Abstract
Green infrastructure (GI) design is advocated as a new paradigm for stormwater management, whereas current knowledge of GI design is mostly based on isolated design strategies used at small-scale sites. This study presents empirical findings from two watershed-scale community projects (89.4 km2 and 55.7 km2) in suburban Houston, Texas. The GI development integrates a suite of on-site, infiltration-based stormwater management designs, and an adjacent community development follows conventional drainage design. Parcel data were used to estimate the site impervious cover area. Observed streamflow and water quality data (i.e., NO3-N, NH3-N, and TP) were correlated with the site imperviousness. Results show that, as of 2009, the impervious cover percentage in the GI site (32.3%) is more than twice that of the conventional site (13.7%). However, the GI site’s precipitation-streamflow ratio maintains a steady, low range, whereas this ratio fluctuates substantially in the conventional site, suggesting a “flashy” stream condition. Furthermore, in the conventional site, annual nutrient loadings are significantly correlated with its impervious cover percentage (p < 0.01), whereas in the GI site there is little correlation. The study concludes that integrated GI design can be effective in stormwater runoff reduction and water quality enhancement at watershed-scale community development.
1. Introduction
Mitigating the development impact on stream hydrology and stormwater quality has been extensively discussed [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Excessive runoff leads to costly flooding events and the export of nitrogen and phosphorous to streams, which become concerns of environmental protection agencies and health agencies [7,8]. The main culprit behind these events is the elevated level of impervious cover as a result of community development. Impervious covers such as rooftops, streets, and parking lots alter the natural hydrological cycle and increase the pollutant loadings [9,10,11]. During the past three decades, imperviousness continues to be the single most important variable to define the amount of urban development, and a considerable number of studies have suggested a definite relationship between impervious areas and watershed stream health [12,13,14]. Watershed degradation generally is a result of a gradual process when impervious cover increases. However, many studies suggest that when impervious cover exceeds a range from 10% to 20%–25%, negative impacts are more prominent, including severe erosion, high nutrient flux, diminished stream species diversity, alteration of stream morphology, and an overall degradation of the aquatic system health [9,15,16,17].
In community development, the conventional drainage solution (curb-and-gutter, drop inlet, and underground piping) transfers stormwater faster than the natural hydrological cycle and may contribute to downstream flooding [18,19,20]. Common mitigation measures such as detention basins focus on peak discharge reduction and present limited success in runoff volume reduction or water quality improvement [2,21]. Moreover, if the basin is located inappropriately, it may aggravate flooding [22,23,24]. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) advocates retrofitting the conventional stormwater system toward using low-impact development (LID) and green infrastructure (GI) design [7,25,26]. GI design typically encompasses open space, parks, green roofs, bioretention and constructed wetlands, decentralized water management (e.g., rainwater harvesting), protection of riparian areas, and various hybrids of pervious surfacing options [26,27]. GI design is based on ecological engineering principles [28,29], and a number of studies have suggested that integrated GI designs can be more effective than single-design strategies [30,31,32]. While the main focus of conventional drainage solution is peak discharge reduction, GI design aims at restoring the predevelopment flow regimes, such as reduction of runoff volume, enhancement of stormwater quality, and maintenance of base flows [33,34,35].
To achieve the above performance benefits, GI design treats runoff close to where it is generated. For instance, runoff is detained or infiltrated onto permeable surfaces on-site. As a result, the amount of effective impervious area (EIA) that directly contributes to runoff is reduced. EIA is a subset of the commonly used term “total impervious area” (TIA), which is often used to define the extent of community development. TIA is the sum of all noninfiltrating surfaces. EIA, or directly connected impervious area, includes only those impervious areas that drain into a piped storm sewer and further discharge into a surface-water body (e.g., parking lot runoff goes directly to a stormwater drain) [36,37]. Recent studies suggest that EIA increases when the connectivity of TIA increases and that development patterns can be better indicators than TIA alone in estimating stormwater runoff and pollutant exports [38,39].
Although community development inevitably increases the TIA, GI design can be effective in reducing the EIA and runoff volume [35,40,41,42]. However, most current knowledge of GI design is based on isolated design strategies used at small-scale sites. Few studies have fully measured the effectiveness of integrated GI design that encompasses entire watersheds [43,44]. This current study presents empirical findings from two watershed-scale community projects in suburban Houston, Texas. One of the projects, The Woodlands, is a renowned large-scale community development. It is a precursor of the USEPA’s GI design initiative: a series of integrated GI design strategies were used to meet flood control and stormwater quality goals [44,45,46,47]. Several recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of The Woodlands GI design on flood mitigation [31,32,46]. In addition to stormwater quantity, this current study further assessed water quality performance of The Woodlands’ GI design with built communities that use the conventional drainage design.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The test-bed watersheds are Panther Creek watershed (The Woodlands, GI design) and Bear Creek watershed (west Houston, conventional drainage design). These two watersheds have different stormwater infrastructures, development densities and patterns, and levels of impervious surface cover (Figure 1, Table 1). Both watersheds belong to the northern humid gulf coastal prairies of Texas and present similar land use land cover conditions before development.
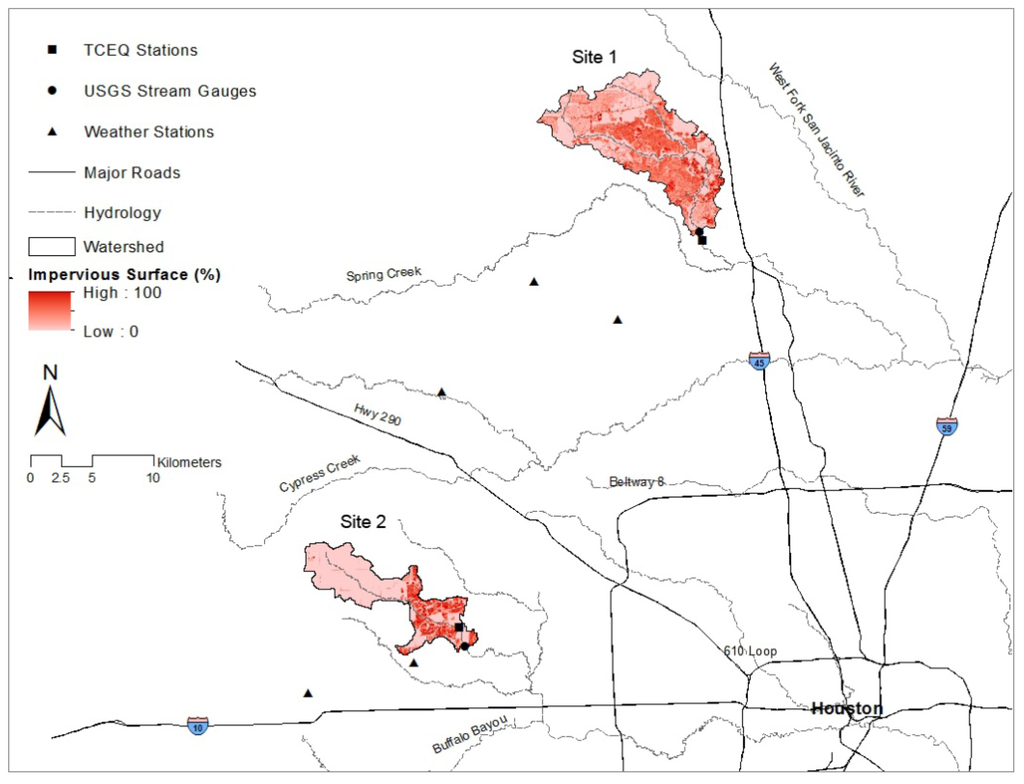
Figure 1.
Study sites Panther Creek watershed (Site 1 The Woodlands green infrastructure development) and Bear Creek watershed (Site 2 conventional development) in Texas. USGS, US Geological Survey. TCEQ, Texas Commission on Environmental Quality.

Table 1.
