Abstract
A kriging regression model is a popular and effective type of surrogate model in computer experiments. A significant challenge arises when the mean function of the model includes polynomial terms with unknown coefficients, leading to identifiability problems and potentially unreliable results. To overcome this problem, Plumlee and Joseph (2018) introduced an orthogonal kriging model. Variable selection for kriging models has been widely considered by researchers in computer experiments. In this paper, we introduce a new method for combining orthogonal kriging with penalized variable selection. Furthermore, an efficient algorithm is given to select the correct mean function. The simulation results and an example study with real data show that the proposed method is superior to others in variable recognition rate and prediction accuracy.
MSC:
62F86; 62J02
1. Introduction
The rapid development of computers has made it possible to simulate some physical processes through computer experiments and has helped us deal with these complex practical problems efficiently. Sacks et al. [1,2] proposed the use of stochastic processes to model deterministic output responses. Kriging models, first proposed by [3], have become a widely used class of surrogate models for deterministic approximation; some empirical studies have shown that kriging is superior to other interpolation techniques [4]. Simpson et al. [5] found that kriging is suitable for the approximation of higher-order and lower-dimensional functions and has high accuracy for nonlinear problems, which makes this type of model attractive to researchers.
A kriging model is called an ordinary kriging model if its mean function has only one constant, and it is called a universal kriging (UK) model if its mean function is partially assumed to have some known variables. Many studies suggest benefits to using a more complex mean function. However, overfitting will occur when the mean function contains many candidate predictors [6,7]. In such cases, variable selection is proposed to avoid overfitting problems for the UK model [8]; the commonly used methods of variable selection are the Bayesian method [9,10] and penalty likelihood method [11,12]. Žilinskas [13,14] have thoroughly examined the axiomatics regarding the application of statistical models to interpret deterministic data. To choose the mean function of a kriging model using the penalty likelihood method, an optimization algorithm may be constructed on the basis of a statistical model. Park [15] proposed an improved penalized blind lasso kriging method that could avoid the need for iterative calculations, but their approach does not account for correlations between sample points. Zhao et al. [16] addressed this limitation with a modified penalized blind kriging (MPBK) method.
A significant challenge arises when the mean of a UK model includes polynomial terms with unknown coefficients, leading to an identifiability problem. If the coefficient estimator of the mean function is poor, then even if the predictions are still good, the interpretability of the mean function is lost. Many researchers have tackled this identifiability problem in numerous studies [17,18,19]. For example, in model calibration, due to the existence of parameter identification problems, we cannot correctly interpret the actual meaning of each variable from the coefficient of the mean function, and sometimes we even misrecognize the part of the mean function, which results in the opposite conclusion. Some scholars have proposed that the identification problem could be overcome by orthogonalizing the mean function and a Gaussian process [20,21,22]. Plumlee and Joseph [23] proposed an orthogonal Kriging model based on previous studies. Recently, Wang et al. [24] proposed a model averaging method for orthogonal kriging models, and the proposed method achieved prediction advantages over others. In brief, the orthogonal kriging model greatly improves the accuracy of parameter estimation and is becoming increasingly meaningful for variable selection problems.
Due to the problem of parameter identification, this study incorporates a variable selection mechanism into the orthogonal Kriging model via penalized likelihood functions. The rest of the paper is structured as follows. The penalized orthogonal Kriging model is proposed in Section 2. Section 3 investigates its performance through simulation studies. A real engineering example is presented in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 concludes the work.
2. Penalized Orthogonal Kriging Model
2.1. Orthogonal Kriging Model
We consider the output response , where x represents a d-dimensional vector-valued input in D. A popular modeling approach is UK, which assumes that is a sum of a trend function and a stochastic process . We express the response as follows:
where is a stochastic process with mean zero and covariance , is a known basis function vector, and is the unknown parameter vector. In many publications on computer experiments, the choice of correlation function is not unique; examples include the exponential correlation function, the correlation function, and the Gaussian correlation function.
A significant challenge arises when the mean function of UK includes polynomial terms with unknown coefficients, leading to identifiability problems. To overcome these problems, Plumlee and Joseph [23] proposed an orthogonal Gaussian model, in which the Gaussian process term is orthogonal to the mean function term. If we let , , and , the orthogonal kriging model is written as
where , is a stochastic process with mean zero and covariance .
In this paper, we only consider the following Gaussian correlation function:
Suppose the set is a subset of , and let be the Gaussian error function. According to [23], the orthogonal version of in (2) can be stated as follows:
where
Given some sampled points , is the corresponding output, . Let , , , , and . For the simplicity, we can use the matrix notation of model (1):
where follows . Then the corresponding log-likelihood function in (1) after removing the constant term is
The parameter estimation can be expressed as
Therefore, the best linear unbiased predictor (BLUP) for at a new point x is
where the vector represents the correlation between the sample point and the predicted point x.
