Treatment of Simulated Coalbed Methane Produced Water Using Direct Contact Membrane Distillation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents and Membrane Module
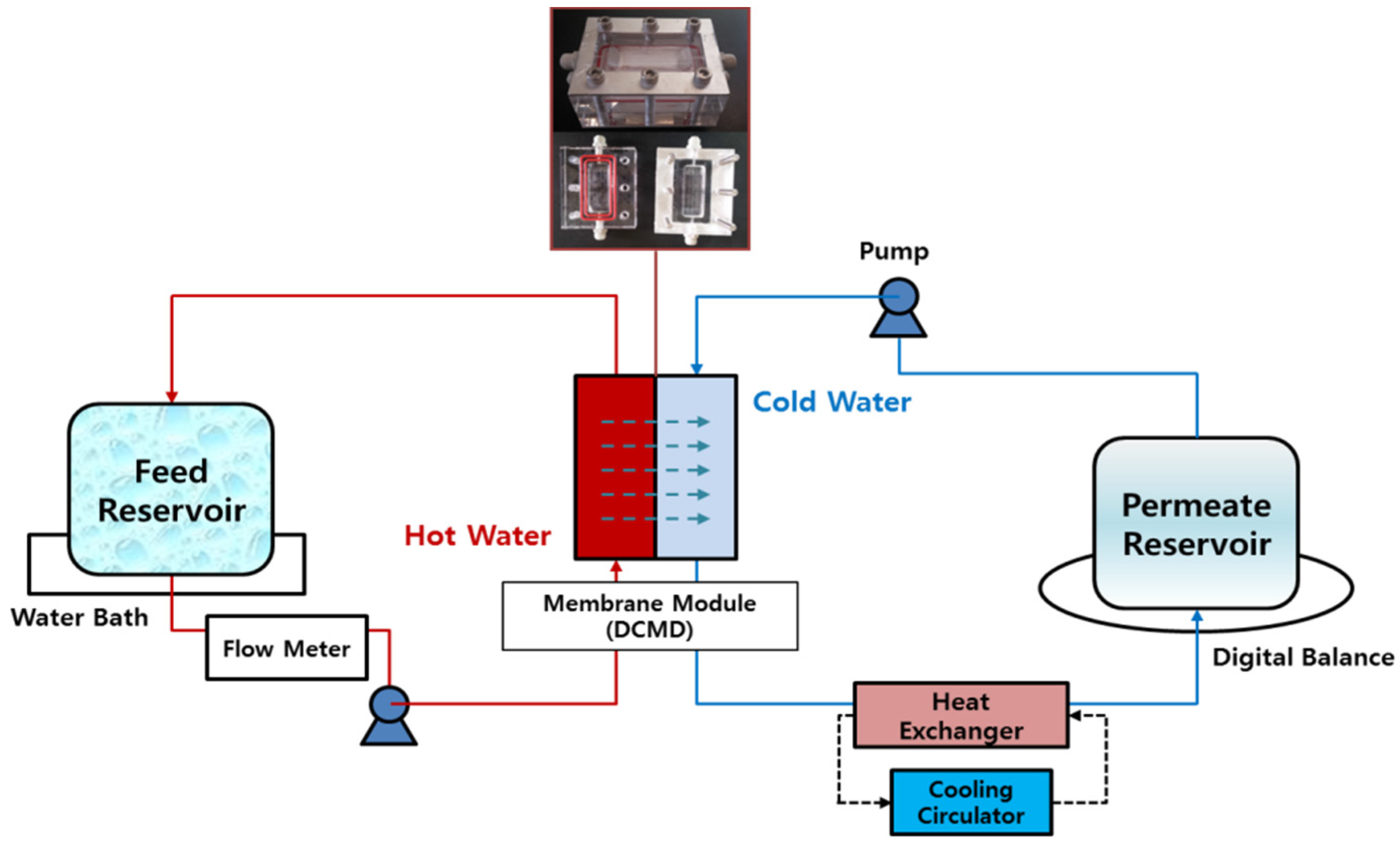
2.2. Set-up of DCMD