Study sites and respective watersheds.
| Watershed | Drainage area (km2) | Development start date | Population | Household number | % Impervious cover (2009) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Panther Creek (Woodlands, GI) | 89.4 | 1974 | 66,143 | 24,655 | 32.3 |
| 2. Bear Creek(comparative) | 55.7 | 1976 | 33,763 | 9,559 | 13.7 |
Notes: Watersheds are defined by the U.S. Geological Survey gauging stations: No. 08068450 (Panther) and No. 08072730 (Bear). Slopes in these two watersheds are less than 1%. Population and household information is based on 2010 U.S. Census Block data.
Development started around the same period in these two watersheds in the 1970s, whereas stormwater management methods differ. The Woodlands has been well-managed as a planned community from its inception [45,47]. Ecological planner Ian McHarg laid out a suite of decentralized, infiltration-based drainage designs to reduce runoff volume and improve water quality [48,49,50,51]. McHarg’s GI design was ahead of his time in that most Houston subdivision communities have been adopting the conventional drainage practices. One of McHarg’s important land planning strategies was to determine building densities and land use based on soil permeability. This is achieved by preserving land with high soil permeability as open space and land with low soil permeability for development. Hence, runoff is infiltrated in close proximity to where it is generated [48]. In addition to the extensive infiltration-based drainage designs, other development strategies also help minimize the TIA and the EIA. Typical streets in The Woodlands are 5 to 8 ft (on average 10%) narrower than Houston subdivision standards for road width [49]. Open surface drainage channels were used to detain runoff, and curb-and-gutter drainage was avoided (Figure 2) ([48], p. 10).
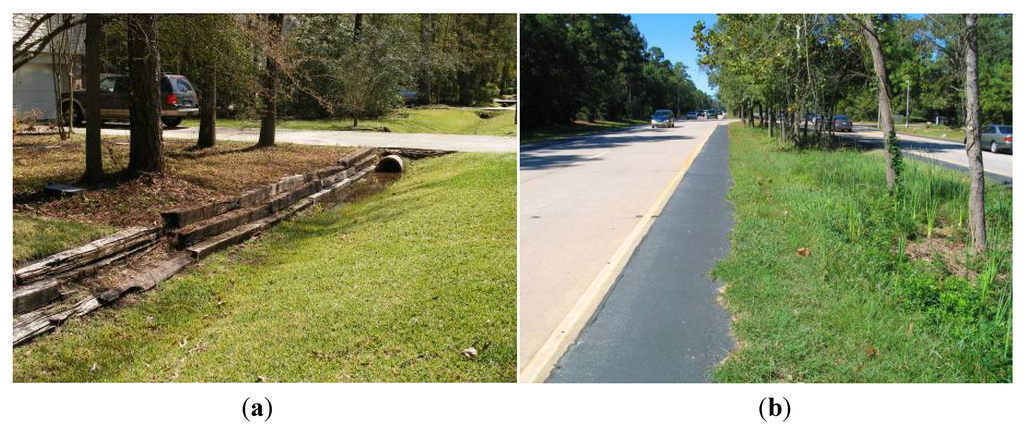

Figure 2.
(a) A typical view in The Woodlands: preserving the original vegetation, minimizing turfgrass areas, and using open surface drainage; (b) A typical collector street in The Woodlands: stormwater drains to the vegetated medium for treatment.
In collector streets, runoff is detained and treated in the vegetated street medium for better water quality (see Figure 2). Check dams were used to retard runoff and further soak it (Figure 3). Porous pavements were used in the commercial district of the first subdivision village and other locales [52]. Wetlands are protected for water quality treatment and to facilitate ecosystem services [53,54,55]. Modeling analyses projected the after-built runoff scenarios and ascertained that runoff is detained as close as possible to where it is generated (Figure 4).
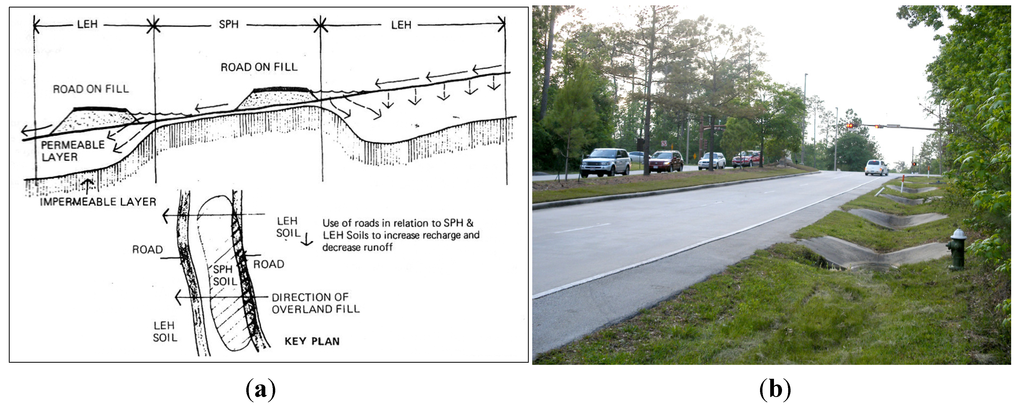
Figure 3.
(a) Open drainage design guideline which promotes impoundment on permeable soils. Check dams retard runoff and increase infiltration. LEH: medium to well-drained soil; SPH (Splendora): poorly drained soil ([50], p. 31) (Image courtesy: WRT); (b) Open surface drainage along collector streets in The Woodlands.
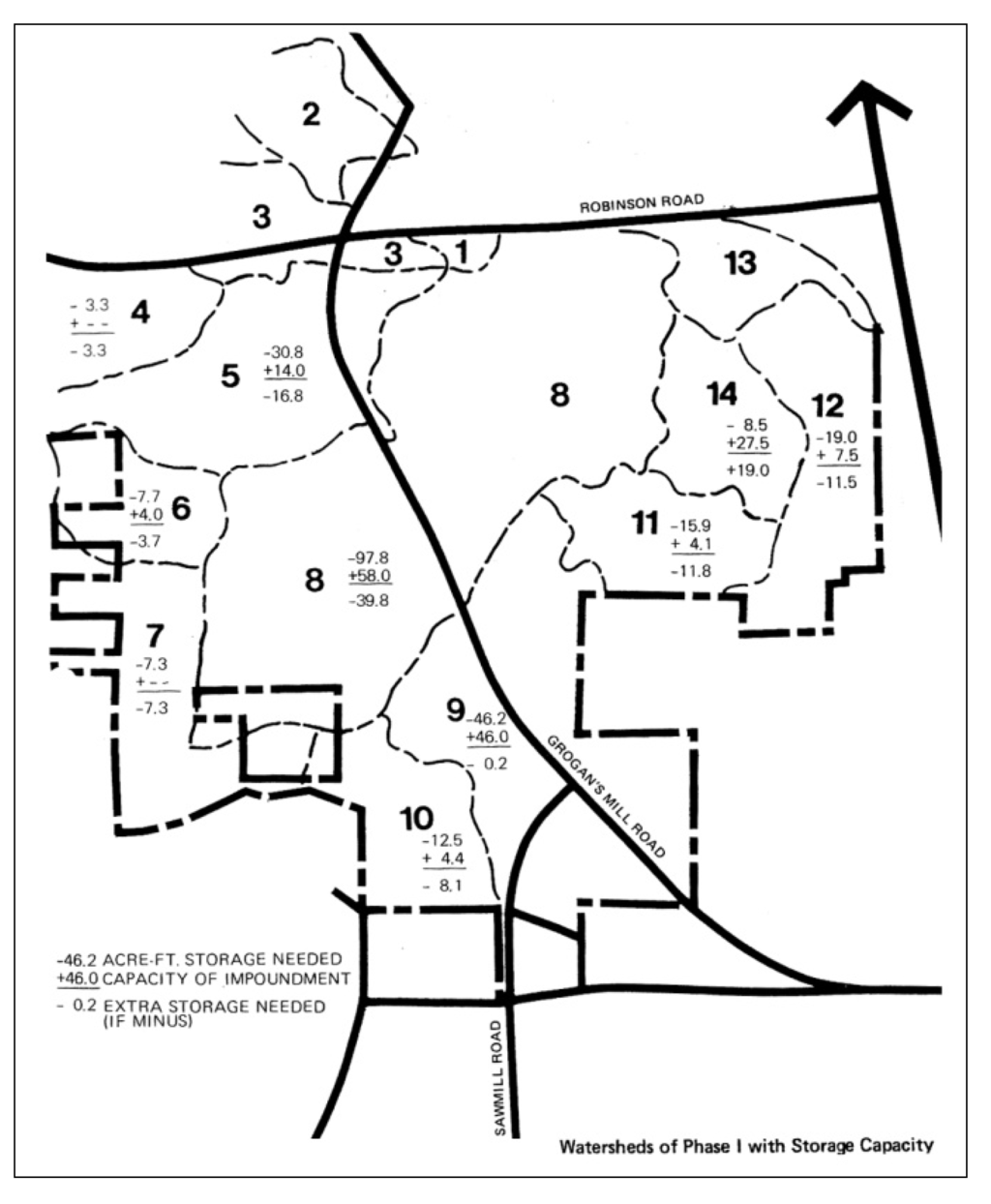
Figure 4.
