Kinetic Analysis of pH Effect on the Paracetamol Degradation by an Ozonation–Blast Furnace Slags Coupled System by Neural Network Approximation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Blast Furnace Slags
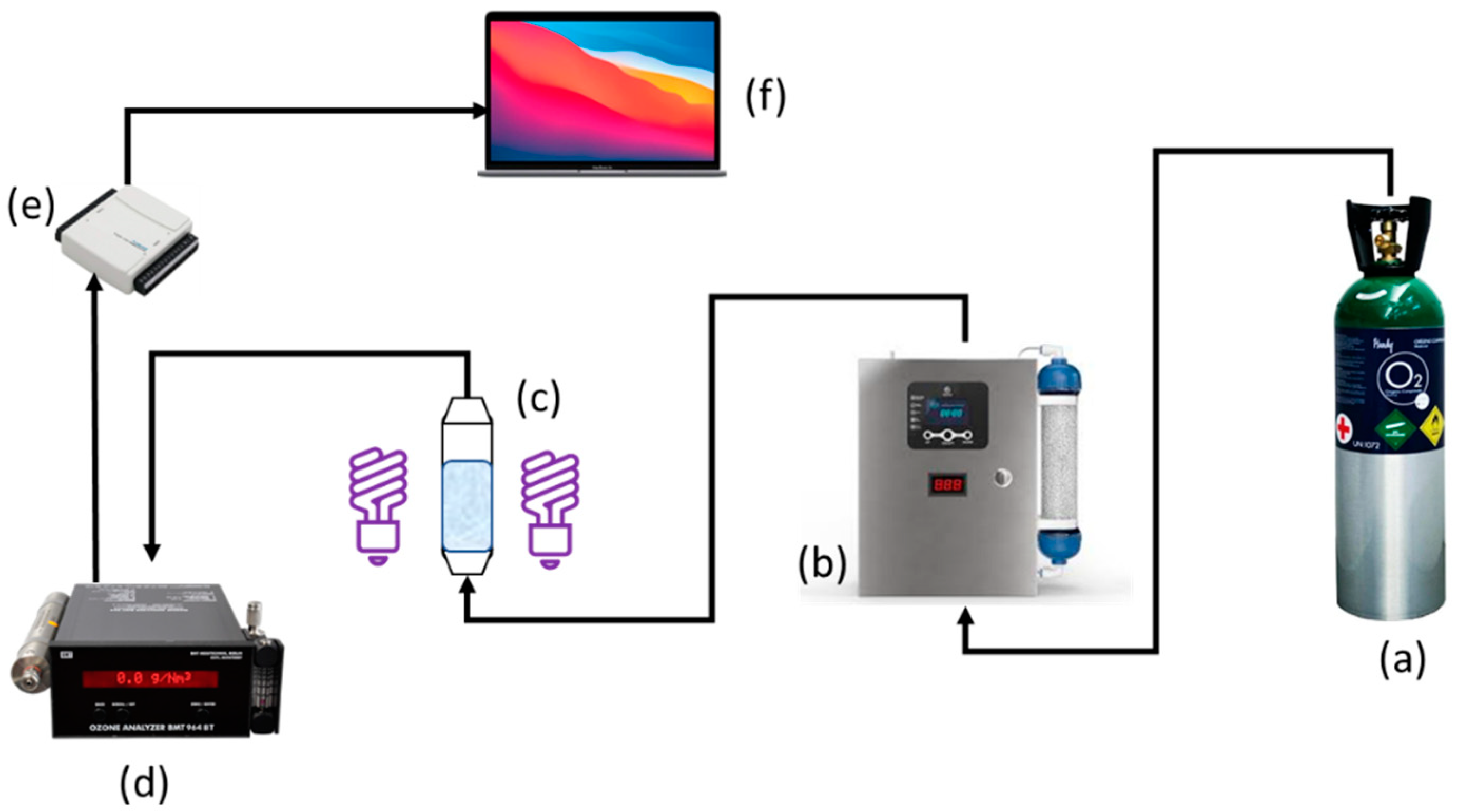
2.3. Ozonation Procedure
2.4. Analytic Method Analysis
2.5. Hybrid Modeling of Ozonation Dynamics Aided by LSTM Approximation
3. Results and Discussion
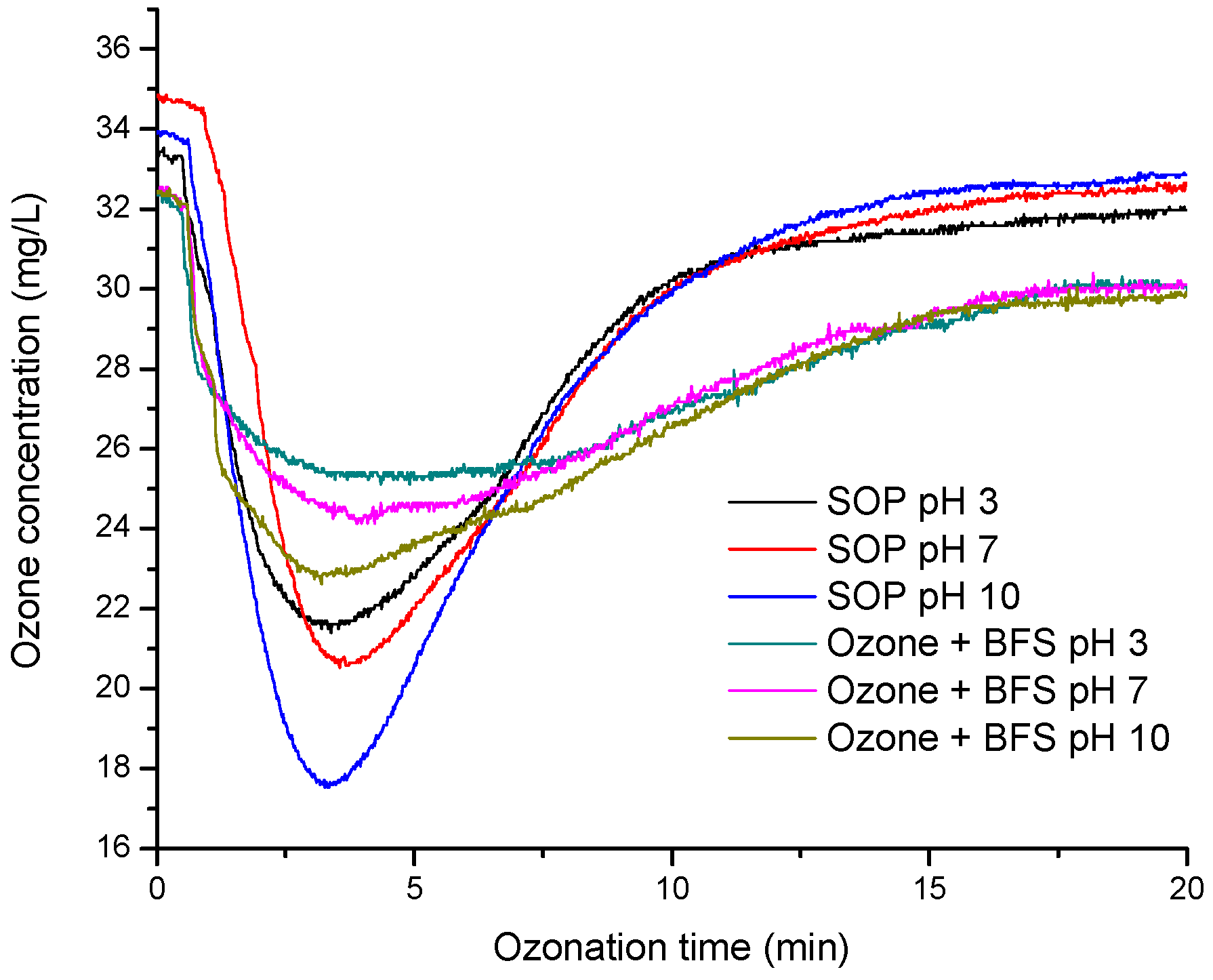
3.1. Ozone Consumption
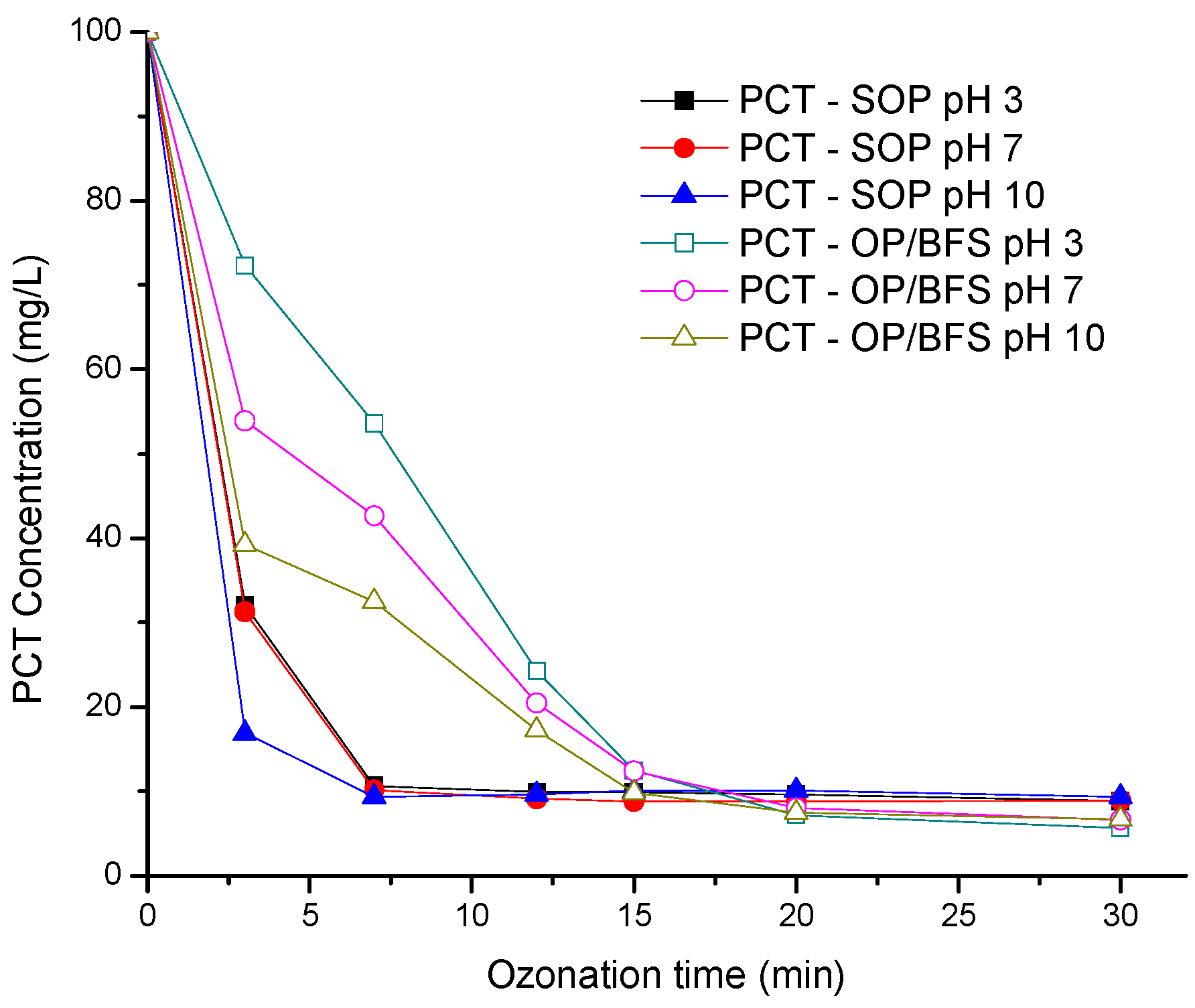
3.2. Paracetamol Decomposition Dynamics and pH Effect
3.3. Effect of Fe3+/Fe2+ on PCT Decomposition
3.4. Effect of MgO on PCT Decomposition
3.5. Effect of Al2O3 and SiO2 on PCT Decomposition
3.6. Final Compound Identification
3.7. Kinetics Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCT | Paracetamol |
| BFSs | Blast furnace slags |
| BOD5 | Biochemical oxygen demand at five days |
| SOP | Simple ozonation process |
| OP | Ozonation process |
| WWT | Wastewater treatment |
| ANNs | Artificial neural networks |
| LSTMs | Long short-term memories |
References
- Peralta-Hernández, J.M.; Brillas, E. A critical review over the removal of paracetamol (aceta minophen) from synthetic waters and real wastewaters by direct, hybrid catalytic, and sequential ozonation processes. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- «Global Market Insights» Global Market Insights, 2023. [En línea]. Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/acetaminophen-market (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Phillips, P.J.; Smith, S.G.; Kolpin, D.W.; Zaugg, S.D.; Buxton, H.T.; Furlong, E.T.; Esposito, K.; Stinson, B. Pharmaceutical formulation facilities as source of opioids and other pharmaceuticals to wastewater treatment, treatment plant effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4910–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, K.H.; Thomas, K.V. Determination of Pharmaceutical compounds in hospitals effluents and their contribution to wastewater treatment works. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 5766–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.; Lai, R.W.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical pollution of the world’s rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- «Market Data Forecast» Market Data Forecast, June 2024. [En línea]. Available online: https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/global-paracetamol-market (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J. Degradation of paracetamol by pure bacterial cultures and their microbial consortium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 3687–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, F.J.S.; Méndez, J.L.A.; Pech-Canché, J.M.; Maldonado, C.S. Main drugs waste generated in household and their ecotoxic potential in Tuxpan, Veracruz, Acta Universitaria. Multidiscip. Sci. J. 2019, 29, e2398. