1. Introduction
As an essential trace element, strontium is a normal component of human bones and teeth, and plays a reinforcing role in bone and tooth strength, especially in the treatment of osteoporosis in the elderly, with very good efficacy [
1]. At the same time, since strontium can participate in the synthesis of cell membrane proteins and enzymes, it is conducive to maintaining the normal cardiovascular function of the human body as well as the excitability of nerves and muscles, and delaying skin aging. Regular drinking of mineral water containing the strontium element has a certain preventive and auxiliary therapeutic effect on common diseases such as human bones and cardiovascular health diseases.
With the gradual maturity of the development and utilization of strontium-rich mineral water resources, scholars both at home and abroad have conducted systematic studies on the distribution patterns of groundwater strontium in different regions, revealing its correlation with processes such as the weathering of carbonate rocks, cation exchange, and deep fluid input. International studies have primarily emphasized the analysis of strontium (Sr) sources in groundwater systems. Koh D.C. et al. utilizing a multi-isotope approach (δ
18O, δ
2H,
3H,
87Sr/
86Sr, δ
13C) for groundwater in volcanic bedrock of Jeju Island, established that dissolved Sr originates from ancient alkaline basalts in lower lava flow sequences [
2]. Kaleem M. et al. demonstrated through hydrogeochemical analyses (including Gibbs diagrams and ionic ratios) of groundwater in Pakistan’s Mor Range that Sr concentrations (mean: 1688 μg/L) significantly exceed those of barium (Ba; mean: 207 μg/L), with Sr enrichment governed by its high mobility and water–rock interactions [
3]. Das Satyabrata et al. identified carbonate lithology as the predominant source of dissolved Sr in the Himalayan Teesta River system [
4]. Musgrove M.’s analysis of 32 principal U.S. aquifers delineated the occurrence and spatial distribution of Sr, revealing that elevated concentrations (>4000 μg/L) predominantly occur in carbonate rock aquifers due to water–rock interactions with Sr-bearing minerals [
5]. Malov A.I. examined Sr formation mechanisms in ancient silicate deposits along the Russian Arctic coast, determining that carbonate dissolution dominates Sr sourcing in low-mineralization waters within paleo-aluminosilicate strata; post-carbonate saturation, precipitation processes initiate while silicate dissolution becomes the primary driver of Sr enrichment in higher-mineralization waters [
6]. In contrast, domestic research has placed greater emphasis on elucidating Sr mobilization processes during water–rock interactions in groundwater systems. Tian Xiaolin proposed that in the Yelangba Structural Basin of Guizhou, atmospheric precipitation infiltrates the subsurface, with prolonged groundwater flow towards the basin center facilitating dissolution and leaching of strontium-bearing minerals (notably celestite and strontianite) within Jurassic sandstone layers, thereby enriching groundwater Sr [
7]. Similarly, Chen Yuanming attributed Sr enrichment in the Tailai Basin primarily to carbonate mineral dissolution (calcite, dolomite) coupled with significant evaporative concentration, while noting minimal contributions from cation exchange [
8]. This emphasis on water–rock interactions is reinforced by Tu Chunlin et al., who identified such processes as the dominant pathway for Sr enrichment, specifically pinpointing calcite weathering and dissolution as the principal source [
9]. Expanding the scope, Sun Houyun et al. linked significantly elevated soil Sr concentrations in Chengde (exceeding national background values) to regional tectonics, with minerals like pyroxene, olivine, and apatite contributing to the Sr-rich signature. They further demonstrated that spatial heterogeneity in groundwater Sr is governed synergistically by structural factors (topography, geological formations) and non-structural factors (groundwater abstraction, industrial/mining activities), where uplift of intrusive rock masses and the development of variably tilted erosional-denudational landforms within volcanic structural basins enhance hydraulic gradients, and incongruent plagioclase dissolution serves as the predominant long-term Sr source [
10,
11]. Quantitative insights from Xu Changqian et al. utilizing a Sr isotope-concentration model, partitioned contributions from distinct source materials (evaporites, carbonates, silicates), revealing evaporite dissolution as the key driver of significant Sr enrichment in mineral waters [
12]. Supporting the mobilization process, Yan Chengyun et al., employing source-tracking analysis, described Sr
2+ release from Sr-rich minerals via water–rock reactions (dissolution, ion exchange) following atmospheric precipitation infiltration into fissures, leading to groundwater enrichment [
13]. Zhu Kebing et al. quantitatively demonstrated through the APCS-MLR model that groundwater chemistry is controlled by four primary factors: water–rock interaction (43.6%), industrial–agricultural composite sources (3.9%), agricultural–domestic sewage sources (10.5%), and unknown sources (42.0%), confirming carbonate weathering (calcite dissolution) as the dominant natural process [
14]. Zhang Xudong et al. adopted a combined approach of numerical simulation and theoretical analysis to reveal the formation mechanism of internal clogging in porous media [
15]. Additionally, Zhang Xudong et al. conducted experimental research on the simultaneous heat-water-salt transport in bare soil under evaporation conditions, explaining the mechanisms governing heat, water, and salt migration during evaporation [
16]. However, existing research has primarily focused on large sedimentary basins or typical geological structural belts, neglecting areas like the northern foothills of Lushan Mountain that have unique geological backgrounds. This has resulted in a significant gap in understanding the genetic mechanisms and spatial differentiation characteristics of high-strontium groundwater in this region. This study takes the northern foothills of Lushan Mountain as the research area and systematically analyzes the distribution characteristics of strontium content in groundwater and its main controlling factors. Constructing a geochemical database of groundwater strontium in the study area has filled the gap in basic hydrological geochemical data for the region, and provides a scientific basis for the development of high-strontium groundwater resources in areas with similar geological backgrounds.
2. Hydrogeological Profile of the Study Area
The research area is located at the southern end of the southeastern wing of the Zibo syncline and belongs to the North China strata. The relationship between the newly exposed and old strata is characterized by a transition from older to newer strata from southeast to northwest. The primarily exposed strata include the Precambrian Taishan Mount Group, Cambrian, Ordovician, and Quaternary strata. The overall stratigraphic dip is towards the northwest, with an angle of 5°to 20°. The research area belongs to the hydrogeological zone of the middle and low hills in the southwest of Shandong Province, and the monoclinic hydrogeological subzone of Pingyin-Linqu County.
2.1. Groundwater Types and Storage Characteristics
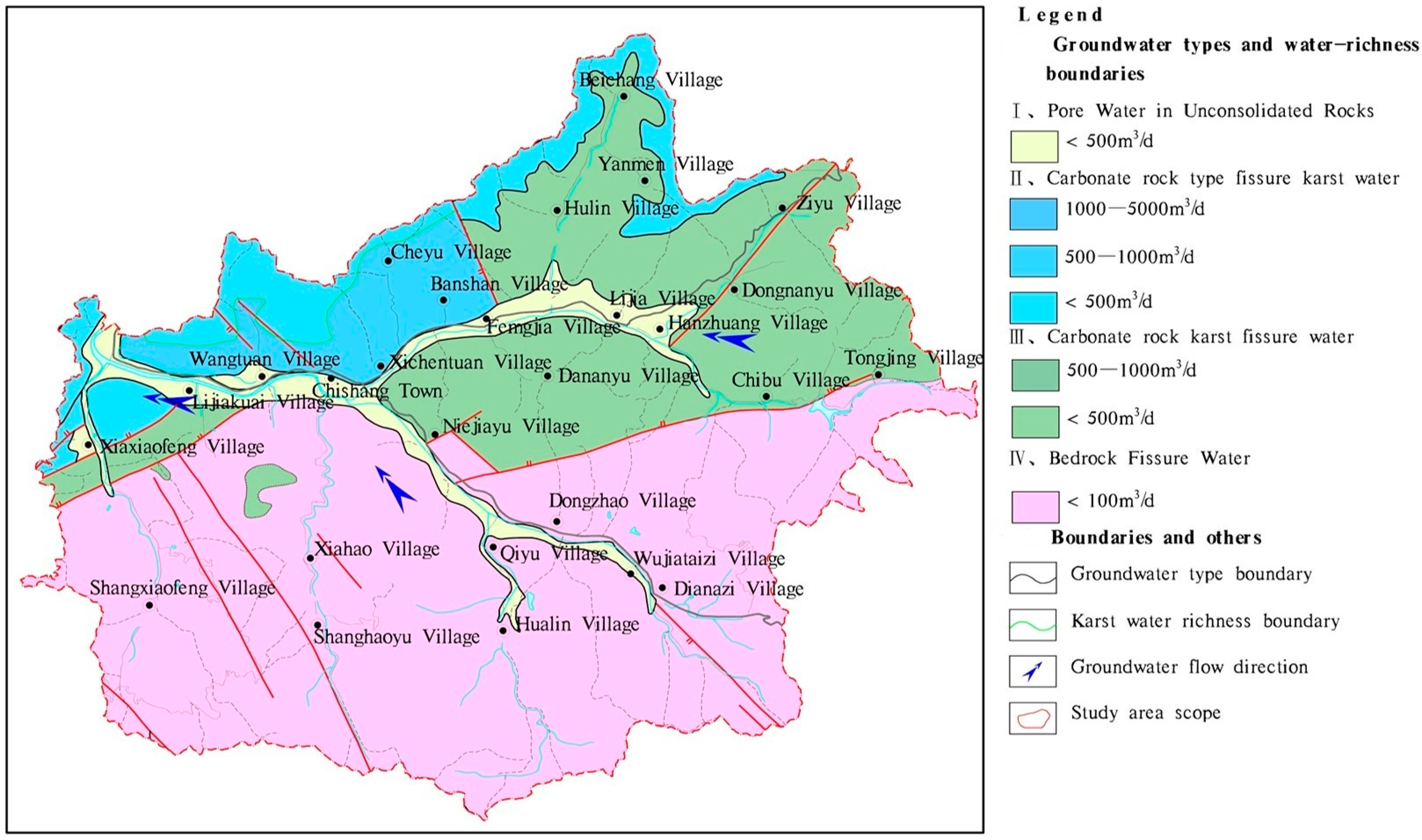
According to the conditions of groundwater storage and lithological characteristics of water-bearing medium, the groundwater in the study area is mainly divided into three types: pore water of loose rock type of the Quaternary System, fissure karst water or karst fissure water of carbonate rock type, and bedrock fissure water (see
Table 1 and
Figure 1).
