Interannual Variations in Water Budget and Vegetation Coverage Dynamics in Desert Ecosystems of Heihe River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Description of Datasets
2.3. Water Balance of the Ecosystem
2.4. Estimation of Soil Water Storage and Its Variations
2.5. Calculation of Soil Water Balance and Residence Time
2.6. Calculation of ET0
3. Results
3.1. Variation Characteristics of Soil Water Storage and Precipitation in Desert Ecosystems
3.2. Variation Characteristics of Evapotranspiration and Potential Evapotranspiration in Desert Ecosystems
3.3. Monthly Variations in Water Budget Components in Desert Ecosystems
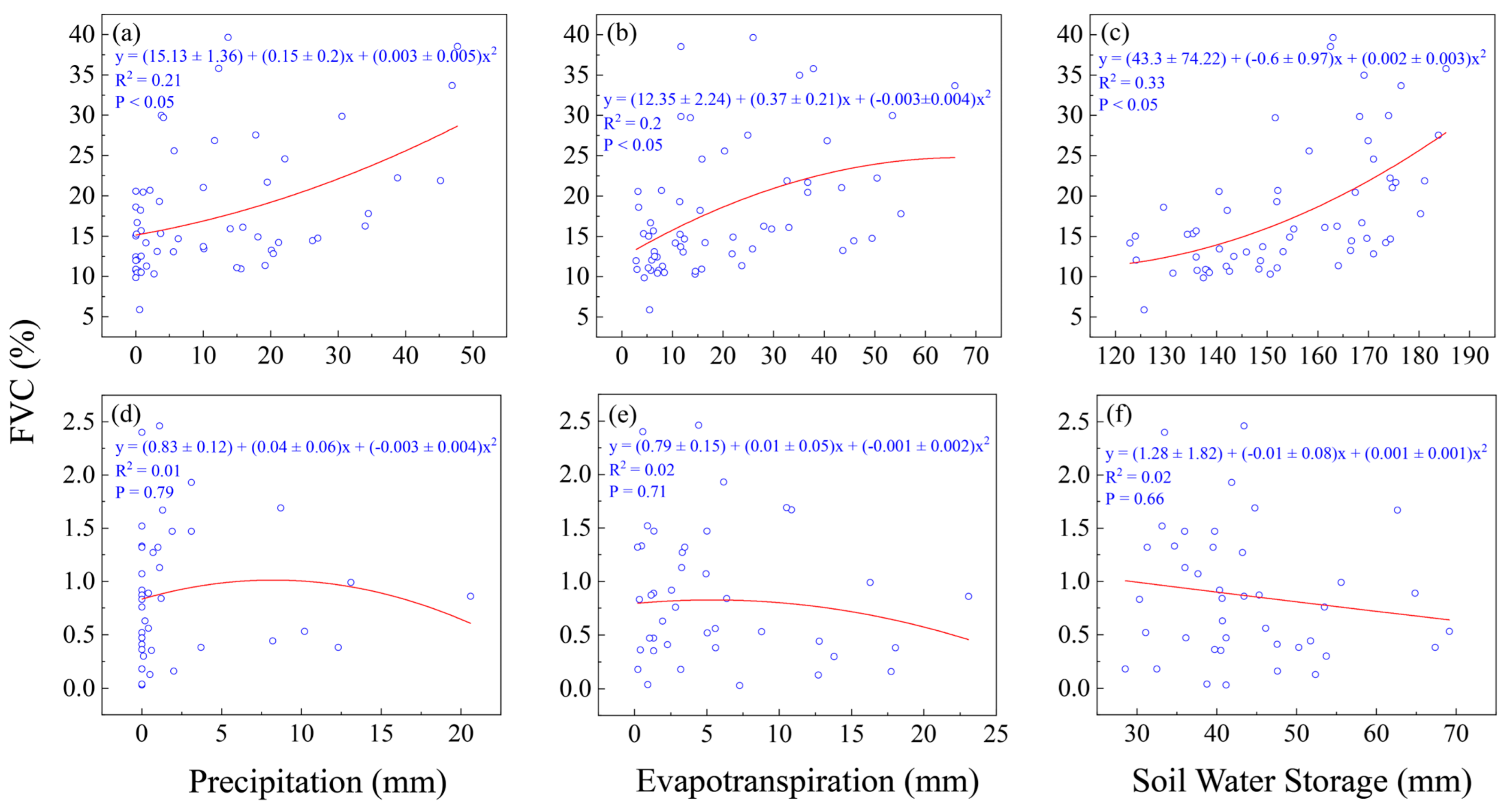
3.4. Response Characteristics of Vegetation Coverage to Water Budget Variations in K. foliatum and R. songarica Deserts of the Middle and Lower Heihe River Basin
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Water Cycle and Water Budget Characteristics of Desert Ecosystems
4.2. Divergent Vegetation–Water Coupling Mechanisms and Their Drivers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.Y.; He, M.Z.; Tang, L. Advances on Phosphorus Cycle and Their Driving Mechanisms in Desert Ecosystems: A Review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5115–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, H. Progress and prospects of climate change impacts on hydrology in the arid region of northwest China. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Yang, X.; Ye, Q.; Wan, K.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Song, X. Assessing Spatial–Temporal Characteristics of Land Desertification from 1990 to 2020 in the Heihe River Basin Using Landsat Series Imagery. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huisingh, D. Combating desertification in China: Monitoring, control, management and revegetation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.J.; Wang, X.D.; Zhou, Z. Integrated Landscape Pattern Optimization in Arid Region: A Case Study of Middle Reaches of Heihe River. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2017, 53, 451–461. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, W. The Concept and Mode of Ecosystem Sustainable Management in Arid Desert Areas of Northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7410–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvertown, J.; Araya, Y.; Gowing, D. Hydrological niches in terrestrial plant communities: A review. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, H.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, H. Holistic evolution of ecosystem in Heihe River Basin from the perspective of eigen microstates. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, B.; Chang, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cleverly, J.; Eamus, D. Evapotranspiration Partitioning, Stomatal Conductance, and Components of the Water Balance: A Special Case of a Desert Ecosystem in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Bao, F.; Xu, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J. The Influence of Precipitation Timing and Amount on Soil Microbial Community in a Temperate Desert Ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1249036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, F.T.; Eldridge, D.J.; Soliveres, S.; Kéfi, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Bowker, M.A.; García-Palacios, P.; Gaitán, J.; Gallardo, A.; Lázaro, R.; et al. Structure and Functioning of Dryland Ecosystems in a Changing World. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2016, 47, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celentano, D.; Rousseau, G.X.; Engel, V.L.; Zelayán, M.; Oliveira, E.C.; Araujo, A.C.M.; Moura, E.G.d. Degradation of Riparian Forest Affects Soil Properties and Ecosystem Services Provision in Eastern Amazon of Brazil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Peng, J.; Niu, J.; Yang, L. Distribution of Desert Riparian Forest Soil Water and Shallow Groundwater in Upstream Basin of Tarim River. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 30, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, J.; Shunjun, H. Estimation of Evapotranspiration in the Desert–Oasis Transition Zone Using the Water Balance Method and Groundwater Level Fluctuation Method—Taking the Haloxylon ammodendron Forest at the Edge of the Gurbantunggut Desert as an Example. Water 2023, 15, 1210. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. Modeling surface water-groundwater interaction in arid and semi-arid regions with intensive agriculture. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 63, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, H.; Fadong, L. Water Sources for Typical Desert Vegetation in the Ebinur Lake Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Y.; Tian, Y.; Shao, C.; Huang, J.; Gu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, R. Potential Variation of Evapotranspiration Induced by Typical Vegetation Changes in Northwest China. Land 2022, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Detection of vegetation coverage changes in the Yellow River Basin from 2003 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, S. Tempo-spatial changes and main anthropogenic influence factors of vegetation fractional coverage in a large-scale opencast coal mine area from 1992 to 2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, W.Z. Changes in Normalized Difference Vegetation Index of Deserts and Dunes with Precipitation in the Middle Heihe River Basin. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 40, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Quan, J.; Zhan, Y.; Teng, Y.; Zhen, W.; He, Z. Characteristics of Vegetation Diversity and Effects of Water in the Desert-Oasis Region in the Middle Reaches of Heihe River Basin. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2021, 36, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Yang, Y.; Che, T. Effects of extreme temperature events on carbon fluxes in different ecosystems in the Heihe River Basin, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2025, 362, 110380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, L.; Cheng, G.; Xiao, H. Quantifying Landscape Structure of the Heihe River Basin, North-West China Using FRAGSTATS. J. Arid. Environ. 2001, 48, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C. Spatial Patch Structure and Adaptive Strategy for Desert Shrub of Reaumuria soongorica in Arid Ecosystem of the Heihe River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1507–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.H. Species Identification and Phylogeography of Six Species in Kalidium. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Tian, C.Y. Drought Tolerance During Seed Germination and Young Seedling Period of Kalidium foliatum Under Different Temperatures. Pratacult. Sci. 2023, 40, 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Casati, P.; Campi, M.; Morrow, D.J.; Fernandes, J.; Walbot, V. Transcriptomic, Proteomic and Metabolomic Analysis of Maize Responses to UV-B: Comparison of Greenhouse and Field Growth Conditions. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Che, T.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Liu, Q.; Rui, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; et al. The Heihe Integrated Observatory Network: A Basin-Scale Land Surface Processes Observatory in China. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Che, T.; Li, X.; Xu, T.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Song, L.; Zhou, J.; et al. A Dataset of Energy, Water Vapor, and Carbon Exchange Observations in Oasis–Desert Areas from 2012 to 2021 in a Typical Endorheic Basin. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 4959–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, W.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Y. China Regional 250 m Fractional Vegetation Cover Data Set (2000–2023); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Eco-hydrological characteristics and ecological adaptation of Reaumuria soongorica along middle and lower reaches of Heihe River Basin. Ph.D. Dissertation, Beijing Normal University, Bejing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka, T.; Kaihotsu, I.; Oyunbaatar, D.; Ganbold, T. Summertime Soil Hydrological Cycle and Surface Energy Balance on the Mongolian Steppe. J. Arid. Environ. 2007, 69, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Different Vegetation Types on Soil Moisture in Deep Loess Soil Profiles. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 703–713. [Google Scholar]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Schwinning, S.; Gebauer, R. Water use in arid land ecosystems. In Physiological Plant Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Chen, J.; Xiong, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B. Responses of soil respiration to rainfall pulses in a natural grassland community on the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2019, 178, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, W.; Chang, X.; Li, S. Response of Soil Moisture to Rainfall Pulse in Desert Region of the Heihe River Basin. J. Desert Res. 2011, 31, 716–722. [Google Scholar]