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez Jaber, I. Tecnológico de Monterrey. Available online: https://tecscience.tec.mx/en/health/groundwater-contamination/ (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Castro-Pastrana, L.I.; Baños-Medina, M.I.; López-Luna, M.A.; Torres-García, B.L. Ecofarmacovigilancia en México: Perspectivas para su implementación. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Farmacéuticas 2015, 46, 16–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, A.; García-Gamboa, M.; Sánchez-Luna, M.S.; Gloria-García, L.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.; Mahlknecht, J. A review of the current environmental status and human health implications of one of the most polluted rivers of Mexico: The Atoyac River, Puebla. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-García, A.; García-Sanz-Salcedo, J.; Carrasco-Amador, J.P.; Segura-Cruz, R. Adsorption of Paracetamol in Hospital Wastewater Through Activated Carbon Filters. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrero-lópez, M.; Castro-Pastrana, L.; Toledo-Wall, M.G.-O.L.; Saldivar-Santiago, M. Análisis de fármacos en aguas residuales de tres hospitales de la ciudad de Puebla, México. Ing. Del Agua 2021, 25, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Moraga, V.; Gaete, H. Evaluación Ecotoxicológica De Las Interacciones Entre Paracetamol E Ibuprofeno Sobre La Microalga De Agua Dulce. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambiental 2024, 40, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koagouw, W.; Stewart, N.A.; Ciocan, C. Long-term exposure of marine mussels to paracetamol: Is time a healer or a killer? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48823–48836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra, A.P.M.; Carretero, S.A.M.; Díaz, H.M.; García, G.X.; Gómez, O.L.M. Gobierno de México. Available online: https://avanceyperspectiva.cinvestav.mx/los-medicamentos-pueden-contaminar-los-sistemas-acuaticos/ (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Wang, M.; Shi, H.; Shao, S.; Lu, K.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Gao, S. Montmorillonite promoted photodegradation of amlodipine in natural water via formation of surface complexes. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Cano, R.; Kolb, M.; Saldaña-Vazquez, R.; Breton-Deval, L.; Cruz-Cano, N.; Aldama-Cervantes, A. Existing evidence on the use of environmental DNA as an operational method for studying rivers: A systematic map and thematic synthesis. Environ. Evid. 2024, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, A.B.C.; Diaper, C.; Parsons, S.A. Partial oxidation by ozone to remove recalcitrance from wastewaters-a review. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.M.; Canonica, S.; Park, G.Y.; Von Gunten, U. Oxidation of pharmaceuticals during ozonation and advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Dhara, S.; Samanta, N.S.; Purkait, M.K. Advancements on ozonation process for wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2024, 202, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Niu, Q.; Wu, S.; Lin, Y.; Biswas, J.K.; Yang, C. Hydroxyl radicals in ozone-based advanced oxidation of organic contaminants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 3059–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.M.; Vazquez-Arenas, J.; Castillo-Araiza, O.O.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Chairez, I.; Salinas, E.; Poznyak, T. Improving ozonation to remove carbamazepine through ozone-assisted catalysis using different NiO concentrations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22184–22194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galina-Licea, A.; Alfaro-Ponce, M.; Chairez, I.; Reyes, E.; Perez-Martínez, A. Assessment of blast furnace slags as a potential catalyst in ozonation to degrade bezafibrate: Degradation study and kinetic study via non-parametric modeling. Processes 2024, 12, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, T.; Chairez, I.; Poznyak, A.S. Ozonation and Biodegradation in Environmental Engineering: Dynamic Neural Network Approach; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Cao, L.; Xu, M.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.Z. Complex reaction processes in combustion unraveled by neural network-based molecular dynamics simulation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abba, S.; Nourani, V.; Elkiran, G. Multi-parametric modeling of water treatment plant using AI-based non-linear ensemble. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2019, 68, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitapure, N.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Exploring the potential of time-series transformers for process modeling and control in chemical systems: An inevitable paradigm shift? Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 194, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzate-Salgado, S.-Y.; Morales-Pérez, A.-A.; Solís-López, M.; Ramírez-Zamora, R.-M. Evaluation of metallurgical slag as a Fenton-type photocatalyst for the degradation of an emerging pollutant: Diclofenac. Catal. Today 2016, 266, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Gao, H.; Liao, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. A novel slag-based Ce/TiO 2 @LDH catalyst for visible light driven degradation of tetracycline: Performance and mechanism. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Reinforce of hydrotalcite-like loaded TiO2 composite material prepared by Ti-bearing blast furnace slag for photo-degradation of tetracycline. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 1013990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangappa, H.S.; Mon, P.P.; Herath, I.; Madras, G.; Lin, C.; Subrahmanyam, C. Modeling Tetracycline Adsorption onto Blast Furnace Slag Using Statistical and Machine Learning Approaches. Sustainability 2024, 16, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Suo, N.; Long, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Y. Preparation of particle electrodes from manganese slag and its degradation performance for salicylic acid in the three-dimensional electrode reactor (TDE). Chemosphere 2019, 216, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasce, L.; Bocero, F.; Ramos, C.; Inchaurrondo, N. Enhanced mineralization of bisphenol A by electric arc furnace slag: Catalytic ozonation. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 16, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Wen, G. Application of metal oxide catalysts for water treatment—A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, L.; Chen, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, J.; Yin, C. Application of heterogeneous catalytic ozonation in wastewater treatment: An overview. Catalysts 2023, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, L.; Sabelfeld, M.; Geissen, S.; Bousselmi, L. Catalytic ozonation of model organic compounds in aqueous solution promoted by metallic oxides. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.M.; Shivanna, S. Visible Light Assisted Photocatalytic Degradation of Chromium (VI) by Using Nanoporous Fe2O3. J. Mater. 2018, 2048, 593947. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Xie, T.