Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life and Ecological Risk Assessment for Sulfamethoxazole in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Screening and Collection
2.2. ALFQC Derivation Methodology
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Acute and Chronic Toxicity of SMX to Aquatic Species
| Rank | Species Scientific Name | Species Groups | Endpoint | ATV (µg/L, ×103) | SMAV (µg/L, ×103) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raphidocelis subcapitata | Algae | EC50 | 9 | 9 | [5] |
| 2 | Ceriodaphnia dubia | Crustacean | EC50 | 15.51 | 15.51 | [38] |
| 3 | Brachionus calyciflorus | Invertebrate | LC50 | 26.27 | 26.27 | [38] |
| 4 | Thamnocephalus platyurus | Crustacean | LC50 | 35.36 | 35.36 | [38] |
| 5 | Moina macrocopa | Crustacean | EC50 | 70.4 | 70.4 | [39] |
| 6 | Xenopus laevis | Amphibian | EC50 | 100 | 100 | [40] |
| 7 | Hydra vulgaris | Invertebrate | LC50 | 100 | 100 | [41] |
| 8 | Dugesia japonica | Worm | LC50 | 126.7 | 126.7 | [42] |
| 9 | Daphnia magna | Crustacean | EC50, LC50 | 96.7–234.18 | 159.83 | [39,43,44] |
| 10 | Oryzias latipes | Fish | LC50 | 562.5 | 562.5 | [45] |
| Rank | Species Scientific Name | Species Groups | Endpoint | CTV (µg/L, ×103) | SMCV (µg/L, ×103) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lemna gibba | Worm | NOEC, LOEC | 0.009–0.11 | 0.03 | [34,46] |
| 2 | Daphnia magna | Crustacean | NOEC, LOEC | 0.12–0.37 | 0.17 | [44] |
| 3 | Micropterus salmoides | Fish | LOEC | 0.3 | 0.3 | [7] |
| 4 | Danio rerio | Fish | NOEC | 0.53 | 0.53 | [47] |
| 5 | Selenastrum capricornutum | Algae | NOEC, LOEC | 0.5–0.61 | 0.55 | [6,48] |
| 6 | Microcystis aeruginosa | Algae | EC50 | 0.55 | 0.55 | [5] |
| 7 | Raphidocelis subcapitata | Algae | NOEC, LOEC | 0.5–0.8 | 0.63 | [49] |
| 8 | Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata | Algae | NOEC | 1.5 | 1.5 | [6] |
| 9 | Chlorella vacuolata | Algae | EC50 | 1.54 | 1.54 | [50] |
| 10 | Chlorella vulgaris | Algae | EC50 | 1.57 | 1.57 | [51] |
| 11 | Brachionus calyciflorus | Invertebrate | EC50 | 9.63 | 9.63 | [38] |
3.2. ALFQC of SMX for China
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment for SMX in China
3.3.1. Concentration of SMX in Surface Waters
3.3.2. Quantitative Risk Assessment for SMX
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SMX | Sulfamethoxazole |
| ALFQC | Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life |
| Long-term ALFQC | Long-Term Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life |
| Short-term ALFQC | Short-Term Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life |
| SSD | Species Sensitivity Distribution |
| AF | Assessment Factor |
| ATV | Acute Toxicity Values |
| CTV | Chronic Toxicity Values |
| NOEC | No Observed Effect Concentration |
| LOEC | Lowest Observed Effect Concentration |
| MATC | Maximum Acceptable Toxicant Concentration |
| SMAV | Species Mean Acute Toxicity Value |
| SMCV | Species Mean Chronic Toxicity Value |
| RQ | Risk Quotient |
| OA | Overlap Area |
References
- Yang, Y.; Song, W.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Du, L.; Xing, W. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global lakes: A review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasannamedha, G.; Kumar, P.S. A review on contamination and removal of sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution using cleaner techniques: Present and future perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.-V.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chao, W.-L.; Yeh, S.-L.; Kuo, D.-L.; Yang, C.