2.2. Penalized Orthogonal Kriging Model
Zhao et al. [16] described a modified penalized blind kriging (MPBK) method for efficiently selecting a global trend model in a universal kriging model. In this subsection, we propose a model in which a variable selection procedure is incorporated in the orthogonal kriging model and the variable selection is achieved using the penalized likelihood. We call it the penalized orthogonal kriging model (POK model for short).
The objective of variable selection is to detect important variables. A penalty function is included in the likelihood that is generally used in variable selection; examples include the lasso [25], the elastic net (EN) penalty [26], the minimax concave penalty (MCP for short) [27], etc. On this basis, we can estimate the coefficients by maximizing the following penalized log-likelihood function:
where is a penalty function. When and are estimated, can be given for the penalty function as follows:
where .
We use the lasso, EN, and MCP as penalty functions in this paper. The EN penalty function is
which is a convex combination of ridge regression and the lasso; and are penalty parameters. When , the EN penalty function is the lasso. The MCP penalty function is
where and are penalty parameters.
A penalty function is included in the likelihood, which faces the challenging work of estimating the parameters in the POK models. Since the penalty term is not a function of and , the maximum likelihood estimate of can be expressed as follows:
Substituting the values of and into , the maximum likelihood estimate of is
The POK predictor, which has the same form as the OUK predictor, is
where .
For the lasso, EN, or MCP as the penalty function, the relevant parameter estimation and algorithm steps can be obtained in a similar way. An iteratively reweighted least angle regression (IRLARS) is performed, as expressed in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: IRLARS algorithm for POK. |
| Step 0: Set up initial values for , , and , and let the counter . While none of the termination conditions is satisfied, do Step 1: Decompose , update , and . The optimal penalty parameters and are obtained by cross-validation. Thus, Step 4: The POK predictor is obtained by substituting the estimated parameters into (4). |
In the IRLARS algorithm, the optimal penalty parameters and are obtained through cross-validation (CV). The sample is randomly divided into K subsets of approximately equal size; among them, (K-1) subsets are used to construct a model, and the left-out subset is used to validate the model. Suppose we are given two parameter sets and of and , respectively. For the given , we randomly split the sample into K subsets of approximately equal size; (K-1) of the subsets are used as training data to obtain the penalty estimator , and the left-out sample is used as testing data to validate the results. The K-fold mean square CV error is as follows:
where is the response in the left-out sample and is the BLUP of by (4). Then, the optimal tuning parameters are as follows:
To balance the prediction accuracy and computational complexity, the 10-fold CV method is used in this paper.
3. Numerical Simulation Study
In this section, the performance of the proposed POK method is compared with that of MPBK methods using two examples from [16].
In simulation studies, performance is evaluated in two aspects: the accuracy of variable selection and the degree of prediction accuracy. The accuracy of variable selection is measured by the active effect identified rate (AEIR), the inactive effect identified rate (IEIR), and the mean size (MS) of variables in the mean function in the repeated simulations. Prediction accuracy is measured by the mean value of the root mean square prediction error (MRMSPE) and the standard deviation of the root mean square prediction error (SDRMSPE), calculated based on the randomly generated testing data.
The simulation studies were carried using the POK and MPBK methods with the lasso, EN, and MCP as penalty functions. MPBK.MCP, MPBK.MCP, and MPBK.EN denote the MPBK method with the lasso, MCP, and EN, respectively, as penalty functions. Furthermore, POK.L, POK.MCP, and POK.EN denote the POK method with the lasso, MCP, and EN, respectively, as penalty functions. In the simulation study, 1000 sample points were randomly selected as testing data, and six methods are evaluated based on 500 simulations.
Example 1
(linear function model from [12]). The known function is defined on a twelve-dimensional (p = 12) input space , where the first six variables , …, have decreasing effects on the on the computer experiment’s output, and the coefficients of the remaining variables , …, are zero. The function is
where , . The experimental designs were generated through Latin hypercube sampling with dimensions, and the responses were generated using (5) independently for training data. Here, we consider sample sizes of , , and , respectively.