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.F.Y.D. Synthesis, photoelectric properties and photocatalytic activity of the Fe2O3/TiO2 heterogeneous photocatalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 8033–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, B.C.; Hoigné, J. Photolysis of Fe (III)-hydroxy complexes as sources of OH radicals in clouds, fog and rain. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulman, M.; Cabot, P.-L.; Centellas, F.; Arias, C.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Garrido, J.A.; Brillas, E. Mineralization of paracetamol by ozonation catalyzed with Fe2+, Cu2+ and UVA light. Appl. Catal. 2006, 66, 228–240. [Google Scholar]
- Quiñones, D.; Álvarez, P.; Rey, A.; Beltrán, F. Removal of emerging contaminants from municipal WWTP secondary effluents by solar photocatalytic ozonation. A pilot-scale study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, D.; Álvarez, P.; Rey, A.; Contreras, S.; Beltrán, F. Application of solar photocatalytic ozonation for the degradation of emerging contaminants in water in a pilot plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldak, D.L.; Hoigné, J.; David, M.M.; Colvile, R.N.; Seyferr, E.; Acker, K.; Wiepercht, W.; Lind, J.A.; Fuzzi, S. The cloudwater chemistry of iron and copper at Great Dun Fell, U.K. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Pignatello, J.J. Dark and photoassisted iron(3+)-catalyzed degradation of chlorophenoxy herbicides by hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Pignatello, J.J. Photochemical reactions involved in the total mineralization of 2,4-D by iron(3+)/hydrogen peroxide/UV. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Moussavi, G.; Mahmoudi, M. Removal of azo and anthraquinone reactive dyes from industrial wastewaters usign MgO nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussavi, G.; Alizadeh, R. The integration of ozonation catalyzed with MgO nanocrystals and the biodegradation for the removal of phenol from saline wastewater. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 97, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekh-Salehi, A.; Moussavi, G.; Yaghmaeian, K. Preparation, characterization and catalytic activity of a novel mesoporous nanocrystalline MgO nanoparticle for ozonation of acetaminophen as an emerging water contaminant. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Waheed, S.; Saleem Joya, K.; Kazmi, M. Catalytic ozonation of paracetamol on zeolite A: Non-radical mechanism. Catal. Commun. 2018, 112, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| System | Initial pH |
|---|---|
| PCT–SOP | 3 |
| PCT–SOP | 7 |
