Abstract
A major attribute of the Earth’s climate that may be affected by global warming is the amplitude of variability in teleconnections. These global-scale processes involve links between oceanic conditions in one locale and weather in another, often distant, locale. An example is the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which can affect rainfall and then the properties of lakes in Europe, Africa, North and South America. It affects rainfall, droughts and the depth of lakes in Florida, USA. It is predicted that the amplitude of variation in the ENSO will increase with global warming and, therefore, droughts will become more severe and periods of rain more intense. We investigated possible effects of climate on the zooplankton in shallow subtropical lakes by studying 16 years of monthly data from six shallow eutrophic lakes located north of Orlando, Florida. Results indicate that water depth and lake volume are tightly coupled with rainfall, as expected. During droughts, when lake depth and volume were greatly reduced, there were intensified cyanobacterial blooms, and the zooplankton shifted towards greater relative biomass of copepods compared to cladocerans. The change of zooplankton was likely due to the intensified selective fish predation in the reduced water volume, and/or selective adverse effects of cyanobacteria on cladocerans. The greatly reduced volume might lead to a ‘perfect storm’ of top-down and bottom-up factors that favor copepods over cladocerans. The mechanism needs further study. Regardless, this study documents a direct link between climate variability and zooplankton composition, and suggests how future changes in climate might affect plankton communities.
Keywords:
climate variability; rainfall; shallow lakes; zooplankton; cladocerans; copepods; cyanobacteria 1. Introduction
Zooplankton dynamics in subtropical lakes are affected, as in other geographic regions, by a myriad of factors, including fish and invertebrate predation, food resource quantity and quality, temperature, stratification, abiotic seston and other attributes of water quality [1,2,3,4]. Conditions external to the lake, including rainfall, air temperature, wind velocity, and loading of nutrient and sediments, can affect those factors either directly or indirectly, as can characteristics within the lake such as bioturbation of sediments by invertebrates and fish, and nutrient uptake by vascular plants [5].
Many areas in the subtropics, as well as other places around the world, have weather and climate patterns influenced by teleconnections with distant oceanic changes, such as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a cycle of sea surface warming and cooling in the equatorial eastern Pacific Ocean, and accompanying air surface pressure change. ENSO is known to affect lake ecosystems in South America [6], Asia [7], North America [8] and Africa [9]. In the case of Florida, when the ENSO is in a positive phase (El Niño), surface waters warm over the Pacific Ocean off the coast of South America, and the teleconnection leads to the Pacific Jet Stream migrating southward so that it crosses the Gulf of Mexico before passing over Florida. As a result, rainfall is higher than average, especially over the southern peninsula in the dry season [10]. When the ENSO is in the cold phase (La Niña), the Pacific Jet Stream passes farther to the north, and the Florida peninsula is drier than normal in the dry season.
We previously documented a strong inverse relationship between yearly mean depth (which is correlated with antecedent rainfall) and cyanobacteria mean and maximal biomass, and a positive relationship between yearly mean depth and maximal cladoceran biomass, in one shallow eutrophic lake in central Florida, where rainfall has the aforementioned relationship with the ENSO [11]. Furthermore, we proposed some mechanisms, including changes in dissolved organic color of the lake water and concentrations of nutrients in a reduced volume during droughts, as contributing factors to a high biomass of cyanobacteria when depth is low. More recently, we documented that the same results occurred for cyanobacteria over a wider range of shallow lakes in that same geographic region, and that water flushing rate was also an important variable affecting cyanobacteria maximal biomass [12].
In the present study, we examined the degree to which variation in rainfall and depth might influence the biomass and taxonomic composition of crustacean zooplankton in shallow eutrophic lakes in subtropical Florida. Prior to analyzing the data, we developed a conceptual model that provides a basis for predictions about the zooplankton responses (Figure 1). We predicted that droughts have an influence on the relative biomass of crustacean zooplankton, favoring copepods over cladocerans. This influence may happen for two reasons both related to a concentration of chemicals or animals in lake water with reduced volume. First, the high densities of omnivorous fish that are present in these and other subtropical lakes are concentrated. The fish prey on zooplankton, and cladocerans are most susceptible [1,2]. Second, the concentration of nutrients stimulates the growth of large inedible cyanobacteria, and this selectively interferes with grazing by filter-feeding cladocerans.
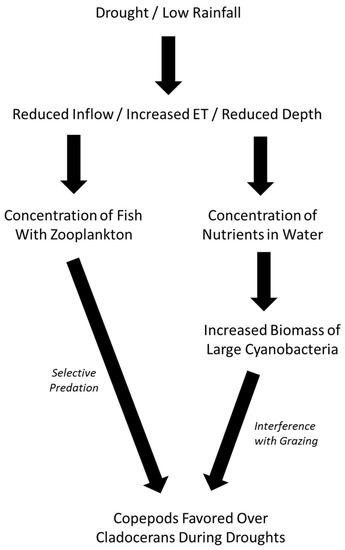
Figure 1.
Conceptual diagram of the predicted effects of variation in climate and rainfall on drought and water depth in the shallow study lakes; the concentration of fish and nutrients in reduced lake volumes; the increased biomass of cyanobacteria in shallower nutrient-enriched water; and the increase in biomass of copepods relative to cladocerans. ET = evapotranspiration.
