Testing Method for Intelligent Loading of Mining Emulsion Pump Based on Digital Relief Valve and BP Neural Network Control Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
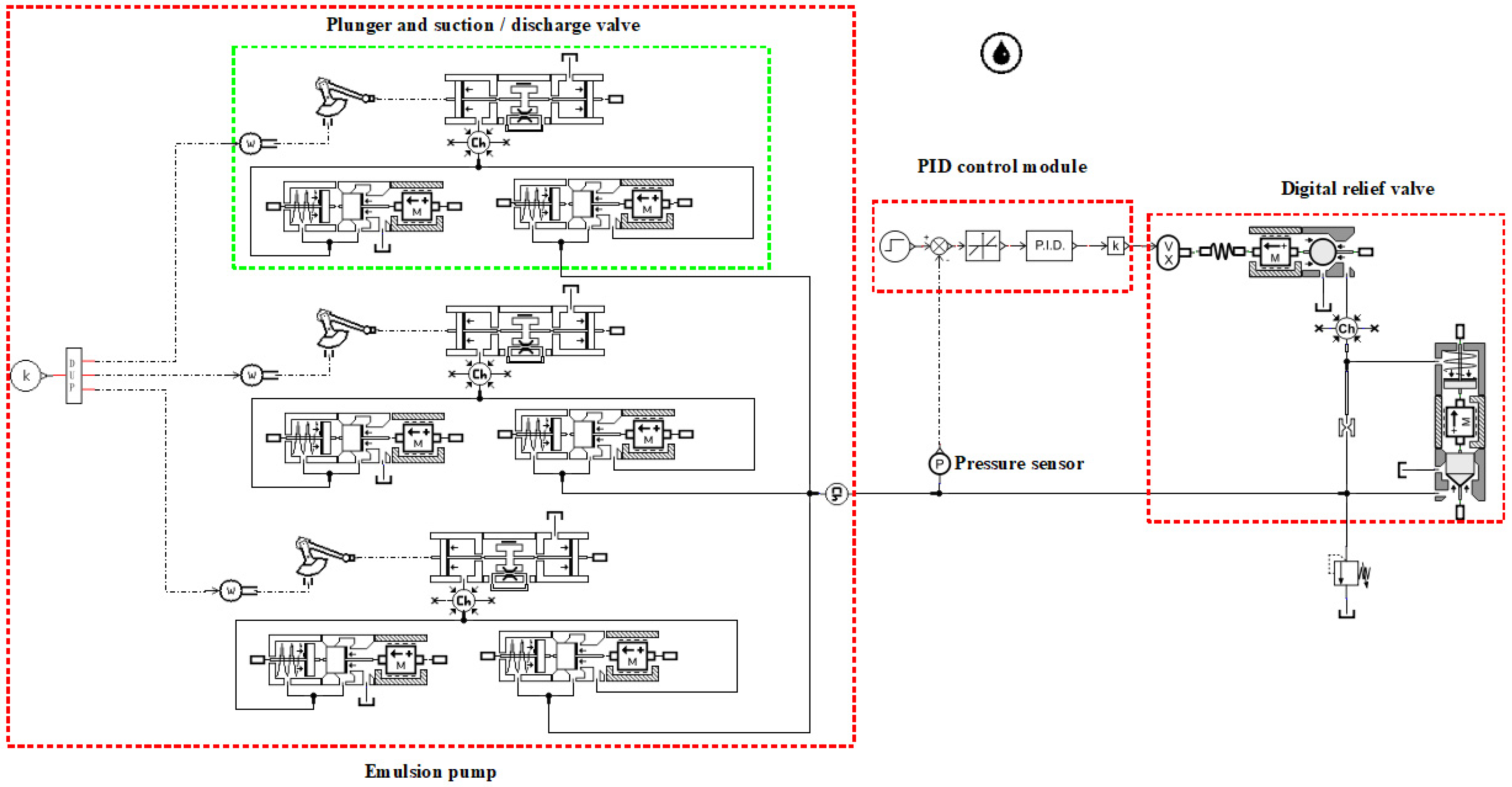
2. Modeling and Pressure Flow Characteristic Analysis of Digital Overflow Valve Loading Hydraulic System
2.1. Mathematical Model for Digital Relief Valve
2.2. Hydraulic System Simulation and Analysis
3. Research on Pressure Control Algorithm Based on BP Neural Network
3.1. Selection of Control Algorithm
3.2. Simulation of Control Algorithm
3.2.1. Data Collection
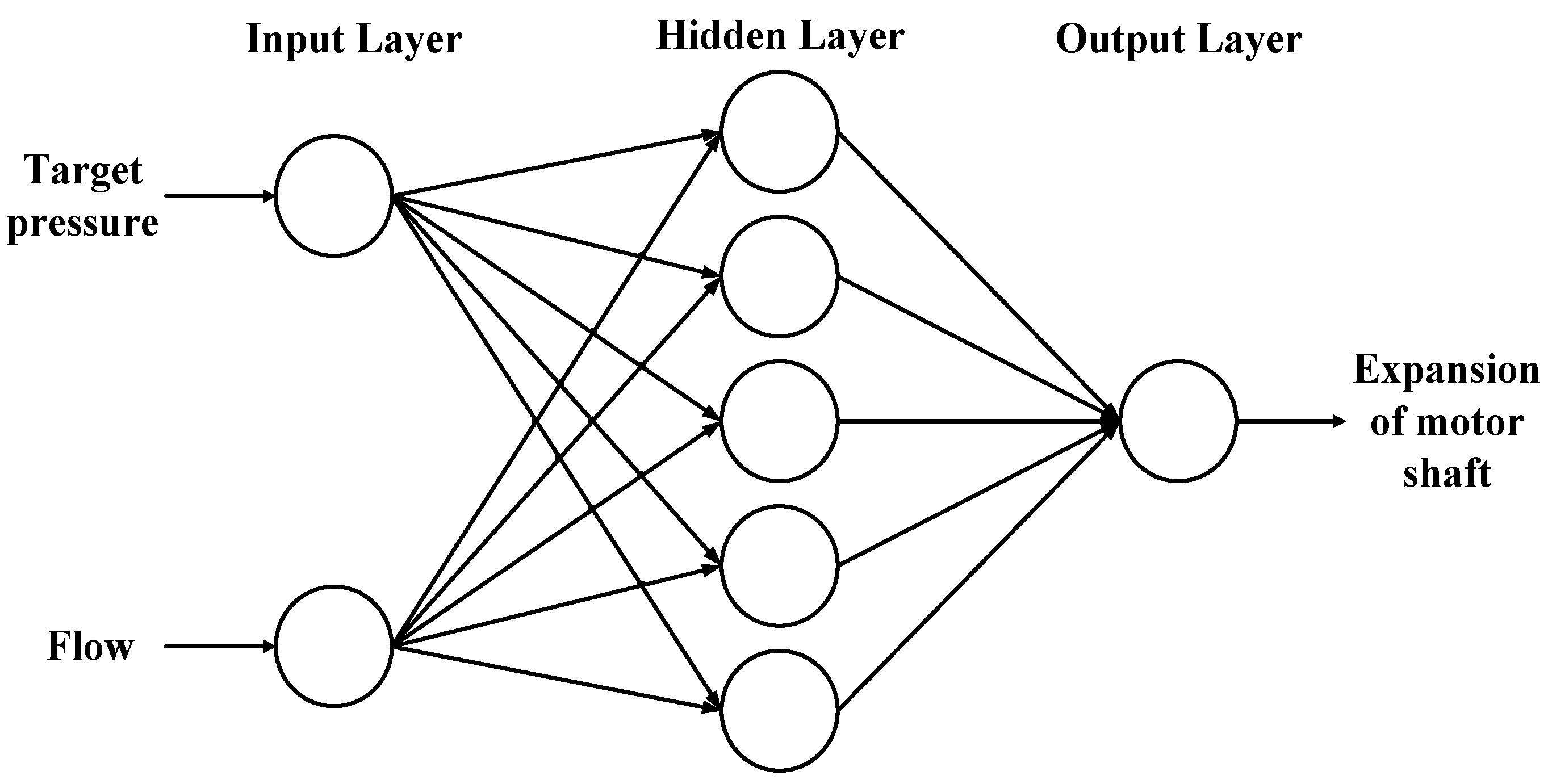
3.2.2. Definition of Neural Network Structure and Parameter
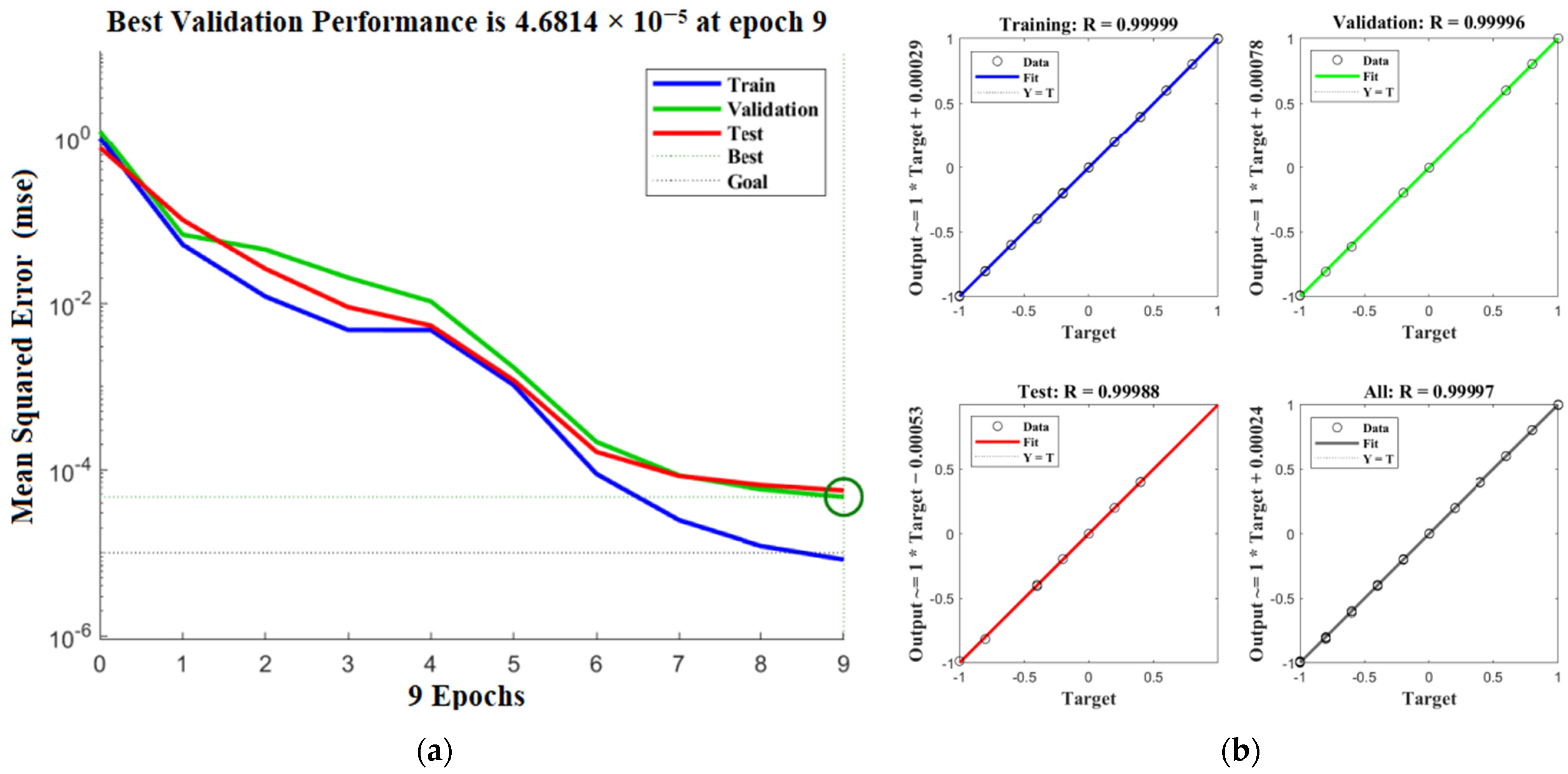
3.2.3. Training and Validation of the Model
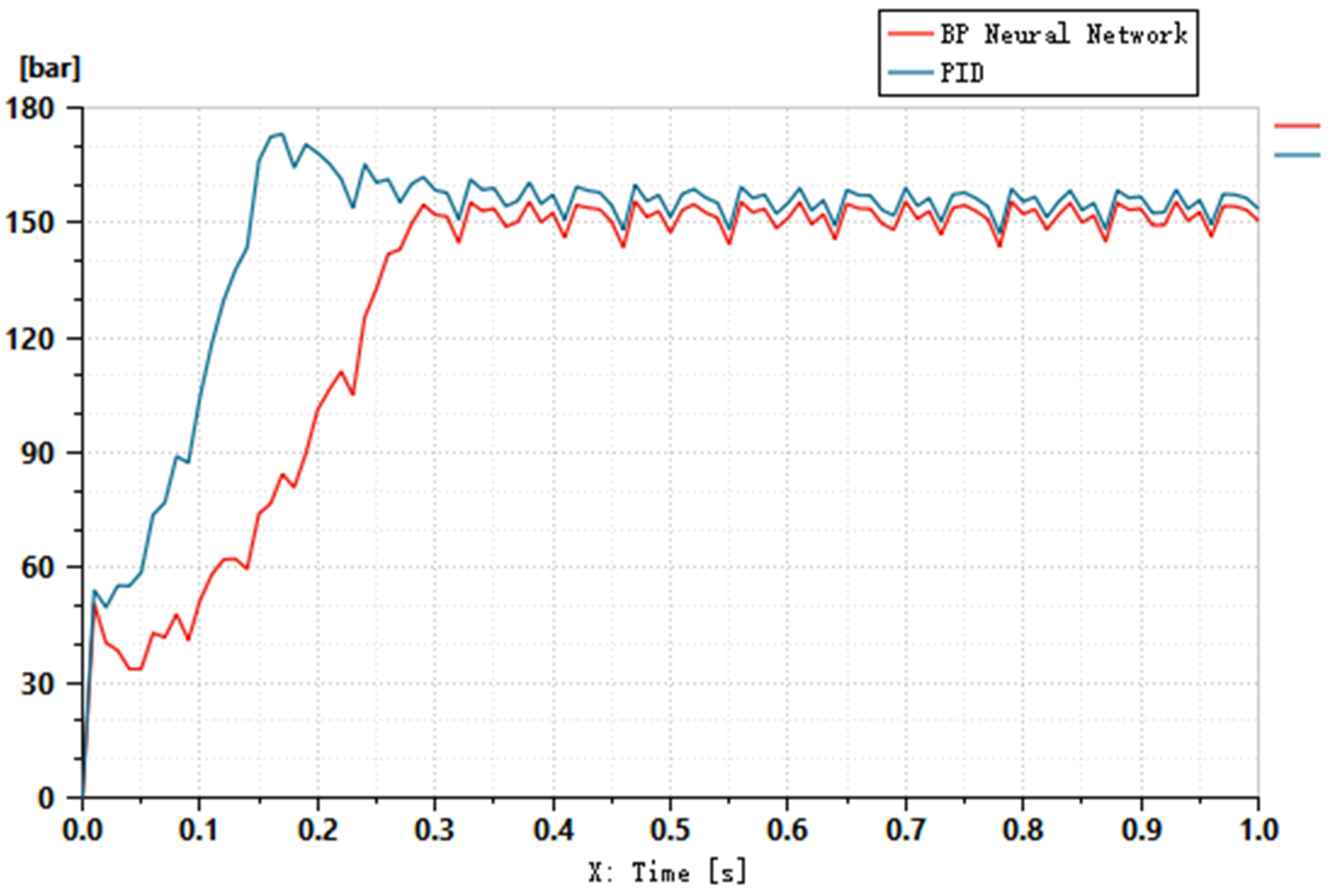
3.2.4. Simulation and Comparison of Control Algorithms
4. Experiment and Discussion
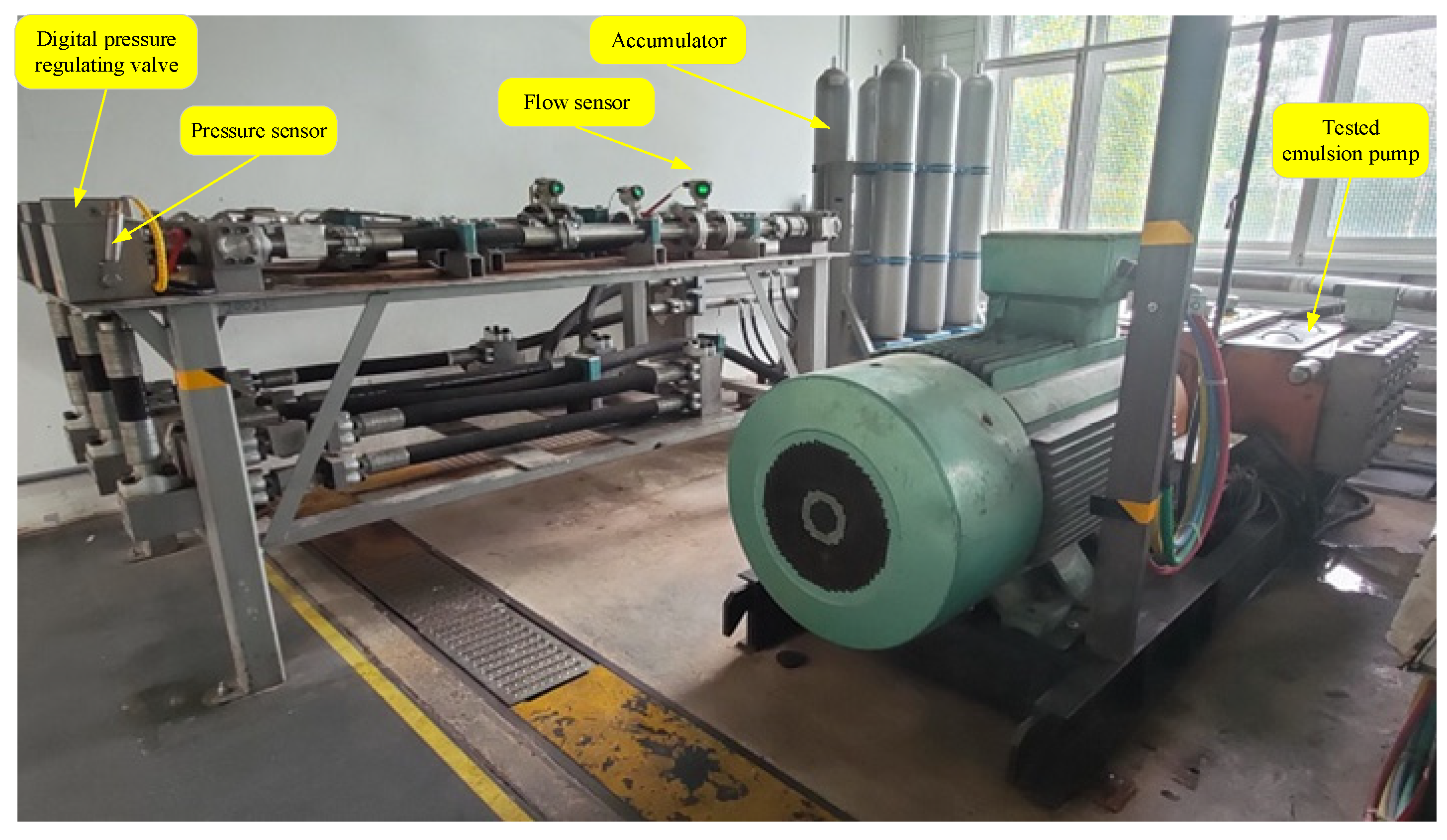
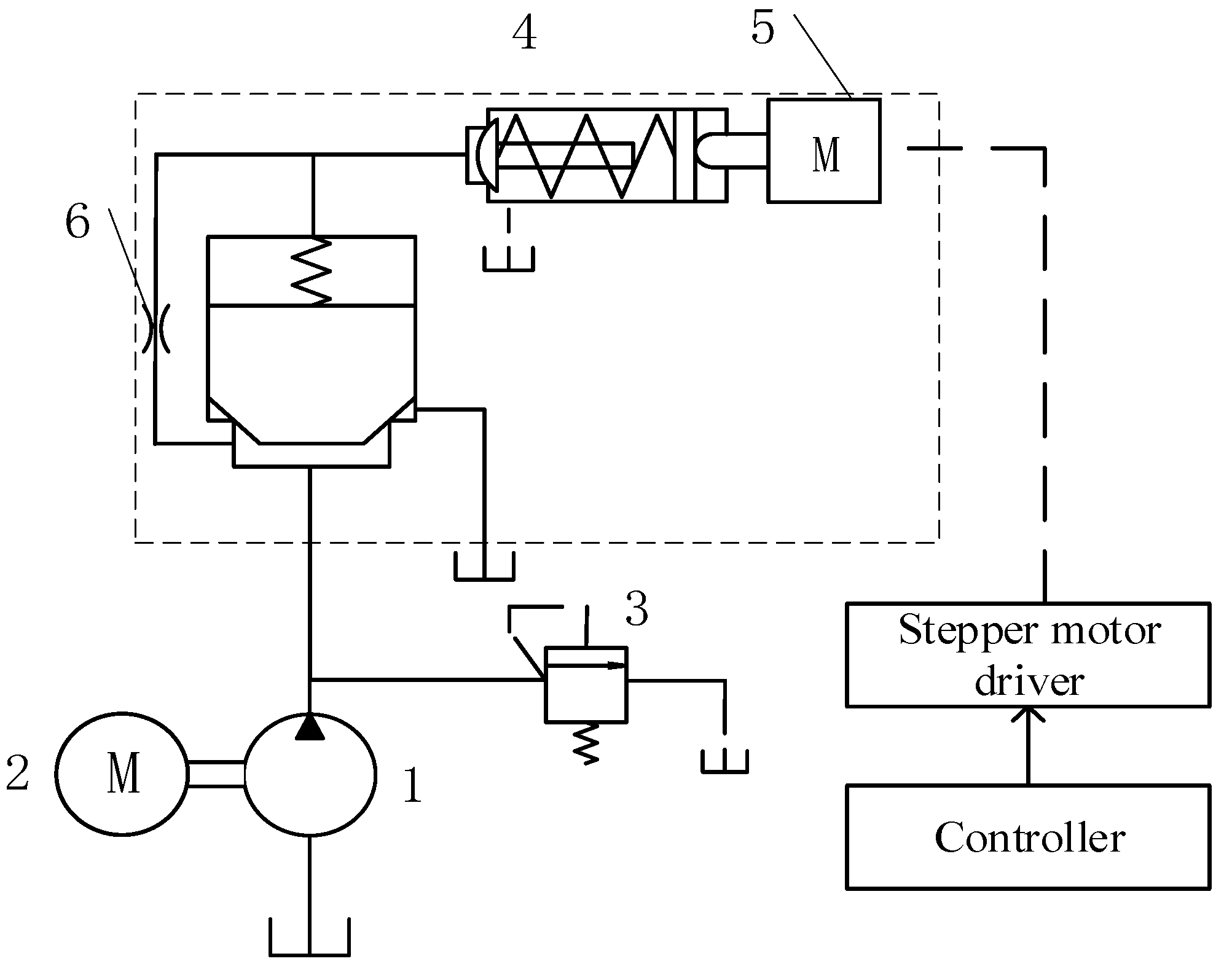
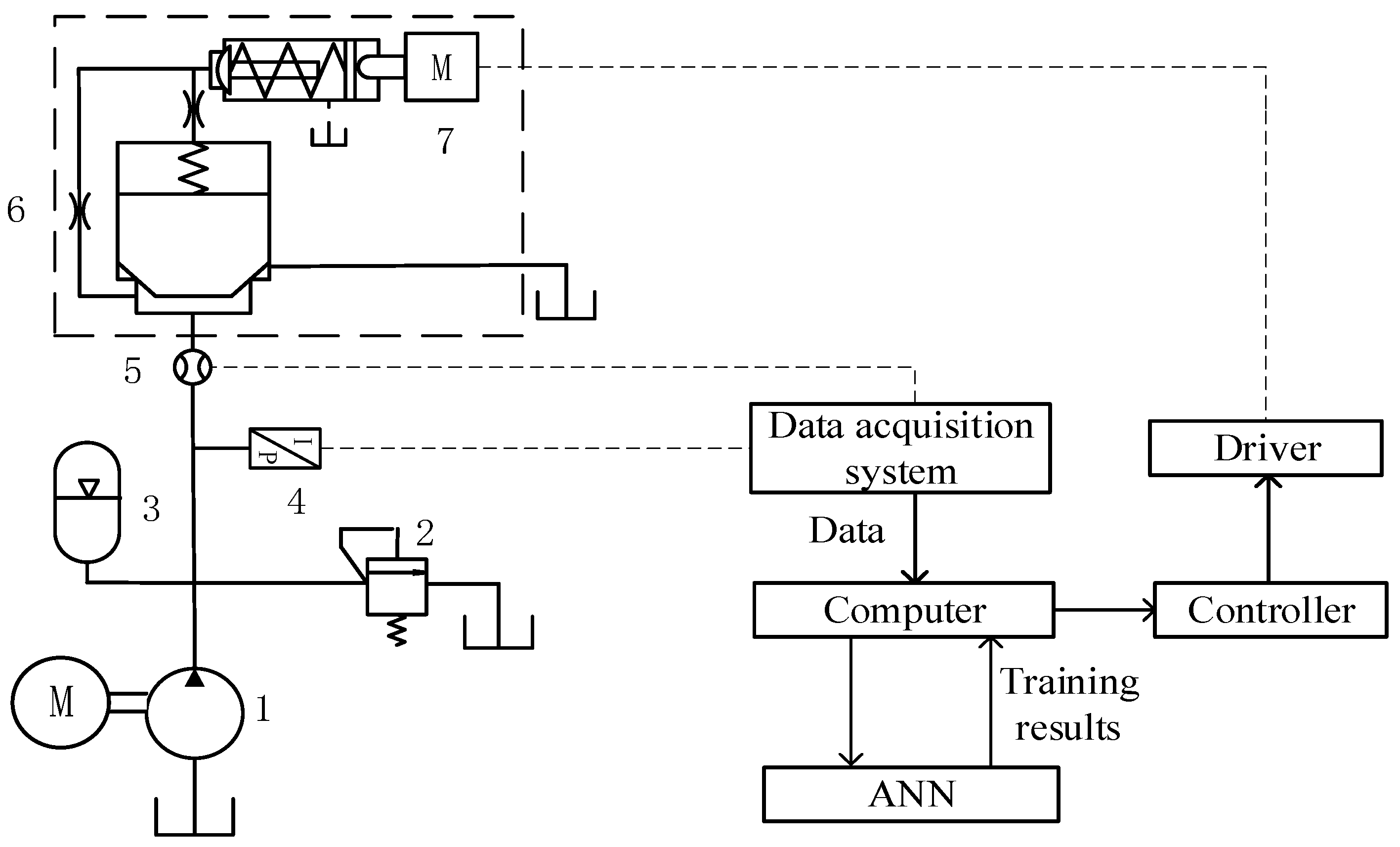
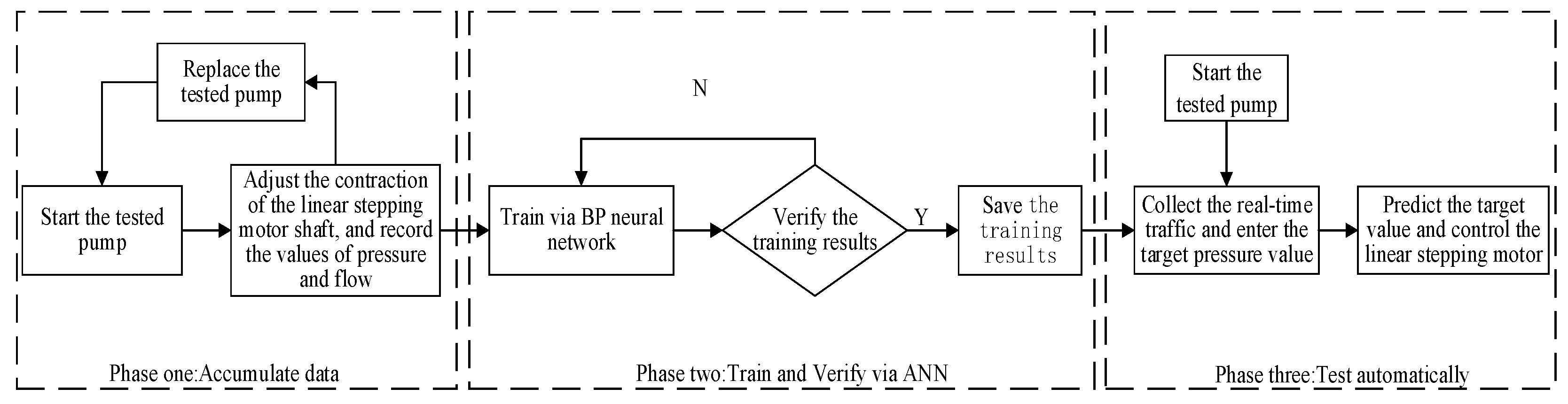
4.1. Development of Test Platform and Test Process
4.2. Test Results and Analysis
