An Integrated Water Resources Solution for a Wide Arid to Semi-Arid Urbanized Coastal Tropical Region with Several Topographic Challenges—A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
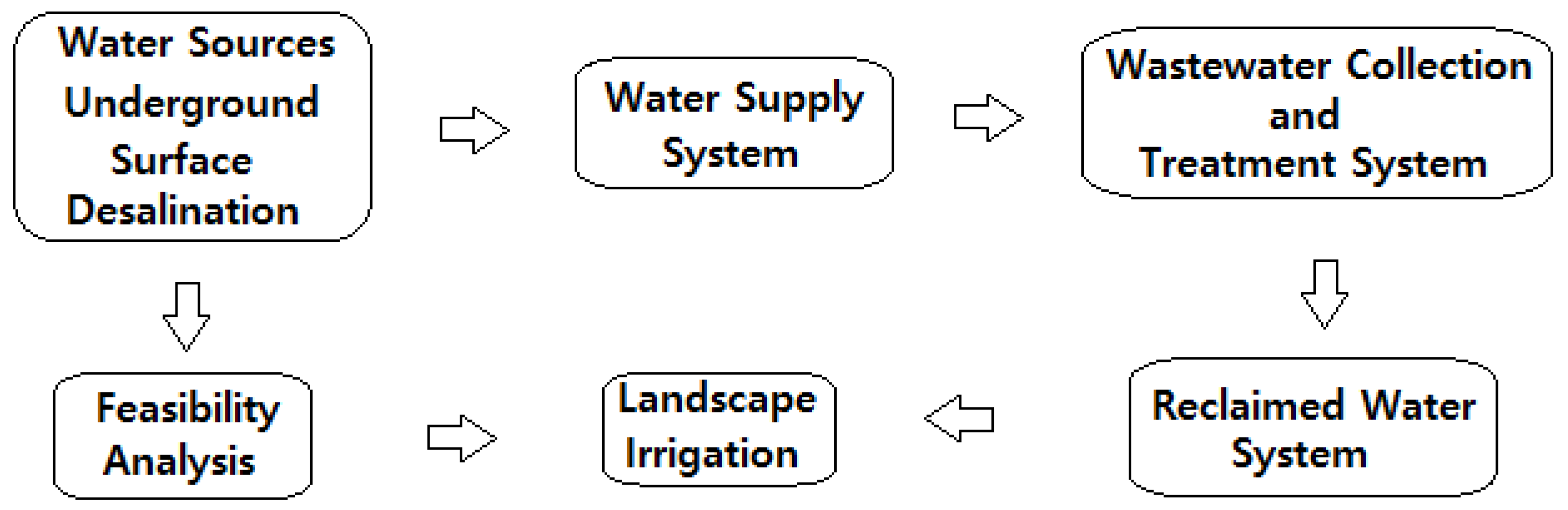
2. Materials and Methods
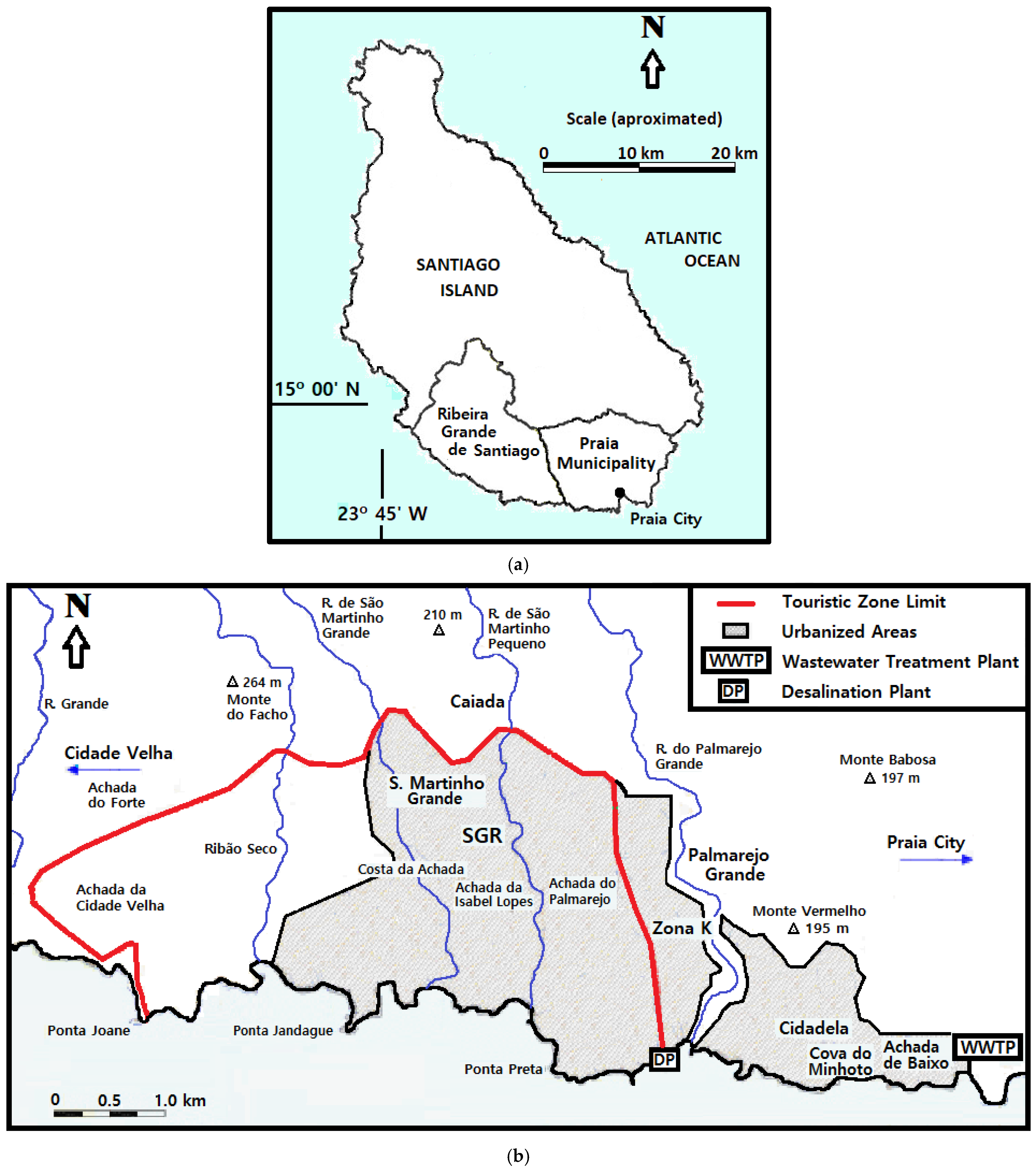
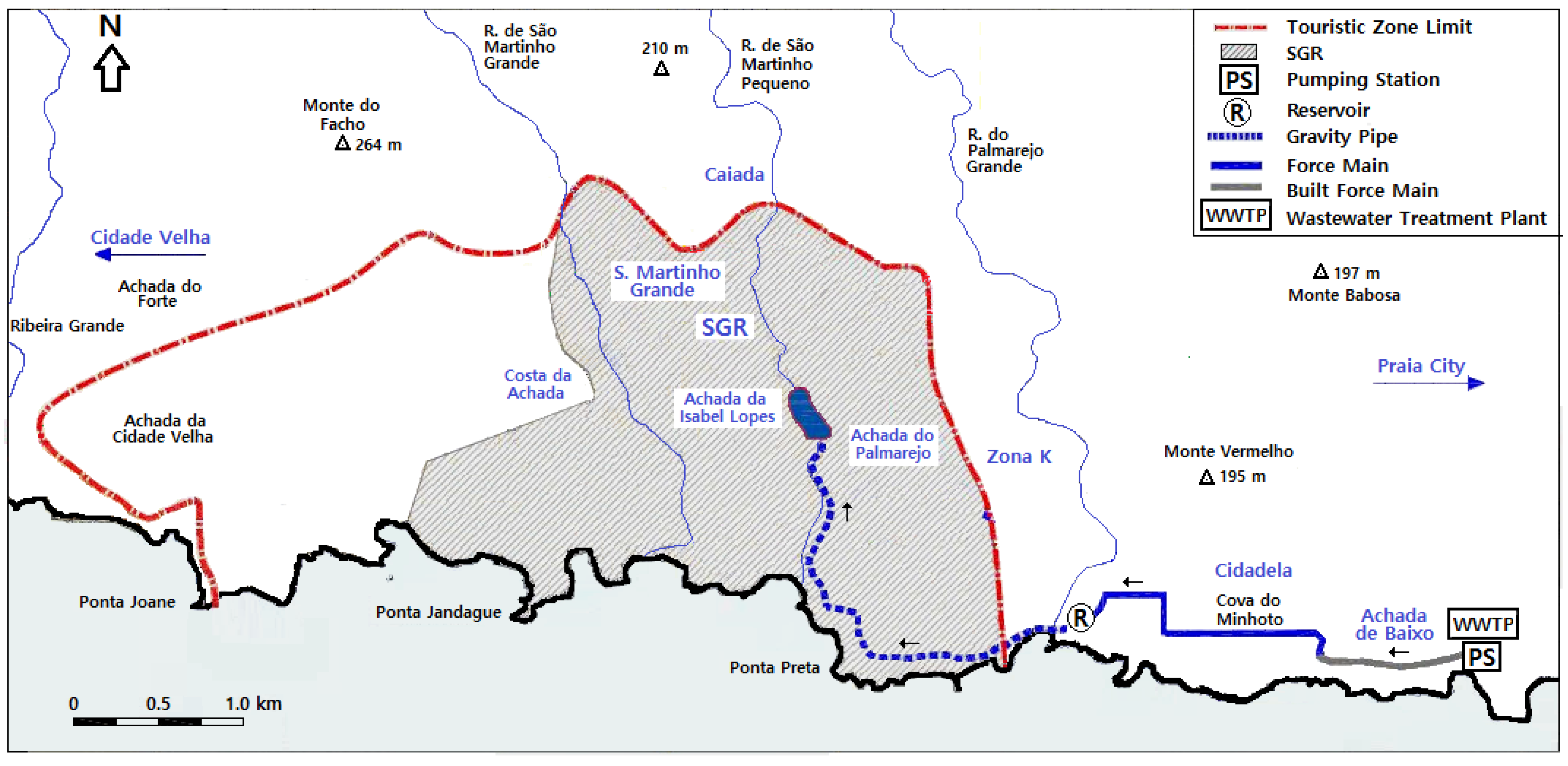
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Requirements of the Systems
2.2.1. Water Supply Network
2.2.2. Wastewater Collection and Treatment System
2.2.3. Irrigation System
2.3. Previous Studies and Performed Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
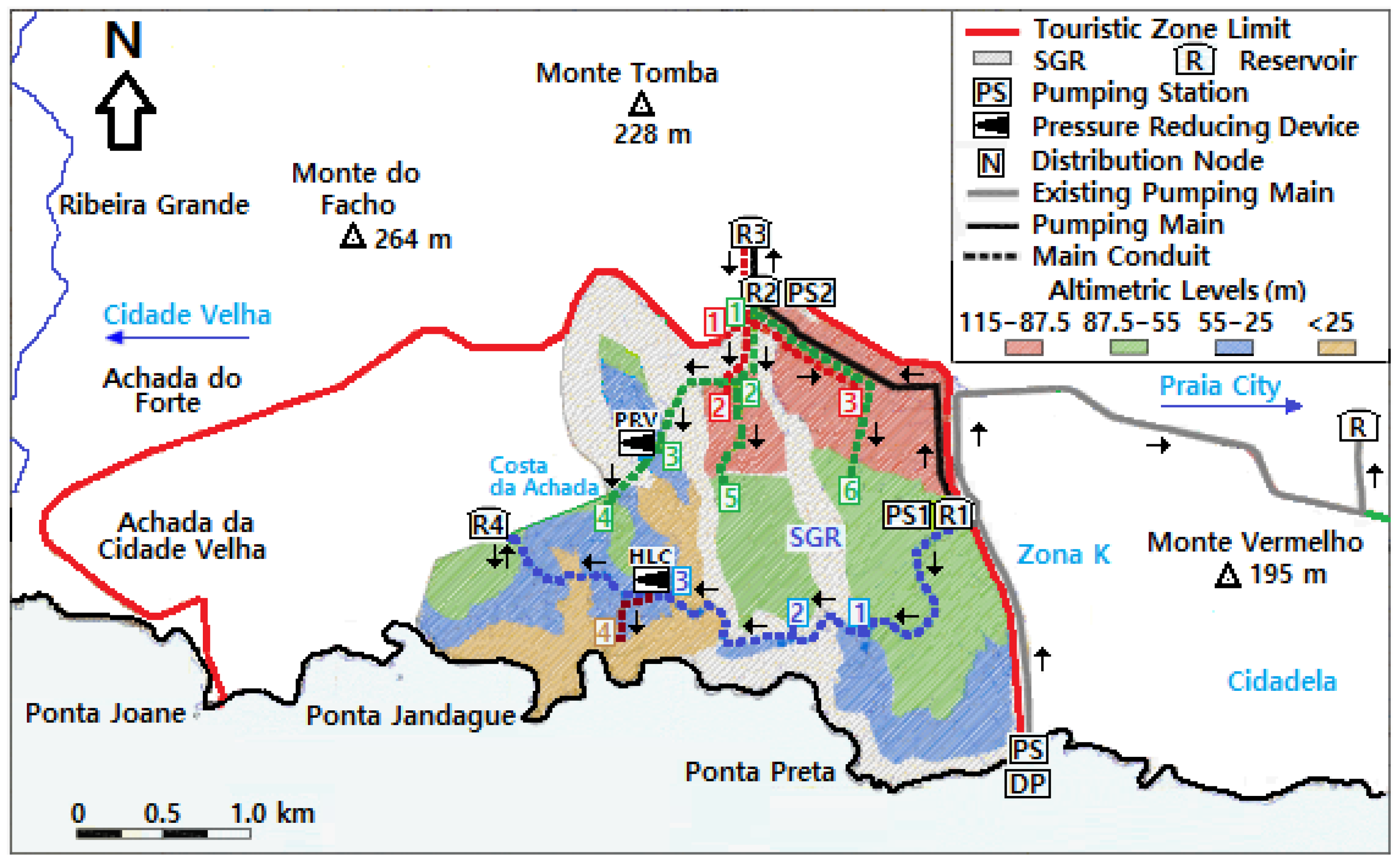
3.1. Water Supply System
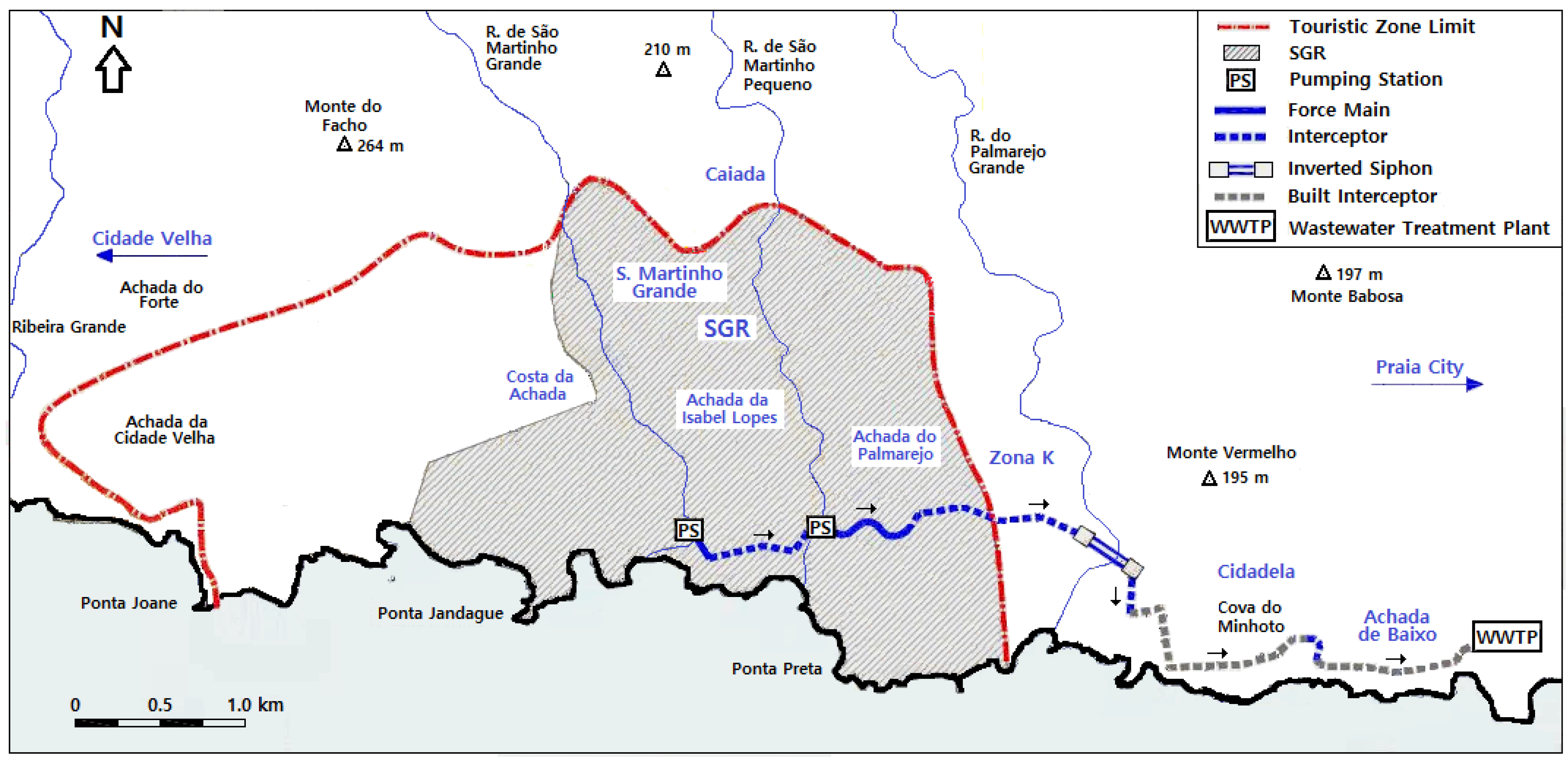
3.2. Sewer Interceptor System
3.3. Recycled Water Pipeline
3.4. Complementary Irrigation Sources and Long-Term Governance
4. Conclusions
5. Recommendations for Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meran, G.; Siehlow, M.; von Hirschhausen, C. The Economics of Water; Springer Water; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Piegdoń, I. The