Application of Improved Robust Local Mean Decomposition and Multiple Disturbance Multi-Verse Optimizer-Based MCKD in the Diagnosis of Multiple Rolling Element Bearing Faults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background Theory of CCERLMDAN
2.1. RLMD Method
2.2. CCERLMDAN Method
2.3. Impulse Signal Decomposition Experiments
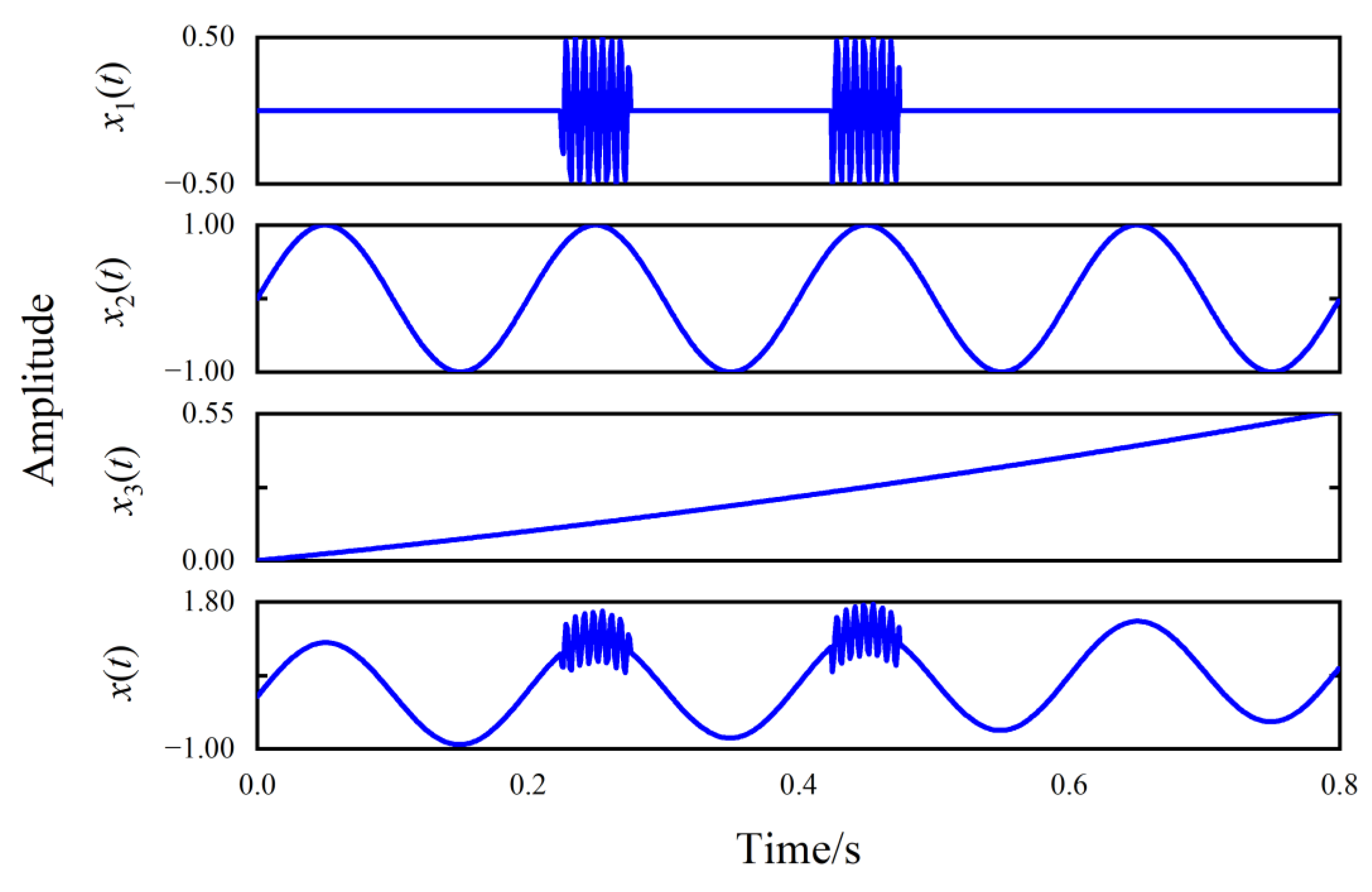
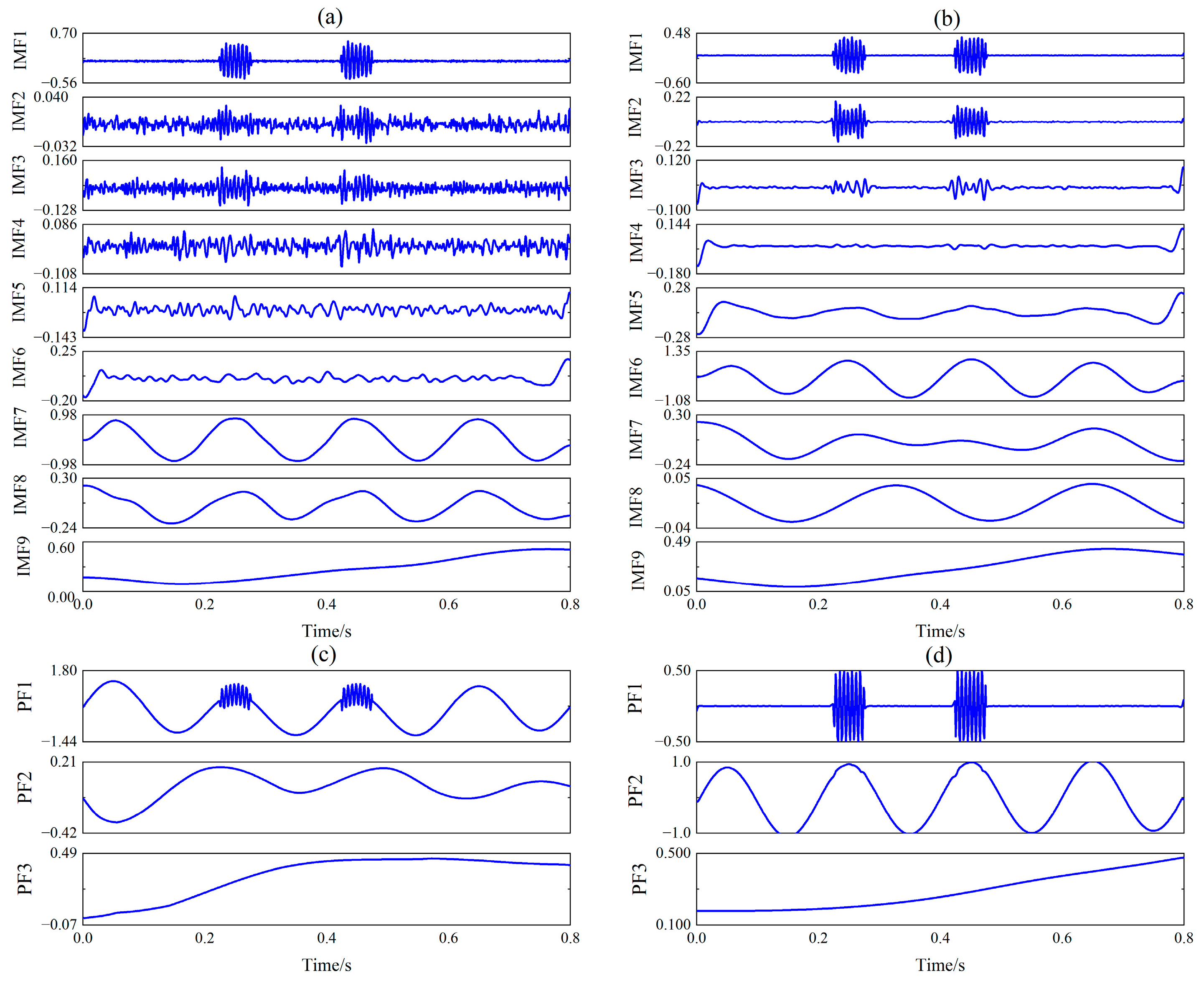
2.4. Synthesis Signal Decomposition Experiments
3. Background Theory of MDMVO
3.1. MVO Method
3.2. MDMVO Method
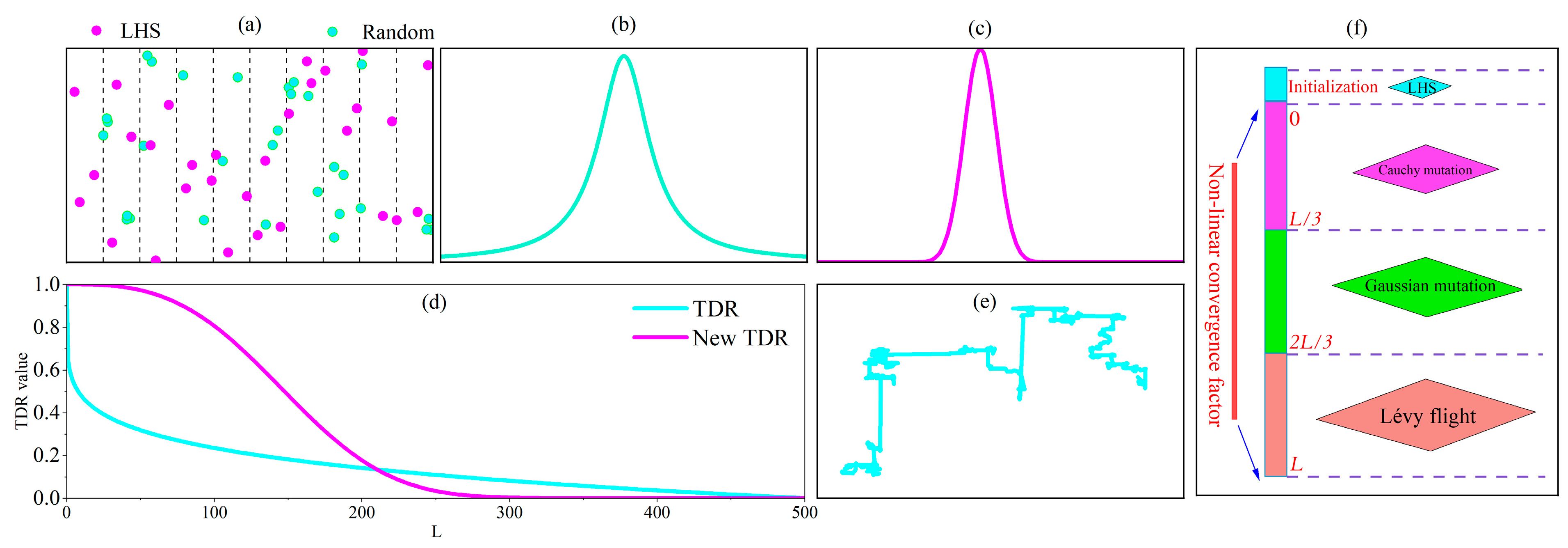
3.2.1. Latin Hypercube Sampling
3.2.2. Nonlinear Convergence Factor
3.2.3. Cauchy Mutation
3.2.4. Gaussian Mutation
3.2.5. Lévy Flight
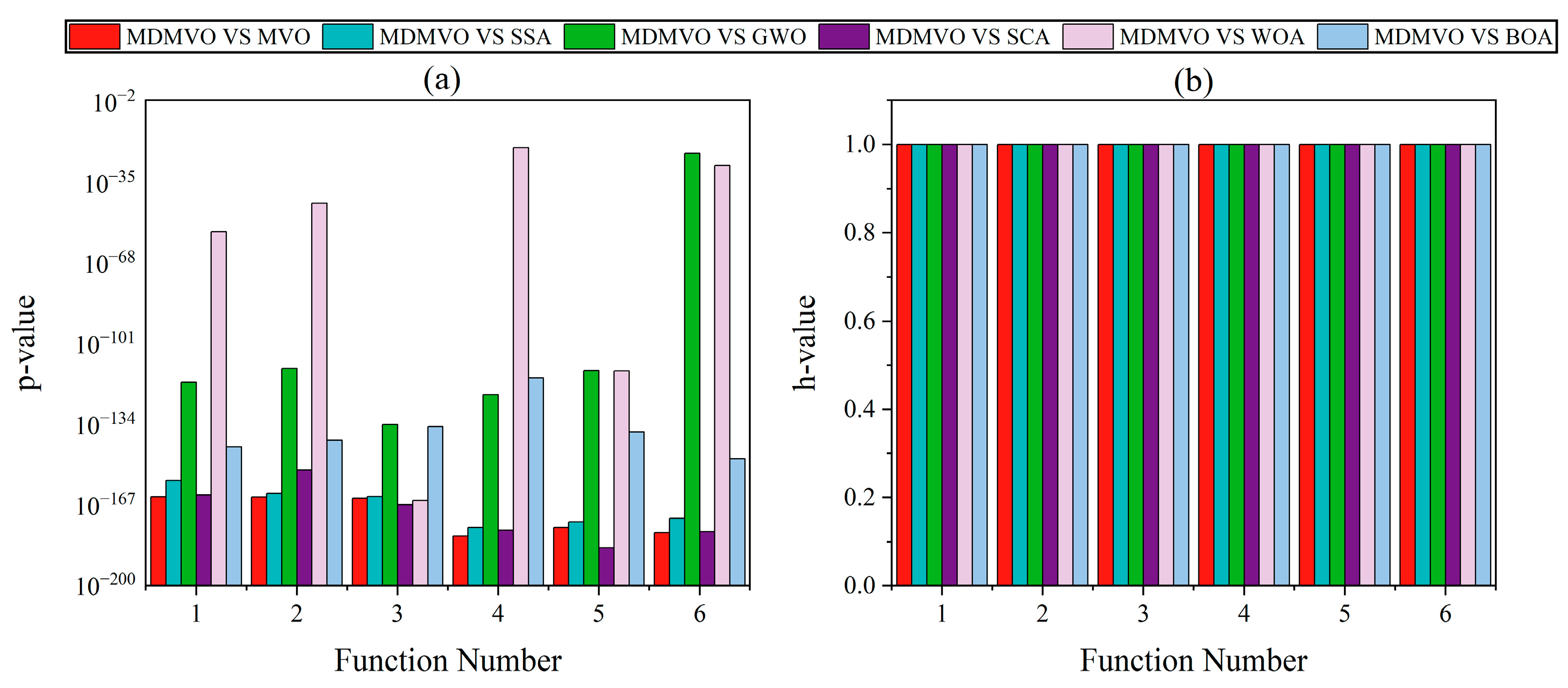
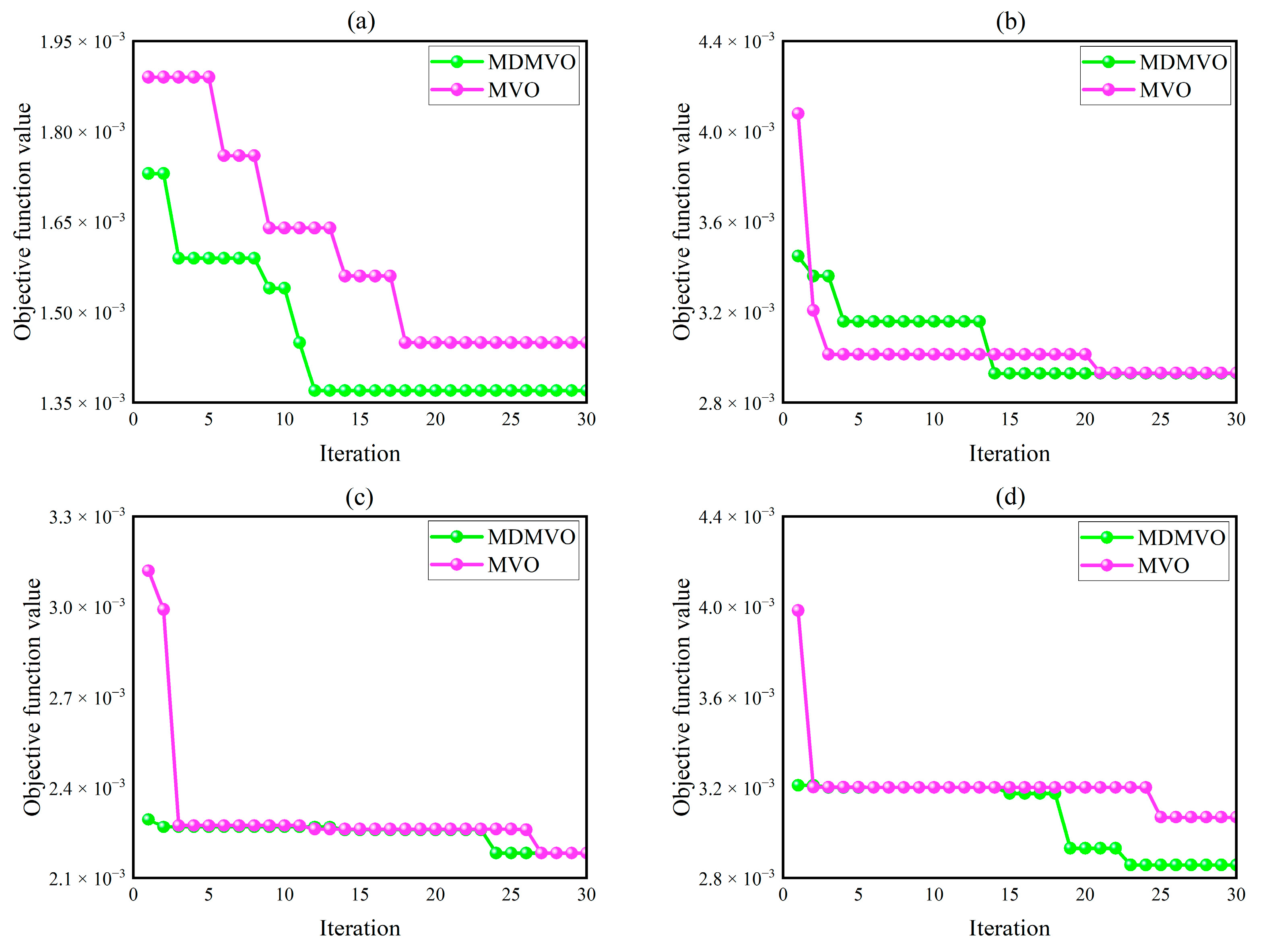
3.2.6. Evaluation of the Exploitation Ability of MDMVO
