Experimental Assessment of the Use of a Novel Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for the Optimization ofWater Consumption in Agricultural Irrigation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (A)
- Protected cultivations: these cultivations are characterized by great intensity and high specialization of the soil, which ultimately leads to the deterioration of the essential nutrients of the soil, to the accumulation of telluric pathogens and to secondary salinization due to the excessive use of fertilizers and/or brackish water. In this context, not only would the adoption of SAP rationalize the amount of used water, but it would also allow modulating (in time) the supply of nutrients, thus avoiding the accumulation of toxic substances in the soil;
- (B)
- Soilless cultivations: in soilless cultivations, plants are grown using mineral nutrient solutions in water, without soil [13]. In open soilless systems, there is a massive waste of water and nutrients, which is responsible for an increase in running costs and in contamination of ground and surface water [14]. The adoption of the SAP to ration the delivery of nutrients to the plants would improve the overall environmental sustainability of these systems. Also for closed systems (in which water recirculates), the use of SAP may help hindering water retention of the plants;
- (C)
- Open-field cultivations: in agriculture, chemically synthesized fertilizers are commonly supplied in larger quantity than actually needed by the plants. Nitrate accumulation in the soil, especially in dry areas, is a typical result of such an excessive use of fertilizers, with negative repercussions on the environment as well as on the product quality, with nitrates being absorbed by the plants and fruit. The presence of nitrates decreases the nutritional quality of the product (especially for leaf vegetables), and increases the risk of developing cancers [15]. The use of certain SAP formulations could allow reducing the amount of fertilizers used and/or limiting nitrate accumulation in the soil.
2. Materials and Methods
- (i)
- Characterization of the absorption capacity of the SAP in both distilled and tap water;
- (ii)
- Evaluation of the effect of the SAP when placed in different types of soil and at different depths, through experiments performed in plant pots; and
- (iii)
- Evaluation of the effect of the SAP in conditions that resembled open-field cultivations.
2.1. Synthesis of Cellulose-Based SAP
2.2. Preliminary Characterization of the Absorption Capacity of the SAP
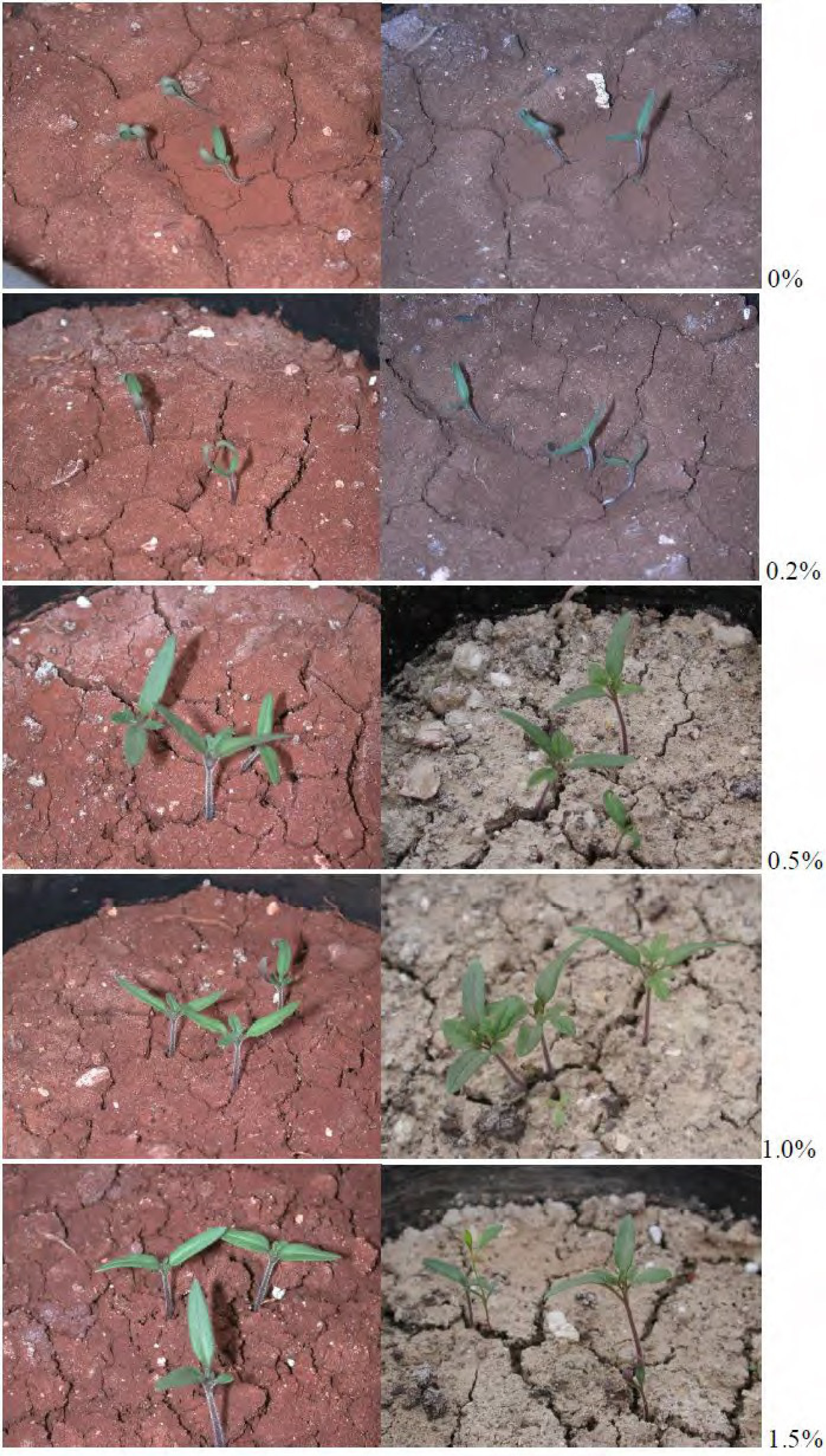
2.3. Selection of Soils and Types of Plants
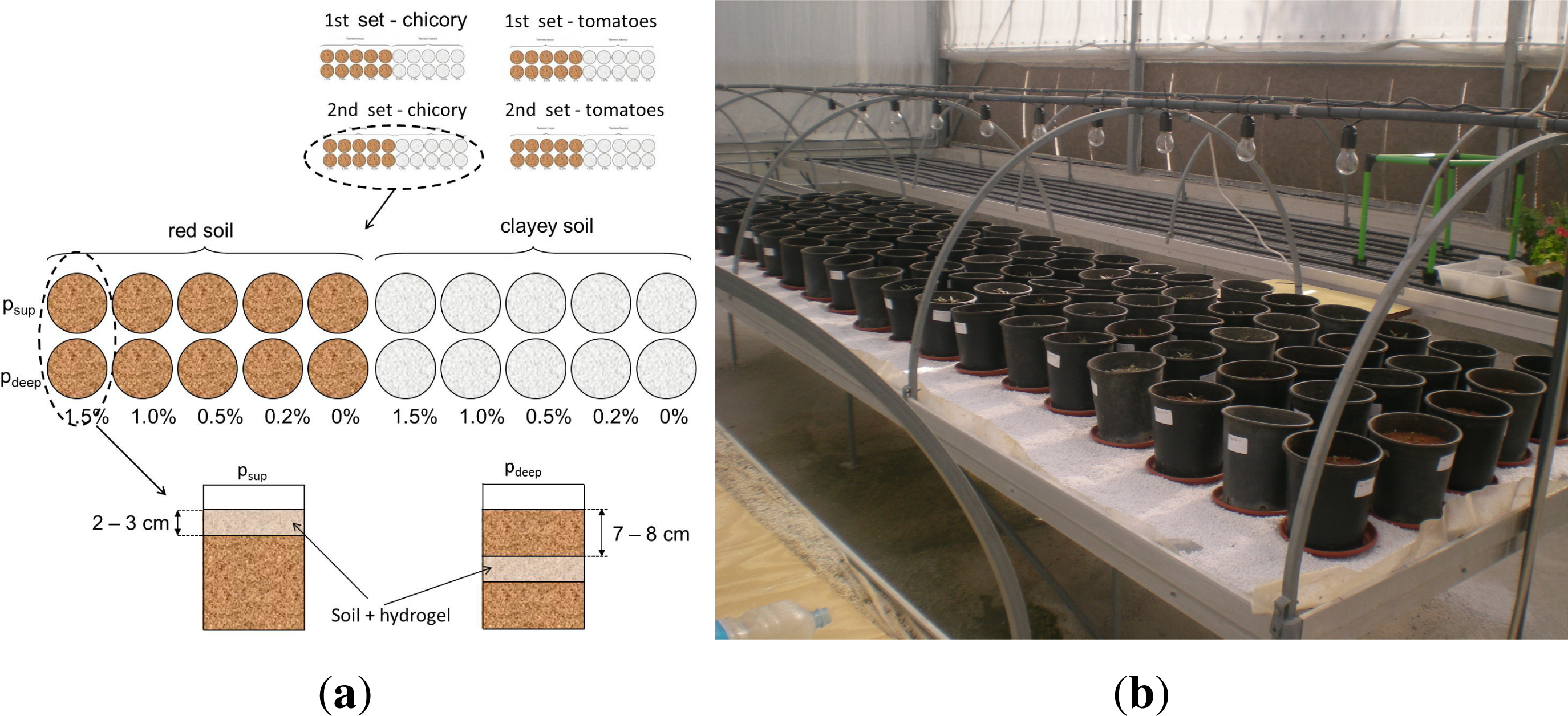
2.4. Experimental Setup for the Evaluation of the Effect of the SAP in the Soil
- (i)
- the value of θs in the sample without SAP (i.e., the reference sample, wSAP = 0) had decreased to 10%; or
- (ii)
- for all the samples, the evaporated water equaled the percentage of water evaporated from the reference sample.