- McKellar, T.T.; Crimmins, M.A. Seasonal precipitation variability controls shallow soil water drought events across the southwestern United States. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2025, 363, 110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Tian, L.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y. Temporal-Spatial Variation of Soil Moisture Content of Different Hippophae rhamnoides Communities in an Alpine Desert. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, L.; He, C.; Zhu, Y. Estimating Regional Soil Moisture Distribution Based on NDVI and Land Surface Temperature Time Series Data in the Upstream of the Heihe River Watershed, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, G.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y. Differences in soil water storage, consumption, and use efficiency of typical vegetation types and their responses to precipitation in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Bai, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, T.; Pang, W.; Han, H.; et al. Soil Moisture in Typical Underlying Surfaces of the Heihe River Basin. Pratacultural Sci. 2022, 39, 2475–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Xing, Y. Coupling the water use of Populus euphratica and Tamarix ramosissima and evapotranspiration partitioning in a desert riparian forest ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xie, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Yu, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, L. Water sources of major plant species along a strong climatic gradient in the inland Heihe River Basin. Plant Soil 2020, 455, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Min, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, C. Shallow Groundwater Regime and Its Driving Forces in the Ejina Oasis. Quat. Sci. 2014, 34, 982–993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y. Differences in water-use strategies along an aridity gradient between two coexisting desert shrubs (Reaumuria soongorica and Nitraria sphaerocarpa): Isotopic approaches with physiological evidence. Plant Soil 2017, 419, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; Li, E.; Wang, S. Responses of two desert shrubs to simulated rainfall pulses in an arid environment, northwestern China. Plant Soil 2019, 435, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Du, E.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Responses of soil respiration to rainfall addition in a desert ecosystem: Linking physiological activities and rainfall pattern. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Zheng, Y.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Lombardozzi, D.; Wang, Y.; Ryu, Y.; Chen, G.; Dong, W.; Hu, Z.; et al. Increased atmospheric vapor pressure deficit reduces global vegetation growth. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
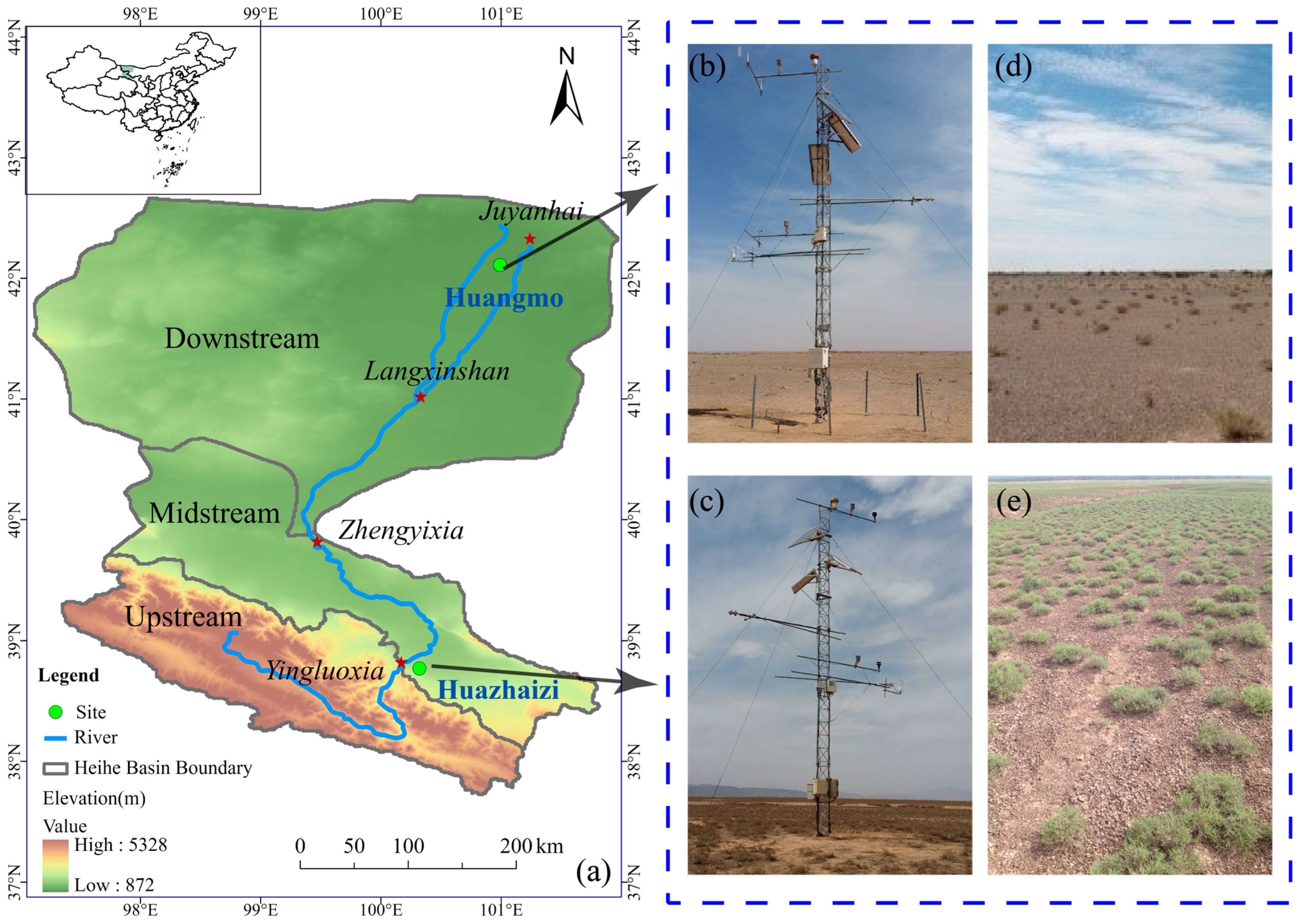

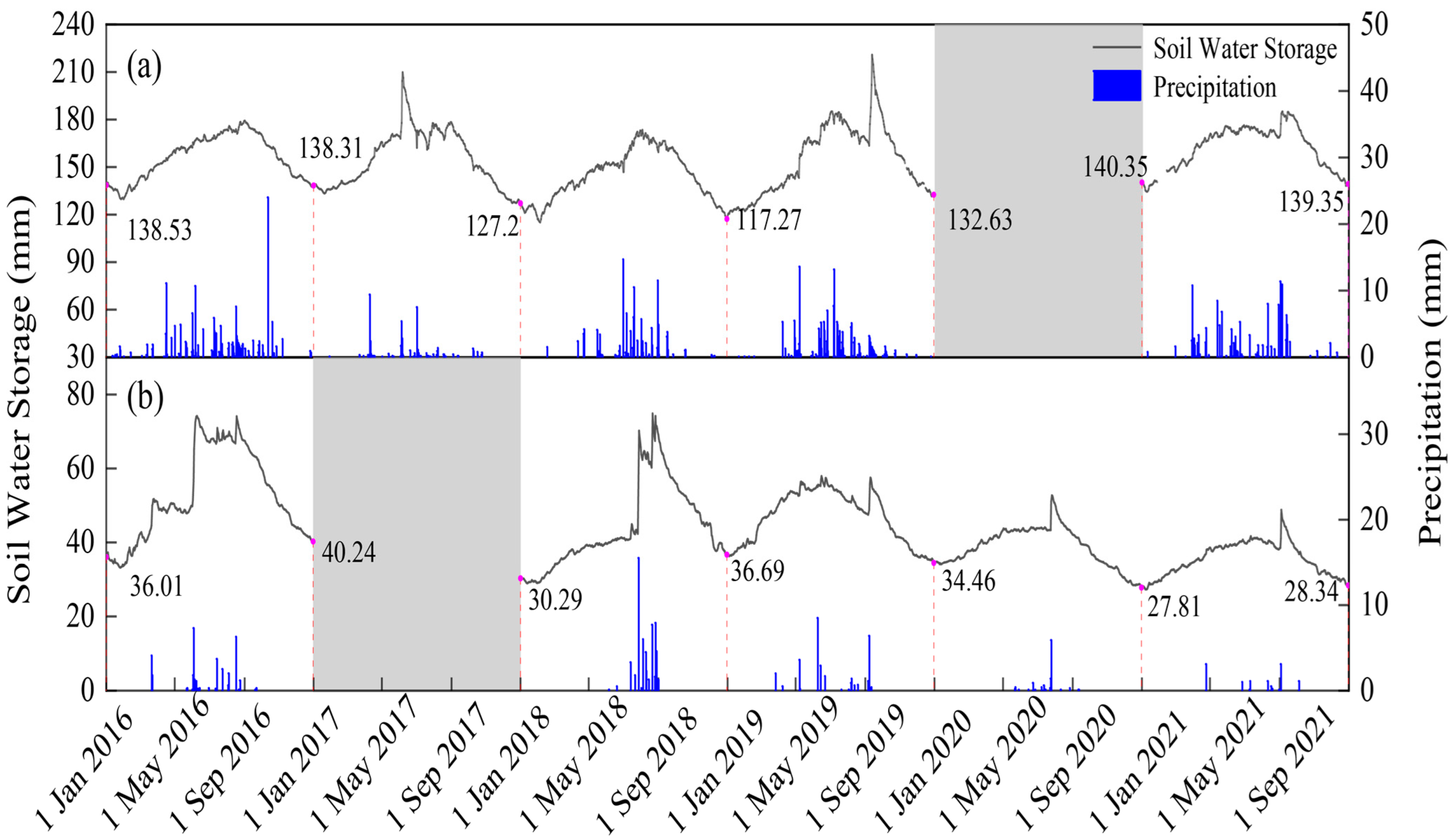
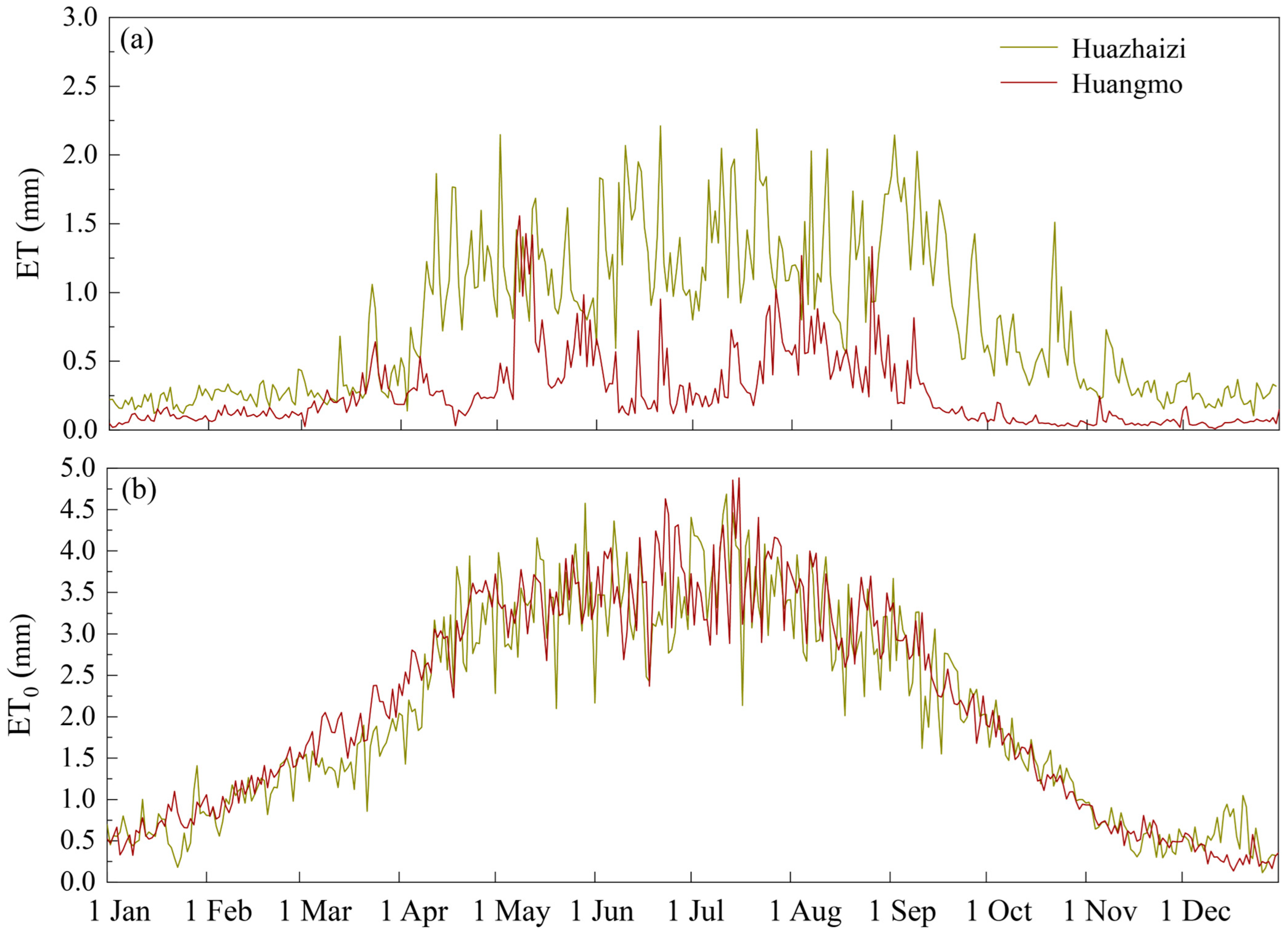
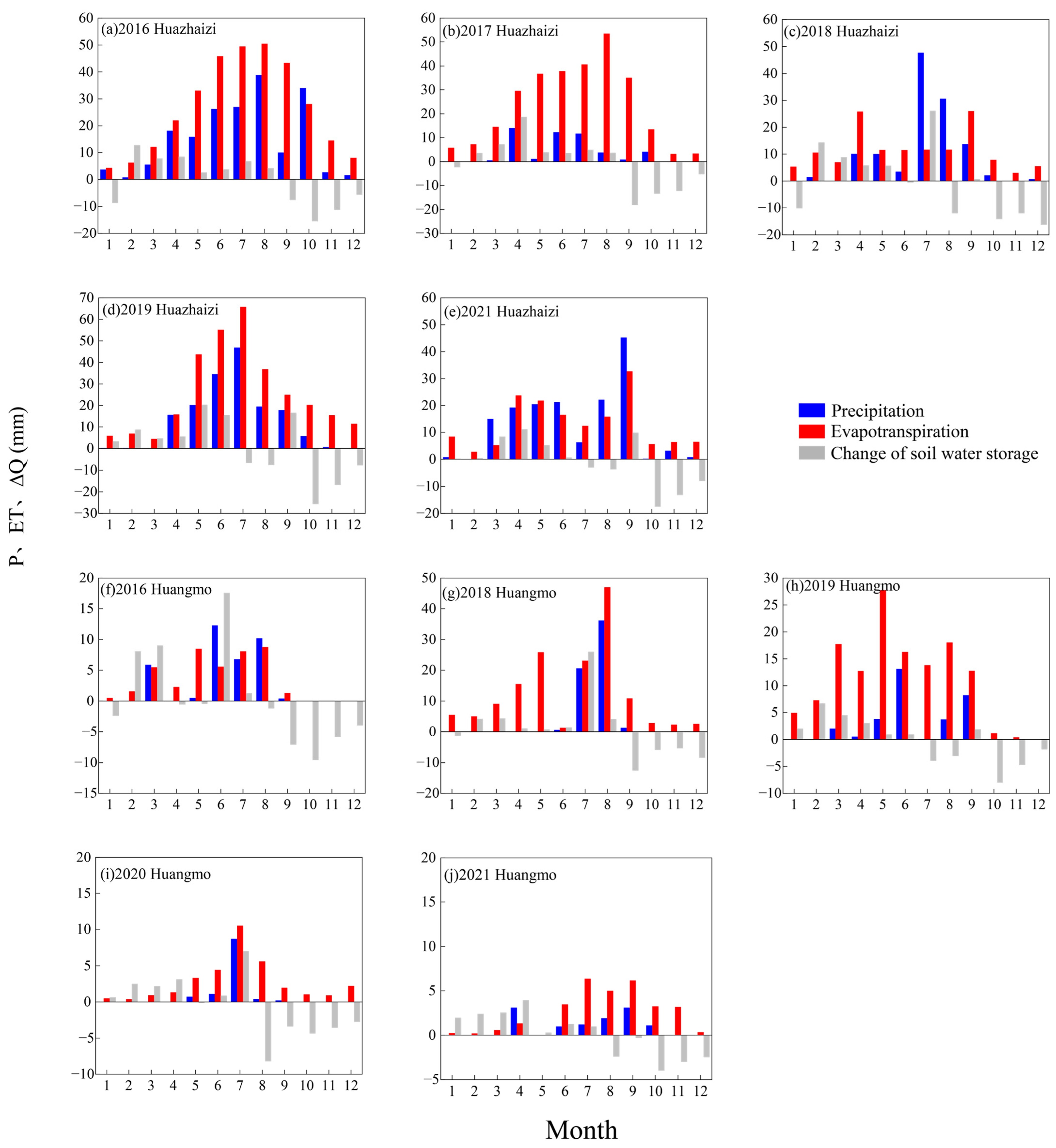

| Parameter | Unit | Kalidium foliatum | Reaumuria soongorica | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Community traits a | Patch numbers | Individuals | 637 ± 291 | 48 ± 11 |
| Patch density | Patches m−2 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | |
| Patch area percentage | % | 7.3 ± 3.9 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | |
| Mean patch area | m2 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | |
| Individual traits a | Plant height | cm | 13.4 ± 1.4 | 23.1 ± 5.5 |
| Shrub volume | cm3 | 3624.85 | 20,042.66 |
