Abstract
Understanding the trophic interactions and community structure of zooplankton is essential for assessing energy transfer in marine ecosystems. This study investigates the spatial and seasonal variations in stable carbon (δ13C) and nitrogen (δ15N) isotopes of dominant mesozooplankton groups across three sub-basins of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Aegean, Cretan, and South Ionian Seas) during two seasonal surveys (October 2014 and May 2015). Zooplankton samples were collected using a WP-2 net and analyzed for taxonomic composition, abundance, biomass, and stable isotopic signatures to assess trophic positioning. The results indicate that copepods dominated the zooplankton community at all stations, with Clausocalanus and Oithona juveniles being the most abundant taxa. Salps contributed significantly at certain stations, reflecting regional variations in the planktonic food web structure. Zooplankton δ15N values exhibited pronounced spatial and seasonal differences, with higher enrichment observed in 2014 compared to 2015. The calculated trophic positions highlight the variability in feeding strategies among copepod species, with Calanus helgolandicus occupying the highest trophic position (TP = 3.34) and Lucicutia spp. the lowest (TP = 1.22). Isotopic niche analysis identified two distinct feeding guilds: a group relying on phytoplankton and microzooplankton and another exhibiting broader trophic plasticity, including omnivorous and carnivorous taxa. These findings underscore the complexity of zooplankton trophic interactions in the Eastern Mediterranean and the role of regional hydrographic conditions in shaping the food web structure. This study provides essential baseline data for future research on the impacts of climate change and nutrient variability on Mediterranean marine ecosystems.
Keywords:
copepods; food webs; trophic position; stable isotopes; oligotrophy; Eastern Mediterranean 1. Introduction
Stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen (δ13C and δ15N, respectively) are a valuable tool for examining trophic relationships across terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystems worldwide [,,]. Establishing baseline or reference values is essential for determining the trophic position of organisms. These reference values may originate from phytoplankton, which serves as the primary food source for epipelagic species, or from particulate organic matter that sustains deep-living organisms. Alternatively, stable isotope values from species with well-defined trophic positions can also serve as reference points [,,].
In the Mediterranean Sea, baseline δ15N values are generally lower than those observed in the open ocean. The Mediterranean Sea’s lower δ15N values are mainly driven by minimal denitrification, enhanced nitrogen fixation, rapid deep-water renewal, and unique nutrient inputs. These factors contrast with the open ocean, where denitrification and deep-water residence times elevate δ15N values []. Koppelmann et al. [,] measured δ15N values ranging from 0.43 to 1.74‰ in suspended particles from the epipelagic zone and from 0.68 to 2.17‰ in sinking particulate organic matter collected in sediment traps from the Levantine Basin. Similarly, studies by Pantoja et al. [] and Sachs and Repeta [] also reported low δ15N values, suggesting that nitrogen fixation may explain these observations. However, Krom et al. [] proposed an alternative explanation for the low δ15N values in the phosphorus-limited Eastern Mediterranean Sea (EMED), noting that the complete consumption of phosphate leaves behind lighter particulate organic nitrogen (PON) with δ15N values of 3.5–4.0‰, alongside heavier nitrate values of 17–20‰. This process may facilitate the export of lighter PON, leading to a lower δ15N baseline in the Mediterranean compared to most open ocean regions.
This low δ15N baseline is also reflected in the mesozooplankton trophic position in the food web. Koppelmann et al. [] observed a similar trend of increasing δ15N with size in zooplankton from the Levantine Basin, where δ15N values ranged from 2.0 to 3.1‰ in the upper 250 m in April 1999. At greater depths, zooplankton δ15N values increased up to 11.5‰ at depths exceeding 3000 m, while particulate organic matter showed only slight increases, from 1.2‰ at 700 m to 1.7–2.5‰ at 2700 m. These findings suggest that the deep Levantine Sea food web may be more complex or reliant on food sources beyond particulate organic matter, a conclusion further supported by subsequent food web analyses conducted in October 2001 [].
The oligotrophic character of the EMED, characterized by low primary productivity, limited dissolved nutrients, and low chlorophyll a concentrations, has been extensively documented since the early 1980s [,,]. Phosphorus limitation has emerged as a key factor influencing these conditions [,,]. In such environments, the abundance of diatoms and dinoflagellates is typically low [,], and phytoplankton alone often fails to meet carbon demands []. As a result, zooplankton often compensate for this limited phytoplankton availability by feeding on microzooplankton, leading to a more opportunistic and omnivorous feeding strategy [,,,]. Mesozooplankters, particularly copepods, play a vital role in pelagic carbon flow processes through their interactions with both higher and lower trophic levels [].
In the context of the KRIPIS ‘Integrated Observatories in the Greek Seas’ Project, two multidisciplinary sub-basin surveys were conducted in October 2014 and May 2015 across three sub-basins of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea: the North Aegean Sea, the Cretan Sea, and the South Ionian Sea. As detailed by Pavlidou et al. [], each of these sub-basins plays a vital role in the Eastern Mediterranean ecosystem, which continues to transition following significant dense water formation events in the Aegean Sea between 1987 and 1995 during the Eastern Mediterranean Transient (EMT). The North Aegean Sea is recognized as a dense water formation area [], the Cretan Sea serves as a key reservoir of heat and salt [], and the South Ionian Sea acts as a crucial conduit for water masses between the Levantine/Cretan and Adriatic Seas [].
