Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Dry-Wet Abrupt Transition Based on Precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
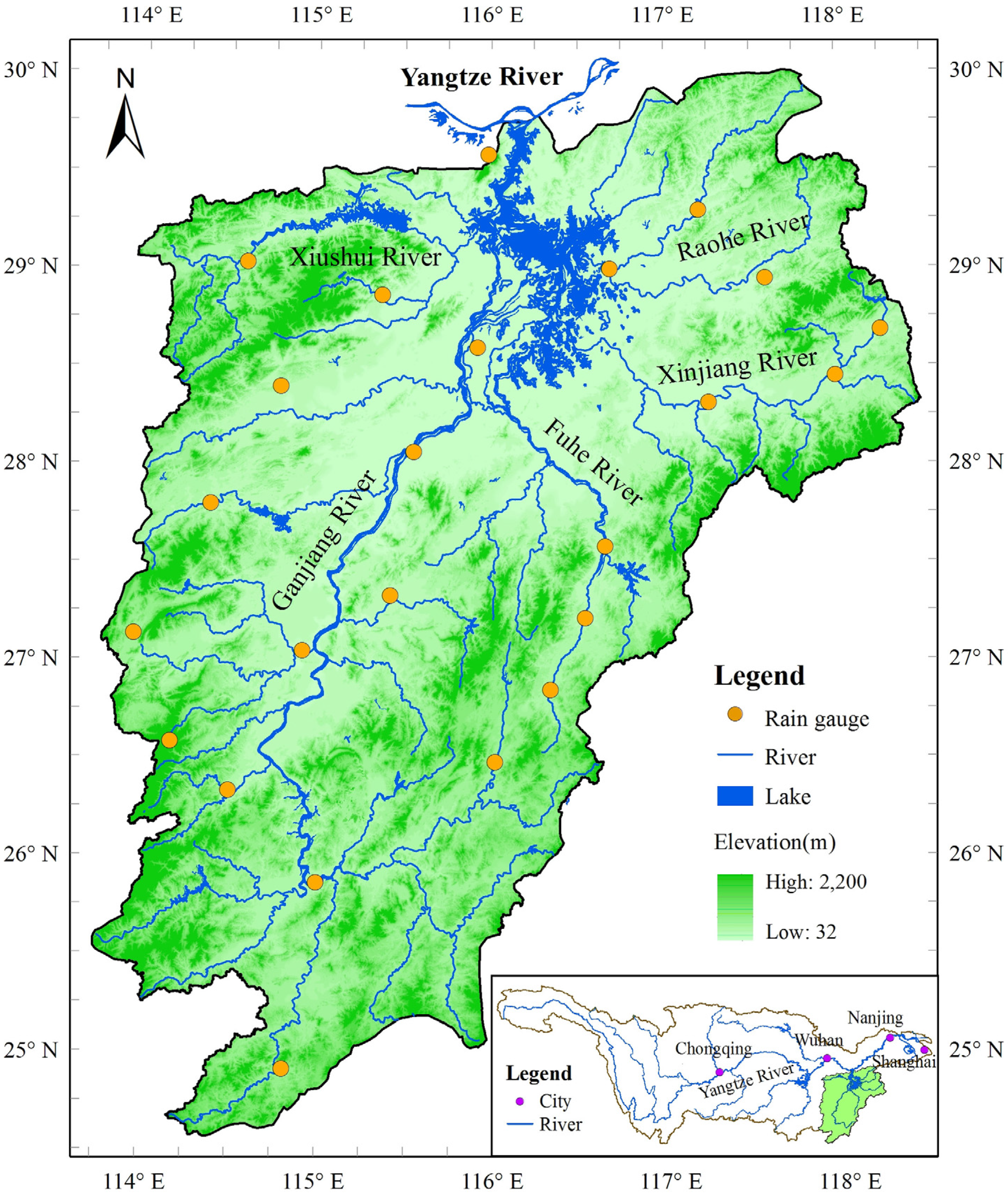
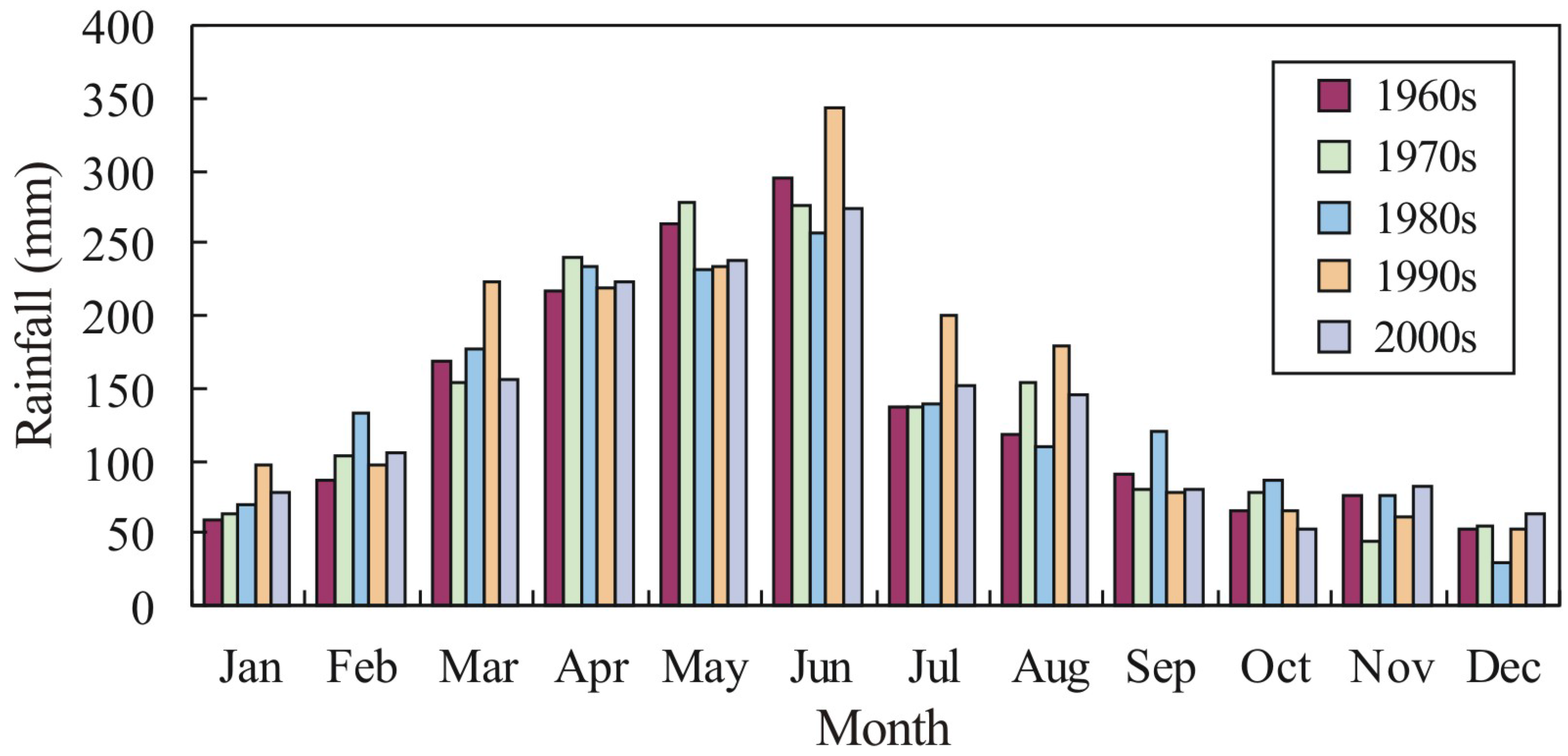
3. Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Intra-Annual Distribution of DWAT in Poyang Lake Basin

| Type | Date | DWATI | Precipitation in Current Month | Precipitation in Previous Month |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High DWATI | Mar. 1996 | 4.28 | 1.04 | −1.04 |
| Mar. 1960 | 2.49 | 0.79 | −1.07 | |
| Feb.1985 | 2.38 | 0.77 | −1.05 | |
| Mar. 1979 | 2.36 | 0.88 | −0.76 | |
| Mar. 2009 | 2.17 | 0.77 | −0.73 | |
| Low DWATI | Sep. 1996 | −5.25 | −1.15 | 1.20 |
| Jul. 2003 | −5.23 | −1.15 | 1.19 | |
| Jul. 1971 | −4.71 | −1.12 | 1.09 | |
| Sep. 2001 | −4.45 | −1.28 | 1.08 | |
| Oct. 1961 | −4.29 | −1.23 | 1.06 |
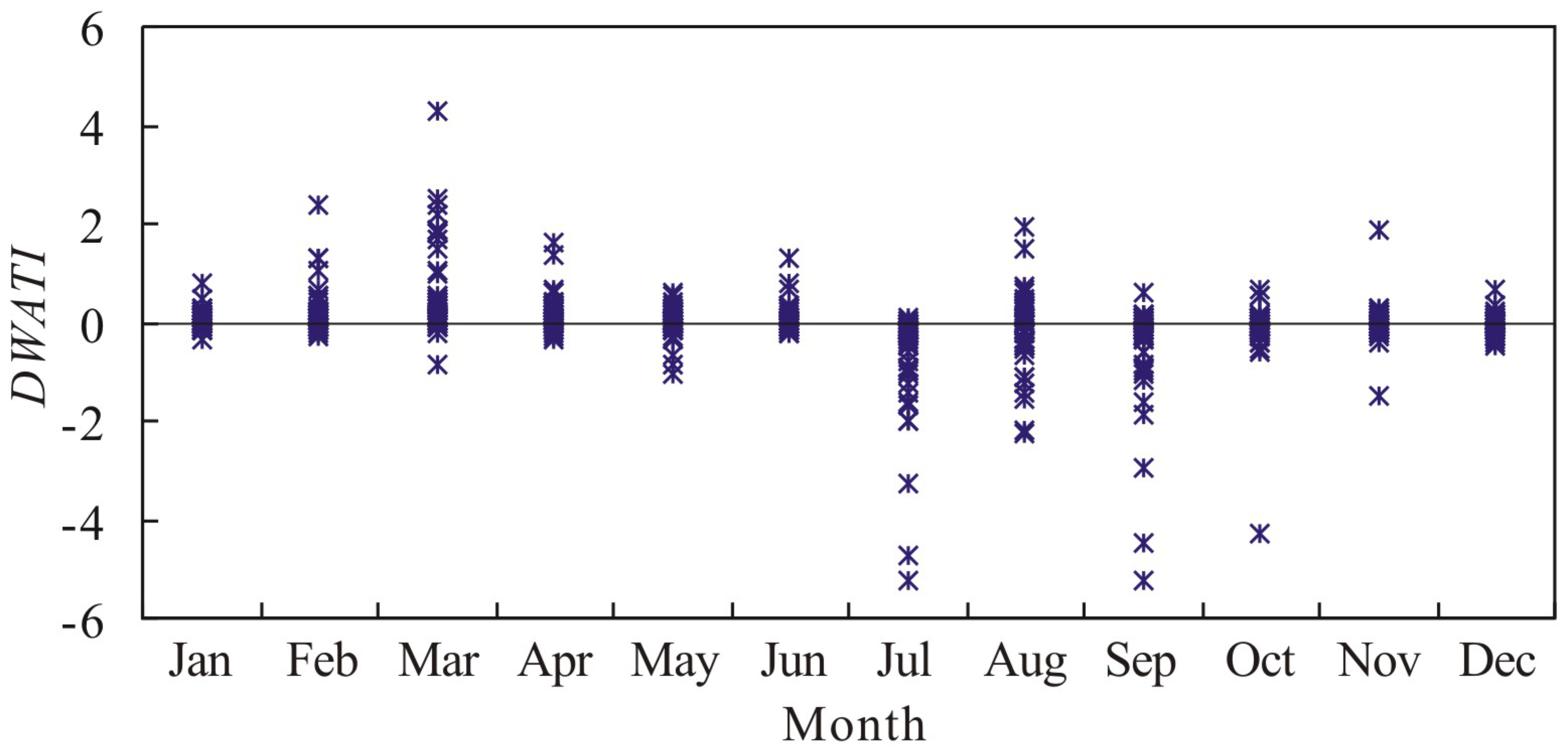
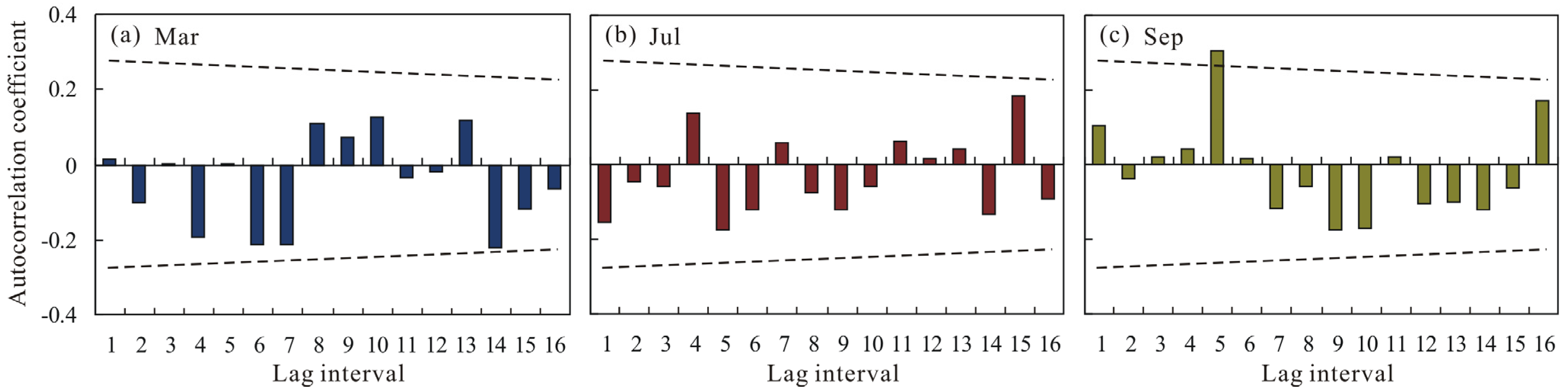
4.2. Inter-Annual Variation Characteristics of DWAT in Poyang Lake Basin
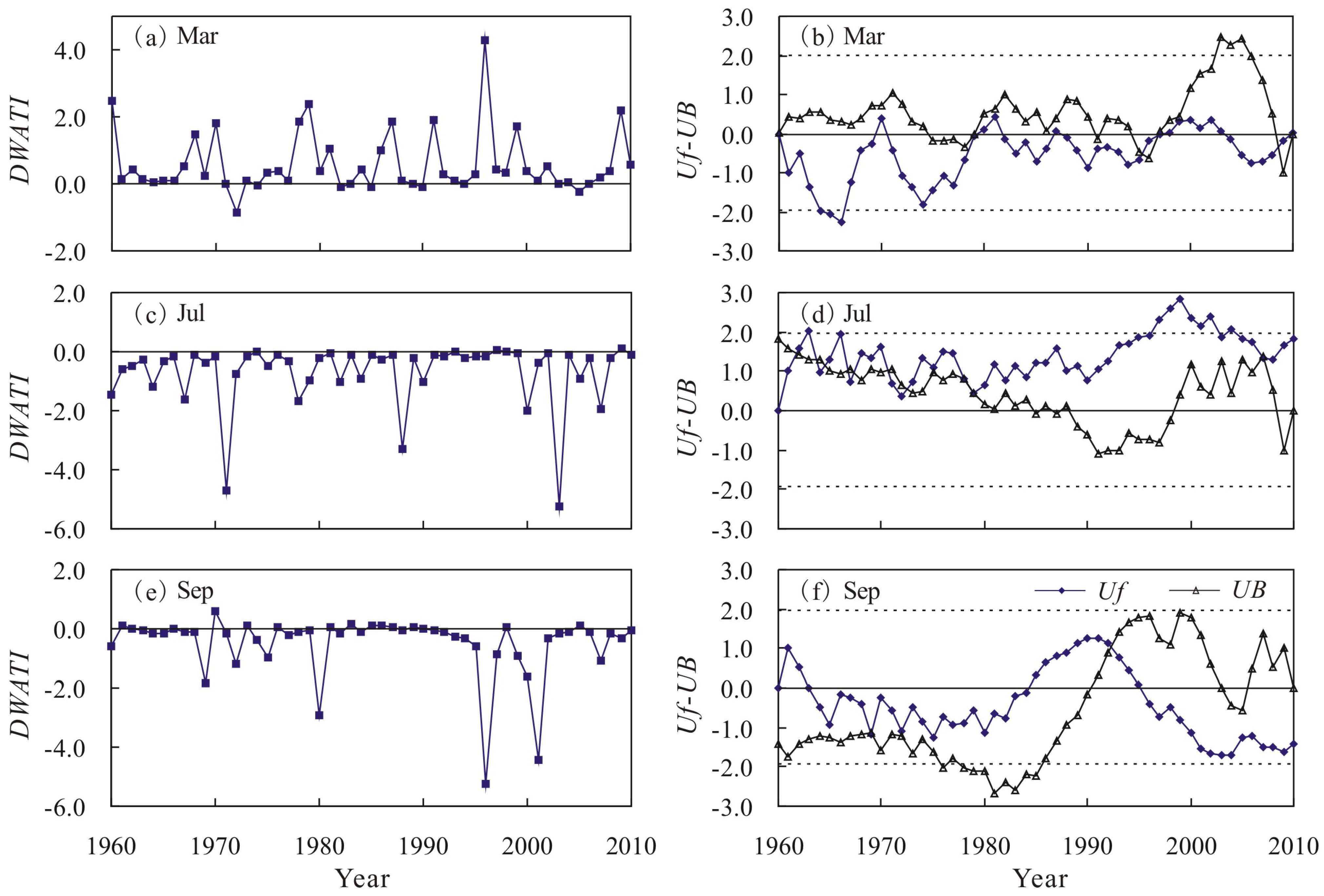
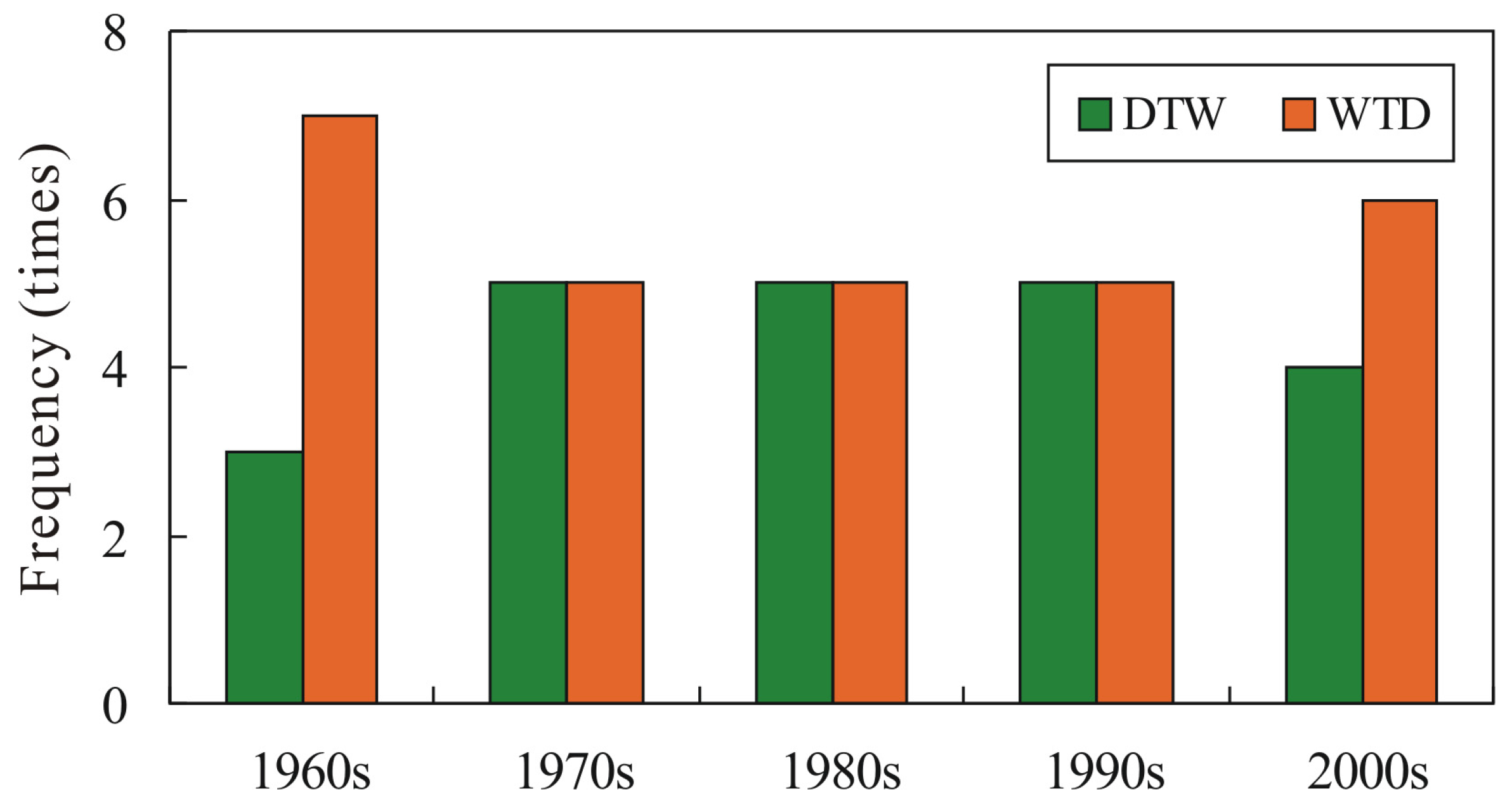
4.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of DWAT in Poyang Lake Basin

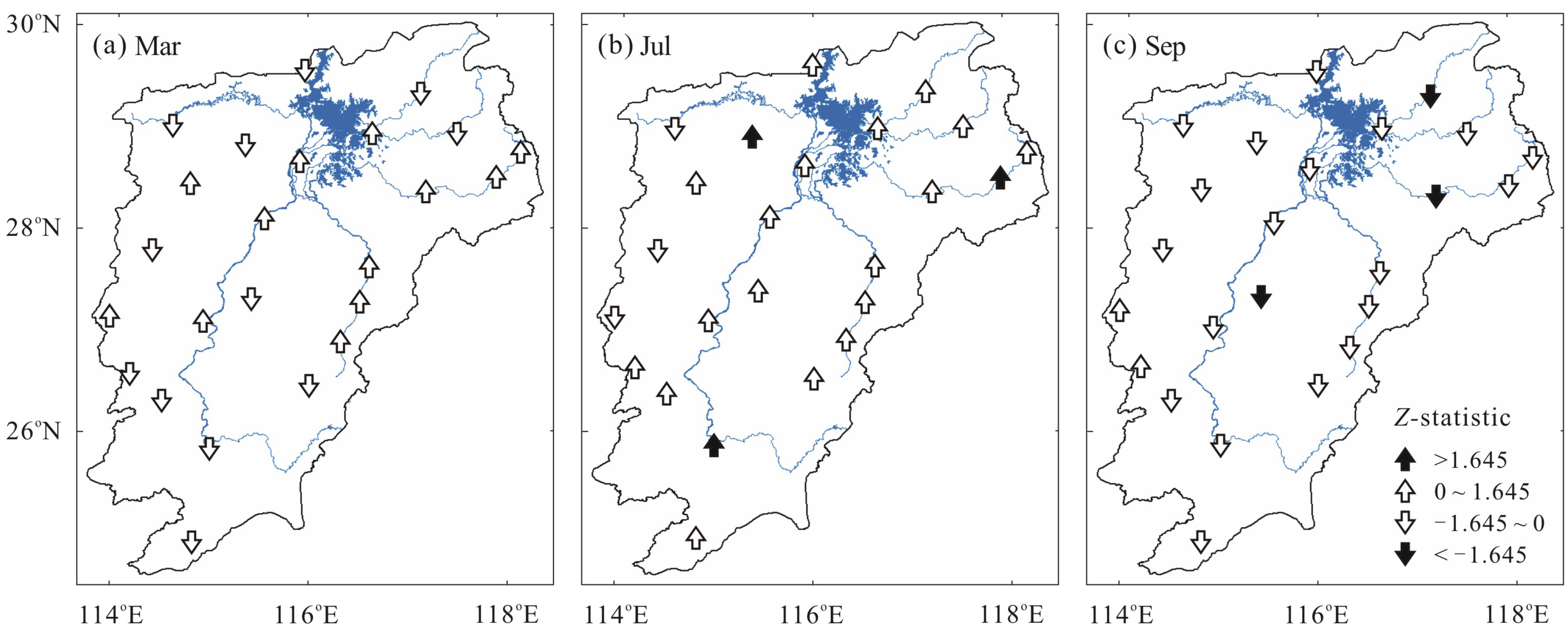
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakayama, T.; Watanabe, M. Role of flood storage ability of lakes in the Changjiang River catchment. Glob. Planet Change 2008, 63, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castellanos, D.; Estrada, F.; Jimenez-Munt, I.; Gorini, C.; Fernandez, M.; Verges, J.; de Vicente, R. Catastrophic flood of the Mediterranean after the Messinian salinity crisis. Nature 2009, 462, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, N. Quantitative