A2DSC-Net: A Network Based on Multi-Branch Dilated and Dynamic Snake Convolutions for Water Body Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Conventional Water Index-Based Approaches
1.2. Machine Learning-Based Methods
1.3. Deep Learning Methods
1.4. Persistent Challenges
- Multi-branch dilated convolution module (MBDC): We design a multi-branch structure composed of dilated convolutions with different receptive fields to capture multi-scale contextual information, thereby improving the extraction of small water bodies.
- Dynamic snake convolution with double attention mechanism: We introduce and adapt dynamic snake convolution to the water body extraction task for the first time. By enabling convolution kernels to adjust their shape and orientation adaptively, and combining them with a double attention mechanism, the model is able to better identify and represent complex water body structures.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Methods
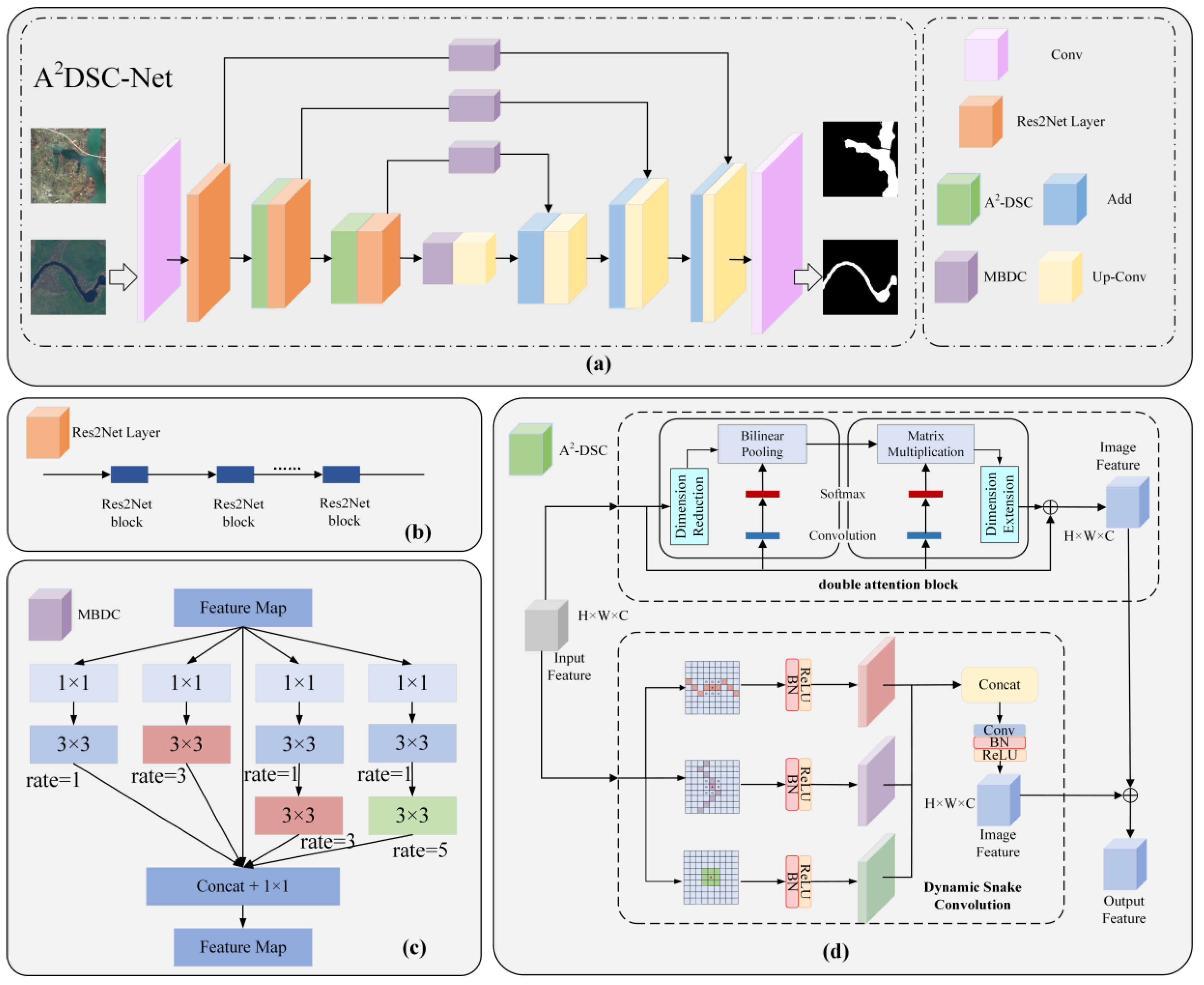
2.2.1. A2DSC-Net Architecture
2.2.2. Multi-Branch Dilated Convolution (MBDC) Module
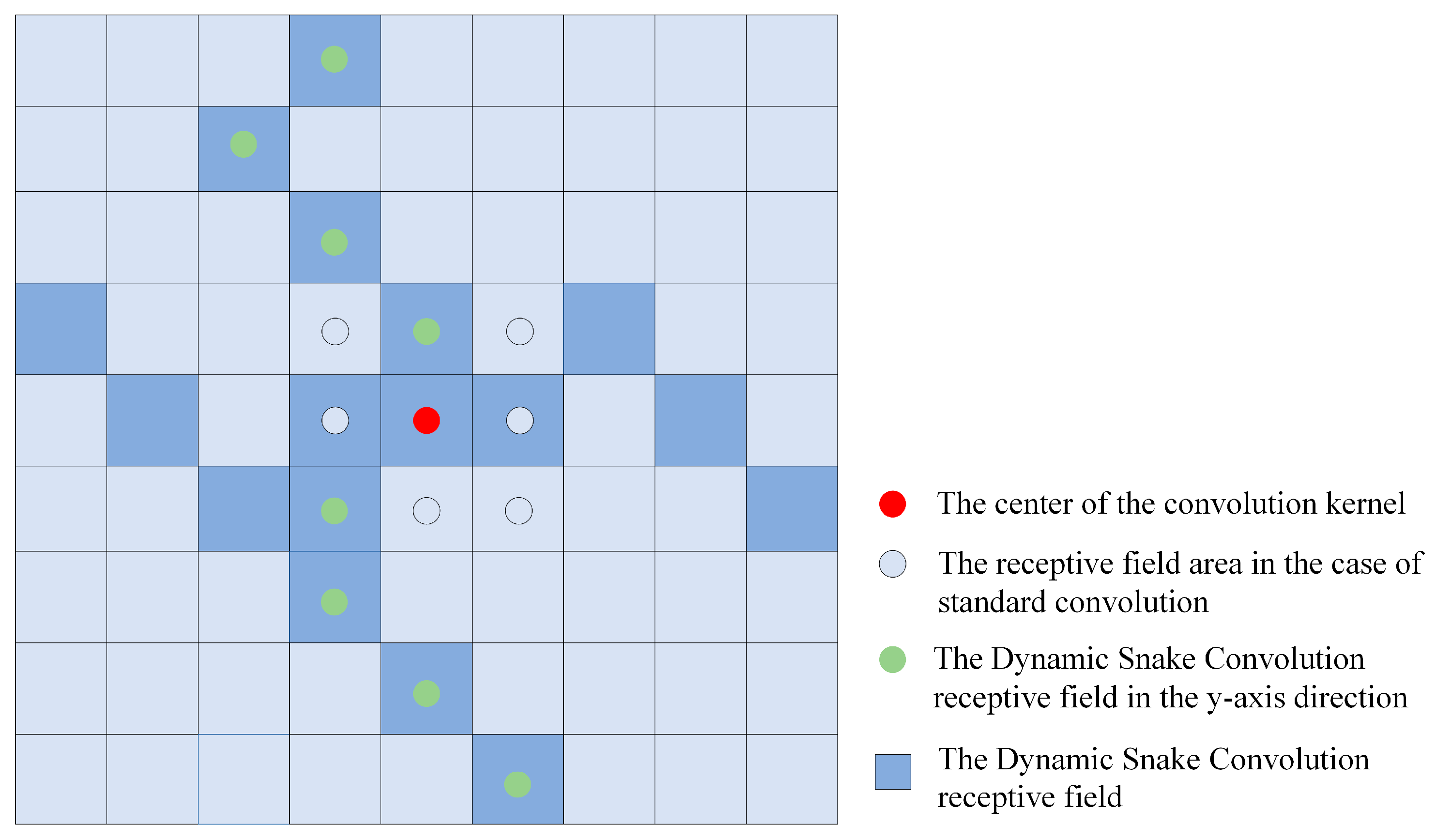
2.2.3. Dynamic Snake Convolution Module
2.3. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
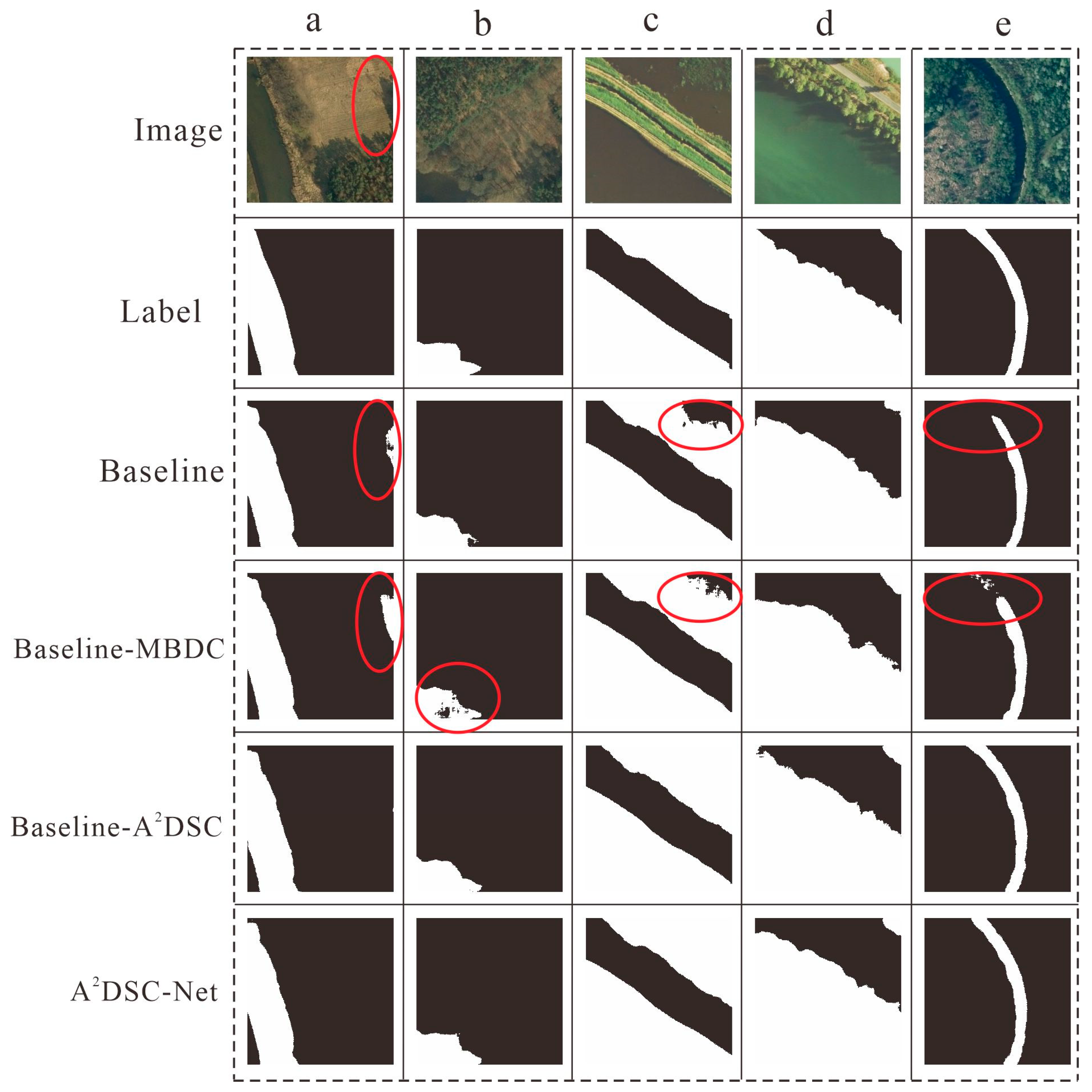
3.1. Ablation Experiments
- Ablation Study of the MBDC Module
- 2.