-W. Effects of sulfamethoxazole and sulfamethoxazole-degrading bacteria on water quality and microbial communities in milkfish ponds. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Sun, F.; Goei, R.; Zhou, Y. Facile fabrication of RGO-WO3 composites for effective visible light photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 207, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Grinten, E.; Pikkemaat, M.G.; van den Brandhof, E.-J.; Stroomberg, G.J.; Kraak, M.H.S. Comparing the sensitivity of algal, cyanobacterial and bacterial bioassays to different groups of antibiotics. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Liu, W.Q.; Nie, X.P.; Guan, C.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, Z.H.; Liao, W. Growth response and toxic effects of three antibiotics on Selenastrum capricornutum evaluated by photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll biosynthesis. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1558–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.W.; Yin, P.; Tian, L.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Tan, B.P.; Niu, J. Interactions between dietary lipid levels and chronic exposure of legal aquaculture dose of sulfamethoxazole in juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 229, 105670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, H.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Fu, Z.; Liao, W.; Giesy, J.P.; Bai, Y. Technical study on national mandatory guideline for deriving water quality criteria for the protection of freshwater aquatic organisms in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Xiao, S.; Naraginti, S.; Liao, W.; Feng, C.; Xu, D.; Guo, C.; Jin, X.; Xie, F. Freshwater water quality criteria for phthalate esters and recommendations for the revision of the water quality standards. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Meng, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Cao, Y.; Liao, H. China embarking on development of its own national water quality criteria system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7992–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Feng, C.; Jin, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, N.; Bai, Y.; Wu, F.; Raimondo, S. A QSAR-ICE-SSD model prediction of the PNECs for alkylphenol substances and application in ecological risk assessment for rivers of a megacity. Environ. Int. 2022, 167, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Jin, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Johnson, A.C.; Xiao, H.; Hollert, H.; Giesy, J.P. Ecological risk assessment of fifty pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Chinese surface waters: A proposed multiple-level system. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, F.; Zuccato, E.; Davoli, E.; Fattore, E.; Castiglioni, S. Risk assessment of a mixture of emerging contaminants in surface water in a highly urbanized area in Italy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 361, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, C.; Liu, D.; Yan, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, F. A review on the water quality criteria of nonylphenol and the methodological construction for reproduction toxicity endocrine disrupting chemicals. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 260, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, B.; Yuan, H.L.; Yu, G. Derivation of water quality criteria for sulfonamide antibiotics using species sensitivity distribution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 39, 184–188. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.Z.; Wang, B.; Yu, G.