Activation of H2O2/PDS/PMS by Iron-Based Biochar Derived from Fenton Sludge for Oxidative Removal of 2,4-DCP and As(III)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations and Chemical Properties of Catalysts
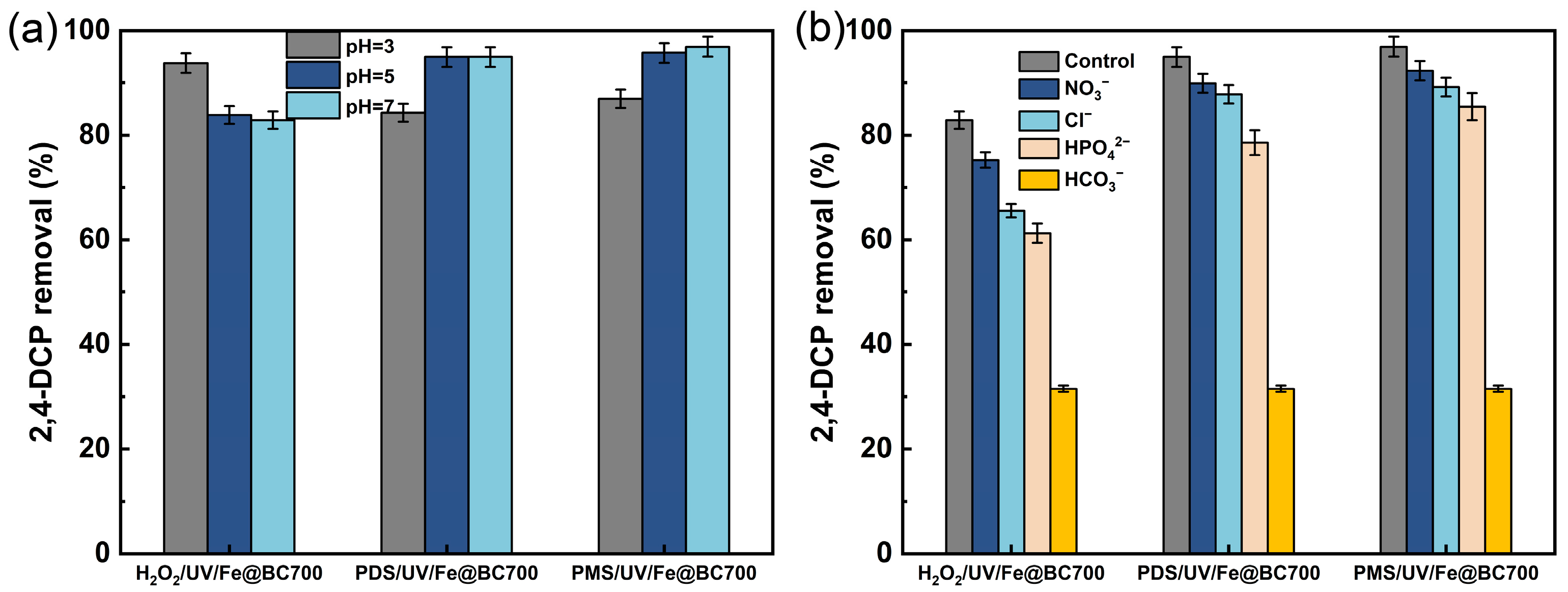
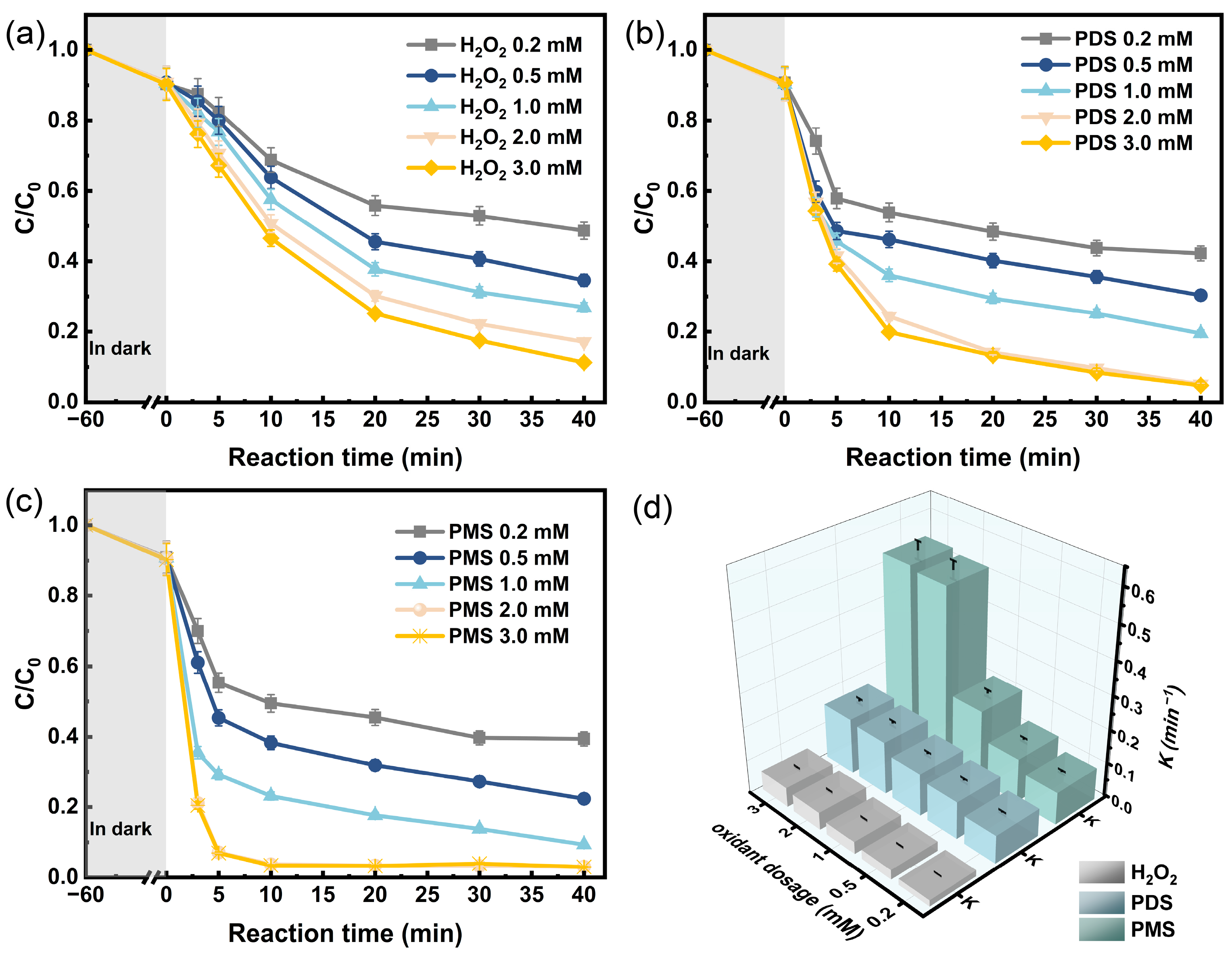
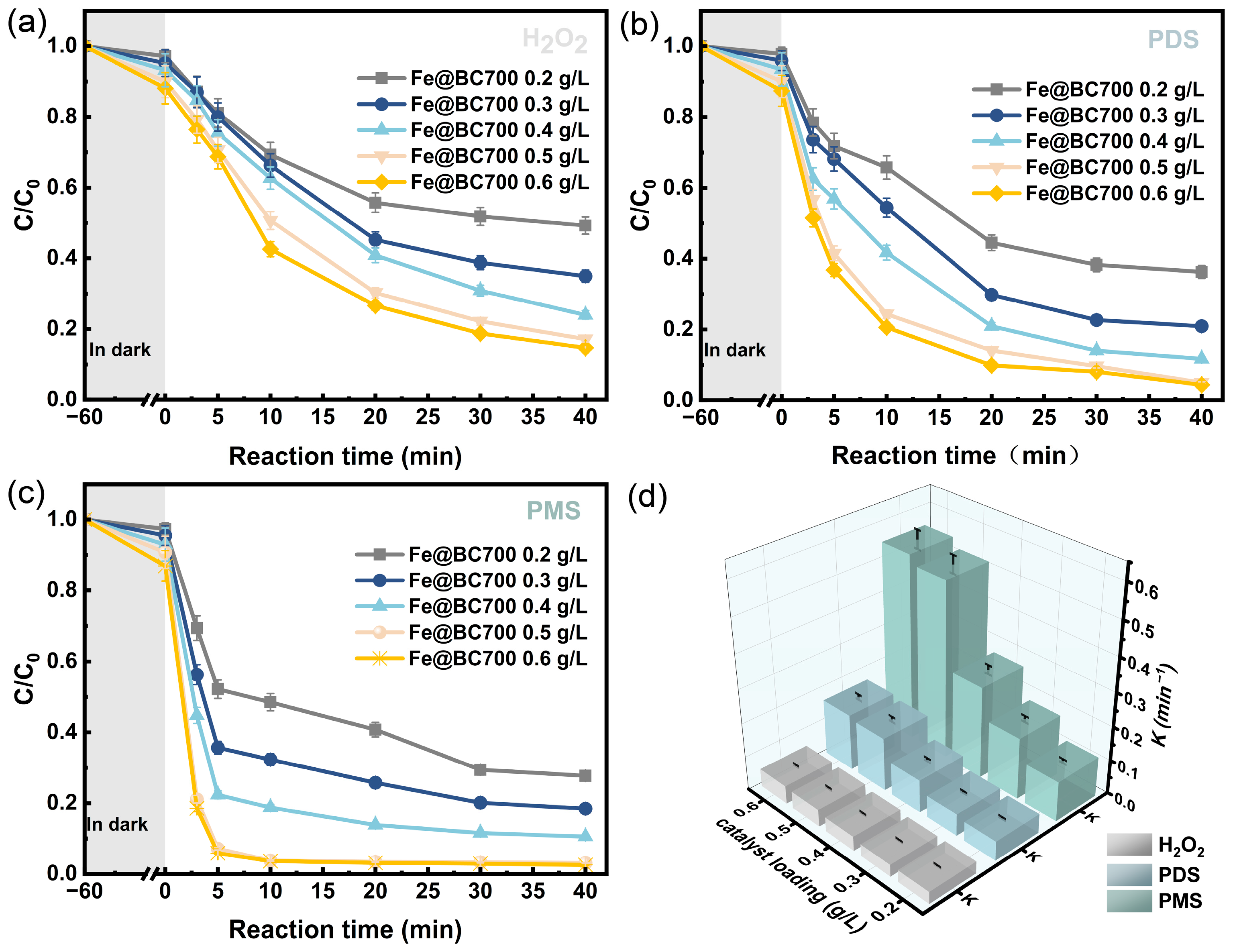
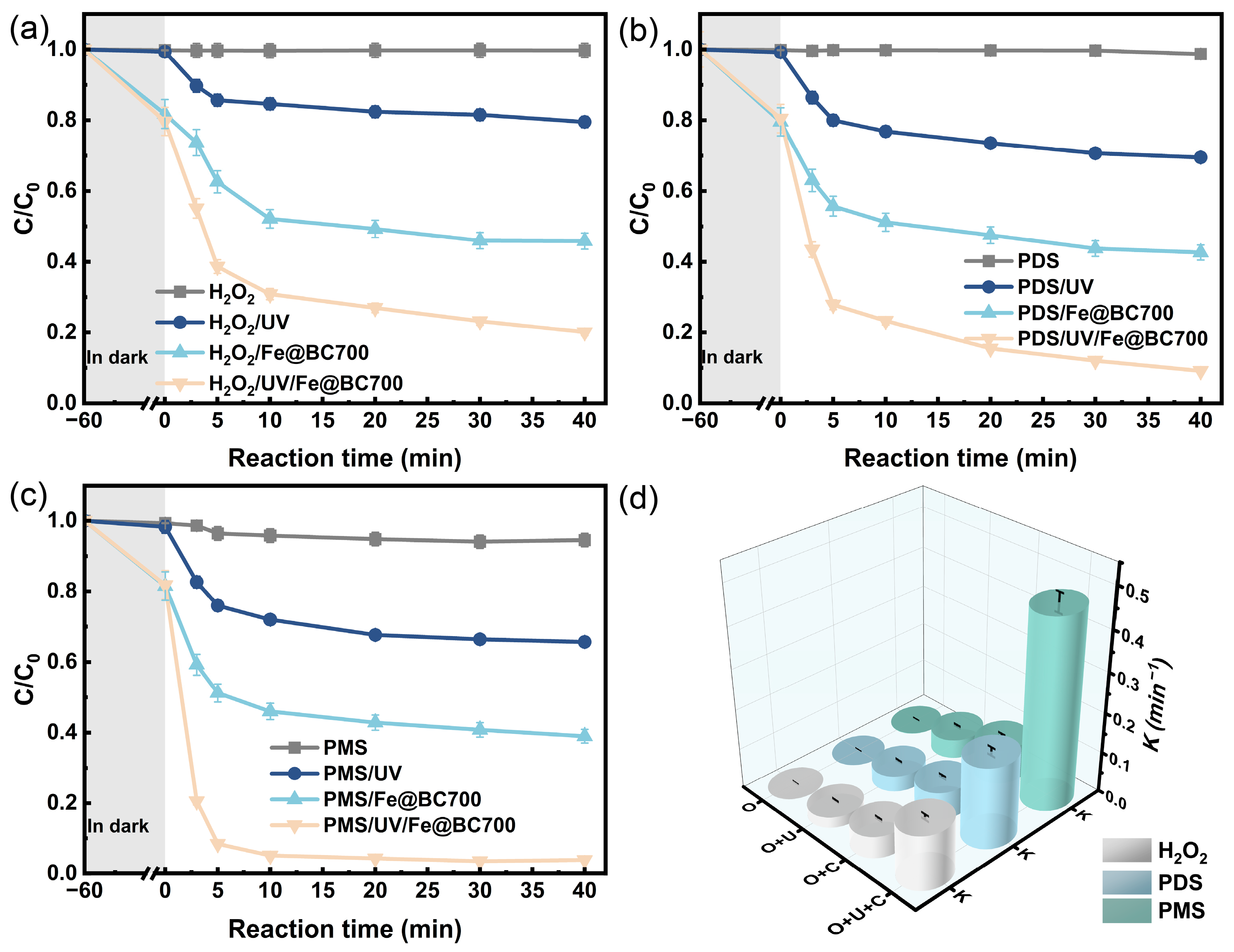
3.2. Degradation of 2,4-DCP Under Different Systems
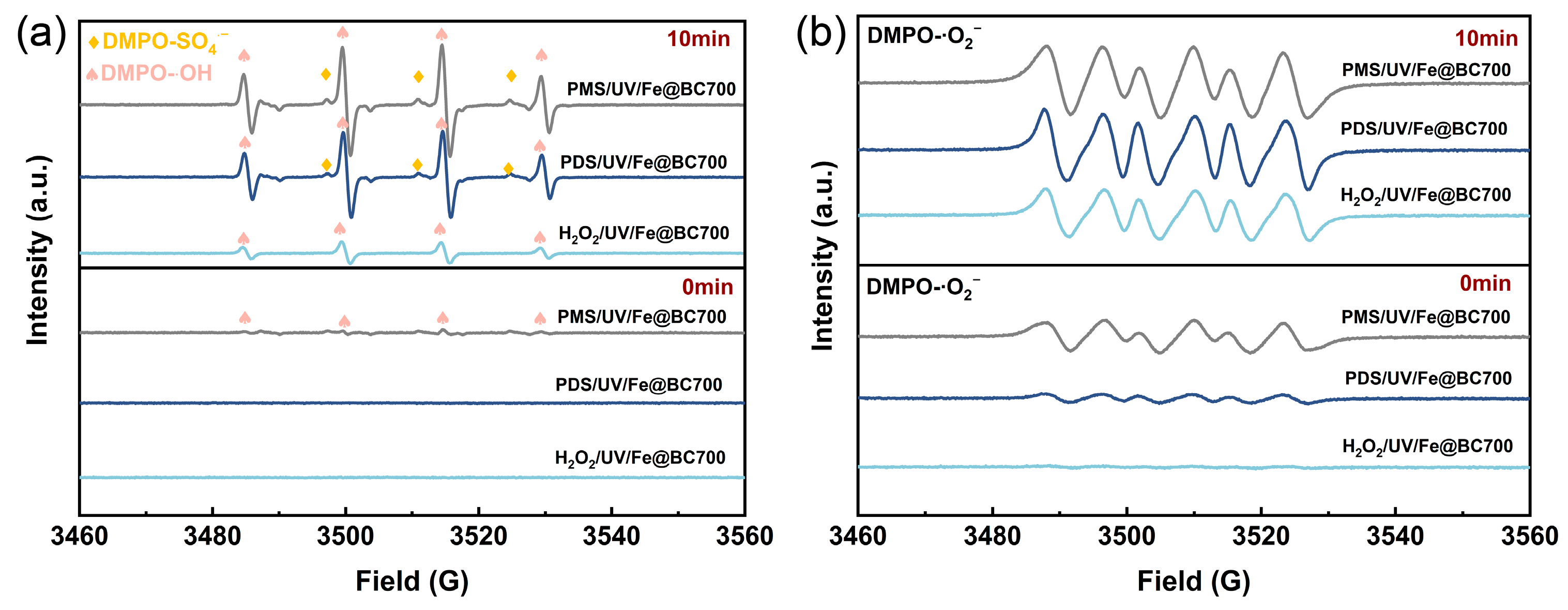
3.3. Radical Quenching Experiments and EPR Studies
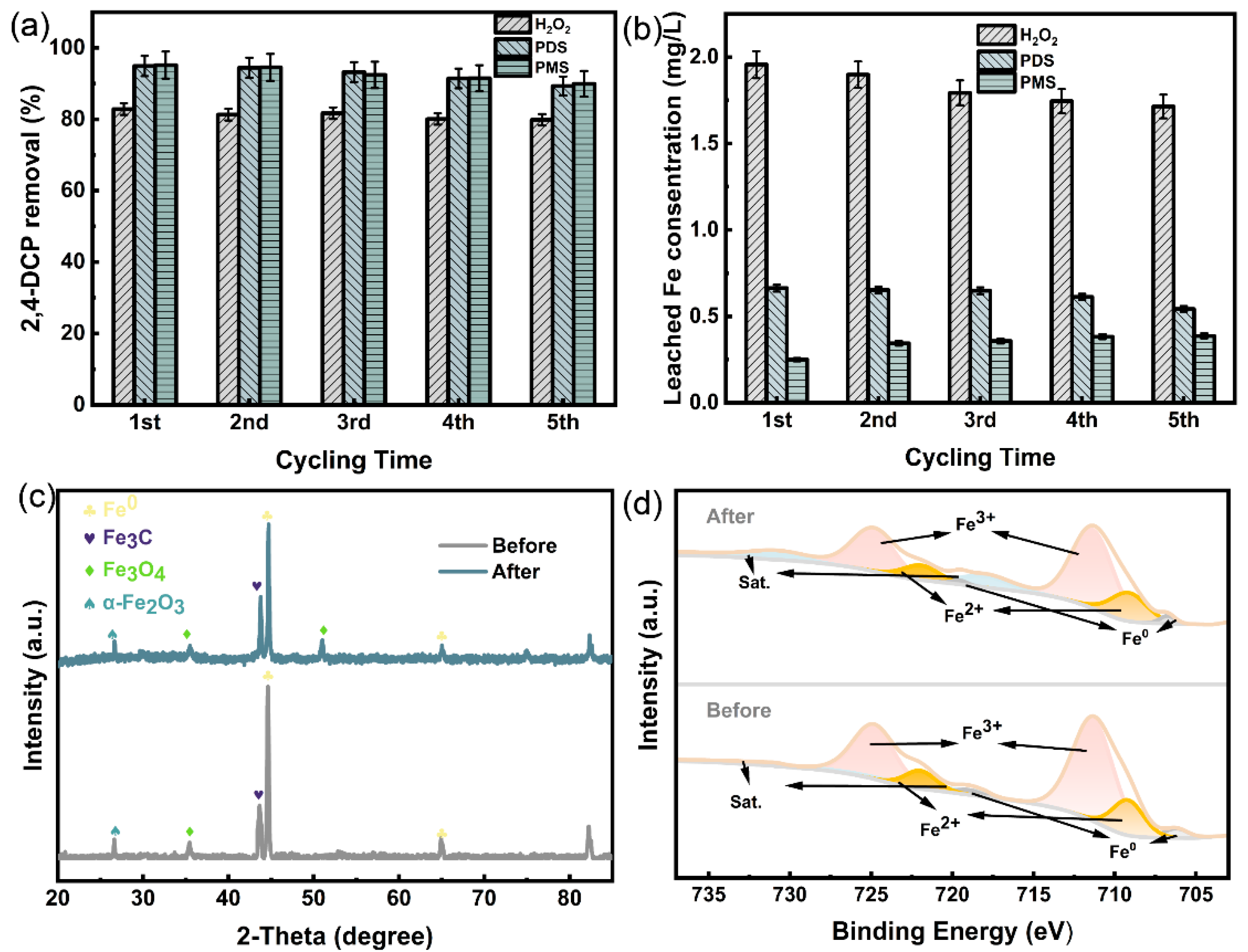
3.4. Stability Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hameed, B.H.; Tan, I.A.W.; Ahmad, A.L. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic modeling and mechanism of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on coconut husk-based activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbinosa, E.O.; Odjadjare, E.E.; Chigor, V.N.; Igbinosa, I.H.; Emoghene, A.O.; Ekhaise, F.O.; Igiehon, N.O.; Idemudia, O.G. Toxicological profile of chlorophenols and their derivatives in the environment: The public health perspective. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 460215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zha, J.; Xu, Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Richardson, K.L.; Wang, Z. Derivation of predicted no effect concentrations (PNEC) for 2,4,6-trichlorophenol based on Chinese resident species. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafarzadeh, N.; Ghanbari, F.; Ahmadi, M. Efficient degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by peroxymonosulfate/magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles/ozone: A novel combination of advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moja, M.M.; Mapossa, A.B.; Chirwa, E.M.N.; Tichapondwa, S. Photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using nanomaterials silver halide catalysts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 11857–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Li, R.; Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Hu, X.; Xiao, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, T. Enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of As(III) by TiO2 modified with Fe3O4 through Ti–O–Fe interface bonds. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects. 2022, 651, 129678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Oh, S.-E.; Yang, J.E.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.; Yu, S.; Pak, D. TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation mechanism of As(III). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.; Amy, G.L.; Prevost, M.; Nour, S.; Jekel, M.; Gallagher, P.M.; Blumenschein, C.D. Kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of adsorption of arsenic onto granular ferric hydroxide (GFH). Water Res. 2008, 42, 3371–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhai, L.; Qiao, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Efficient removal of As(V) from aqueous media by magnetic nanoparticles prepared with Iron-containing water treatment residuals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.K.