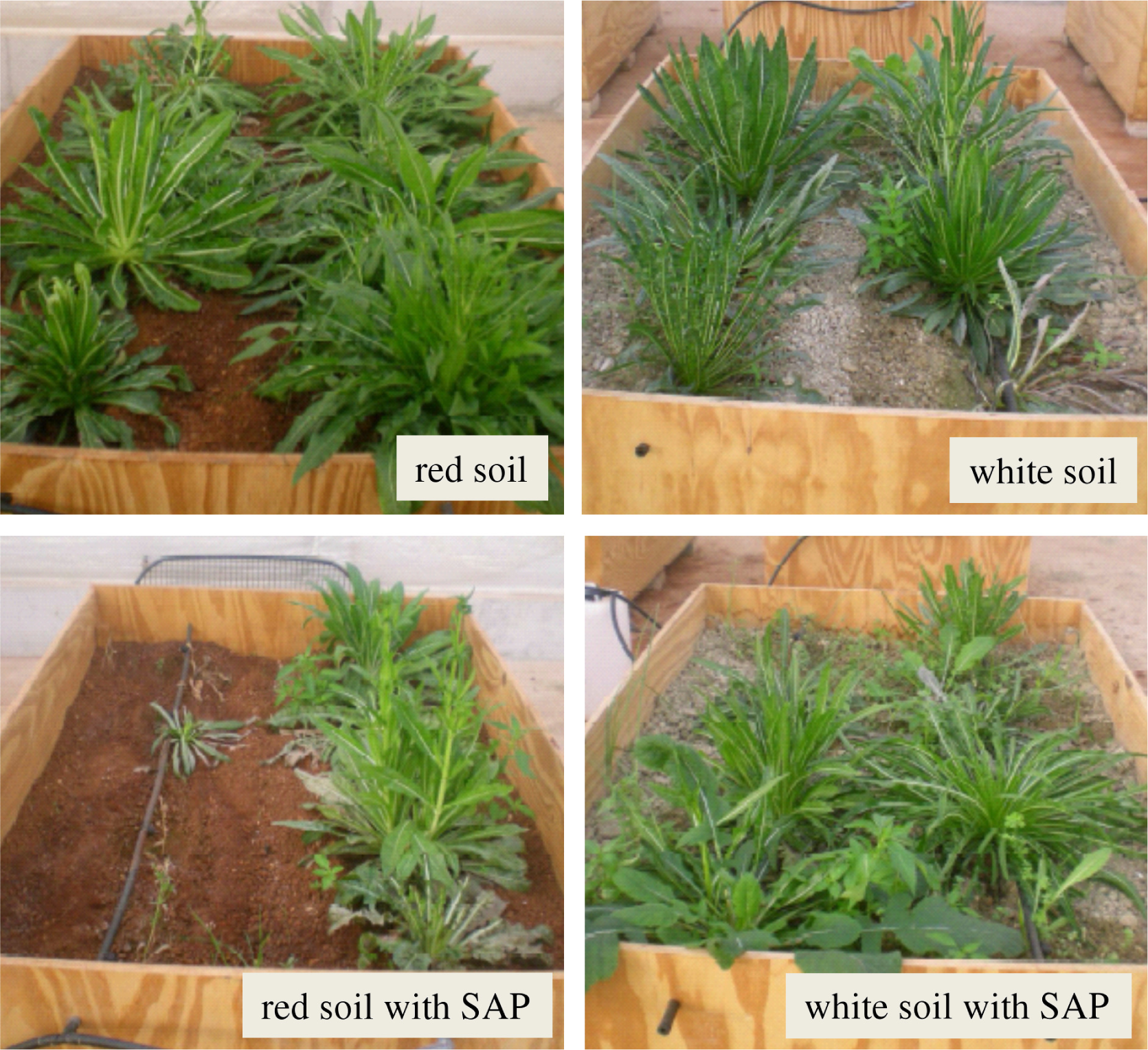
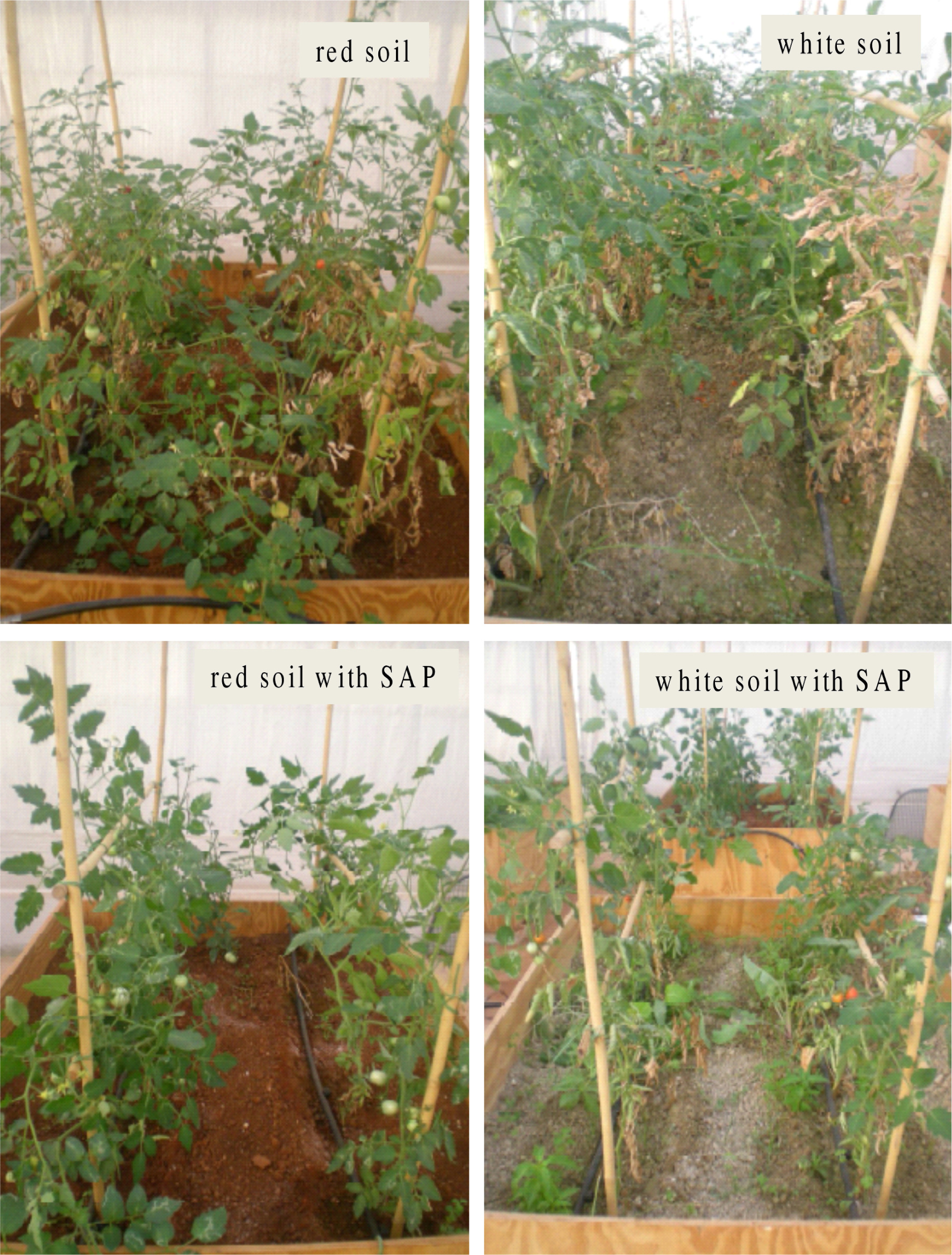
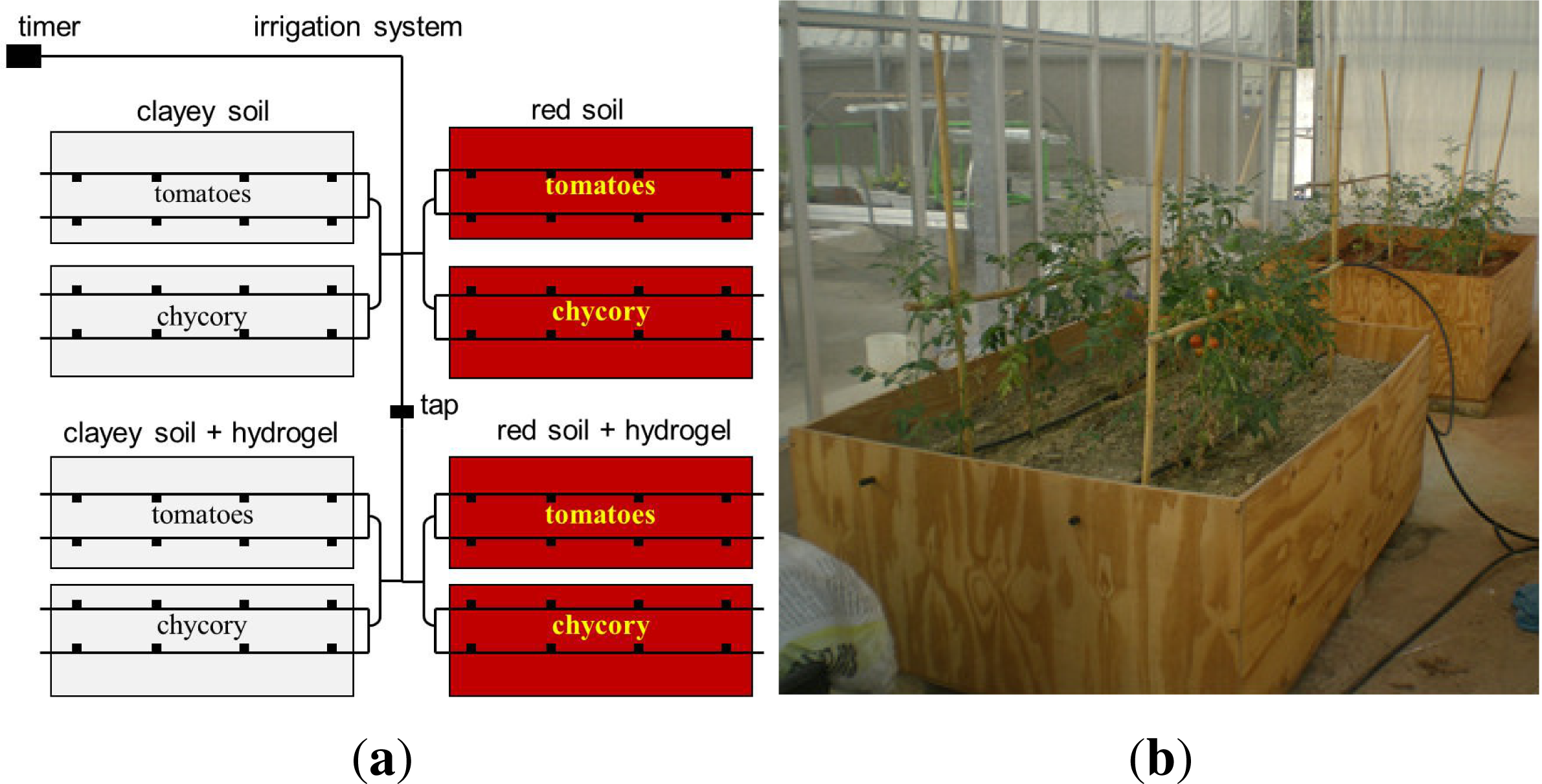
2.5. Experimental Setup for Mimicking Open-Field Cultivations