We recognize that the temporal dynamics of zooplankton and phytoplankton are affected by factors occurring at multiple temporal scales. These include: (1) year-to-year variations in attributes such as depth and flushing that are affected by climate; (2) seasonal variations driven by attributes such as incident solar radiation and temperature; and (3) short-term variations driven by stochastic factors such as periods of intense rainfall, cloud cover, water inflow and calm or windy conditions. Seasonal dynamics of plankton in subtropical lakes have been extensively studied and documented [2,3] and, in fact, comparisons have been made with standard plankton models developed for temperate regions in multiple papers [4]. Monthly data are insufficient to discern responses to short-term variations in weather. This study, therefore, is restricted to discerning year-to-year variations in the zooplankton, and attempting to develop linkages with variability in climate, rainfall and depth.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Lakes
Data were obtained from six lakes (Figure 2) located in the Upper Ocklawaha River Basin, north of Orlando, Florida, between 28°55′ N 81°50′ W and 28°34′ N 81°33′ W. The lakes are shallow, with mean depths ranging from 1.4–3.4 m, and ranging in size from 5–127 km2 (Table 1). The lakes are eutrophic, with total phosphorus (TP) from 38–131 µg L−1, total nitrogen (TN) from 1.8–4.7 mg L−1 and chlorophyll a (Chl-a) from 35–115 µg L−1. All of the lakes are strongly dominated by filamentous and colonial cyanobacteria that attain exceptionally high biomass, i.e., blooms [13], and some lakes have displayed downward trends in nutrients and Chl-a, attributed to nutrient-control programs in the watershed [13,14]. The lakes all have high densities of omnivorous fish [15,16], which is typical for lowland subtropical lakes [2,17,18].
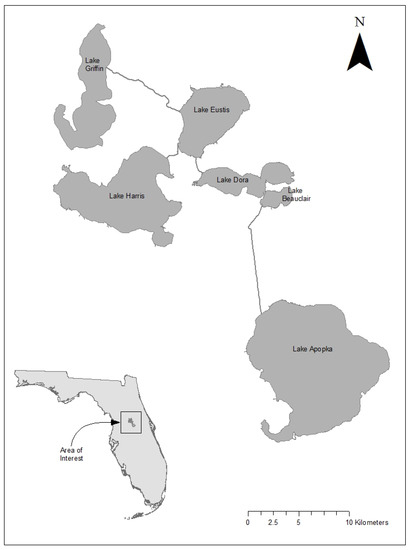
Figure 2.
Map showing the six study lakes and their location in Florida, USA.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the six study lakes in central Florida, USA. Data are means calculated from monthly data collected over the period from January 1999 to August 2016.
In these interconnected lakes, water flows northward from Lake Apopka to Beauclair and Dora, northeastward from Harris, converges in Eustis, and then flows to Griffin. Finally, the water discharges from Lake Griffin into the Ocklawaha River. During droughts, some of these flows may reverse. The lakes have residential development on their shorelines and water is periodically discharged from them to prevent flooding of lakeside property. Havens et al. [12] showed that this management results in cutting off the top of hydrographs, with a plateau related to the maximal water level beyond which shoreline flooding would occur in each of the lakes. The watershed surrounding the lakes has many land uses. In some areas it is highly urbanized, in other areas it is used for agriculture, and there are homes on much of the waterfront. There also are areas with natural wetlands adjacent to the lakes. A detailed analysis is beyond the scope of this paper; however, land use can readily be seen in Google Earth. Furthermore, there are a large number of reports that deal with land use, nutrient loads, nutrient reduction programs and changes in nutrient concentrations within the lakes. Summary reports can be obtained by contacting the St. Johns River Water Management District.
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Methods
Daily rainfall data were obtained from the US National Weather Service meteorological station in Lisbon, Florida, located centrally in the lake region. The lakes were sampled monthly from January 1999 to August 2016, at one to three sites in each lake, and the collected samples were integrated, or the data were averaged for each sampling occasion. Lake volume and area were calculated from the measured lake surface elevation using formulas based on bathymetric maps of the lakes. Mean depth was the quotient of volume divided by area. Flushing rates in each lake were determined from hydrologic budgets maintained by the St. Johns Water Management District. Water temperatures were measured at 0.5 m depth with a YSI or Hydrolab meter and water transparency (SD) was measured with a 20-cm white Secchi disk. Water samples for analysis of total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN = NO3 + NO2 + NH4), soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), were collected and preserved following standard methods [19]. Phytoplankton samples were collected from each location at 0.5 m and 1.0 m depths with a Van Dorn bottle. The two samples were mixed in a larger plastic container and then an aliquot was placed into an amber plastic bottle and fixed with Lugol’s solution. To collect zooplankton, 2 L of the same mixed water was filtered through a 75 μm plankton net, until November 2004, and then through a 35 μm net afterwards. These samples were also preserved with Lugol’s solution. The change in mesh size affected the collection efficiency of rotifers and nauplii, and, therefore, we report here only on the biomass of adult cladocerans, copepods and copepodids, which are known to be effectively captured by a 115 μm mesh net in Florida lakes [20].
The water samples were analyzed for TP, TN, SRP DIN, and dissolved organic color in the laboratory by standard US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) methods [19]. Phytoplankton was analyzed by the membrane-filtration technique [21] on a Leica DMLB compound microscope at 630 × with a minimum count threshold of 400 natural units (colonies, filaments and uni-cells). These units were measured and their biovolumes determined based on the volumes of regular geometric solids. Population and total biovolumes were calculated according to Hillebrand et al. [22]. Aliquots of the zooplankton samples were enumerated at 100× until at least 200 individuals had been counted and the entire contents of each sample were scanned at lower magnification for rare species. In each sample, 10% of the individuals of each crustacean species were measured at 100× in order to estimate dry weights from body lengths using published length-weight relationships [23]. The biomass of each population was then calculated by multiplying numeric density (individuals L−1) times mean individual biomass (μg). This was done for each crustacean species, and then sums of species population biomass were made for cladocerans, calanoids and cyclopoids. Adults and copepodids were combined for data analysis.
