Effects of Permafrost Degradation on the Hydrological Regime in the Source Regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Winter Discharge and Winter Discharge Ratio
2.3.2. Recession Flow
2.3.3. Ratio of Qmax/Qmin
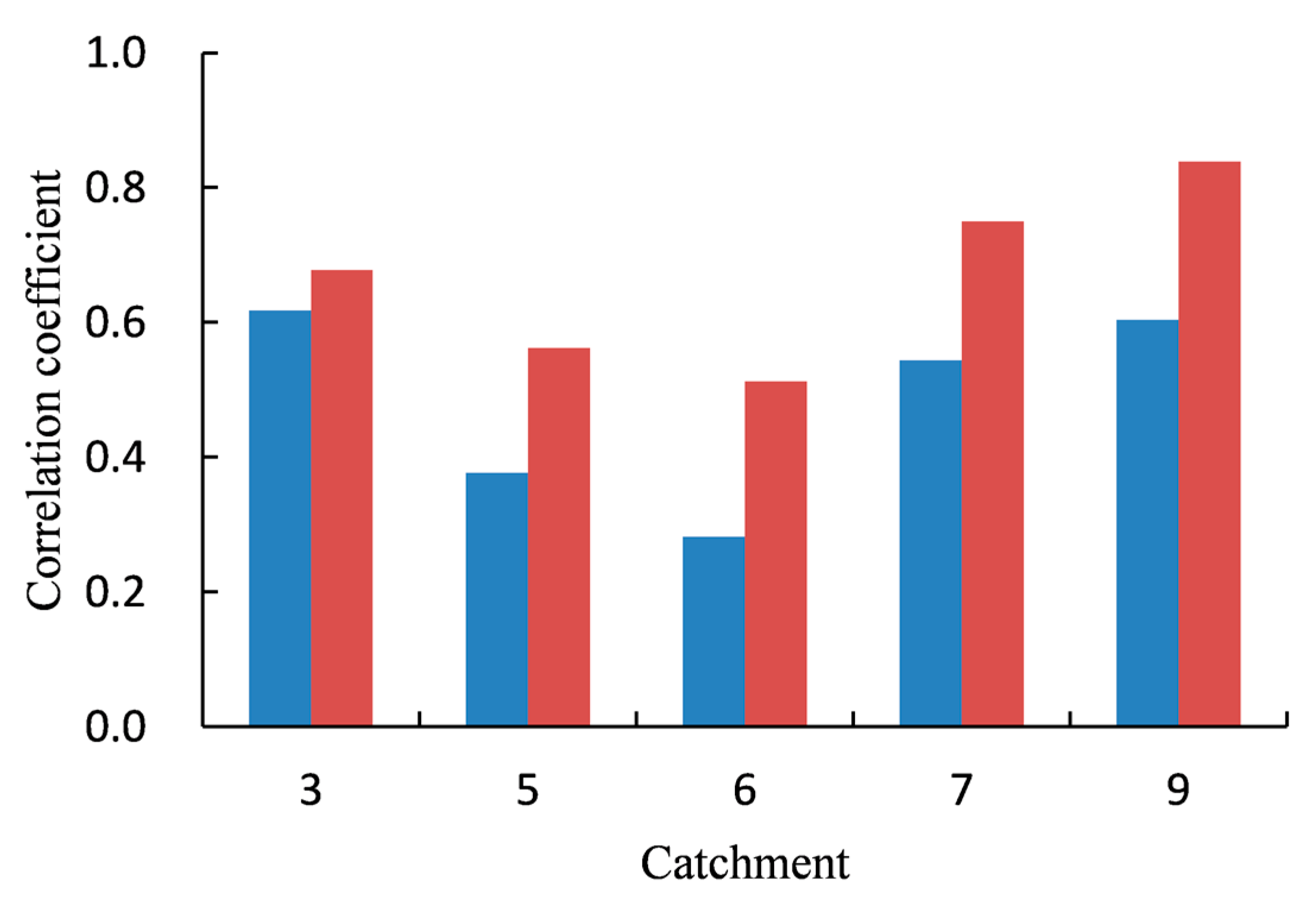
2.3.4. Correlation Analysis between Summer Precipitation and Winter Discharge
3. Results
3.1. Hydrological Regime Changes
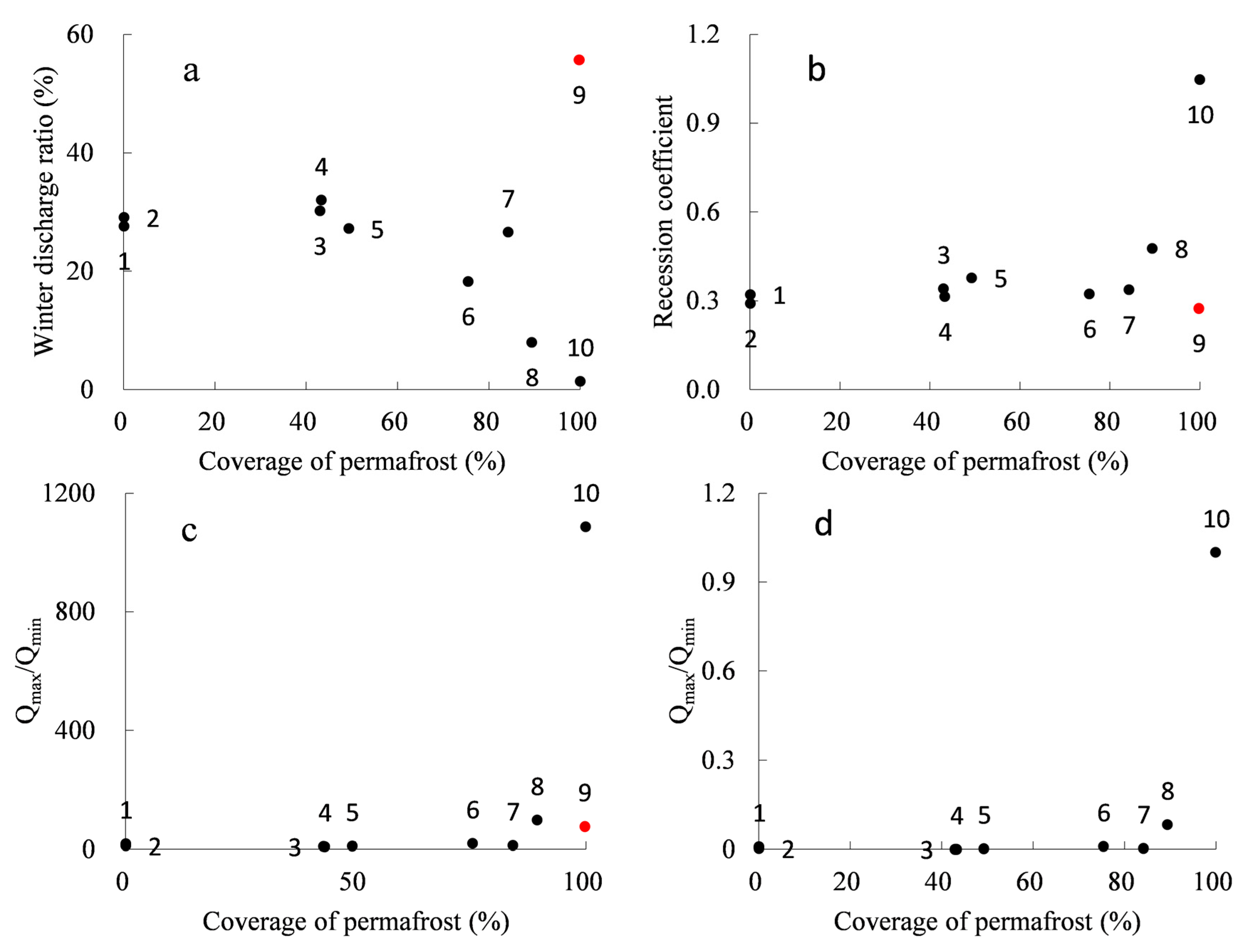
3.2. Relation between Hydrological Variables and Permafrost Coverage
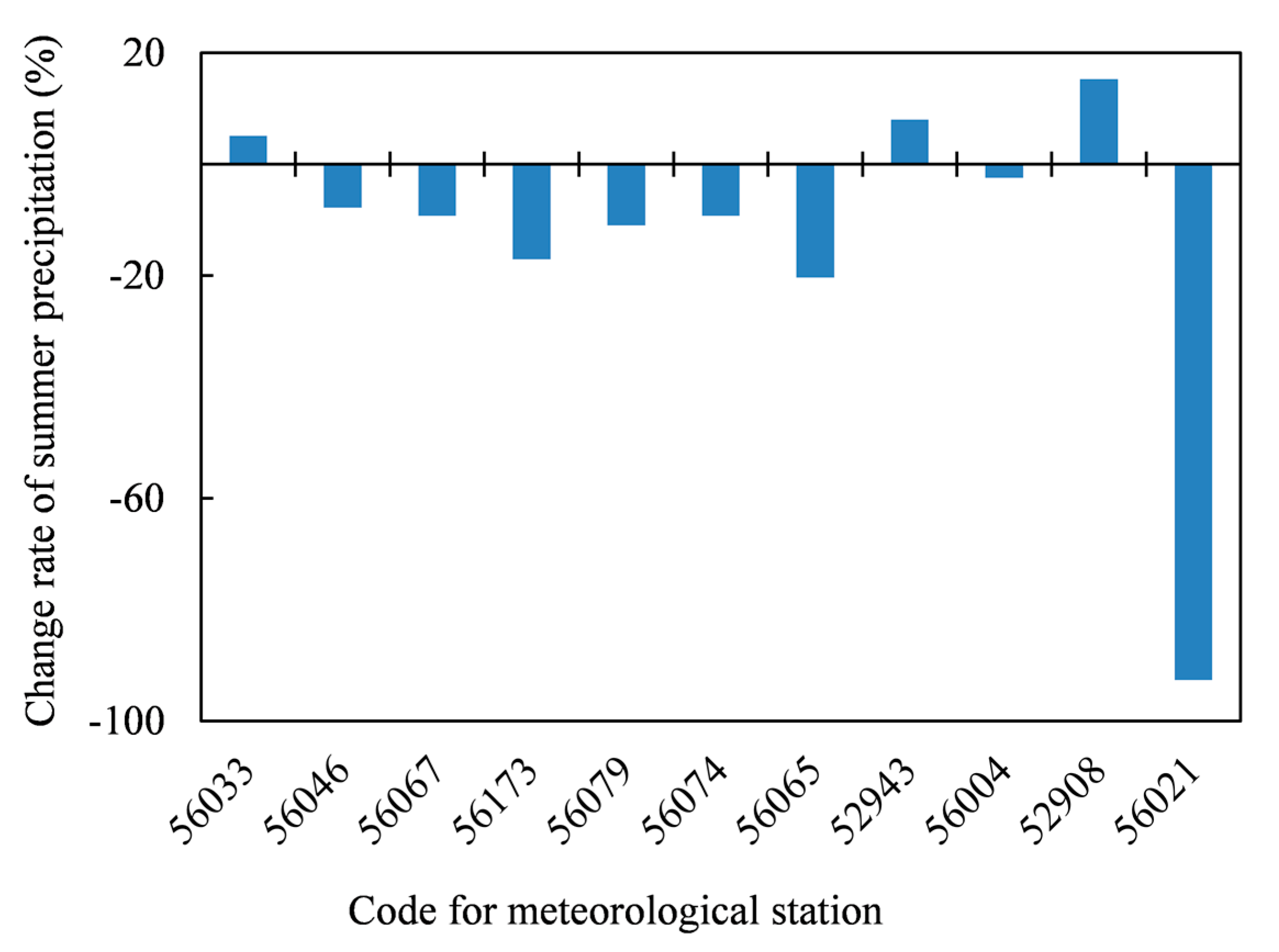
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mcbean, G.; Alekseev, G.; Chen, D.; Forland, E.; Fyfe, J.; Groisman, P.Y.; King, R.; Melling, R.; Vose, R.; Whitfield, P.H. Chapter 2—Arctic Climate: Past and Present. In Arctic Climate Impact Assessment; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pepin, N.; Bradley, R.S.; Diaz, H.F.; Baraer, M.; Caceres, E.B.; Forsythe, N.; Fowler, H.; Greenwood, G.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Liu, X.D.; et al. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzman, L.D.; Deal, C.J.; McGuire, A.D.; Mernild, S.H.; Polyakov, I.V.; Walsh, J.E. Trajectory of the Arctic as an integrated system. Ecol. Appl. 2013, 23, 1837–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurylyk, B.L.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B.; McKenzie, J.M. Climate change impacts on groundwater and soil temperatures in cold and temperate regions: Implications, mathematical theory, and emerging simulation tools. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvoord, M.A.; Kurylyk, B.L. Hydrologic impacts of thawing permafrost—A review. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Ye, B.; Li, J.; Sheng, Y. Effect of permafrost degradation on hydrological processes in typical basins with various permafrost coverage in Western China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.K.; Kane, D.L.; Carey, S.K.; Yang, D. Progress in permafrost hydrology in the new millennium. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2008, 19, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Kane, D.L. Variation of hydrological regime with permafrost coverage over Lena Basin in Siberia. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connon, R.F.; Quinton, W.L.; Craig, J.R.; Hayashi, M. Changing hydrologic connectivity due to permafrost thaw in the lower Liard River valley, NWT, Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4163–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, Y.; Frampton, A.; Lyon, S.W. Using streamflow characteristics to explore permafrost thawing in northern Swedish catchments. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Jacques, J.M.; Sauchyn, D.J. Increasing winter baseflow and mean annual streamflow from possible permafrost thawing in the Northwest Territories, Canada. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvoord, M.A.; Striegl, R.G. Increased groundwater to stream discharge from permafrost thawing in the Yukon River basin: Potential impacts on lateral export of carbon and nitrogen. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, M.A.; Ye, H.; Yang, D.; Shiklomanov, A.; McDonald, K.C. Divergence in seasonal hydrology across northern Eurasia: Emerging trends and water cycle linkages. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, 3151–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; Pavelsky, T.M.; MacDonald, G.M.; Shiklomanov, A.I.; Lammers, R.B. Rising minimum daily flows in northern Eurasian rivers: A growing influence of groundwater in the high-latitude hydrologic cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2007, 112, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennermalm, A.K.; Wood, E.F.; Troy, T.J. Observed changes in pan-arctic cold-season minimum monthly river discharge. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 923–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bense, V.F.; Ferguson, G.; Kooi, H. Evolution of shallow groundwater flow systems in areas of degrading permafrost. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; McKenzie, J.; Voss, C.; Wu, Q. Exchange of groundwater and surface-water mediated by permafrost response to seasonal and long term air temperature variation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 3138–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, T.P.; Voss, C.I.; Walvoord, M.A. Impacts of climate, lake size, and supra- and sub-permafrost groundwater flow on lake-talik evolution, Yukon Flats, Alaska (USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.G.; Ge, S.; Liang, S. Analysis of groundwater flow in mountainous, headwater catchments with permafrost. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 9564–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.K. Permafrost hydrology in North America. Atmos. Ocean 1986, 24, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzman, L.D.; Bettez, N.D.; Bolton, W.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Dyurgerov, M.B.; Fastie, C.L.; Griffith, B.; Hollister, R.D.; Hope, A.; Huntington, H.P. Evidence and implications of recent climate change in Northern Alaska and other Arctic regions. Clim. Chang. 2005, 72, 251–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.A.; Everdingen, R.O.V. Changes in hydrogeologic regimes in permafrost regions due to climatic change. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 1994, 5, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.; Hinzman, L.; Alessa, L.; Cassano, J.; Chambers, M.; Falkner, K.; Francis, J.; Gutowski, W.J.; Holland, M.; Holmes, R.M. The arctic freshwater system: Changes and impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2007, 112, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, S.K.; Woo, M.K. Slope runoff processes and flow generation in a subarctic, subalpine catchment. J. Hydrol. 2001, 253, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, J.M.; Sudicky, E.A.; Peltier, W.R.; Tarasov, L. Dynamics of groundwater recharge and seepage over the Canadian landscape during the Wisconsinian glaciation. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.L. The Impact of Hydrologic Perturbations on Arctic Ecosystems Induced by Climate Change; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Kubota, J.; Ohata, T.; Vuglinsky, V.; Mizuyama, T. Seasonal changes in runoff characteristics on a permafrost watershed in the southern mountainous region of eastern Siberia. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Armstrong, R.; Robinson, D.; Brodzik, M.J. Streamflow response to seasonal snow cover changes over large Siberian watersheds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, S.W.; Destouni, G. Changes in catchment-scale recession flow properties in response to permafrost thawing in the Yukon river basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, S.W.; Destouni, G.; Giesler, R.; Humborg, C.; Mörth, M.; Seibert, J.; Karlsson, J.; Troch, P.A. Estimation of permafrost thawing rates in a sub-arctic catchment using recession flow analysis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 6, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C.; Kokelj, S.A.; Kokelj, S.V.; Hedstrom, N. The process of winter streamflow generation in a subarctic Precambrian Shield catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4179–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, V.; Kooi, H.; Bense, V. Potential controls on cold-season river flow behavior in subarctic river basins of Siberia. J. Hydrol. 2013, 489, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Jin, H. Permafrost and groundwater on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and in northeast China. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, T. Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Maskey, S.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Zhao, H. Streamflow trends and climate linkages in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3399–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, G. Eco-environmental changes and causative analysis in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Environmentalist 2000, 20, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G. Problems on zonation of high-altitude permafrost. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1984, 39, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, W. Computer simulation and mapping of the regional distribution of permafrost along the Qinghai-Xizang Highway. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2000, 22, 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Li, S.; Cheng, G.; Wang, S.; Li, X. Permafrost and climatic change in China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2000, 26, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X. Simulation of the decadal permafrost distribution on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (China) over the past 50 years. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2012, 23, 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Prange, M.; Merkel, U. Precipitation and temperature changes in the major Chinese river basins during 1957–2013 and links to sea surface temperature. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S.; Junfeng, L. Variations of snow cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in China between 1960 and 1999. J. Glaciol. 2007, 53, 420–426. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, S. Temporal and spatial variations of precipitation in Northwest China during 1960–2013. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déry, S.J.; Wood, E.F. Decreasing river discharge in northern Canada. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallaksen, L.M. A review of baseflow recession analysis. J. Hydrol. 1995, 165, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Zhang, T.; Cao, L.; Kang, S.; Sillanpää, M. Reduced winter runoff in a mountainous permafrost region in the northern Tibetan Plateau. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 126, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Qin, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L. Study on temperature variations and its anomaly patterns over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2003, 22, 524–530. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Pei, T.; Zhou, C. Research progresses of surface temperature characteristic change over Tibetan Plateau since 1960. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Xu, D.; Wan, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Periodic regularity of the base flow in the headwater region of the Yellow river and affecting factors. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Streletskiy, D.A.; Tananaev, N.I.; Opel, T.; Shiklomanov, N.I.; Nyland, K.E.; Streletskaya, I.D.; Tokarev, I.; Shiklomanov, A.I. Permafrost hydrology in changing climatic conditions: Seasonal variability of stable isotope composition in rivers in discontinuous permafrost. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 095003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