I Pore water of loose rock type
This type of groundwater is mainly distributed on both sides of valleys of Zi River and its tributaries Zhaozhuang River, Lijia River, and other rivers. The aquifer consists of sand and gravel of the fourth system, and its thickness is generally less than 10 m. The water level of this type of groundwater is shallow, and it is significantly affected by the seasons, and the main sources of recharge are atmospheric precipitation and river seepage. Due to the thin thickness of the aquifer, the water yield property of the aquifer is low. In the area from Chihshang to Lijiakuai, the valley of Zi River is wider, the river runoff is slower, the water yield property is relatively high, and the water influx of a single well is less than 500 m3/d.
II Carbonate-rock-type karst fissure water and fissure karst water
II-1 Carbonate-rock-fissure karst water
It is mainly distributed in the middle and low mountainous areas mainly located north of Zi River and east of Lijiakuai Village, and the lithology of the aquifer is mainly Cambrian-Ordovician Sanshanzi Formation, middle-thin mud crystal tuff in the Chaomidian Formation, and middle-thick layer dolomite. The water influx of a single well is generally 500–1000 m3/d. In the area of Xiaofengkou, the Ordovician strata are exposed in the valley of Zi River, receiving atmospheric precipitation infiltration and surface water seepage and recharge, with high water yield property, and the water influx of a single well is more than 1000 m3/d.
II-2 Carbonate-rock-type karst fissure water
Mainly distributed in the northeastern part of the study area, the lithology of the aquifer is mainly Cambrian Zhangxia Formation and Zhushadong Formation tuff. The water influx of a single well is generally less than 1000 m m3/d, and the type of groundwater is mostly HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg type or HCO3-SO4-Ca type.
III Bedrock fissure water
This type of groundwater is mainly distributed in the southern and southwestern edges of the study area, and the lithology of the aquifer is dominated by granitic gneiss, with good integrity of the rock body. The depth of the weathering layer is between 10 and 30 m, and the thickness of the effective aquifer shows a spatial variation from 8 to 25 m. The main groundwater storage medium is the bedrock tectonic fissure network and weathered pore zone, constituting a typical bedrock fissure diving system. Restricted by the degree of fissure development, the water influx of a single well is generally less than 100 m3/d. The hydrochemical type of this type of groundwater is mostly HCO3-SO4-Ca type.
2.2. Groundwater Recharge, Runoff, and Discharge Conditions
The geomorphology of the study area as a whole is featured by mountains on three sides and the central low level, with the low mountains on the north, south, and east sides and the gradual terrain on the west side, forming the confluence of lowlands with Zi River valley as the center. Driven by the topographic elevation difference, the groundwater mainly originates from the highlands on the southwest, south, and east sides, converging along a topographic gradient into the central Zi River valley. Due to the karst development in the tectonic fracture zone, the Zi River fracture zone becomes the main conduit for groundwater, prompting the rapid flow of water here and the formation of a strong runoff zone, and flows northward out of the study area near the Zi River valley near Xiaofengkou.
Metamorphic rocks are widely exposed in the southwest, south, and southeast of the study area, and the bedrock in this area is weathered significantly and the vegetation cover is sparse. Atmospheric precipitation shows two transport paths in this area: part of the water infiltrates rapidly through the rock fissure network forming groundwater recharge, and the other part is controlled by the topography to converge as surface runoff and migrate to the low-lying areas of the terrain.
The recharge sources of carbonate aquifer systems in the region are diversified, which mainly include the following three ways: first, the vertical infiltration recharge of atmospheric precipitation; secondly, the lateral runoff input of bedrock fracture water in adjacent metamorphic rock areas. In addition, it also includes regional recharge caused by seepage in the Zi River. The dense development of fault systems in the geological tectonic zone distributed along the river leads to the formation of multiple seepage channels and natural spillover points in the river channel, which promotes frequent interaction between surface water and groundwater. That is, the surface water in the upstream section continues to leak to recharge the aquifer, while the groundwater overflows to recharge the river channel in some downstream sections.
In terms of the groundwater discharge mechanism, there are three typical drainage modes in the study area: artificial mining activities, river runoff, and natural spring discharge. Among them, the natural discharge system is represented by many springs on the pond, which constitute an important discharge channel of the regional groundwater system.
Additionally, soil properties within the study area, influenced by topography, parent material, and vegetation cover, are predominantly sandy loam to medium loam. The soil permeability exhibits distinct spatial heterogeneity characterized as ‘high in mountainous areas, moderate on slopes, and low in localized clay-rich layers’. This permeability variation profoundly influences both the groundwater recharge processes and the concomitant solute transport. High-permeability zones (e.g., mountainous areas) experience substantial and rapid recharge, facilitating the efficient transport of mineral elements (such as strontium, Sr) into the aquifer. This enables groundwater Sr concentrations to readily approach the equilibrium concentration dictated by rock weathering and dissolution. Moderate-permeability zones (e.g., slopes) maintain a relatively stable supply of mineral elements. Concurrently, the soil’s filtration and adsorption capacity is significant, effectively purifying recharge water. This reduces the input of impurities and complex chemical reactants that could disrupt mineral concentration equilibria, contributing to the relative stability of groundwater Sr concentrations. Low-permeability zones (localized clay layers) significantly constrain recharge volume, resulting in a slow Sr replenishment rate. However, if the background Sr concentration within the aquifer is already elevated, this low recharge coupled with slow renewal rates paradoxically favors the long-term persistence of Sr concentrations, making them less susceptible to perturbations from surface environmental conditions.
3. Research Method
3.1. Sample Collection and Testing
This study aims to reveal the enrichment characteristics and migration patterns of strontium (Sr2+) in different aquifer formations. Based on the characteristics of the groundwater dynamics field, sampling points are set along the runoff path in hydrogeochemical zones such as recharge areas, runoff zones, and discharge areas, and the spatial gridding method is used to ensure the hydrogeological representativeness of the sampled areas. The design of the sampling network follows the principle of continuity in water chemical evolution, achieving balanced coverage of the entire study area. Sample collection strictly follows sampling specifications. Sampling containers are soaked in a 10% nitric acid solution for 48 h, then rinsed with ultra-pure water, and undergo a three-stage drying process. During field operations, production wells are selected as sampling points. After continuously flushing the well tubing for more than 30 min, samples are taken when the conductivity fluctuation is less than 5%. A standardized operation is used during the sampling process, which involves thoroughly rinsing the container three times with the water to be tested to effectively eliminate background interference from the container. The obtained water samples are preserved in a dark, temperature-controlled refrigerator at 4 °C, ensuring that laboratory analysis is completed within 24 h.
A total of 26 groups of water samples were collected in the study area (including 5 sampling points to take samples in the high water seasons and low water seasons) (see
Figure 2). Samples were collected, stored, and transported in accordance with relevant specifications. All samples were tested by the laboratory of the 801 Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology Brigade of Shandong Province of Geology and Minerals Bureau, which has national certification and testing qualifications.
3.2. Hydrogeochemical Analysis Methods
The enrichment mechanism of strontium in groundwater is driven by the collaboration of multiple processes, and its occurrence characteristics are closely related to the interactions between water and rock (dissolution, leaching, exchange adsorption) as well as hydrological geochemical conditions. This study employs a multi-scale analysis method to systematically analyze the contribution of rock weathering, mineral dissolution, cation exchange, and evaporation-concentration effects to the migration and enrichment of Sr2+. The specific methods are as follows:
- (1)
Analysis of Rock Weathering Effects
Mainly based on the mineral composition and isotopic tracing techniques, rock weathering effects analysis methods provide a comprehensive assessment of the source-sink effects of rock weathering on Sr2+. The main methods are as follows: ① Determine the mineral composition of aquifer rock samples (feldspar, mica, carbonate rock) through X-ray diffraction, and distinguish the relative contributions of silicate rock and carbonate rock weathering by combining strontium isotope ratios (87Sr/86Sr); ② Quantify the control intensity of rock weathering on water chemistry types by utilizing the cation weathering index ([Na+ K+]/[Ca2+ Mg2+]) and Gibbs diagram (TDS/[Na+/(Na+ Ca2+)]); ③ Calculate the contribution of the weathering rates of various mineral phases to the release of Sr2+ using a mass balance model of major elements.