2.3. Statistical Analysesiagram
Statistical analyses were undertaken to test the relationships in the conceptual diagram (Figure 1), starting at the top and working to the bottom. Because we did not have a time-series of fish data, we examined just these relationships: mean depth vs. rainfall; cyanobacteria vs. mean depth; crustacean zooplankton vs. cyanobacteria; and crustacean zooplankton vs. mean depth. All analyses were done with Systat Version 13.
The relationship between mean depth and rainfall was examined separately for each lake, using the depth calculated in the sampling month and cumulative rainfall over periods of time prior to the sampling events.
The annual mean and maximal biovolumes of cyanobacteria (one datum from each lake in each year of sampling) were plotted against yearly mean depths. Least squares regression was used to quantify the relationships. Linear models fit the data as well as non-linear models, depending on which gave statistically significant results.
For each lake, time series of total cladocerans, calanoids and cyclopoids were plotted for the period or record to allow visualization of both the seasonal dynamics and year-to-year variation in biomass. Time series of cyanobacteria biovolume were superimposed on these zooplankton graphs. We then examined the relationship between the annual mean and maximal biomass of cladocerans, calanoids and cyclopoids with depth and cyanobacteria, in some cases fitting non-linear models when they resulted in significantly higher regression coefficients than linear models. We also examined the degree to which the ratio of cladocerans to copepods was influenced by mean depth and cyanobacteria using regression analysis, and again this led to fitting non-linear models.
Significant statistical relationships between zooplankton and attributes such as cyanobacteria might reflect coincident long-term trends rather than co-variation with factors related to shorter-term climate and weather variability. To exclude this case we took the annual maximal biomass of cladocerans, calanoids and cyclopoids, and the annual maximal biovolume of cyanobacteria, and conducted non-parametric correlation analyses with year as the independent variable. We also used a Mann–Kendall trend test for long-term trends in the raw time-series data of cyanobacteria biovolume, because several lakes have documented declines in TP, TN and Chl-a following nutrient reduction programs.
Finally, a redundancy analysis (RDA) was performed using the annual mean data to identify the power of independent environmental variables (TP, TN, SRP, DIN, temperature, Chl-a, dissolved organic color, flushing rate, mean depth, SD, rainfall and cyanobacteria biovolume) on explaining the variation in the dependent zooplankton variables (cladocerans, calanoids and cyclopoids). The analysis was run using Canoco 4.5 [24] with yearly-averaged data from each lake.
2.4. Data
The raw data used in this study, including all physical, chemical and biological parameters from each lake, are available from the corresponding author upon written request by email.
3. Results
As predicted, mean depth was positively related to rainfall, and the greatest amount of variability in mean depth was explained by the cumulative amount of rainfall measured in the basin during the preceding 25 months, the period of time that provided the best fit to the data, presumably reflecting saturation of soils in the drainage basin and later release into the lakes (Figure 3). That variable explained 37~60% of mean depth variation. Linear regressions represented the data just as well as non-linear regression models, even though it is evident in the figures that depth has a plateau (at a flood control level) in each lake.
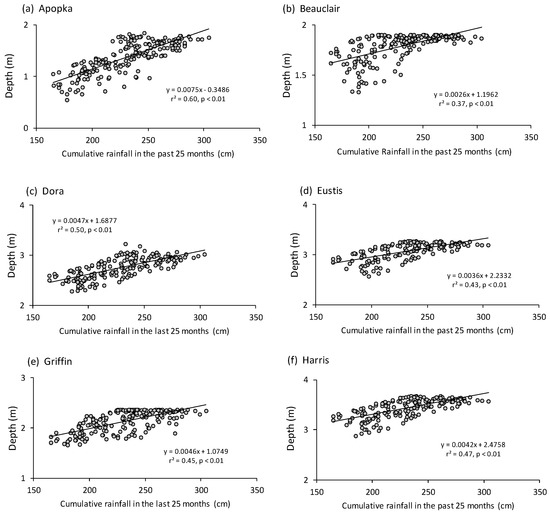
Figure 3.
Relationships between rainfall (cumulative amount in prior 25 months) and depth in the six study lakes (a–f). Each filled circle is an individual sampling date and the lines are least squares linear regressions with equations, regression coefficients and significance levels provided.
There was no long-term trend in the maximal yearly biovolume of cyanobacteria in any of the lakes, and while the Mann–Kendall test revealed some trends in means, they were not consistent among lakes. Biovolume significantly decreased in Lake Apopka, while it increased in Lakes Beauclair and Dora. The other lakes displayed no significant long-term trends. Cyanobacteria biovolume declined with increased mean depth, whether considered as the yearly mean or the yearly maximum (Figure 4a,b). Although depth explained just 19% and 11% of the variation in mean and maximal biovolume, respectively, it was statistically significant.
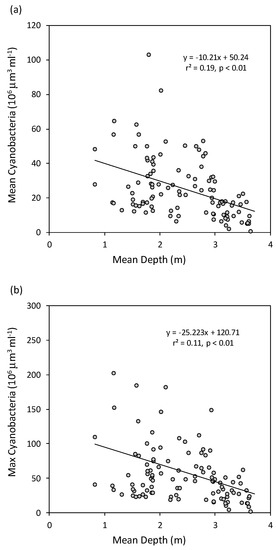
Figure 4.