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Sharma, V.K.; Ray, A.K. Photocatalytic oxidation of arsenic(III): Evidence of hydroxyl radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Ruettimann, T.; Hug, S.J. pH dependence of Fenton reagent generation and As(III) oxidation and removal by corrosion of zero valent iron in aerated water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7424–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Rapid degradation of p-arsanilic acid with simultaneous arsenic removal from aqueous solution using Fenton process. Water Res. 2016, 89, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, R.; Kolthoff, I.M.; Meehan, E.J. Arsenic(IV) as an intermediate in the induced oxidation of arsenic(III) by the iron(II)-persulfate reaction and the photoreduction of iron(III). I. Absence of oxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2385–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review [Review]. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Luo, Z.; Wei, Z.; Luo, S.; Spinney, R.; Yang, W.; Dionysiou, D.D. Activation of peroxymonosulfate/persulfate by nanomaterials for sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation technologies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2018, 19, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Song, C.; Zhou, Q.; Xue, W.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. The optimized Fenton-like activity of Fe single-atom sites by Fe atomic clusters–mediated electronic configuration modulation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2300281120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Dai, Z.; Meng, H.; Duan, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ao, Z.; Wang, S.; An, T. Peroxydisulfate activation by positively polarized carbocatalyst for enhanced removal of aqueous organic pollutants. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Wu, M.-S. UV/S2O82− process for degrading polyvinyl alcohol in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Process. 2014, 85, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y.; Indrawirawan, S.; Wang, S. Insights into heterogeneous catalysis of persulfate activation on dimensional-structured nanocarbons. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4629–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.-Y. Enhancement strategies for efficient activation of persulfate by heterogeneous cobalt-containing catalysts: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyekunle, D.T.; Gendy, E.A.; Ifthikar, J.; Chen, Z. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by metal and non-metal catalyst for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Xie, M.; Kong, L.; Natarajan, V.; Ma, L.; Zhan, J. The magnetic biochar derived from banana peels as a persulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Lai, B.; Liu, C.; He, Y.; Yao, G.; Li, N. Recent progress on heterogeneous Fe-based materials induced persulfate activation for organics removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ji, R.; Li, W.; Lan, Y.; Guo, J. Waste self-heating bag derived iron-based composite with abundant oxygen vacancies for highly efficient Fenton-like degradation of micropollutants. Chemosphere 2023, 326, 138499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.V.; Jiao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Nidheesh, P.V. Iron-based persulfate activation process for environmental decontamination in water and soil. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cui, F. Iron sludge-derived magnetic Fe0/Fe3C catalyst for oxidation of ciprofloxacin via peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 365, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Cheng, M.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, Q. Iron-mediated activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate in both homogeneous and heterogeneous ways: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Shi, X.; Li, L.; Cheng, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Yi, H.; Qin, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Enhancing iron redox cycling for promoting heterogeneous Fenton performance: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Chen, C.; Ren, N.; Xing, D. Zero-valent iron and biochar composite with high specific surface area via K2FeO4 fabrication enhances sulfadiazine removal by persulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, M.; Gong, Q.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z. One-step preparation of ZVI-sludge derived biochar without external source of iron and its application on persulfate activation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Liang, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Continuously feeding fenton sludge into anaerobic digesters: Iron species change and operating stability. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S. A review on sustainable reuse applications of Fenton sludge during wastewater treatment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.M.; Abdul Raman, A.A.; Asghar, A. A review on approaches for addressing the limitations of Fenton oxidation for recalcitrant wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 126, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, E.R.B.; Silva, E.J.; Lopes, W.S.; do Nascimento, M.R.; Leite, V.D.; de Sousa, J.T. Fenton treatment of sanitary landfill leachate: Optimization of operational parameters, characterization of sludge and toxicology. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 2637–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-J.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, C.-G.; Bae, S.; Park, S.-J. Use of thermally activated Fenton sludge for Cd removal in zinc smelter wastewater: Mechanism and feasibility of Cd removal. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Mian, M.M.; Zhang, W.