- (2)
Mineral Dissolution Modeling
The method of reverse hydrogeochemical modeling (PHREEQC) can be used to reveal the competitive mechanisms of strontium-containing mineral dissolution and to construct a mineral phase database for aquifers (celestine, strontianite, calcite, dolomite). The mineral dissolution/precipitation state can be determined by using the saturation index (SI) calculation, where the formula is as follows:
SI = log(IAP/Ksp), IAP is the ion activity product and Ksp is the solubility product constant.
- (3)
Quantitative Characterization of Cation Exchange
The quantitative characterization of cation exchange can be based on the classical hydrological discrimination system, analyzing the adsorption–desorption behavior of Sr
2+ from multiple dimensions, mainly using the following methods: ① The Langmuir and Freundlich isothermal adsorption models were adopted (25 °C constant temperature shaking table experiment, initial Sr
2+ concentration 0–100 mg/L) to fit the adsorption capacity (Qmax) and affinity constants (KL, KF) of montmorillonite and kaolinite; ② Based on the Scholler (1967) dual-parameter discrimination system, the cation exchange direction was characterized using CAI1 and CAI2 indices, combined with Sr
2+ concentration to assess the impact of exchange effects on strontium migration [
17]; ③ The competition adsorption strength of Na
+-Sr
2+ can be quantified through sodium adsorption ratio.
- (4)
Evaporation-Concentration Effect Discrimination
The method for discriminating the evaporation-concentration effect mainly uses Cl− as a conservative tracer to quantitatively assess the contribution of evaporation through a combination of ionic ratio analysis and isotopic techniques: ① The relative contributions of evaporation concentration and mineral dissolution to Sr2+ enrichment are differentiated by analyzing the trends of Na/Cl and Sr/Cl molar ratios; ② The coupling relationship between evaporation intensity and groundwater residence time is clarified by using the local evaporation line (LEL) constructed by hydrogen and oxygen isotopes (δ2H, δ18O), in combination with tritium isotope (3H) dating data; ③ Establish an Sr2+-Cl− enrichment coefficient model to evaluate the nonlinear amplification effect of the evaporation process on strontium concentration.
This study will integrate multiple sources of data through multivariate statistics and numerical simulation, using correlation analysis to identify the coupling relationships between Sr2+ and key factors such as TDS, Na+, and SO42−. At the same time, this study will quantify the control intensity of rock weathering on water chemistry types using Gibbs diagrams, and simulate the strontium migration and enrichment pathways in the multi-process interaction situation through PHREEQC reverse hydrogeochemical modeling, and cross-validate with the Scholler dual-parameter system model to break through the scale limitations of traditional hydrochemical analysis.
4. Test Results and Analysis
- (1)
Chemical characteristics of groundwater in the study area
The chemical characteristics of groundwater in the study area show obvious differentiation. The hydrochemical type of groundwater in Quaternary loose rock pore water is mainly HCO
3·SO
4-Ca type; the chemical type of groundwater in bedrock fissure water is mainly HCO
3·SO
4-Ca, HCO
3-Ca, or HCO
3-Ca·Mg, and so on. The chemical types of groundwater in carbonate fracture-karst systems are mainly HCO
3·SO
4-Ca, HCO
3-Ca, or HCO
3-Ca·Mg. The chemical type of groundwater at CSSY19 sampling point is SO
4-Ca Mg, and that at the CSSY02 sampling points is SO
4-Ca (see
Table 2 and
Figure 3).
According to the dominant anions in
Table 2, the water chemical types mainly include HCO
3 type and HCO
3-SO
4 type, and the cation combination is dominated by Ca type and Ca-Mg type.
- (1)
HCO3 type groundwater
This type of water body is distributed in a continuous manner in the study area. Sampling and analysis during the dry season showed that the mineralization ranged from 264–403 mg/L, and the total hardness ranged from 180.81 to 348.31 mg/L. As the main recharge alternate active zone of the groundwater system, the water quality characteristics of this section are controlled by the dissolution–precipitation balance of carbonate rocks (limestone, dolomite). Abundant precipitation infiltration recharge, steep hydraulic slopes, and efficient water–rock interactions promote the formation of typical low-mineralized HCO3− type water with calcium as the dominant cation.
- (2)
HCO3-SO4 type groundwater
This type of water body is mainly stored in the Cambrian stratigraphic development area in the central and western regions. The water quality monitoring data showed that the mineralization ranged from 221 to 996 mg/L in the flat water period, and the total hardness distribution ranged from 140.97 to 795.86 mg/L. The ionic composition is characterized by Ca2+ predominance of cations, and local Ca-Mg transition type. In the Cambrian limestone aquifer in the southwest of the region, due to the sluggish groundwater runoff, the continuous dissolution and release of gypsum components in the aquifer medium led to a significant increase in the concentration of SO42− ions. This hydrogeochemical process causes a significant dianion signature in the region.
- (3)
Distribution characteristics of strontium content in groundwater
Strontium-rich groundwater represents a significant mineral resource. According to the ⟪National Food Safety Standard: Drinking Natural Mineral Water⟫ (GB 8537-2018) [
18], water meeting the standard for drinking natural mineral water is classified as strontium-containing mineral water when its strontium concentration exceeds 0.2 mg/L. For strontium levels ranging from 0.2 mg/L to 0.4 mg/L, the temperature of the water source must be ≥25 °C. According to the water quality analysis data (
Table 2) during the dry season, the maximum strontium content in all samples was 12.4 mg/L, and the average was 2.13 mg/L. Among the 21 groups of groundwater quality analysis samples, 20 groups had strontium content exceeding 0.2 mg/L, accounting for 95.24% of the samples up to the standards. The strontium content exceeded 0.4 mg/L, accounting for 71.43% of the samples up to the standards. The strontium content of 8 groups of samples exceeded 1.0 mg/L, 33.33% of the samples up to the standard (see
Figure 4).
Among the 21 groups of samples, 8 groups are bedrock fissure water of massive rock type, with strontium concentration content of 0.18–5.42 mg/L, averaging 1.33 mg/L; 12 groups are fissure karst water or karst fissure water of Cambrian-Ordovician system, with strontium concentration content of 0.207–12.41 mg/L, averaging 2.79 mg/L; and 1 group of pore water, with strontium concentration content of 0.631 mg/L.
