L.; Manninen, H.I.; Partanen, P.K.; Tulla, H.; Vainio, P.A. How should we estimate carotid stenosis using magnetic resonance angiography? Neuroradiology 1996, 38, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Ramiro, S.; Duftner, C.; Besson, F.L.; Bley, T.A.; Blockmans, D.; Brouwer, E.; Cimmino, M.A.; Clark, E.; Dasgupta, B.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, F.; Pipitone, N.; Salvarani, C.; Schmidt, W.A. Imaging of vasculitis: State of the art. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 30, 688–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blockmans, D.; Luqmani, R.; Spaggiari, L.; Salvarani, C. Magnetic resonance angiography versus 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in large vessel vasculitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, I.; Nakagawa, T.; Himeno, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Numano, F.; Shibuya, H. Takayasu arteritis: Diagnosis with breath-hold contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MR angiography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 11, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, Y.H.; Han, B.K.; Koh, E.M.; Kim, D.K.; Do, Y.S.; Lee, W.R. Takayasu′s arteritis: Assessment of disease activity with contrast-enhanced MR imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, M.; Cobelli, F.D.; Baldissera, E.; Dagna, L.; Schiani, E.; Sabbadini, M.; Del Maschio, A. Takayasu arteritis: Intravascular contrast medium for MR angiography in the evaluation of disease activity. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, W279–W284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spira, D.; Xenitidis, T.; Henes, J.; Horger, M. MRI parametric monitoring of biological therapies in primary large vessel vasculitides: A pilot study. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, E.; Flamm, S.D.; White, R.D.; Schvartzman, P.R.; Mascha, E.; Hoffman, G.S. Takayasu arteritis: Utility and limitations of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, C.; Eriksson, P.; Zachrisson, H. Vascular ultrasound for monitoring of inflammatory activity in Takayasu arteritis. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2020, 40, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Handa, N.; Matsumoto, M.; Hougaku, H.; Ogawa, S.; Oku, N.; Itoh, T.; Moriwaki, H.; Yoneda, S.; Kimura, K.; et al. Carotid lesions detected by B-mode ultrasonography in Takayasu′s arteritis: “Macaroni sign” as an indicator of the disease. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1991, 17, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betrains, A.; Blockmans, D. Diagnostic approaches for large vessel vasculitides. Open Access Rheumatol. 2021, 13, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papathanasiou, N.D.; Du, Y.; Menezes, L.J.; Almuhaideb, A.; Shastry, M.; Beynon, H.; Bomanji, J.B. 18F-Fludeoxyglucose PET/CT in the evaluation of large-vessel vasculitis: Diagnostic performance and correlation with clinical and laboratory parameters. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e188–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Wei, D.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Cai, J.; Fan, L.; Yu, J.; Ma, W.; Song, L.; Zhou, X. 118F-FDG PET/CT plays a unique role in the management of Takayasu arteritis patients with atypical manifestations. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, M.-D. FDG PET-CT in the diagnosis of Takayasu arteritis presenting as fever of unknown origin: A case report. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 47, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargin, G.; Senturk, T.; Sahin, O. 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of Takayasu′s arteritis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 1173–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, S.; Mittal, B.R.; Gayana, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Sharma, A.; Jain, S. F-18 FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of Takayasu arteritis: An experience from the tropics. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Cho, A.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.W.; Ha, Y.J.; Jung, S.J.; Park, M.C.; Lee, J.D.; Lee, S.K.; Park, Y.B. The role of (18) F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography in the assessment of disease activity in patients with Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, D.; Haraguchi, G.; Ishihara, T.; Ohigashi, H.; Inagaki, H.; Suzuki, J.-I.; Hirao, K.; Isobe, M. Role of FDG PET-CT in Takayasu arteritis: Sensitive detection of recurrences. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawakol, A.; Migrino, R.Q.; Bashian, G.G.; Bedri, S.; Vermylen, D.; Cury, R.C.; Yates, D.; LaMuraglia, G.M.; Furie, K.; Houser, S.; et al. In vivo 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging provides a noninvasive measure of carotid plaque inflammation in patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucerius, J.; Hyafil, F.; Verberne, H.J.