-H. Synthesis of magnetic nZVI@biochar catalyst from acid precipitated black liquor and Fenton sludge and its application for Fenton-like removal of rhodamine b dye. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Jang, M.; Cho, S.-H.; Khim, J.; Cannon, F.S. A continuous pilot-scale system using coal-mine drainage sludge to treat acid mine drainage contaminated with high concentrations of Pb, Zn, and other heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ye, G.; Du, Y.; Zeng, L.; Hao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J. Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres on graphene oxide as an efficient heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for the advanced treatment of biotreated papermaking effluent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 39199–39209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Wang, J.J.; Xiao, R.; Tafti, N.; DeLaune, R.D.; Seo, D.-C. Degradation of orange G by Fenton-like reaction with Fe-impregnated biochar catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Kan, E. FeCl3-activated biochar catalyst for heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole in water. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S.; Wu, X. Enhancing supercapacitor performance through rapid charge transport induced by magnetic field-driven spin polarization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 682, 161690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Sui, X.; Sun, S.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, W. Tribocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using Fe2O3 nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 14364–14373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Kuang, S.; Ren, P.; Xie, B. Persulfate oxidation of tetracycline, antibiotic resistant bacteria, and resistance genes activated by Fe doped biochar catalysts: Synergy of radical and non-radical processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, S.; Cai, H.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, W.; Yi, H.; Fu, C.; et al. Ultra-thin Fe3C nanosheets promote the adsorption and conversion of polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 18, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Guo, D.; Qiu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z. Thermal conversion of a promising phytoremediation plant (Symphytum officinale L.) into biochar: Dynamic of potentially toxic elements and environmental acceptability assessment of the biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on biochar’s characteristics and speciation and environmental risks of heavy metals in sewage sludge biochars. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Chen, D.; Mao, P.; Jiang, X.; Sun, A.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Shen, J. Synthesis of magnetic hydrochar from Fenton sludge and sewage sludge for enhanced anaerobic decolorization of azo dye AO7. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Pu, S.