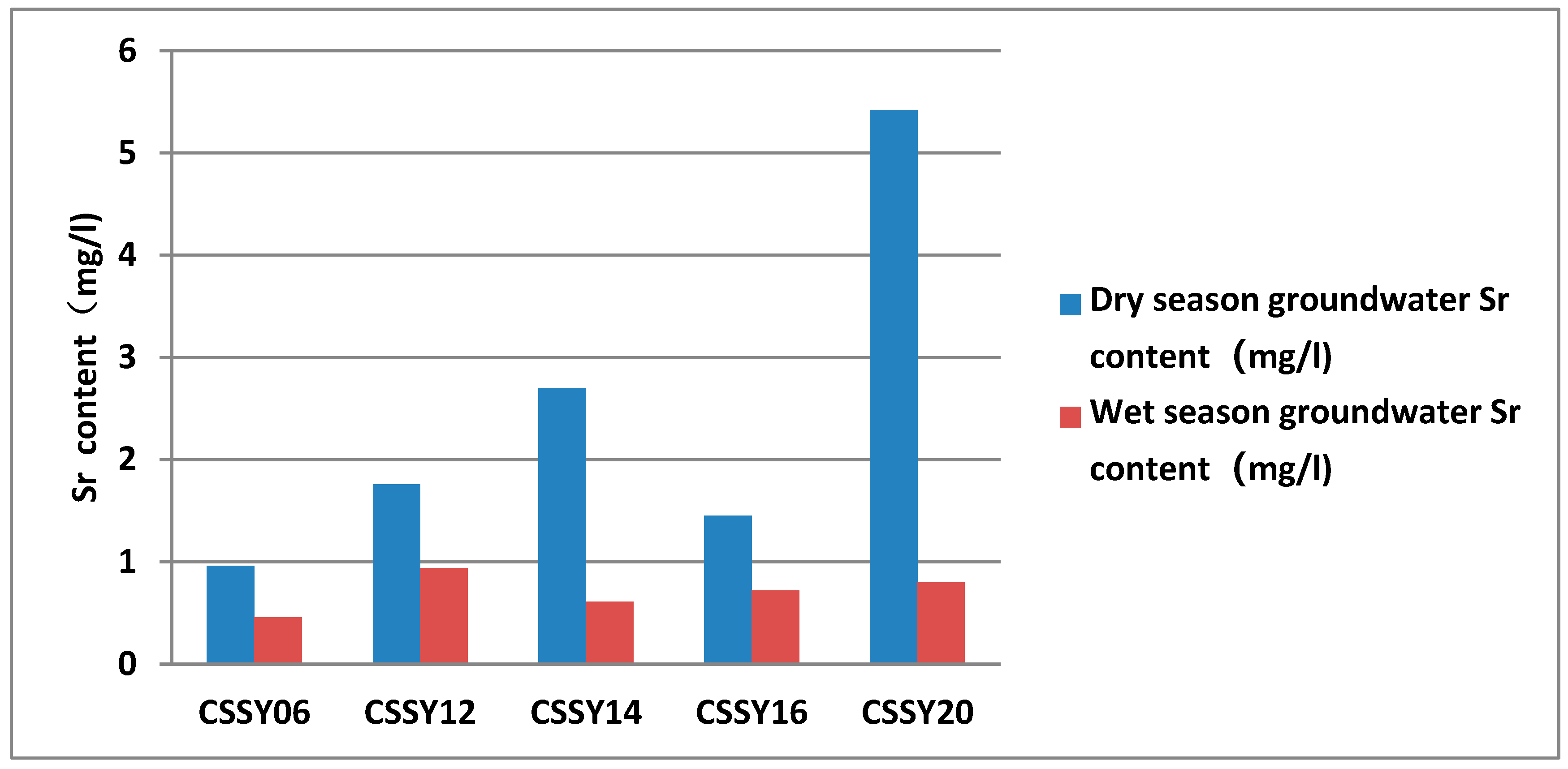
In order to more accurately analyze the characteristics of strontium content changes in the groundwater in the study area, a comparative analysis of water samples collected during the high water period and dry water period was carried out (
Figure 5). The high water period (June to September) is characterized by abundant rainfall. Significant volumes of rainwater rapidly infiltrate the subsurface. This infiltration provides substantial direct recharge to the groundwater through the vadose zone, markedly increasing the recharge rate. Concurrently, this influx of fresh water dilutes the ionic concentrations within the groundwater. Furthermore, despite partial consumption of shallow groundwater by vegetation through evapotranspiration, overall evaporative losses are relatively low during this period. Consequently, the system experiences ample water replenishment and minimal concentration effects. Thus, the dominant processes in the wet season are “Recharge-Dilution-Migration”. Conversely, during the dry water period (December to April), precipitation and infiltration rates drastically decline, resulting in insufficient groundwater recharge and falling water tables. This leads to sluggish groundwater flow, significantly prolonging the contact time between the water and aquifer minerals. This prolonged interaction enhances mineral dissolution and release. Additionally, evaporation rates are notably higher during the dry season, particularly in areas with shallow groundwater (e.g., phreatic water), where enhanced evaporation concentrates dissolved minerals. Dilution effects diminish or cease entirely during this period, leading to elevated concentrations of dissolved minerals in the groundwater. Therefore, the dominant processes in the dry season are “Stagnation-Concentration-Accumulation”. From the figure, it can be seen that the strontium concentration in groundwater during the