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Lindner, O.; Sciagra, R.; Agostini, D.; Übleis, C.; Gimelli, A.; Hacker, M.; et al. Position paper of the Cardiovascular Committee of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) on PET imaging of atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, P.C.; Alehashemi, S.; Bagheri, A.A.; Civelek, A.C.; Cupps, T.R.; Kaplan, M.J.; Malayeri, A.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Novakovich, E.; Bluemke, D.A.; et al. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography as an imaging biomarker in a prospective, longitudinal cohort of patients with large vessel vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.; Han, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, W.; Zhang, K.; Quan, Z.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Performance of the PET vascular activity score (PETVAS) for qualitative and quantitative assessment of inflammatory activity in Takayasu’s arteritis patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 3107–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, X. Application progress of multiple imaging modalities in Takayasu arteritis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eladawi, N.; Elmogy, M.; Ghazal, M.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Mahmoud, H.; Alhalabi, M.T.; Ahmed, A.; Riad, A.; Keynton, R.; Schaal, S.; et al. Optical coherence tomography: A review. In Diabetes and Fundus OCT, 1st ed.; El-Baz, A.S., Suri, J.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 191–221. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.; Duguid, G. Optical coherence tomography—A review of the principles and contemporary uses in retinal investigation. Eye 2004, 18, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Donato, G.; Pasqui, E.; Alba, G.; Giannace, G.; Panzano, C.; Cappelli, A.; Setacci, C.; Palasciano, G. Clinical considerations and recommendations for OCT-guided carotid artery stenting. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 18, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohad, S.; Zhu, A.; Krishnan, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Cox, J.; Henry, T.D. Optical coherence tomography guided carotid artery stent procedure: Technique and potential applications. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 91, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasarikovski, C.R.; Ramjist, J.; da Costa, L.; Black, S.E.; Cardinell, J.; Yang, V.X.D. Optical coherence tomography as an adjunct during carotid artery stenting for carotid atherosclerotic disease. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2020, 30, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Feng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Dong, J.; Zhang, B.; Gao, P.; Chen, Y.; et al. Frequency-domain optical coherence tomography for intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: Feasibility, safety, and preliminary experience. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 678443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subban, V.; Raffel, O.C. Optical coherence tomography: Fundamentals and clinical utility. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 1389–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donisan, T.; Balanescu, D.V.; Mouhayar, E.; Tayar, J.; Iliescu, C. Coronary lesions in Takayasu arteritis with chronic myelogenous leukemia—Intravascular assessment with optical coherence tomography and fractional flow reserve. Circ. J. 2018, 83, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, M.; Peregud-Pogorzelska, M.; Stachowiak, P.; Brzosko, M.; Kornacewicz-Jach, Z. Optical coherence tomography imaging during endovascular treatment of a patient with Takayasu arteritis. Kardio. Pol. 2016, 74, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Casscells, W.; Hathorn, B.; David, M.; Krabach, T.; Vaughn, W.K.; McAllister, H.A.; Bearman, G.; Willerson, J.T. Thermal detection of cellular infiltrates in living atherosclerotic plaques: Possible implications for plaque rupture and thrombosis. Lancet 1996, 347, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capistrant, T.D.; Gumnit, R.J. Detecting carotid occlusive disease by thermography. Stroke 1973, 4, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.B.; Smyth, J.V.; Tullo, A.B.; Efron, N. Ocular temperature in carotid artery stenosis. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1999, 76, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Echeverria, A.; Poi, M.J. Infrared thermography in the diagnosis and management of vasculitis. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2017, 3, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Dijk, A.C.; Truijman, M.T.B.; Hussain, B.; Zadi, T.; Saiedie, G.; de Rotte, A.A.J.; Liem, M.I.