Despite the ecological importance of these ecosystems, research on trophic interactions in the Eastern Mediterranean using stable isotopes remains scarce [,,,,,].
In this study, we focus on stable isotope analyses of zooplankton from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea, particularly emphasizing nitrogen isotopes as indicators for assessing trophic levels and food web dynamics. This study, therefore, aims to elucidate the dietary preferences and feeding strategies of dominant zooplankton taxa/species through stable nitrogen and carbon isotopic analyses. Additionally, we provide insights into the community structure, abundance, and biomass of the studied area, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the region’s mesozooplankton dynamics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Samples were collected during two expeditions aboard the R/V AEGAEO at three stations in the three EMED sub-basins in October 2014 (KR1) and May 2015 (KR2); the selected stations were located in the North Aegean Sea (M02), the Ionian Sea (NESTOR), and the Cretan Sea (M3A) (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Sampling stations (red bullets) during 2014 and 2015 expeditions: North Aegean Sea (M02), Ionian Sea (NESTOR), and Cretan Sea (M3A).
Each of these sub-basins plays a crucial role in the functioning of the Eastern Mediterranean, which remains in a transitional state following the intense dense water formation events that occurred in the Aegean Sea between 1987 and 1995 during the EMT. The northern Aegean Sea (M02) serves as a dense water formation region and is the frontal zone where Black Sea water enters [], the Cretan Sea (M3A) acts as a major heat and salt reservoir for the Eastern Mediterranean [], and the southern Ionian Sea (NESTOR) functions as a key passage for water masses between the Levantine/Cretan and Adriatic Seas [].
A standard closing WP-2 net from Hydrobios (Kiel, Germany) with a mesh size of 200 μm was used at all three sites during midday. Samples for composition, isotope analyses, and biomass were collected by vertical hauls (0.5 m s−1) according to the “Zooplankton methodology manual” [] (Table 1). Two hauls were conducted at each station: one for composition and biomass, and the other for stable isotopes. These hauls covered varying depth ranges: 0 to 350 m at M3A, 0 to 500 m at M2, and 0 to 700 m at Nestor.

Table 1.
Station data for October 2014 (KR1) and May 2015 (KR2). The local time (UTC +2 h) denotes the open time of the nets.
The volume of the filtered water from the WP-2 net (V = A × L, m3) was determined by considering the net mouth area (A, m2) and the length of the deployed wire (L, m). The final thickness of the sampled layer (ΔD, m) and the vertical extent of the layer (ΔL = Li − Lf, m) were calculated by accounting for the wire angle α (ΔD = ΔL cos α). This filtered water volume was then used to calculate the mesozooplankton abundance per cubic meter for each haul []. After each haul, the nets were thoroughly rinsed, and the samples were split on board using a Folsom splitter. One half was reserved for biomass analysis, while the other was preserved in a seawater solution of sodium tetraborate-buffered formaldehyde (4% final concentration) for subsequent zooplankton composition and abundance assessments.
Temperature and salinity (conductivity) profiles across the water column were obtained using a Sea–Bird Electronics 11plus™ CTD deck unit connected to a Sea–Bird Electronics™ 9plus underwater unit and a Sea–Bird Electronics 32-rosette sampler with twenty-four 10 L Niskin bottles. A summary of the environmental conditions in the study area is provided in Table 2, with additional details available in Pavlidou et al. []. Environmental data were retrieved from the SeaDataNet Pan-European infrastructure for ocean and marine data management (https://www.seadatanet.org, accessed on 20 March 2025).

Table 2.
Mean integrated values of the environmental parameters in the different stations for October 2014 (KR1) and May 2015 (KR2).
2.2. Dry Weight Biomass
The subsample for bulk biomass determination was filtered onto pre-weighed and pre-combusted glass fiber filters (Whatman GF/C), then dried at 60 °C for 24 h on board []. The dry weight (mg) of the samples was calculated by subtracting the initial filter weight from the final weight, and the biomass (mg DW m−3) was extrapolated based on the total volume of water sampled by the net (Table 3).

Table 3.
Spatial distribution of zooplankton total abundance (ind m−3) and biomass (mg DW m−3).
2.3. Microscopic Analyses
Taxonomic identification and counting of zooplankton were conducted in the laboratory using an Olympus SZX12 dissecting microscope. Copepods were identified to the species level when possible, while other groups were classified to higher taxonomic levels. Holoplanktonic organisms, excluding copepods, as well as meroplankton, were identified at broader taxonomic levels. Siphonophores were counted as part of their colonies. Abundance was expressed as the number of individuals per cubic meter (ind m−3), while relative abundance (%) indicated the evenness of species distribution within the community.
2.4. Stable Isotopes
To prepare the WP-2 samples for carbon and nitrogen isotope analysis, zooplankton were first washed on board using seawater on a gauze disk (5 cm diameter, 200 μm mesh size). The gauze was then stored in a freezer at −20 °C until further analysis. Upon arrival in the laboratory, the samples were thawed in a cooling box filled with ice for species identification prior to isotope analysis. A subsample was placed under a stereomicroscope in a Petri dish filled with seawater (salinity 38) and kept on ice. Individual zooplankton were carefully selected and sorted to the species or genus level. They were then rinsed briefly with distilled water to remove any remaining salt. After washing, the individuals were transferred onto glass fiber filters (GF/C 25 mm). For copepods, only males and females without eggs, and the CIV and CV copepodite stages, were used in isotope analyses. The number of individuals chosen for each species/genus/taxa are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
δ15N, δ13C (‰), and C/N values of specific taxa from frozen samples sorted by sampling site and corresponding depth level; n (ind) = number of replicates and individuals/replicate. Trophic position (TP) determined using δ15N values of POM used as baseline (TL = 1.5) listed depth levels.