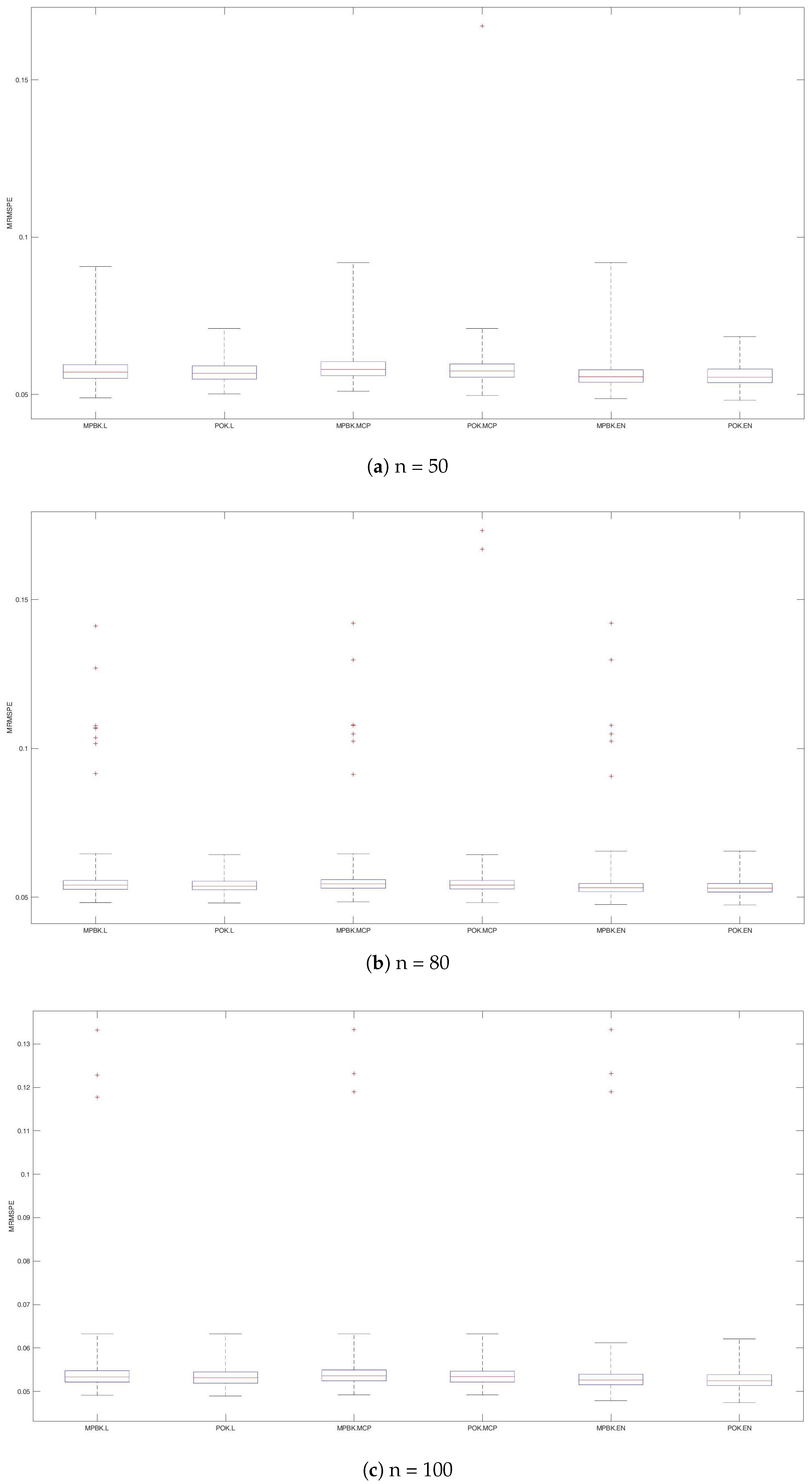
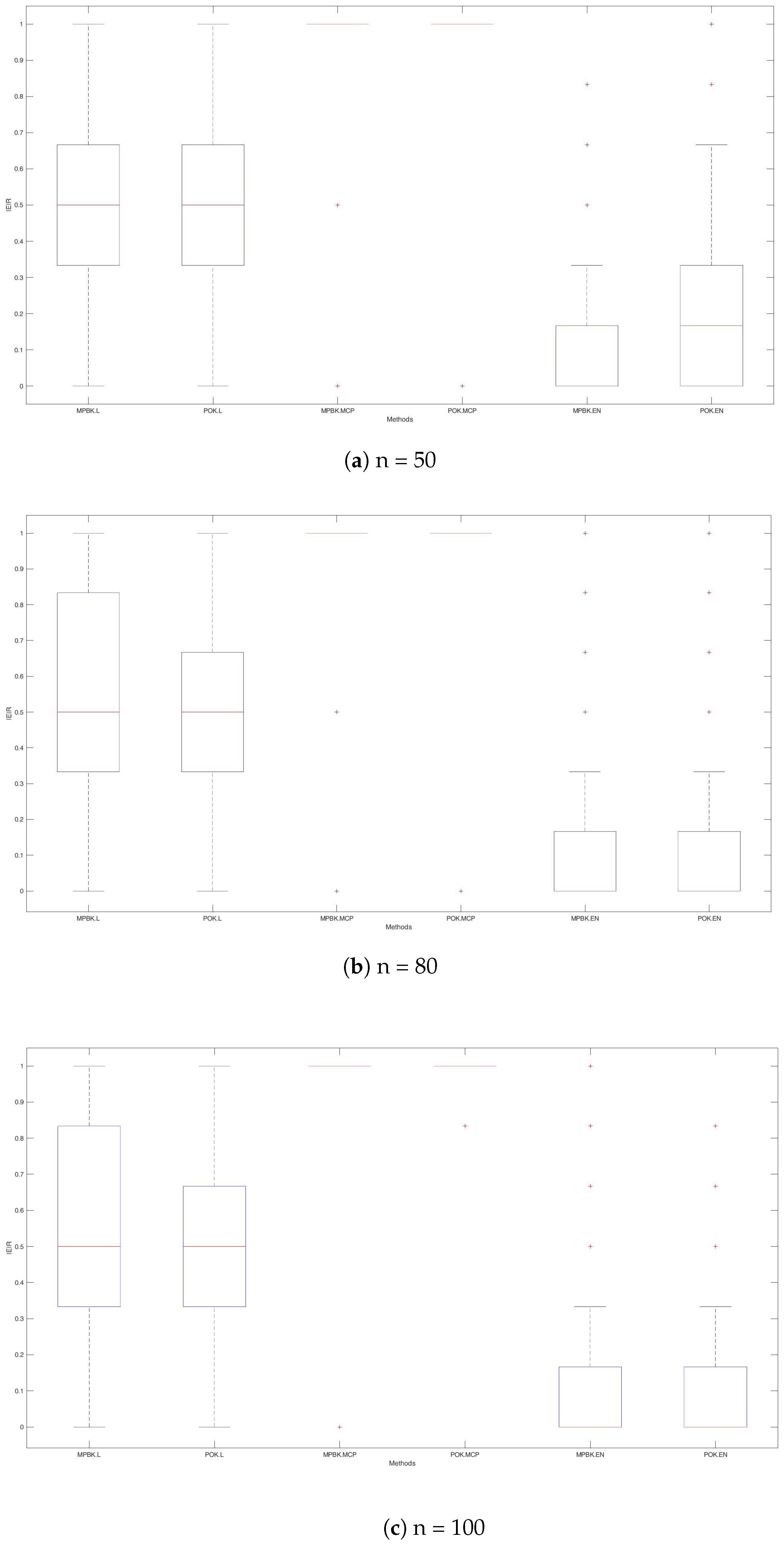
The variable selection performances of the six methods are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3. According to Table 1 and Figure 2, MPBK.L, MPBK.MCP, POK.L, POK.MCP, POK.Lm and POK.EN exhibit more