3. Experimental Results
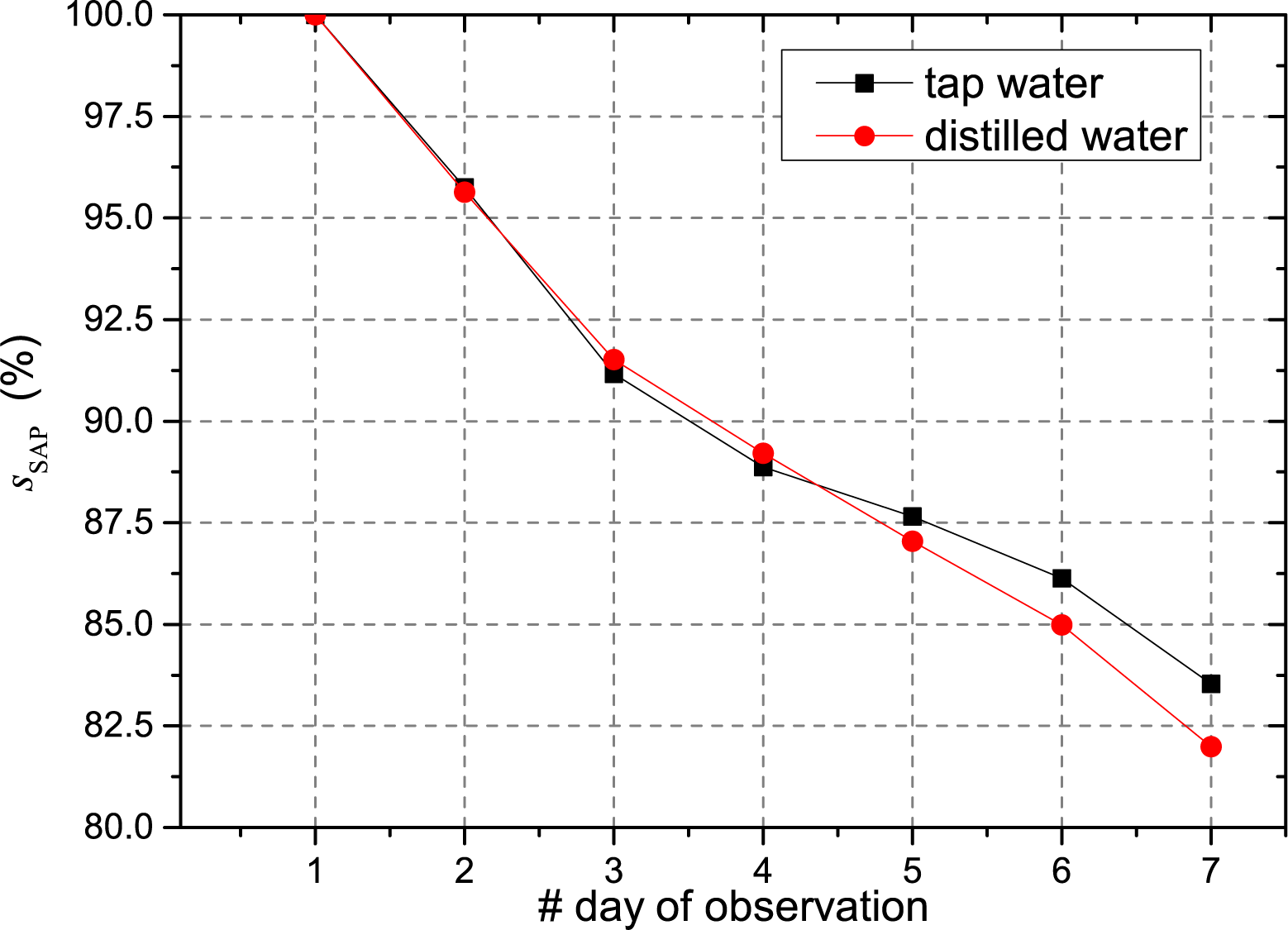
3.1. Absorption Capacity of the SAP
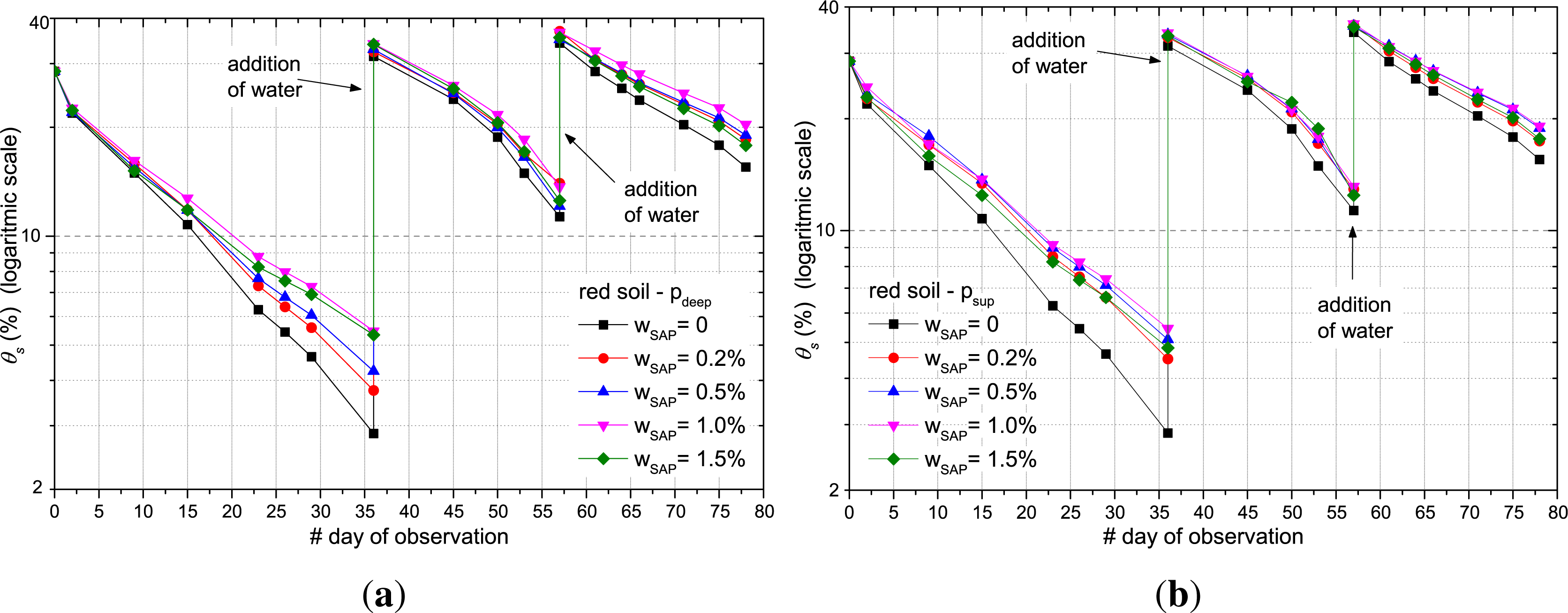