Relationships between mean depth and (a) yearly mean cyanobacteria biomass, and (b) yearly maximal cyanobacterial biomass. The filled circles are annual means from each year of sampling in the six study lakes. Solid lines are least squares linear regression model fits to the data, with equations, regression coefficients and significance levels provided.
The dry weight biomass of cladoceran zooplankton was highly variable from year to year and between lakes. Sometimes there was temporal synchronization of biomass peaks (Figure 5). There were also long-term trends in some of the lakes, regarding the maximal biomass attained in each year. However, those trends (yearly maxima, Mann–Kendall test with year) were only statistically significant (p < 0.05) in Lakes Beauclair and Dora, where cladocerans increased. In regard to seasonality, cladoceran biomass generally displayed a short-lasting peak in January to March. Maximal biomass ranged from less than 20 to more than 1000 μg dry weight L−1. There was not a statistically significant relationship between the annual peak biomass of cladocerans and water depth (data not shown to avoid redundancy with other figures, because of the lack of relationship). However, cladocerans never had their peak in biomass coincident with the peak in cyanobacteria biovolume.
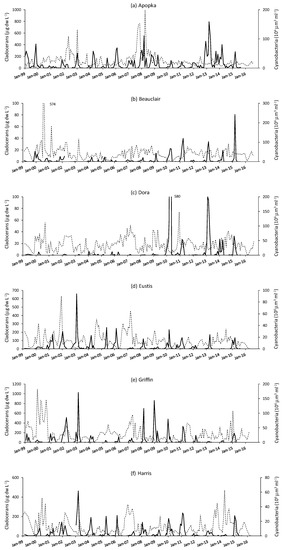
Figure 5.
Time series of monthly data of cladoceran dry weight biomass (primary X axis, solid line) and cyanobacteria biovolume (secondary X axis, dashed line) from 1999 to 2016 in the six study lakes (a–f).
Calanoid biomass also displayed some long-term trends (Figure 6). These were statistically significant (p < 0.05) in Lakes Dora (decrease), Eustis (decrease) and Griffin (decrease). In most years and lakes, maximal biomass of calanoid copepods occurred, like cladocerans, in January to March, but sometimes calanoid biomass peaked in the summer and exhibited a bimodal pattern in some years. Like cladocerans, there sometimes was peak biomass synchronization among nearby lakes. Maximal calanoid biomass ranged from below 20 to more than 500 μg L−1 dry weight, i.e., the same range as observed for cladocerans. Calanoid biomass did not appear to be related to mean depth, as there were instances that high biomass coincided with low depth (e.g., 2008–2009 in Lake Apopka) but at other times high biomass corresponded with high depth (e.g., 2005 in Lake Griffin and 2003 in Lake Harris). Likewise, a consistent relationship between calanoid biomass and cyanobacteria biovolume was not evident. There were cases where low biomass of calanoids coincided with peak biomass of cyanobacteria, (e.g., 2002 in Lake Apopka) but also cases where extreme high calanoid biomass coincided with a near-record high cyanobacteria biomass (e.g., 2008 in the same lake).
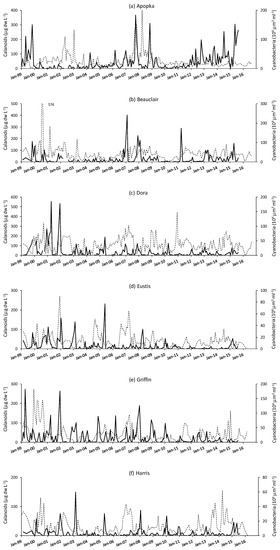
Figure 6.
Time series of monthly data of calanoid dry weight biomass (primary X axis, solid line) and cyanobacteria biovolume (secondary X axis, dashed line) from 1999 to 2016 in the six study lakes (a–f).
There were only significant (p < 0.05) long-term trends of cyclopoid biomass (Figure 7) in Lakes Eustis (decrease) and Harris (decrease). Cyclopoids presented a seasonal pattern more akin to calanoids than to cladocerans, with biomass peaks at various times in the year, and sometimes there were peaks two or more times in a year. Cyclopoid biomass peaks ranged from below 20 to ca. 200 μg L−1 dry weight per sample, i.e., they never attained the high biomass seen with cladocerans and calanoids. There was not a significant relationship between the magnitude of cyclopoid biomass peaks and water depth. Sometimes, a high peak corresponded with low depth (e.g., 2007 in Lake Apopka), while at other times a high peak corresponded with high depth (e.g., 2003 in Lake Harris). Likewise, there was not a clear relationship between cyclopoid biomass peaks and the biovolume of cyanobacteria. In some cases, when a high biovolume of cyanobacteria occurred, cyclopoid biomass was low (e.g., late 2010 in Lake Dora), while in other cases, a substantive peak in cyclopoid biomass coincided with very high biomass of cyanobacteria (e.g., 2000 in Lake Griffin).
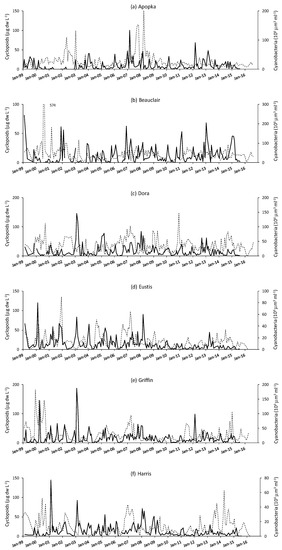
Figure 7.