pronounced overfitting tendencies than MPBK.EN and POK.EN, resulting in substantially higher MS and IEIR values. This indicates that MPBK.EN and POK.EN achieve better identification in variable selection.

Table 1.
Data simulation results for Example 1.
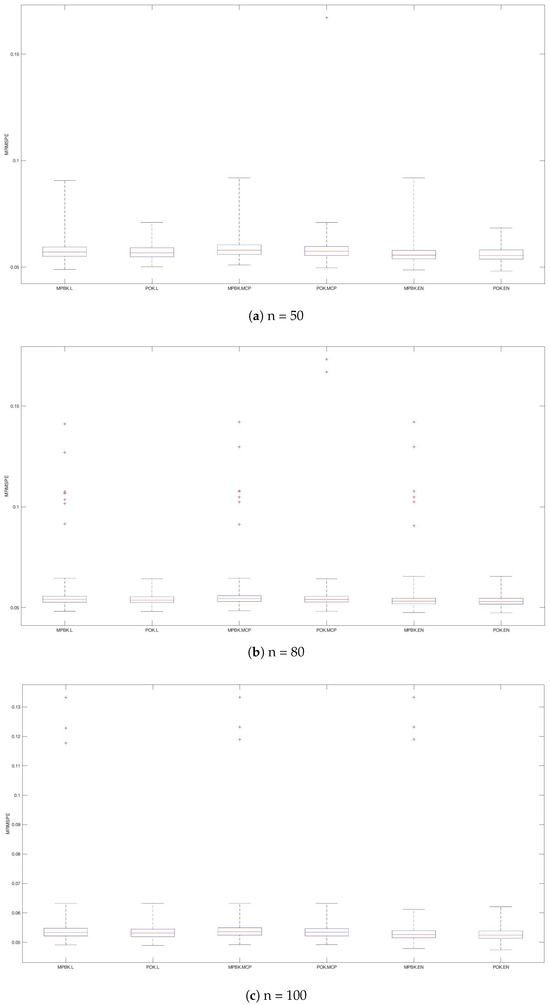
Figure 1.