- (1)
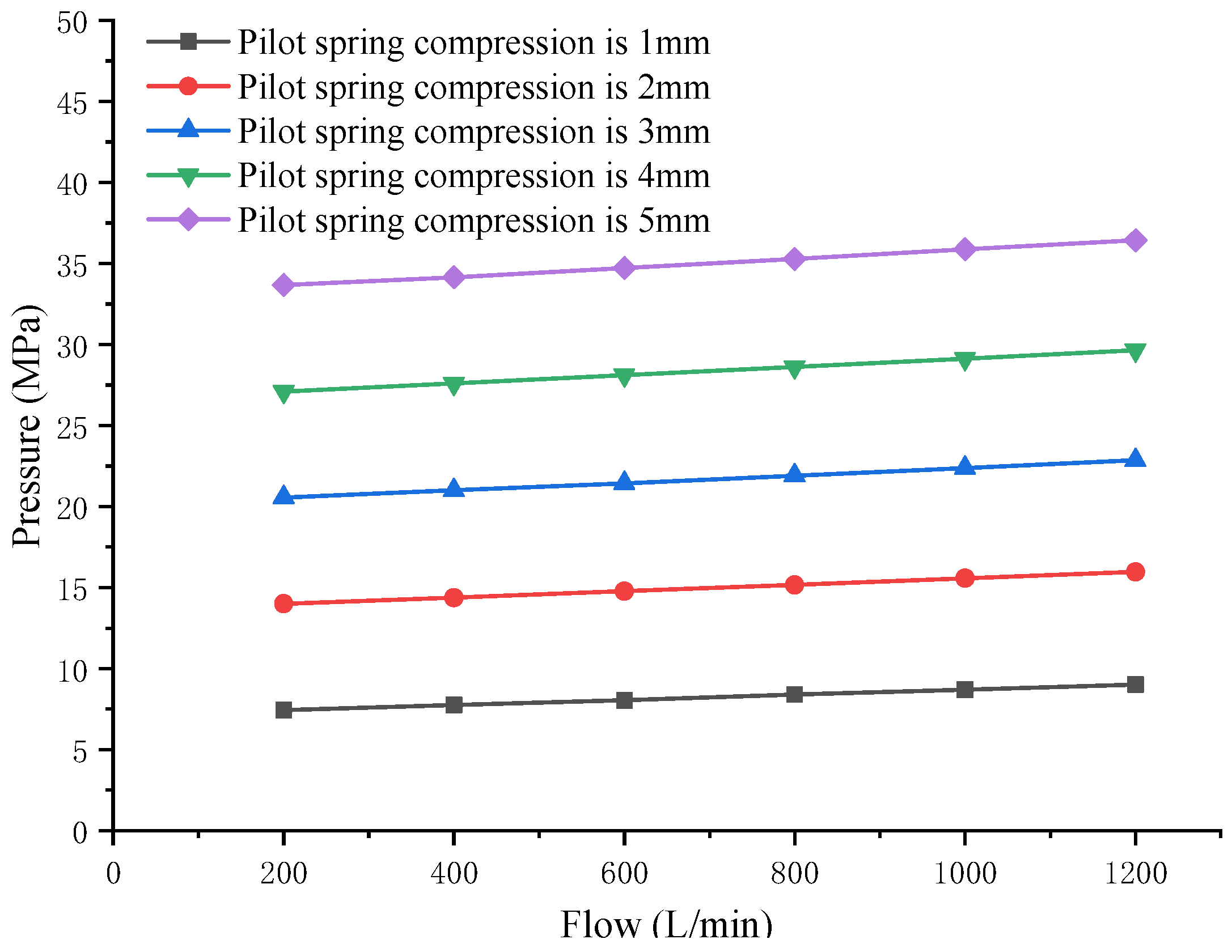
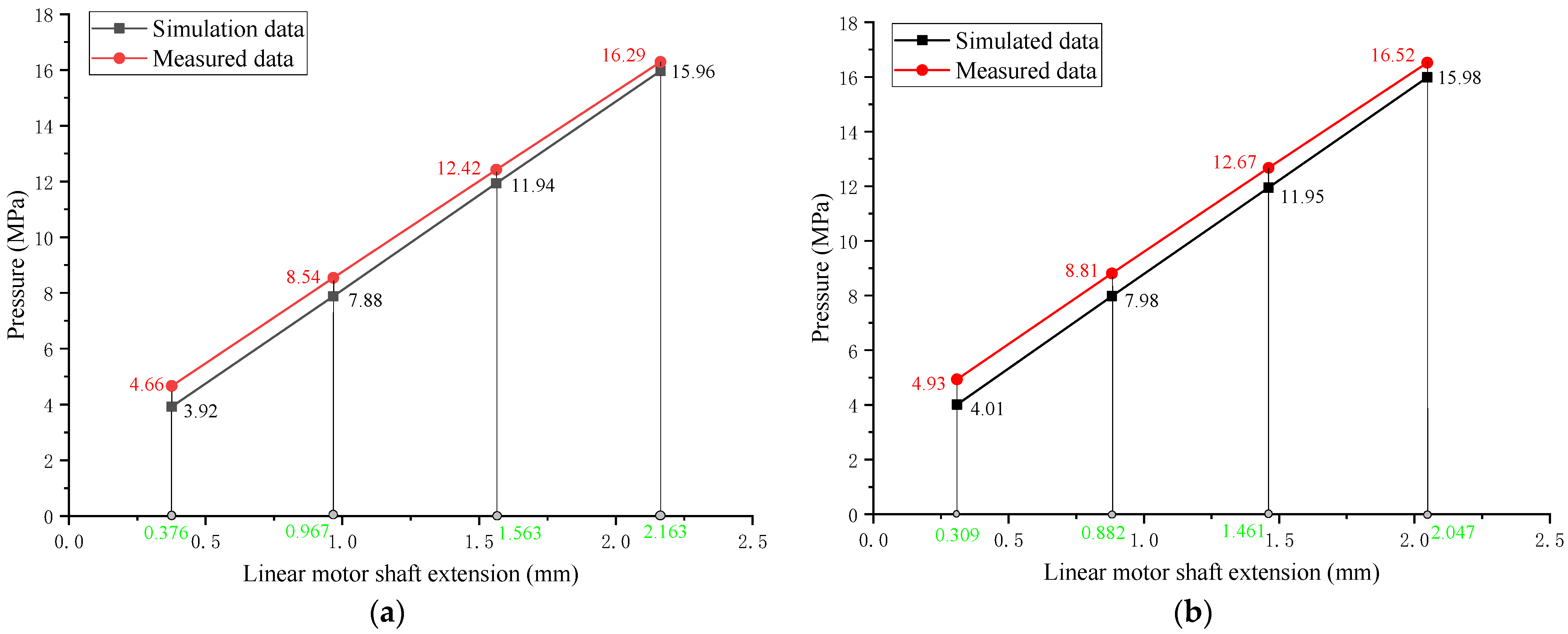
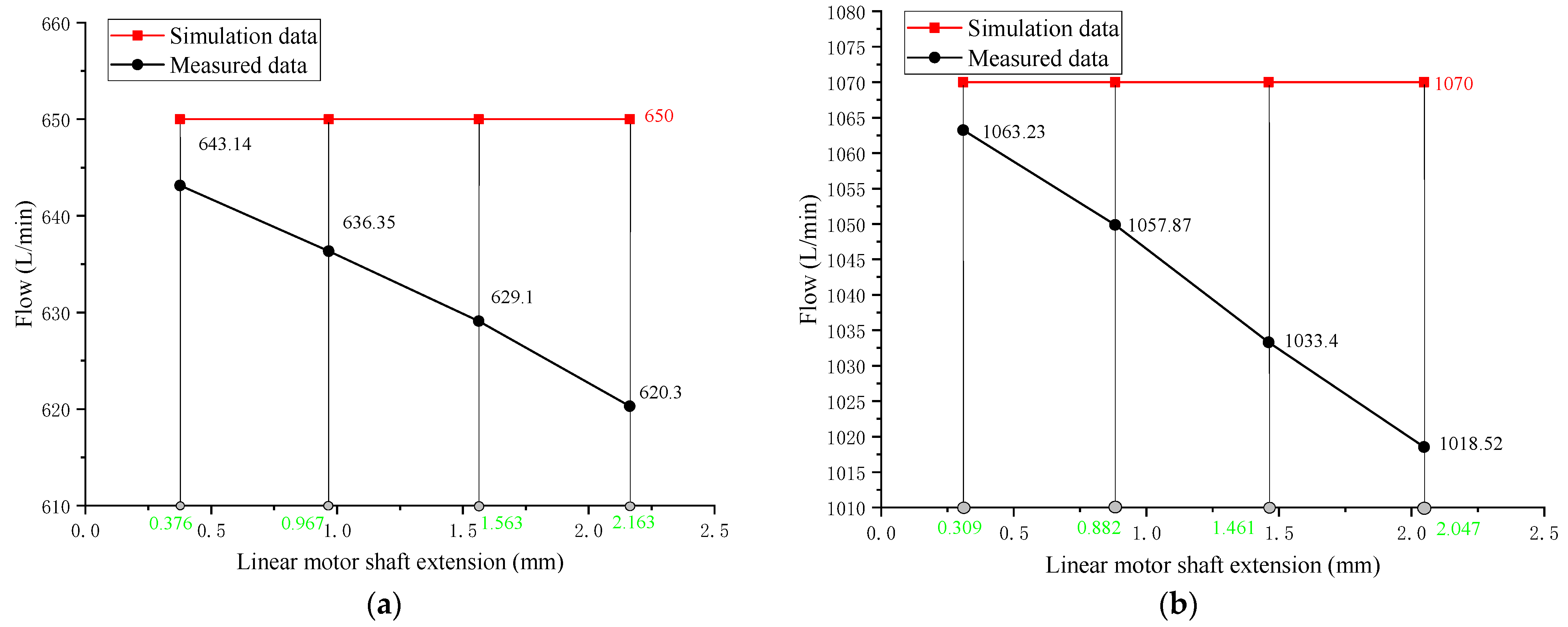
- The resistance loss caused by the hydraulic pipeline and other structures of the test system causes the actual pressure value to be higher than the predicted pressure, and the greater the flow of the tested pump, the greater the resistance loss.
- (2)
- The volumetric efficiency of the emulsion pump is not constant; it decreases with the increase in pressure, which can be clearly deduced from Figure 13. However, the shaft extension of the linear stepping motor is predicted according to the theoretical flow, which affects the prediction accuracy to a certain extent.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.X.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.L. Super-wetting, photoactive TiO2 coating on amino-silane modified PAN nanofiber membranes for high efficient oil-water emulsion separation application. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 580, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuanlaor, K.; Chatchai, P. Photoelectrocatalytic reactor improvement towards oil-in-water emulsion degradation. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 279, 111568. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Meng, L.; Yuan, X.; Qiao, Z. Research and Experimental Analysis of Hydraulic Cylinder Position Control Mechanism Based on Pressure Detection. Machines 2022, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, D.L.; Wei, W.S.; Li, S.B. Analysis of the Movement Characteristics of the Pump Valve of the Mine Emulsion Pump Based on the Internet of Things and Cellular Automata. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Gao, H.W.; Xie, Y. Hybrid Excavator Test Bed Hydraulic Load System Design. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 605–607, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.H.; Guo, G.; Dong, W.K. Modeling and Simulation of Emulsion Pump Station Pressure Control System Based on Electro-Hydraulic Proportional Relief Valve. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 190–191, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.Z.; Zhao, G.F.; Yao, C.; Ma, Z.K.; Ding, S.L.; Ma, X.Z. Study of Nonlinear Characteristics and Model Based Control for Proportional Electromagnet. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 2549456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Chen, F.X.; Zhu, R.F.; Huang, X.L.; Sang, N.; Yang, G.L.; Zhang, C. A Review on Disturbance Analysis and Suppression for Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor. Actuators 2021, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, R.G.; Qin, Y.J. Design and Performance Analysis of Digital Pressure Relief Valve of Water-Based Hydraulic. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 387, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.L.; Tian, M.Q.; Wan, L.Y.; Dai, H.Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.J.; Liu, F.Q. Characteristic Analysis of Digital Large Flow Emulsion Relief Valve. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5820812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.R.; Dai, H.Z.; Zeng, Q.L.; Lu, Z.G.; Sun, Z.Y.; Tian, M.Q.; Lu, Y.J. Characteristic Analysis of Digital Emulsion Relief Valve Based on the Hydraulic Loading System. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 8866919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, K.; Karmakar, R. Dynamic analysis of pilot operated pressure relief valve. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2002, 10, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.J.; Guo, K.H. Modelling and analysis for a pilot relief valve using CFD method and deformation theory of thin plates. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2015, 58, 979–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.B.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw. 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Li, J.T.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H. Fitting Analysis and Research of Measured Data of SAW Micro-pressure Sensor based on BP Neural Network. Measurement 2020, 105, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.H.; Yue, L.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Di, H.G.; Gao, F.; Li, S.C.; Zhou, Y.D.; Hua, D.X. Research on BP network for retrieving extinction coefficient from Mie scattering signal of lidar. Measurement 2020, 164, 108028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.M.; Sun, H.B.; Guo, J.Q.; Lao, L.Y.; Wu, S.D.; Zhang, J.F. Experimental Study on Water Pipeline Leak Using In-Pipe Acoustic Signal Analysis and Artificial Neural Network Prediction. Measurement 2021, 186, 110094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

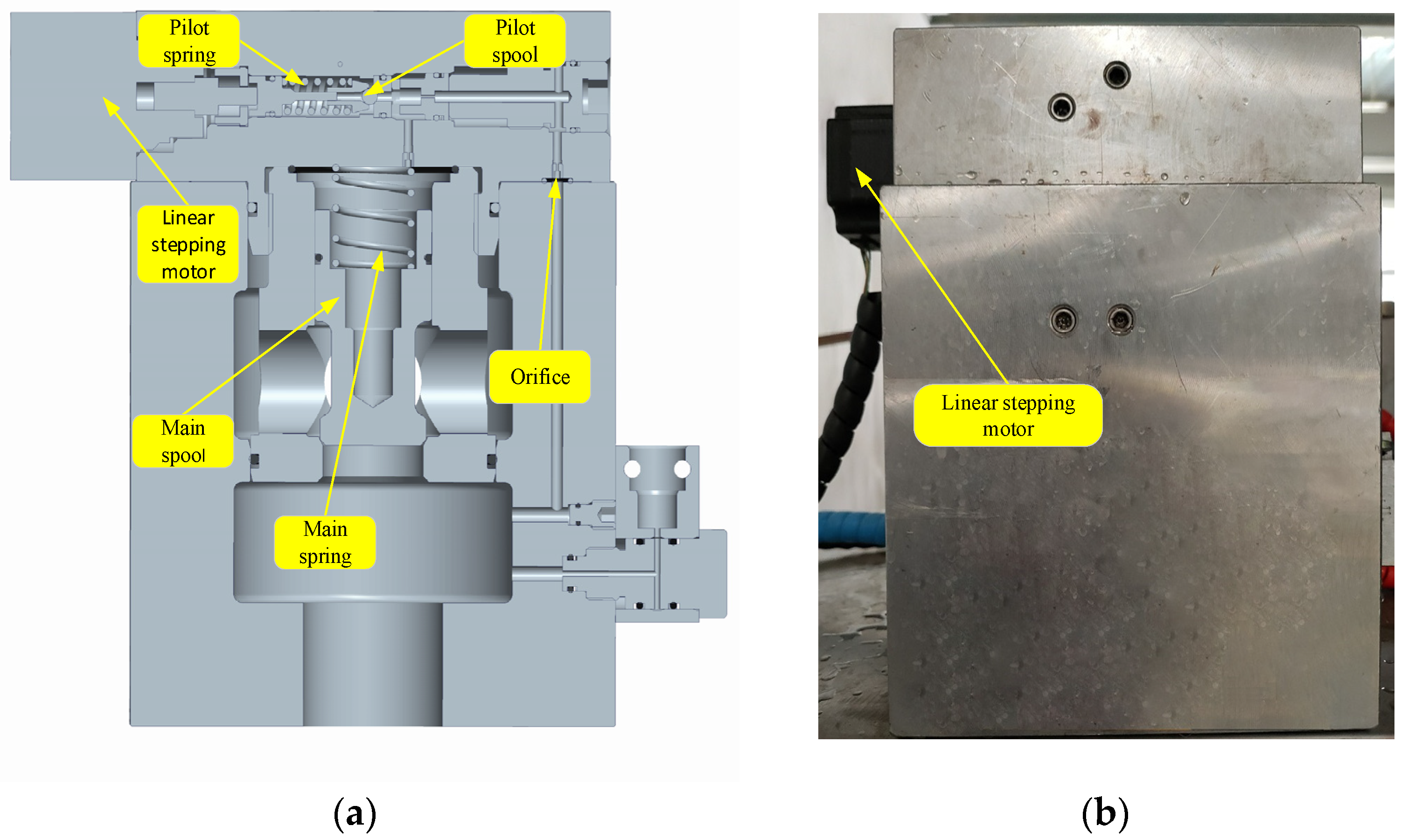

| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Pilot valve seat diameter (mm) | 5 |
| Pilot valve spool diameter (mm) | 5.5 |
| Pilot spring stiffness (mm) | 100 |
| Pilot valve spool mass (g) | 8 |
| Pilot valve seat half cone angle (°) | 20 |
| Coefficient of viscous friction of pilot spool (N/(m/s)) | 100 |
| Diameter of upper chamber of main spool (mm) | 42 |
| Main spool lower chamber diameter (mm) | 38 |
| Main spring stiffness (N/mm) | 20 |
| Damping hole diameter (mm) | 0.8 |
| Main spool mass (g) | 100 |
| Main spool half taper angle (°) | 30 |
| Main spool static friction (N) | 30 |
| Coefficient of viscous friction of main spool (N/(m/s)) | 400 |
| Initial compression of main spring (mm) | 10 |
| Flow (L/min) | Shaft Extension of Linear Stepping Motor (mm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 4.5 | 5 | |
