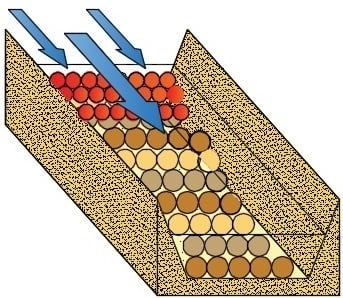
Using a Modified Lane’s Relation in Local Bed Scouring Studies in the Laboratory Channel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
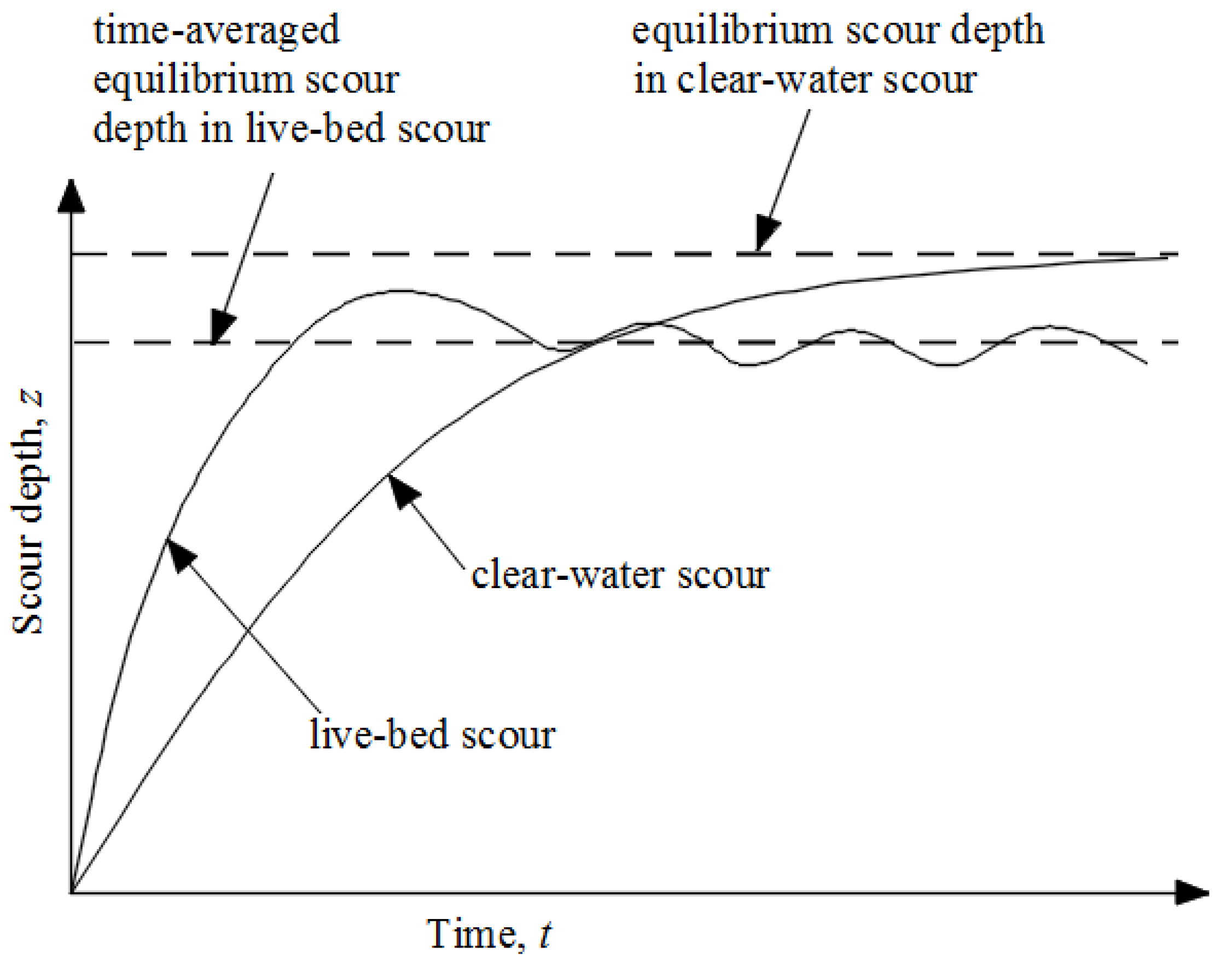
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Modified Lane's Relation
2.2. Aim and Scope of Research

2.3. Description of the Test Stand
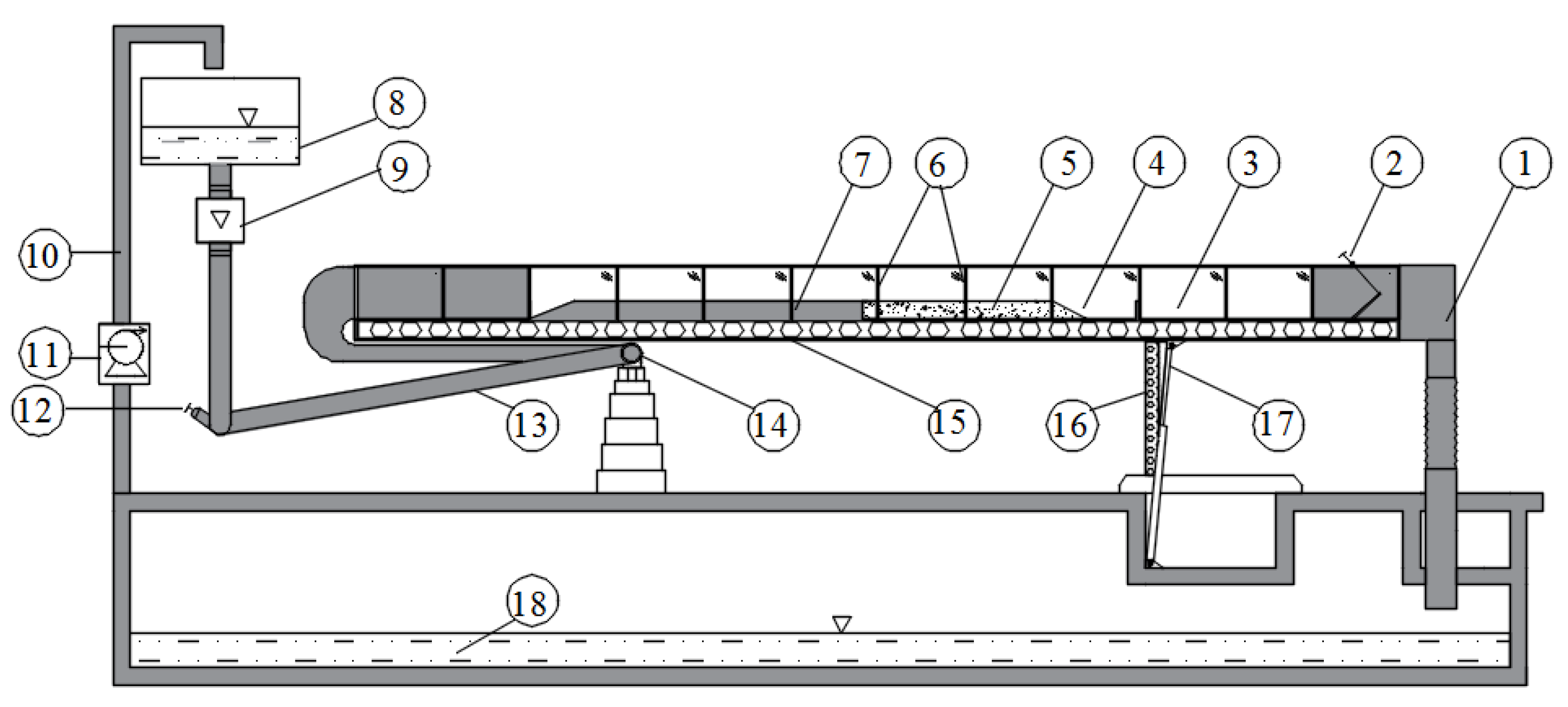

2.4. Methodology and the Scope of the Study

| Number of Measurement | Qw | H | q | T | ν | Vs | t | zmax | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m3·s−1) | (m) | (m3·s−1∙m−2) | (°C) | (1×10−6∙m2·s−1) | (-) | (m3) | (h) | (cm) | |
