Assessing Risks at a Former Chemical Facility, Nanjing City, China: An Early Test of the New Remediation Guidelines for Waste Sites in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Site Setting, Operational History, and Initial Investigations
2.3. Collection of Soil and Groundwater Samples
2.4. Analytical Methodology
2.5. Data Screening and Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soils
3.2. Groundwater
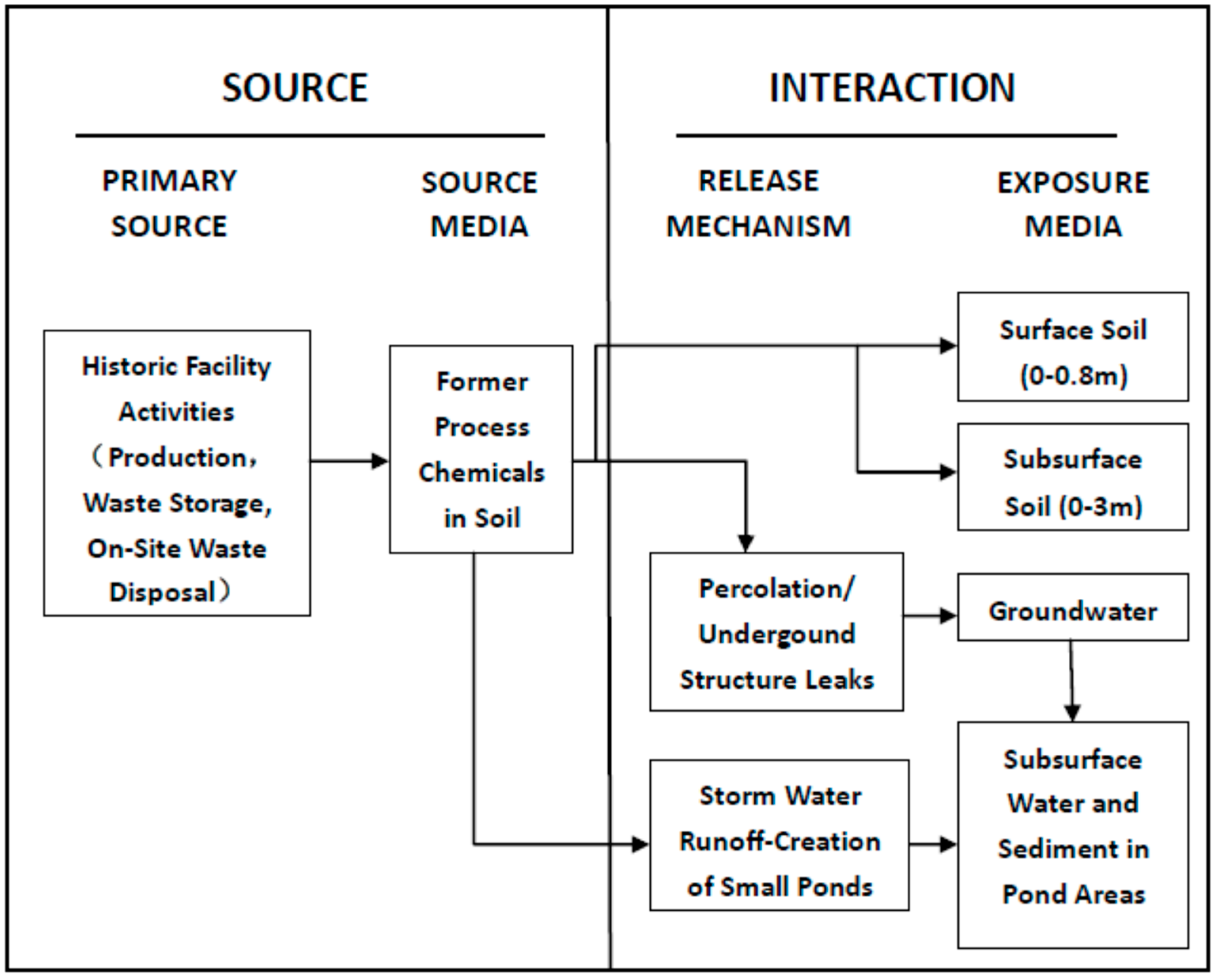
3.3. Conceptual Model
3.4. Risk Assessment
3.4.1. Exposure Assessment
3.4.2. Toxicity Assessment
3.4.3. Risk Characterization
3.4.4. Calculating Risk Control Values
4. Summary and Conclusions
4.1. Future Land Use and Exposure Scenarios
4.2. Co-Located Contaminated Sites
4.3. Receptors
4.4. Country-Specific Exposure and Screening Values
4.5. Risk-Control Values
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, G.; Zhang, L.; Mol, A.P.; Wang, T.; Lu, Y. Why small and medium chemical companies continue to pose severe environmental risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Pizzol, L.; Critto, A.; Zhang, H.; Lv, S.; Marcomini, A. Regional risk assessment approaches to land planning for industrial polluted areas in China: The Hulubeier region case study. Environ. Int. 2014, 65, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP). Technical Guidelines for Environmental Site Investigation (HJ25.1-2014). 2014. Available online: http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/trhj/trjcgfffbz/201402/t20140226_268358.htm (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP). Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Contaminated Sites (HJ25.2-2014). 2014. Available online: http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/trhj/trjcgfffbz/201402/t20140226_268358.htm (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP). Technical Guidelines for Site Soil Remediation (HJ25.4-2014). 