| Pressure (MPa) | |||||||||||
| 200 | 1.10 | 4.18 | 7.44 | 10.73 | 14.00 | 17.27 | 20.56 | 23.83 | 27.10 | 30.39 | 33.67 |
| 400 | 1.32 | 4.46 | 7.75 | 11.08 | 14.38 | 17.71 | 21.01 | 24.29 | 27.60 | 30.90 | 34.15 |
| 600 | 1.51 | 4.69 | 8.04 | 11.43 | 14.78 | 18.09 | 21.43 | 24.76 | 28.10 | 31.43 | 34.73 |
| 800 | 1.72 | 4.95 | 8.39 | 11.76 | 15.16 | 18.54 | 21.91 | 25.27 | 28.61 | 31.94 | 35.28 |
| 1000 | 1.95 | 5.23 | 8.69 | 12.11 | 15.57 | 18.95 | 22.38 | 25.73 | 29.13 | 32.52 | 35.88 |
| 1200 | 2.21 | 5.51 | 9.01 | 12.51 | 15.96 | 19.39 | 22.85 | 26.23 | 29.64 | 33.07 | 36.43 |
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Plunger diameter (mm) | 65 |
| Plunger stroke (mm) | 105 |
| Suction valve diameter (mm) | 51 |
| discharge valve diameter (mm) | 51 |
| Crank speed (rad/min) | 436 |
| Maximum dead zone value (bar) | 8 |
| Minimum dead zone value (bar) | −8 |
| PID output gain | 0.0001 |
| Target Pressure (MPa) | Shaft Extension of Linear Stepping Motor (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| 650 L/min Pump | 1070 L/min Pump | |
| 4 | 0.376 | 0.309 |
| 8 | 0.967 | 0.882 |
| 12 | 1.563 | 1.461 |
| 16 | 2.163 | 2.047 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, H. Testing Method for Intelligent Loading of Mining Emulsion Pump Based on Digital Relief Valve and BP Neural Network Control Algorithm. Machines 2022, 10, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100896
Tian J, Liu W, Wang H. Testing Method for Intelligent Loading of Mining Emulsion Pump Based on Digital Relief Valve and BP Neural Network Control Algorithm. Machines. 2022; 10(10):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100896
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jie, Wenchao Liu, and Hongyao Wang. 2022. "Testing Method for Intelligent Loading of Mining Emulsion Pump Based on Digital Relief Valve and BP Neural Network Control Algorithm" Machines 10, no. 10: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100896
APA StyleTian, J., Liu, W., & Wang, H. (2022). Testing Method for Intelligent Loading of Mining Emulsion Pump Based on Digital Relief Valve and BP Neural Network Control Algorithm. Machines, 10(10), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100896