- Ablation Study of the A2-DSC Module
3.2. Comparative Experiments
3.2.1. Comparative Experiments on the GID Dataset
3.2.2. Comparative Experiments on the LandCover.ai Dataset
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global Lake Responses to Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, L.; Vanderkelen, I.; Gudmundsson, L.; Tan, Z.; Perroud, M.; Stepanenko, V.M.; Debolskiy, A.V.; Droppers, B.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Woolway, R.I.; et al. Attribution of Global Lake Systems Change to Anthropogenic Forcing. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The Use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Body with the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI). Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A New Technique for Surface Water Mapping Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Guo, H.; Du, J.; Duan, Z. A Robust Multi-Band Water Index (MBWI) for Automated Extraction of Surface Water from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malahlela, O.E. Inland Waterbody Mapping: Towards Improving Discrimination and Extraction of Inland Surface Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 4574–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ni, Y.; Pang, Z.; Li, X.; Ju, H.; He, G.; Lv, J.; Yang, K.; Fu, J.; Qin, X. An Effective Water Body Extraction Method with New Water Index for Sentinel-2 Imagery. Water 2021, 13, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, W.; Yin, X. A Comparison of Different Water Indices and Band Downscaling Methods for Water Bodies Mapping from Sentinel-2 Imagery at 10-M Resolution. Water 2022, 14, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Danaher, T. A Water Index for SPOT5 HRG Satellite Imagery, New South Wales, Australia, Determined by Linear Discriminant Analysis. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5907–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Study on the Automatic Extraction of Water Body from TM Image Using Decision Tree Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Photoelectronic Detection and Imaging 2007: Related Technologies and Applications, Beijing, China, 26 September 2007; p. 662502. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jia, M.; Chen, N.; Wang, W. Long-Term Surface Water Dynamics Analysis Based on Landsat Imagery and the Google Earth Engine Platform: A Case Study in the Middle Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Rui, X. A High-Precision Water Body Extraction Method Based on Improved Lightweight U-Net. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; He, G.; Jiang, W.; Yin, R.; Yan, L.; Leng, W. A Multi-Scale Water Extraction Convolutional Neural Network (MWEN) Method for GaoFen-1 Remote Sensing Images. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2020, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M. Lightweight Deep Neural Network Method for Water Body Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images with Multisensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, Z.; Shen, Q.; Cheng, G.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. Water Body Extraction from Very High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Data Based on Fully Convolutional Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z. An Information-Expanding Network for Water Body Extraction Based on U-Net. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1502205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hong, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, A. Automated Extraction of Lake Water Bodies in Complex Geographical Environments by Fusing Sentinel-1/2 Data. Water 2021, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Gao, G.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D. Extraction of Water Bodies from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Based on a Deep Semantic Segmentation Network. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, R.; Kumar, L.S. Multi Scale Feature Extraction Network with Machine Learning Algorithms for Water Body Extraction from Remote Sensing Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 6349–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; He, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G. Dynamic Snake Convolution Based on Topological Geometric Constraints for Tubular Structure Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1 October 2023; pp. 6047–6056. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.; Yuan, W.; Tang, L. DCP-Net: An Efficient Image Segmentation Model for Forest Wildfires. Forests 2024, 15, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shi, G.; Zhu, C. Dynamic Serpentine Convolution with Attention Mechanism Enhancement for Beef Cattle Behavior Recognition. Animals 2024, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Imasu, R.; Dhaka, S.K.; Patra, P.K. Domain Adaptation and Fine-Tuning of a Deep Learning Segmentation Model of Small Agricultural Burn Area Detection Using High-Resolution Sentinel-2 Observations: A Case Study of Punjab, India. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhao, C.; Lin, J.; Jiao, C.; Zheng, G.; Zhu, J.; Pan, X.; Han, X. Improved Spectral Water Index Combined with Otsu Algorithm to Extract Muddy Coastline Data. Water 2022, 14, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Du, S.; Bai, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Water Extraction from Optical High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery: A Multi-Scale Feature Extraction Network with Contrastive Learning. GIScience Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2166396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.-Y.; Xia, G.-S.; Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; You, S.; Zhang, L. Land-Cover Classification with High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Using Transferable Deep Models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguszewski, A.; Batorski, D.; Ziemba-Jankowska, N.; Dziedzic, T.; Zambrzycka, A. LandCover.Ai: Dataset for Automatic Mapping of Buildings, Woodlands, Water and Roads from Aerial Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1102–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.-H.; Cheng, M.-M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Yang, M.-H.; Torr, P. Res2Net: A New Multi-Scale Backbone Architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Hou, X.; Cottrell, G. Understanding Convolution for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 1451–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. A2-Nets: Double Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]





| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | IoU (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 95.95 | 94.33 | 90.72 | 95.13 |
| Baseline-MBDC | 95.5 | 94.8 | 90.75 | 95.15 |
| Baseline-A2DSC | 95.23 | 94.93 | 90.63 | 95.08 |
| A2DSC-Net | 95.69 | 95.29 | 91.37 | 95.49 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | IoU (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 97.47 | 94.56 | 92.3 | 95.99 |
| Baseline-MBDC | 97.2 | 95.59 | 93.02 | 96.38 |
| Baseline-A2DSC | 96.91 | 96.85 | 93.95 | 96.88 |
| A2DSC-Net | 96.98 | 97.08 | 94.23 | 97.03 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | IoU (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3+ | 92.58 | 94.33 | 87.7 | 93.45 |
| U-Net | 95.4 | 94.89 | 90.74 | 95.15 |
| PSPNet | 93.24 | 92.09 | 86.33 | 92.66 |
| DANet | 95.36 | 91.6 | 87.69 | 93.44 |
| A2DSC-Net | 95.69 | 95.29 | 91.37 | 95.49 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | IoU (%) | F1-Score(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3+ | 92.7 | 94.77 | 88.19 | 93.72 |
| U-Net | 96.61 | 94.56 | 91.52 | 95.57 |
| PSPNet | 96.18 | 95.11 | 91.65 | 95.64 |
| DANet | 96.35 | 95.3 | 91.98 | 95.82 |
| A2DSC-Net | 96.98 | 97.08 | 94.23 | 97.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhang, P. A2DSC-Net: A Network Based on Multi-Branch Dilated and Dynamic Snake Convolutions for Water Body Extraction. Water 2025, 17, 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182760
Zhang S, Zhang C, Zhao Q, Ma J, Zhang P. A2DSC-Net: A Network Based on Multi-Branch Dilated and Dynamic Snake Convolutions for Water Body Extraction. Water. 2025; 17(18):2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182760
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuai, Chao Zhang, Qichao Zhao, Junjie Ma, and Pengpeng Zhang. 2025. "A2DSC-Net: A Network Based on Multi-Branch Dilated and Dynamic Snake Convolutions for Water Body Extraction" Water 17, no. 18: 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182760
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhang, C., Zhao, Q., Ma, J., & Zhang, P. (2025). A2DSC-Net: A Network Based on Multi-Branch Dilated and Dynamic Snake Convolutions for Water Body Extraction. Water, 17(18), 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182760