| PCT–SOP | 10 |
| PCT–BFS | 3 |
| PCT–BFS | 7 |
| PCT–BFS | 10 |
| Physic | Chemical |
|---|---|
| Solid | FeO: 40% |
| Color grey | CaO: 22% |
| Density: 1.67 kg/m3 | SiO2: 14% |
| Hardness: 7 in Mohs scale | MgO: 8.5% |
| Particle size: 3/8–¾ in | Al2O3: 5.3% |
| MnO2: 1.6% |
| Reaction System | pHi | pHf | Electrical Conductivity (µS/cm)i | Electrical Conductivity (µS/cm)f |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT–SOP pH 3 | 3 | 3 | 54.9 | 413 |
| PCT–SOP pH 7 | 7 | 3.5 | 77.7 | 319 |
| PCT–SOP pH 10 | 10 | 3.6 | 106.8 | 127.7 |
| PCT OP/BFS pH 3 | 3 | 6.9 | 201.1 | 226.2 |
| PCT OP/BFS pH 7 | 7 | 6.7 | 80.8 | 239.6 |
| PCT OP/BFS pH 10 | 10 | 7.2 | 108.4 | 208.1 |
| Experimental System | Oxalic Acid Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| PCT–SOP pH 3 | 81.62 |
| PCT–SOP pH 7 | 61.29 |
| PCT–SOP pH 10 | 95.96 |
| PCT OP/BFS pH 3 | 74.01 |
| PCT OP/BFS pH 7 | 71.58 |
| PCT OP/BFS pH 10 | 107.13 |
| System | pH | Reaction Rate Constant | Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT | 3 | 123.12 | [−12.87,+12.87] |
| 7 | 247.34 | [−5.61,+5.61] | |
| 10 | 432.15 | [−13.98,+13.98] | |
| PCT + BFS | 3 | 216.39 | [−16.34,+16.34] |
| 7 | 329.12 | [−11.45,+11.45] | |
| 10 | 617.83 | [−25.23,+25.23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Oseguera, A.; Pérez-Martínez, A.; Alfaro-Ponce, M.; Chairez, I.; Reyes, E. Kinetic Analysis of pH Effect on the Paracetamol Degradation by an Ozonation–Blast Furnace Slags Coupled System by Neural Network Approximation. Water 2025, 17, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091364
García-Oseguera A, Pérez-Martínez A, Alfaro-Ponce M, Chairez I, Reyes E. Kinetic Analysis of pH Effect on the Paracetamol Degradation by an Ozonation–Blast Furnace Slags Coupled System by Neural Network Approximation. Water. 2025; 17(9):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091364
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Oseguera, Andrea, Arizbeth Pérez-Martínez, Mariel Alfaro-Ponce, Isaac Chairez, and Elizabeth Reyes. 2025. "Kinetic Analysis of pH Effect on the Paracetamol Degradation by an Ozonation–Blast Furnace Slags Coupled System by Neural Network Approximation" Water 17, no. 9: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091364
APA StyleGarcía-Oseguera, A., Pérez-Martínez, A., Alfaro-Ponce, M., Chairez, I., & Reyes, E. (2025). Kinetic Analysis of pH Effect on the Paracetamol Degradation by an Ozonation–Blast Furnace Slags Coupled System by Neural Network Approximation. Water, 17(9), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091364