Methods and Applications of Risk Assessment and Management on Main Meteorological Disasters; Beijing Normal University Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, C.J.; Li, H.R.; Yang, L.S.; Wu, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Liao, Y.F. Spatial and temporal changes in flooding and the affecting factors in China. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Zhang, K.M.; Luo, T.; Fu, X.H. An analysis of the drought and flood hazard characteristics and risks during the pre-rainy season in South China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 1195–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.Y.; Liu, N. Flood area and damage estimation in Zhejiang, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Chen, Z.; Ren, X.; Yang, G. Analysis of historical floods on the Yangtze River, China: Characteristics and explanations. Geomorphology 2009, 113, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.N.; Shao, Q.X.; Chen, X.H.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.G. Flood changes during the past 50 years in Wujiang River, South China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3561–3569. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Zhou, T.; Wu, B.; Li, T.; Luo, J.J. Projection of future precipitation changes over China with a high-resolution global atmospheric model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 28, 464–476. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.W.; Li, J.P.; He, J.H.; Jiang, Z.H. Large-scale atmospheric singularities and summer long-cycle droughts-floods abrupt alternation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.L.; Yang, H.W.; Zhang, S.X.; Wang, K.; Shen, B.Z. A preliminary research on the reason of a sharp turn from drought to flood in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in late spring and early summer of 2011. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 1009–1026. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, Q. Spatio-temporal variations of drought-flood abrupt alternation during main flood season in East River Basin. Pearl River 2012, 5, 29–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Ding, X.J.; Xu, M.; Luo, L.S. Climate characters of typical droughts-floods abrupt alternation events in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 115–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Tian, H.; Ding, X. Climate characteristics of precipitation and phenomenon of drought-flood abrupt alternation during main flood season in Huaihe River basin. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2009, 30, 31–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Z.M.; Xiao, Y. Variation of the total runoff into Poyang Lake and drought-flood abrupt alternation during the past 50 years. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2013, 21, 845–856. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.W.; He, J.H.; Li, J.P.; Jiang, Z.H. The summer drought-flood coexistence in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and analysis of its air-sea background feathers in anomalous years. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 30, 570–577. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Shao, D.G.; Yao, C.L. Causes and countermeasures of sudden changing from drought to waterlogging in Huaibei Region. J. China Inst. Water Resour. Hydropower Res. 2007, 5, 26–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.D.; Chen, J.Q. Flood/drought variability in the Yangtze Delta and association with the climatic changes from the Guliya ice core: A wavelet approach. Quat. Int. 2008, 189, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Zhao, G.N.; Peng, J.; Hu, J.F. Precipitation characteristics over five major river systems of Poyang drainage areas in recent 50 years. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2009, 18, 615–619. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Xu, M.; Luo, L.S.; Ding, X.J. Climate characteristics of drought-flood abrupt change events in Huaihe River basin. J. China Hydrol. 2012, 31, 73–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.F.; Zhang, J.C.; Min, J.J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhuang, J.Y.; Lin, J. Drought-flood abrupt alternation based on runoff in the Huaihe River Basin during rainy season. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 679–686. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, T.; Shankman, D. Impact of the Three-Gorges Dam and water transfer project on Changjiang floods. Glob. Planet Change 2013, 100, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Fang, J.; Xu, W.; Shi, P.J. Analysis of dry/wet conditions using the standardized precipitation index and its potential usefulness for drought/flood monitoring in Hunan Province, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, I.; Fraedrich, K.; Jiang, J.M.; Sutera, A. Spatio-temporal variability of dry and wet periods in eastern China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 79, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z. Observed changes of drought/wetness episodes in the Pearl River basin, China, using the standardized precipitation index and aridity index. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2008, 98, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Su, B.; Gao, C.; Jiang, T. Spatial variation and trends in PDSI and SPI indices and their relation to streamflow in 10 large regions of China. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.; Westra, S.; Phatak, A.; Lambert, M.; van den Hurk, B.; McInnes, K.; Risbey, J.; Schuster, S.; Jakob, D.; Stafford-Smith, M. A compound event framework for understanding extreme impacts. WIREs Clim. Change 2014, 5, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; AghaKouchak, A.; Phillips, T.J. Changes in concurrent monthly precipitation and temperature extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.; Alexander, E.; Nairn, J.R. Increasing frequency, intensity and duration of observed global heatwaves and warm spells. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Meehl, G.A.; Parmesan, C.; Changnon, S.A.; Karl, T.R.; Mearns, L.O. Climate extremes: Observations, modeling, and impacts. Science 2000, 289, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F. Projected changes in drought occurrence under future global warming from multi-model, multi-scenario, IPCC AR4 simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2008, 31, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, M.; Henderson, M.; Ye, Q. Observed trends of precipitation amount, frequency, and intensity in China, 1960–2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.N.; Venugopal, V.; Sengupta, D.; Madhusoodan, M.S.; Xavier, P.K. Increasing trends of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science 2006, 314, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.M.; Wu, H.T. Climatology