Time series of monthly data on cyclopoid dry weight biomass (primary X axis, solid line) and cyanobacteria biovolume (secondary X axis, dashed line) from 1999 to 2016 in the six study lakes (a–f).
There were significant inverse non-linear relationships between the yearly mean and maximal biomass of cladocerans and the yearly mean biomass of cyanobacteria (Figure 8a,b), albeit explaining a small amount of the total variability. However, there were not significant relationships for calanoids and cyclopoids (Figure 8c–f). The ratio of cladoceran to copepod biomass was higher when cyanobacteria peak biomass was low, and it dropped to near zero when peak cyanobacteria biomass was high. Non-linear regression models explained 18% of the variation in the relationship between the zooplankton ratio and mean annual biomass of cyanobacteria, and 20% of the variation in the relationship with the maximal annual biomass of cyanobacteria (Figure 9a,b). There were not significant relationships between mean or maximal biomass of any crustacean group and mean depth, nor was there a significant correlation between the cladoceran to copepod ratio and mean depth. There was a tendency in the data for cladocerans to be less abundant at shallower depth and the opposite to be the case for copepods, but the data were highly scattered and regression models could not explain even 1% of the variability.
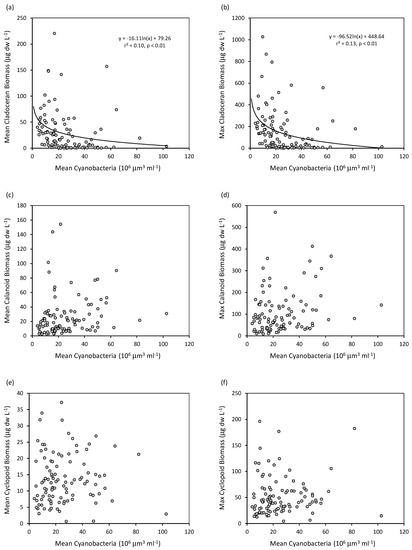
Figure 8.
Relationships between the yearly mean and maximal biomass of cladocerans (a,b), calanoids (c,d) and cyclopoids (e,f) with yearly mean biovolume of cyanobacteria in the six study lakes. Each filled circle represents one year and lake. Logarithmic regressions are fitted to the relationships for cladocerans, which are statistically significant. No significant relationships exist for calanoids or cyclopoids.
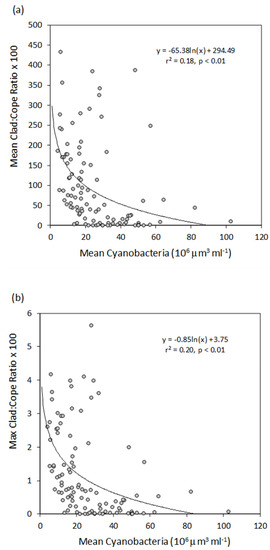
Figure 9.
Relationship between the ratio of yearly mean cladoceran to copepod biomass (a) and yearly maximum cladoceran to copepod biomass (b) and the yearly mean biovolume of cyanobacteria. Each filled circle represents one year and lake. Logarithmic regressions are fitted to both datasets.
The redundancy analysis explained 35% of the variation in the zooplankton data along the first axis and 12% of the variation along the second axis (Figure 10). On the first axis, there was a strong separation of cladocerans and cyanobacteria. Calanoids and cyclopoids were positively associated with cyanobacteria on this axis. There were not strong associations of the biological variables with the environmental variables, except that cladocerans were negatively associated with flushing, water temperature and dissolved organic color, and positively associated with Secchi transparency. Cyanobacteria was negatively associated with depth, as we observed in an earlier study where this relationship was stronger, when not including the zooplankton in the multi-variate analysis. The RDA separated the lakes into distinct clusters, reinforcing the fact that their plankton dynamics vary despite proximity and hydrologic connectivity.
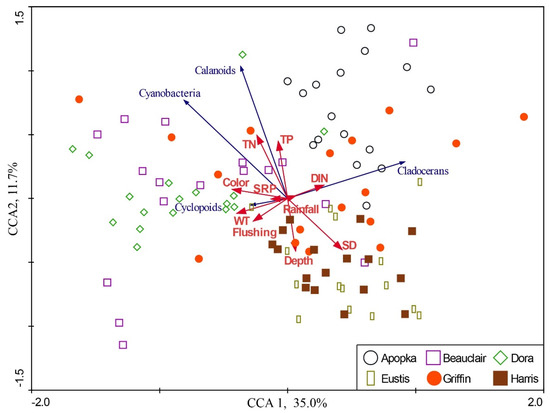
Figure 10.
Results of redundancy analysis, showing the first two canonical axes and the biological and environmental variables. Directions of vectors indicate correlations with the axes, with longer vectors indicating a higher degree of correlation. The first axis explains 35% of the overall variation in this dataset, while the second axis explains just under 12%. The most significant result is that cladocerans are separated from copepods and cyanobacteria along the first axis. One also can observe that the six lakes are separated in this two-dimensional space, indicating that they differ in their environmental conditions and zooplankton composition, despite being in close proximity and connected by canals.