2014. Available online: http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/trhj/trjcgfffbz/201402/t20140226_268360.htm (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- Ciba Specialty Chemicals (CSC). Optical Brighteners: Fluorescent Whitening Agents for Plastics, Paints, Imaging and Fibers. Available online: www.cibasc.com (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). National Field Manual for the Collection of Water-Quality Data. 2015. Available online: http://water.usgs.gov/owq/FieldManual/ (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- Beijing Municipal Administration of Quality and Technology Supervision (BMAQTS). Screening Levels for Soil Environmental Risk Assessment of Sites (DB11/T 811-2011), Beijing, 2011. Available online: http://www.doc88.com/p-1738086361850.html (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- Dutch Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment (VROM). Dutch Standards (Version 2009). 2009. Available online: http://www.esdat.net/Environmental%20Standards/Dutch/annexS_I2000Dutch%20Environmental%20Standards.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). USEPA Region 9 Preliminary Remediation Goals (USEPA PRGs, Version Nov. 2012). 2012. Available online: http://www.esdat.net/Environmental_Standards.aspx (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- The Administration of Technical Supervision (ATS). Chinese Quality Standard for Groundwater (GB/T 14848-9). Chinese Standard Press: Beijing, 1993. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/3/6710.html (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- Somaratne, N.; Zulfic, H.; Ashman, G; Vial, H.; Swaffer, B.; Frizenschaf, J. Groundwater risk assessment model (GRAM): Groundwater risk assessment models for wellfield protection. Water 2013, 5, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, G.W. Developing conceptual models for complex ecological risk assessments. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 1999, 5, 375–396. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Ding, Z. Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic, mercury and other metals in urban street dusts from a mega-city, Nanjing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshyash, B.E.; Delkash, M.; Scholz, M. Response of vegetables to cadmium-enriched soil. Water 2014, 6, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congress of the United States. The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA); Public Law 96-510, United States Code 42, 9601 et seq.; Congress of the United States: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Forslund, J.; Samakovlis, E.; Johansson, M.V.; Barregard, L. Does remediation save lives? On the cost of cleaning up arsenic-contaminated sites in Sweden. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sampling Points and Depth (m) | Benzene | Toluene | Xylenes | Ethyl Benzene | Chloro Benzene | 1,4-Dichloro Benzene | 1,2,4-Trichloro Benzene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 71-43-2 | 108-88-3 | 1330-20-7 | 100-41-4 | 108-90-7 | 106-46-7 | 120-82-1 |
| S4, 0.7 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 10.4 | 1.64 | 2.03 | 0.025 |
| DW5, 8.5 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1.46 |
| DW5, 10.9 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.16 |
| SW8, 1.5 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.1 | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| SLSRAS | 1.4 | 3300 | 100 | 860 | 64 | - | - |
| DIV-S | 1.2 | 320 | 17 | 110 | 15 | 19 | 11 |
| DTV-S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PRGs | 5.1 | 4700 | 280 | 25 | 130 | 11 | 26 |
| Sampling Points and Depth (m) | Benzene | Toluene | Xylenes | Ethyl Benzene | Chloro Benzene | 1,4-Dichloro Benzene | 1,2,4-Trichloro Benzene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 71-43-2 | 108-88-3 | 1330-20-7 | 100-41-4 | 108-90-7 | 106-46-7 | 120-82-1 |
| W2, 3 | 0.6 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 39.3 | 753 |
| W3, 3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 35.9 |
| S2, 3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 5.5 |
| S3, 3 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.25 | 6 | 1 | 14.4 | 425 |
| S4, 3 | 22.1 | 89.1 | 0.25 | 1200 | 638 | 1625 | 7300 |
| S1, 3 | 123 | 3.5 | 0.25 | 505 | 2400 | 4117 | 4800 |
| W4, 3.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 6.1 | 16.1 | 5.9 |
| SW5, 3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1.8 |
| DW5, 10 | 1.2 | 61 | 128 | 166 | 42 | 41.9 | 1353 |
| W7, 9 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| W8, 4 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 19 | 9.9 | 57.4 |