Modeling analysis on runoff storage in Phase I development (8 km2), with no excessive runoff allowed ([50], p. 9) (Image courtesy: WRT).
Historical extreme storm events attested to the success of McHarg’s integrated GI design. The Woodlands survived 100-year storms in 1979 and 1994 with little property damage, while several adjacent communities and Houston (50 km to the south) were severely flooded [56,57]. In addition, the first phase development alone would save $14 million in construction costs compared with the conventional drainage method [45]. However, residents did not appreciate the aesthetics of the GI design. Market studies showed that most residents preferred visually appealing conventional drainage design (e.g., curb-and-gutter street). The rustic appearance of natural vegetation and unmaintained understory are contrary to average American’s preference for a manicured lawn (see Figure 2a) [54,58]. As a result, starting around 1985, a hybrid approach was used in the later phases of development—conventional underground pipe drainage was introduced in subdivisions [59]. After 1997, McHarg’s approach was largely abandoned when The Woodlands was sold to a different developer [46,58].
Bear Creek watershed is located in the fast growing west Houston region. Population in this region has surpassed 1 million since 1999 [60]. Over 34% of the residential community development in Greater Houston is projected to occur here, given the fact that Houston is currently one of the most rapidly expanding regions in the nation [61]. Bear Creek watershed presents typical subdivision developments: cookie-cutter lot layout, turfgrass-dominated landscaping, and curb-and-gutter and underground pipe drainage (Figure 5). Bear Creek watershed is part of residential development areas, designated by the West Houston Association (WHA) [60] and City of Houston General Plan [62]. There are significant flooding and water quality concerns in this region [63].
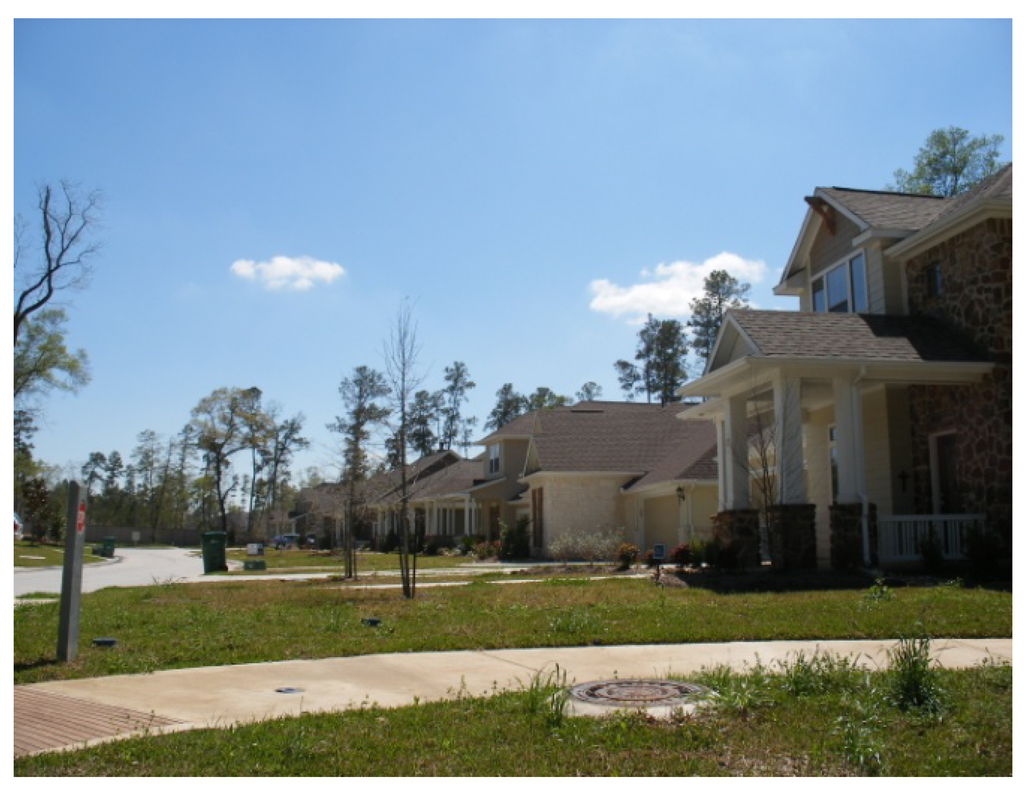

Figure 5.
Typical neighborhood views in comparative Houston communities in the Bear Creek watershed (less consideration of preserving vegetation and curb-and-gutter conventional drainage).
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Development Data
In land use planning, three data sources and methods are generally used to capture the impervious cover area: (1) use parcel data to quantify the impervious area [36,64]; (2) classify Landsat remote sensing imagery to extract the impervious area [3,65,66]; and (3) digitize high-resolution aerial photographs to delineate the impervious area [66,67]. This study used the first data source to quantify impervious cover area. Parcel data provide the parcel boundary and location, parcel area, building type, year built, and building square footage. Road information was obtained from the Texas Transportation Institute [68].
2.2.2. Soil Data
Soil infiltration capacity can be assessed through examining the area of hydrologic soil groups in the two watersheds. The soil dataset used was the 1:24,000 scale Soil Survey Geographic (SSURGO) database developed by the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) [69]. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) [70] defines four hydrological oil groups (A, B, C, and D) based on soil infiltration rates. A soils are sandy and loamy sand soils; B soils are sandy loam and loam soils; C soils are silt loam and sandy clay loam soils; and D soils are clay loam, silty clay loam, and clay soils. A soils have the highest infiltration rate, B and C soils have moderate infiltration rates, and D soils have the lowest infiltration rate.
2.2.3. Precipitation Data
Historical precipitation data were obtained from the National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) [71]. The Thiessen polygon method [72] was used to estimate precipitation for each watershed. Three weather stations (COOPID No. 411956, No. 419076, and No. 414300) were identified for Panther Creek watershed, and three other stations (COOPID No. 412206, No. 414704, and No. 414313) are used for Bear Creek watershed (see Figure 1). The area weighted percentage of each station was used to calculate the composite precipitation value.
2.2.4. Streamflow and Water Quality Data
Streamflow and water quality data of 2002–2009 were used for comparison. Streamflow data were collected from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) gauge stations No. 08068450 and No. 08072730 [73], at the watershed outlets (see Figure 1). Water quality data were obtained from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) [74] stations No. 16628 and No. 17484. The TCEQ also collects streamflow data when water quality data are collected but with some data gaps. Because the TCEQ monitoring stations are placed close to the USGS gauge stations (see Figure 1), the USGS streamflow data were used for consistency. Since 2000, the TCEQ has been collecting 5 to 12 water quality samples each year for each station. Water-quality samples were consistently obtained on the same day at these two stations. The date of sampling during a particular month was irregular, and the samples may not necessarily have been taken after a rainfall event. Nutrient-related parameters that show consistent records from these two stations were analyzed, including nitrate-nitrogen (NO3-N), ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), and total phosphorous (TP). If in either site there were fewer than six samples for a year, that year was excluded from the analysis.