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; Koudstaal, P.J.; et al. Intraplaque hemorrhage and the plaque surface in carotid atherosclerosis: The Plaque At Risk study (PARISK). Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jander, S.; Sitzer, M.; Schumann, R.; Schroeter, M.; Siebler, M.; Steinmetz, H.; Stoll, G. Inflammation in high-grade carotid stenosis: A possible role for macrophages and T cells in plaque destabilization. Stroke 1998, 29, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staub, D.; Partovi, S.; Schinkel, A.F.L.; Coll, B.; Uthoff, H.; Aschwanden, M.; Jaeger, K.A.; Feinstein, S.B. Correlation of carotid artery atherosclerotic lesion echogenicity and severity at standard US with intraplaque neovascularization detected at contrast-enhanced US. Radiology 2011, 258, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Thompson, M.M.; Jones, L.; London, N.J.M.; Bell, P.R.F.; Naylor, A.R.; Brindle, N.P. Angiogenesis and the atherosclerotic carotid plaque: An association between symptomatology and plaque morphology. J. Vasc. Surg. 1999, 30, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Nagatsuka, K.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Watanabe, A.; Kannki, H.; Iihara, K. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the evaluation of neovascularization in atherosclerotic carotid artery plaques. Stroke 2014, 45, 3073–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varetto, G.; Gibello, L.; Castagno, C.; Quaglino, S.; Ripepi, M.; Benintende, E.; Gattuso, A.; Garneri, P.; Zan, S.; Capaldi, G.; et al. Use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in carotid atherosclerotic disease: Limits and perspectives. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 293163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, D.; Partovi, S.; Imfeld, S.; Uthoff, H.; Baldi, T.; Aschwanden, M.; Jaeger, K. Novel applications of contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging in vascular medicine. Vasa 2013, 42, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Kate, G.L.; van den Oord, S.C.H.; Sijbrands, E.J.G.; van der Lugt, A.; de Jong, N.; Bosch, J.G.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; Schinkel, A.F.L. Current status and future developments of contrast-enhanced ultrasound of carotid atherosclerosis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2013, 57, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Han, H.; Dai, W.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Spatio-temporal quantification of carotid plaque neovascularization on contrast enhanced ultrasound: Correlation with visual grading and histopathology. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 50, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Deng, Y.-B.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.-N.; Bi, X.-J. Correlation of carotid plaque neovascularization detected by using contrast-enhanced US with clinical symptoms. Radiology 2009, 251, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, K.; Kato, T.; Oura, K.; Narumi, S.; Sasaki, M.; Fujiwara, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nomura, J.-I.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Preoperative cervical carotid artery contrast-enhanced ultrasound findings are associated with development of microembolic signals on transcranial Doppler during carotid exposure in endarterectomy. Atherosclerosis 2017, 260, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Oikawa, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Ogasawara, Y.; Sato, Y.; Narumi, S.; Kato, T.; Oura, K.; Terayama, Y.; Sasaki, M.; et al. Comparison of three-dimensional T1-weighted magnetic resonance and contrast-enhanced ultrasound plaque images for severe stenosis of the cervical carotid artery. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, F.; Li, Y.; Pang, L.; Du, W.; Wu, Z.; et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for monitoring arterial inflammation in Takayasu arteritis. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Li, C.L.; Ma, L.L.; Cui, X.M.; Dai, X.M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Huang, B.J.; Jiang, L.D. Value of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography of the carotid artery for evaluating disease activity in Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, K.; Kato, T.; Ohba, H.; Terayama, Y. Evaluation of intraplaque neovascularization using superb microvascular imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 2348–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artul, S.; Nseir, W.; Armaly, Z.; Soudack, M. Superb microvascular imaging: Added value and novel applications. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2017, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, M.; Zou, M.; Li, S.; Ge, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cai, S.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Assessment of carotid intraplaque neovascularization using superb microvascular imaging in high risk of stroke individuals: Results from a community-based study. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, M.; Skagen, K.; Scott, H.; Lindberg, B.; Russell, D.; Skjelland, M. Carotid plaque neovascularization detected with superb microvascular imaging ultrasound without using contrast media. Stroke 2019, 50, 3121–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-B.; Zhou, J.; Feng, L.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.-C. Value of superb micro-vascular imaging in predicting ischemic stroke in patients with carotid atherosclerotic plaques. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Fujiwara, S.; Oura, K.; Oikawa, K.; Chida, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoshida, K.; Kubo, Y.; Maeda, T.; Itabashi, R.; et al. Superb microvascular imaging ultrasound for cervical carotid artery stenosis for prediction of the development of microembolic signals on transcranial Doppler during carotid exposure in endarterectomy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra 2021, 11, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Xie, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, K.; Bai, Z.; Zheng, A.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Assessment of neovascularization of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques using superb microvascular imaging: A comparison with contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging and histology. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, W.; Sato, T.; Iino, T.; Seki, K.; Watanabe, H. Visualization of arterial wall vascularization using superb microvascular imaging in active-stage Takayasu arteritis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 20, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Tahara, N.; Hirakata, S.; Kaieda, S.; Tahara, A.; Maeda-Ogata, S.; Bekki, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Honda, A.; Igata, S.; et al. Signal intensity of superb micro-vascular imaging associates with the activity of vascular inflammation in Takayasu arteritis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, W.; Suto, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Watanabe, H. An advanced ultrasound application used to assess peripheral vascular diseases: Superb microvascular imaging. J. Echocardiogr. 2021, 19, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.Z.; Huang, Y.H.; Shen, H.L.; Liu, X.T. Clinical applications of superb microvascular imaging in the liver, breast, thyroid, skeletal muscle, and carotid plaques. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, W.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Lihong, V.W. Photoacoustic computed tomography of human extremities. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Jain, A.; Guleria, A.; Misra, D.P.; Goel, R.; Danda, D.; Misra, R.; Kumar, D. Circulatory glutamine/glucose ratio for evaluating disease activity in Takayasu arteritis: A NMR based serum metabolomics study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 180, 113080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Modality | Accessibility | Ease of Use | Purpose/Use | Radiation | Principal Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSA | Low | Low | Diagnosis/Treatment | Yes | Invasive; lack of information on the vessel wall |
| CTA | High | High | Diagnosis/Monitoring | Yes | Cannot be used in patients with renal failure or allergies to contrast media |
| MRI/MRA | Low | High | Diagnosis | No | Cannot be performed when some types of metals are present in the body or in patients with claustrophobia |
| DUS | High | High | Diagnosis/Monitoring | No | Examiners’ technical proficiency strongly affects the result; subjective; acoustic shadow |
| PET | Low | High | Diagnosis/Monitoring | Yes | Lack of criteria for positivity (FDG uptake); low resolution for small vessels |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oura, K.; Yamaguchi Oura, M.; Itabashi, R.; Maeda, T. Vascular Imaging Techniques to Diagnose and Monitor Patients with Takayasu Arteritis: A Review of the Literature. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11111993
Oura K, Yamaguchi Oura M, Itabashi R, Maeda T. Vascular Imaging Techniques to Diagnose and Monitor Patients with Takayasu Arteritis: A Review of the Literature. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11111993
Chicago/Turabian StyleOura, Kazumasa, Mao Yamaguchi Oura, Ryo Itabashi, and Tetsuya Maeda. 2021. "Vascular Imaging Techniques to Diagnose and Monitor Patients with Takayasu Arteritis: A Review of the Literature" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11111993
APA StyleOura, K., Yamaguchi Oura, M., Itabashi, R., & Maeda, T. (2021). Vascular Imaging Techniques to Diagnose and Monitor Patients with Takayasu Arteritis: A Review of the Literature. Diagnostics, 11(11), 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11111993