| CQSG | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| DIV-G | 30 | 1000 | 70 | 150 | 180 | 50 | 10 |
| DTV-G | 0.2 | 7 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.03 |
| PRGs | 0.45 | 110 | 19 | 1.5 | 7.8 | 0.48 | 0.4 |
| Environmental Media | Protect Target | Sources | Receptor | No. | Exposure Routes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Human Health | Surficial soil | Adults | 1 | Oral Ingestion |
| 2 | Dermal Contact | ||||
| 3 | Particle Inhalation | ||||
| 4 | Inhalation of Contaminants in Vapor in Outdoor Air | ||||
| Subsurface soil | Adults | 5 | Inhalation of Contaminants in Vapor in Outdoor Air | ||
| 6 | Inhalation of Contaminants in Vapor in Indoor Air | ||||
| Groundwater | Human Health | Ground-water | Adults | 7 | Consumption |
| 8 | Inhalation of Contaminants in Vapor in Outdoor Air | ||||
| 9 | Inhalation of Contaminants in Vapor in Indoor Air |
| Parameter Symbol | Benzene | Toluene | Xylenes | Ethyl Benzene | Chloro Benzene | 1,4-Dichloro Benzene | 1,2,4-Trichloro Benzene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Csur | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 10.4 | 1.64 | 2.03 | 1.46 |
| Csub | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cgw | 0.123 | 0.0891 | 0.128 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 4.12 | 7.3 |
| Parameter Symbol | Benzene | Toluene | Xylenes | Ethyl Benzene | Chloro Benzene | 1,4-Dichloro Benzene | 1,2,4-Trichloro Benzene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
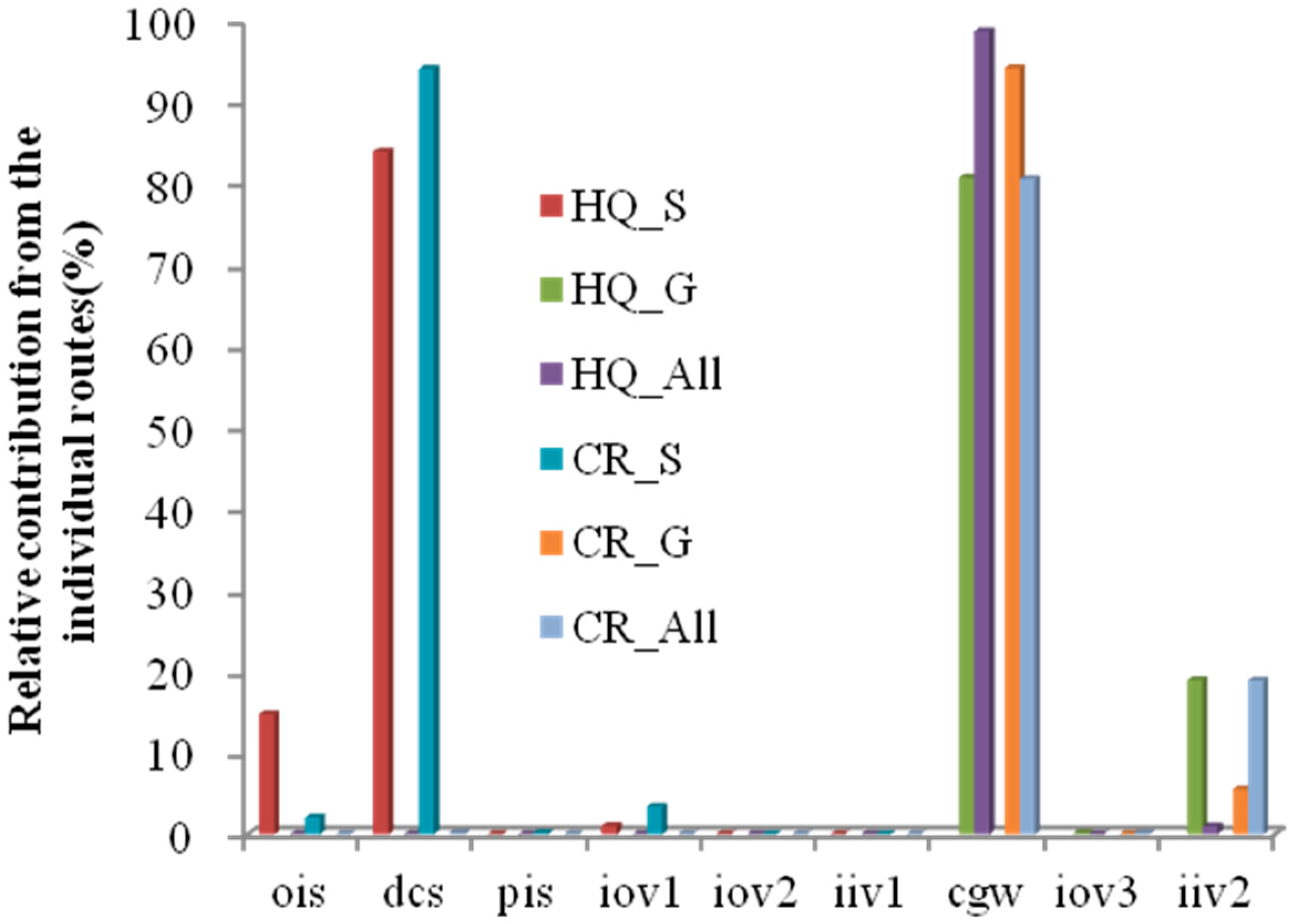
| HQois | 7.45 × 10−8 | 6.05 × 10−6 | 6.05 × 10−6 | 6.29 × 10−4 | 4.96 × 10−4 | 1.75 × 10−4 | 3.53 × 10−4 |
| HQdcs | 2.15 × 10−4 | 1.08 × 10−5 | 4.30 × 10−7 | 3.58 × 10−3 | 2.82 × 10−3 | 9.98 × 10−4 | 5.02 × 10−3 |
| HQpis | 2.33 × 10−7 | 1.40 × 10−9 | 7.00 × 10−8 | 2.91 × 10−6 | 9.19 × 10−6 | 7.11 × 10−7 | 2.04 × 10−4 |
| HQiov1 | 4.08 × 10−6 | 2.45 × 10−8 | 1.22 × 10−6 | 5.09 × 10−5 | 1.61 × 10−4 | 1.24 × 10−5 | 3.57 × 10−3 |
| HQiov2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| HQiiv1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| HIn1 | 2.19 × 10−4 | 1.68 × 10−5 | 7.77 × 10−6 | 4.26 × 10−3 | 3.49 × 10−3 | 1.19 × 10−3 | 9.15 × 10−3 |