| 1 | 0.020 | 0.10 | 0.003 | 16.8 | 1.086 | 14.72 | 0.00153 | 7.25 | 0.42 |
| 2 | 0.025 | 0.10 | 0.004 | 16.5 | 1.094 | 14.65 | 0.01841 | 10.50 | 3.41 |
| 3 | 0.025 | 0.12 | 0.004 | 16.1 | 1.104 | 14.56 | 0.00151 | 6.50 | 0.41 |
| 4 | 0.030 | 0.10 | 0.005 | 16.5 | 1.094 | 14.65 | 0.03701 | 5.00 | 4.74 |
| 5 | 0.030 | 0.15 | 0.005 | 16.7 | 1.089 | 14.70 | 0.00151 | 6.00 | 0.47 |
| 6 | 0.035 | 0.12 | 0.006 | 16.3 | 1.099 | 14.61 | 0.04681 | 8.50 | 5.64 |
| 7 | 0.035 | 0.15 | 0.006 | 15.9 | 1.109 | 14.52 | 0.00404 | 7.50 | 2.17 |
| 8 | 0.040 | 0.10 | 0.007 | 16.0 | 1.107 | 14.54 | 0.09746 | 9.25 | 11.82 |
| 9 | 0.040 | 0.12 | 0.007 | 17.2 | 1.076 | 14.81 | 0.05500 | 10.50 | 9.28 |