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.B. Water quality criteria for sulfonamide antibiotics based on QSAR and ICE models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 170–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, T.; Sun, R.R.; Wang, Y.N. Ecological risk assessment and water quality criteria of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in surface waters. J. Environ. Health 2018, 35, 531–535. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Shi, T.; Wu, X.; Cao, H.; Li, X.; Hua, R.; Tang, F.; Yue, Y. The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in Lake Chaohu, China: Seasonal variation, potential source and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Wu, Q.; Liu, P.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Kwon, B.-O.; Choi, K.; Ryu, J.; et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments and water from the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.; Purohit, M.; Diwan, V.; Chandran, S.P.; Riggi, E.; Parashar, V.; Tamhankar, A.J.; Lundborg, C.S. Monitoring of water quality, antibiotic residues, and antibiotic-resistant escherichiacoli in the kshipra river in India over a 3-year period. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairigo, P.; Ngumba, E.; Sundberg, L.-R.; Gachanja, A.; Tuhkanen, T. Contamination of surface water and river sediments by antibiotic and antiretroviral drug cocktails in low and middle-income countries: Occurrence, risk and mitigation strategies. Water 2020, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Ji, K.; Kim, C.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Kwon, B.; Kho, Y.; Park, K.; Kim, K.; Choi, K. Pharmaceutical residues in streams near concentrated animal feeding operations of Korea—Occurrences and associated ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Moreau-Guigon, E.; Labadie, P.; Alliot, F.; Teil, M.-J.; Blanchard, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence of antibiotics in rural catchments. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabino, J.A.; de Sá Salomão, A.L.; de Oliveira Muniz Cunha, P.M.; Coutinho, R.; Marques, M. Occurrence of organic micropollutants in an urbanized sub-basin and ecological risk assessment. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Gao, M.; Wang, L. Prevalence of veterinary antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in the surface water of a livestock production region in northern China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; An, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, B. Distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in a typical effluent–receiving river (Wangyang River) in north China. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Hu, J.; Wu, X.; Peng, H.; Wu, S.; Dong, Z. Occurrence and source apportionment of sulfonamides and their metabolites in Liaodong Bay and the adjacent Liao River basin, North China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Leung, K.S.-Y.; Wong, J.W.-C.; Selvam, A. Preliminary occurrence studies of antibiotic residues in Hong Kong and Pearl River Delta. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Meng, Q.; Liu, R.; Li, W. The derivation of seawater quality criteria and ecological risk assessment of Tonalide. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 298, 118287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xi, X.; Yu, G.; Cao, Q.; Wang, B.; Vince, F.; Hong, Y. Pharmaceutical compounds in aquatic environment in China: Locally screening and environmental risk assessment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.-y.