MRMSPEs for Example 1.
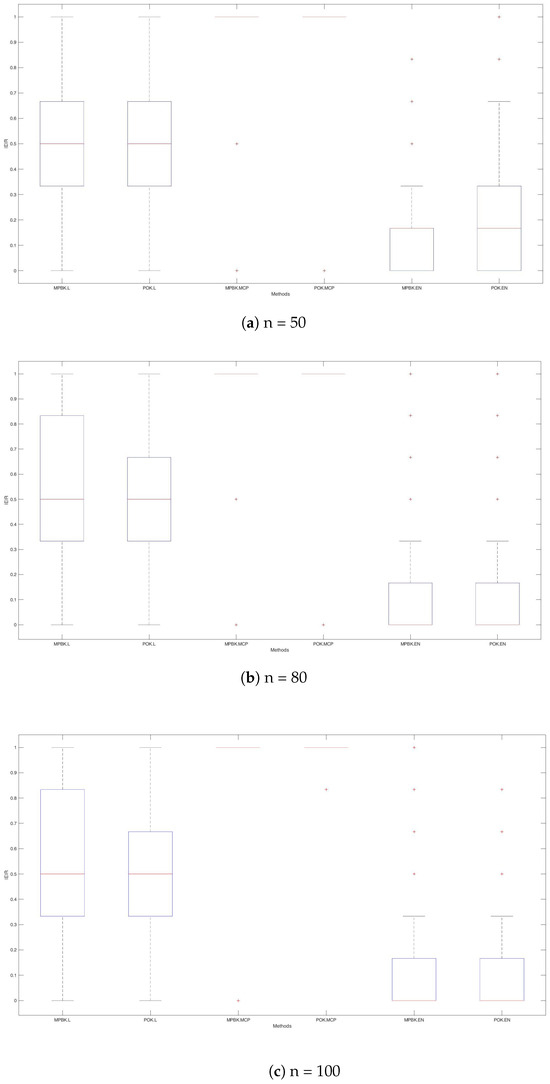
Figure 2.
IEIRs for Example 1.
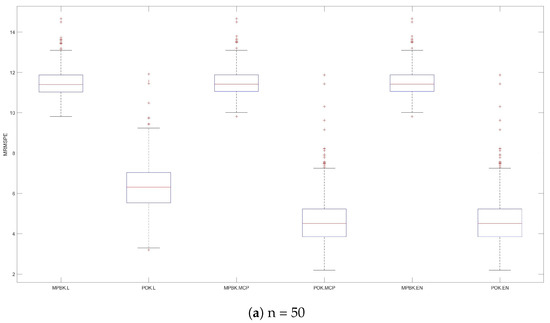
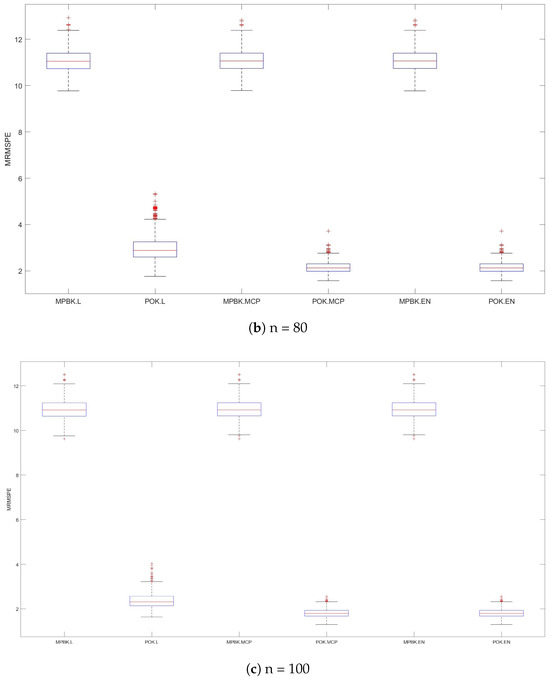
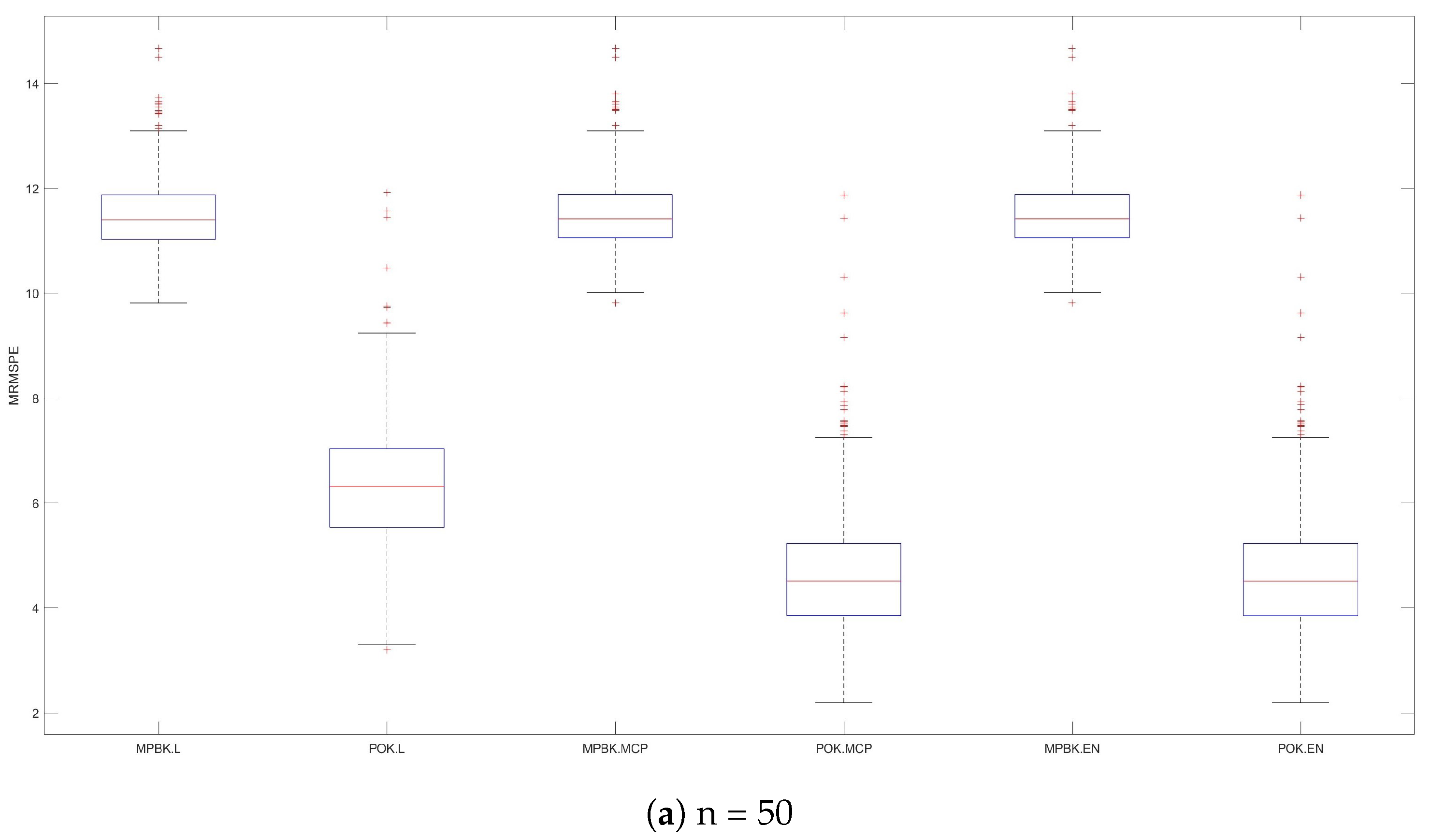
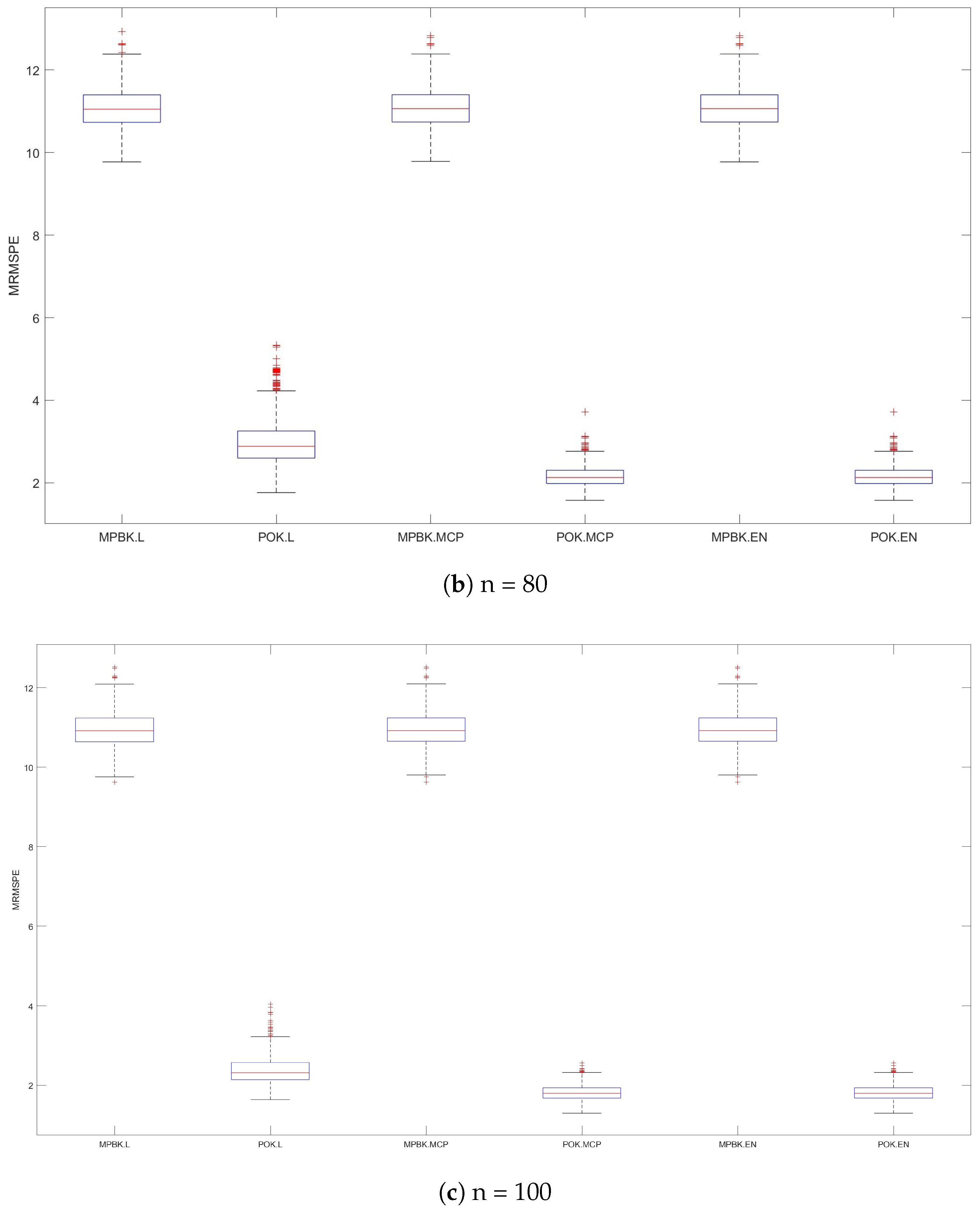
Figure 3.
MRMSPEs for Example 2.
The simulation results in Table 1 and Figure 1 demonstrate that POKs achieve higher AEIRs and lower MRMSEPs and SDRMSPEs than their MPBK counterparts across all three penalty functions, despite showing similar patterns of behavior. Notably, POK.EN has the smallest MRMSEP and SDRMSPE. In summary, POK.EN demonstrates superior overall performance in linear function scenarios, excelling in both variable selection accuracy and prediction quality compared to alternative methods.