2.3. Analysis
Three sets of analyses were conducted to compare the impacts of different drainage methods on flow regime and water quality. The first set of analyses assessed development extent and soil conditions to provide background conditions of stormwater quantity and quality comparisons. Geographic Information System (GIS) was used to analyze the parcel data. Building footprint and other impervious cover areas were calculated and sorted by year built, which provides the state of development in the watershed each year. Road surface area was estimated by multiplying the road length by the average width of the roads in the watershed [64]. A majority of the developments in this study have sidewalks on both sides of the road. Hence, the road length was doubled for the sidewalk length. Estimation was also made of the driveway impervious area. Previous studies have used the number of garage stalls multiplied by the average width (3 m) of the driveway [75,76]. However, parcel data do not provide driveway information. The Woodlands Residential Development Standards specified the front yard setback distance: “a garage or garage addition must be set back at least 16 feet (4.88 m) from the side property line” ([77], Section 2.1, p. 14). This setback distance was multiplied by the width of a two-stall garage (6 m) to approximate the driveway impervious area in The Woodlands, calculated by Equation (1):
Driveway area (m2) = Front yard setback (m) × 3 m × Number of garage stalls
Then, this driveway area was multiplied by the total number of parcels in the watershed to estimate the total driveway areas. Likewise, estimation of driveway area was made for Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed), based on the 20-ft (6.1-m) garage setback distance for local streets [78]. GIS was also used to analyze the percentages of different hydrologic soil groups, which will provide insights into the overall stormwater infiltration capacities of the study sites. Soil condition is of particular importance to The Woodlands because McHarg’s unique development concept is to preserve high-infiltration soils for stormwater management.
The second set of analyses examined the relationships of watershed streamflow volume and streamflow-precipitation ratio with impervious cover percentage. Streamflow depths and streamflow-precipitation ratios were examined for water years 2002–2009 for each watershed. A water year, according to the USGS definition, is from October of the preceding year to September of the current year (i.e., water year 2002 = 1 October 2001 to 30 September 2002).
Streamflow-precipitation ratio (as %) for each year were calculated by dividing annual streamflow (m) by annual precipitation (m), and multiplying by 100. Annual streamflow depth (m) is calculated by dividing the total streamflow volume (m3) by the watershed area (m2), using Equation (2) below:
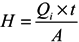 where H is the watershed annual streamflow depth (m); Qi is the annual mean flow at year i (m3∙s–1); t is a constant, 31,536,000 s, the total number of seconds in a year; and A (m2) is the watershed area. This method assumes a uniform depth of precipitation falling onto the watershed; therefore, flow volume is standardized and becomes comparable.
where H is the watershed annual streamflow depth (m); Qi is the annual mean flow at year i (m3∙s–1); t is a constant, 31,536,000 s, the total number of seconds in a year; and A (m2) is the watershed area. This method assumes a uniform depth of precipitation falling onto the watershed; therefore, flow volume is standardized and becomes comparable.
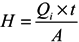
The third set of analyses examined annual nutrient export. This study used the annual flow-weighted method developed by Littlewood [79,80] to calculate nutrient loadings for NO3-N, NH3-N, and TP, according to Equation (3):
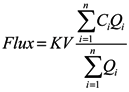 where K is the conversion factor to adjust for units and intervals of sampling; V is the annual accumulative flow (calculated from continuous data) (m3∙s–1); Ci is the concentration measured at the day and time of the ith sample (mg∙L–1); and Qi is the flow rate measured at the day and time of the ith sample (mg∙L–1).
where K is the conversion factor to adjust for units and intervals of sampling; V is the annual accumulative flow (calculated from continuous data) (m3∙s–1); Ci is the concentration measured at the day and time of the ith sample (mg∙L–1); and Qi is the flow rate measured at the day and time of the ith sample (mg∙L–1).
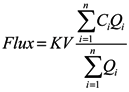
Regression analysis was conducted for each watershed, with the independent variable being watershed impervious coverage (%), and pollutant loading being the dependent variables. Each point on the graphs therefore represents a year. Regression significance testing, R2 calculations, and parameter estimates were performed with the SPSS statistical package.
3. Results
3.1. Impervious Cover
Figure 6 shows the accumulative impervious cover percentage of the two sites with development from 2002 to 2009. It is evident that Site 1 (GI) shows a higher impervious cover percentage than Site 2 (conventional) across the study period. As of 2009, the percentage of impervious cover in Site 1 (GI, 32.3%) is more than twice that of the Site 2 (conventional, 13.7%).
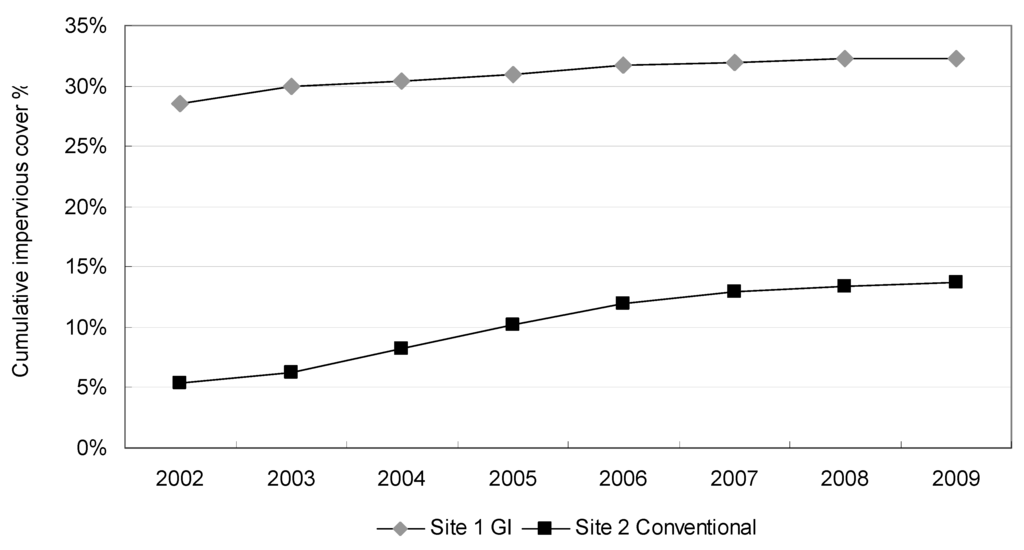
Figure 6.
Accumulative percentages of impervious cover area of Site 1 (Panther Creek watershed, The Woodlands green infrastructure development) and Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed, conventional development), 2002–2009.
3.2. Hydrologic Soil Group Distribution
Table 2 and Figure 7 show the area distribution of four hydrologic soil groups in Sites 1 and 2. These four soil groups were further divided into two groups: A & B (sandy and loam), and C & D (silt and clay), in order to show the overall stormwater infiltration capacity (e.g., good versus poor). It is evident that stormwater infiltration capacity of Site 1 (GI) is lower than that of Site 2 (conventional), because Site 1 has a much lower percentage of A & B soils (38.7% versus 80.2% in Site 2).

Table 2.