abundant water period has decreased considerably, but it is still larger than 0.4 mg/L, and the strontium content meets the strontium-containing mineral water standard of the National Standard for Food Safety: Drinking Natural Mineral Water (GB 8537-2018). The strontium content of groundwater during the dry period ranges from 0.962 to 5.42 mg/L, with an average of 2.46 mg/L; the strontium content of groundwater in the abundant water period ranged from 0.46 to 0.94 mg/L, with an average of 0.71 mg/L. The strontium content of groundwater samples in the high water period accounts for 14.76% to 53.40% of that in the dry period.
- (4)
Characteristics of spatial distribution of strontium content in groundwater
Although the strontium content of groundwater in the study area generally reaches the standard of mineral water, it still shows a certain pattern in spatial distribution. The strontium content of groundwater in the Cambrian Zhangxia Formation and Steamed Buns Formation is more than that in the Cambrian Chaomidian Formation, Sanshanzi Formation, and Ordovician strata in the carbonate fissure karst water-bearing rock groups. The strontium content of groundwater near large-scale fractures in the same water-bearing rock group is larger than that of groundwater not controlled by large fractures. For example, the strontium content of groundwater in the vicinity of Niejiayu Village, Dongnanyu Village, and Fengjia Village near the fracture ranges from 4.35 to 12.41 mg/l, which is much higher than that in the wells in the vicinity of the non-major fracture (
Figure 6).
- (5)
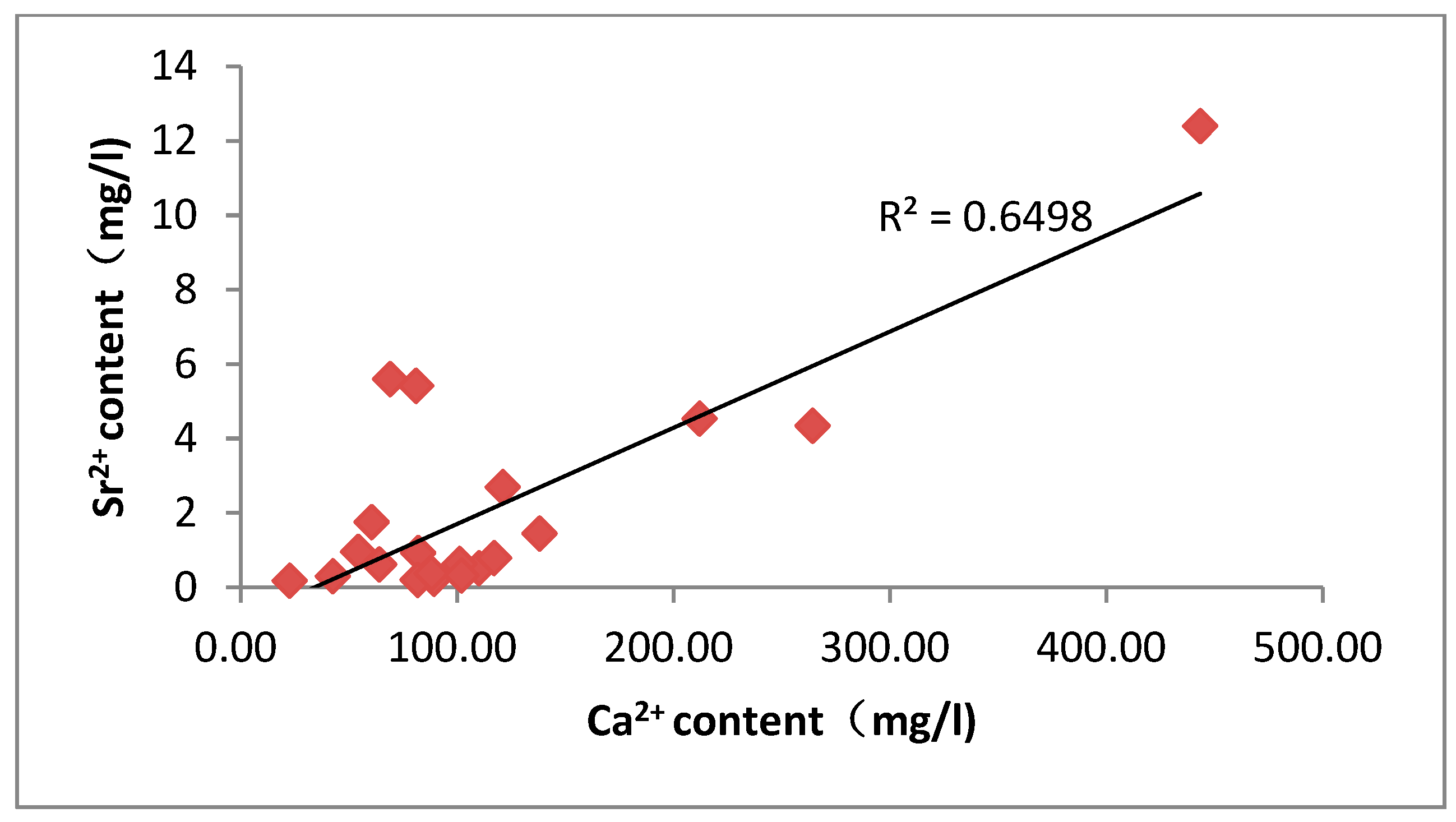
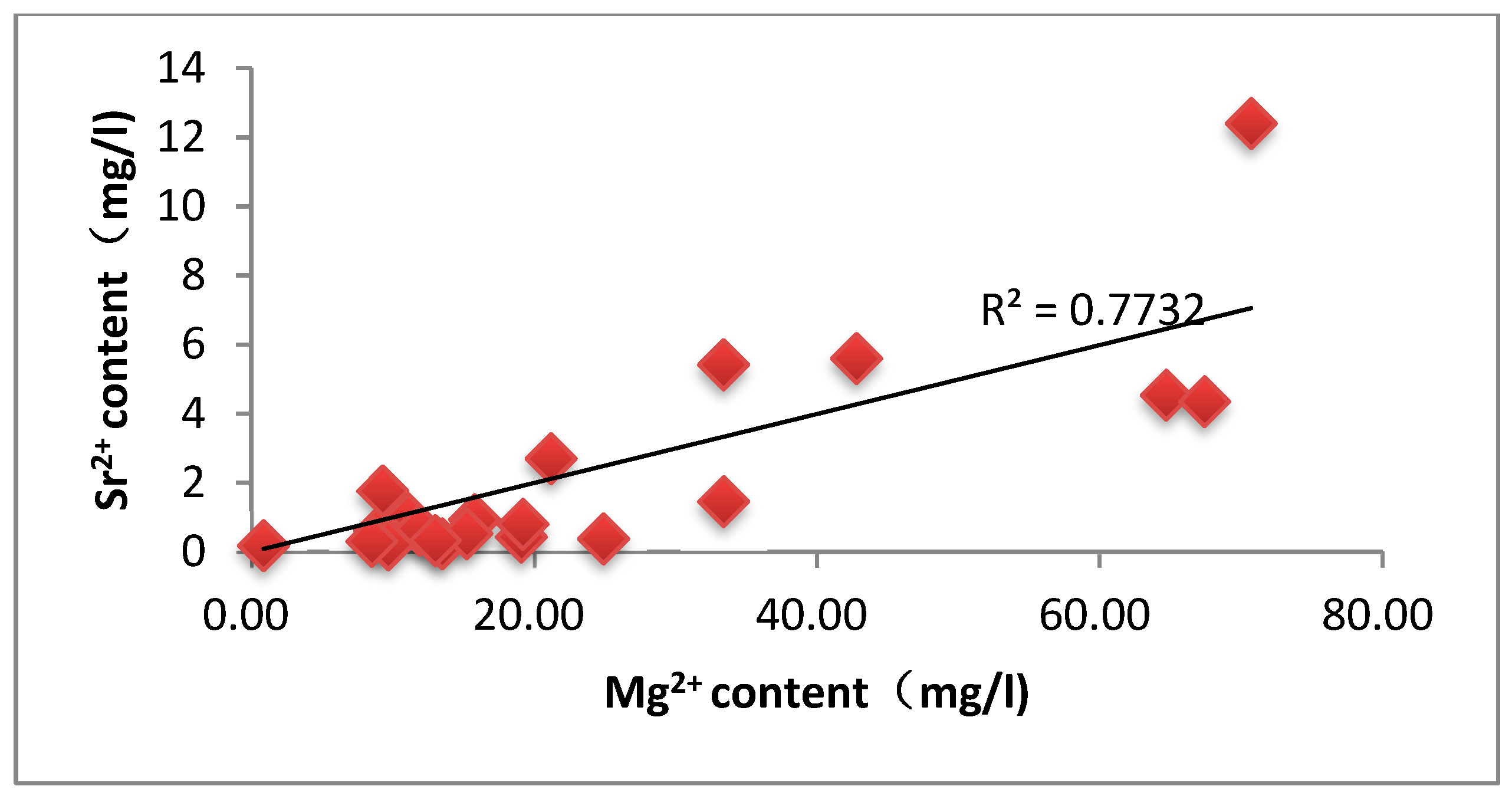
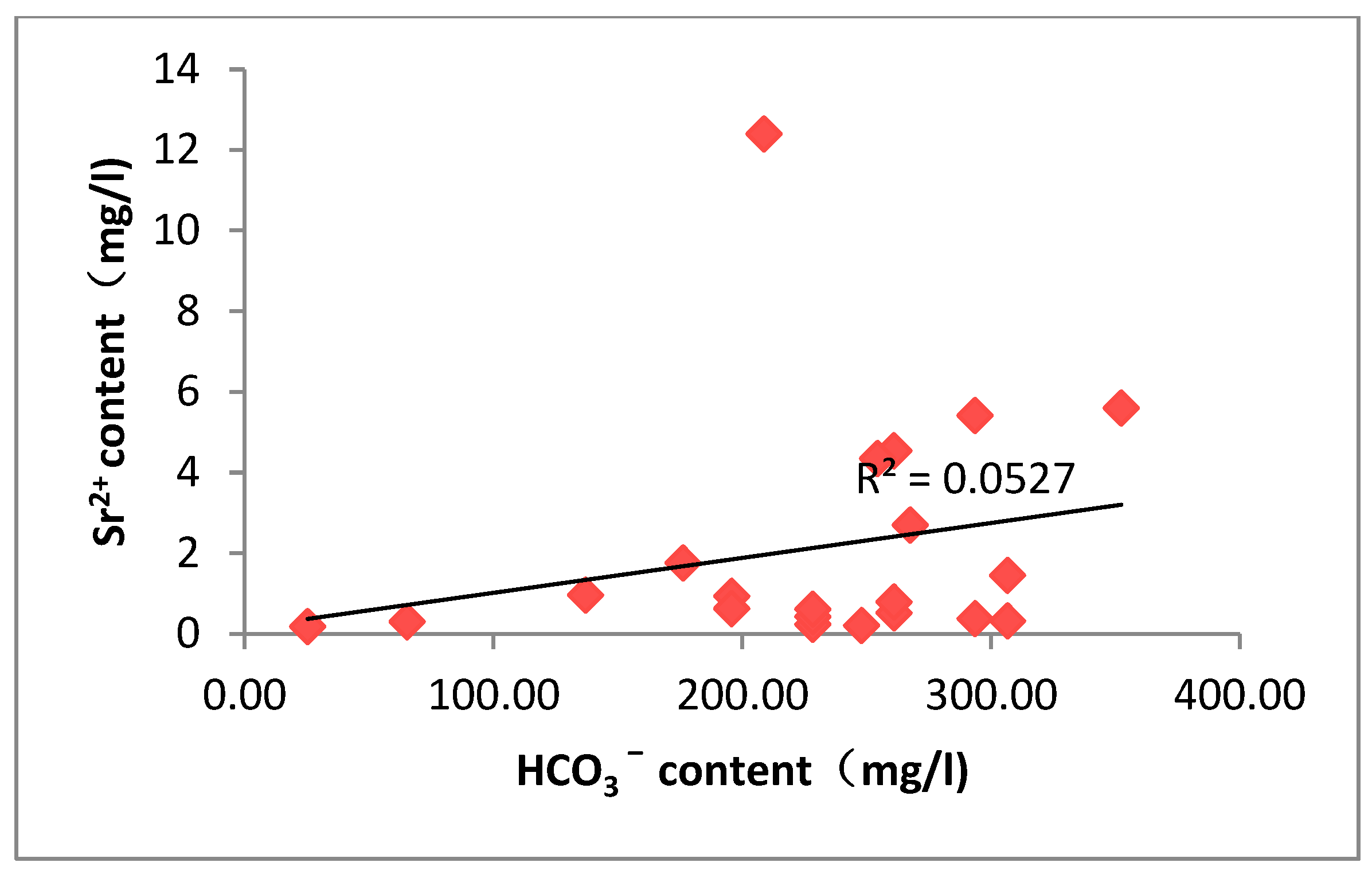
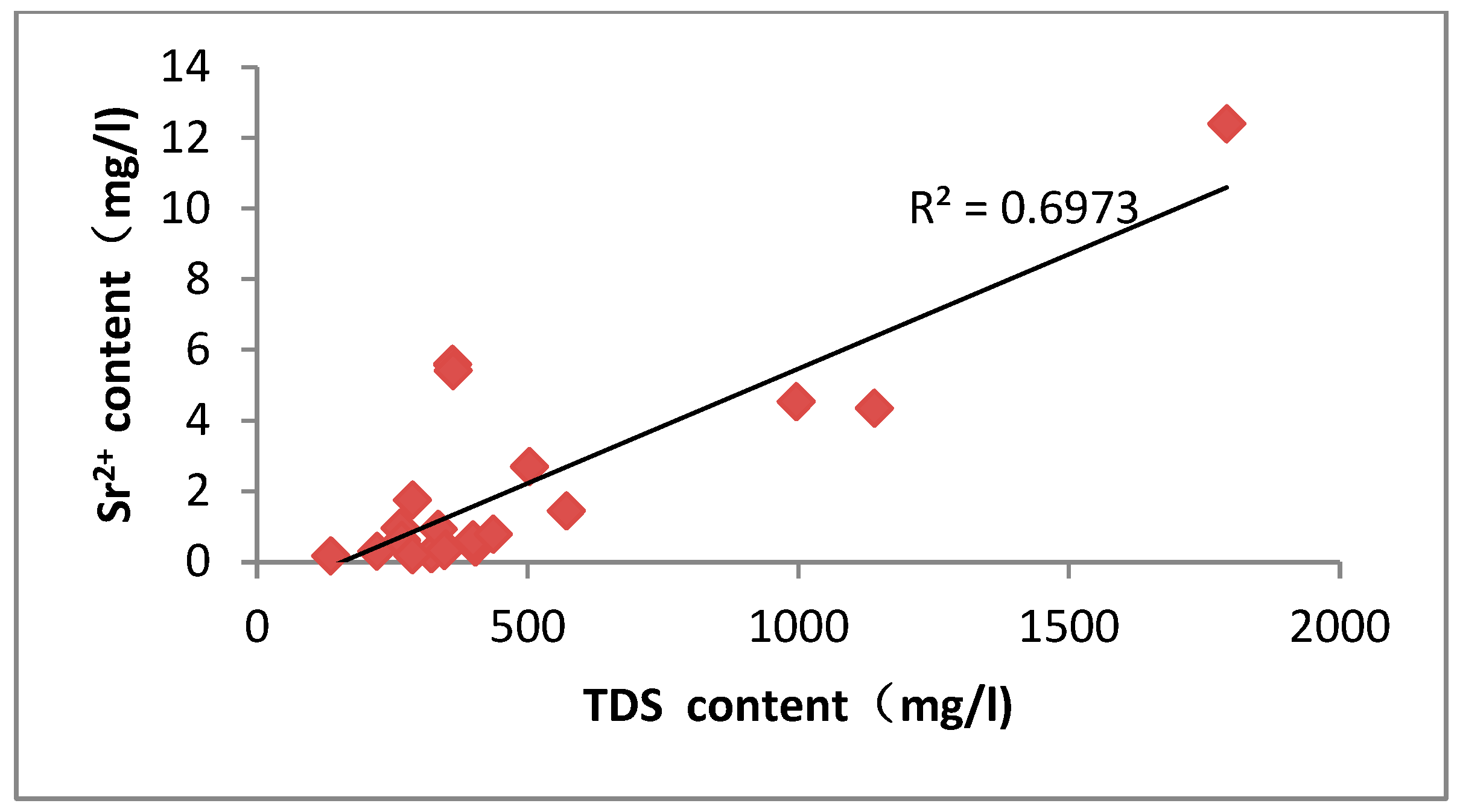
Analysis of the correlation between groundwater strontium content and each component
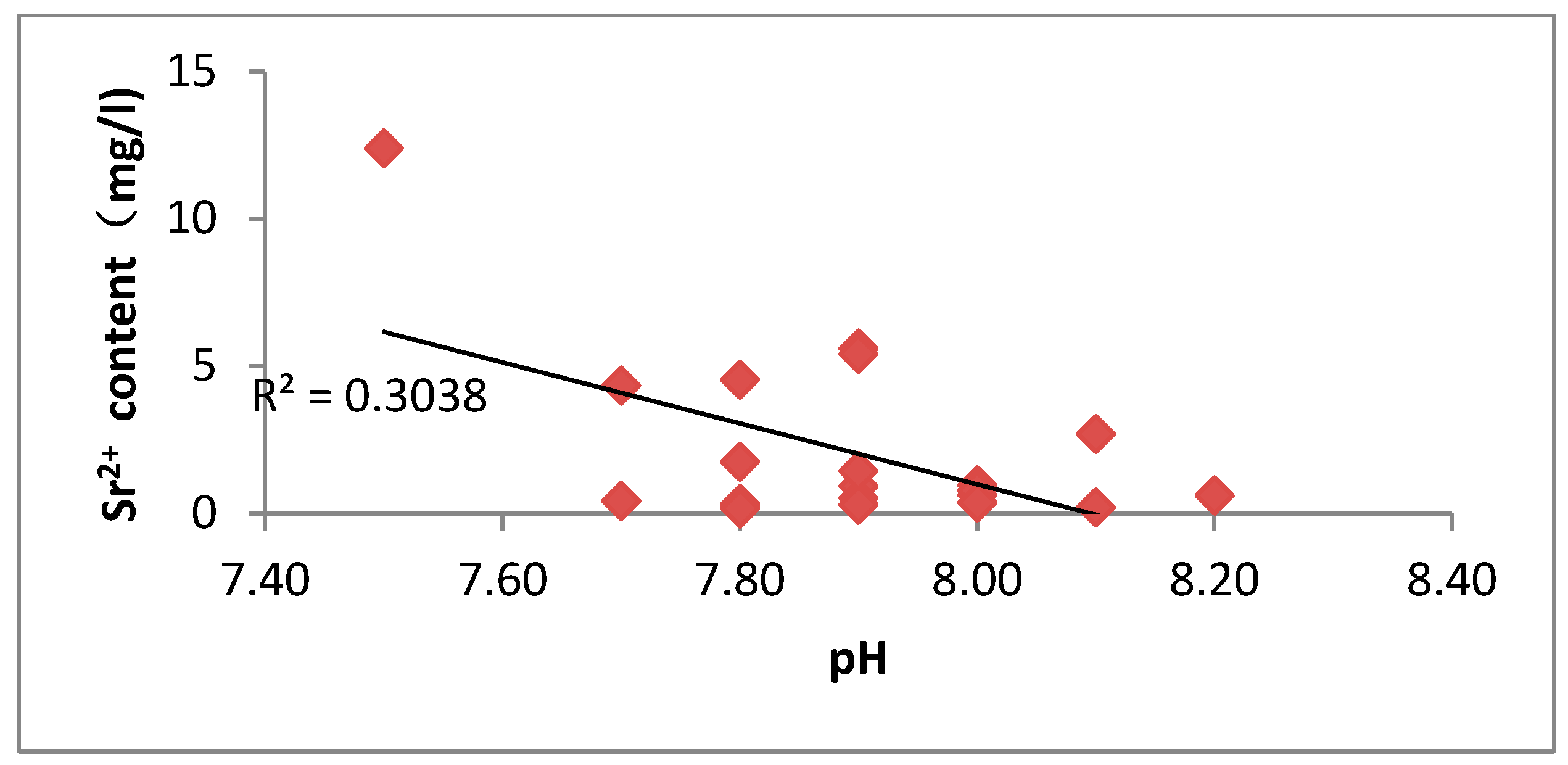