The filters were folded and placed into small Eppendorf tubes for drying at 60 °C for 24 h. To obtain the precise dry weight of the organic material, the weight of the assembled filters was subtracted from the blank weight, which had been previously determined. The dried filters, along with the animals, were then placed into 5 × 9 mm zinc capsules. The sealed capsules were stored in a 96-well plate and kept in a bag containing silica gel until they were ready to be loaded into the auto-sampler of the mass spectrometer.
Stable isotope studies were performed at the UC Davis Stable Isotope Facility. Stable isotope values are expressed in δ notations as parts per thousand (‰), where X is 13C or 15N and R the corresponding ratio of 15N/14N or 13C/12C. The standard reference materials were Vienna Pee Dee Belemnite for carbon and atmospheric N2 for nitrogen:
δX (‰) = ((Rsample/Rstandard) − 1) × 1000
2.5. Data Treatment and Statistical Analysis
Multivariate analyses were performed to examine the spatial differentiation of the zooplankton community, if any, combining abundance and composition. Spatial differentiation of the zooplankton community among stations was visualized by a non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix created from the datasets of each station based on square root transformed abundances with Primer 7.0 software [].
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on environmental parameters (dissolved oxygen (DO), temperature (T), salinity (S), nitrates (NO3), and phosphate (PO4)) as well as biological variables (chlorophyll-a (Chla-a), zooplankton abundance, and biomass) from all sampling stations in October 2014 (KR1) and May 2015 (KR2). The analysis, conducted using Primer version 7.0, aimed to identify any seasonal or spatial patterns in the zooplankton communities.
The trophic position (TP) was estimated with the δ15N values of the copepod samples using a trophic enrichment factor (TEF) of 3.4‰ following the suggestions of Post []. The stable isotope signatures of filtered water samples were used as a baseline (Table 4). The following formula was used to calculate the trophic position:
where TPconsumer are the sampled copepods and TLbase the trophic level of POM. The baseline was set to an intermediate value of 1.5, since POM consists mostly of phytoplankton (TL = 1) and micro- and mesozooplankton (TL = 2) [,]. δ15N represents the applied TEF of 3.4‰ per trophic level.
TPonsumer = TLbase + (δ15Nconsumer − δ15Nbase)/δ15N
The isotopic niche width (‰2) was estimated using the standard ellipse function (SEA) in the Stable Isotope Analysis package (SIAR, v4.2.2) in R (R Core Team, 2016), following the methodology outlined by Jackson et al. []. The ellipses were calculated in SIAR’s default mode, which includes 40% of the data, and a correction (SEAc) was applied for small sample sizes. The individual isotopic niche width (SEAc) was calculated for each taxon. In addition to the individual niche width, the overlap of competing niches was assessed to identify any groups occupying the same niche. To do this, a Bayesian estimate of standard ellipses was calculated using the Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipse sub-function (SIBER), allowing for the comparison of niche width areas (SEAb). The overlapping areas of the isotopic niches were also analyzed, and their proportions were determined using standard ellipse niche widths. The isotopic niche widths of the copepod taxa were visualized with standard ellipses (SEAc) and convex hulls to explore their trophic positioning and potential resource partitioning. The standard ellipses represent the core isotopic niche space of each species, while the convex hulls illustrate the full range of isotopic values, reflecting the extent of dietary variation [].
3. Results
3.1. Zooplankton Abundance and Biomass Distribution
Zooplankton abundance varied across the three geographic areas (M3A, M02, and NESTOR), with a mean value of 60 ind m−3 (KR2-NESTOR) and a max value of 276 ind m−3 (KR1-M02). Biomass values ranged from 0.46 mg DW m−3 (KR1-NESTOR) to 1.05 mg DW m−3 (KR1-M02) (Table 3).
Zooplankton biomass (mg DW m−3) and abundance (ind m−3) were tested for normality using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and both variables were found to be normally distributed (p > 0.05). A t-test was used to compare biomass and abundance between the years 2014 and 2015, and no statistically significant differences were found for either variable (p > 0.05). Similarly, no significant spatial differences were detected between sampling stations across the years (p > 0.05). Additionally, zooplankton biomass and abundance were not significantly correlated in 2014 (p > 0.05); however, a significant positive correlation was observed between biomass and abundance in 2015 (p < 0.05).
The principal component analysis (PCA) (Figure 2) revealed distinct spatial patterns in environmental variables across the sampling stations. The first principal component (PC1) was primarily driven by phosphate (PO4), which exhibited strong positive loading, indicating its significant role in differentiating the stations. The second principal component (PC2) was influenced by salinity (S) and temperature (T), suggesting their contribution to environmental variability. Dissolved oxygen (DO), nitrate (NO3), and biological variables, including biomass, abundance, and Ch-a, clustered closely together, highlighting their strong interrelationship. Spatially, KR1-M02 was positioned in the lower-left quadrant, indicating distinct environmental conditions compared to KR2-NESTOR and KR1-NESTOR, which were grouped in the upper-right quadrant. Meanwhile, KR2-M02 appeared closely associated with nitrate and dissolved oxygen, suggesting a dynamic biogeochemical environment, whereas KR2-M3A and KR1-M3A were positioned towards the upper-left quadrant, aligning with salinity and temperature influences.