Failure Risk Analysis of the Water Supply Network. Water 2023, 15, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimoch, I.; Bartkiewicz, E.; Machnik-Slomka, J.; Klosok-Bazan, I.; Rak, A.; Rusek, S. Sustainable Water Supply Systems Management for Energy Efficiency: A Case Study. Energies 2021, 14, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A. Wastewater Treatment and Reuse for Sustainable Water Resources Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, V.; Santos, A.S.P.; Lima, M. Decision support tools for water reuse: A systematic review. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 90, 2713–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkareem, M.; Mansour, A.M.; Akawy, A. Securing water for arid regions: Rainwater harvesting and sustainable groundwater management using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 36, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Cañas, J.; Moreno-Pérez, M.F. Water and Irrigation Management in Arid and Semiarid Zones. Water 2021, 13, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, G.; Palenzuela, P.; Ktori, R.; Alarcón-Padilla, D.C.; Zaragoza, G.; Fayad, S.; Xevgenos, D.; Parada, M.P. Thermal seawater desalination for irrigation purposes in a water-stressed region: Emerging value tensions in full-scale implementation. Desalination 2025, 593, 118213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, R.; Prudhomme, C. SW—Soil and Water: Climate Change and Water Resources Management in Arid and Semi-arid Regions: Prospective and Challenges for the 21st Century. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 81, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingale, S.M.; Jat, M.K.; Khare, D. Integrated urban water management modelling under climate change scenarios. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanekely, M.; Scholz, M.; Al-Faraj, F. Strategic Framework for Sustainable Management of Drainage Systems in Semi-Arid Cities: An Iraqi Case Study. Water 2016, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaeed, B.S.; Hunt, D.V.L.; Sharifi, S. A Sustainable Water Resources Management Assessment Framework (SWRM-AF) for Arid and Semi-Arid Regions—Part 1: Developing the Conceptual Framework. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-J.; Xiong, Y.-C.; Li, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-X.; Li, F.-M.; Wang, H.-Y.; Li, L.-L. Integrated water resources management and water users’ associations in the arid region of northwest China: A case study of farmers’ perceptions. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadri, A.; Saidi, M.E.M.; El Khalki, E.M.; Aachrine, B.; Saouabe, T.; Elmaki, A.A. Integrated water management under climate change through the application of the WEAP model in a Mediterranean arid region. J. Water Clim. Change 2022, 13, 2414–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.W. Integrated Urban Water Management: Arid and Semi-Arid Regions; Urban Water Series–UNESCO-IHP; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISSN 1749-0790. [Google Scholar]
- Nydrioti, I.; Sebos, I.; Kitsara, G.; Assimacopoulos, D. Effective management of urban water resources under various climate scenarios in semiarid mediterranean areas. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, C.; Githiora, Y.W.; Sithole, S.; Owuor, M.A. Nature-based solutions for water resource management in Africa’s arid and sem-arid lands (ASALs): A systematic review of existing interventions. Nat.-Based Solut. 2024, 6, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zeng, W.; Qiu, J. Integrated water risk early warning framework of the semi-arid transitional zone based on the water environmental carrying capacity (WECC). J. Arid Land 2023, 15, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moursy, M. Water Sensitive Urban Design in Hot Dry Climates: A Framework and Transition Strategy for the MENA Region—A Case Study of Alexandria, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, HafenCity University Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Electra, Empresa de Electricidade e Água, Cabo Verde. Relatório e Contas, Exercícios de 2001 a 2023; Electra: Mindelo, Cape Verde, 2002 to 2024.