The ionic correlation analysis of groundwater showed that Sr2+ concentration was positively correlated with Ca2+, Mg2+, and total dissolved solids (TDS), with all the correlation coefficients higher than 0.5. The geochemical feature reveals that the distribution of strontium ions in the study area is mainly controlled by the dissolution process of carbonate minerals, especially by the mechanism of the weathering, dissolution, and release of calcium-containing minerals, such as calcite and dolomite. The study data also revealed the inverse correlation features between strontium concentration and water body pH. When the pH value decreases, the enrichment degree of Sr2+ in the aqueous environment shows an upward trend, which reflects that acidic conditions are more favorable for the dissolution activation of strontium-bearing minerals. The mechanism of action is manifested as follows: the alkaline environment enhances the activity of carbonate ions in the solution, which on the one hand inhibits the sustained dissolution of calcite minerals through the homoionic effect, and on the other hand promotes the participation of strontium in the dissolved state in the process of carbonate precipitation, and this dual action ultimately leads to a decrease in the concentration of soluble strontium in the aqueous phase. Further analysis reveals that the increase of calcite supersaturation significantly accelerates the solid-phase transport process of elemental strontium when the pH exceeds 8.5.
5. Analysis of the Causes for Strontium-Rich Groundwater in the Study Area
In order to investigate the hydrochemical driving mechanism of Sr2+ enrichment in the groundwater system, this study systematically analyzes the influences of key hydrogeochemical processes on strontium transport and enrichment, such as rock weathering, mineral solubilization and filtration, cation adsorption and evaporation-concentration, and then elucidates the mechanism of the formation of high-strontium-content groundwaters.