| 10 | 0.040 | 0.15 | 0.007 | 17.0 | 1.081 | 14.77 | 0.01900 | 8.00 | 4.23 |
| 11 | 0.040 | 0.20 | 0.007 | 16.8 | 1.086 | 14.72 | 0.00240 | 6.00 | 0.59 |
| 12 | 0.043 | 0.12 | 0.007 | 16.6 | 1.091 | 14.68 | 0.06800 | 8.50 | 7.64 |
| 13 | 0.045 | 0.15 | 0.008 | 16.0 | 1.107 | 14.54 | 0.04500 | 8.50 | 6.29 |
3. Results and Discussion
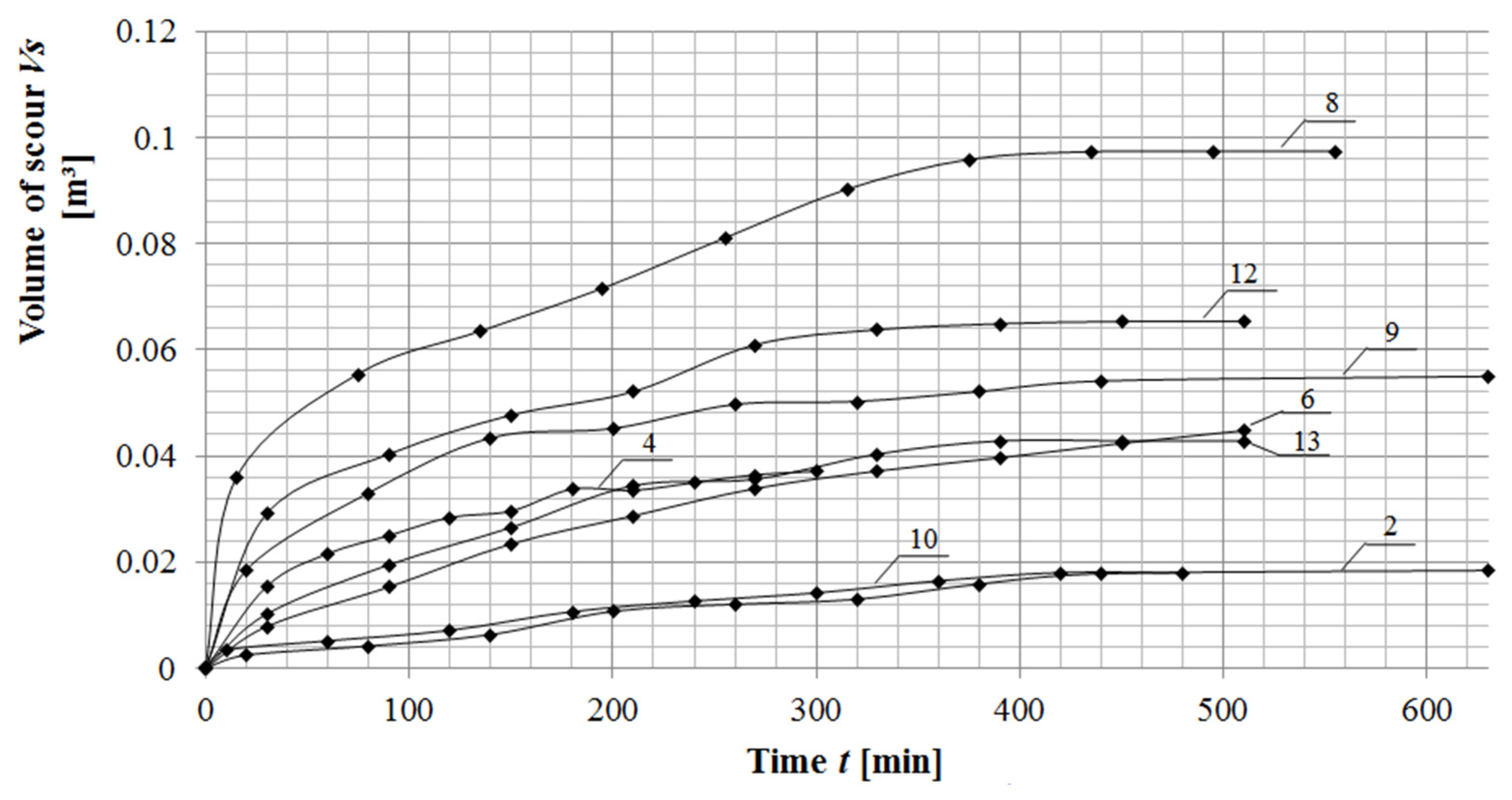

| No of Measurement | Qw | H | Qs | S | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m3·s−1) | (m) | (1 × 10−6·m3·s−1) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (1 × 10−6 m3·s−1) | (1 × 10−6 m3·s−1) | |
| 1 | 0.020 | 0.10 | 0.059 | 14.72 | 5.80 | 0.0005 | 0.15 | 10.00 |