Hydrologic soil groups in Site 1 (Panther Creek watershed, The Woodlands green infrastructure development) and Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed, conventional development).
| Hydrologic soil groups | Site 1 (GI) | Site 2 (conventional) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 8.3% | 0 |
| B | 30.4% | 80.2% |
| C | 40.1% | 9.8% |
| D | 19.9% | 9.0% |
| Water | 1.2% | 0.9% |
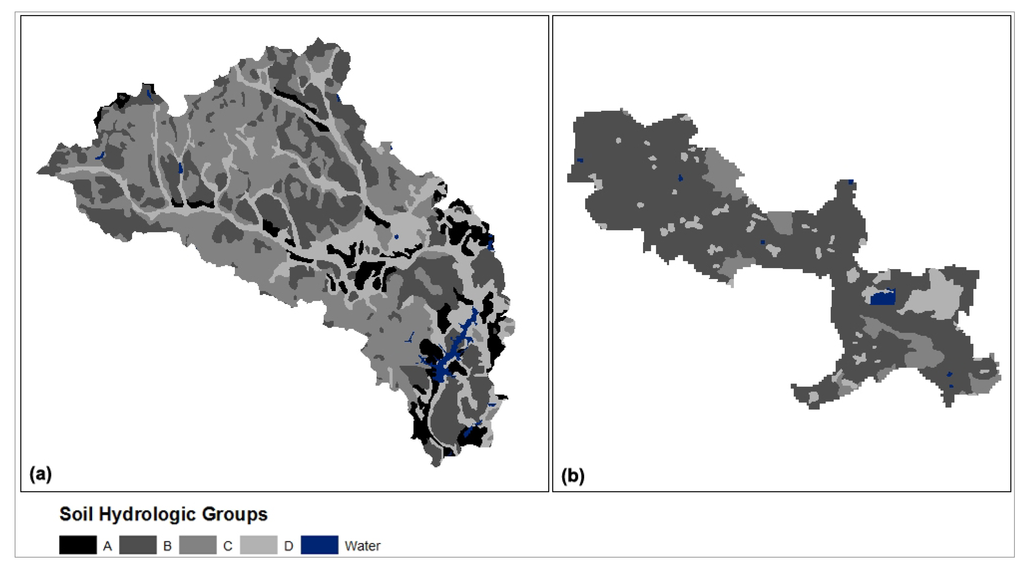
Figure 7.
Area distribution of four hydrologic soil groups and water surface in Site 1 (Panther Creek watershed, The Woodlands green infrastructure development) and Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed, conventional development).
3.3. Precipitation and Streamflow
Figure 8 shows the annual precipitation in Sites 1 and 2 (approximately 45 km from each other). Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the annual precipitation depths (m) and the annual streamflow-precipitation ratios (%) at Sites 1 and 2, respectively. The average precipitation of 2002–2009 at Site 1 (GI, 1.48 m) is 15.3% higher than that at Site 2 (conventional, 1.28 m). Despite this, Site 1’s streamflow volume is 6% lower than that of Site 2. More importantly, Site 1 (GI)’s precipitation-streamflow ratio is kept within a steady, lower range (32%–49%) than that of Site 2 (conventional, 30%–66%). Site 2’s more fluctuating ratio suggests a “flashy” stream condition.
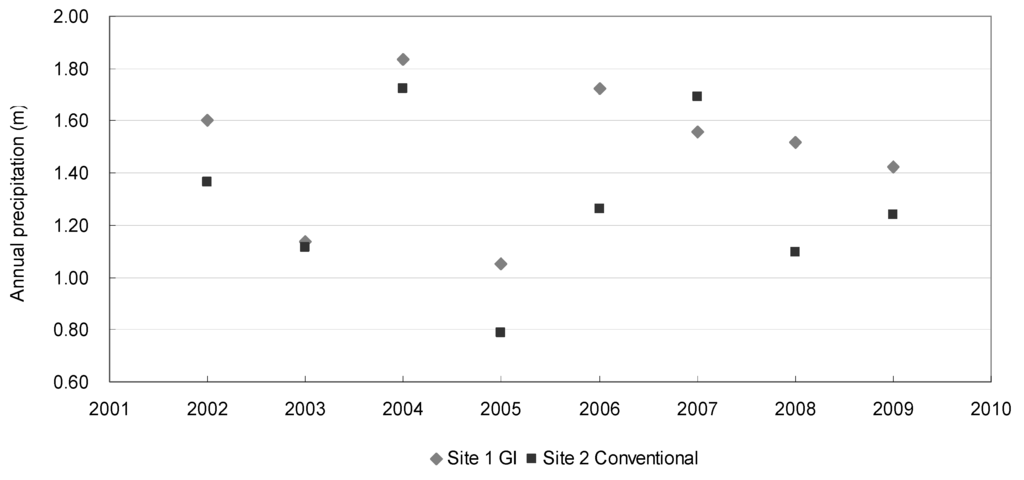
Figure 8.
Annual precipitation in Site 1 (Panther Creek watershed, The Woodlands green infrastructure development) and Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed, conventional development), 2002–2009.
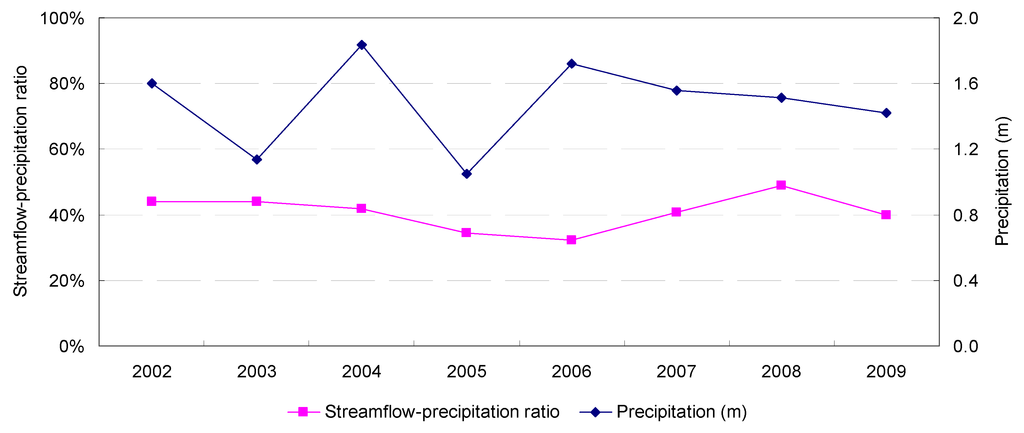
Figure 9.
Annual streamflow-precipitation ratio and precipitation depth of Site 1 (Panther Creek watershed, The Woodlands green infrastructure development), 2002–2009.
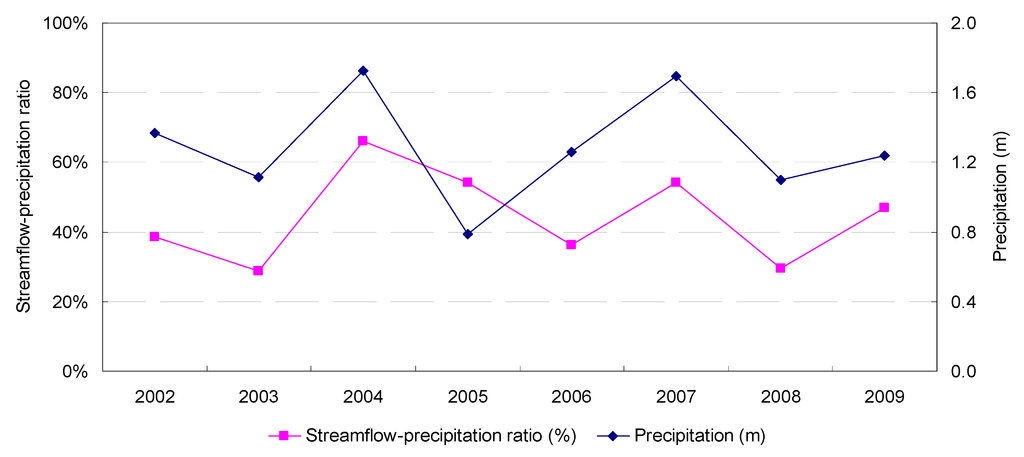
Figure 10.
Annual streamflow-precipitation ratio and precipitation depth of Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed, conventional development), 2002–2009.