- Diogo, A.F. Análise dos Estudos Existentes dos Sistemas de Abastecimento de Água, Drenagem de Águas Residuais Comunitárias e Reutilização de Águas Residuais Tratadas para Rega do Empreendimento Santiago Golf Resort, Cabo Verde; Projecto Hidráulica Recursos Hídricos e Ambiente–Santiago Resort, DEC–FCTUC; IPN: Coimbra, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Diogo, A.F. Relatório de Progresso dos Projectos dos Sistemas de Abastecimento de Água, Drenagem de Águas Residuais e Reutilização de Águas Residuais Comunitárias Tratadas para Rega do Empreendimento Santiago Golf Resort, Cabo Verde; Projecto Hidráulica Recursos Hídricos e Ambiente–Santiago Resort, DEC–FCTUC; IPN: Coimbra, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Diogo, A.F. Relatório Final do Trabalho de Consultadoria dos Projectos dos Sistemas de Abastecimento de Água, Drenagem de Águas Residuais e Reutilização de Águas Residuais Comunitárias Tratadas para Rega do Empreendimento Santiago Golf Resort, Cabo Verde; Projecto Hidráulica Recursos Hídricos e Ambiente–Santiago Resort, DEC–FCTUC; IPN: Coimbra, Portugal, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Diogo, A.F.; Oliveira, A.L. Sistemas de drenagem e reutilização de águas residuais comunitárias da zona Sudoeste do município da Praia, Cabo Verde. Um caso de estudo. In Proceedings of the 5th Luso-Mozambican Engineering Congress CLME, Maputo, Mozambique, 2–4 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Diogo, A.F.; Oliveira, A.L.; Franca, T.C. Sistema de abastecimento do empreendimento Santiago Golf Resort, Cabo Verde. Uma Solução de Engenharia. In Proceedings of the 5th Luso-Mozambican Engineering Congress CLME, Maputo, Mozambique, 2–4 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Diogo, A.F.; Tavares, P.L.; Oliveira, A.L. O Projecto Hidráulica Recursos Hídricos e Ambiente—Santiago Resort e a Gestão. Sustentável dos Recursos Hídricos. In Proceedings of the 6th Luso-Mozambican Engineering Congress CLME, 3rd Mozambique Engineering Congress, Maputo, Mozambique, 29 August–2 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort—Trabalhos Externos de Infra-Estruturas, Interceptor de Esgotos, Troço em Pressão Entre a Ribeira Pequena e a Cidadela, Projecto de Execução; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort—Trabalhos Externos de Infra-Estruturas, Interceptor de Esgotos, Troço Gravítico Entre a Quinta da Achada e a Ribeira Pequena, Projecto de Execução; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort—Sistema de Recolha de Águas Residuais, Estação de Bombagem de Águas Residuais da Ribeira Pequena. Poço Húmido e Instalação para Gerador de Recurso, Projecto de Execução; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort—Infra-Estruturas da Quinta da Achada 2–Tomo III–Rede de Esgotos Pluviais; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Ante-Projecto de Infra-Estruturas Gerais de Abastecimento de Água Potável ao Empreendimento Santiago Golf Resort; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Ante-Projecto de Infra-Estruturas Gerais de Drenagem de Águas Residuais do Empreendimento Santiago Golf Resort; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- INE, Instituto Nacional de Estatística de Cabo Verde. Dia do Município da Praia, 19 de Maio de 2022, Dados Estatísticos do Município. 2022. Available online: https://ine.cv/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/municipio-da-praia.pdf (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- República de Cabo Verde, Boletim Oficial, I Série, Número 19. Leis Nº 63/VI/2005, 64/VI/2005 e 65/VI/2005, 9 May 2005.
- AMS. Associação dos Municípios de Santiago. 2008. https://sites.google.com/view/amscv/home.
- SCEP (Serviço Cartográfico do Exército Português). Carta de Cabo Verde, Escala 1:25000, Folha n.º 58, 1969.
- República de Cabo Verde, Boletim Oficial, I Série. Número 2, Decreto-Lei Nº 2/93, 1 February 1993.
- República de Cabo Verde, Boletim Oficial, I Série. Número 48, Suplemento, Decreto Regulamentar nº 09/98, 31 December 1998.
- Diogo, A.F.; Resende, R.A.; Oliveira, A.L. Optimised Selection of Water Supply and Irrigation Sources—A Case Study on Surface and Underground Water, Desalination, and Wastewater Reuse in a Sahelian Coastal Arid Region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudocivil, Estudos, Projectos e Obras de Engenharia Civil, Lda. Santiago Golf-Resort, Cabo Verde, Redes de Infra-Estruturas Gerais, ZDTI Sul da Praia e Zona K, Interceptor de Esgotos, Anteprojecto; Estudocivil: Lisboa, Portugal, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ecoserviços, Gestão de Sistemas ecológicos, Lda. Santiago, Golf–Resort, ETAR da Praia, Cabo Verde, Reutilização do Efluente; Ecoserviços: Lisboa, Portugal, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Naston Ltd. Praia wastewater sewage treatment plant. In Acceptance Performance Testing; Naston Ltd.: Brooklands-Weybridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Képpel Seghers. Water Solutions. UNITANK®—Wastewater Treatment, 2006; Képpel Seghers: Willebroek, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Topiaris, Estudos e Projectos de Arquitectura Paisagista, Lda. Santiago Golf Resort, Cidade da Praia–Cabo Verde, Estudo de Viabilidade de Implantação de Vegetação; Topiaris: Lisboa, Portugal.