Figure 2.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of dissolved oxygen (DO), temperature (T), salinity (S), nitrates (NO3), phosphate (PO4), Chla-a, zooplankton abundance, and biomass for all sampling stations in October 2014 (KR1) and May 2015 (KR2).
3.2. Mesozooplankton Community Composition and Distribution
The communities throughout the entire water column, for both sampling periods, were dominated by Copepoda at all stations, with relative abundances ranging from 58% (KR1-M02) to 89% (KR1-NESTOR). Salpa were particularly important at station KR1-M02, with a maximum relative abundance of 31%. Other prominent taxa included Appendicularia, which had high relative abundances at stations KR2-M02 and KR2-NESTOR (3% and 7%, respectively), and Ostracoda, which showed relative abundances ranging from 1% to 7% at almost all stations, except KR1-M02 and KR2-M02. Additionally, the cladoceran Penilia avirostris was present only at station KR1-M02, with a relative abundance of 4%. All other taxa were of low significance, with relative abundances ranging from 1% to 6% (Figure 3).
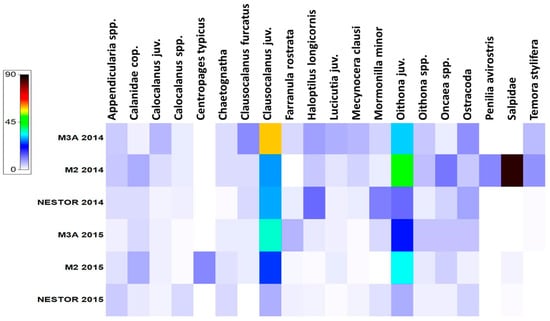
Figure 3.
Heat map with dominant zooplankton abundances (Calanidae cop. refers to the total number of copepodites from the Calanidae family).
Among copepods, Clausocalanus and Oithona juveniles dominated all stations for both seasons, with relative abundances ranging from 10 to 29% and from 12 to 30%, respectively. Other dominant species were Mormonilla minor and Haloptilus longicornis, showing high relative abundances (10% and 12%, respectively) at station KR1-NESTOR, whereas at all other stations ranged from 0 to 5%. Other important taxa were Oncaea spp. for almost all stations and species Clausocalanus furcatus for stations KR1-M3A and KR1-NESTOR. Centropages typicus was present only at station KR2-M02, exhibiting high abundance values, placing it in the list of dominant species of this station (Figure 3).
The differences in taxa composition drove the separation of samples into groups based on hierarchical clustering and non-metric MDS (Figure 4). Two groups of samples were distinguished at a similarity level of 70%. The first group consisted of samples from stations KR1-M3A, KR1-NESTOR, KR2-M3A, and KR2-NESTOR, whereas the second group consisted of samples from KR1-M02 and KR2-M02 (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
Hierarchical clustering (up) and non-metric MDS (down) of the stations from both sampling periods KR1 and KR2.
3.3. Stable Isotopic Composition of Prominent Zooplankton Taxa
The WP-2 samples provided sufficient material for the stable isotope analysis of six different taxa for 2014 and ten for 2015, with replicates whenever possible (Table 4). According to the results, H. longicornis, Corycaeus spp., Pleuromamma spp., C. helgolandicus, Doliolidae spp., and Chaetognatha spp. were arranged around values of −22.0‰ in δ13C, and Oithona spp., Lucicutia spp., C. typicus, Clausocalanus spp., and Oncaea spp., along with some exceptions from H. longicornis and Corycaeus spp., were arranged around values of −23.0‰ in δ13C. There was a distinct difference in δ15N between taxa, among stations and year/season with H. longicornis and Corycaeus spp. showing the highest variation both among stations and years ranging from 4.58 to 6.20‰ and 1.59 to 4.17‰, respectively (Table 4). Moreover, the mean δ15N values for each station revealed a higher δ15N signal at station M02, followed by M3A and NESTOR, for both seasons (Figure 5).
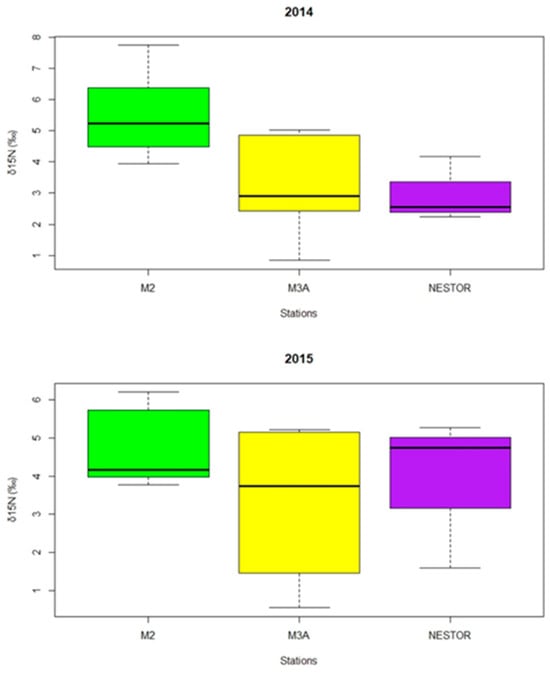
Figure 5.
Distribution of the δ15N values measured in zooplanktonic taxa collected at the three stations in the EMed in October 2014 and May 2015. (The central line within each box represents the median, while the box limits correspond to the first (Q1) and third (Q3) quartiles).
