Threshold of Slope Instability Induced by Rainfall and Lateral Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Basis
2.1. Infiltration Equation
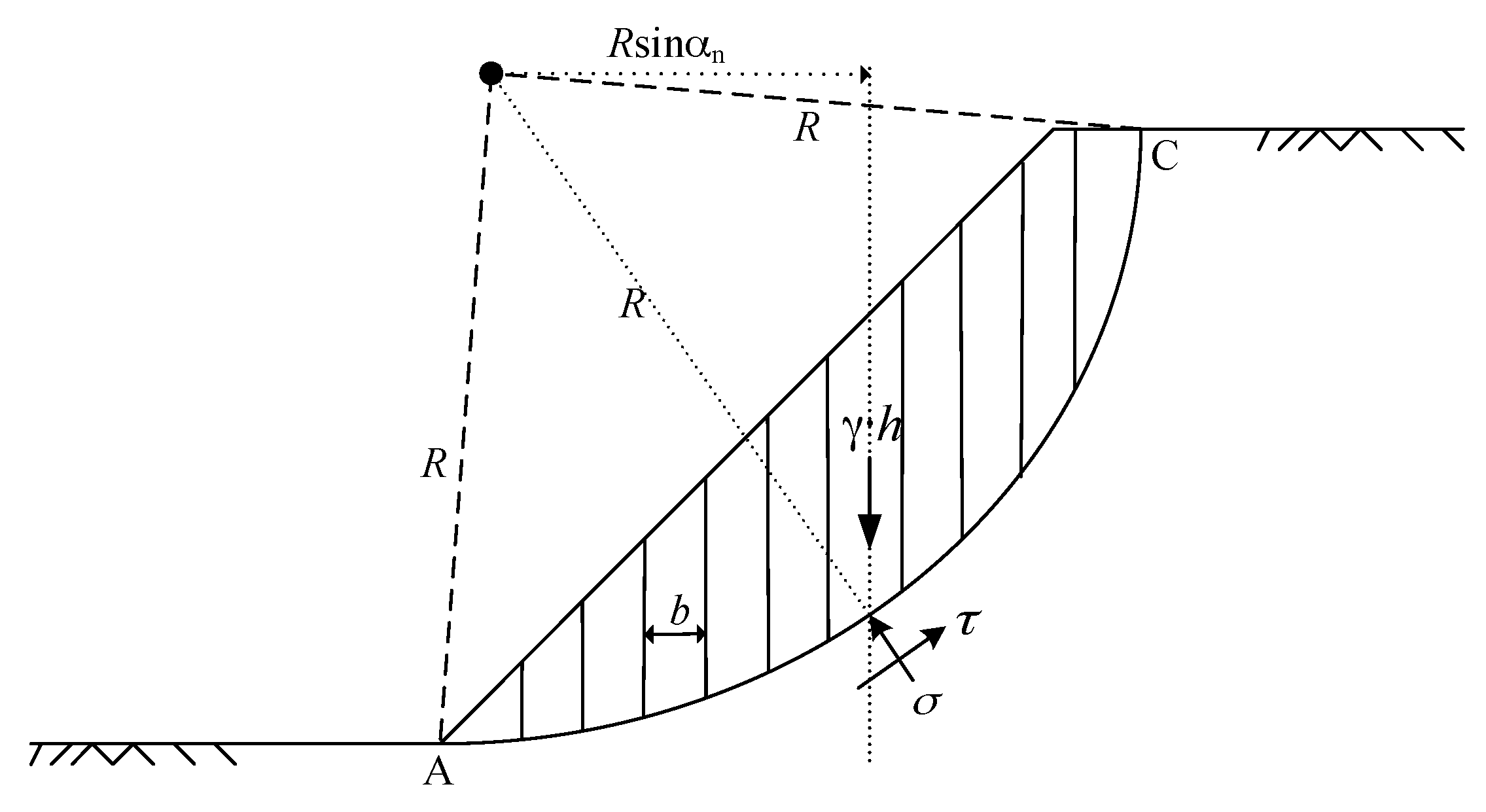
2.2. Slope Stability Analysis
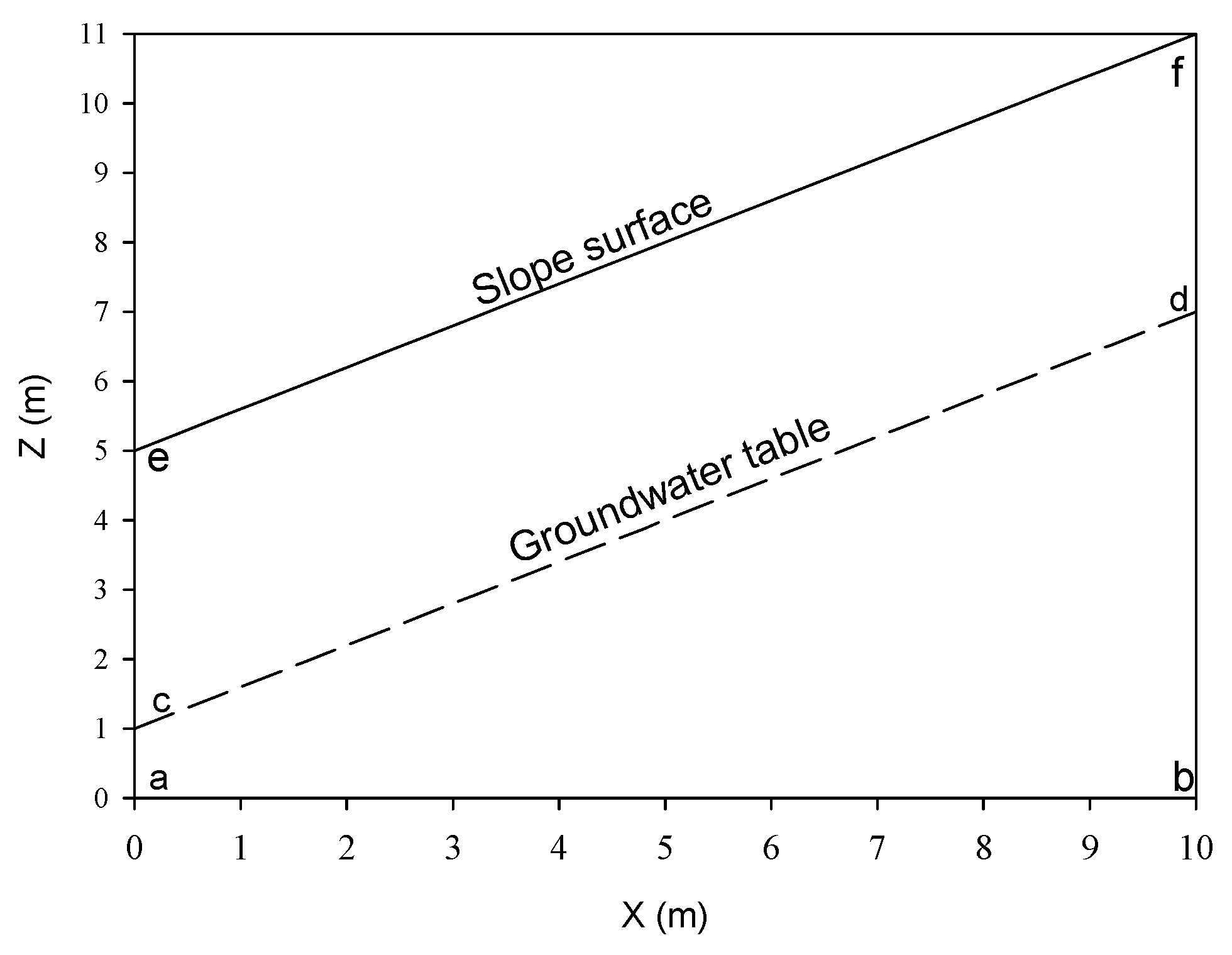
3. Computational Procedure
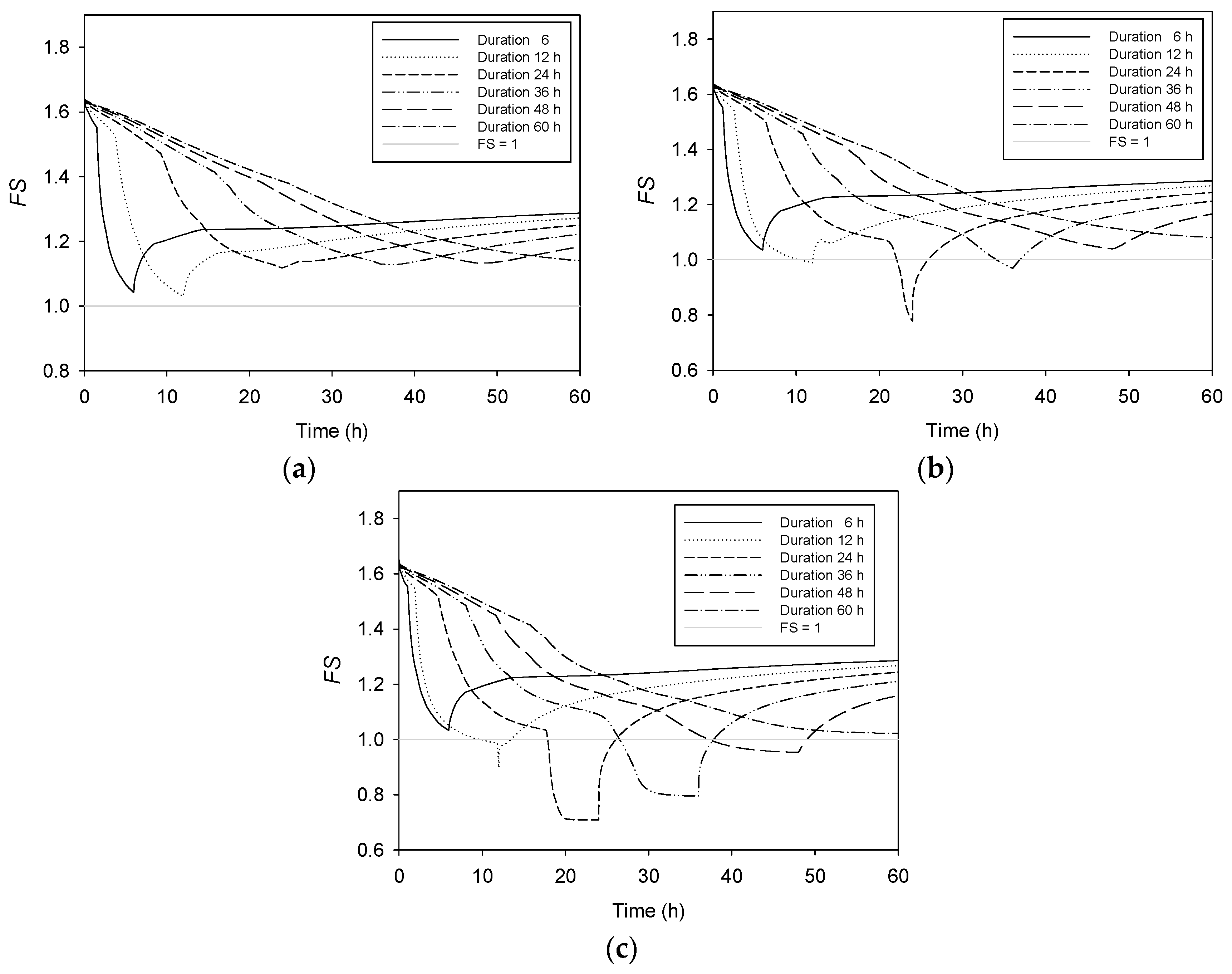
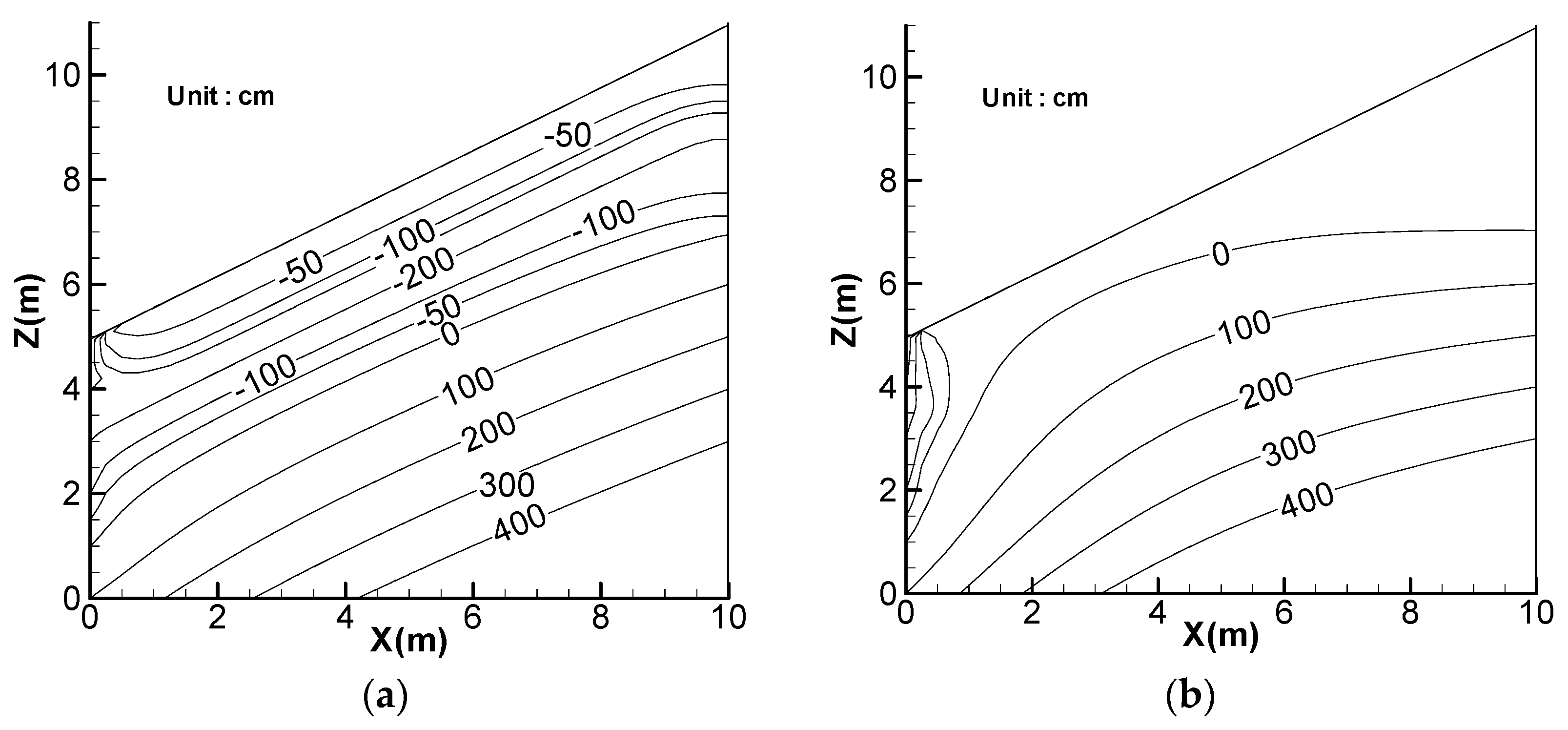
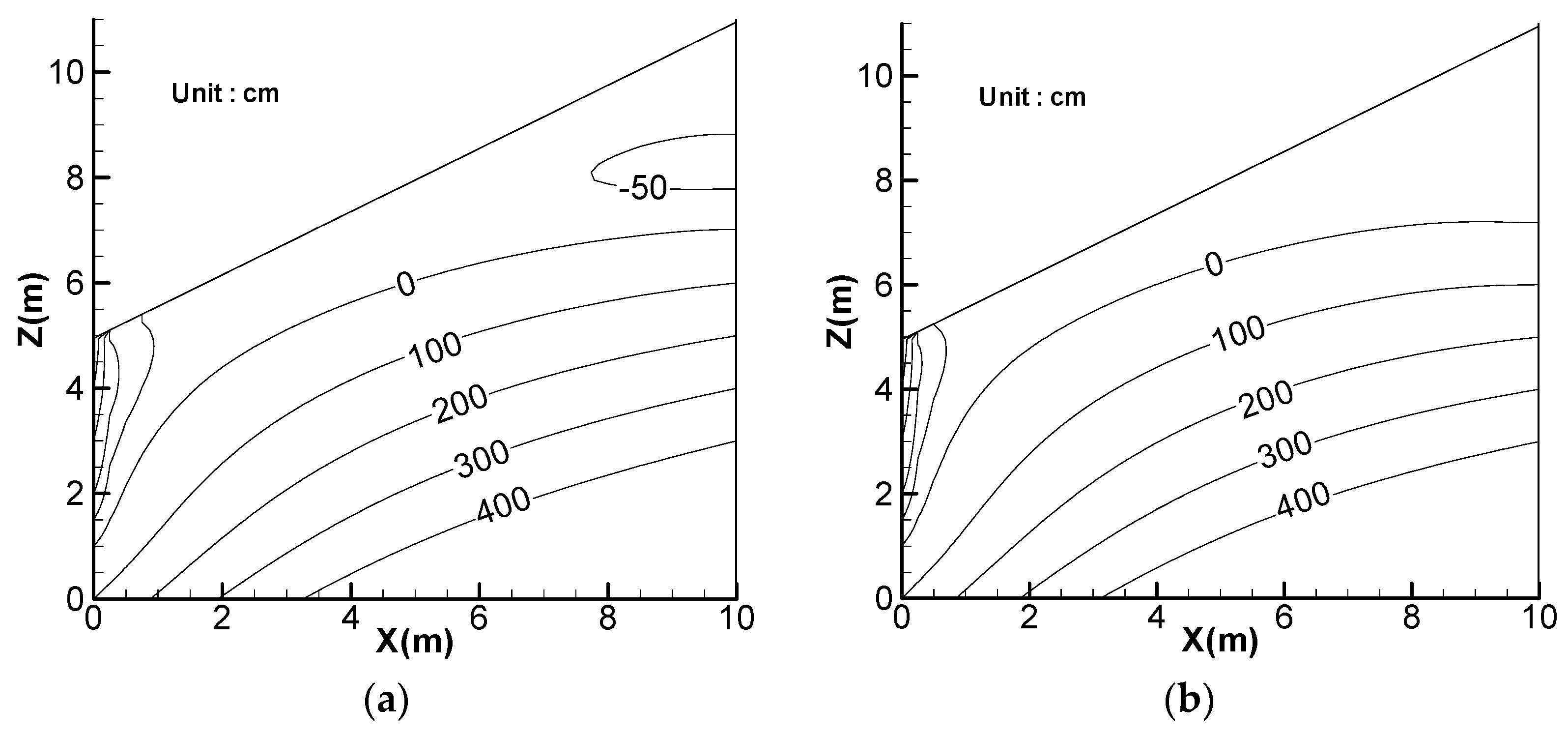
4. Effect of Rainfall Amount
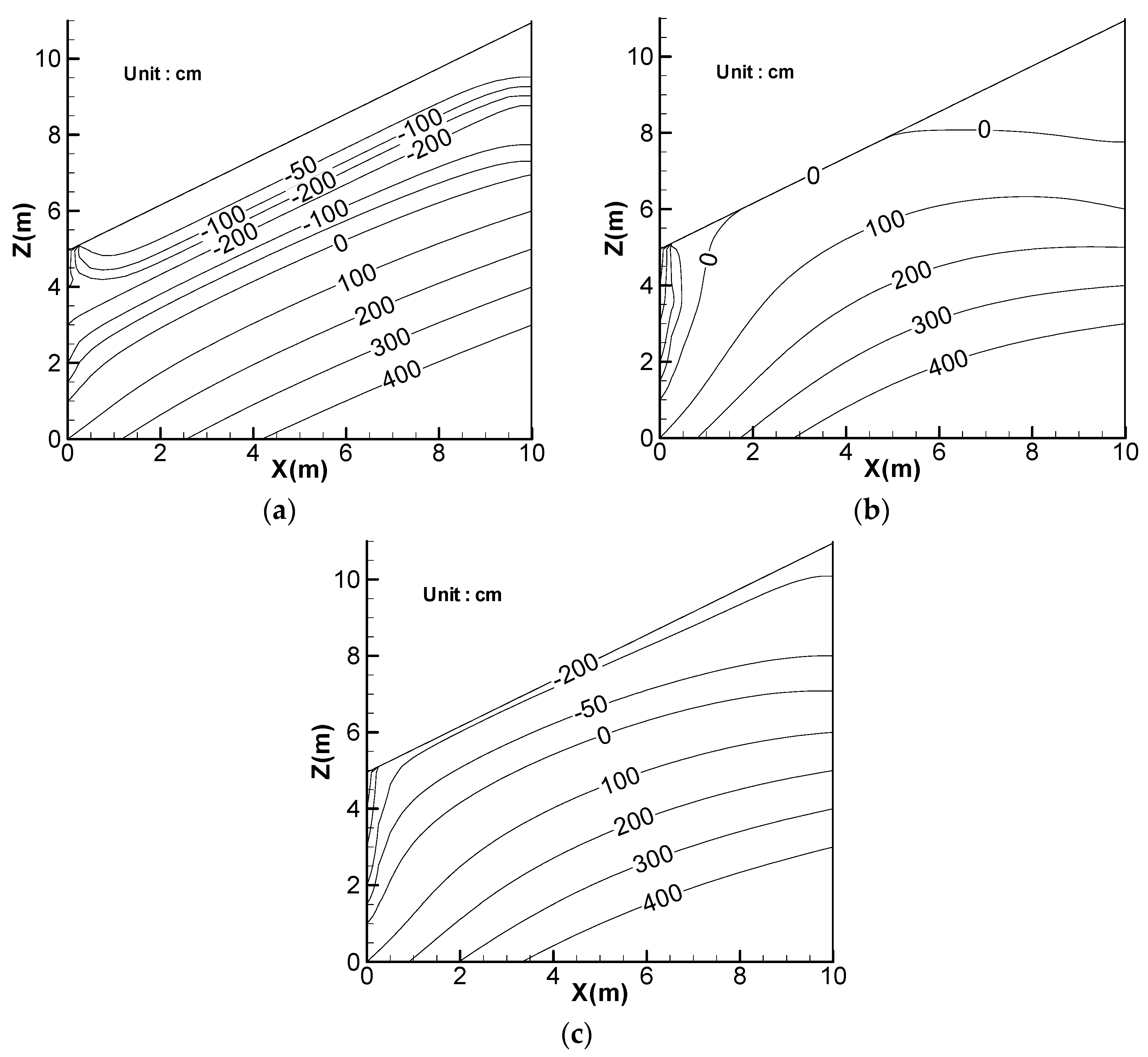
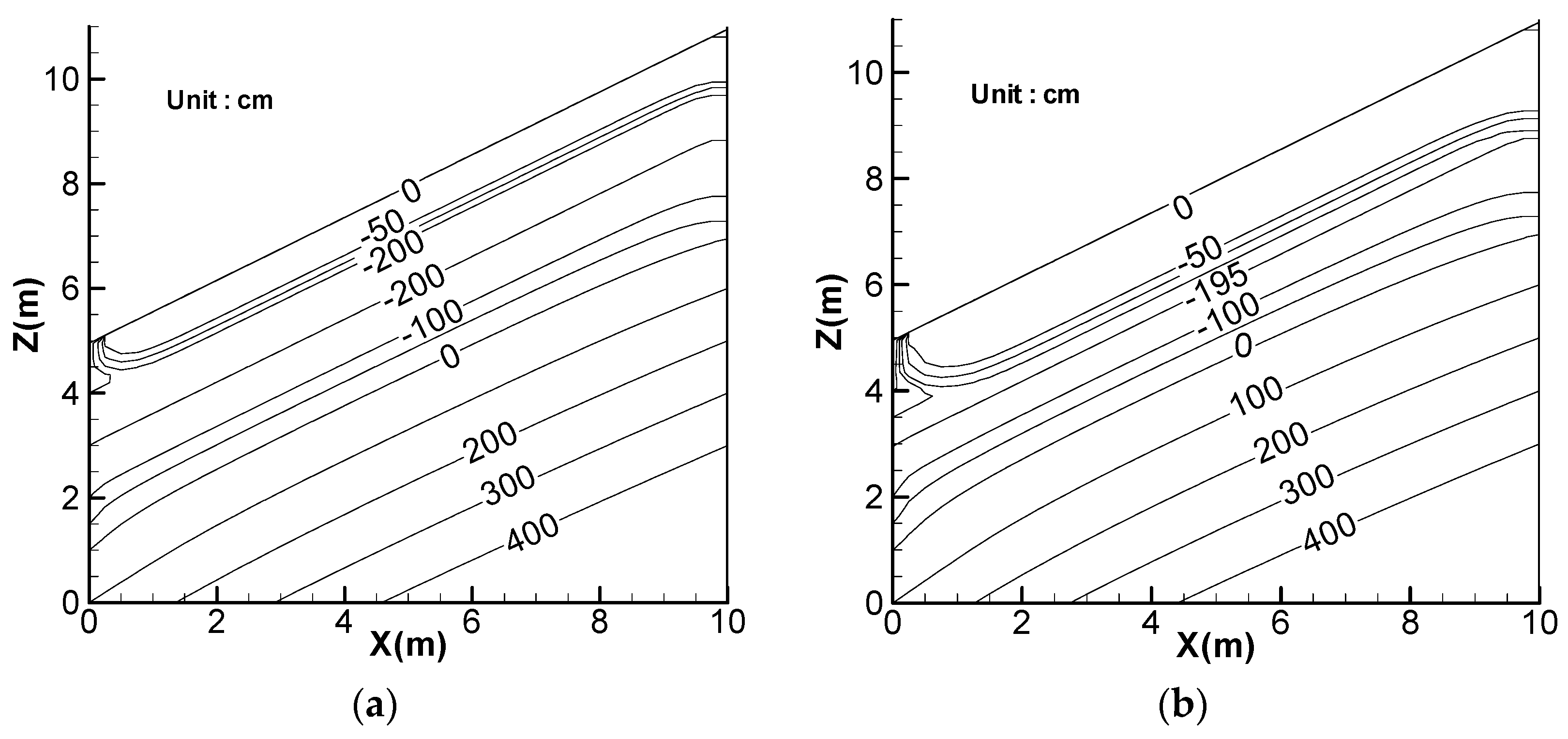
5. Effect of Lateral Flow
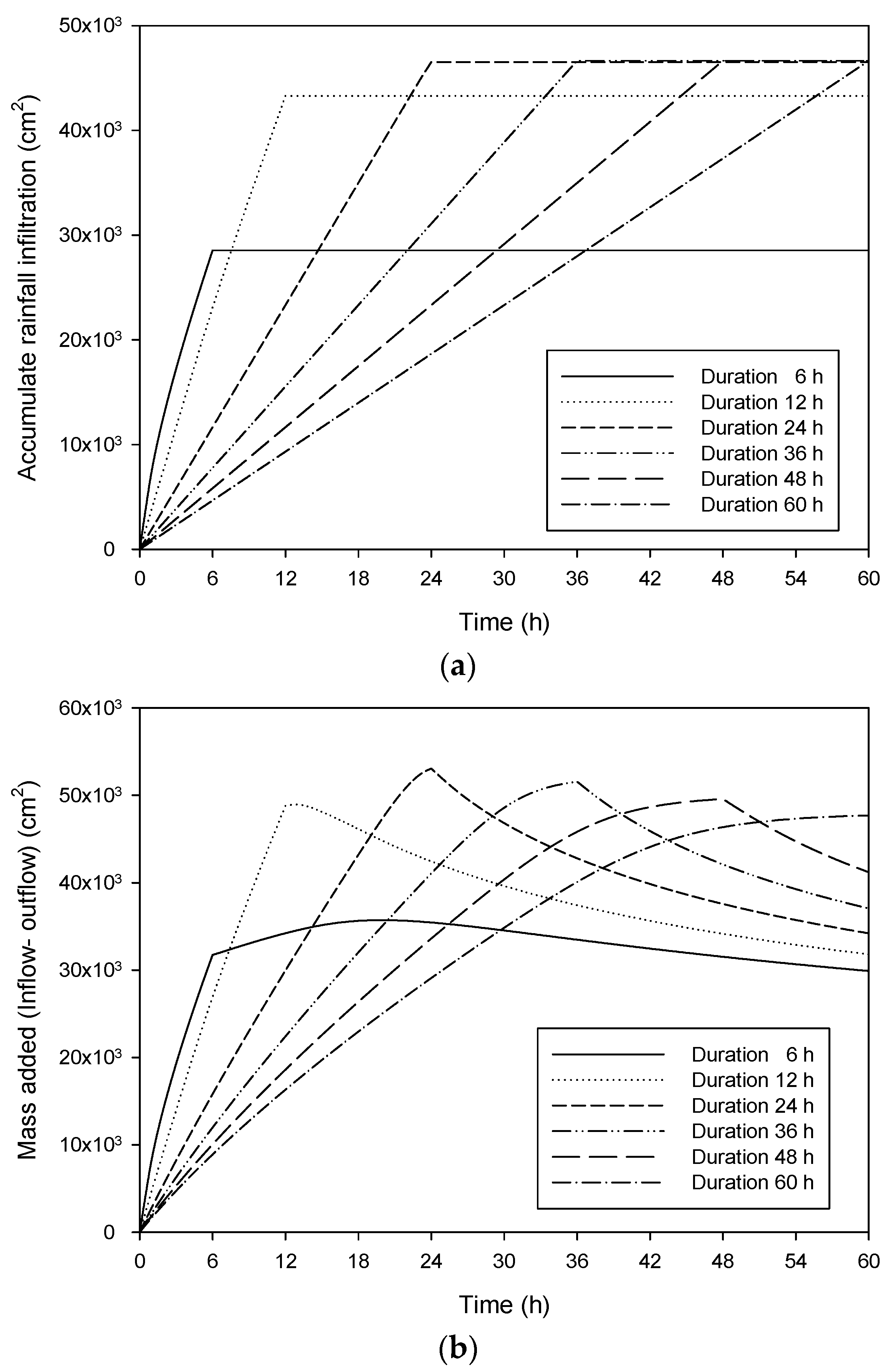
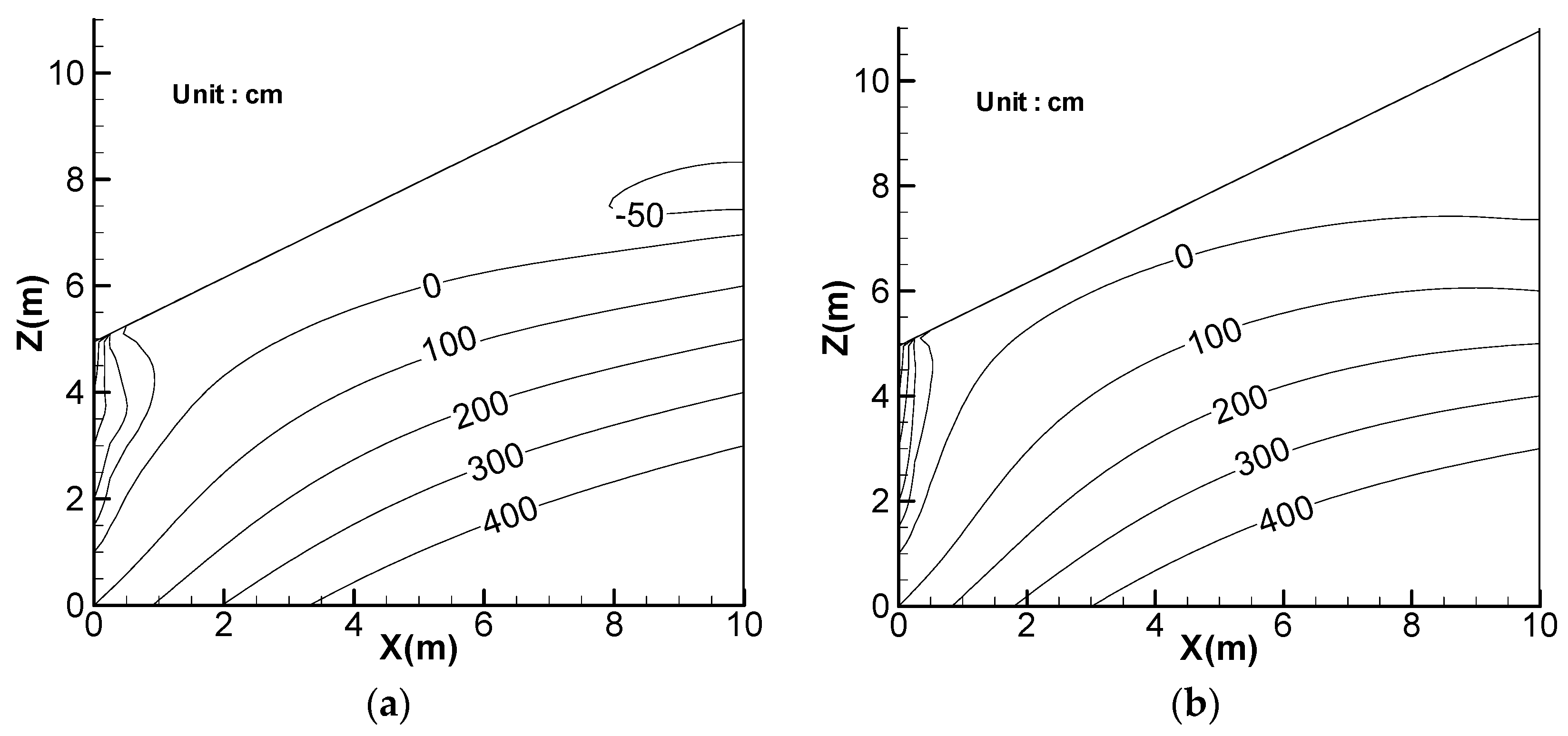
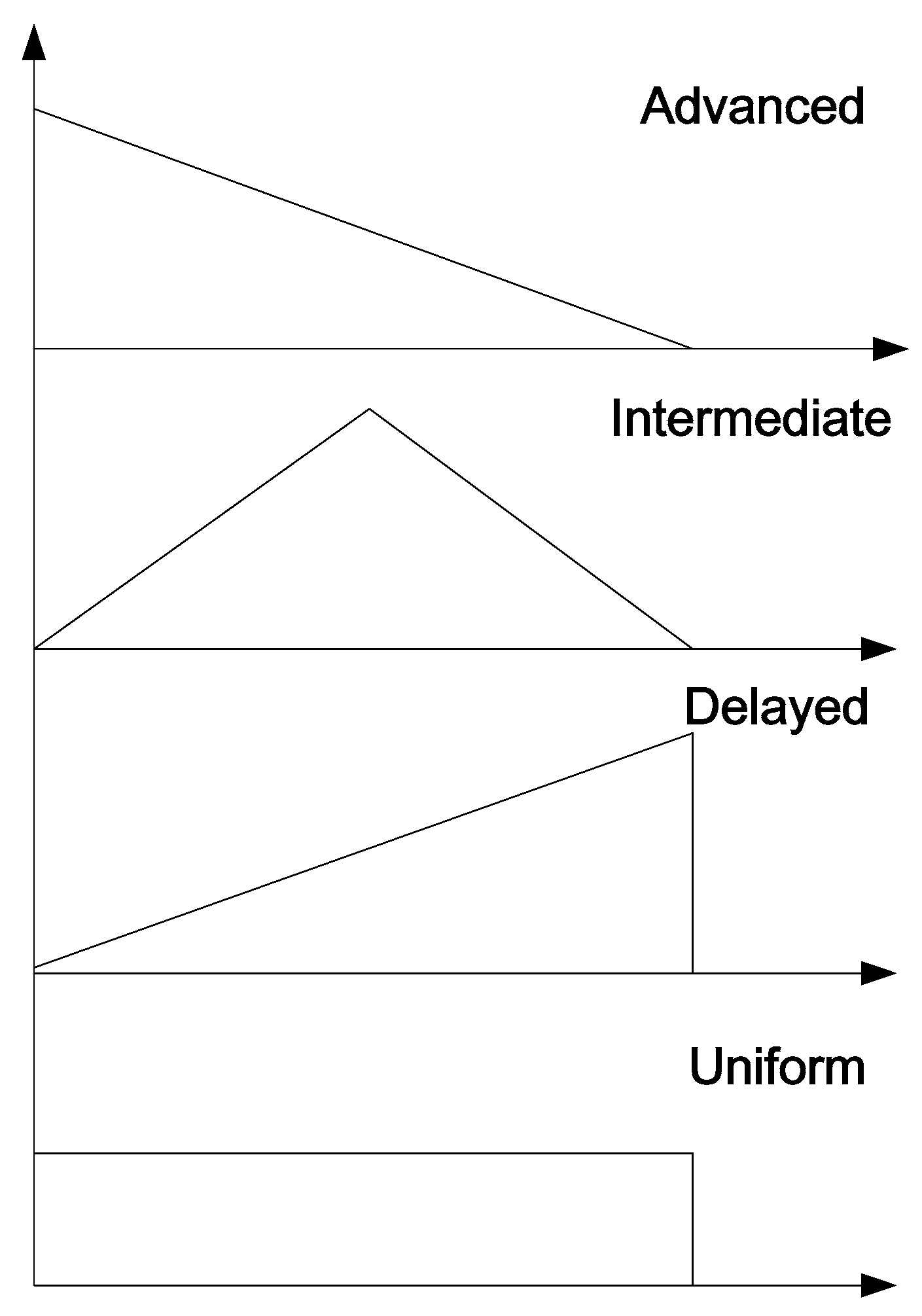
6. Effect of Rainfall Pattern
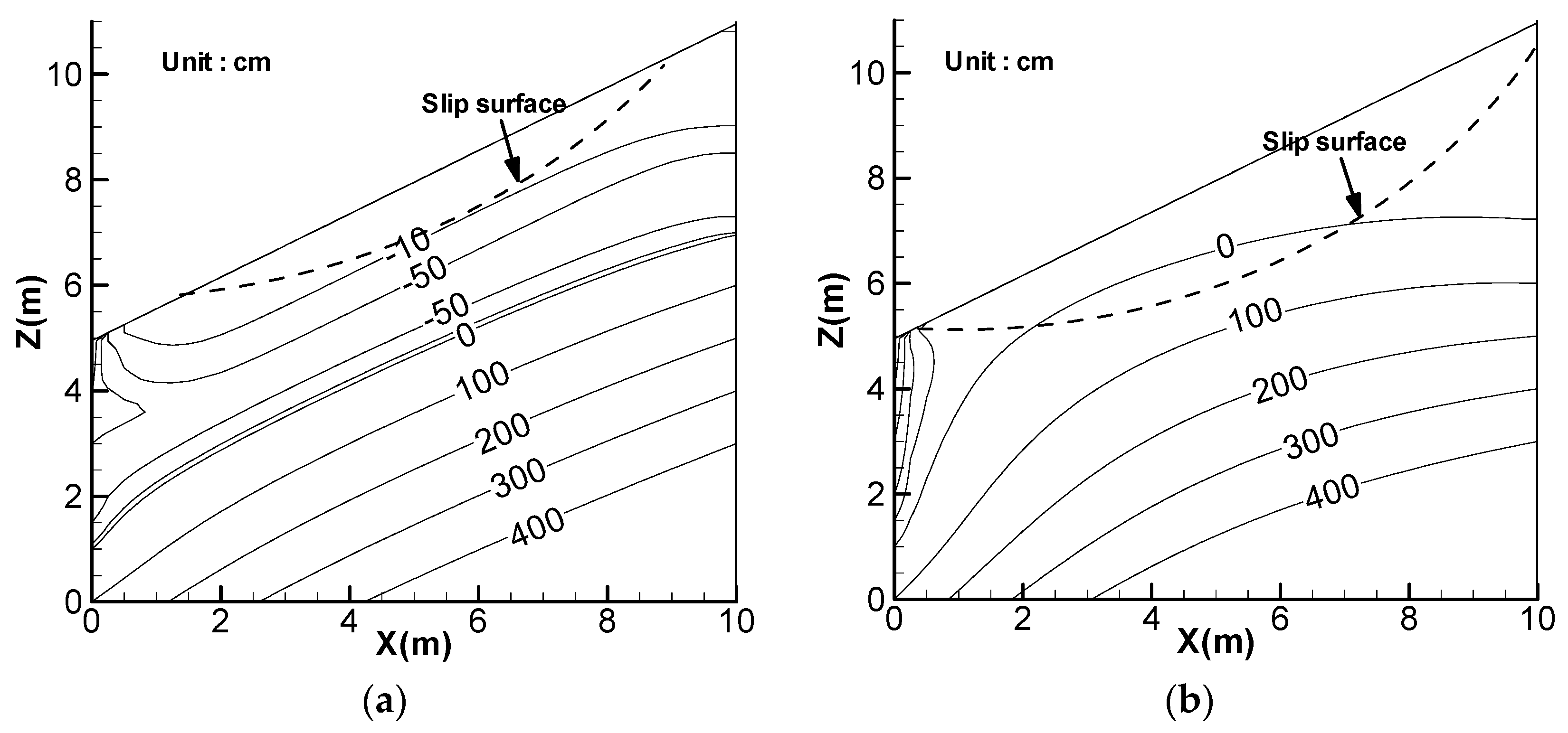
7. Discussion of Landslide Threshold
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, R. Debris flows originating from soil slips during rainstorms in Southern California. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1974, 7, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, E.W.; Premchitt, J.; Phillipson, H.B. Relationship between rainfall and landslides in Hong Kong. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Landslides, Toronto, ON, Canada, 16–21 September 1984; Canadian Geotechnical Society: Richmond, BC, Canada, 1984; pp. 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- Caine, N. The rainfall intensity: Duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows. Geogr. Ann. A 1980, 62, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.H. Rainfall conditions for abundant debris avalanches, San Francisco Bay region, California. Calif. Geol. 1985, 38, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Jibson, R.W. Debris flows in Southern Puerto Rico. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 1989, 236, 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek, G.F.; Morgan, B.A.; Campbell, R.H. Debris-flow hazards in the blue ridge of central Virginia. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2000, 6, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govi, M.; Mortara, G.; Sorzana, P.F. Eventi idrologici e frane. Geol. Appl. Idrogeol. 1985, 2, 395–401. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Glade, T. Modelling landslide-triggering rainfalls in different regions of New Zealand-The soil water status mode. Z. Geomorphol. Suppl. 2000, 122, 63–84. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, F.; Ugai, K. Numerical analysis of rainfall effects on slope stability. Int. J. Geomech. 2004, 4, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, E.J.; Burbank, D.W.; Putkonen, J.K.; Pratt-Sitaula, B.A.; Ojha, T. Rainfall thresholds for landsliding in the Himalayas of Nepal. Geomorphology 2004, 63, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-L. The influence of rainstorm pattern on shallow landslide. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-L.; Wang, J.-K. Examination of influences of rainfall patterns on shallow landslides due to dissipation of matric suction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, A.; Bosco, G. Role of soil suction in understanding the triggering mechanisms of flow slides associated with rainfall. In Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, And Assessment, Proceedings of Second International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation, Taipei, Taiwan, 16–18 August 2000; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, B.D.; Znidarcic, D. Stability analyses of rainfall induced landslides. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-L.; Chen, H.-E.; Yang, J.-C. Numerical modeling of rainstorm-induced shallow landslides in saturated and unsaturated soils. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Widger, R.A. The shear strength of unsaturated soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1978, 15, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M. Landslide triggering by rain infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.L.; Savage, W.Z.; Godt, J.W. Trigrs—A Fortran Program for Transient Rainfall Infiltration and Grid-Based Regional Slope-Stability Analysis; version 2.0; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008.
- Tsai, T.-L.; Yang, J.-C. Modeling of rainfall-triggered shallow landslide. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asch, T.W.J.; Hendriks, M.R.; Hessel, R.; Rappange, F.E. Hydrological triggering conditions of landslides in varved clays in the French Alps. Eng. Geol. 1996, 42, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.; Frattini, P. Distributed modelling of shallow landslides triggered by intense rainfall. Nat. Hazard. Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, R.F.; Skaugset, A.E. Modelling effects of forest canopies on slope stability. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B.; Fusi, N.; Dal Negro, P. Shallow landslides in pyroclastic soils: A distributed modelling approach for hazard assessment. Eng. Geol. 2004, 73, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Lee, C.; Zhou, C.; Martin, C. Dynamic characteristics analysis of shallow landslides in response to rainfall event using GIS. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Fagherazzi, S.; Rigon, R. Potential for landsliding: Dependence on hyetograph characteristics. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Troncone, A. A method for the analysis of soil slips triggered by rainfall. Géotechnique 2012, 62, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, M.; D’Alpaos, A.; Agostini, A.D.; Stevan, G.; Tessari, G.; Genevois, R. A process-based model for the definition of hydrological alert systems in landslide risk mitigation. Nat. Hazard. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 3343–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Donato, A.; Troncone, A. A simplified method for predicting rainfall-induced mobility of active landslides. Landslides 2017, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zheng, H. Phreatic line calculation and stability analysis of slopes under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuations and rainfall. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 54, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Rahardjo, H.; Leong, E.-C. Effect of antecedent rainfall patterns on rainfall-induced slope failure. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 137, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.W. The use of pore-pressure coefficients in practice. Geotechnique 1954, 4, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, M.A.; Bouloutas, E.T.; Zarba, R.L. A general mass-conservative numerical solution for the unsaturated flow equation. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.-E.; Tsai, T.-L.; Yang, J.-C. Threshold of Slope Instability Induced by Rainfall and Lateral Flow. Water 2017, 9, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090722
Chen H-E, Tsai T-L, Yang J-C. Threshold of Slope Instability Induced by Rainfall and Lateral Flow. Water. 2017; 9(9):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090722
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hung-En, Tung-Lin Tsai, and Jinn-Chuang Yang. 2017. "Threshold of Slope Instability Induced by Rainfall and Lateral Flow" Water 9, no. 9: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090722
APA StyleChen, H.-E., Tsai, T.-L., & Yang, J.-C. (2017). Threshold of Slope Instability Induced by Rainfall and Lateral Flow. Water, 9(9), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090722