- Onno Schaap Consultadoria. Anteprojecto de Rega e Drenagem para Santiago Golfe, Cabo Verde, Ilha de Santiago; Onno Schaap Consultadoria: Estoril, Portugal, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Atelier Difusor de Arquitectura Lda. Projectos do Plano Urbanístico Detalhado PUD.18, de Requalificação Urbana das Povoações Dentro e na Periferia da ZDTI Sul da Praia, Promotor Santiago Golf Resort, S.A., Cabo Verde; Atelier Difusor de Arquitectura Lda.: Praia, Cape Verde, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Estudocivil, Estudos, Projectos e Obras de Engenharia Civil, Lda. Santiago Golf-Resort, Cabo Verde, Loteamento da Quinta da Achada -1ª Fase. Infra-estruturas Gerais, Anteprojecto; Estudocivil: Lisboa, Portugal, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Estudocivil, Estudos, Projectos e Obras de Engenharia Civil, Lda. Santiago Golf-Resort, Cabo Verde, Loteamento da Quinta da Achada -1ª Fase. Infra-estruturas Gerais, Projecto de Execução; Estudocivil: Lisboa, Portugal, 2001; Volume 3, Rede de abastecimento de água e rede de rega e incêndio. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort, Cabo Verde—Infra-Estruturas Externas e Comuns, Estudo Prévio e Pré-Dimensionamento; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort, Cabo Verde—Sistema de Abastecimento de Água Potável ao Resort; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- WATG (Wimberly Allison Tong & Goo). Santiago Golf Resort. Final Concept. London, England, 2005.
- WATG (Wimberly Allison Tong & Goo). Masterplan Zoning, Estrela Golf Resort, Estrela Santiago, Cape Verde, 2007.
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort—Trabalhos Externos de Infra-Estruturas, Água Reciclada, Troço Gravítico Entre a Cidadela e a Ribeira Pequena, Projecto de execução; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento Campos—Projectos e Serviços, S.A. Santiago Golf Resort—Adutora de água Reciclada. Troço da Ligação Cidadela–Palmarejo Baixo; Coina: Barreiro, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M.; FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Crop Evapotranspiration–Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements–FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56. Rome. 1998. https://www.fao.org/4/X0490E/X0490E00.htm.
- Osório, T. Marcação de Furos/Poços-Zonas a Jusante “Ribeiras de São Martinho Grande e São Martinho Pequeno”; Santiago Golf Resort, S.A.: Praia, Cape Verde.
- Silva, E.P.; Sabino, A.A. Estudo Hidrológico das Bacias Hidrográficas das Ribeiras de S. Martinho Pequeno, S. Martinho Grande, Calheta de S. Martinho e Ribão Seca; Santiago Golf Resort: Praia, Cape Verde, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, E.P.; Sabino, A.A. Projecto de Derivação de Águas de Escoamento Superficial de São Martinho Grande para São Martinho Pequeno e Construção de Reservatórios Escavados; Santiago Golf Resort: Praia, Cape Verde, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- MA (Ministério do Ambiente). Decreto-Lei n.º 236/98 de 1 de Agosto, Diário da República–I Série-A, Nº 176, 1 August 1998; pp. 3676–3722.
- Metcalf & Eddy Inc.; Tchobanoglous, G.; Stensel, H.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Burton, F. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volumes 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- MOPTC (Ministério das Obras Públicas Transportes e Comunicações). Regulamento Geral dos Sistemas Públicos e Prediais de Distribuição de Água e de Drenagem de Águas Residuais, Decreto Regulamentar n.º 23/95, de 23 de Agosto, Diário da República–I Série-B, Nº 194, 23 August 1995, pp. 5284–5319.