Example 2
(borehole function ([28])).
The input space is a rectangular interval [0.05, 0.015] × [100, 5000] × [63,070, 115,600] × [990, 1110] × [63.1, 116] × [700, 820] × [1120, 1680] × [9855, 12,045], and the samples were generated through Latin hypercube sampling with dimensions and sample sizes of , , and . We set the mean value function as a linear function,
The variable selection performances of six methods are shown in Table 2 and Figure 3. Table 2 demonstrates that POK.L exhibits larger MRMSEPs than POK.MCP and POK.EN, while the latter two methods behave similarly, perhaps due to the strong compression effect of the lasso penalty, and all three POK methods demonstrate significantly smaller MRMSEP values than their MPBK counterparts. Figure 3 provides further evidence of this phenomenon, demonstrating POK.MCP and POK.EN’s consistent superiority in prediction accuracy across diverse parameter configurations.

Table 2.
Data simulation results for example 2.
4. Real Data Example
In this section, our proposed method is applied to analyze an engineering problem called piston slap noise. Piston slap is an undesirable engine noise caused by the secondary motion of the piston. Through computer experiments, six factors are varied to reduce piston slap noise. These six factors are cylinder liner (), location of peak pressure (), skirt length (), skirt profile (), skirt oval ovality (), and pin offset (). The relevant dataset for the example comes from [29], which includes 100 observations with six input variables.