| HQcgw | 1.86 | 6.74 × 10−2 | 3.87 × 10−3 | 7.26 × 10−1 | 7.26 | 3.56 | 4.42 × 10 |
| HQiov3 | 6.98 × 10−4 | 3.28 × 10−6 | 2.01 × 10−4 | 2.31 × 10−4 | 3.84 × 10−3 | 2.44 × 10−4 | 6.15 × 102 |
| HQiiv2 | 1.03 × 10−1 | 4.83 × 10−4 | 2.96 × 10−2 | 3.41 × 10−2 | 5.66 × 10−1 | 3.59 × 10−2 | 1.06 × 10 |
| HIn2 | 1.96 | 6.79 × 10−2 | 3.36 × 10−2 | 7.60 × 10−1 | 7.83 | 3.60 | 6.70 × 102 |
| CRois | 5.78 × 10−10 | / | / | 4.81 × 10−8 | / | 4.61 × 10−9 | 1.78 × 10−8 |
| CRdcs | 1.82 × 10−9 | / | / | 2.43 × 10−7 | / | 2.09 × 10−7 | / |
| CRpis | 3.79 × 10−12 | / | / | 5.06 × 10−10 | / | 4.34 × 10−10 | / |
| CRiov1 | 6.63 × 10−11 | / | / | 8.84 × 10−9 | / | 7.59 × 10−9 | / |
| CRiov2 | 0.00 | / | / | 0.00 | / | 0.00 | / |
| CRiiv1 | 0.00 | / | / | 0.00 | / | 0.00 | / |
| CRn1 | 2.47 × 10−9 | / | / | 3.01 × 10−7 | / | 2.22 × 10−7 | / |
| CRcgw | 2.84 × 10−5 | / | / | 5.55 × 10−5 | / | 9.35 × 10−5 | 8.89 × 10−4 |
| CRiov3 | 1.13 × 10−8 | / | / | 4.01 × 10−8 | / | 1.49 × 10−7 | / |
| CRiiv2 | 1.67 × 10−6 | / | / | 5.91 × 10−6 | / | 2.19 × 10−5 | / |
| CRn2 | 3.01 × 10−5 | / | / | 6.14 × 10−5 | / | 1.16 × 10−4 | / |
| Parameter Symbol | Benzene | Toluene | Xylenes | Ethyl Benzene | Chloro Benzene | 1,4-Dichloro Benzene | 1,2,4-Trichloro Benzene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCVSois | 6.61 × 102 | 1.32 × 104 | 3.31 × 105 | 1.65 × 104 | 3.31 × 103 | 1.16 × 104 | 1.65 × 103 |
| HCVSdcs | 1.16 × 102 | 2.33 × 103 | 5.81 × 104 | 2.91 × 103 | 5.81 × 102 | 2.03 × 103 | 2.91 × 102 |
| HCVSpis | 2.02 × 108 | 3.36 × 1010 | 6.73 × 108 | 6.73 × 109 | 3.36 × 108 | 5.38 × 109 | 1.35 × 107 |
| HCVSiov1 | 1.15 × 107 | 1.92 × 109 | 3.85 × 107 | 3.85 × 108 | 1.92 × 107 | 3.08 × 108 | 7.70 × 105 |
| HCVSiov2 | 1.13 × 106 | 2.65 × 108 | 9.75 × 106 | 9.23 × 107 | 5.99 × 106 | 2.51 × 108 | 7.45 × 103 |
| HCVSiiv1 | 3.32 × 105 | 5.12 × 107 | 1.20 × 106 | 9.78 × 106 | 1.18 × 106 | 3.19 × 107 | 2.24 × 10 |
| HCVSn | 9.88 × 10 | 1.98 × 103 | 4.72 × 104 | 2.47 × 103 | 4.94 × 102 | 1.73 × 103 | 2.04 × 10 |
| HCVGcgw | 2.45 × 103 | 5.75 × 105 | 2.12 × 104 | 2.00 × 105 | 1.30 × 104 | 5.45 × 105 | 1.62 × 105 |