- (1)
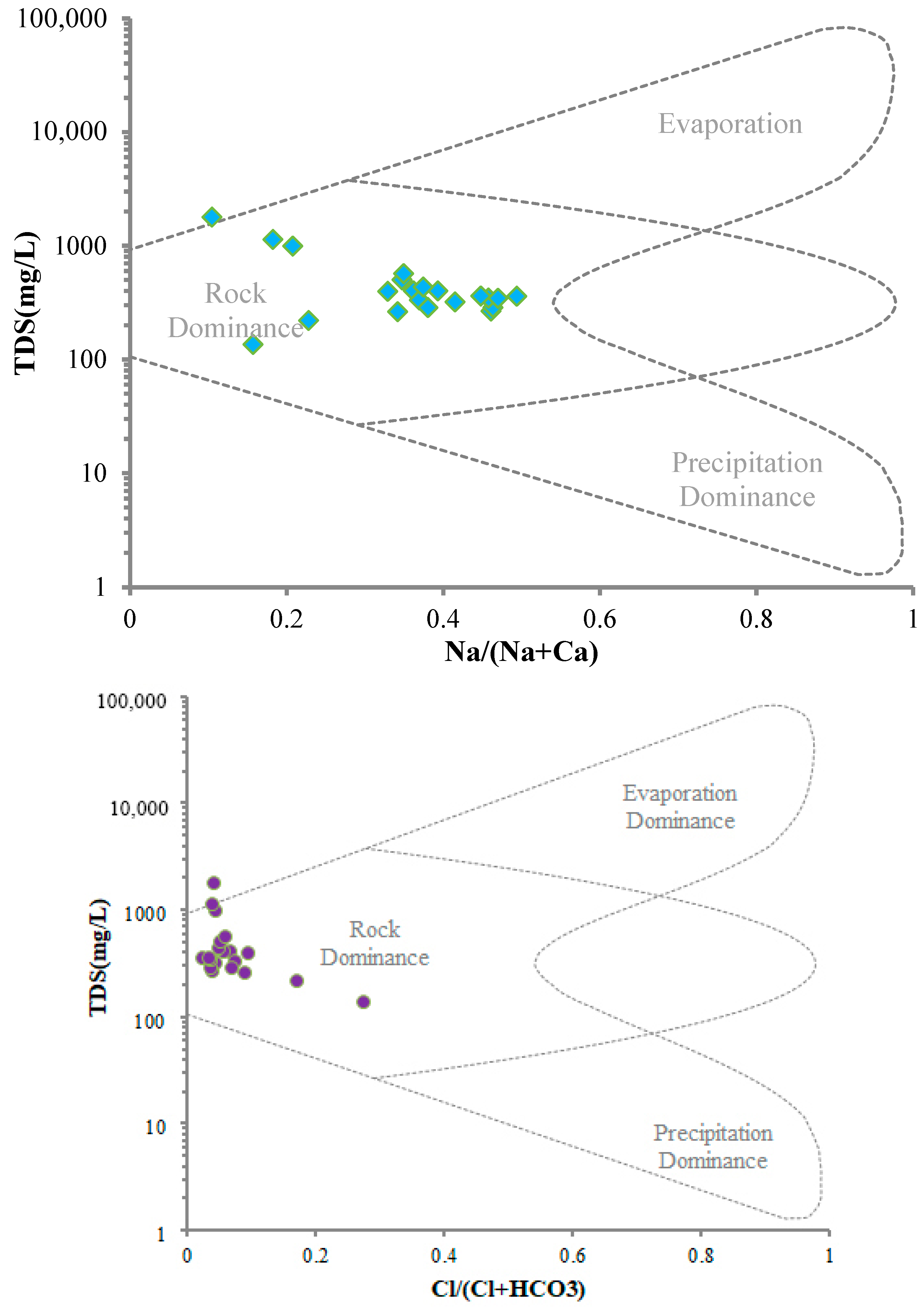
Gibbs diagram
As an important tool to characterize the hydrochemical evolution process, Gibbs plotting realizes the multivariate analysis of the ion source of the regional water body through the spatial clustering characteristics of the key parameters of water–rock interaction. By constructing a two-dimensional distribution model of the ratio of TDS to anions and cations, the method can effectively identify different causes for hydrochemical phases, such as rock weathering-dominated, evaporation-crystallization-controlled, and atmospheric-input types, which provides a semi-quantitative characterization tool for revealing the hydrochemical evolution pathways [
19]. It is shown that the multidimensional and visual analysis of this diagram can not only screen the dominant geochemical processes, but also reflect the phase characteristics of solute transport within different hydrogeological units.
With Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) and Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) as double index coordinates, combined with TDS (total dissolved solids) parameters, the Gibbs plot constructs a three-dimensional discrimination system: when both ratios are >0.5 and TDS is low, it indicates that the source of chemical components in this kind of water samples is mainly controlled by atmospheric precipitation; when both ratios are <0.5 or close to 0.5, it corresponds to a medium TDS region reflecting that the chemical components of the groundwater in this region are mainly affected by the weathering of the rocks; and when both ratios and TDS increase synchronously, it indicates the influence features of the evaporation-concentration process.
The spatial distribution characteristics of the sampling data in the study area show (
Figure 13) that most of the water sampling points are concentrated in the rock weathering domain where Cl
−/(Cl
− + HCO
3−) and Na
+/(Na
+ + Ca
2+) double ratios are below 0.5, indicating that the chemical weathering process of bedrock minerals is the main source of the ionic component of groundwater in this area, which is significantly correlated with the regional hydrogeochemical background.
- (2)
Evaporation-Concentration
During the evaporation-concentration process, water–rock interactions show a dual effect: on the one hand, it leads to an overall increase in the concentration of dissolved ions, and on the other hand, it precipitates carbonate minerals such as calcite and dolomite by inducing them to reach a supersaturated state, thereby reducing the Ca
2+/Na
+ ratio in the water column. This mineral change process significantly contributes to the secondary transport enrichment of Sr
2+ by enhancing the sustained dissolution and release of calcareous minerals [
20]. Gibbs’ diagram of the study area (
Figure 13) shows that some water sample points are distributed along the evaporation-concentration trend zone and the Sr
2+ concentration is significantly and positively correlated with the intensity of evaporation, corroborating the important contribution of this process to strontium element enrichment.
- (3)
Rock weathering
Cation molar concentration ratios serve as effective tracers of hydrogeochemical processes, and Mg
2+/Na
+ versus Ca
2+/Na
+ binary synergistic diagrams were constructed to assess the relative contributions of major weathering processes to the chemical composition of groundwater [
21,
22,
23]. By calculating the stoichiometric relationships of the dominant cations, the input flux share of the groundwater hydrochemical composition by processes such as silicate rock weathering, carbonate rock weathering, and evaporate salt weathering can be effectively distinguished. The spatial clustering feature of this ratio model can reveal the geochemical weight distribution law of different weathering end elements on the basin scale.
The spatial distribution of the study data in the feature map (
Figure 14) shows that the vast majority of the samples are concentrated in the area of global average carbonate weathering or close to the area, confirming that carbonate weathering is the main controlling source of the ionic component of the groundwater in this area. The weathering process continuously releases characteristic ions such as Ca
2+ and Mg
2+, resulting in a significant synergistic migration pattern with Sr
2+, which is mutually verified with the dominant mechanism of rock weathering as revealed by the Gibbs’ diagrams, and together they elucidate the mechanism of formation of the regional high strontium groundwater.
- (4)
Mineral dissolution
The ionic assemblage characteristics of the groundwater in the study area show that the weathering process of carbonate rocks is the main controlling factor in controlling the hydrochemical evolution, in which the dominant ionic components such as Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− are mainly obtained from dissolution and filtration of carbonate minerals. The regional geological section reveals that the Cambrian-Ordovician carbonate construction is widely exposed, and the lithology is characterized by a chert-dolomite sequence dominated by easily soluble minerals such as calcite and dolomite. During groundwater transport, the persistent geochemical interactions between the host medium and the surrounding rocks prompted the progressive dissolution of calcite, dolomite, and other minerals, causing the migration and transformation of their characteristic ionic components to the aqueous phase.
In order to reveal the mechanisms of hydrochemical interactions in the groundwater system, the PHREEQC (v3.0) hydrogeochemical simulation software was used to calculate the Ca
2+ activity and the saturation index (SI) of minerals such as calcite, dolomite, and gypsum in the groundwater system [
24]. First, input the chemical composition data of the target water sample, including pH, temperature, and concentrations of major ions (such as Ca
2+, Mg
2+, HCO
3−, SO
42−, Cl
−, etc.). Then, select the built-in thermodynamic database to obtain the solubility product constants (Ksp) of minerals such as calcite, dolomite, and gypsum, as well ion activity coefficient calculation parameters. The software calculates the activity of each ion based on the ionic association model (such as the Debye–Hückel or Pitzer equation), thereby determining the activity value of Ca
2+. For the mineral saturation index, PHREEQC assesses the tendency of minerals to dissolve or precipitate by comparing the ionic activity product (IAP) in the solution with the corresponding mineral’s Ksp and using the formula SI = log(IAP/Ksp). The calculation results quantitatively reveal the chemical equilibrium state between groundwater and minerals, providing key geochemical evidence for analyzing water–rock interactions and mineralization potential. Based on the results of the calculations, correlation analyses were carried out between Sr
2+ concentration and mineral saturation indices as well as Sr
2+ and Ca
2+ activity.