4. Discussion
How will the zooplankton in shallow subtropical lakes change in response to global warming and associated changes in the Earth’s climate? The answer to this question is very complex because, as summarized by Jeppesen et al. [25], there is a variety of factors that could change, and affect the zooplankton, in addition to direct effects of increased temperature. Those factors include changes in sediment resuspension, resource composition, and occurrence of cyanobacterial toxins, fish community structure, and the availability of vascular plant beds as refuges from predators. One of the most-studied effects is warming of lakes, which has been examined with controlled experiments, space-for-time substitutions, time-series analyses, paleolimnology and with mathematical models.
A climate driver that has not been given much attention, yet could be highly important, is variation in water depth controlled by climate cycles such as the ENSO. If there is considerable variation in water depth and volume in shallow lakes, this can influence many ecological conditions, and in turn affect the zooplankton. During drought periods with lower depth, there may be expansion of vascular plants [26], a concentration of predators with their prey, and a concentration of nutrients that might stimulate cyanobacteria blooms [11]. In periods of shallow depth, shallow lakes also may be more prone to sediment resuspension, because the same amount of wind at the water surface will create greater shearing stress at the surface of the lake sediments.
It is known that in certain regions of the world, teleconnections such as the ENSO affect various physical, chemical and biological properties of lakes [6,7,8]. It is also projected that with further global warming, the variation between the warm and cold phases of the ENSO will become more extreme [27], leading to more extreme droughts and more intense rain events in areas affected by a teleconnection to that ocean cycle.
We examined long-term datasets on the zooplankton from six lakes in subtropical Florida in a region where rainfall and lake depth are affected by the ENSO [11], focusing on lakes with a very simple ecosystem structure because of a lack of any substantive vascular submerged plants. This provided an opportunity to assess responses of the zooplankton to climate variability mediated by changes in just the water temperature, chemistry and/or pelagic community composition. In an earlier study that focused just on cladoceran responses in one of the six lakes [11], it was observed that the maximal biomass of cladocerans was low in drought/low-water years, whereas it was much higher in years after high rainfall/deeper water. The difference was attributed to two possible effects: (1) negative effects of cyanobacteria, which were significantly more abundant in low-water years; and/or (2) negative effects of the lake’s predominately omnivorous fish, which presumably were more concentrated with the zooplankton prey in low water years. The lakes all had very high densities of year 1 to 3 gizzard shad [15,16] and in years with less water in the lakes, there logically were more fish per cubic meter of water.
In the present study, we expanded the scope to include a larger number of lakes, and considered the responses of cladocerans compared to calanoid and cyclopoid copepods. We developed a simple conceptual model that predicts a decline in the relative biomass of cladocerans relative to copepods during drought periods, because of the effects of a concentration of lake water on both predators and food resources. In these shallow lakes, there were considerable changes in volume over the period of record (Apopka, 75%, Beauclair 55%, Dora 81%, Eustis 32%, Griffin 40% and Harris 30%) and we predicted that at the lower end of the volume range, fish are concentrated with zooplankton and nutrients are concentrated with phytoplankton. Thus, greater predation on cladocerans coincided with increased interfere of feeding by those indiscriminate filter-feeders.
The results of this study support the conceptual diagram (Figure 1). Variation in rainfall explained a high percentage of the variation in lake depth, and as documented in earlier studies [10], rainfall over the Florida peninsula is tightly coupled with the ENSO. In turn, the biovolume of cyanobacteria—both the annual mean and the annual maxima—were significantly related to water depth in the lakes. The peak biomass of cyanobacteria was much greater in years when the lakes were shallow and held a lower volume of water than in years with deeper water and greater volume. This phenomenon has been observed in many other shallow eutrophic lakes, and documented as a concentration of nutrients in the water column that subsequently stimulates algal growth in the warm water where depth does not present an issue for light limitation [6,11,12]. We could not discern any relationships between depth and the biomass of crustacean zooplankton; however, as predicted, there was an inverse relationship between cladoceran biomass and cyanobacteria biovolume, but no such relationships for cyclopoids and calanoids. In sum, the result support the hypothesis that ENSO-generated droughts have the potential to shift the zooplankton towards copepod dominance during periods when there is very high biomass of cyanobacteria in subtropical lakes with high internal stores of nutrients.
While we were able to quantify relationships between rainfall and depth, between depth and cyanobacteria, and between cyanobacteria and cladocerans, we did not find a significant direct relationship between cladocerans and depth. In part, this reflects the fact that in each of those mentioned relationships, only a portion of the variation was explained. But also, it reflects the complex conditions that influence how the zooplankton respond to changes in depth among the lakes. This might be influenced by the degree to which reduced depth affected the lake volume, the amount of wind resuspension of sediments, and other attributes that we could not quantify.
It is not possible, based on the results, to determine the relative importance of changes in fish predation vs. cyanobacteria effects in driving the observed changes in dominance between cladocerans and copepods. A time-series study does not lend itself to determining the importance of these two mechanisms, because they likely are influenced by the same physical attribute: a concentration or dilution of lake water. In the case of fish predation, we know that these lakes have some of the highest recorded densities of omnivorous and planktivorous fish [15,16], and that their intense predation is largely responsible for the very low zooplankton to phytoplankton ratios and lack of large Daphnia in Florida and other subtropical lakes [1,2]. Simply by having the same number of fish concentrated with their prey in 30% to 81% less water volume could explain the changes in zooplankton, as cladocerans are highly sensitive to fish predation compared to copepods [28], in particular the dominant and relatively small species in Florida lakes, Arctodiaptomus dorsalis, which has the ability to avoid predation by executing rapid escape maneuvers [2]. In Lake Griffin, which was subjected to shad harvesting between 2000 and 2010, the highest zooplankton peaks, dominated by cladocerans, happened when shad catch per unit effort had been substantially reduced [29].