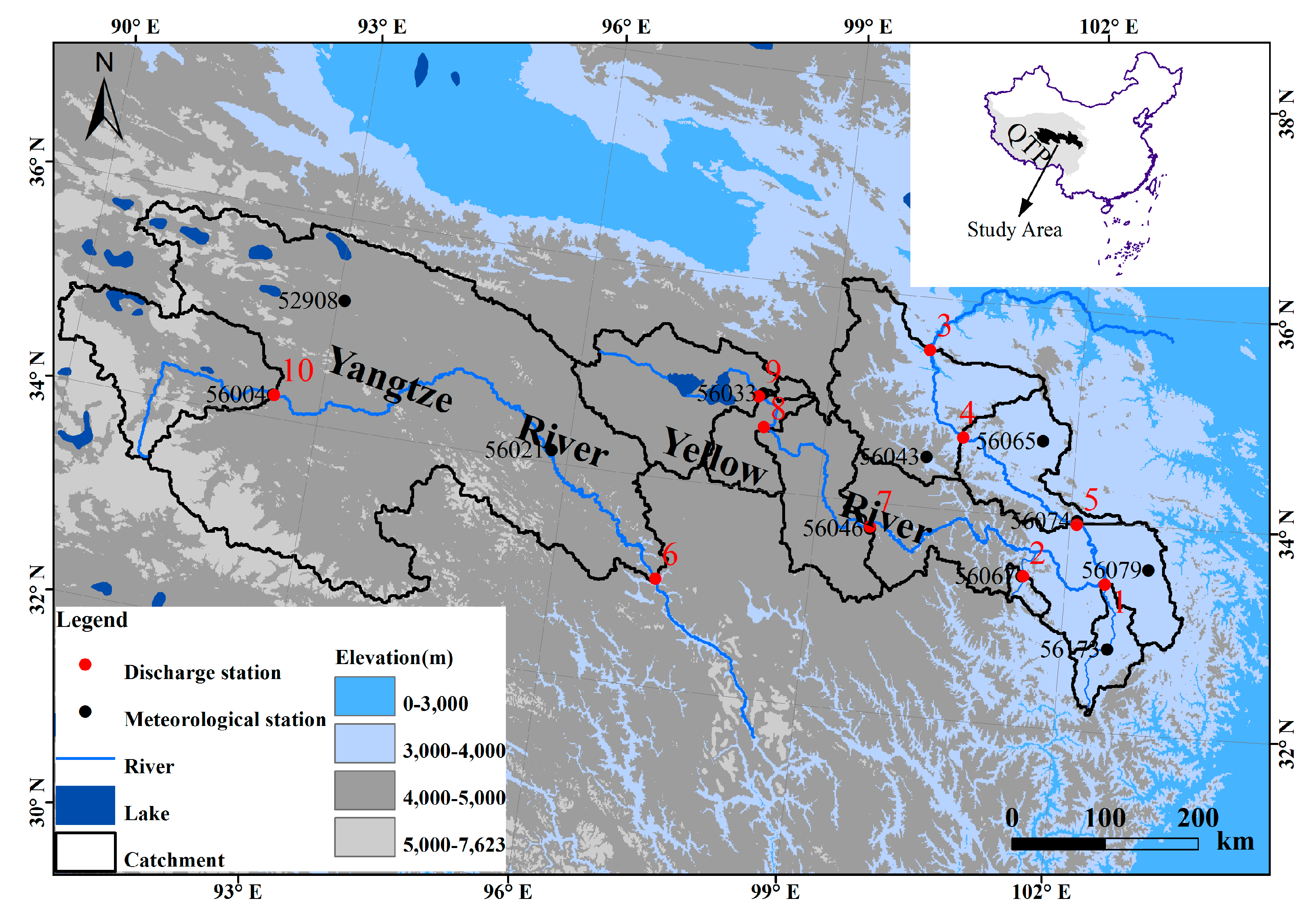
| River Name | Discharge Station | Code a | Lon. (°E) | Lat. (°N) | Ele. (m) | Area (km2) | Coverage of Permafrost (%) b | Mean Discharge (m3/s) | Available (Missing) Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | Annual | |||||||||
| Bai River | Tangke | 1 | 102.47 | 33.42 | 3399 | 5374 | 0.1 | 16.9 | 61.2 | 1981–2014 (1985) |
| Shakequ | Jiuzhi | 2 | 101.50 | 33.43 | 3711 | 1248 | 0.2 | 5.1 | 17.4 | 1988–2014 |
| Yellow River | Tangnag | 3 | 100.15 | 35.50 | 2632 | 121,972 | 43.0 | 188.2 | 636.4 | 1956–2014 |
| Yellow River | Jungong | 4 | 100.65 | 34.70 | 4176 | 98,414 | 43.3 | 165.8 | 536.6 | 1980–2014 |
| Yellow River | Maqu | 5 | 102.08 | 33.97 | 3383 | 86,048 | 49.3 | 119.9 | 451.1 | 1956–2014 |
| Tongtian River | Zhimenda | 6 | 97.22 | 33.03 | 3536 | 137,740 | 75.4 | 71.7 | 411.4 | 1957–2014 |
| Yellow River | Jimai | 7 | 99.65 | 33.77 | 3925 | 45,019 | 84.2 | 34.5 | 128.6 | 1956–2014 |
| Requ | Huanghe | 8 | 98.27 | 34.60 | 4220 | 6446 | 89.4 | 1.3 | 19.1 | 1991–2014 |
| Yellow River | Huangheyan | 9 | 98.17 | 34.88 | 4176 | 20,930 | 99.8 | 13.9 | 22.2 | 1976–2014 |
| Tuotuohe | Tuotuohe | 10 | 92.45 | 34.22 | 4533 | 15,924 | 100.0 | 0.3 | 29.3 | 1959–2014 (2010, 2012) |
| Code a | Lat. (°N) | Lon. (°E) | Ele. (m) | Mean Precipitation (mm) | Available Years | Representative Catchment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Summer b | ||||||
| 52908 | 35.22 | 93.08 | 4612 | 290.8 | 192.2 | 1956–2015 | 6 |
| 56004 | 34.22 | 92.43 | 4533 | 291.0 | 122.4 | 1956–2015 | 6,10 |
| 56021 | 34.12 | 95.80 | 4175 | 411.7 | 27.0 | 1956–2015 | 6 |
| 56033 | 34.92 | 98.22 | 4272 | 321.6 | 183.0 | 1953–2015 | 3,4,5,7,8,9 |
| 56043 | 34.48 | 100.23 | 3719 | 512.5 | 291.7 | 1959–2015 | 3 |
| 56046 | 33.75 | 99.65 | 3968 | 552.1 | 293.7 | 1956–2015 | 3,4,5,7 |
| 56065 | 34.73 | 101.60 | 3500 | 580.1 | 319.0 | 1959–2015 | 3,4 |
| 56067 | 33.43 | 101.48 | 3629 | 746.9 | 196.4 | 1958–2015 | 2,3,4,5 |
| 56074 | 34.00 | 102.08 | 3471 | 600.9 | 326.5 | 1967–2015 | 3,4,5 |
