Optimizing the Air Dissolution Parameters in an Unpacked Dissolved Air Flotation System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DAF Design
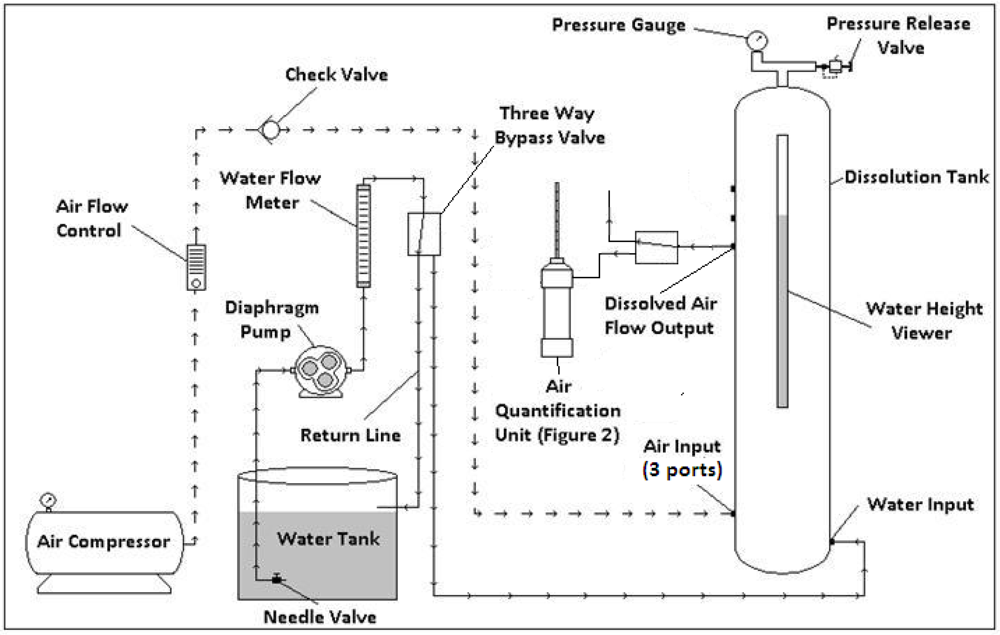
2.2. Quantification of Dissolved Air

2.3. Process Variables Testing
2.3.1. Pressure
2.3.2. Temperature
2.3.3. Hydraulic Retention Time
2.3.4. Air Flow
2.3.5. Maximum Production
3. Results
3.1. Pressure
 )The retention time (11 min), temperature (21 °C), and air flow (8.5 L/h) were held constant. The microbubble volume was measured at pressures of 345, 414, 483, 552, and 621 kPa; (
)The retention time (11 min), temperature (21 °C), and air flow (8.5 L/h) were held constant. The microbubble volume was measured at pressures of 345, 414, 483, 552, and 621 kPa; (  )The power consumed by the pump at each pressure was correlated to volume of bubbles produced.
)The power consumed by the pump at each pressure was correlated to volume of bubbles produced.
 )The retention time (11 min), temperature (21 °C), and air flow (8.5 L/h) were held constant. The microbubble volume was measured at pressures of 345, 414, 483, 552, and 621 kPa; (
)The retention time (11 min), temperature (21 °C), and air flow (8.5 L/h) were held constant. The microbubble volume was measured at pressures of 345, 414, 483, 552, and 621 kPa; (  )The power consumed by the pump at each pressure was correlated to volume of bubbles produced.
)The power consumed by the pump at each pressure was correlated to volume of bubbles produced.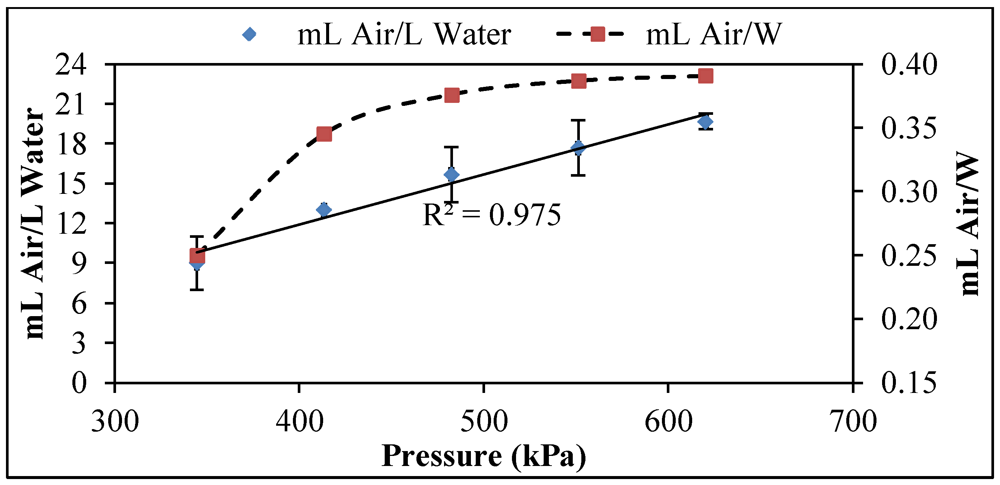
3.2. Power Consumption
3.3. Temperature
 (3)
(3) - Kc = Henry constant
- Ho = heat absorbed in the evaporation of 1 mol of gas from solution, kcal/kmol
- R = universal gas constant, 1.987 kcal/kmol
- T = absolute temperature, °K
- K = individual gas constant