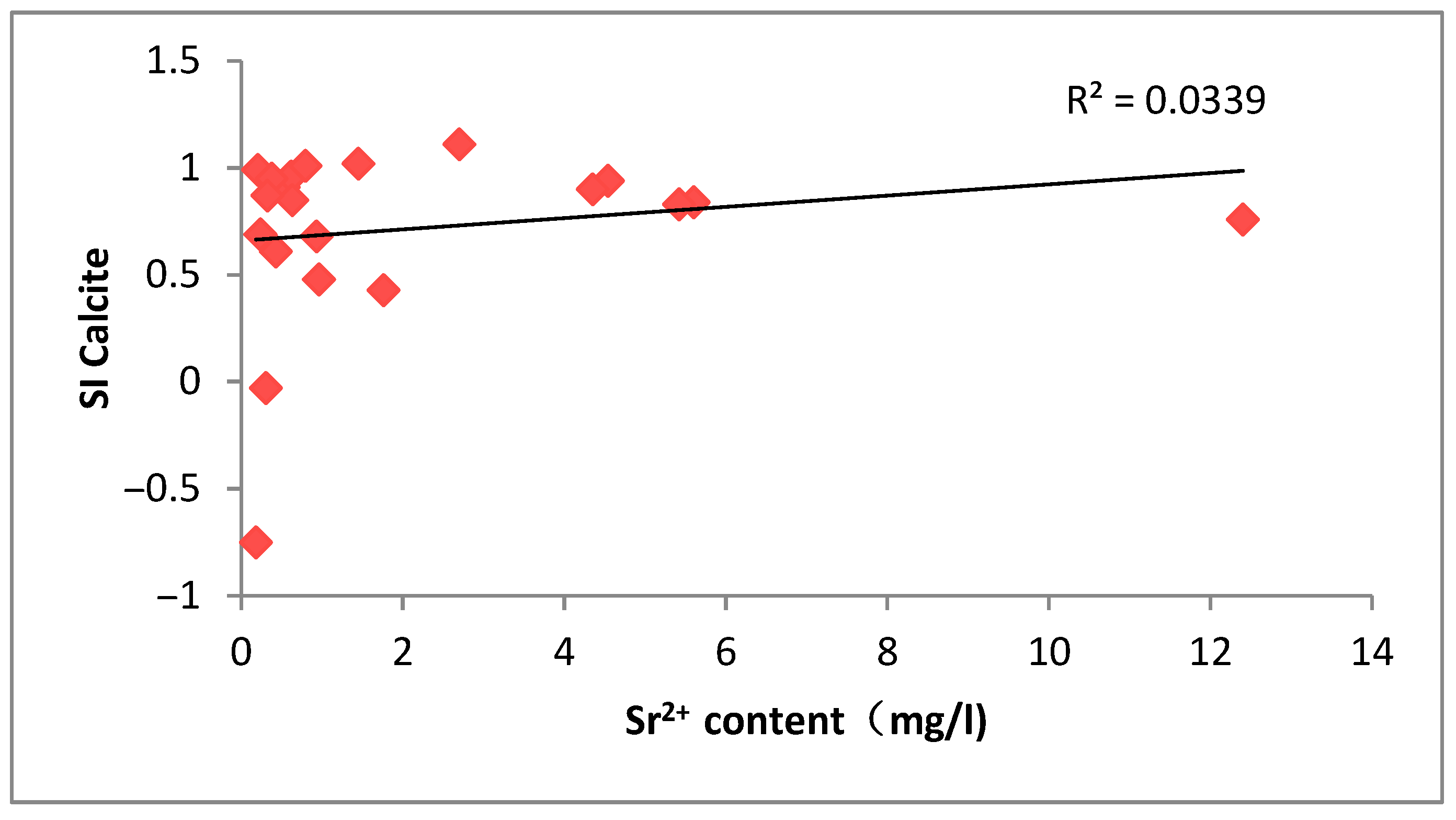
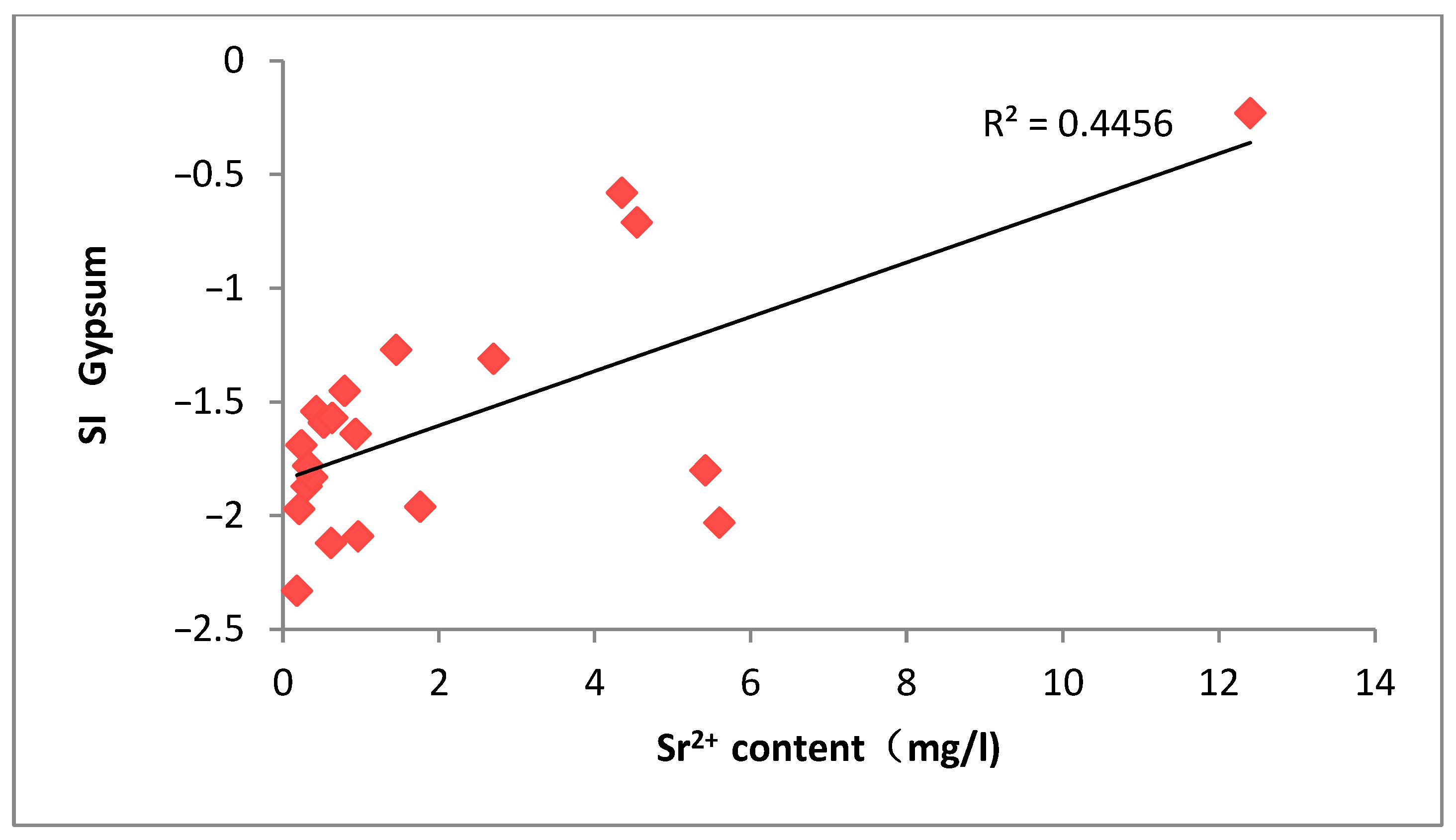
As can be seen from
Figure 15,
Figure 16 and
Figure 17, the Sr
2+ concentration and the saturation index of minerals such as calcite, dolomite, and gypsum all showed a certain positive correlation, indicating that the change in Sr
2+ concentration is mainly controlled by the dissolution process of calcite, dolomite, and other calcareous minerals [
8]. The experimental data show that with the enhancement of the dissolution of calcite, dolomite, and other carbonate minerals, their corresponding solution supersaturation indices show a regular increasing trend, accompanied by a simultaneous increase in strontium ion concentration, which confirms the dominant role of the dissolution process of calcareous minerals in the migration and transformation of strontium elements. It is worth noting that the values of dissolution equilibrium parameters of different calcareous minerals (including calcite, dolomite, and gypsum) in the groundwater samples in the study area are relatively close, and all of them are synchronized with the strontium ion concentration, which suggests that the dissolution–precipitation process of the three minerals may jointly regulate the geochemical behavior of strontium in the study area.
- (5)
Cation exchange
The Cation Exchange Index (CAI), proposed by Scholler (1967) as a bivariate discriminant framework, quantitatively reflects the intensity and direction of reverse cation exchange (Na
+ and K
+ displacing adsorbed Ca
2+ and Mg
2+) in aquifer media through equivalent concentration ratios of specific anions and cations in aqueous systems. Based on the two-parameter discriminant system established by Scholler, the strength of the exchange reaction at the water–rock interface was quantitatively characterized by the cation alternate adsorption indices CAI1 and CAI2, which were calculated as follows [
8]:
The index system is a clear indicator of the phase state: when the reverse exchange of adsorbed Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the Na+ and K+ replacement medium occurs, the CAI index shows a positive value; conversely, when the positive exchange of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the replacement of adsorbed Na+ and K + occurs, the index shows a negative value, and its absolute value directly reflects the intensity of the exchange reaction.
The groundwater CAI index in the study area generally showed positive values (
Figure 18), revealing that the hydrochemical environment is dominated by the reverse replacement of adsorbed Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ states by Na
+ and K
+ [
25]. Although Sr
2+ and Ca
2+ have geochemical behavioral similarities and may theoretically be desorbed from the sediment surface into the aqueous phase through such exchange processes, correlation analysis based on the concentration of Sr
2+ and CAI indices (
Figure 19 and
Figure 20) showed that they did not show a statistically significant correlation (R
2 < 0.15). This confirms that cation-exchange kinetics does not have a significant controlling effect on the migratory enrichment of Sr
2+ in this zone, and its contribution is much smaller than that of the dominant processes such as rock weathering and evaporative concentration.