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Ge, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, W.; Shi, J.; Li, X.-y. Development of ecological risk assessment for Diisobutyl phthalate and di-n-octyl phthalate in surface water of China based on species sensitivity distribution model. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, Y.; Song, K.; Xie, F.; Li, H.; Sun, F. Derivation of water quality criteria of zinc to protect aquatic life in Taihu Lake and the associated risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MEEC. Technical Guideline for Deriving Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Organisms (HJ831-2022); Minisitry of Ecology and Environment of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Brain, R.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Richards, S.M.; Sanderson, H.; Sibley, P.K.; Solomon, K.R. Effects of 25 pharmaceutical compounds to Lemna gibba using a seven-day static-renewal test. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Test No. 221: Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- MEEC. Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Aquatic Organisms-Phenol; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Li, W.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, B.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z. Development of aquatic life criteria for tonalide (AHTN) and the ecological risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Pascarella, L.; Parrella, A. Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, K. Hazard assessment of commonly used agricultural antibiotics on aquatic ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.M.; Cole, S.E. A toxicity and hazard assessment of fourteen pharmaceuticals to Xenopus laevis larvae. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.; Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. An investigation into the acute and chronic toxicity of eleven pharmaceuticals (and their solvents) found in wastewater effluent on the cnidarian, Hydra attenuata. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H. Acute toxicity of 30 pharmaceutically active compounds to freshwater planarians, Dugesia japonica. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2013, 95, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Jeong, D.H.; Choi, K. Environmental levels of ultraviolet light potentiate the toxicity of sulfonamide antibiotics in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. Effects of selected pharmaceuticals on growth, reproduction and feeding of Daphnia magna. Fresenius Environ. 2013, 22, 2583–2589. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Jung, J.; Park, S.; Kim, P.-G.; Park, J. Aquatic toxicity of acetaminophen, carbamazepine, cimetidine, diltiazem and six major sulfonamides, and their potential ecological risks in Korea. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brain, R.A.; Ramirez, A.J.; Fulton, B.A.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W. Herbicidal effects of sulfamethoxazole in Lemna gibba: Using p-aminobenzoic acid as a biomarker of effect. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8965–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madureira, T.V.; Rocha, M.J.; Cruzeiro, C.; Rodrigues, I.; Monteiro, R.A.F.; Rocha, E. The toxicity potential of pharmaceuticals found in the Douro River estuary (Portugal): Evaluation of impacts on fish liver, by histopathology, stereology, vitellogenin and CYP1A immunohistochemistry, after sub-acute exposures of the zebrafish model. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Nagase, H.; Ozawa, M.; Endoh, Y.S.; Goto, K.; Hirata, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Yoshimura, H. Evaluation of antimicrobial agents for veterinary use in the ecotoxicity test using microalgae. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.H.; Ying, G.G.; Su, H.C.; Stauber, J.L.; Adams, M.S.; Binet, M.T. Growth-inhibiting effects of 12 antibacterial agents and their mixtures on the freshwater microalga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialk-Bielinska, A.; Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Uebers, U.; Böschen, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Matzke, M. Ecotoxicity evaluation of selected sulfonamides. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, W.; Sochacka, J.; Wardas, W. Toxicity and biodegradability of sulfonamides and products of their photocatalytic degradation in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, J.O. Aquatic environmental risk assessment for human use of the old antibiotic sulfamethoxazole in Europe. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Witter, J.D.; Spongberg, A.L.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and associated environmental risks in the central and lower Yangtze river, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 106, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Meyer, M.T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.-a.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Shu, W. Determination of antibiotics in sewage from hospitals, nursery and slaughter house, wastewater treatment plant and source water in Chongqing region of Three Gorge Reservoir in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Zi, C.F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Gan, X.M.; Peng, X.Y.; Gao, X.; Guo, J.-S. Pollution level and ecological risk assessment of typical pharmaceutically active compounds in the river basins of main districts of Chongqing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Jiang, L.; Han, Q.; Xue, J.Y.; Ye, H.; Cao, G.M.; Lin, K.F.; Cui, C.Z. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of thirteen sulfonamides antibiotics in a drinking water source in East China. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 2515–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.; Xu, G. Antibiotics in the surface water of Shanghai, China: Screening, distribution, and indicator selecting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9836–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Shang, J.; Shen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Peng, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; et al. Distribution and risk characteristics of antibiotics in China surface water from 2013 to 2024. Chemosphere 2025, 375, 144197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, M. Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment of Jianghan Plain, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y.; Gan, Y.; Guo, W.; Dong, C.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, K. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers: A case study at Jianghan Plain, central China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 135, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.J.; Cao, S.; Mu, S. Characteristics of concentrations of antibiotics in typical drinking water sources in a city in Jiangsu Province. Water Resour. Prot. 2016, 32, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, L.; Hu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Yu, Z. Occurrence, spatiotemporal distribution and potential ecological risks of antibiotics in Dongting Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhao, H.; Hou, L.; Yang, Y. Application of passive sampling in assessing the occurrence and risk of antibiotics and endocrine disrupting chemicals in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Nie, M.; Shi, H.; Gu, L. Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Cao, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J. Seasonal variation, flux estimation, and source analysis of dissolved emerging organic contaminants in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, H.; Li, J. Sources, distribution and potential risks of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Qingshan Lake basin, Eastern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 96, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, S.; Geng, C.; Zhang, X. Occurrence and sources of antibiotics and their metabolites in river water, WWTPs, and swine wastewater in Jiulongjiang River basin, south China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 9075–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Chen, B.; Bai, R.; Song, P.; Lin, H. Contamination of sulfonamide antibiotics and sulfamethazine-resistant bacteria in the downstream and estuarine areas of Jiulong River in Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12104–12113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, L.; Luo, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Occurrence of selected antibiotics in Jiulongjiang River in various seasons, South China. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Qiu, X.; Chen, B.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, G.; Huang, H.; et al. Antibiotics pollution in Jiulong River estuary: Source, distribution and bacterial resistance. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Tang, J.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.-D. Levels, spatial distribution and sources of selected antibiotics in the East River (Dongjiang), South China. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, K.; Sun, X.-L.; Zhao, L.-R.; Zhang, Y.-B. Occurrence and distribution of the environmental pollutant antibiotics in Gaoqiao mangrove area, China. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.X.; Chen, Q.; Lei, M. Simultaneous determination of trace antibiotics in surface water by isotope-diluted high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Environ. Chem. 2016, 35, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.F.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Tao, R.; Su, H.C.; Liu, Y.S. Spatial and seasonal distribution of selected antibiotics in surface waters of the Pearl Rivers, China. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2011, 46, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Li, N.; Zheng, H.; Lin, H. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in river water in Hong Kong. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 125, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Yang, W.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Huang, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, R.J.; Huang, K. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks of sulfonamides in the Qinzhou Bay, South China. Environ Sci. 2013, 33, 1664–1669. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L. Occurrence and health risk assessment of antibiotics in drinking water of a city in Southern China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 657, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Antibiotic contamination in a typical developing city in south China: Occurrence and ecological risks in the Yongjiang River impacted by tributary discharge and anthropogenic activities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 92, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, T.B.; Leung, H.W.; Loi, I.H.; Chan, W.H.; So, M.K.; Mao, J.Q.; Choi, D.