The carbon–nitrogen (C/N) ratio was estimated, providing insights into the nutritional composition of the taxa/species. The C/N ratio for most taxa/species ranged between 2.77 and 5.10, indicating a balanced composition of protein and energy. However, Lucicutia spp. at the NESTOR station exhibited a ratio of 1.76, suggesting that these individuals are highly protein-rich but lower in energy content. In contrast, C. helgolandicus showed C/N ratios of 9.70 and 10.24, indicating energy-rich but comparatively less protein-dense organisms. No significant differences (p > 0.05) were observed between years for Corycaeus spp. (NESTOR), Chaetognatha (M2), and Chaetognatha (NESTOR), or among stations for Chaetognatha (NESTOR-M2). Regarding trophic levels (TP), C. helgolandicus had the highest trophic position (TP) at 3.34, while Lucicutia spp. had the lowest at 1.22 (Table 4).
3.4. Isotopic Niche Analysis
The analysis revealed two primary isotopic clusters among the copepod taxa. The first group, including Corycaeus spp., Lucicutia spp., Clausocalanus spp., Oithona spp., and Oncaea spp., exhibited lower δ15N values, suggesting a diet primarily based on phytoplankton and microzooplankton. These species occupied a narrower isotopic niche, indicating a relatively specialized feeding strategy with limited dietary variation (Figure 6).

Figure 6.
Stable isotope biplot with standard ellipses representing the trophic niche width of 40% corrected for small sample size (SEAc) of copepods sampled from all stations during 2014 and 2015. The dashed lines show the associated convex hulls.
In contrast, the second group, composed of Haloptilus longicornis and Chaetognatha, displayed higher δ15N values and a broader isotopic niche width. The larger niche space suggests a more flexible feeding strategy, potentially incorporating omnivorous or carnivorous diets. This group likely exploits a wider range of food resources, including larger prey such as mesozooplankton (Figure 6).
4. Discussion
This study provides a comprehensive assessment of zooplankton community structure, abundance, biomass distribution, and stable isotope signatures across three distinct geographic areas/basins in the Mediterranean Sea (Aegean Sea (M02), Ionian Sea (NESTOR) and Cretan Sea (M3A)). The results indicate spatial and temporal variations in zooplankton abundance and biomass, with copepods being the dominant taxa across all sampling stations. These findings align with previous studies that have highlighted the critical role of copepods in pelagic food webs, particularly in oligotrophic systems such as the Eastern Mediterranean [,,,,,,,].
The multivariate analyses revealed distinct spatial structuring of environmental conditions and zooplankton communities across the study sites. The PCA indicated that phosphate (PO4) was a primary driver of environmental variability, with dissolved oxygen (DO), nitrate (NO3), and biological variables (biomass, abundance, chlorophyll-a) closely linked. These environmental gradients were further reflected in the nMDS and hierarchical clustering analyses, which showed a distinct grouping of stations based on zooplankton community composition. The clustering results suggest that stations influenced by higher phosphate concentrations exhibit different biological communities compared to those associated with higher salinity and temperature. Notably, stations grouped together in the nMDS plot corresponded well with PCA patterns, indicating that zooplankton assemblages are structured by nutrient availability and hydrographic conditions. The separation of stations in the nMDS further supports the influence of environmental gradients on community composition, with phosphate-rich areas fostering distinct zooplankton assemblages compared to stations characterized by different nutrient regimes. These findings highlight the strong coupling between physical–chemical parameters and biological structure, reinforcing the role of phosphate as a key factor shaping zooplankton distributions in the study region [,,,,].
The dominance of copepods across all stations, with relative abundances ranging from 58% to 89%, is consistent with their well-established ecological significance in marine ecosystems [,,]. Salps were of particular significance at the station with distinct environmental conditions, according to PCA results, KR1-M2, where they reached a maximum relative abundance of 31%, indicating the potential for variable community composition across stations. The role of salps as important components of the pelagic food web has been previously recognized, especially in oligotrophic systems like the Mediterranean Sea, where their ability to filter large volumes of water can significantly influence nutrient cycling [].
Among the copepods, Clausocalanus and Oithona juveniles were consistently dominant across all stations, further emphasizing the importance of these genera in structuring the mesozooplankton community []. Other species, such as Mormonilla minor and Haloptilus longicornis, exhibited station-specific dominance, particularly at KR1-NESTOR, highlighting the spatial heterogeneity in community composition within the Mediterranean basin.
Centropages typicus is a widely distributed calanoid copepod, prevalent in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea, and is recognized as one of the most common and abundant species in the neritic waters of this region [,]. Notably, this species was recorded exclusively at station KR2-M02, underscoring the variability in species distribution driven by local environmental conditions, as confirmed by PCA (Figure 2). The clustering of zooplankton samples through hierarchical clustering and non-metric multidimensional scaling (MDS) revealed station-specific community structures, with station M02 standing out as distinct from the others. This station is located in the frontal zone where Black Sea water enters the North Aegean Sea [,]. The presence of C. typicus at M02, alongside species like Penilia avirostris, suggests the interaction between coastal and open-sea communities, influenced by hydrographic conditions. These findings highlight the importance of local environmental factors, such as water mass mixing, in shaping species distribution. Additionally, the occurrence of C. typicus at this station aligns with observations that species typical of neritic environments are also found in offshore waters, suggesting a broader spatial distribution and potential ecological significance within the Mediterranean basin [].