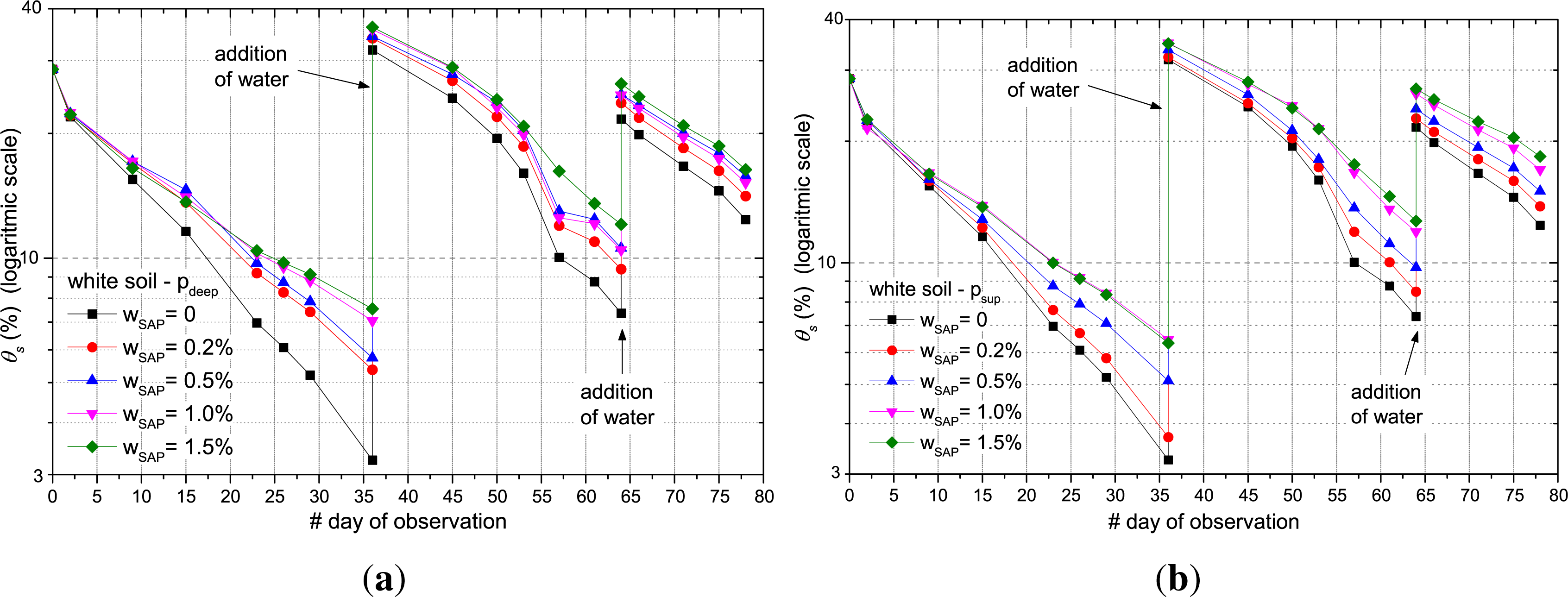
3.2. Evaluation of the Efficiency of the SAP after Several Water Absorption/Desorption Cycles
- (1)
- on the 36th day, one litre of water was added to both types of soil;
- (2)
- on the 57th day, 0.8 L of water was added only for the red soil;
- (3)
- on the 64th day, 0.5 L of water was added only to the clayey soil.