| Algorithm 1. The pseudocode for MDMVO algorithm. |
| Assign values for parameters , , , and , , |
| Define objective function |
| Latin hypercube sampling initial Multi-Verse population |
| Get the current optimal universe |
| While |
| Update and |
| For |
| Calculate the inflation rate (fitness) of universes |
| if |
| Create the new Position of universes using Equation (13) |
| if better than |
| end if |
| if |
| Create the new Position of universes using Equation (14) |
| If better than |
| end if |
| if |
| Create the new Position of universes using Equation (18) |
| if better than |
| end if |
| for |
| Calculate the random variable and update the Position of the universes |
| end for |
| Update the convergence curve |
| end for |
| End |
4. Proposed Method
4.1. Maximum Correlated Kurtosis Deconvolution (MCKD)
4.2. MDMVO-Based MCKD
| Algorithm 2. MDMVO-based MCKD |
| Step 1: Define the initial parameters of the MDMVO algorithm and the MCKD influence parameter search interval. set the universe population size to 20, the maximum number of iterations to 30, the MDMVO algorithm wormhole existence probability to 0.2 and to 1. The sampling frequency is . The fault characteristic frequency , fault period and fault pulse interval of each component of the bearing are calculated according to the bearing parameters. Set the MCKD method parameters , , . |
| Step 2: Initialize the position of the universe, obtain the best universe and the position of the best universe . |
| Step 3: Update the wormhole existence probability and travel distance rate , compare the universe expansion rate value during the iteration, and update the optimal universe expansion rate if the