| 2 | 0.025 | 0.10 | 0.487 | 14.65 | 5.80 | 0.0007 | 1.23 | 17.50 |
| 3 | 0.025 | 0.12 | 0.065 | 14.56 | 4.83 | 0.0003 | 0.19 | 7.50 |
| 4 | 0.030 | 0.10 | 2.056 | 14.65 | 5.80 | 0.0014 | 5.19 | 42.00 |
| 5 | 0.030 | 0.15 | 0.070 | 14.70 | 3.87 | 0.0004 | 0.27 | 12.92 |
| 6 | 0.035 | 0.12 | 1.530 | 14.61 | 4.83 | 0.0010 | 4.62 | 35.00 |
| 7 | 0.035 | 0.15 | 0.150 | 14.52 | 3.87 | 0.0005 | 0.56 | 17.50 |
| 8 | 0.040 | 0.10 | 2.927 | 14.54 | 5.80 | 0.0013 | 7.34 | 52.00 |
| 9 | 0.040 | 0.12 | 1.455 | 14.81 | 4.83 | 0.0010 | 4.46 | 40.00 |
| 10 | 0.040 | 0.15 | 0.660 | 14.77 | 3.87 | 0.0009 | 2.52 | 34.46 |
| 11 | 0.040 | 0.20 | 0.111 | 14.72 | 2.90 | 0.0002 | 0.56 | 8.00 |