2.3. Experimental Procedures and Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Performance of DCMD Systems
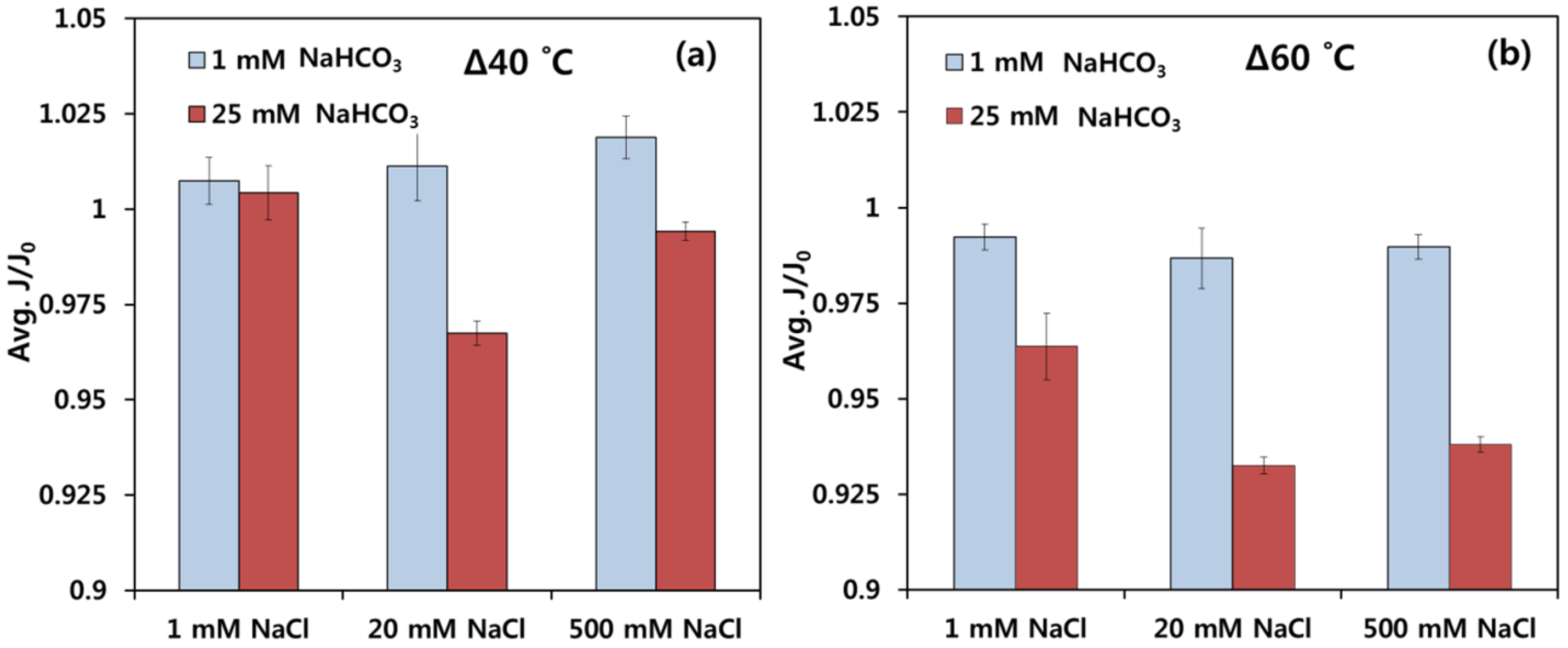
3.2. Permeate Flux Variation at Δ40 °C and Δ60 °C
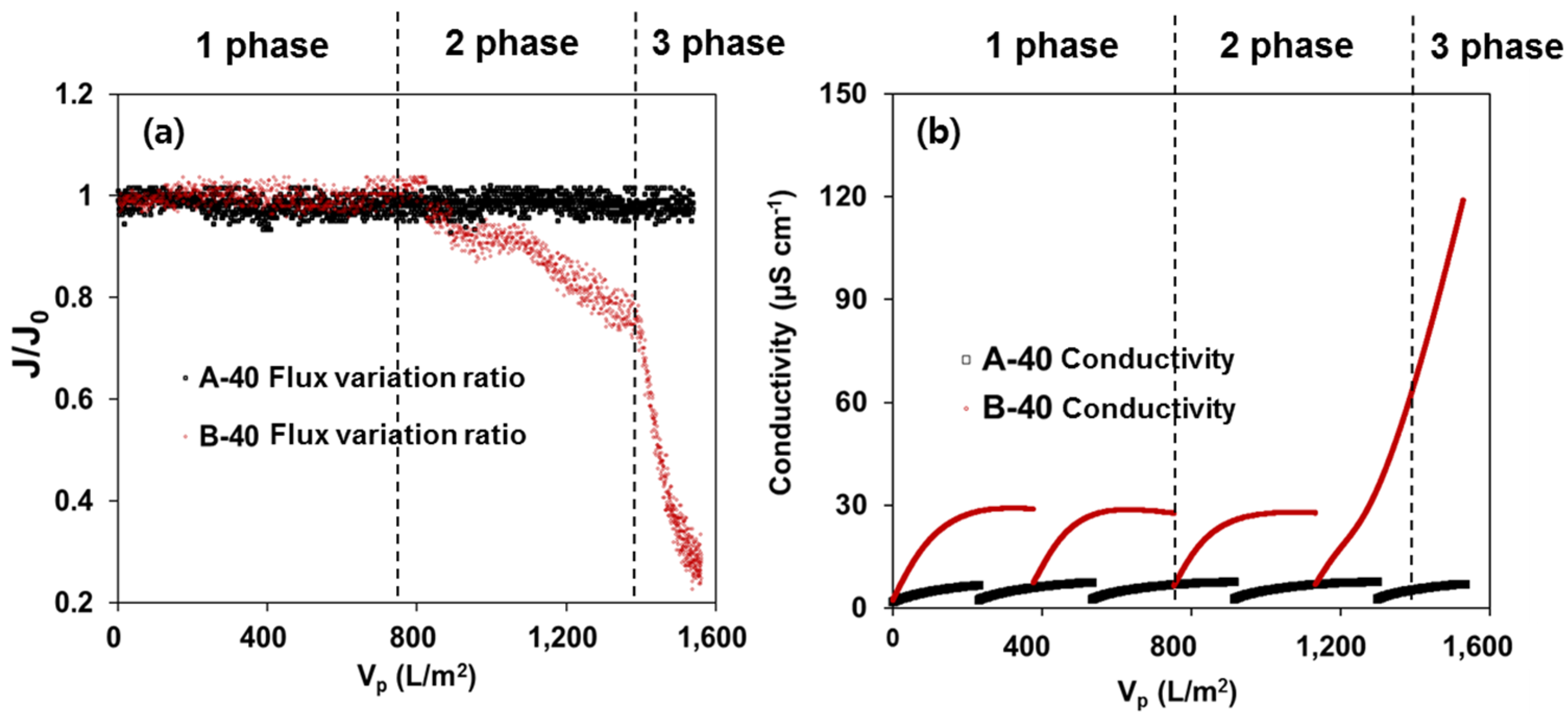
3.3. Long-Term Distillation