 (4)
(4) - D = the diffusivity of the gas, m2/s
- k’ = Bolzmann constant, 1.38 × 10−23 J/°K
- T = the absolute temperature, °K
- α = radius of the solute molecule, m
- µ = viscosity of the solvent, kg/m*s
3.4. Hydraulic Retention Time

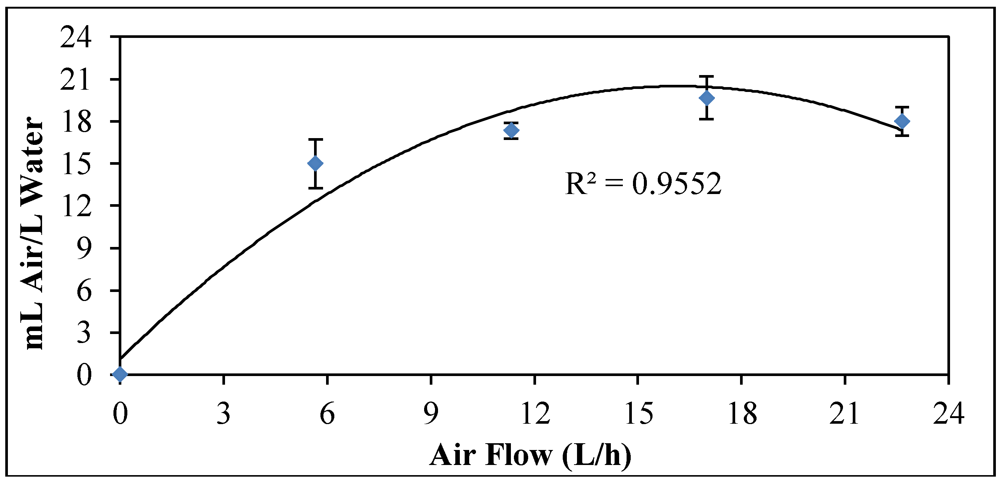
3.5. Air Flow
3.6. Maximum Bubble Production

4. Conclusions
References
- Telang, A. Waste water treatment systems. In Proceedings of the 22nd WEDC Conference, New Delhi, India, 9-13 September 1996.
- Chung, T.; Kim, D. Significance of pressure and recirculation in sludge thickening by dissolved air flotation. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Kim, W.; Dockko, S. Collision efficiency factor of bubble and particle in DAF: Theory and experimental verification. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Edzwald, J. Principles and applications of dissolved air flotation. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 31, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf & Eddy, Inc. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, C.; Smith, B.; Valentine, G. Rethinking dissolved air flotation (DAF) design for industrial pretreatment. In Proceedings of 2000 WEF and Purdue University Industrial Wastes Technical Conference; St. Louis, MO, USA, May 2000; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2000; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrot, V.; Huang, Z.; Legendre, D.; Guiraud, P. Experimental determination of particles capture efficiency in flotation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 7359–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Kim, T.; Kim, J. Effects of floc and bubble size on the efficiency of the dissolved air flotation (DAF) process. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Faust, S.; Aly, O. Chemistry of Water Treatment, 2nd ed; Ann Arbor Press: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Haarhoff, J.; van Vuuren, L. Design parameters for dissolved air flotation in South Africa. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 31, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Haarhoff, J.; Rykaart, E. Rational design of packed saturators. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 31, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach, S.; Haarhoff, J. A simplified method for assessing the saturation efficiency at full-scale dissolved air flotation plants. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Haarhoff, J.; Steinback, S. A model for the prediction of the air composition in pressure saturators. Water Res. 1996, 30, 3074–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rijk, S.; Jaap, G.; den Blanken, J. Bubble size in flotation thickening. Water Res. 1994, 28, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.; Souza, M.; Smith, R. Overview of flotation as a wastewater treatment technique. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, E. Gas transfer to and across an air-water interface. Tellus 1977, 29, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broecker, W.; Peng, T. Gas exchange rates between air and sea. Tellus 1974, 26, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlyssides, A.; Mai, S.; Barampouti, E. Size distribution formed by depressurizing air-saturated water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ouyang, F. Hydrodynamic characteristics of the process of depressurization of saturated water. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 1994, 2, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Dassey, A.; Theegala, C. Optimizing the Air Dissolution Parameters in an Unpacked Dissolved Air Flotation System. Water 2012, 4, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4010001
Dassey A, Theegala C. Optimizing the Air Dissolution Parameters in an Unpacked Dissolved Air Flotation System. Water. 2012; 4(1):1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleDassey, Adam, and Chandra Theegala. 2012. "Optimizing the Air Dissolution Parameters in an Unpacked Dissolved Air Flotation System" Water 4, no. 1: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4010001
APA StyleDassey, A., & Theegala, C. (2012). Optimizing the Air Dissolution Parameters in an Unpacked Dissolved Air Flotation System. Water, 4(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4010001