| HCVGiov3 | 2.25 × 103 | 3.47 × 105 | 8.16 × 103 | 6.64 × 104 | 8.00 × 103 | 2.16 × 105 | 1.30 × 103 |
| HCVGiiv2 | 6.25 × 10−1 | 1.16 × 10 | 3.39 × 102 | 1.38 × 10 | 6.65 | 3.93 × 10 | 1.35 × 10 |
| HCVGn | 6.61 × 10−2 | 1.32 | 3.29 × 10 | 1.65 | 3.31 × 10−1 | 1.16 | 1.65 × 10−1 |
| RCVSois | 4.33 × 10 | / | / | 2.16 × 102 | / | 4.41 × 102 | 8.21 × 10 |
| RCVSdcs | 7.61 | / | / | 3.81 × 10 | / | 7.75 × 10 | 1.44 × 10 |
| RCVSpis | 2.58 × 104 | / | / | 3.16 × 105 | / | 7.17 × 104 | / |
| RCVSiov1 | 1.48 × 103 | / | / | 1.81 × 104 | / | 4.10 × 103 | / |
| RCVSiov2 | 1.44 × 102 | / | / | 4.33 × 103 | / | 3.34 × 103 | / |
| RCVSiiv1 | 3.13 × 10−1 | / | / | 9.40 | / | 7.26 | / |
| RCVSn | 3.00 × 10−1 | / | / | 7.52 | / | 6.61 | 1.44 × 10 |
| RCVGcgw | 4.25 × 10 | / | / | 4.59 × 102 | / | 4.24 × 102 | / |
| RCVGiov3 | 2.88 × 10−1 | / | / | 3.11 | / | 2.88 | / |
| RCVGiiv2 | 3.05 × 10−2 | / | / | 2.16 × 10−2 | / | 8.48 × 10−2 | / |
| RCVGn | 4.26 × 10−3 | / | / | 2.15 × 10−2 | / | 4.34 × 10−2 | 8.21 × 10−3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ye, S.; Wu, J.; Stahl, R.G., Jr. Assessing Risks at a Former Chemical Facility, Nanjing City, China: An Early Test of the New Remediation Guidelines for Waste Sites in China. Water 2017, 9, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090657
Zhang Y, Ye S, Wu J, Stahl RG Jr. Assessing Risks at a Former Chemical Facility, Nanjing City, China: An Early Test of the New Remediation Guidelines for Waste Sites in China. Water. 2017; 9(9):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090657
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanhong, Shujun Ye, Jichun Wu, and Ralph G. Stahl, Jr. 2017. "Assessing Risks at a Former Chemical Facility, Nanjing City, China: An Early Test of the New Remediation Guidelines for Waste Sites in China" Water 9, no. 9: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090657
APA StyleZhang, Y., Ye, S., Wu, J., & Stahl, R. G., Jr. (2017). Assessing Risks at a Former Chemical Facility, Nanjing City, China: An Early Test of the New Remediation Guidelines for Waste Sites in China. Water, 9(9), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090657