3.4. Nutrient Export Loading
Figure 11, Table 3 and Table 4 show the regression analysis between nutrient loading and impervious cover percentage. The results reveal that nutrient loadings are tightly correlated with impervious cover in Site 2 (conventional). In contrast, in Site 1 (GI), there is little correlation between nutrient loadings and the extent of impervious ground cover. These analyses further suggest that GI design can create a robust system that is tolerant to development impacts. Thus, nutrient loadings show a similar response to streamflow volume analyses. NO3-N export increased in Site 2 (conventional) after development; however, little change was found in Site 2 (GI). NH3-N export showed a similar trend as NO3-N export from Site 2 (conventional). Likewise, TP export presented a significant (p < 0.01) trend in Site 2 (conventional), whereas no trend was found for Site 1 (GI).
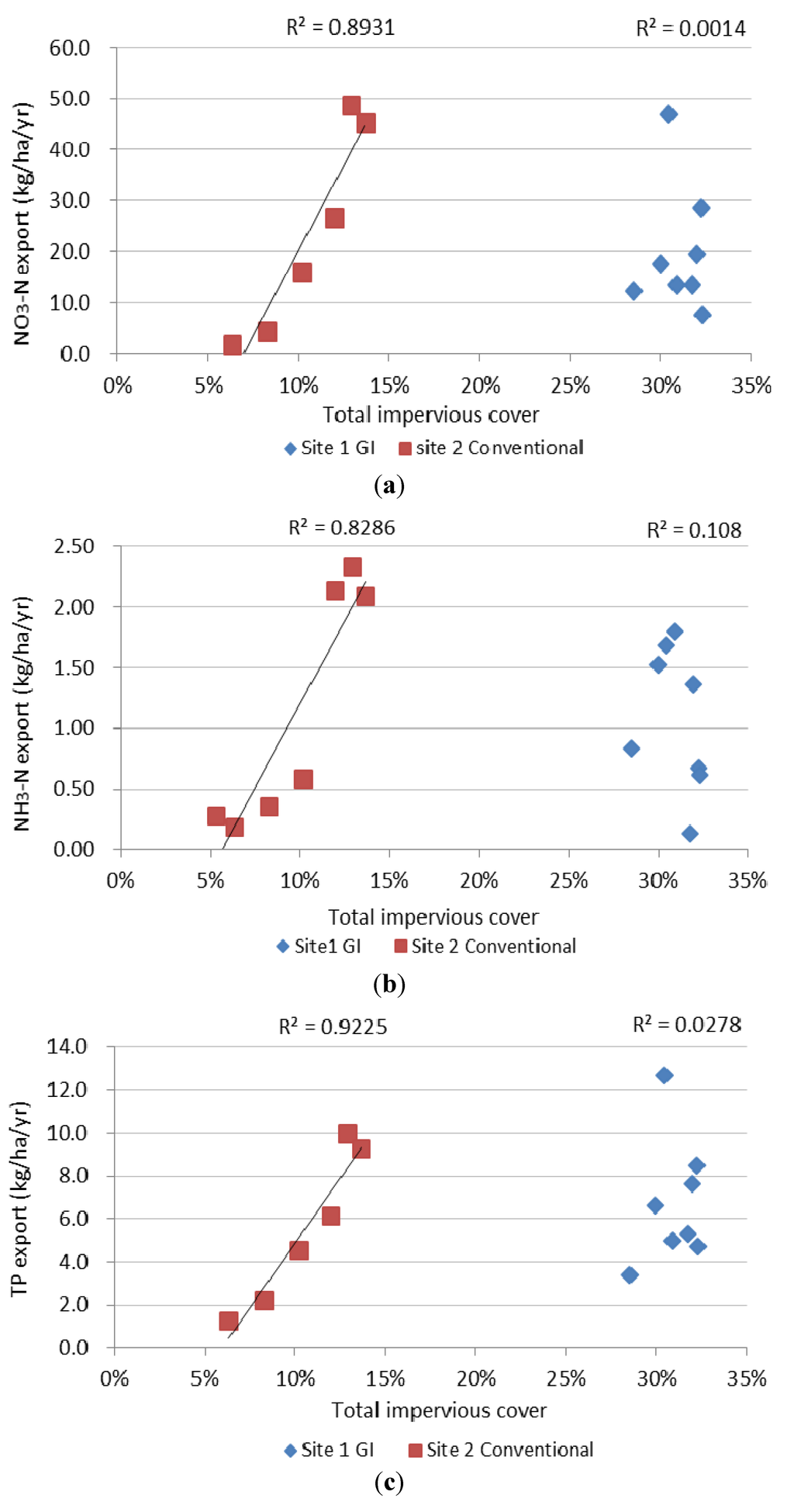
Figure 11.
Annual loadings of nutrient exports from Site 1 (Panther Creek watershed, The Woodlands green infrastructure development) and Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed, conventional development), 2002–2009: (a) NO3-N, (b) NH3-N, and (c) TP.

Table 3.
Relationship between watershed impervious cover percentage and nutrient loading in Site 1 (Panther Creek watershed, The Woodlands green infrastructure development).
| Nutrient | R2 | Equation | P-value | Sample size (2002–2009) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3-N | 0.108 | NA | 0.427 | 58 |
| NO3-N | 0.001 | NA | 0.930 | 33 |
| TP | 0.028 | NA | 0.693 | 33 |

Table 4.
Relationship between watershed impervious cover percentage and nutrient loading in Site 2 (Bear Creek watershed, conventional development).
| Nutrient | R2 | Equation | P-value | Sample size (2002–2009) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3-N | 0.829 | y = 0.028x − 0.002 | 0.004 | 78 |
| NO3-N | 0.894 | y = 0.666x − 0.046 | 0.004 | 57 |
| TP | 0.923 | y = 0.12x − 0.007 | 0.002 | 56 |
Note: x is watershed impervious cover percentage; and y is nutrient loading.
4. Discussion
The eight years of empirical data yield consistent results showing that GI design produces less development impact on the flow regime and better stormwater quality than the conventional drainage design. As of 2009, the percentage of impervious cover in Site 1 (GI, 32.3%) is more than twice that of the Site 2 (conventional, 13.7%). In addition, Site 1 (GI)’s total precipitation is 15.3% higher than that of Site 2 (conventional). Further, Site 1 (GI) has a much lower runoff infiltration capacity than Site 2 (conventional) (e.g., 38.7% versus 80.2% of A & B soils). The opposite is true, however, when comparing watershed outputs—the Site 1 (GI) streamflow volume and streamflow-precipitation ratio are lower than those of Site 2 (conventional). Therefore, the differences in streamflow response can be largely attributed to the different drainage designs.
Figure 9 and Figure 10 show that Site 2 (conventional) streamflow is more sensitive to precipitation and that it has a lower runoff storage capacity than Site 1 (GI). Large variability of streamflow-precipitation ratio suggests “flashy” stream conditions. In wet years such as 2004 and 2007, streamflow-precipitation ratios in Site 2 (conventional) increased dramatically. In contrast, Site 1 (GI) maintained a stable flow regime, which can be interpreted as low disturbance on the riparian habitat and riverine ecology. Likewise, water quality analyses showed consistency with the findings in streamflow. Nutrient exports from Site 1 (GI) are in general lower than that of Site 2 (conventional) (see Figure 11).
This study also demonstrates that GI design can be applied across different scales. The study shows that large-scale GI performance (e.g., a few thousand acres) can be as effective as in site-level scales (e.g., 10–50 acres). GI design was implemented across various scales in The Woodlands. At the regional scale, lands with large patches of sandy soils were preserved as open space to infiltrate runoff [45]. Road alignment considered sandy soil locations where check dams were built to slow runoff velocity (see Figure 3) [31,50]. At the site level, a Landscape Clearance Index was developed to ensure the minimum clearance of vegetation. This index specified guidelines to preserve vegetation under different soil conditions in order to achieve the objective of zero runoff from individual parcels ([51], p. 46).