rate of the universe’s expansion is higher than it currently is; otherwise, keep the universe as it is. Update the best universe individual and the best universe position . |
| Step 4: If the condition that the universe is best or if the maximum iteration has been achieved, output the best solution, otherwise go to step 3. |
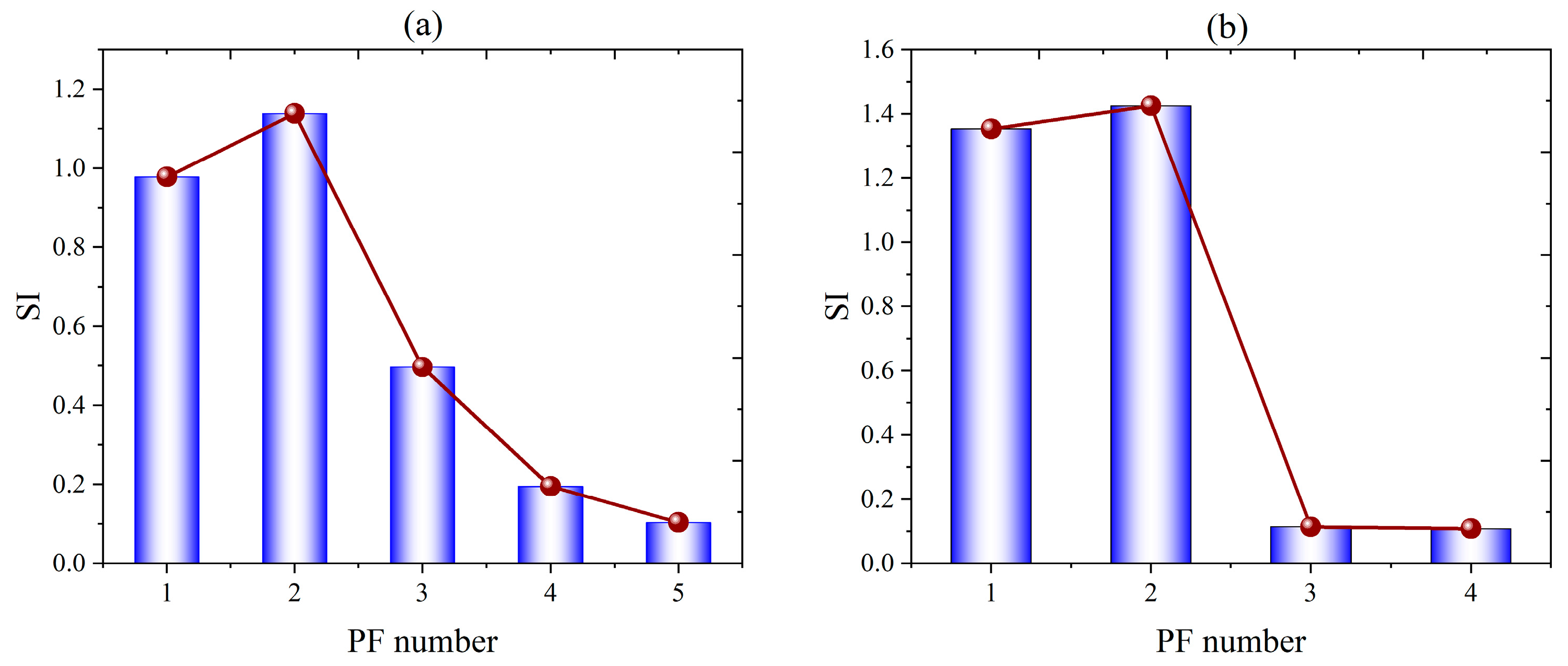
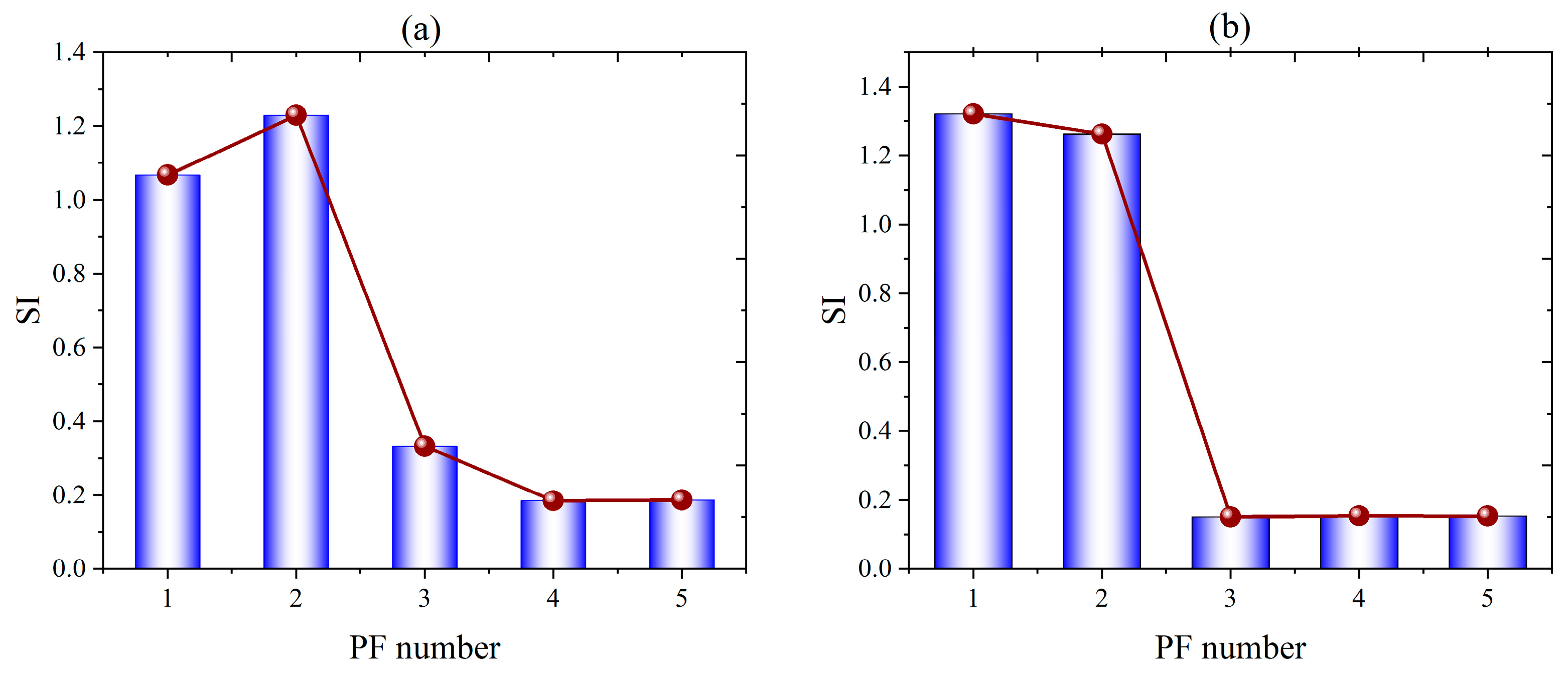
4.3. Selection of Sensitive PF
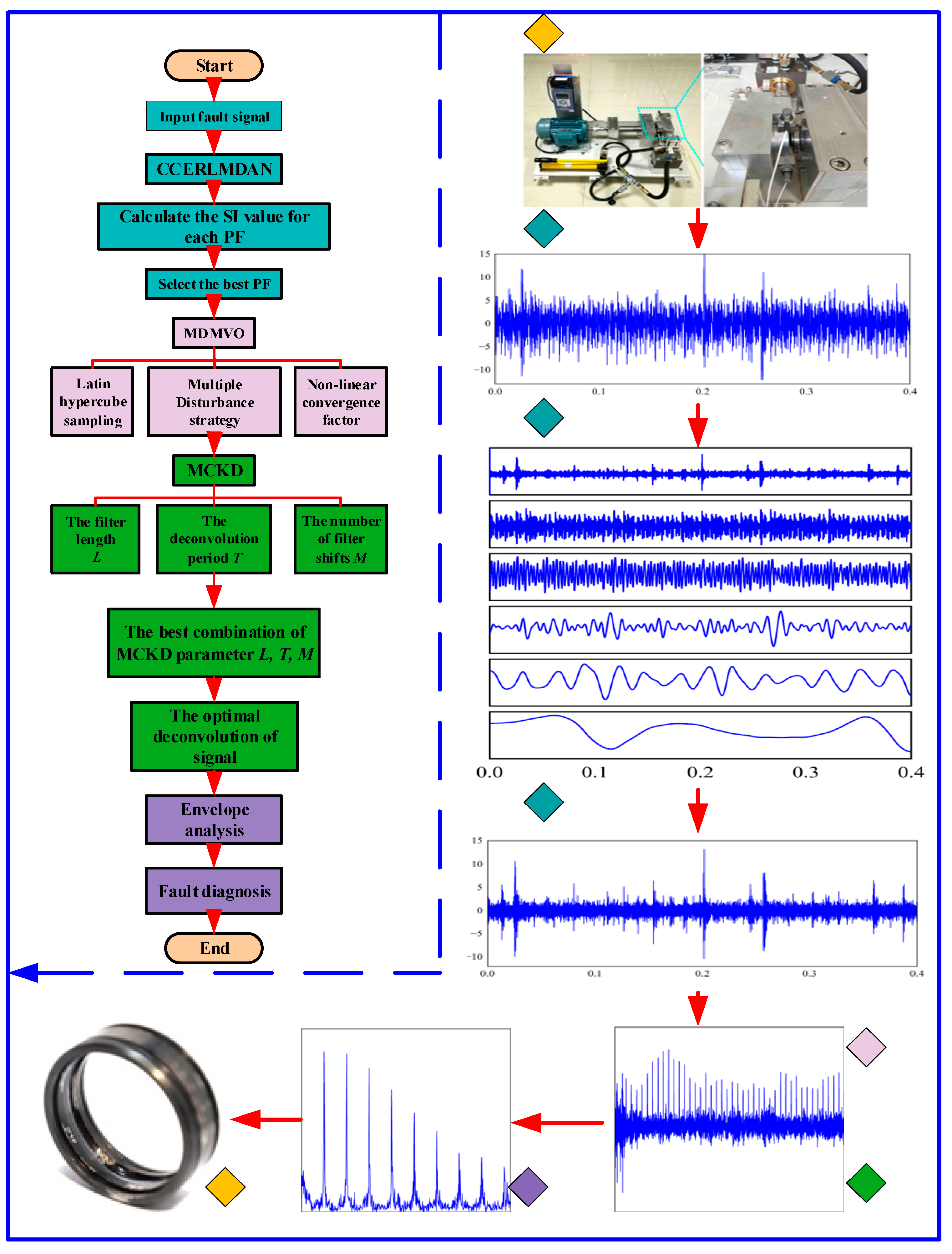
4.4. The Proposed Time—Frequency Method for Diagnosing Rolling Element Bearing Faults
| Algorithm 3. CCERLMDAN and MDMVO-based MCKD |
| Step 1: The rolling element bearing vibration signal collected by the sensor is decomposed into a series of PF components by CCERLMDAN. |
| Step 2: The SI value of each PF component is calculated, and the best PF component is selected according to the principle of maximum SI. |