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zheng, G.; Martin, M.; et al. Antibiotics in the Hong Kong metropolitan area: Ubiquitous distribution and fate in Victoria Harbour. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikaros, A.G.; Chrysikopoulos, C.V. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) detected in lakes around the world—A review. Environ. Adv. 2021, 6, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in coastal water of the Bohai Bay, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2913–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Meng, T.; Zhang, S. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of typical antibiotics in environmental media in China. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 6894–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gao, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, distribution and risks of antibiotics in urban surface water in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X. Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the Laizhou Bay, China: Impacts of river discharge. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Hua, X. Antibiotics in water and sediments from Liao River in Jilin province, China: Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Zou, S.; Ling, Z.; Wang, G.; Yan, W. A preliminary investigation on the occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Yellow River and its tributaries, China. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

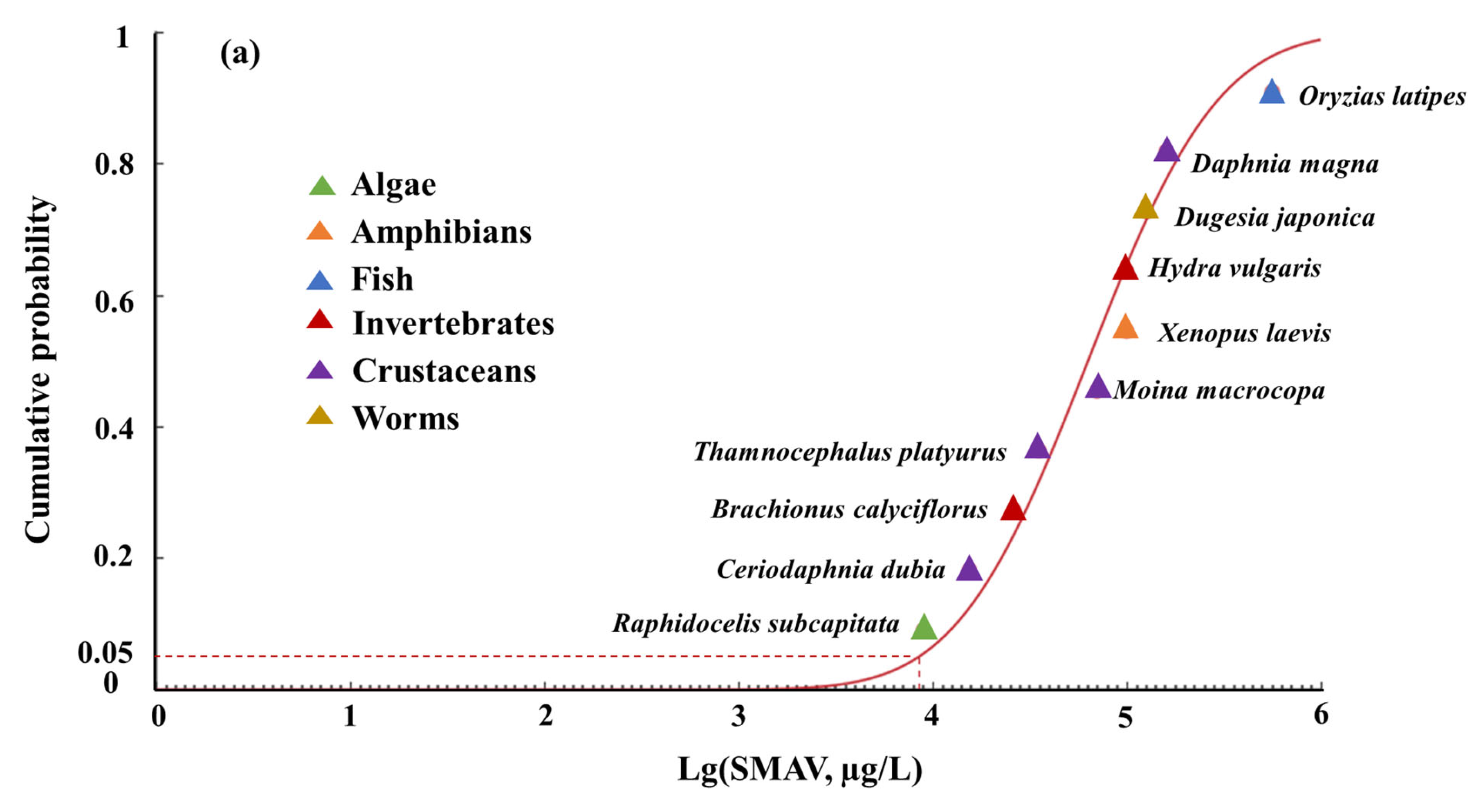
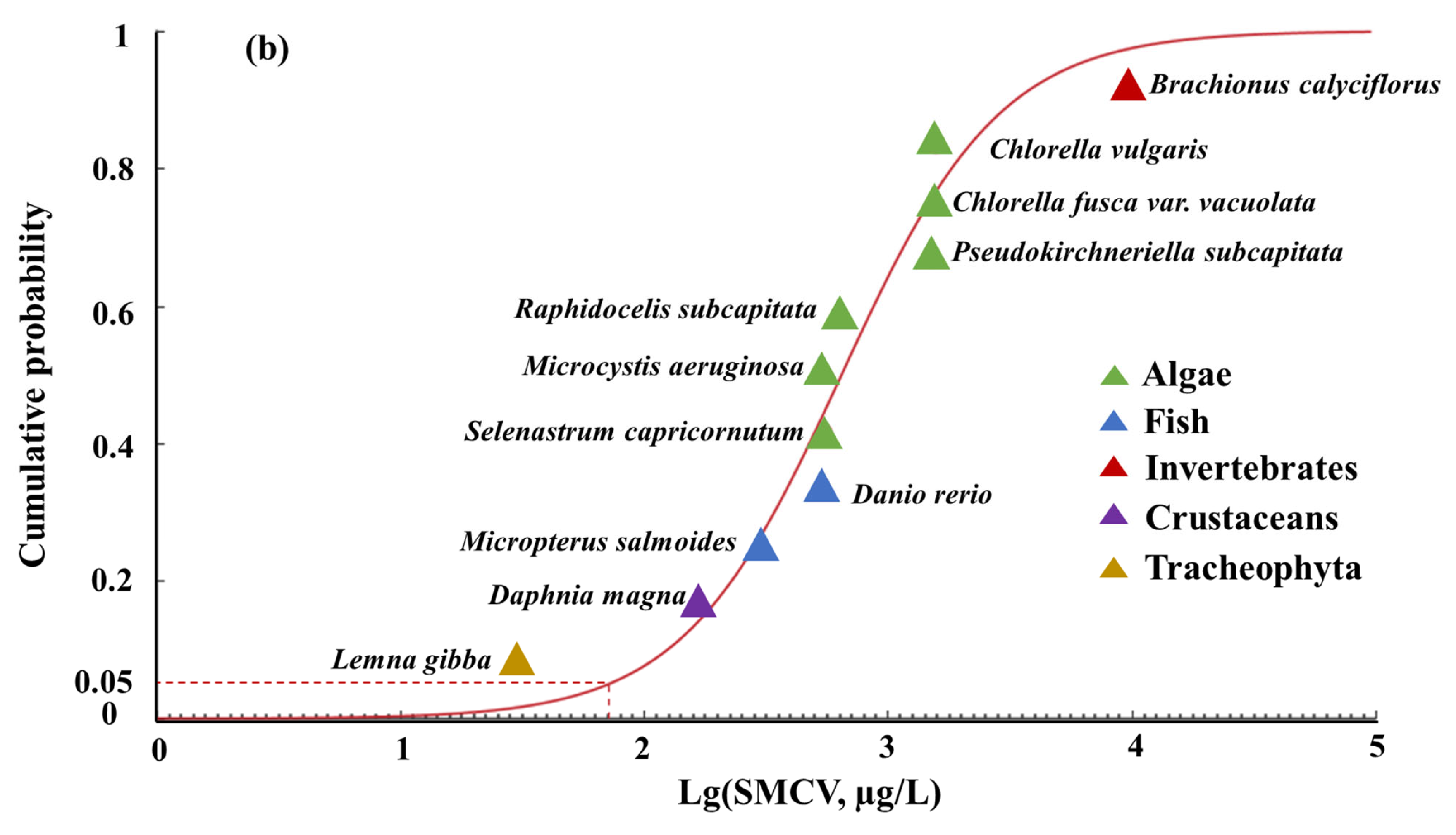


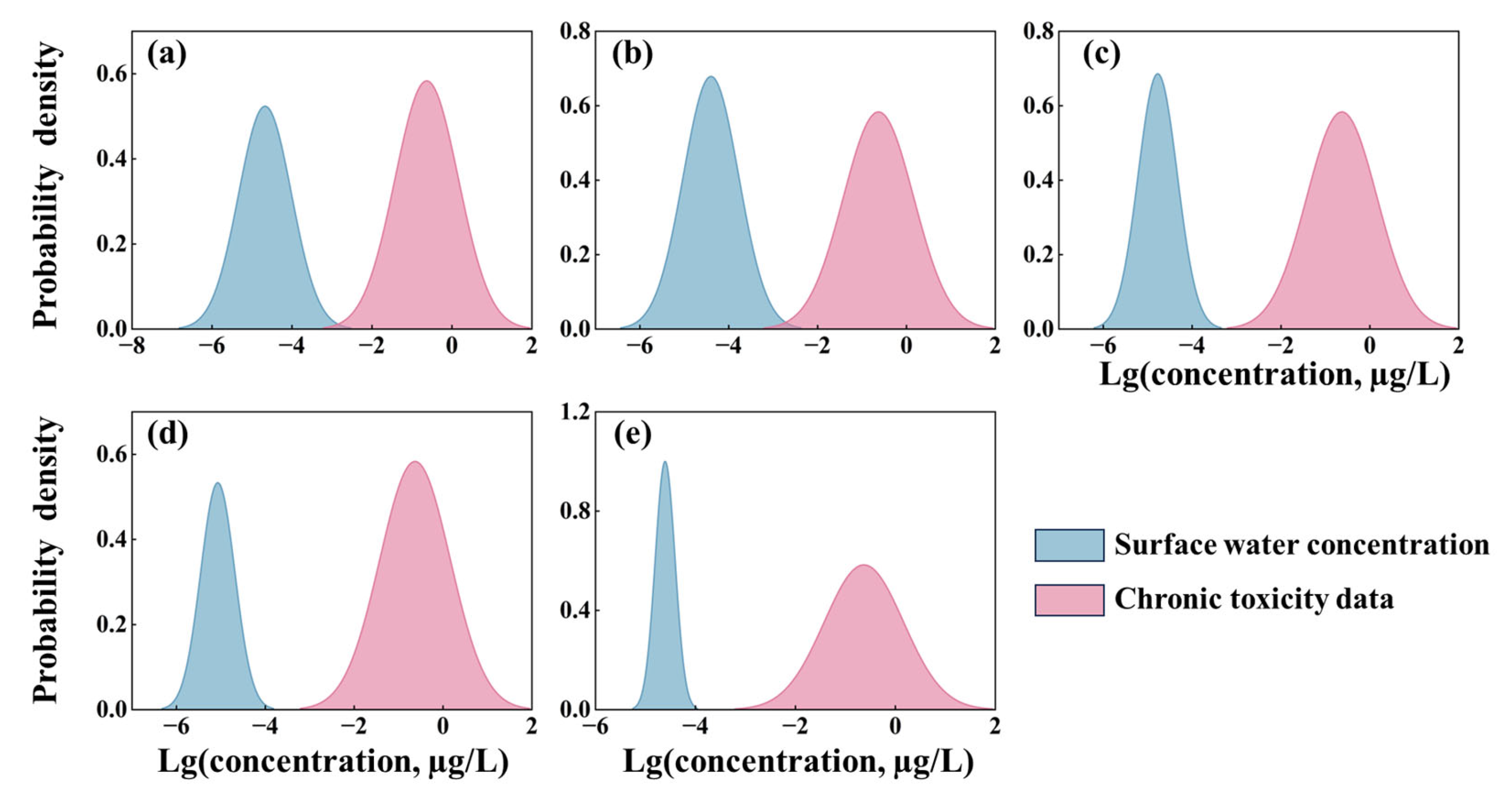
| ALFQC | Sensitive Species | Model | RMSE | p Value | HC5 (µg/L) | ALFQC (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term ALFQC | Raphidocelis subcapitata Ceriodaphnia dubia | Normal distribution | 0.0543 | >0.05 | 8489 | 2829 |
| Log-normal distribution | 0.0588 | >0.05 | 9449 | - | ||
| logistic distribution | 0.0619 | >0.05 | 8748 | - | ||
| Log-logistic distribution | 0.0646 | >0.05 | 9878 | - | ||
| Long-term ALFQC | Limnodynastes peronii Lemna gibba | logistic distribution | 0.0626 | >0.05 | 70.91 | 23.63 |
| Normal distribution | 0.0669 | >0.05 | 56.01 | - | ||
| Log-logistic distribution | 0.0634 | >0.05 | 86.49 | - | ||
| Log-normal distribution | 0.0811 | >0.05 | 62.02 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Y. Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life and Ecological Risk Assessment for Sulfamethoxazole in China. Water 2026, 18, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010045
Zhang Z, Fan Y, Wang L, Zhang W, Bai Y. Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life and Ecological Risk Assessment for Sulfamethoxazole in China. Water. 2026; 18(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zeya, Yili Fan, Lan Wang, Weibo Zhang, and Yingchen Bai. 2026. "Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life and Ecological Risk Assessment for Sulfamethoxazole in China" Water 18, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010045
APA StyleZhang, Z., Fan, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, W., & Bai, Y. (2026). Freshwater Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life and Ecological Risk Assessment for Sulfamethoxazole in China. Water, 18(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010045