3.3. Experimental Results for the Cultivation Mimicking Open-Field Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barlow, P.M. Ground water in fresh water-salt water environments of the Atlantic Coast, Circular 1262; U.S. Geological Survey, 2003. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/2003/circ1262/pdf/circ1262.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2014).
- Saguy, I.S.; Singh, R.P.; Johnson, T.; Fryer, P.J.; Sastry, S.K. Challenges facing food engineering. J. Food Eng 2013, 119, 332–342. [Google Scholar]
- Nestlé. Meeting the Global Water Challenge, 2011; Creating Shared Value Summary Report 2011. Available online: http://www.nestle.com/asset-library/Documents/Library/Documents/Corporate_Social_Responsibility/Nestle-CSV-Summary-Report-2011-EN.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2014).
- Provenzano, G.; Tarquis, A.M.; Rodriguez-Sinobas, L. Soil and irrigation sustainability practices. Agric. Water Manag 2013, 120, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vico, G.; Porporato, A. From rainfed agriculture to stress-avoidance irrigation: I. A generalized irrigation scheme with stochastic soil moisture. Adv. Water Resour 2011, 34, 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Ines, A.V.; Honda, K.; Gupta, A.D.; Droogers, P.; Clemente, R.S. Combining remote sensing-simulation modeling and genetic algorithm optimization to explore water management options in irrigated agriculture. Agric. Water Manag 2006, 83, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Belaqziz, S.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Jarlan, L.; Page, M.L.; Kharrou, M.; Adnani, M.E.; Chehbouni, A. A new irrigation priority index based on remote sensing data for assessing the networks irrigation scheduling. Agric. Water Manag 2013, 119, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Blanco, M.; Lorite, I.; Santos, C. An innovative remote sensing based reference evapotranspiration method to support irrigation water management under semi-arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag 2014, 131, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y. Optimization of the irrigation water resources for agricultural sustainability in Tarim River Basin, China. Agric. Water Manag 2012, 107, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Paydar, Z.; Qureshi, M. Irrigation water management in uncertain conditions—Application of modern portfolio theory. Agric. Water Manag 2012, 115, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Talaat, H.A.; Sorour, M.; Aboulnour, A.; Shaalan, H.; Ahmed, E.M.; Awad, A.M.; Ahmed, M. Development of a multi-component fertilizing hydrogel with relevant techno-economic indicators. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci 2008, 3, 764–770. [Google Scholar]
- Horie, K.; Barón, M.; Fox, R.; He, J.; Hess, M.; Kahovec, J.; Kitayama, T.; Kubisa, P.; Maréchal, E.; Mormann, W.; et al. Definitions of terms relating to reactions of polymers and to functional polymeric materials: (IUPAC Recommendations 2003). Pure Appl. Chem 2004, 76, 889–906. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lorenzo, R.; Pisciotta, A.; Santamaria, P.; Scariot, V. From soil to soil-less in horticulture: Quality and typicity. Ital. J. Agron 2013, 8, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Vox, G.; Teitel, M.; Pardossi, A.; Minuto, A.; Tinivella, F.; Schettini, E. Sustainable greenhouse systems. In Sustainable Agriculture: Technology, Planning and Management; Salazar, A., Rios, I., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, S.E.; Irving, D.E.; Milham, P.J. A critical evaluation of on-farm rapid tests for measuring nitrate in leafy vegetables. Sci. Hortic 2012, 134, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura, T.; Namba, T. Preparation and application of high-performance superabsorbent polymers. Superabsorbent Polym 1994, 573, 112–127. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhouse, J.; Johnson, M. Effect of superabsorbent polymers on survival and growth of crop seedlings. Agric. Water Manag 1991, 20, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Orts, W.J.; Sojka, R.E.; Glenn, G.M. Biopolymer additives to reduce erosion-induced soil losses during irrigation. Ndustrial Crops Prod 2000, 11, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.; Liu, M.; Zhan, F.; Guo, M. Factors on the preparation of carboxymethylcellulose hydrogel and its degradation behavior in soil. Carbohydr. Polym 2004, 58, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Nnadi, F.; Brave, C. Environmentally friendly superabsorbent polymers for water conservation in agricultural lands. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag 2011, 2, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Modelli, A.; Rondinelli, G.; Scandola, M.; Mergaert, J.; Cnockaert, M.C. Biodegradation of chemically modified flax fibers in soil and in vitro with selected bacteria. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 596–602. [Google Scholar]
- Demitri, C.; Scalera, F.; Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Potential of cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels as water reservoir in agriculture. Int. J. Polym. Sci 2013, 2013. Article 435073. [Google Scholar]
- Sannino, A.; Pappadá, S.; Madaghiele, M.; Maffezzoli, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Nicolais, L. Crosslinking of cellulose derivatives and hyaluronic acid with water-soluble carbodiimide. Polymer 2005, 46, 11206–11212. [Google Scholar]
- Demitri, C.; Marotta, F.; Sannino, A.; Ron, E.; Zohar, Y.; Ambrosio, L. Rheological and mechanical comparison between natural dietary fibers and a novel superabsorbent biodegradable hydrogel (SAEF). Proceedings of the 24th European Conference on Biomaterials (ESB2011), Dublin, Ireland, 4–9 September 2011.