Concentrating gizzard shad in a reduced volume of water also could lead to greater relative nutrient effects in the water column. These omnivores also search food in the sediments. They transport massive quantities of nutrients to the water column [30], and the nutrient transport would impact the water more during droughts than during times of deeper water and greater volume. Finally, just a simple concentration effect, even lacking sediment transport, would lead to increased concentrations of nutrients, which favor phytoplankton growth. Cyanobacteria are known to have a greater relative effect on filter-feeding cladocerans than on copepods, so this too could be a reason for the change in community structure during droughts. For example, DeMott and Moxter [31] demonstrated in laboratory experiments that copepods have a high degree of behavioral flexibility in feeding, being able to feed size-selectively on filaments and colonies and avoid toxic forms. They concluded that these attributes ‘can be adaptive in lakes with significant populations of cyanobacteria’. Likewise, Bouvy et al. [32] and Koski et al. [33] found that copepods frequently coexist with dense cyanobacteria by grazing on alternative food items. Ger et al. [34] note that ‘in contrast, cladocerans have little ability to discriminate among individual food types and this may be an advantage when there is a high abundance of nutritious algae, while it is an impediment when there are toxic cyanobacteria in the water. DeMott [35] concluded that when toxic cyanobacteria dominate, the only option for cladocerans is to reject all particles that are collected by their feeding apparatus. Fabre et al. [36] recently evaluated the effects of toxic Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (the dominant species in most of the lakes that we studied) on a copepod (Notodiaptomus) and a cladoceran (Daphnia). The clearance rates of the cladoceran were significantly more affected by the presence of the cyanobacteria, and the authors concluded that this suggests ‘differential consequences for their survival and success in warm freshwaters’. Many other laboratory, field and mesocosm studies also demonstrated greater impacts of cyanobacteria blooms on cladocerans than on copepods [37,38,39,40,41,42].
In summary, we identified a linkage between variation in rainfall and lake depth in a group of shallow eutrophic lakes in central Florida, USA, where we had earlier documented a relationship between the ENSO sea surface temperature anomaly and rainfall [11]. The lakes have many features of shallow lakes throughout the subtropics, where climate variation linked with the ENSO also influences rainfall and drought. We documented that when the lakes are shallow and their volume is greatly reduced, cyanobacteria becomes more abundant, and the ratio of cladocerans to copepods declines coincidently. The available data do not allow us to differentiate between changes in fish predation vs. cyanobacteria effects on the zooplankton. It may be that during droughts, when lake volume is greatly reduced, there is a ‘perfect storm’ of adverse conditions for cladocerans. They are impacted by increases in both top-down control by fish and bottom-up control by inedible or harmful food resources. Regardless, this study indicates that climate variability can affect not only water depth but also the structure of the plankton food web in shallow lakes where rainfall is affected by teleconnections. Because the magnitudes of both positive and negative ENSO sea-surface anomalies are expected to increase with global warming [27], there is a potential for much greater variability in the dominance of cladoceran vs. copepod zooplankton in shallow eutrophic lakes in future decades.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the St. Johns River Water Management District for providing the long-term water quality and plankton data used in this study.
Author Contributions
Gaohua Ji and Karl Havens analyzed the data and developed the initial and final versions of this manuscript. John Beaver contributed his expertise and insights by conducting all the analysis of zooplankton samples and some of the phytoplankton samples, and by supporting the writing of the final manuscript. Rolland Fulton provided the long-term data and contributed his expertise by supporting writing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Jacobsen, B.A.; Hansen, R.S.; Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Mazzeo, N.; Branco, C.W.C. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulation-the successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Beaver, J.R. Composition, size, and biomass of zooplankton in large productive Florida lakes. Hydrobiologia 2011, 668, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Adrian, R.; De Senerpont Domis, L.; Elser, J.J.; Gaedke, U.; Ibelings, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Lürling, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Mooij, W.M.; et al. Beyond the plankton ecology group (PEG) model: Mechanisms driving plankton succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evolut. Syst. 2012, 43, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straile, D. Zooplankton biomass dynamics in oligotrophic versus eutrophic conditions: A test of the PEG model. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Schelske, C.L. The importance of considering biological processes when setting total maximum daily loads (TMDL) for phosphorus in shallow lakes and reservoirs. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 113, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, B.; Diogo, F.Â.O.; Mauro, M.; Marc, P.; Ariadne, M. Occurrence of Cylindrospermopsis (cyanobacteria) in 39 Brazilian tropical reservoirs during the 1998 drought. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, K.; Cho, E.-A.; Kim, H.-W.; Joo, G.-J. Microcystis bloom formation in the lower Nakdong River, South Korea: Importance of hydrodynamics and nutrient loading. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cleave, K.; Lenters, J.D.; Wang, J.; Verhamme, E.M. A regime shift in Lake Superior ice cover, evaporation, and water temperature following the warm El Niño winter of 1997–1998. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darchambeau, F.; Borges, A.V.; Sarmento, H.; Leporcq, B.; Isumbisho, P.M.; Alunga, G.; Masilya, P.M.; Descy, J.-P. Teleconnections between ecosystem productivity and climate indices in a tropical great lake. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2013, Vienna, Austria, 7–12 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abtew, W.; Trimble, P. El Niño–Southern Oscillation link to South Florida hydrology and water management applications. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 4255–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Fulton, R.S.; Beaver, J.R.; Samples, E.E.; Colee, J. Effects of climate variability on cladoceran zooplankton and cyanobacteria in a shallow subtropical lake. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Ji, G.; Beaver, J.R.; Fulton, R.S., III; Teacher, C.E. Dynamics of cyanobacteria blooms are linked to the hydrology of shallow Florida lakes and provide insight into possible impacts of climate change. Hydrobiologia 2017. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, R.S. Nutrient Loading and Water Quality Trends in the Upper Ocklawaha Basin Lakes through 2014; St. Johns River Water Management District: Palatka, FL, USA, 2016; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Coveney, M.F.; Lowe, E.F.; Battoe, L.E.; Marzolf, E.R.; Conrow, R. Response of a eutrophic, shallow subtropical lake to reduced nutrient loading. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1718–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.J.; Allen, M.S.; Schaus, M.H.; Buck, D.G.; Beaver, J.R. Evaluating short-term effects of omnivorous fish removal on water quality and zooplankton at a subtropical lake. Hydrobiologia 2010, 655, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.J.; Allen, M.S. A whole-lake density reduction to assess compensatory responses of gizzard shad Dorosoma cepedianum. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Iglesias, C.; De Mello, F.T.; Clemente, J.M.; Jensen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, C.; Mazzeo, N.; Meerhoff, M.; Lacerot, G.; Clemente, J.M.; Scasso, F.; Kruk, C.; Goyenola, G.; García-Alonso, J.; Amsinck, S.L.; et al. High predation is of key importance for dominance of small-bodied zooplankton in warm shallow lakes: Evidence from lakes, fish exclosures and surface sediments. Hydrobiologia 2011, 667, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, J.F.; McKee, G.D. Methods of Chemical Analysis of Water and Waste; Section 9.3, USEPA/600/4-79/020; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1983.
- Havens, K.E.; East, T.L.; Beaver, J.R. Experimental studies of zooplankton-phytoplankton-nutrient interactions in a large subtropical lake (Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA). Freshw. Biol. 1996, 36, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, C.D. Enumeration of freshwater phytoplankton concentrated on the membrane filter1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1960, 5, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.-D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, E. The estimation of the abundance and biomass of zooplankton in samples. In A Manual on Methods for the Assessment of Secondary Productivity in Fresh Waters; Downing, J.A., Rigler, F.H., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 228–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide to Canoco for Windows: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Davidson, T.A.; Trolle, D.; Sondergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Beklioglu, M.; Brucet, S.; Volta, P.; Gonzalez-Bergonzoni, I.; et al. Climate change impacts on lakes: An integrated ecological perspective based on a multi-faceted approach, with special focus on shallow lakes. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 88–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Sharfstein, B.; Brady, M.A.; East, T.L.; Harwell, M.C.; Maki, R.P.; Rodusky, A.J. Recovery of submerged plants from high water stress in a large subtropical lake in Florida, USA. Aquat. Bot. 2004, 78, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Santoso, A.; Wang, G.; Yeh, S.-W.; An, S.-I.; Cobb, K.M.; Collins, M.; Guilyardi, E.; Jin, F.-F.; Kug, J.-S.; et al. ENSO and greenhouse warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.; Murphy, D.W.; Fan, L.; Webster, D.R. Sensory-motor systems of copepods involved in their escape from suction feeding. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2015, 55, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, R.S.; Godwin, W.F.; Schaus, M.H. Water quality changes following nutrient loading reduction and biomanipulation in a large shallow subtropical lake, Lake Griffin, Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 2015, 753, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaus, M.H.; Vanni, M.J.; Wissing, T.E.; Bremigan, M.T.; Garvey, J.E.; Stein, R.A. Nitrogen and phosphorus excretion by detritivorous gizzard shad in a reservoir ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, W.R.; Moxter, F. Foraging cyanobacteria by copepods: Responses to chemical defense and resource abundance. Ecology 1991, 72, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, B.; Marc, P.; Marc, T. Effects of a cyanobacterial bloom (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) on bacteria and zooplankton communities in ingazeira reservoir (Northeast Brazil). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 25, 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Koski, M.; Schmidt, K.; Engstrom-Ost, J.; Viitasalo, M.; Jonasdottir, S.; Repka, S.; Sivonen, K. Calanoid copepods feed and produce eggs in the presence of toxic cyanobacteria Nodularia spumigena. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 878–885. [Google Scholar]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.-A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMott, W.R. The role of taste in food selection by freshwater zooplankton. Oecologia 1986, 69, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, A.; Lacerot, G.; de Paiva, R.R.; Soares, M.C.S.; de Magalhães, V.F.; Bonilla, S. South American PSP toxin-producing Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) decreases clearance rates of cladocerans more than copepods. Hydrobiologia 2017, 785, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrlack, T.; Dittmann, E.; Borner, T.; Christoffersen, K. Effects of cell-bound microcystins on survival and feeding of Daphnia spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadouani, A.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; Prepas, E.E. Effects of experimentally induced cyanobacterial blooms on crustacean zooplankton communities. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S. Ecology of harmful cyanobacteria. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Granéli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lurling, M.; van der Grinten, E. Life-history characteristics of Daphnia exposed to dissolved microcystin-LR and to the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa with and without microcystins. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, L.-A.; Gustafsson, S.; Rengefors, K.; Bomark, L. Cyanobacterial chemical warfare affects zooplankton community composition. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perga, M.E.; Domaizon, I.; Guillard, J.; Hamelet, V.; Anneville, O. Are cyanobacterial blooms trophic dead ends? Oecologia 2013, 172, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).