| 12 | 0.043 | 0.12 | 2.222 | 14.68 | 4.83 | 0.0012 | 6.75 | 51.60 |
| 13 | 0.045 | 0.15 | 1.471 | 14.54 | 3.87 | 0.0009 | 5.53 | 40.50 |

- -
- initial water discharge before the flood occurrence with
- -
- peak-flow water discharge with
| No. of Measurement | Qw | H | zmax | Qs | Rb | Fr | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m3·s−1) | (m) | (m) | (1 × 10−6·m3·s−1) | (m) | (Pa) | (-) | () | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| 1 | 0.020 | 0.10 | 0.0042 | 0.059 | 0.0923 | 0.45 | 0.0451 | 0.021 | 12.1 | 0.0320 | 0.35 |
| 2 | 0.025 | 0.10 | 0.0341 | 0.487 | 0.0923 | 0.63 | 0.0631 | 0.025 | 14.2 | 0.0328 | 0.44 |
| 3 | 0.025 | 0.12 | 0.0041 | 0.065 | 0.1088 | 0.32 | 0.0319 | 0.018 | 10.0 | 0.0311 | 0.33 |
| 4 | 0.030 | 0.10 | 0.0474 | 2.056 | 0.0923 | 1.27 | 0.1263 | 0.036 | 20.2 | 0.0345 | 0.52 |
| 5 | 0.030 | 0.15 | 0.0047 | 0.070 | 0.1325 | 0.52 | 0.0518 | 0.023 | 13.0 | 0.0323 | 0.28 |
| 6 | 0.035 | 0.12 | 0.0564 | 1.530 | 0.1088 | 1.07 | 0.1064 | 0.033 | 18.5 | 0.0341 | 0.46 |
| 7 | 0.035 | 0.15 | 0.0217 | 0.150 | 0.1325 | 0.65 | 0.0648 | 0.025 | 14.3 | 0.0328 | 0.33 |
| 8 | 0.040 | 0.10 | 0.1182 | 2.927 | 0.0923 | 1.18 | 0.1173 | 0.034 | 19.2 | 0.0343 | 0.70 |
| 9 | 0.040 | 0.12 | 0.0928 | 1.455 | 0.1088 | 1.07 | 0.1064 | 0.033 | 18.8 | 0.0342 | 0.53 |