The candidate variable set includes all linear main effects, quadratic main effects, and two-factor interaction effects, resulting in a total of 72 basis variables. We perform 5-fold cross-validation, using one of the five subsets as the test set and the rest as the training set. Six methods are compared, and the simulation results are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Data simulation results for piston slap noise.
As displayed in Table 3, POK models outperform MPBK models in both prediction accuracy and model simplicity. Specifically, OPBK.L and OPBK.EN achieve the smallest prediction errors. These results indicate that the POK framework not only enhances predictive capability but also yields more parsimonious models.
5. Conclusions
Variable selection for Kriging models has been widely considered by researchers in computer experiments. Since accurate estimation of mean functions is important in many application, variable selection plays an important role in solving the overfitting problem and improving the prediction accuracy of models. This paper introduces a variable selection method using POK. The simulation results indicate that the POK model shows great advantages in both variable recognition rate and prediction accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.G.; Formal analysis, J.Z.; Writing—original draft, X.Z.; Writing—review & editing, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Aerospace Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hainan Province under Grant ATIC2023010001 and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 11871294.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sacks, J.; Schiller, S.B.; Welch, W.J. Designs for computer experiments. Technometrics 1989, 31, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, J.; Welch, W.J.; Mitchell, T.J.; Wynn, H.P. Design and analysis of computer experiments. Stat. Sci. 1989, 4, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krige, D.G. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 1951, 52, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Laslett, G.M. Kriging and splines: An empirical comparison of their predictive performance in some applications. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, T.W.; Mauery, T.M.; Korte, J.J.; Mistree, F. Kriging models for global approximation in simulation-based multidisciplinary design optimization. AIAA J. 2001, 39, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.D.; Simpson, T.W. Use of kriging models to approximate deterministic computer models. AIAA J. 2005, 43, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Seepersad, C.C.; Joseph, V.R.; Allen, J.K.; Wu, C. Building surrogate models based on detailed and approximate simulations. J. Mech. Des. 2006, 128, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, W.J.; Buck, R.J.; Sacks, J.; Wynn, H.P.; Mitchell, T.J.; Morris, M.D. Screening, predicting, and computer experiments. Technometrics 1992, 34, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkletter, C.; Bingham, D.; Hengartner, N.; Higdon, D.; Ye, K.Q. Variable selection for Gaussian process models in computer experiments. Technometrics 2006, 48, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.R. Limit kriging. Technometrics 2006, 48, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sudjianto, A. Analysis of computer experiments using penalized likelihood in Gaussian Kriging models. Technometrics 2005, 47, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y. Penalized blind kriging in computer experiments. Stat. Sin. 2011, 21, 1171–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilinskas, A. Axiomatic approach to statistical models and their use in multimodal optimization theory. Math. Program. 1982, 22, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilinskas, A. On similarities between two models of global optimization: Statistical models and radial basis functions. J. Glob. Optim. 2010, 48, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I. Lasso Kriging for efficiently selecting a global trend model. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 1527–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, M.; Li, X. Modified Penalized Blind Kriging for efficiently selecting a global trend model. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2023, 93, 3052–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, J.S.; Reich, B.J. Adding spatially-correlated errors can mess up the fixed effect you love. Am. Stat. 2010, 64, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciorek, C.J. The importance of scale for spatial-confounding bias and precision of spatial regression estimators. Stat. Sci. 2010, 25, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, R.; Wu, C.J. Efficient calibration for imperfect computer models. Ann. Stat. 2015, 43, 2331–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, B.J.; Hodges, J.S.; Zadnik, V. Effects of residual smoothing on the posterior of the fixed effects in disease-mapping models. Biometrics 2006, 62, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Haran, M. Dimension reduction and alleviation of confounding for spatial generalized linear mixed models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2013, 75, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, E.M.; Schliep, E.M.; Hooten, M.B.; Hoeting, J.A. Restricted spatial regression in practice: Geostatistical models, confounding, and robustness under model misspecification. Environmetrics 2015, 26, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumlee, M.; Joseph, V.R. Orthogonal gaussian process models. Stat. Sin. 2018, 28, 601–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, J.; Liang, H.; Li, X. Optimal model average prediction in orthogonal kriging models. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2024, 37, 1080–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H. Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 894–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.D.; Ylvisaker, M.D. Bayesian design and analysis of computer experiments: Use of derivatives in surface prediction. Technometrics 1993, 35, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.T.; Li, R.; Sudjianto, A. Design and Modeling for Computer Experiments; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).