The analysis of stable isotopes of nitrogen (δ15N) and carbon (δ13C) provided valuable insights into the trophic ecology of prominent copepod taxa. The δ15N values for various copepods exhibited considerable variability between stations and years, with H. longicornis and Corycaeus spp. showing the highest δ15N values for 2014, whereas C. typicus and C. helgolandicus for 2015, indicating differences in their trophic positions and feeding strategies []. The higher δ15N values at station M02, followed by M3A and NESTOR, further support the notion of spatial variability in nitrogen cycling and food web dynamics across the Mediterranean Sea, as previously observed by Koppelmann et al. [] and Krom et al. []. These differences in isotopic signatures reflect both the local nutrient dynamics and the specific feeding behaviors of different copepod species, with some taxa potentially feeding at higher trophic levels or incorporating nitrogen from different sources, such as nitrogen fixation or dissolved organic nitrogen [].
According to the C/N ratio results, the presence of taxa with a C/N ratio of 1.76 (e.g., Lucicutia spp.) suggests that this sample is highly protein-rich but lower in energy content, indicating nitrogen limitation or higher protein synthesis rates []. These organisms might be critical for predators focusing on growth or reproduction. Species or taxa with a C/N ratio in the range of 3.5–5.0 are more balanced in terms of protein and energy. This group likely represents a versatile prey category that is suitable for a broad range of predators []. Lastly, species with a C/N ratio of 10 (e.g., C. helgolandicus) indicate energy-rich but comparatively less protein-dense organisms. These may serve as a key food source for energy storage in predators [].
The variation in C/N ratios highlights the functional diversity within the samples. Some species are optimal for energy transfer (like C. helgolandicus), while others provide vital protein (e.g., species with C/N~1.76). This mix indicates a healthy and diverse zooplankton community capable of supporting various trophic levels. Also, the broader range of C/N ratio (from 1.76 to 10) reflects a well-balanced ecosystem where different zooplankton species fulfill complementary roles. This may also suggest temporal or spatial variability in environmental conditions, influencing their biochemical composition [,].
The calculated trophic levels suggest that C. helgolandicus occupies a higher trophic position (TP = 3.34), while Lucicutia spp. is positioned at the base of the mesozooplankton food web (TP = 1.22). These results corroborate previous research demonstrating species-specific differences in feeding strategies and trophic interactions among copepods [,].
The isotopic niche analysis revealed two distinct feeding guilds. One group, consisting of Corycaeus spp., Lucicutia spp., Clausocalanus spp., Oithona spp., and Oncaea spp., exhibited lower δ15N values, indicating reliance on primary producers or microzooplankton. The second group, comprising H. longicornis and Chaetognatha, displayed broader isotopic niches and higher δ15N values, suggesting a more carnivorous diet [,]. The observed niche overlap between certain species indicates potential resource competition or shared feeding strategies, reinforcing the complexity of trophic interactions within Mediterranean zooplankton communities []. However, the separation between the two main groups implies distinct feeding guilds, reducing direct competition. The observed niche differentiation aligns with previous studies [] that have highlighted the role of dietary specialization and trophic plasticity in structuring copepod communities [,]. Overall, the isotopic niche analysis provides valuable insights into the feeding strategies and trophic interactions of Mediterranean copepods. The differentiation between specialists and generalists highlights the complexity of mesozooplankton food webs and underscores the importance of stable isotope approaches in marine ecological studies.
In conclusion, this study highlights the complexity of zooplankton community composition and isotopic signatures in the Mediterranean Sea. The variation in zooplankton abundance, biomass, and stable isotopic values across stations and seasons underscores the need for further research into the ecological processes driving these patterns. Understanding these processes is crucial for predicting the impacts of environmental change on Mediterranean marine ecosystems, particularly in the context of ongoing climate change and nutrient dynamics [,].
5. Conclusions
This study provides a novel contribution to understanding the structure and dynamics of zooplankton communities in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea by integrating both environmental and biological data across spatial and temporal scales. The findings highlight the significant role of environmental gradients, particularly phosphate concentrations, in shaping zooplankton distributions and community composition. The use of multivariate techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA) and non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) revealed distinct spatial patterns and trophic interactions, further emphasizing the complex interplay between environmental factors and zooplankton assemblages.
This study’s unique contribution lies in its detailed exploration of how local environmental conditions, such as nutrient availability and hydrographic factors, drive the variability in zooplankton communities across the Eastern Mediterranean basins. The occurrence of species like Centropages typicus at specific stations underlines the importance of localized factors, such as water mass mixing, in influencing species distribution. Moreover, the isotopic niche analysis revealed feeding guilds within the zooplankton community, providing insights into the trophic ecology and resource partitioning among key species. This distinction between specialists and generalists based on their feeding strategies and isotopic signatures enriches our understanding of the complexity of mesozooplankton food webs in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea.
Additionally, the assessment of C/N ratios provided a deeper understanding of the functional roles of different species within the food web, revealing how zooplankton taxa contribute to energy and protein cycling in the ecosystem. These insights are crucial for understanding the broader ecological processes that underpin marine food webs, especially in the context of environmental change. The study’s findings underscore the need for ongoing research into the drivers of zooplankton community composition and their potential responses to the changing environmental conditions in the Mediterranean, particularly in light of ongoing climate and nutrient dynamics. Ultimately, this research contributes to improving our predictive capacity for ecosystem responses to environmental stressors in this ecologically significant region.