Moreover, this study confirms with previous studies that integrated GI design strategies are better than a single strategy [30,31,44]. This is because Site 1’s GI design mimics the natural hydrological cycle by keeping the portion of runoff that originally infiltrates underground. Soil and vegetation medium further improve water quality. In other words, the decentralized, on-site runoff treatment reduced the EIA after The Woodlands development.
The effectiveness of single GI designs is often reported in the literature, such as pollutant removals of rain gardens, green roofs, and porous pavements [81,82,83,84,85], and the USEPA’s current guidelines are also focusing on performance measures of individual GI designs [7]. This study contributes to the USEPA’s guidelines by demonstrating that integrated GI design strategies are effective in reducing the EIA and improving water quality. Site 1 (GI) presents a much higher TIA than Site 2 (conventional) (ca. 2.4–5.4 times). However, its streamflow volume is 6% less than that of Site 2 (conventional). This means that the EIA of Site 1 (GI)—the direct contributor to runoff volume and quality impairment—is considerably lower than Site 1’s TIA (32.3%). Site 1’s EIA can be even lower than Site 2 (conventional)’s TIA (13.7%), because the impervious surface areas in Site 2 (conventional) are considered to be well connected for efficient drainage design.
However, the efficacy of McHarg’s GI design may not be fully revealed because of the research design of this study. McHarg’s GI design innovations were primarily used in the early phases of community development, during which McHarg presided the design [45]. Unfortunately, residents do not appreciate some of the GI designs (e.g., bioswale) [52]. As a result, a hybrid approach which combined McHarg’s design and conventional drainage design were used in the later phases of development [58,59]. About one third of The Woodlands’ early phases (i.e., followed McHarg’s design) do not lie in the Panther Creek watershed. Hence, performance of GI design may be underestimated due to these study limitations. Also, the study cannot completely tease out the performance of The Woodlands early and later development phases in respect to their stormwater performance, because they were treated together as one study site (i.e., Site 1).
Another study limitation is that the small water-quality sample size may decrease the precision of nutrient loading estimations. The TCEQ uses a sampling frequency of one month to meet the monitoring objectives in western Houston areas. Littlewood’s method used in this current study is based on these discrete water-quality data to estimate annual mass loads [79,80]. The precision range and confidence level of estimation decrease when the sampling frequency (e.g., monthly) and the length of the estimation period (e.g., five years) decrease. A sampling frequency that is too low (e.g., less than six samples per year) is not recommended—a principle followed in this study. In addition, estimates for dry years exhibit higher precision than those for wet years. This study used the best available data and the study period contains normal variations of dry versus wet years.
Finally, the 1.01 km2 (250-acre) lake in Site 1 (GI, The Woodlands) upstream of the TCEQ gauge station is likely to dilute the concentration of pollutants contributed by the upstream areas of the lake. This study cannot tease out this lake dilution effect and the effect presents some limitations. However, according to the original design [86], the lake is intended to serve as a recreation amenity and as a flood control device in The Woodlands comprehensive stormwater management plan. Therefore, this integrated design strategy showed success in flood control and water quality improvement. Nonetheless, future studies are called for to evaluate the performance of each individual strategy and to compare it with the overall efficacy of the integrated strategy, as shown in this current study.
5. Conclusions
This study compares the stormwater management performance of GI design and conventional design at large-scale community developments (89.4 km2 and 55.7 km2). Empirical evidence strongly suggests that integrated GI application can be effective in stormwater runoff reduction and water quality improvement. Despite a much higher TIA, GI design results in a much lower runoff volume, compared with conventional design. Further, nutrient outputs are significantly correlated with the extent of development in the conventional site, whereas there is little correlation in the GI site.
In the United States and many parts of the world, community development continues to be a major development project and covers a large territory of land. The status quo of stormwater management practices increasingly draws criticism for causing environmental quality problems. This study shows that integrated GI design can help achieve multiple stormwater management goals and may provide a cost-effective solution. In addition to the enormous construction cost savings, the potential flooding costs and potential pollution treatment costs can be avoided. Future studies need to directly assess the EIA and GI performance during peak events. Further studies are also needed to test GI performance in different climatic conditions and to improve the aesthetics of GI design based on public input.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments which greatly improved this paper. This research was supported by the Utah Agricultural Experiment Station, Utah State University (approved as journal paper number 8608) and the NSF EPSCoR grant EPS 1208732 awarded to Utah State University, as part of the State of Utah Research Infrastructure Improvement Award. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Utah Agricultural Experiment Station and the National Science Foundation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage: The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, D.B.; Jackson, C.R. Urbanization of aquatic systems: Degradation thresholds, stormwater detection, and the limits of mitigation. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1997, 33, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Booth, D.; Hill, K.; Coburn, B.; Avolio, C.; Coe, S.; Spirandelli, D. The impact of urban patterns on aquatic ecosystems: An empirical analysis in Puget lowland sub-basins. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, F.; DeFee, B.B. Urbanization and its effect on runoff in the Whiteoak Bayou watershed, Texas. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, C.A.; Roesner, L.A. Tools for the Evaluation of Stormwater Management Practices that Provide Ecological Stability in Urban Streams. In Cities of the Future: Towards Integrated Sustainable Water and Landscape Management; Novotny, V., Breckenridge , L., Brown, P., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007; pp. 174–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, C.Y.; Li, M.-H. The effect of urbanization on stream hydrology in hillslope watersheds in central Texas. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3706–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Managing Wet Weather with Green Infrastructure: Action Strategy 2008. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/npdes/pubs/gi_action_strategy.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2012).
- Brabec, E. Imperviousness and land use policy: Toward an effective approach to watershed planning. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, T.R. The importance of imperviousness. Watershed Prot. Tech. 1994, 1, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Schueler, T.R. Impacts of Impervious Cover on Aquatic Systems; Watershed Protection Research Monograph No. 1; Center for Watershed Protection: Ellicott City, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Brabec, E.; Schulte, S.; Richards, P.L. Impervious surfaces and water quality: A review of current literature and its implications for watershed planning. J. Plan. Lit. 2002, 16, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyons, J.; Kanehl, P.; Bannerman, R.T. Impacts of urbanization on stream habitat and fish across multiple scales. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.J. Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, A.I. Linking urban form, land cover pattern, and hydrologic flow regime in the Puget Sound Lowland. Urban Ecosyst. 2012, 15, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.D. Urbanization and stream quality impairment. Water Resourc. Bull. 1979, 15, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, D.B.; Karr, J.R.; Schauman, S.; Konrad, C.P.; Morley, S.A.; Larson, M.G.; Burges, S.J. Reviving urban streams: Land use, hydrology, biology, and human behavior. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 40, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Schueler, T.R.; Fraley-McNeal, L.; Cappiella, K. Is impervious cover still important? Review of recent research. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.K. Storm-water infiltration for peak-flow control. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1995, 121, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.K. Introduction to Stormwater; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, M.J.; Meyer, J.L. Streams in the urban landscape. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 333–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, L.; Revitt, D.M.; Ellis, J.B. A systematic approach for the comparative assessment of stormwater pollutant removal potentials. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.B.; Marsalek, J. Overview of urban drainage: Environmental impacts and concerns, means of mitigation and implementation policies. J. Hydraul. Res. 1996, 34, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxted, J.; Shaver, E.; Council, A.R. The Use of Retention Basins to Mitigate Stormwater Impacts to Aquatic Life. In Proceedings of National Conference on Retrofit Opportunities for Water Resource Protection in Urban Environments, EPA/625/R-99/002, Chicago, IO, USA, 9–12 February 1998.