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Bai, Y. Hierarchical porous structured polysulfide supported nZVI/biochar and efficient immobilization of selenium in the soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Voroney, R.P.; Price, G.W.; White, A.J. Sulfur-enriched biochar as a potential soil amendment and fertiliser. Soil Res. 2017, 55, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Tong, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, J. Biochar supported sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron for the reduction of nitrobenzene. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22161–22168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Tang, J.; Huang, Y.; Gai, L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Liber, K.; Gong, Y. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Huang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J. Preparation of a novel graphene oxide/Fe-Mn composite and its application for aqueous Hg(II) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Wang, J.J.; Seo, D.-C. Comparison of catalytic activity for treating recalcitrant organic pollutant in heterogeneous Fenton oxidation with iron-impregnated biochar and activated carbon. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Hu, H.; Zheng, H.; Hu, H.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Nonprecious bimetallic Fe, Mo-embedded N-enriched porous biochar for efficient oxidation of aqueous organic contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, C.; Yang, H.; Jin, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, C.; Li, G.; Tang, Y.; Fang, X. Exploring the effect of different precursor materials on Fe-loaded biochar catalysts for toluene removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yoon, S.; Pasturel, M.; Bae, S.; Hanna, K. Interactions between nanoscale zerovalent iron (NZVI) and silver nanoparticles alter the NZVI reactivity in aqueous environments. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Liang, J.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Ji, F. A comparative study of free chlorine and peroxymonosulfate activated by Fe(II) in the degradation of iopamidol: Mechanisms, density functional theory (DFT) calculatitons and formation of iodinated disinfection by-products. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Su, H.-W. Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Hou, H.; Liang, S.; Qiu, J.; Tao, S.; Yang, L.; Yu, W.; Xiao, K.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; et al. Sludge-derived biochar with multivalent iron as an efficient Fenton catalyst for degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Mishra, I.M.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kumar, V. Oxidative removal of bisphenol A by UV-C/peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Kinetics, influence of co-existing chemicals and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M.; Gohari, F. Degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in aqueous solutions using peroxymonosulfate/activated carbon/UV process via sulfate and hydroxyl radicals. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Xin, X. Radical induced degradation of acetaminophen with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as heterogeneous activator of peroxymonosulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.-D.; Dong, Z.; Lim, T.-T. Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: Current development, challenges and prospects. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 194, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Song, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Tang, J. Simultaneous removal of 2,4-DCP and Cr(VI) in water by gBC@nZVI: Cr(V) mediated ROS formation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gao, M.; Deng, Y.; Khan, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Song, Z.; Qiu, W. Efficient oxidation and adsorption of As(III) and As(V) in water using a Fenton-like reagent, (ferrihydrite)-loaded biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Banik, C.; Rathke, S.J.; Laird, D.A. Arsenic sorption on zero-valent iron-biochar complexes. Water Res. 2018, 137, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, D.; Huang, Q.; Song, Z.; Chau, H.W. Arsenic removal in aqueous solution by a novel Fe-Mn modified biochar composite: Characterization and mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Song, Z.; Khan, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Qiu, W. Enhanced As(III) removal from aqueous solution by Fe-Mn-La-impregnated biochar composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yi, Y.; Fang, Z. Remediation of cadmium or arsenic contaminated water and soil by modified biochar: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Liang, M.; Ding, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. Fe3O4/Mulberry stem biochar as a potential amendment for highly arsenic-contaminated paddy soil remediation. Toxicologist 2024, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Song, J.; Han, W.; Yeung, K.L.; Zhou, S.; Mo, C.-H. Iron-organic frameworks as effective fenton-like catalysts for peroxymonosulfate decomposition in advanced oxidation processes. npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.G.; Srinivas, M.; ArunaKumari, M.L. Heterogeneous advanced photo- Fenton process using peroxymonosulfate and peroxydisulfate in presence of zero valent metallic iron: A comparative study with hydrogen peroxide photo-Fenton process. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 13, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shao, B.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z.; Liang, Q.; He, Q.; Wu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by biochar-based catalysts and applications in the degradation of organic contaminants: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 128829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jia, N.; Zhou, L.; Lei, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Photo-Fenton-like degradation of antibiotics by inverse opal WO3 co-catalytic Fe2+/PMS, Fe2+/H2O2 and Fe2+/PDS processes: A comparative study. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Su, J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, H.; Qian, H. An amorphous zero-valent iron decorated by Fe3O4 significantly improves the Fenton-like reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 929, 167306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Activation of persulfate by nanosized zero-valent iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and transformation products of NZVI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.-D.; Cui, Y.; Ji, S.; Du, L.; Jiang, F.-Z. Iron-based nitrogen-rich metal–organic framework structure for activation of hydrogen peroxide and peroxymonosulfate for ultra-efficient tetracycline degradation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 680, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.-F.; Huang, F.; Yang, W.-J.; Wang, S.-L.; Yuan, T.-Y.; Liao, B.-H. Effects of nano-Fe3O4-modified biochar on iron plaque formation and Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Han, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zang, S.; Qi, L. Fast and efficient As(III) removal from water by bifunctional nZVI@NBC. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Deng, Y.; Shu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ye, S.; Chen, Q.; Yang, H.; Yang, L. Phytoremediation plants (ramie) and steel smelting wastes for calcium silicate coated-nZVI/biochar production: Environmental risk assessment and efficient As(V) removal mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 156924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Y.; Li, Y. Fabrication of magnetic carbon composites from peanut shells and its application as a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst in removal of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 324, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-G.; Yoon, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, E.-j.; Chang, Y.-S. Comparative study of peroxide oxidants activated by nZVI: Removal of 1,4-dioxane and arsenic(III) in contaminated waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Wang, Q.; Yu, F.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y. Efficient degradation of 2,4-dichlorophphenol in groundwater using persulfate activated by nitrogen-doped biochar-supported nano zero-valent iron. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Dou, M.; Zhang, Q.; Huo, K.; Han, C.; Shi, J. Sewage sludge pyrolysis ‘kills two birds with one stone’: Biochar synergies with persulfate for pollutants removal and energy recovery. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Cui, J.; Zhang, F.; Xiangli, P.; Wei, L.; Yang, D.; Liang, Y.; Cui, J. Enhanced degradation of ofloxacin by activation of peroxymonosulfate with biochar-FeVO4 under visible light assistance: The role of biochar in mediating charge transfer and mechanism insight. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 652, 159236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chang, T.