| Step 3: The MDMVO-based MCKD is used to enhance the fault impulses contained in the selected best PF component and select the best combination of MCKD parameters , and . |
| Step 4: Envelope demodulation analysis is used for the best deconvoluted signal in order to extract the bearing fault characteristic frequencies and to determine the fault type. |
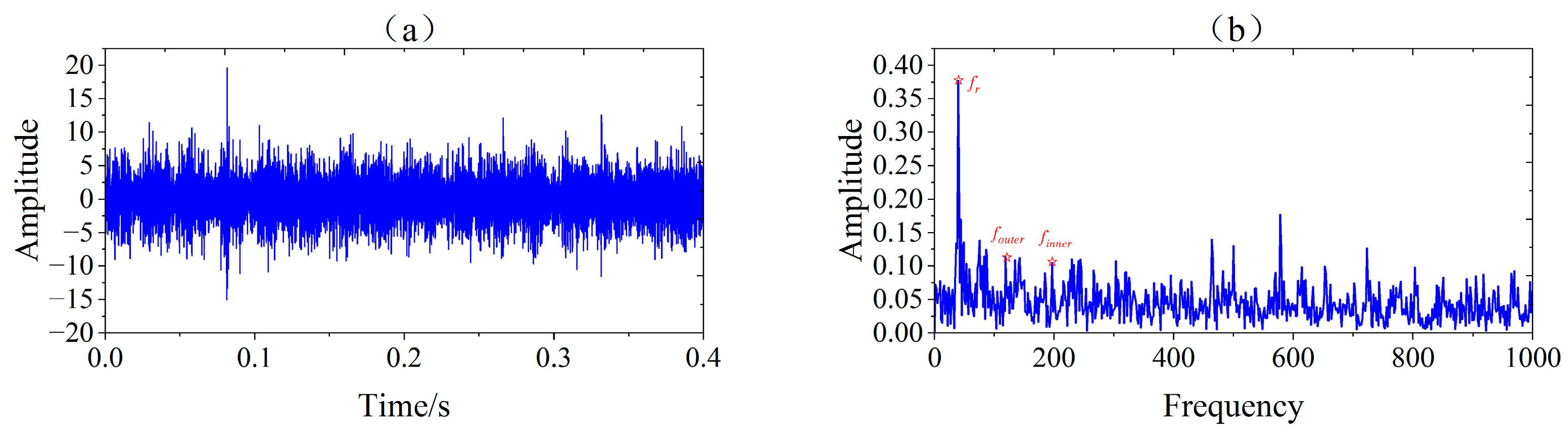
5. Practical Application
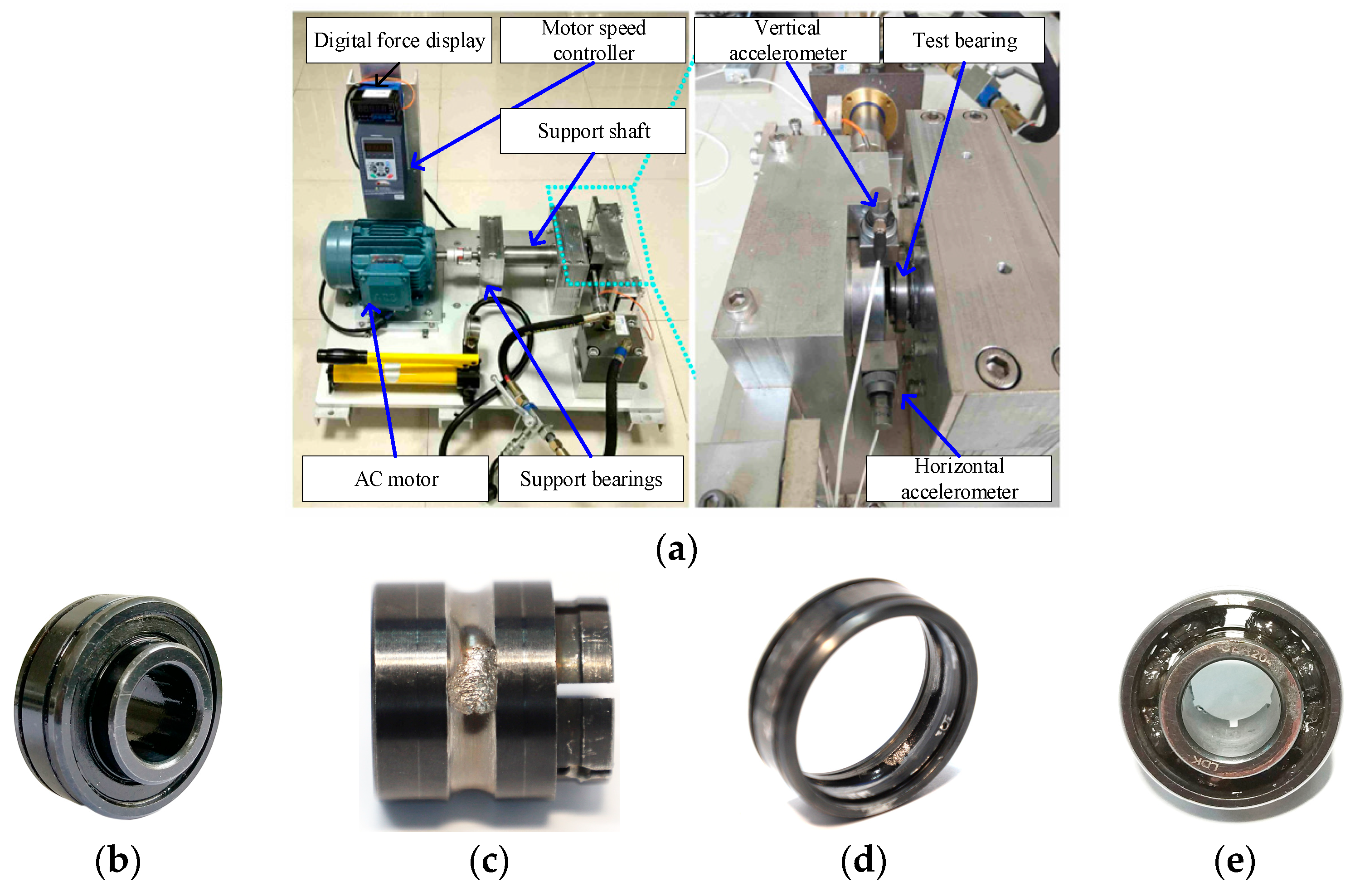
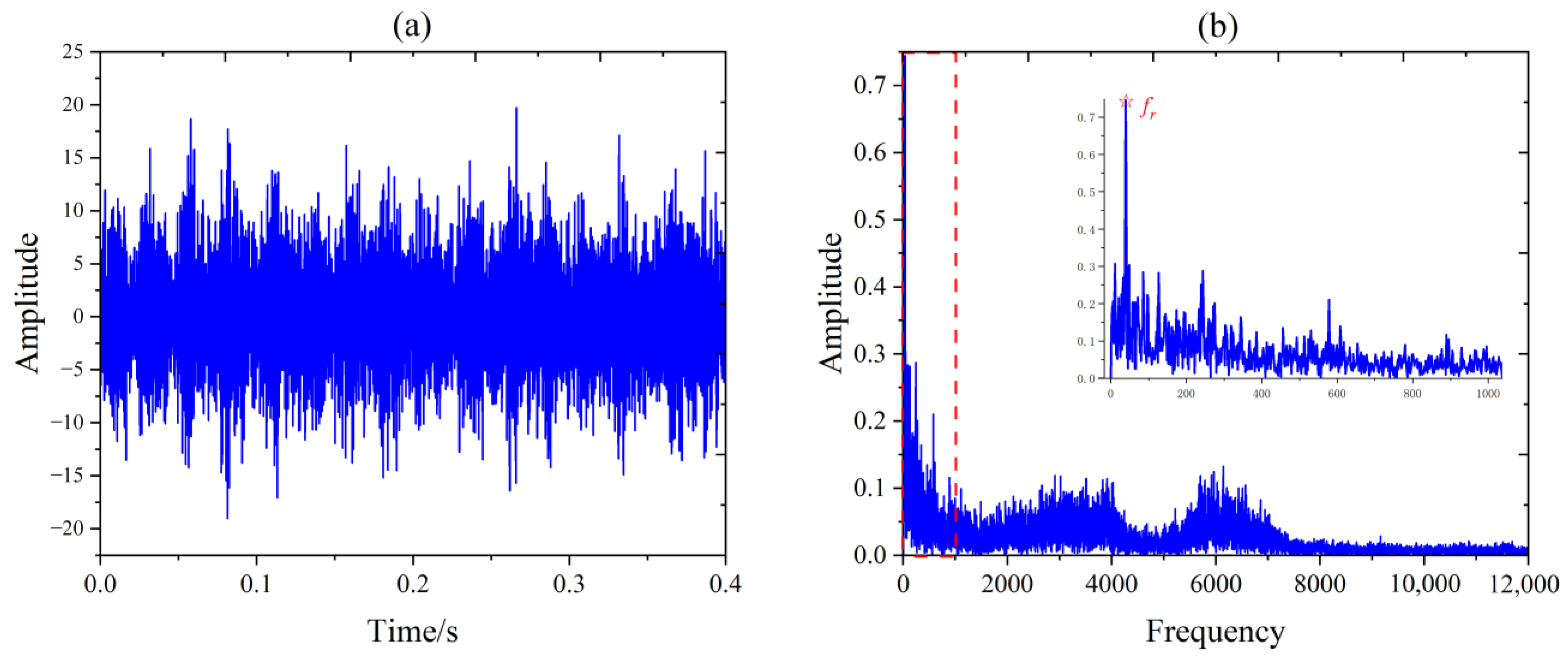
5.1. Data Acquisition
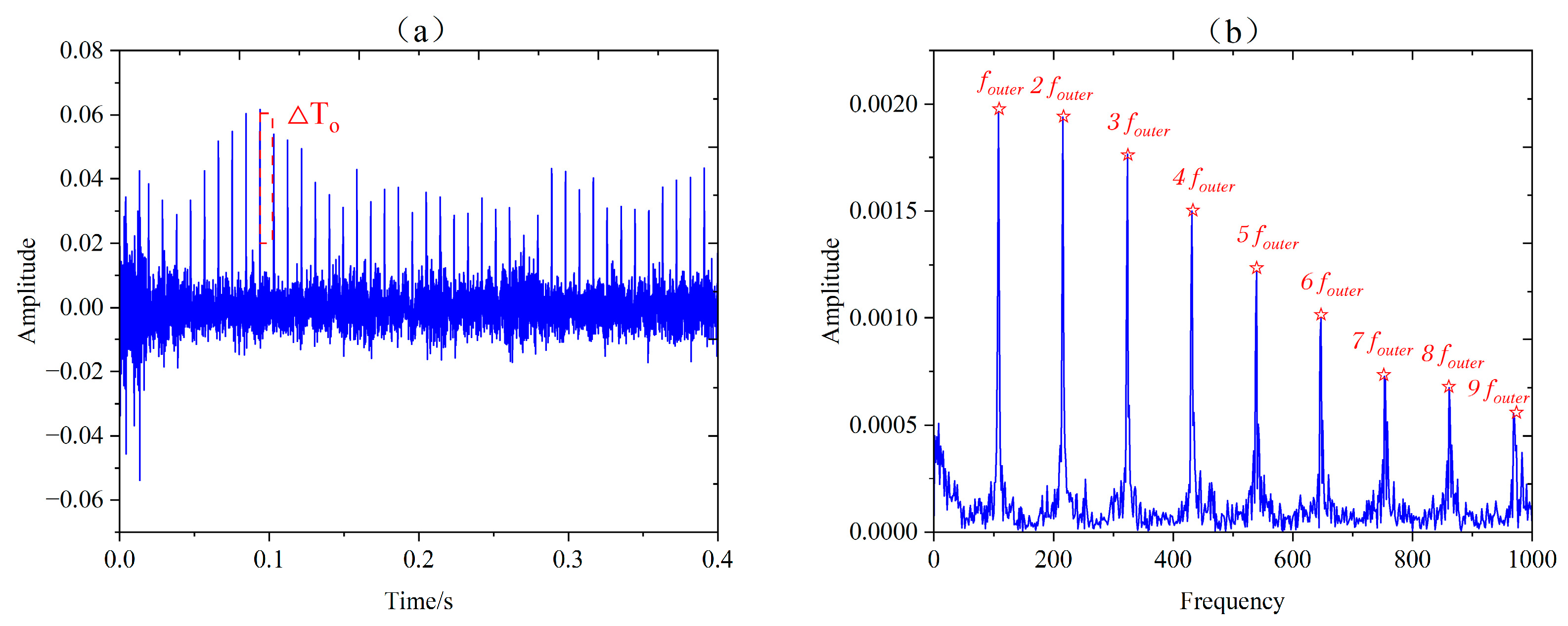
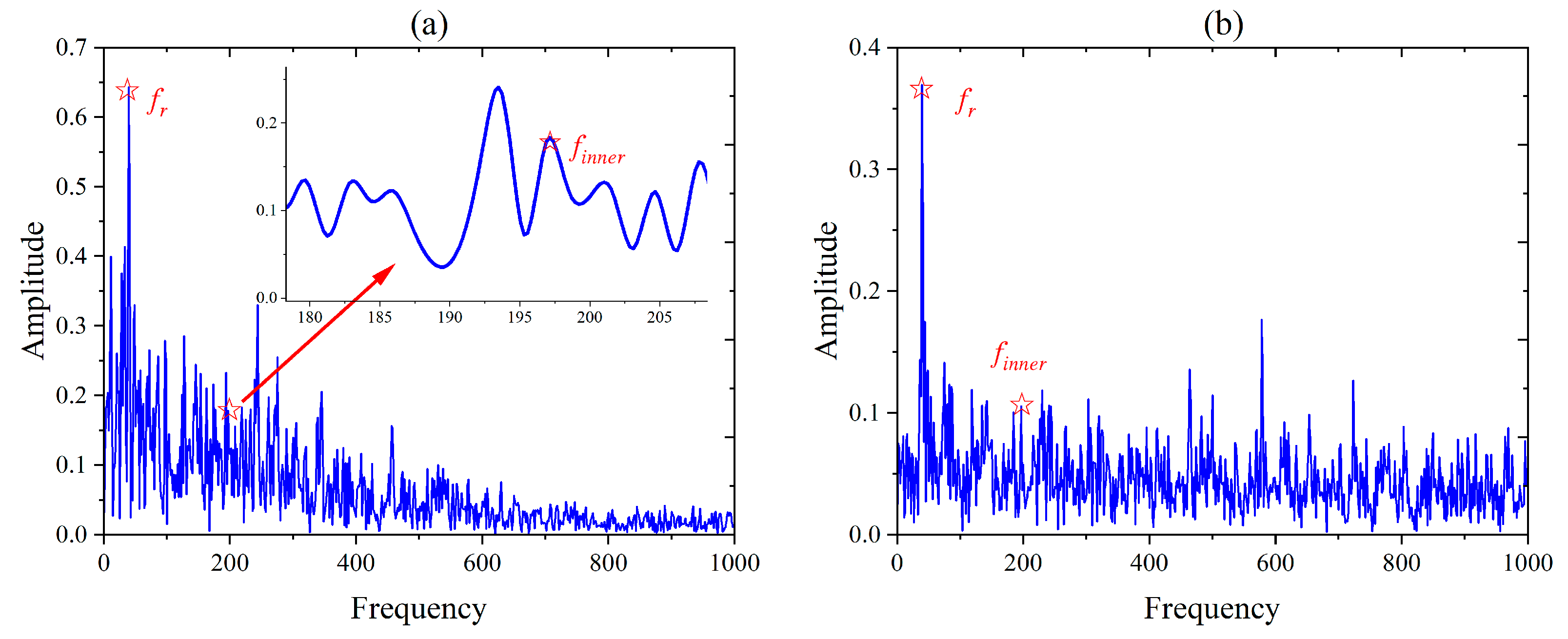
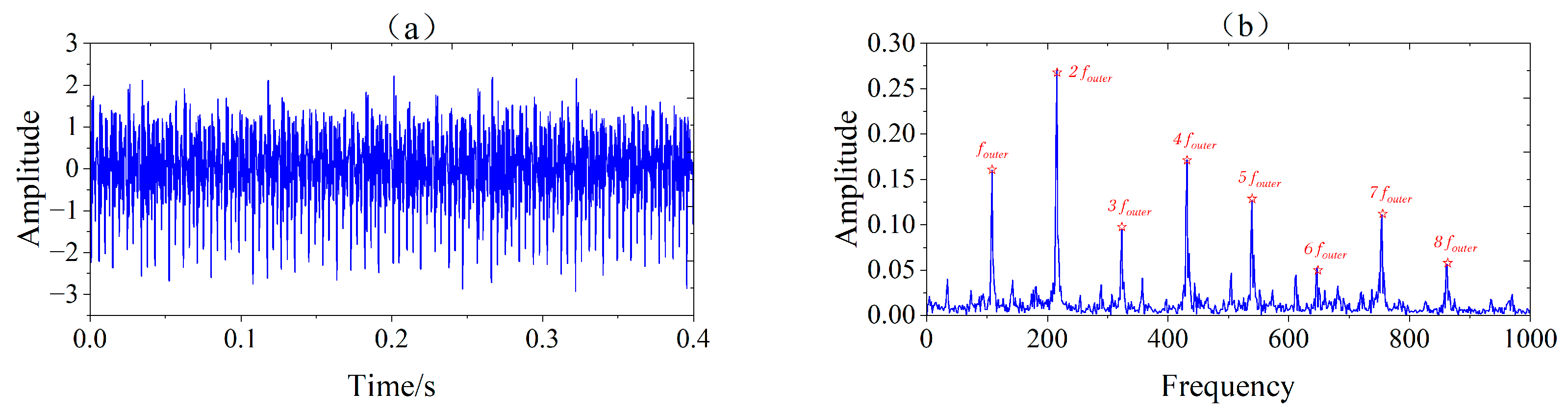
5.2. Experiment and Analysis of Outer Race Fault in Rolling Element Bearings
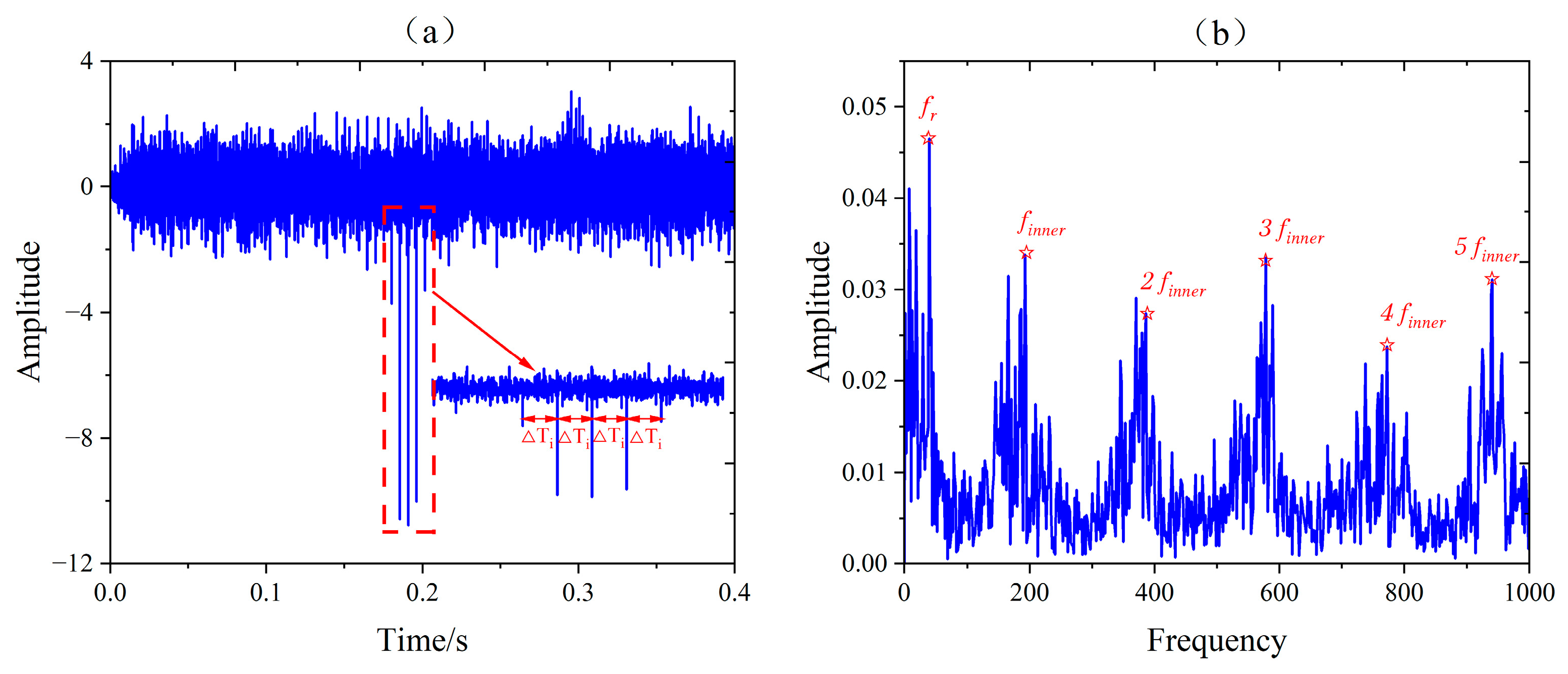
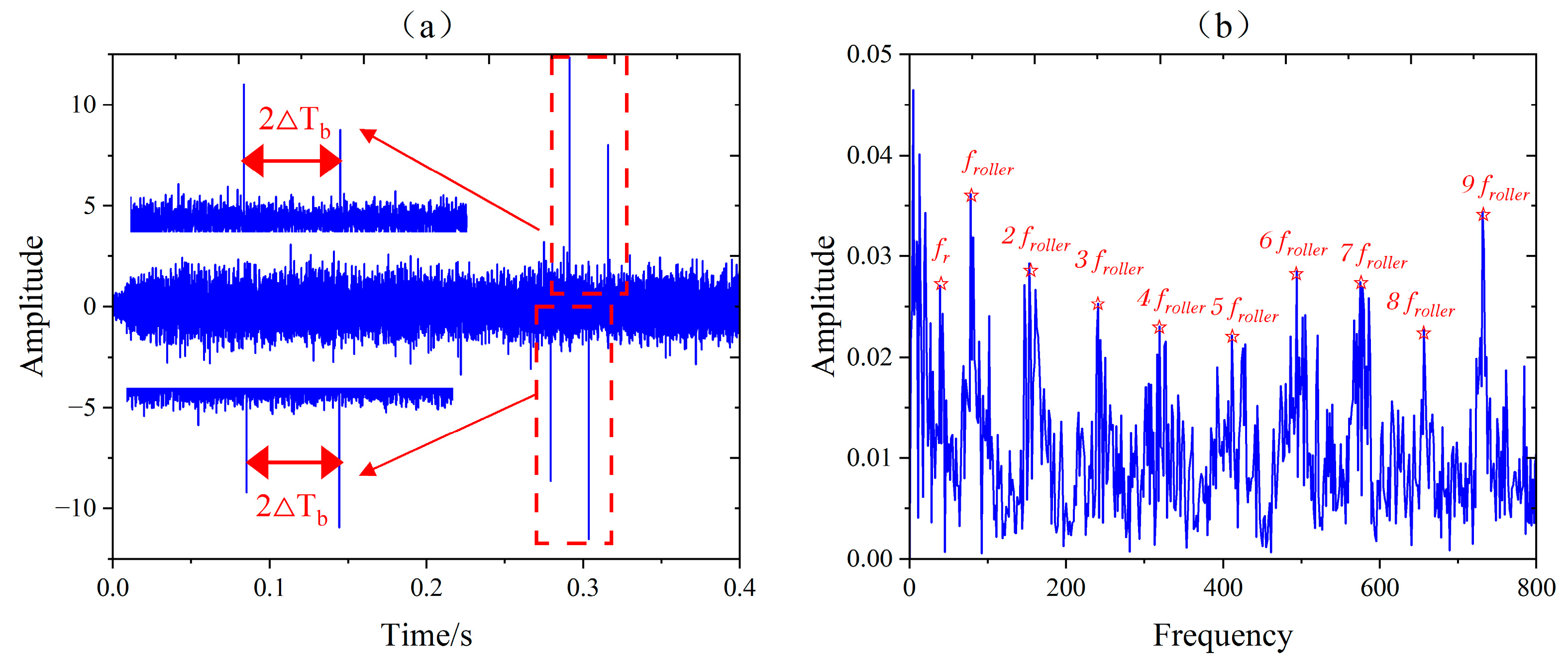
5.3. Experiment and Analysis of Compound Fault in Rolling Element Bearings
5.4. Contrast Verification
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The CCERLMDAN method proposed in this paper further suppresses the modal mixing effect and improves the decomposition performance of the RLMD method. Compared with the RLMD method, the CCERLMDAN method can better eliminate the noise interference contained in the original signal, and extract the fault information hidden in the signal.
- (2)
- In this paper, an improved MDMVO algorithm is proposed. Through Latin hypercube sampling, nonlinear convergence factor and multiple disturbance strategies, the MVO algorithm is optimized globally. Therefore, the MDMVO algorithm obtains better optimization finding accuracy and convergence speed compared to the original MVO algorithm.