| 10 | 0.040 | 0.15 | 0.0423 | 0.660 | 0.1325 | 1.17 | 0.1166 | 0.034 | 19.6 | 0.0344 | 0.38 |
| 11 | 0.040 | 0.20 | 0.0059 | 0.111 | 0.1692 | 0.33 | 0.0331 | 0.018 | 10.4 | 0.0312 | 0.25 |
| 12 | 0.043 | 0.12 | 0.0764 | 2.222 | 0.1088 | 1.28 | 0.1276 | 0.036 | 20.3 | 0.0345 | 0.57 |
| 13 | 0.045 | 0.15 | 0.0629 | 1.471 | 0.1325 | 1.17 | 0.1166 | 0.034 | 19.2 | 0.0342 | 0.43 |
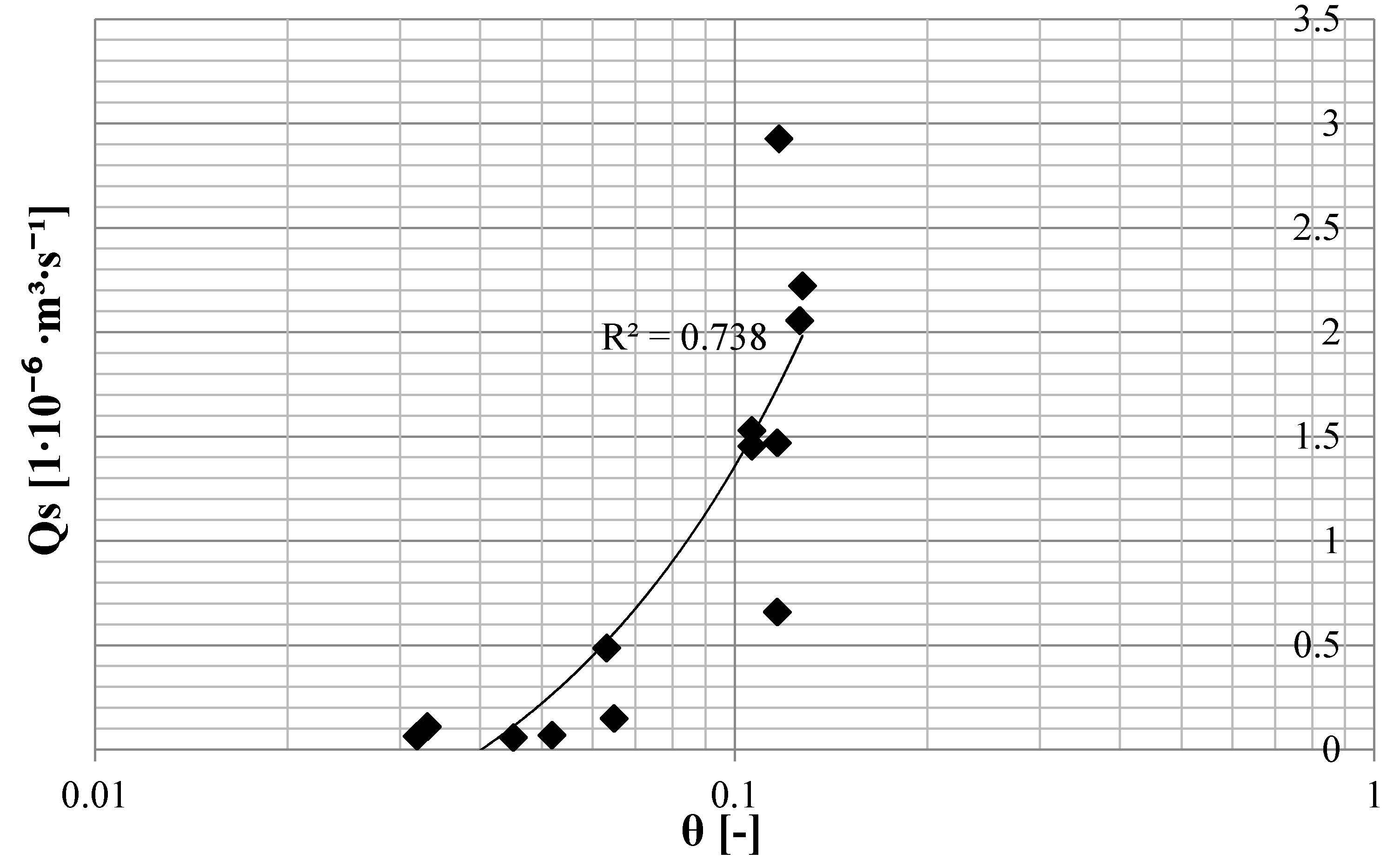
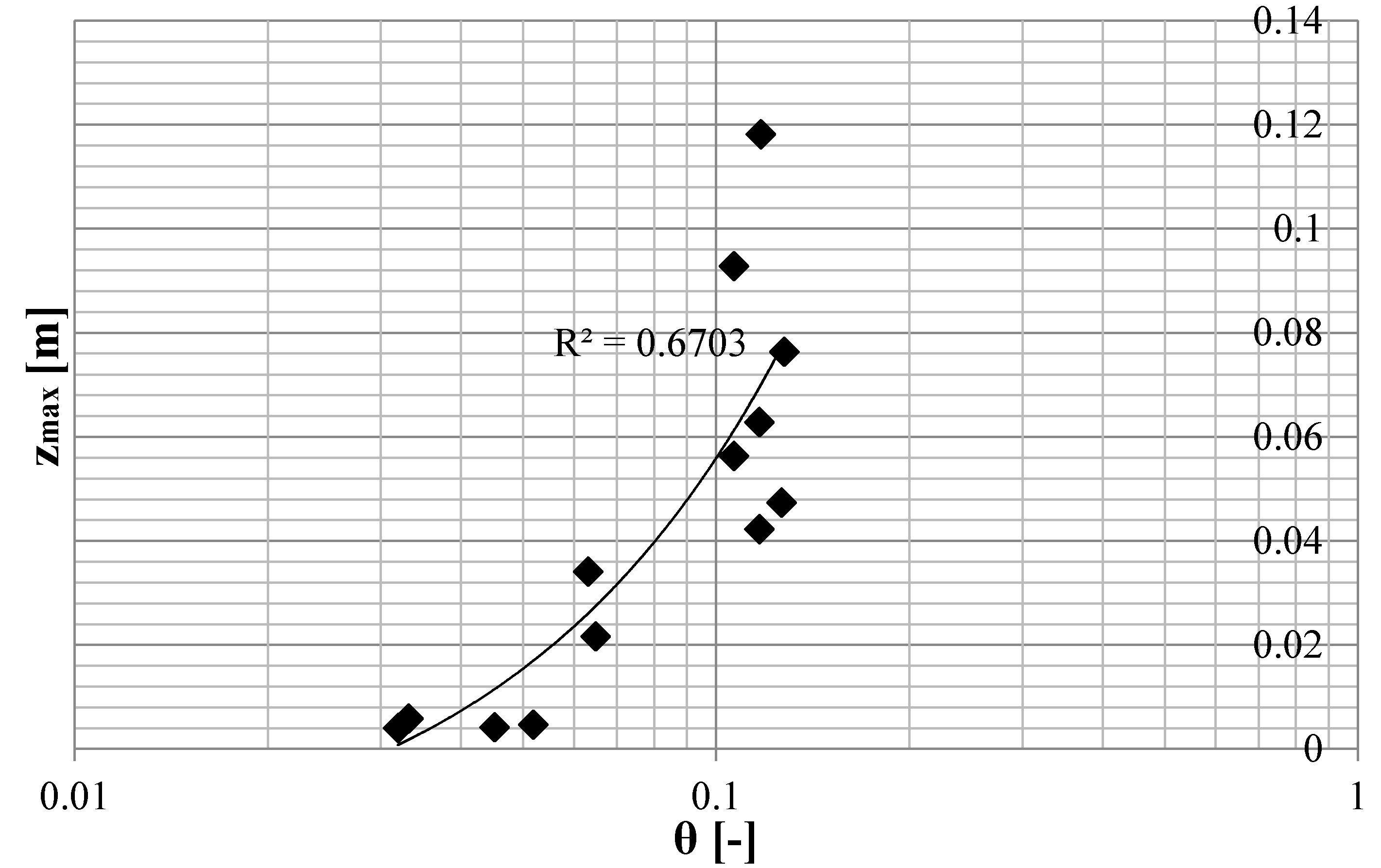
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lane, E.W. The importance of fluvial morphology in hydraulic engineering. In Proceedings of American Society of Civil Engineers, New York, NY, USA, July 1955; pp. 1–17.