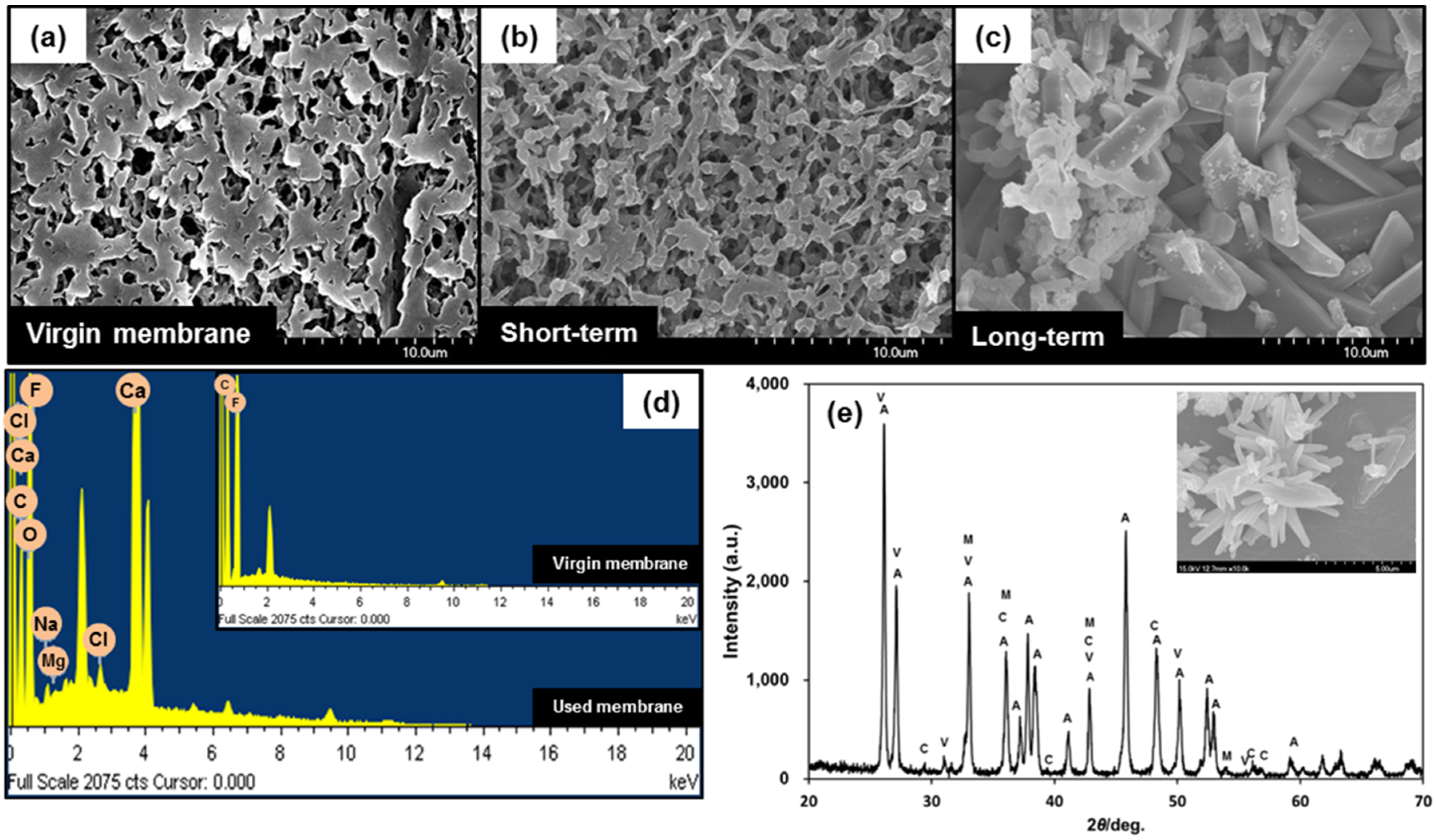
3.4. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBM | Coalbed methane |
| TDS | Total dissolved solids |
| DCMD | Direct contact membrane distillation |
| RO | Reverse osmosis |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| FE-SEM | Field-emission scanning electron microscope |
| EDS | Energy dispersive spectrometer |
References
- Nuccio, V.F. Coal-Bed Methane: Potential and Concerns; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs123-00/fs123-00/pdf (accessed on 2 Feburary 2012).