- (3)
- Aiming at the shortcomings of the MCKD method in fault feature extraction of rolling element bearings under a strong noise environment, a parameter-adaptive optimization MCKD fault feature extraction method is proposed. Using the MDMVO, avoiding the interference of human subjective factors on the selection of MCKD parameters and achieving the best deconvolution of fault signals.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, X. Complete ensemble local mean decomposition with adaptive noise and its application to fault diagnosis for rolling bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 106, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z. An improved local characteristic-scale decomposition to restrict end effects, mode mixing and its application to extract incipient bearing fault signal. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 156, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, J. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on time-delayed feedback monostable stochastic resonance and adaptive minimum entropy deconvolution. J. Sound Vibr. 2017, 401, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Z.; Song, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, H.K. Seizure Prediction in EEG Signals Using STFT and Domain Adaptation. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachori, R.B.; Nishad, A. Cross-terms reduction in the Wigner–Ville distribution using tunable-Q wavelet transform. Signal Process. 2016, 120, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X. The fault feature extraction and classification of gear using principal component analysis and kernel principal component analysis based on the wavelet packet transform. Measurement 2014, 54, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xing, F.; Pan, S.; Yuan, R.; Lv, Y. Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearings Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Genetic Algorithm-Optimized Wavelet Threshold Denoising. Machines 2022, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The Empirical Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert Spectrum for Nonlinear and Non-Stationary Time Series Analysis. Proc. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ompokov, V.D.; Boronoev, V.V. Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert-Huang Transform. In Proceedings of the 2019 Russian Open Conference on Radio Wave Propagation (RWP), Kazan, Russia, 1–6 July 2019; Volume 1, pp. 222–223. [Google Scholar]
- Valdes, G.; O’Reilly, B.; Diaz, M. A Hilbert-Huang transform method for scattering identification in LIGO. Class. Quantum Gravity 2017, 34, 235009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alaifari, R.; Wellershoff, M. Uniqueness of STFT phase retrieval for bandlimited functions. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2021, 50, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.P.; Liang, M.; Chu, F.L. Recent advances in time-frequency analysis methods for machinery fault diagnosis: A review with application examples. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 38, 165–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, Z.K.; Zhang, W.M.; Meng, G. Parameterised time-frequency analysis methods and their engineering applications: A review of recent advances. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 119, 182–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.M.A.; Manjunath, T.C. Vibration Signal Analysis using Time and Timefrequency Domain: Review. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering (ICPCSI), Chennai, India, 21–22 September 2017; pp. 1808–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.S. The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG perception data. J. R. Soc. Interface 2005, 2, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.S.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, S.Y. Voltage Disturbance Signals Identification Based on ILMD and Neural Network. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 2058007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.H.; Wang, L.P.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.G.; Yu, G. Elimination of end effects in LMD by Bi-LSTM regression network and applications for rolling element bearings characteristic extraction under different loading conditions. Digit. Signal Prog. 2020, 107, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, M.G.A.; Hussein, T.M.; Mokhiamar, O. An adaptive variational mode decomposition based on sailfish optimization algorithm and Gini index for fault identification in rolling bearings. Measurement 2021, 173, 108514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Jin, Y.Q.; Zuo, M.J.; Feng, Z.P. Time-frequency representation based on robust local mean decomposition for multicomponent AM-FM signal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 95, 468–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, F. Bearing Fault Diagnosis with Variable Speed Based on Fractional Hierarchical Range Entropy and Hunter-Prey Optimization Algorithm-Optimized Random Forest. Machines 2022, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, A.N.L.; Deo, R.C.; Ali, M.; Abdulla, S.; Raj, N. Novel short-term solar radiation hybrid model: Long short-term memory network integrated with robust local mean decomposition. Appl. Energy 2021, 298, 117193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhu, J.M.; Ding, Z.N. Daily PM2.5 and PM10 forecasting using linear and nonlinear modeling framework based on robust local mean decomposition and moving window ensemble strategy. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2022, 114, 108110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.M.; Yang, Z.X.; Wang, S. Study on mode mixing problem of empirical mode decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2016 Joint International Information Technology, Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Xi’an, China, 3–5 October 2016; Volume 59, pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.R.; Shieh, J.S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Torres, M.E. Improved complete ensemble EMD: A suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 14, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Randall, R.B. Enhancement of autoregressive model based gear tooth fault detection technique by the use of minimum entropy deconvolution filter. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, G.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, M.J. Maximum correlated Kurtosis deconvolution and application on gear tooth chip fault detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 33, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H. Compound Fault Diagnosis Using Optimized MCKD and Sparse Representation for Rolling Bearings. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 3508509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.J.; Wang, X.L.; He, Y.L. Diagnosis of compound faults of rolling bearings through adaptive maximum correlated kurtosis deconvolution. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Q. Application of improved MCKD method based on QGA in planetary gear compound fault diagnosis. Measurement 2019, 139, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S.M. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. SCA: A Sine Cosine Algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 96, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Hatamlou, A. Multi-Verse Optimizer: A nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bi, F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G. An Engine Fault Detection Method Based on the Deep Echo State Network and Improved Multi-Verse Optimizer. Energies 2022, 15, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhao, X. Multi-UAVs Cooperative Reconnaissance Task Allocation Under Heterogeneous Target Values. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 70955–70963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.D.; Fang, Y.M.; Liu, L.; Xu, M.; Li, Q. A covariance-based Moth-flame optimization algorithm with Cauchy mutation for solving numerical optimization problems. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2022, 119, 108538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Xu, H.S.; Ma, J.M.; Jia, Z.C. A Feature Selection Method of the Island Algorithm Based on Gaussian Mutation. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 1438999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campeau, W.; Simons, A.M.; Stevens, B. The evolutionary maintenance of Levy flight foraging. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.Y.; Zhang, S. An approach to eliminating end effects of EMD through mirror extension coupled with support vector machine method. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2019, 23, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Akhenia, P.; Bhavsar, K.; Panchal, J.; Vakharia, V. Fault severity classification of ball bearing using SinGAN and deep convolutional neural network. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C-J. Eng. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 3864–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lei, Y.G.; Li, N.P.; Li, N.B. A Hybrid Prognostics Approach for Estimating Remaining Useful Life of Rolling Element Bearings. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2020, 69, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, J. Fast computation of the kurtogram for the detection of transient faults. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
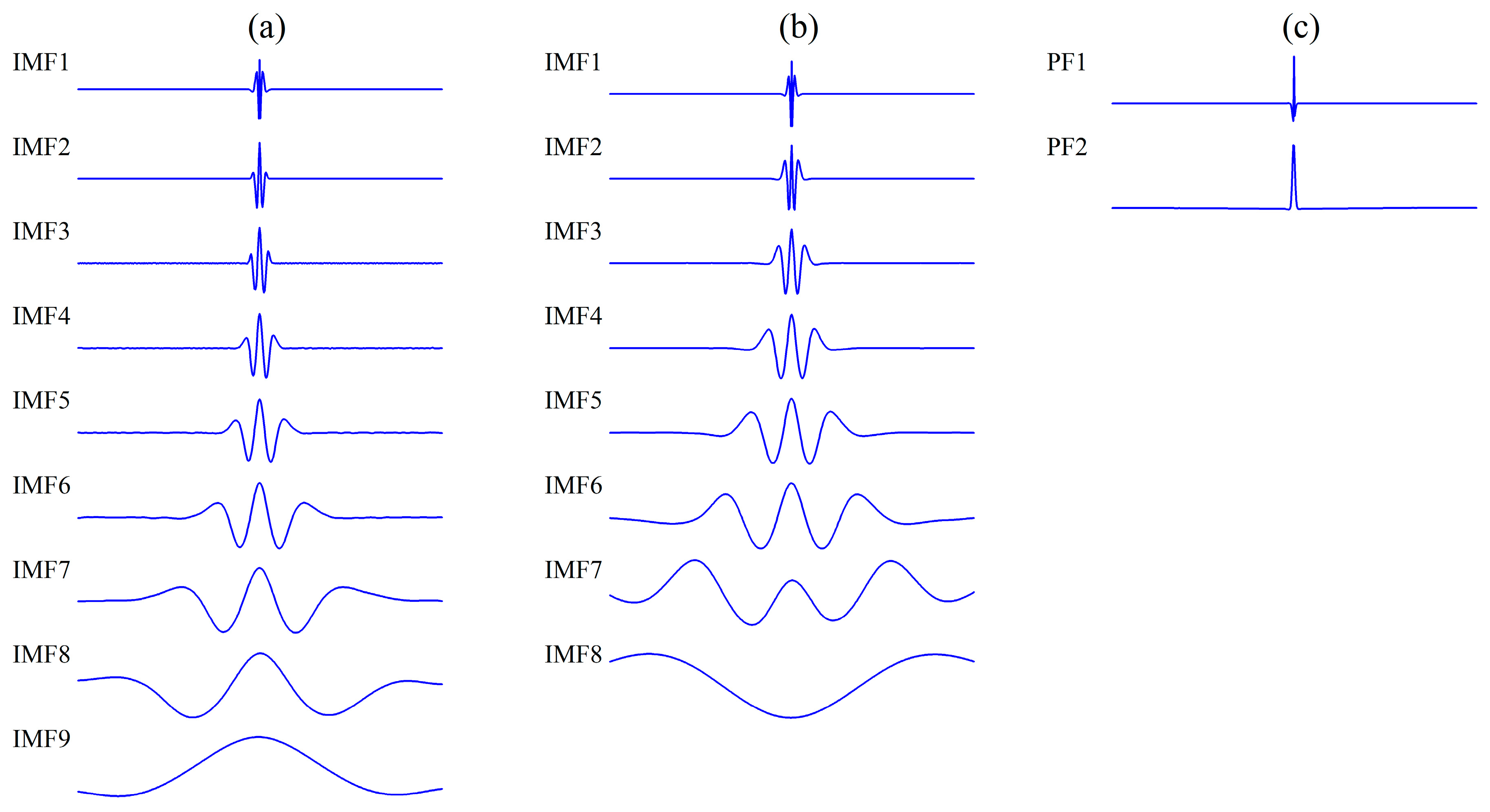
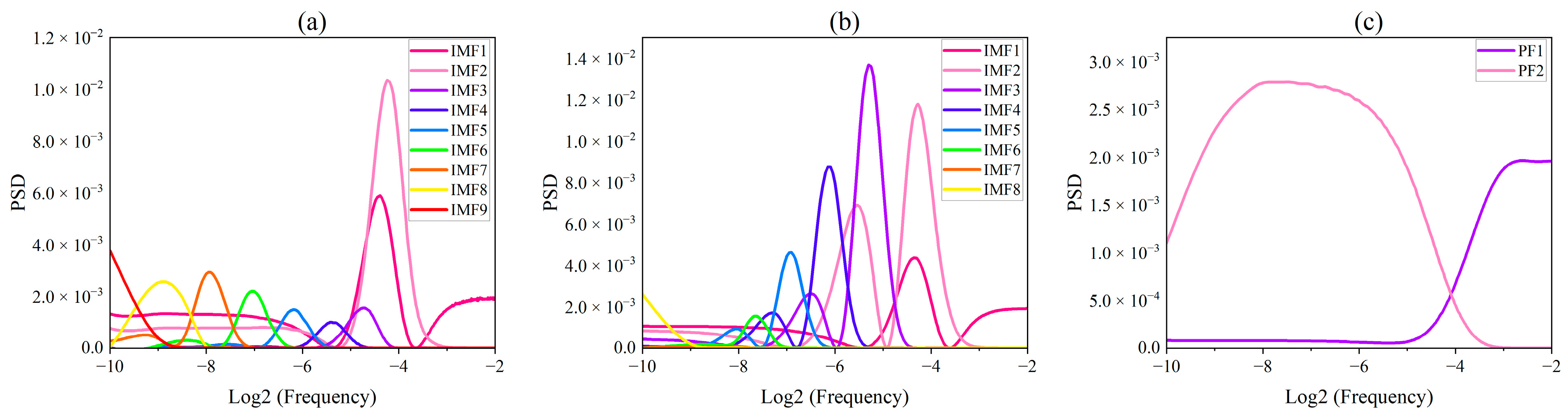
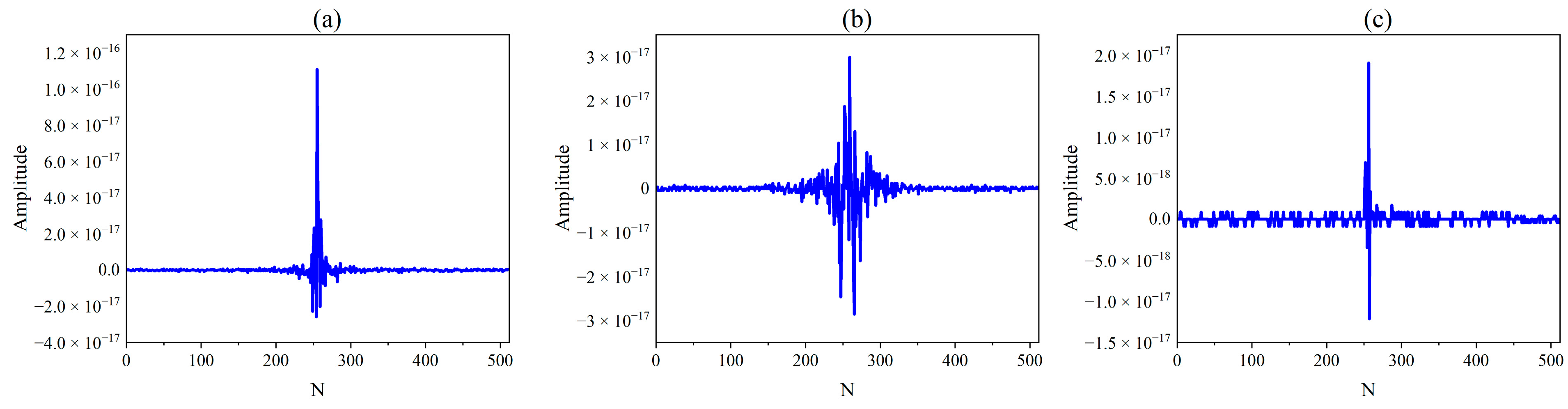
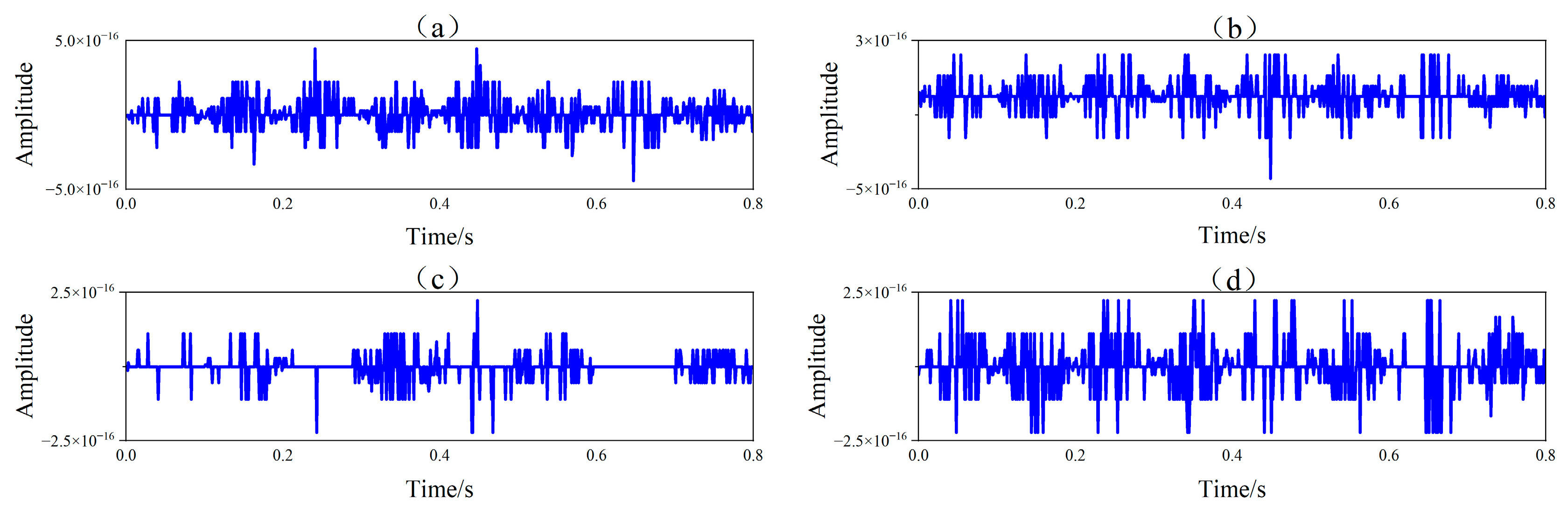






| Method | IO | Cor1 | Cor2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CEEMDAN | 0.7936 | 0.4496 | 0.4502 |
| ICEEMDAN | 0.7504 | 0.4705 | 0.3473 |
| CCERLMDAN | 0.0365 | 0.8721 | 0.5470 |
| Method | IO | Cor1 | Cor2 | Cor3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEEMDAN | 0.1476 | 0.9818 | 0.9621 | 0.9613 |
| ICEEMDAN | 0.1419 | 0.9853 | 0.9828 | 0.9489 |
| RLMD | 0.1517 | 0.1627 | −0.1353 | 0.8185 |
| CCERLMDAN | 0.0270 | 0.9973 | 0.9955 | 0.9852 |
| Function | Dim | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−10, 10] | 0 | |
| 30 | [100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−5.12, 5.12] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−32, 32] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−600, 600] | 0 |
| ID | Metric | MDMVO | MVO | SSA | GWO | SCA | WOA | BOA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best | 0.00 × 100 | 0.58 × 100 | 2.51 × 10−8 | 5.94 × 10−28 | 0.01 × 100 | 1.10 × 10−82 | 1.03 × 10−11 | |
| F1 | AVG | 0.00 × 100 | 1.19 × 100 | 1.61 × 10−7 | 7.30 × 10−26 | 3.01 × 101 | 2.38 × 10−74 | 1.25 × 10−11 |
| SD | 0.00 × 100 | 0.39 × 100 | 3.56 × 10−7 | 1.57 × 10−25 | 7.30 × 101 | 9.02 × 10−74 | 1.09 × 10−12 | |
| Best | 2.20 × 10−170 | 0.43 × 100 | 0.45 × 100 | 8.62 × 10−17 | 1.91 × 10−4 | 8.03 × 10−59 | 2.25 × 10−9 | |
| F2 | AVG | 4.21 × 10−152 | 0.89 × 100 | 2.16 × 100 | 6.69 × 10−16 | 0.02 × 100 | 2.36 × 10−51 | 4.86 × 10−9 |
| SD | 1.30 × 10−151 | 0.35 × 100 | 1.44 × 100 | 4.28 × 10−16 | 0.03 × 100 | 8.35 × 10−51 | 9.49 × 10−10 | |
| Best | 1.26 × 10−174 | 1.04 × 100 | 3.97 × 100 | 9.01 × 10−8 | 7.77 × 100 | 1.55 × 100 | 5.36 × 10−9 | |
| F3 | AVG | 2.39 × 10−150 | 1.95 × 100 | 1.11 × 101 | 6.46 × 10−7 | 3.45 × 101 | 4.52 × 101 | 6.21 × 10−9 |
| SD | 7.56 × 10−150 | 0.79 × 100 | 3.97 × 100 | 5.06 × 10−7 | 1.08 × 101 | 2.56 × 101 | 4.37 × 10−10 | |
| Best | 0.00 × 100 | 5.71 × 101 | 2.19 × 101 | 5.68 × 10−14 | 0.02 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | |
| F4 | AVG | 0.00 × 100 | 1.24 × 102 | 5.27 × 101 | 0.48 × 100 | 4.42 × 101 | 0.00 × 100 | 3.86 × 101 |
| SD | 0.00 × 100 | 3.02 × 101 | 1.72 × 101 | 1.27 × 100 | 4.12 × 101 | 0.00 × 100 | 7.78 × 101 | |
| Best | 8.88 × 10−16 | 1.05 × 100 | 1.50 × 100 | 7.90 × 10−14 | 8.56 × 100 | 8.88 × 10−16 | 3.70 × 10−9 | |
| F5 | AVG | 8.88 × 10−16 | 2.33 × 100 | 2.42 × 100 | 1.56 × 10−13 | 1.41 × 101 | 4.20 × 10−15 | 5.93 × 10−9 |
| SD | 0.00 × 100 | 3.28 × 100 | 0.59 × 100 | 4.52 × 10−14 | 0.04 × 100 | 2.27 × 10−15 | 7.68 × 10−10 | |
| Best | 0.00 × 100 | 0.68 × 100 | 0.01 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 0.02 × 100 | 0.00 × 100 | 7.13 × 10−13 | |
| F6 | AVG | 0.00 × 100 | 0.85 × 100 | 0.02 × 100 | 0.01 × 100 | 0.89 × 100 | 0.01 × 100 | 4.55 × 10−12 |
| SD | 0.00 × 100 | 0.07 × 100 | 0.02 × 100 | 0.01 × 100 | 0.34 × 100 | 0.04 × 100 | 2.43 × 10−12 |
| Calculation formula of inner race fault | |
| Calculation formula of outer race fault | |
| Calculation formula of roller fault |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Zhu, A.; Song, Y.; Ma, G.; Bai, X.; Guo, Y. Application of Improved Robust Local Mean Decomposition and Multiple Disturbance Multi-Verse Optimizer-Based MCKD in the Diagnosis of Multiple Rolling Element Bearing Faults. Machines 2022, 10, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100883
Lu X, Zhu A, Song Y, Ma G, Bai X, Guo Y. Application of Improved Robust Local Mean Decomposition and Multiple Disturbance Multi-Verse Optimizer-Based MCKD in the Diagnosis of Multiple Rolling Element Bearing Faults. Machines. 2022; 10(10):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100883
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xiang, Ao Zhu, Yaqi Song, Guoli Ma, Xingzhen Bai, and Yinjing Guo. 2022. "Application of Improved Robust Local Mean Decomposition and Multiple Disturbance Multi-Verse Optimizer-Based MCKD in the Diagnosis of Multiple Rolling Element Bearing Faults" Machines 10, no. 10: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100883
APA StyleLu, X., Zhu, A., Song, Y., Ma, G., Bai, X., & Guo, Y. (2022). Application of Improved Robust Local Mean Decomposition and Multiple Disturbance Multi-Verse Optimizer-Based MCKD in the Diagnosis of Multiple Rolling Element Bearing Faults. Machines, 10(10), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100883