- Aderibigbe, O.; Rajaratnam, N. Effect of sediment gradation on erosion by plane turbulent wall jets. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, R.; Marion, A. Time evolution of scouring downstream of bed sills. J. Hydraul. Res. 2003, 41, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, M.A.; Marion, A.; Comiti, F.; Gaudio, R. Local scouring in low and high gradient streams at bed sills. J. Hydraul. Res. 2002, 40, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, B. The physics of local scour at bridge piers. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion, Tokyo, Japan, 5–7 November 2008.
- Dust, D.; Wohl, E. Conceptual model for complex river responses using an expanded Lane’s relation. Geomorphology 2012, 139–140, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Q.; Liu, X.; Nanson, G.C. Commentary on a “conceptual model for complex river responses using an expanded Lane’s diagram by David Dust and Ellen Wohl”. Geomorphology 2014, 209, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A. Fluvial System; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Barbhuiya, A.K.; Dey, S. Local scour at abutments: A review. Sadhana 2004, 29, 449–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabert, J.; Engeldinger, P. Etude des Affouillements Autour des Piles des Ponts; Laboratoire d’Hydraulique: Chatou, France, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Brookes, A. Channelized Rivers—Perspectives for Environmental Management; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Church, M. Channel morphology and typology. In The River Handbook; Calow, P., Petts, G.E., Eds.; Blecwell; Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1992; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hickin, E.J. The analysis of river-planform responses to changes in discharge. In River Channel Changes; Gregory, K.J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Werburton, J.; Danks, M.; Wishart, D. Stability of an upland gravel-bed stream Swinhope Burn, Northern England. Catena 2002, 49, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Castal Seas; Aqua Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, P. Results of Specific Density Calculations for Sand and Crushed Aggregate; The Laboratory of Chemistry and Water and Wastewater Technology, Warsaw University of Life Sciences (WULS-SGGW): Warszawa, Poland, 2009. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Popek, Z. Bedload transport conditions in small lowland river. Treatises and Monographs. WULS-SGGW, Warsaw (in Polish) Schumm, S.A. 1969: River metamorphosis. J. Hydraul. Div. American Soc. Civ. Eng. 2006, 95, 255–273. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R. Separate roughness coefficients for channel bottom and sides. Eng. News Rec. 1933, 111, 652–653. [Google Scholar]
- Indlekofer, H. Überlagerung von Rauhigkeitseinflüssen beim Abfluß in Offenen Gerinnen; Mitteilungen Institut für Wasserbau und Wasserwirtschaft, RWTH Aachen: Heft, Germany, 1981; Volume 37, pp. 105–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kubrak, J.; Nachlik, E. Hydraulic Basics of River Channels Bandwidth Calculations; Warsaw University of Life Sciences: Warszawa, Poland, 2003. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bollrich, G.; Preißler, G. Hydromechanik, Band 1; Verlag für Bauwesen: Berlin, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zanke, U. Grundlagen der Sedimentbewegung; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Urbański, J.; Hejduk, L. The analysis of local scour size formed after flood event. Monografie Komitetu Gospodarki Wodnej 2014, XX, 389–399. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiraga, M.; Popek, Z. Using a Modified Lane’s Relation in Local Bed Scouring Studies in the Laboratory Channel. Water 2016, 8, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010016
Kiraga M, Popek Z. Using a Modified Lane’s Relation in Local Bed Scouring Studies in the Laboratory Channel. Water. 2016; 8(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiraga, Marta, and Zbigniew Popek. 2016. "Using a Modified Lane’s Relation in Local Bed Scouring Studies in the Laboratory Channel" Water 8, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010016
APA StyleKiraga, M., & Popek, Z. (2016). Using a Modified Lane’s Relation in Local Bed Scouring Studies in the Laboratory Channel. Water, 8(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010016