Author Contributions
M.P. and S.Z. designed the study and wrote the paper. M.P. analyzed taxonomic data and performed the statistical analyses. S.Z. supervised the study, provided constructive comments, and revised and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Greek National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF) program ‘KRIPIS integrated observatories in the Greek seas’ (MIS 451724) and by the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Program ACTNOW: Advancing understanding of Cumulative Impacts on European marine biodiversity, ecosystem functions and services for human well being (No 101060072).
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
Environmental data were provided through SeaDataNet Pan-European infrastructure for ocean and marine data management (https://www.seadatanet.org, accessed on 20 March 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Boecklen, W.J.; Yarnes, C.T.; Cook, B.A. On the Use of Stable Isotopes in Trophic Ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 42, 411–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B. Stable Isotope Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 521. [Google Scholar]
- Rundel, P.W.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Nagy, K.A. (Eds.) Stable Isotopes in Ecological Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; p. 544. [Google Scholar]
- Pantoja, S.; Repeta, D.J.; Sachs, J.P.; Sigman, D.M. Stable isotope constraints on the nitrogen cycle of the Mediterranean Sea water column. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2002, 49, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppelmann, R.; Halsband-Lenk, C.; Weikert, H. The Stable Isotope Signature of Mesozooplankton in the Levantine Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). In Oceanography of Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea; Yilmaz, A., Ed.; TUBITAK: Ankara, Türkiye, 2003; pp. 814–820. [Google Scholar]
- Koppelmann, R.; Weikert, H.; Lahajnar, N. Vertical distribution of mesozooplankton and its δ15N signature at a deep-sea site in the Levantine Sea (eastern Mediterranean) in April 1999. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.P.; Repeta, D.J. Oligotrophy and nitrogen fixation during eastern Mediterranean sapropel events. Science 1999, 286, 2485–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krom, M.D.; Herut, B.; Mantoura, R.F.C. Nutrient budget for the Eastern Mediterranean: Implications for phosphorus limitation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppelmann, R.; Böttger-Schnack, R.; Möbius, J.; Weikert, H. Trophic relationships of zooplankton in the eastern Mediterranean based on stable isotope measurements. J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.; Ketchum, B.; Richards, F. The Influence of Organisms on the Composition of Sea Water. In The Sea 2; Hill, M.N., Ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1963; pp. 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, T.; Townsend, D.W.; El Sayed, S.Z.; Trees, C.C.; Azov, Y. Optical transparency, chlorophyll and primary productivity in the Eastern Mediterranean near the Israeli coast. Oceanol. Acta 1984, 7, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Yacobi, Y.Z.; Zohary, T.; Kress, N.; Hecht, A.; Robarts, R.D.; Waiser, M.; Wood, A.M.; Li, W.K.W. Chlorophyll distribution throughout the southeastern Mediterranean in relation to the physical structure of the water mass. J. Mar. Syst. 1995, 6, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krom, M.D.; Kress, N.; Brenner, S.; Gordon, L.I. Phosphorus limitation of primary productivity in the Eastern Mediterranean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krom, M.D.; Brenner, S.; Kress, N.; Neori, A.; Gordon, L.I. Nutrient dynamics and new production in a warm core eddy from the Eastern Mediterranean. Deep-Sea Res. 1992, 39, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignateadis, L.; Vounatsou, P.; Karydis, M. A possible method for evaluating oligotrophy and eutrophication based on nutrient concentration scales. Mar. Poll. Bull. 1992, 24, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbet, A.; Landry, M.R. Mesozooplankton influences on the microbial food web: Direct and indirect trophic interactions in the oligotrophic open ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudy, R.; Youssara, F.; Diaz, F.; Raimbault, P. Biomass, metabolism and nutrition of zooplankton in the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean). Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Christaki, U.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Montresor, M.; Ribera D’Alcala, M.; Vaque, D.; Zingone, A. Plankton in the open mediterranean Sea: A review. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1543–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleppel, G.S. On the diets of calanoid copepods. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 99, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbet, A.; Saiz, E. The ciliate–copepod link in marine ecosystems. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 38, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervoudaki, S.; Nielsen, T.G.; Christou, E.D.; Siokou-Frangou, I. Zooplankton distribution and diversity in a frontal area of the Aegean Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2006, 2, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, E.C.; Wethey, D.S.; Woodin, S.A. Climate change and increased environmental variability: Demographic responses in an estuarine harpacticoid copepod. Ecol. Model. 2007, 209, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, A.; Velaoras, D.; Karageorgis, A.P.; Rousselaki, E.; Parinos, C.; Dähnke, K.; Möbius, J.; Meador, T.B.; Psarra, S.; Frangoulis, C.; et al. Seasonal variations of biochemical and optical properties, physical dynamics and N stable isotopic composition in three northeastern Mediterranean basins (Aegean, Cretan and Ionian Seas). Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2020, 171, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, V.; Georgopoulos, D. Hydrology and circulation in the North Aegean (eastern Mediterranean) throughout 1997 and 1998. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2002, 3, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Krokos, G.; Theocharis, A. Recurrent intrusions of transitional waters of Eastern Mediterranean origin in the Cretan Sea as a tracer of Aegean Sea dense water formation events. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 135, 113–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensi, M.; Velaoras, D.; Meccia, V.L.; Cardin, V. Effects of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea circulation on the thermohaline properties as recorded by fixed deep-ocean observatories. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 112, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapa, M.; Koppelmann, R.; Zervoudaki, S.; Wunsch, C.; Peters, J.; Parinos, C.; Paraschos, F.; Gogou, A.; Möllmann, C. Trophic positioning of prominent copepods in the epi- and mesopelagic zone of the ultra-oligotrophic eastern Mediterranean Sea. Deep-Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 164, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannides, C.C.S.; Zervoudaki, S.; Frangoulis, C.; Lange, M.A. Mesozooplankton stable isotope composition in Cyprus coastal waters and comparison with the Aegean Sea (eastern Mediterranean). Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, V.; Georgopoulos, D.; Drakopoulos, P.G. The role of the North Aegean in triggering the recent Eastern Mediterranean climatic changes. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 26103–26126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Krokos, G.; Nittis, K.; Theocharis, A. Dense intermediate water outflow from the Cretan Sea: A salinity driven, recurrent phenomenon, connected to thermohaline circulation changes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 4797–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameoto, D.; Wiebe, P.; Runge, J.; Postel, L.; Dunn, J.; Miller, C.; Coombs, S. Metabolism. In ICES Zooplankton Methodology Manual; Harris, R.P., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2000; pp. 455–532. [Google Scholar]
- Postel, L.; Fock, H.; Hagen, W. 4 Biomass and abundance Some decades after Johannes Mu. In ICES Zooplankton Methodology Manual; Academic Press: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; Primer-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 1995; p. 144. [Google Scholar]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models. methods and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Montana, C.G.; Post, D.M. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 2007, 88, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapa, M.; Zervoudaki, S.; Tsangaris, C.; Velaoras, D.; Koppelmann, R.; Psarra, S.; Moellmann, C. Zooplankton distribution and electron transport system activity in the Cretan Passage, Eastern Mediterranean. Deep. Res. Part II 2019, 164, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Zervoudaki, S.; Christou, E.D.; Zervakis, V.; Georgopoulos, D. Variability of mesozooplankton spatial distribution in the North Aegean Sea, as influenced by the Black Sea waters outflow. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.T. The importance of small planktonic copepods and their roles in pelagic marine food webs. Zool. Stud. 2004, 43, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapa, M.; Yebra, L.; Koppelmann, R.; Zervoudaki, S. Ecological Application of Biomarkers to Mesozooplankton Communities in the Mediterranean Sea. In Zooplankton Challenges in a Changing World; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, G.C.; Richardson, A.J.; Robinson, C. Climate change and marine plankton. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paffenhöfer, G.A. On the ecology of marine cyclopoid copepods (Crustacea. Copepoda). J. Plankton Res. 1993, 15, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervoudaki, S.; Christou, E.D.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Örek, H.; Gucu, A.C.; Giannakourou, A.; Pitta, P.; Terbiyik, T.; Yϋcel, N.; Moutsopoulos, T.; et al. Copepod communities, production and grazing in the Turkish Straits System and the adjacent northern Aegean Sea during spring. J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 86, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guschina, I.A.; Harwood, J.L. Algal lipids and effect of the environment on their biochemistry. In Lipids in Aquatic Ecosystems; Arts, M.T., Brett, M.T., Kainz, M.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, V. Salp and pyrosomid blooms and their importance in biogeochemical cycles. In The Biology of Pelagic Tunicates; Bone, Q., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, M.G.; Christou, E.D.; Di Capua, I.; de Puelles, M.F.; Fonda-Umani, S.; Molinero, J.C.; Nival, P.; Siokou-Frangou, I. Temporal variability of Centropages typicus in the Mediterranean Sea over seasonal-to-decadal scales. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 72, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, V.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Georgopoulos, D.; Souvermezoglou, E. Vertical diffusion and oxygen consumption during stagnation periods in the deep North Aegean. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2003, 50, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, S.E.; Lindsay, F.S.; Pates, J.M. Seasonal variability in sea surface oceanographic conditions in the Aegean Sea (eastern Mediterranean): An overview. J. Mar. Syst. 1997, 13, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Wiebe, P.; Lenz, J.; Skjoldal, H.R.; Huntley, M. (Eds.) ICES Zooplankton Methodology Manual; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Koski, M. Carbon:nitrogen ratios of Baltic Sea copepods—Indication of mineral limitation? J. Plankton Res. 1999, 21, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutomu, I.; McKinnon, A.D. Metabolism and chemical composition of zooplankton and hyperbenthos from the Great Barrier Reef waters, North Queensland, Australia. Plankton Benthos. Res. 2012, 7, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Robins, D.B. Effects of preservation on wet weight, dry weight, nitrogen and carbon contents of Calanus helgolandicus (Crustacea: Copepoda). Mar. Biol. 1982, 71, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranguren-Riaño, N.J.; Guisande, C.; Shurin, J.B.; Jones, N.T.; Barreiro, A.; Duque, S.R. Amino acid composition reveals functional diversity of zooplankton in tropical lakes related to geography, taxonomy and productivity. Oecologia 2018, 187, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, W.; Larsson, U. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of crustacean zooplankton in the Baltic Sea: Implications for nutrient recycling. J. Plankton Res. 1999, 21, 2309–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinero, J.C.; Ibanez, F.; Nival, P.; Buecher, I.; Souissi, S. North Atlantic climate and northwestern Mediterranean plankton variability. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möllmann, C.; Müller-Karulis, B.; Kornilovs, G.; St John, M.A. Effects of climate and overfishing on zooplankton dynamics and ecosystem structure: Regime shifts, trophic cascade, and feedback loops in a simple ecosystem. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).