| 56079 | 33.58 | 102.97 | 3441 | 649.3 | 339.5 | 1957–2015 | 1,3,4,5 |
| 56173 | 32.80 | 102.55 | 3492 | 750.0 | 351.1 | 1960–2015 | 1,3,4,5 |
| Code | Winter Discharge | Winter Discharge Ratio | Recession Coefficient | Qmax/Qmin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (m3/s) | β | Mean (%) | β | Mean | β | Mean | β | |
| 1 | 16.9 | 2.00 | 27.59 | 0.03 | 0.32 | −0.06 | 18.12 | −2.96 |
| 2 | 5.1 | −1.10 | 29.04 | −0.05 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 12.15 | 3.59 |
| 3 | 188.2 | 0.90 | 30.15 | 0.01 | 0.34 | −0.01 | 9.43 | −0.20 |
| 4 | 165.8 | 0.00 | 31.96 | 0.02 | 0.31 | −0.03 | 9.10 | −1.13 |
| 5 | 119.9 | −2.38 | 27.16 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 10.86 | 0.40 |
| 6 | 71.7 | 1.09 | 18.23 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.01 | 19.35 | 0.49 |
| 7 | 34.5 | 1.56 | 26.57 | 0.01 | 0.34 | −0.02 | 12.54 | −0.36 |
| 8 | 1.3 | 0.30 | 7.95 | 0.00 | 0.48 | −0.02 | 98.21 | −12.59 |
| 9 | 13.9 | 0.21 | 55.68 | 0.01 | 0.27 | −0.03 | 76.72 | −0.42 |
| 10 | 0.3 | −0.15 | 1.38 | −0.01 | 1.05 | 0.09 | 1086.79 | 12.40 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Yang, Y. Effects of Permafrost Degradation on the Hydrological Regime in the Source Regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Water 2017, 9, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110897
Wang X, Chen R, Yang Y. Effects of Permafrost Degradation on the Hydrological Regime in the Source Regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Water. 2017; 9(11):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110897
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiqiang, Rensheng Chen, and Yong Yang. 2017. "Effects of Permafrost Degradation on the Hydrological Regime in the Source Regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China" Water 9, no. 11: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110897
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, R., & Yang, Y. (2017). Effects of Permafrost Degradation on the Hydrological Regime in the Source Regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Water, 9(11), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110897