- ALL Consulting. Handbook on Coalbed Methane Produced Water: Management and Beneficial Use Alternatives; U.S. Department of Energy: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hamawand, I.; Yusaf, T.; Hamawand, S.G. Coal seam gas and associated water: A review paper. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2013, 22, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumlee, M.H.; Debroux, J.-F.; Taffler, D.; Graydon, J.W.; Mayer, X.; Dahm, K.G.; Hancock, N.T.; Guerra, K.L.; Xu, P.; Drewes, J.E.; et al. Coalbed methane produced water screening tool for treatment technology and beneficial use. J. Unconv. Oil Gas Resour. 2014, 5, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.J.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, L. Coalbed methane produced water in China: Status and environmental issues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6964–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majee, U.; Chattopadhyay, G.N.; Chaudhury, S. Monitoring of soil environment under influence of coal bed water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, A.; Gawde, A.; Cantrell, C.L.; Baxter, H.L.; Joyce, B.L.; Stewart, C.N.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Effects of Produced Water on Soil Characteristics, Plant Biomass, and Secondary Metabolites. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRC. Management and Effects of Coalbed Methane Produced Water in the Western United States; National Research Council of the National Academies, The National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Drewes, J.E. Viability of nanofiltration and ultra-low pressure reverse osmosis membranes for multi-beneficial use of methane produced water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Gray, S.; Duke, M.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Scaling control during membrane distillation of coal seam gas reverse osmosis brine. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Chivas, A.R.; Nelemans, B.; Duke, M.; Gray, S.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Treatment of RO brine from CSG produced water by spiral-wound air gap membrane distillation—A pilot study. Desalination 2015, 366, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangarkar, B.L.; Sane, M.G.; Guddad, M. Reverse Osmosis and Membrane Distillation for Desalination of Groundwater: A Review. ISRN Mater. Sci. 2011, 2011, 523124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffour, N.; Lattemann, S. Renewable energy-driven innovative energy-efficient desalination technologies. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, F.; Ruskowitz, J.A. Renewable water: Direct contact membrane distillation coupled with solar ponds. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbatly, R.; Chiam, C.K. Evaluation of geothermal energy in desalination by vacuum membrane distillation. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Dumee, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, J.D.; Duke, M.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S. Advances in Membrane Distillation for Water Desalination and Purification Applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Payo, M.C.; Izquierdo-Gil, M.A.; Fernandez-Pineda, C. Air gap membrane distillation of aqueous alcohol solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 169, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.K.; Rhadfi, T.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A.; Khraisheh, M.; Hilal, N. Reducing flux decline and fouling of direct contact membrane distillation by utilizing thermal brine from MSF desalination plant. Desalination 2016, 379, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.D.; Cath, T. A scaling mitigation approach during direct contact membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.; Ghaffour, N.; Al-Saadi, A.S.; Amy, G. Performance of different hollow fiber membranes for seawater desalination using membrane distillation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 2786–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, M.M.A.; Kargari, A.; Bastani, D.; Fatehi, L. Production of drinking water from seawater using membrane distillation (MD) alternative: Direct contact MD and sweeping gas MD approaches. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 2372–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidani, S.; Curcio, E.; Macedonio, F.; Profio, G.D.; Al-Hinai, H.; Drioli, E. Potential of membrane distillation in seawater desalination: Thermal efficiency, sensitivity study and cost estimation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.M.; Ma, Z.; Liao, X.; Kosaraju, P.B.; Irish, J.R.; Sirkar, K.K. Pilot plant studies of novel membranes and devices for direct contact membrane distillation-based desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahm, K.G.; Guerra, K.L.; Xu, P.; Drewes, J.E. Composite Geochemical Database for Coalbed Methane Produced Water Quality in the Rocky Mountain Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7655–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Sirkar, K.K.; Gilron, J. Studies on scaling of membranes in desalination by direct contact membrane distillation: CaCO3 and mixed CaCO3/CaSO4 systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1844–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Prakash, P.; Sirkar, K.K. Deoiled Produced Water Treatment Using Direct-Contact Membrane Distillation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13439–13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.W.