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, J. Insight into enhanced tetracycline photodegradation by hematite/biochar composites: Roles of charge transfer, biochar-derived dissolved organic matter and persistent free radicals. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 420, 132118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichtweis, J.; Silvestri, S.; Welter, N.; Vieira, Y.; Zaragoza-Sánchez, P.I.; Chávez-Mejía, A.C.; Carissimi, E. Wastewater containing emerging contaminants treated by residues from the brewing industry based on biochar as a new CuFe2O4/biochar photocatalyst. Environmentalist 2021, 150, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Remya, N.; Singhal, N.; Dubey, B.K. Walnut shell biochar supported TiO2-g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalyst for solar photocatalytic degradation of Congo red. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023, 13, 9537–9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fe@BC300 | Fe@BC500 | Fe@BC700 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Area (m2/g) | 5.27 | 21.75 | 122.47 |
| Pore Size (nm) | 0.95 | 1.09 | 1.30 |
| Pore Volume (m3/g) | 0.0012 | 0.0059 | 0.049 |
| Photocatalyst | Photocatalytic Condition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light and Target Pollutant | Oxidation | Catalysts (g/L) | Time (min) | Iron Leaching (mg/L) | Removal % | Ref. | |
| FVC | Vis, ofloxacin 10 mg/L | PMS | 0.7 | 150 | / | 95.2 | [89] |
| Hem/BC-5 | Vis, TC 10 mg/L | H2O2 | 0.2 | 90 | 0.45 | 96.1 | [90] |
| CFO1B3 | Vis, RhB 50 mg/L | H2O2 | 1 | 20 | 1.02 | 100 | [91] |
| WSB | Vis, CR 10 mg/L | H2O2 | 1 | 180 | / | 60 | [92] |
| Fe@BC700 | UV, 2,4-DCP 100 mg/L | PMS | 0.5 | 40 | 0.78 | 100 | This work |
| Fe@BC700 | UV, As(III) 5 mg/L | PMS | 0.5 | 40 | 0.78 | 96.2 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, C.; Huang, R.; Mao, W.; Wu, Z.; Wei, C.; Li, A.; Zhou, J. Activation of H2O2/PDS/PMS by Iron-Based Biochar Derived from Fenton Sludge for Oxidative Removal of 2,4-DCP and As(III). Water 2025, 17, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050765
Ling C, Huang R, Mao W, Wu Z, Wei C, Li A, Zhou J. Activation of H2O2/PDS/PMS by Iron-Based Biochar Derived from Fenton Sludge for Oxidative Removal of 2,4-DCP and As(III). Water. 2025; 17(5):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050765
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Chutong, Renting Huang, Wei Mao, Zhiming Wu, Cui Wei, Anze Li, and Jinghong Zhou. 2025. "Activation of H2O2/PDS/PMS by Iron-Based Biochar Derived from Fenton Sludge for Oxidative Removal of 2,4-DCP and As(III)" Water 17, no. 5: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050765
APA StyleLing, C., Huang, R., Mao, W., Wu, Z., Wei, C., Li, A., & Zhou, J. (2025). Activation of H2O2/PDS/PMS by Iron-Based Biochar Derived from Fenton Sludge for Oxidative Removal of 2,4-DCP and As(III). Water, 17(5), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050765