- Demitri, C.; Del Sole, R.; Scalera, F.; Sannino, A.; Vasapollo, G.; Maffezzoli, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Nicolais, L. Novel superabsorbent cellulose-based hydrogels crosslinked with citric acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 2008, 110, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar]
- Raucci, M.G.; Alvarez-Perez, M.A.; Demitri, C.; Sannino, A.; Ambrosio, L. Proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of hMSCs on cellulose-based hydrogels. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater 2012, 10, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Sannino, A.; Demitri, C.; Madaghiele, M. Biodegradable cellulose-based hydrogels: Design and applications. Materials 2009, 2, 353–373. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, F.; del Nobile, M.A.; Mensitieri, G.; Nicolais, L. Water sorption in cellulose-based hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 1996, 60, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Sannino, A.; Nicolais, L. Concurrent effect of microporosity and chemical structure on the equilibrium sorption properties of cellulose-based hydrogels. Polymer 2005, 46, 4676–4685. [Google Scholar]
- Demitri, C.; Giuri, A.; Raucci, M.; Giugliano, D.; Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A.; Ambrosio, L. Preparation and characterization of cellulose-based foams via microwave curing. Interface Focus 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, A.; Madaghiele, M.; Demitri, C.; Scalera, F.; Esposito, A.; Esposito, V.; Maffezzoli, A. Development and characterization of cellulose-based hydrogels for use as dietary bulking agents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 2010, 115, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.C.; Evands, R.C.; Paul, J.L. Fertilizer salts reduce hydration of polyacryamide gels and affect physical properties of gel-amended container media. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci 1990, 115, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Hussien, R.; Donia, A.; Atia, A.; El-Sedfy, O.; El-Hamid, A.; Rashad, R. Studying some hydro-physical properties of two soils amended with kaolinite-modified cross-linked poly-acrylamides. Catena 2012, 92, 172–178. [Google Scholar]



| Parameter | White soil | Red soil |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.21 | 8.35 |
| Electrical conductivity | 154.3 μS/cm | 146.9 μS/cm |
| Organic content | 17,613.75 mg/kg (1.76%) | 24,593.88 mg/kg (2.46%) |
| N (total) | 0.784 g/kg | 1.008 g/kg |
| Na | 4.11 meq/100 g | 2.77 meq/100 g |
| Ca | 100.798 meq/100 g | 133.03 meq/100 g |
| Mg | 12.86 meq/100 g | 16.45 meq/100 g |
| K | 2.65 meq/100g | 3.78 meq/100 g |
| Assimilable P2O5 | 203.99 meq/100 g | 195.72 meq/100 g |
| Limestone (total) | 4% | 8% |
| Sample | SAP (g) | Wadd(g) | Wnot−abs (g) | Wabs (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 1.01 | 100.04 | 25.40 | 74.64 |
| #2 | 1.00 | 100.06 | 25.30 | 74.76 |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cannazza, G.; Cataldo, A.; De Benedetto, E.; Demitri, C.; Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A. Experimental Assessment of the Use of a Novel Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for the Optimization ofWater Consumption in Agricultural Irrigation Process. Water 2014, 6, 2056-2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072056
Cannazza G, Cataldo A, De Benedetto E, Demitri C, Madaghiele M, Sannino A. Experimental Assessment of the Use of a Novel Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for the Optimization ofWater Consumption in Agricultural Irrigation Process. Water. 2014; 6(7):2056-2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072056
Chicago/Turabian StyleCannazza, Giuseppe, Andrea Cataldo, Egidio De Benedetto, Christian Demitri, Marta Madaghiele, and Alessandro Sannino. 2014. "Experimental Assessment of the Use of a Novel Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for the Optimization ofWater Consumption in Agricultural Irrigation Process" Water 6, no. 7: 2056-2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072056
APA StyleCannazza, G., Cataldo, A., De Benedetto, E., Demitri, C., Madaghiele, M., & Sannino, A. (2014). Experimental Assessment of the Use of a Novel Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for the Optimization ofWater Consumption in Agricultural Irrigation Process. Water, 6(7), 2056-2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072056