- Perez-Pedini, C.; Limbrunner, J.F.; Vogel, R.M. Optimal location of infiltration-based best management practices for storm water management. J. Water Resourc. Plan. Manag. 2005, 131, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince George’s County, Department of Environmental Resources. Low-Impact Development Design Strategies: An Integrated Design Approach; Department of Environmental Resources, Programs and Planning Division: Prince George’s County, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, M.A.; McMahon, E.T. Green Infrastructure: Linking Landscapes and Communities; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tzoulas, K.; Korpela, K.; Venn, S.; Yli-Pelkonen, V.; Kaźmierczak, A.; Niemela, J.; James, P. Promoting ecosystem and human health in urban areas using green infrastructure: A literature review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 81, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, S.D.; Bolton, S.M.; Fridley, J.L. Design principles for ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 18, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.; Brown, E.J. G.; Wells, E. Ecological design applied. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, E.L.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bengtsson, L. Inner city stormwater control using a combination of best management practices. Ecol. Eng. 2004, 22, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, M.-H. Ecological engineering in a new town development: Drainage design in The Woodlands, Texas. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, M.-H.; Li, S. Design-with-Nature for Multifunctional Landscapes: Environmental Benefits and Social Barriers in Community Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 5433–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. Green Infrastructure for Cities: The Spatial Dimension. In Cities of the Future: Towards Integrated Sustainable Water and Landscape Management; Novotny, V., Brown, P., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007; pp. 267–283. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, M. Low impact development practices: A review of current research and recommendations for future directions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 186, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, M.E.; Clausen, J.C. Stormwater runoff and export changes with development in a traditional and low impact subdivision. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M.; Veenhuis, J.E. Effective impervious area in urban runoff modeling. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.S.; Burian, S.J. Determining effective impervious area for urban hydrologic modeling. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.H.; Shuster, W.D. Assessing impervious surface connectivity and applications for watershed management. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, A.I.; Glenn, E.M. Spatial patterns of urban development from optimization of flood peaks and imperviousness-based measures. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman-Dodds, J.K.; Bradley, A.A.; Potter, K.W. Evaluation of hydrologic benefits of infiltration based urban storm water management. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Brander, K.E.; Owen, K.E.; Potter, K.W. Modeled impacts of development type on runoff volume and infiltration performance. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2004, 40, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataki, D.E.; Carreiro, M.M.; Cherrier, J.; Grulke, N.E.; Jennings, V.; Pincetl, S.; Pouyat, R.V.; Whitlow, T.H.; Zipperer, W.C. Coupling biogeochemical cycles in urban environments: Ecosystem services, green solutions, and misconceptions. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, M.; Zellner, M.; Minor, E.; Gonzalez-Meler, M.; Cotner, L.; Massey, D.; Ahmed, H.; Elberts, M.; Sprague, H.; Wise, S.; et al. Using Green Infrastructure to Manage Urban Stormwater Quality: A Review of Selected Practices and State Program. Available online: http://www.uic.edu/labs/minor/GreenInfrastructureStudy.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2012).
- American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA). Green Infrastructure Project Database. Available online: http://www.asla.org/stormwatercasestudies.aspx (accessed on 15 August 2012).
- McHarg, I.L. A Quest for Life: An Autobiography; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Li, M.-H. Assessing planning approaches by watershed streamflow modeling: Case study of the Woodlands, Texas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 99, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedient, P.; Flores, A.; Johnson, S.; Pappas, P. Floodplain storage and land-use analysis at the Woodlands, Texas. Water Resour. Bull. 1985, 21, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, McHarg, Roberts, and Todd (WMRT). Woodlands New Community: An Ecological Inventory; WMRT: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, McHarg, Roberts, and Todd (WMRT). Woodlands New Community: Guidelines for Site Planning; WMRT: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, McHarg, Roberts, and Todd (WMRT). Woodlands New Community: Phase One: Land Planning and Design Principles; WMRT: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, McHarg, Roberts, and Todd (WMRT). Woodlands New Community: An Ecological Plan; WMRT: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Kutchin, J.W. How Mitchell Energy & Development Corp. Got Its Start and How It Grew: An Oral History and Narrative Overview; Mitchell Energy & Development Corporation: The Woodlands, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth, A. Planning lessons from three US new towns of the 1960s and 1970s—Irvine, Columbia, and The Woodlands. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2002, 68, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, A. Reforming Suburbia: The Planned Communities of Irvine, Columbia, and The Woodlands; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Ellis, C.D. Determining the effects of local development regulations on landscape structure: Comparison of The Woodlands and North Houston, TX. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girling, C.L.; Helphand, K.I. Yard, Street, Park: The Design of Suburban Open Space; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). National Weather Service Storm Data and Unusual Weather Phenomena. 2000. Available online: http://www.srh.noaa.gov/hgx/severe/2000/apr00hgx.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2008).
- Galatas, R.; Barlow, J. The Woodlands: The Inside Story of Creating a Better Hometown; Urban Land Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Girling, C.L.; Kellett, R. Skinny Streets and Green Neighborhoods: Design for Environment and Community; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- West Houston Association (WHA). 2003 Demographic & Development Trends. WHA: Houston, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau (2011). Texas Gains the Most in Population Since the Census. Available online: http://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb11-215.html (accessed on 10 June 2012).
- City of Houston General Plan. Available online: http://www.houstontx.gov/planning/_GeneralPlan/cohPlans.html (accessed on 10 April 2012).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Texas 2010 Integrated Report 303(d) List. Available online: http://www.tceq.texas.gov/assets/public/compliance/monops/water/10twqi/2010_303.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2012).
- Rogers, G.O.; DeFee, B.B. Long-term impact of development on a watershed: Early indicators of future problems. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 73, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Shandas, V.; Alberti, M. Exploring the role of vegetation fragmentation on aquatic conditions: Linking upland with riparian areas in Puget Sound lowland streams. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Light, D.L. The national aerial photography program as a geographic informaiton system resource. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1993, 59, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, D.B.; Jarnagin, T.S. Changes in anthropogenic impervious surfaces, precipitation and daily streamflow discharge: A historical perspective in a mid-atlantic subwatershed. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 471–489. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Transportation Institute. GIS Road Data. Available online: http://tti.tamu.edu/group/transplanning/research-areas/gps-and-gis-analyses/ (accessed on 5 August 2008).
- Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). Soil Survey Geographic (SSURGO) Data. Available online: http://soildatamart.nrcs.usda.gov/ (accessed on 5 March 2012).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). National Soil Survey Handbook; Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS): Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- National Climatic Data Center (NCDC). Daily Precipitation. Available online: http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov (accessed on 15 April 2012).
- Hann, C.T.; Barfield, B.J.; Hayes, J.C. Design Hydrology and Sedimentology for Small Catchments; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Daily Mean Streamflow. Available online: http://www.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 10 April 2012).
- Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). Surface Water Quality Monitoring Database; Texas Commission on Environmental Quality: Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, J.B. Paving over paradise: How land use regulations promote residential imperviousness. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 69, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, B.; Bullen, J.L. Urban form and watershed management: How zoning influences residential stormwater volumes. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Design 2006, 33, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Community Associations of the Woodlands, Texas. Residential Development Standards; Community Associations of the Woodlands, Texas: The Woodlands, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, T.X. Code of Ordinances: Chapter 42 Subdivisions, Developments and Platting. Available online: http://library.municode.com/HTML/10123/level4/COOR_CH42SUDEPL_ARTIIIPLST_DIV2ST.html#COOR_CH42SUDEPL_ARTIIIPLST_DIV2ST_S42-122RI-WWI (accessed on 5 July 2012).
- Littlewood, I.G. Estimating Constituent Loads in Rivers: A Review; Report No. 117; Institute of Hydrology: Wallingford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood, I.G. Hydrological regimes, sampling strategies, and assessment of errors in mass load estimates for United Kingdom rivers. Environ. Int. 1995, 21, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.P.; Hunt, W.F.; Traver, R.G.; Clar, M. Bioretention technology: Overview of current practice and future needs. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, M.E.; Clausen, J.C. A field evaluation of rain garden flow and pollutant treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 167, 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, B.K. Porous Pavements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Berndtsson, J.C. Green roof performance towards management of runoff water quantity and quality: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire, B.G.; Clausen, J.C. Effect of a modular extensive green roof on stormwater runoff and water quality. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 963–969. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, G.T.; King, J.O. The Woodlands: New Community Development 1964–1983; Texas A&M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).