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.D. Heat and Mass-Transfer in Membrane Distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 33, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchrit, R.; Boubakri, A.; Hafiane, A.; Bouguecha, S.A. Direct contact membrane distillation: Capability to treat hyper-saline solution. Desalination 2015, 376, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alklaibi, A.M.; Lior, N. Heat and mass transfer resistance analysis of membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Shi, J.; Won, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Maeng, S.K.; Song, K.G. Membrane distillation combined with an anaerobic moving bed biofilm reactor for treating municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2015, 71, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, L.; Ghaffour, N.; Alsaadi, A.S.; Nunes, S.P.; Amy, G.L. Performance evaluation of the DCMD desalination process under bench scale and large scale module operating conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.B.; Ma, R.; Zhang, W.; Fane, A.G.; Li, J. Direct contact membrane distillation mechanism for high concentration NaCl solutions. Desalination 2006, 188, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Wang, J.L. Treatment of radioactive wastewater using direct contact membrane distillation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Li, B.; Sirkar, K.K.; Gilron, J.L. Direct contact membrane distillation-based desalination: Novel membranes, devices, larger-scale studies, and a model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 2307–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; He, F.; Song, L.; Gilron, J.; Sirkar, K.K. Desalination with a cascade of cross-flow hollow fiber membrane distillation devices integrated with a heat exchanger. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 1780–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Bouchrit, R.; Hafiane, A.; Bouguecha, S.A. Fluoride removal from aqueous solution by direct contact membrane distillation: Theoretical and experimental studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10493–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Treatment of high salinity solutions: Application of air gap membrane distillation. Desalination 2012, 287, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.J.; Bubela, B. Transformation of Nesquehonite into Hydromagnesite. Chem. Geol. 1973, 12, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Alkaline scaling in the membrane distillation process. Desalination 2008, 228, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Desalination of thermally softened water by membrane distillation process. Desalination 2010, 257, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Gao, X.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Study of membrane fouling in cross-flow vacuum membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinger, D.M.; Swaminathan, J.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A.; Lienhard, J.H. Scaling and fouling in membrane distillation for desalination applications: A review. Desalination 2015, 356, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muryanto, S. Calcium Carbonate Scale Formation in Pipes: Effect of Flow Rates, Temperature, and Malic Acid as Additives on the Mass and Morphology of the Scale. Procedia Chem. 2014, 9, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.H.; Wang, F.; Giammar, D.E. Precipitation of magnesium carbonates as a function of temperature, solution composition, and presence of a silicate mineral substrate. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2011, 28, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto, B.; Martos, C.; Peña, J.L.; Rodríguez, R.; Pastor, G. Effects in the solubility of CaCO3: Experimental study and model description. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 324, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakulski, K.; Gryta, M. Water demineralisation by NF/MD integrated processes. Desalination 2005, 177, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Influence of polypropylene membrane surface porosity on the performance of membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, O.S.; Savenko, V.S. Influence of Dissolved Organic-Matter on the Kinetics of Homogeneous Precipitation of Aragonite in Seawater. Okeanologiya 1994, 34, 833–841. [Google Scholar]
- Pokrovsky, O.S. Precipitation of calcium and magnesium carbonates from homogeneous supersaturated solutions. J. Cryst. Growth 1998, 186, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Salts | Concentration (mM) |
|---|---|
| NaCl | 1, 20, 500 |
| CaCl2·2H2O | 5 |
| MgCl2 | 5 |
| NaHCO3 | 1, 25 |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Supplier | Millipore (GVHP) |
| Pore size (μm) | 0.22 |
| Thickness (μm) | 125 |
| Porosity (%) | 75 |
| Effective area (m2) | 1.75 × 10−3 |
| Contact angle (°) | 118 |
| Short-Term Distillation | Long-Term Distillation | |
|---|---|---|
| Distillation time | 360 min | 5400 min |
| Transmembrane temperature (ΔT) | 40 °C and 60 °C | 40 °C |
| Cross-flow velocity (CFV) | 0.18 m·s−1 | 0.18 m·s−1 |
| pH of feed solution | 8.3 | 8.3 |
| Measurement | Flux, Conductivity | |
| Characterization | - | FE-SEM/EDS, XRD |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, D.-W.; Song, H.; Yoon, K.; Kim, S.; Han, J.; Cho, J. Treatment of Simulated Coalbed Methane Produced Water Using Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Water 2016, 8, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050194
Cho D-W, Song H, Yoon K, Kim S, Han J, Cho J. Treatment of Simulated Coalbed Methane Produced Water Using Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Water. 2016; 8(5):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050194
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Dong-Wan, Hocheol Song, Kwangsuk Yoon, Sewoon Kim, Jeongmin Han, and Jinwoo Cho. 2016. "Treatment of Simulated Coalbed Methane Produced Water Using Direct Contact Membrane Distillation" Water 8, no. 5: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050194
APA StyleCho, D.-W., Song, H., Yoon, K., Kim, S., Han, J., & Cho, J. (2016). Treatment of Simulated Coalbed Methane Produced Water Using Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Water, 8(5), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050194