and changes in tropical oceanic rainfall characteristics inferred from Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) data (1998–2009). J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A.; Vecchi, G.A. Changing frequency of heavy rainfall over the Central United States. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, C.J.; Liu, S.C.; Fu, C.; Dai, A.; Sun, Y. How much do precipitation extremes change in a warming climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Fu, C.; Shiu, C.J.; Chen, J.P.; Wu, F. Temperature dependence of global precipitation extremes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Solomon, S.; Dai, A.; Portmann, R.W. How often will it rain? J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4801–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The changing character of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.M.; Mitchell, J.F.; Brady, A.J. Summer drought in northern midlatitudes in a time-dependent CO2 climate experiment. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 662–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniston, M. Trends in joint quantiles of temperature and precipitation in Europe since 1901 and projected for 2100. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L07707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Swain, D.L.; Touma, D. Anthropogenic warming has increased drought risk in California. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Cheng, L.; Mazdiyasni, O.; Farahmand, A. Global warming and changes in risk of concurrent climate extremes: Insights from the 2014 California drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8847–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Ye, X.C. The changing patterns of floods in Poyang Lake, China: Characteristics and explanations. Nat. Hazards 2015, 76, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q. Variation of floods characteristics and their responses to climate and human activities in Poyang Lake, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, T. Annual and seasonal streamflow responses to climate and land-cover changes in the Poyang Lake basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 355, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, T. Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Li, X.H.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Q. Variation of reference evapotranspiration and its contributing climatic factors in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 6151–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.H.; Xu, C.Y. Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.C. Capabilities of satellite-based precipitation to estimate the spatiotemporal variation of flood/drought class in Poyang Lake basin. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric test against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.J.; Hörmann, G.; Fohrer, N.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhai, J.Q. Streamflow trends and climate variability impacts in Poyang Lake basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, E.V.; Stefan, H.G. Stream flow in Minnesota: Indicator of climate change. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, S.L.; Xu, C.Y.; Singh, V.P. Historical temporal trends of hydro-climatic variables and runoff response to climate variability and their relevance in water resource management in the Hanjiang basin. J. Hydrol. 2007, 344, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, J.Y. Impact of climate change on water resources in the Tarim river basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Phinney, B. Canadian streamflow trend detection: impacts of serial and cross-correlation. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, M.N.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Gachon, P.; Sushama, L.; St-Hilaire, A. Identification of hydrological trends in the presence of serial and cross correlations: a review of selected methods and their application to annual flow regimes of Canadian rivers. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Ye, X. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Dry-Wet Abrupt Transition Based on Precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water 2015, 7, 1943-1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051943
Li X, Ye X. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Dry-Wet Abrupt Transition Based on Precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water. 2015; 7(5):1943-1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051943
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianghu, and Xuchun Ye. 2015. "Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Dry-Wet Abrupt Transition Based on Precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China" Water 7, no. 5: 1943-1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051943
APA StyleLi, X., & Ye, X. (2015). Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Dry-Wet Abrupt Transition Based on Precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water, 7(5), 1943-1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051943