| Site | Year | Precipitation P (mm) | Evapotranspiration ET (mm) | Change in Soil Water Storage (0–100 cm) ΔQ (mm) | Residual Term of Water Budget (mm) | Soil Water Storage (0–40 cm) Q (mm) | Soil Water Residence Time τ (day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huazhaizi | 2016 | 184.4 | 317.45 | −0.73 | 132.33 | 65.14 | 75 |
| 2017 | 48.4 | 281.01 | −10.22 | 222.39 | 64.72 | 52 | |
| 2018 | 119.8 | 137.33 | −9.93 | 7.6 | 57.06 | 163 | |
| 2019 | 161.3 | 306.68 | 13.55 | 158.93 | 66.04 | 75 | |
| 2021 | 154.4 | 157.77 | −1 | 2.37 | 67.78 | 158 | |
| Mean | 133.7 | 240.05 | −1.67 | 104.72 | 64.15 | 105 | |
| Huangmo | 2016 | 36.1 | 42.04 | 4.23 | 9.70 | 18.02 | 144 |
| 2018 | 58.7 | 150.83 | 6.4 | 98.53 | 16.31 | 38 | |
| 2019 | 31.4 | 132.79 | −2.14 | 99.2 | 15.34 | 43 | |
| 2020 | 11.1 | 32.95 | −6.6 | 15.25 | 11.07 | 154 | |
| 2021 | 11.4 | 30.11 | 0.49 | 17.96 | 10.69 | 133 | |
| Mean | 29.7 | 77.74 | 0.47 | 48.13 | 14.29 | 102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Cao, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, P. Interannual Variations in Water Budget and Vegetation Coverage Dynamics in Desert Ecosystems of Heihe River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182660
Liu J, Cao W, Yuan Y, Li S, Wang P. Interannual Variations in Water Budget and Vegetation Coverage Dynamics in Desert Ecosystems of Heihe River Basin. Water. 2025; 17(18):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiayin, Wenyang Cao, Yuan Yuan, Siying Li, and Pei Wang. 2025. "Interannual Variations in Water Budget and Vegetation Coverage Dynamics in Desert Ecosystems of Heihe River Basin" Water 17, no. 18: 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182660
APA StyleLiu, J., Cao, W., Yuan, Y., Li, S., & Wang, P. (2025). Interannual Variations in Water Budget and Vegetation Coverage Dynamics in Desert Ecosystems of Heihe River Basin. Water, 17(18), 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182660