- Diogo, A.F.; Oliveira, M.C. A preliminary numerical approach for the study of compressed air injection in inverted siphons. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, A.F.; Oliveira, M.C. A simplified approach for the computation of steady two-phase flow in inverted siphons. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, A.F.; Moura, P.M. Self-cleansing velocity in upward three-phase steady pipe-flow. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2023, 23, 847–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, A.F.; Moura, P.M. Experimental study of two and three-phase steady flows in inclined rising pipes. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2025, 165, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faldo Design. Project Estrela Santiago, Proposed Location and Conceptual Cross Section for the Golf Course Irrigation Lake, Drawing Number 1056.SK.03; Santiago Golf Resort: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Heia, J.T.; Isah, M.E.; Masuda, S.; Matsubae, K.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.-Y.; Sano, D. Quantifying health risks from wastewater reclamation and agricultural reuse using life cycle assessment and quantitative microbial risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 977, 179363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Gamboa, L.; Lahora, A.; Martínez-López, S.; Ayuso-García, L.M.; Martínez-Alcalá, I. Risk Assessment of Micropollutants for Human and Environmental Health: Alignment with the Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive in Southeastern Spain. Toxics 2025, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, A.F.L. Hidroquímica e Qualidade das Águas Subterrâneas da ilha de Santiago—Cabo Verde. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, A.M.P.B.V. Modelação Hidrológica e da Rega para Condições de Escassez Visando a Gestão da Água em Santiago, Cabo Verde. Ph.D. Thesis, ISA, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- CPLP—Comunidade dos Países de Língua Portuguesa. Autoridades Nacionais—Cabo Verde. 2025. Available online: https://agua.cplp.org/institucional/autoridades-nacionais/cabo-verde/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- CPLP—Comunidade dos Países de Língua Portuguesa. Monitoramento da Qualidade da Água—Cabo Verde. 2025. Available online: https://agua.cplp.org/temas-tecnicos/monitoramento-da-qualidade-da-agua/cabo-verde/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
| Location | Type of Plants or of Irrigated Area | Average Requirements (mm/day) | Maximum Average Requirements * (mm/day) | Irrigated Area (ha) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGR | Flower planters | 2.5 | - | 0.28 | [44] |
| Landscape irrigation | 5.2 | - | 4.20 | ||
| Chão Bom—Tarrafal | Horticulture | 5.4 | - | - | [44] |
| SGR Golf | Greens | 5.3 | 7.6 | 3.10 | |
| Tees, fairways, and rough | 4.6 | 6.7 | 38.4 | [45] | |
| S. Martinho Grande and Caiada Villages | Shrubs in flower beds | 5.2 | - | 0.07 | |
| Trees and bushes | 2.75 ** | - | 0.07 ** | [46] |
| Stream | Basin Area A (ha) | Perimeter P (m) | Length 1 L (m) | Gravelius 2 Coefficient GC (-) | Form 3 Factor Ff (-) | Main Channel Highest Elevation (m) | Highest Elevation (m) | Length L (m) | Average Slope (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palmar. G. | 580 | 11,500 | 5300 | 1.34 | 0.21 | 170 | 259 | 5000 | 3.4 |
| S. Mart. P. | 700 | 18,100 | 9000 | 1.92 | 0.09 | 335 | 345 | 8800 | 3.8 |
| S. Mart. G. | 2600 | 35,000 | 18,100 | 1.92 | 0.08 | 1000 | 1055 | 17,900 | 5.6 |
| Ribão Seco | 330 | 8800 | 4150 | 1.36 | 0.19 | 221 | 264 | 4100 | 5.4 |
| Rain Gauge Station | Elevation Z (m) | Mean Annual Precipitation (mm) | Median Annual Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. J. Baptista | 50 | 141.2 | 128.8 |
| Praia Airport | 64 | 158.7 | 157.1 |
| S. Martinho Pequeno | 152 | 202 | 172.4 |
| Trindade | 204 | 198.8 | 191.1 |
| Santana | 388 | 279.9 | 277 |
| Curralinho | 818 | 485.8 | 506.7 |
| Annual Precipitation P (mm) = a + b × Z | Coefficient a (mm) | Coefficient b (-) | Coefficient of Determination R2 (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 122.28 | 0.4372 | 0.9927 |
| Median | 104.52 | 0.4809 | 0.9908 |
| Hydrographic Basin | Average Elevation (m) | Mean Annual Precipitation (mm) | Median Annual Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| R. S. Martinho Peq. | 181 | 201.4 | 191.6 |
| R. S. Martinho Grand. | 403.5 | 298.7 | 298.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diogo, A.F.; Oliveira, A.L. An Integrated Water Resources Solution for a Wide Arid to Semi-Arid Urbanized Coastal Tropical Region with Several Topographic Challenges—A Case Study. Water 2025, 17, 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182750
Diogo AF, Oliveira AL. An Integrated Water Resources Solution for a Wide Arid to Semi-Arid Urbanized Coastal Tropical Region with Several Topographic Challenges—A Case Study. Water. 2025; 17(18):2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182750
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiogo, António Freire, and António Luís Oliveira. 2025. "An Integrated Water Resources Solution for a Wide Arid to Semi-Arid Urbanized Coastal Tropical Region with Several Topographic Challenges—A Case Study" Water 17, no. 18: 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182750
APA StyleDiogo, A. F., & Oliveira, A. L. (2025). An Integrated Water Resources Solution for a Wide Arid to Semi-Arid Urbanized Coastal Tropical Region with Several Topographic Challenges—A Case Study. Water, 17(18), 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182750






