Divergent Response of Blue Carbon Components and Microbial Communities in Sediments to Different Shellfish Zones of Geligang, Liaodong Bay, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Sample Design
2.3. Basic Sediment Properties
2.4. Sediment DNA Extraction and Metagenome Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of DOC, POC, MBC
3.2. Relationship Among Sediment Enzyme Activity with Different Carbon Fractions
3.3. Effects of Different Shellfish Zones on C Cycling-Related Composition and Gene Abundance of Sediment Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. The Presence of Gastropods Increased Sediment POC and MBC
4.2. Microbial Community Responses to Shellfish Habitat
4.3. The Presence of Shellfish in Sediment Influences Genes Involved in C Cycling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| POC | Particulate organic carbon |
| MBC | Microbial biomass carbon |
| BE | Bullacta exarata |
| UT | Umbonium thomasi |
| MV | Mactra veneriformis |
| MM | Meretrix meretrix |
| PL | Potamocorbula laevis |
| PPO | Polyphenol oxidase |
| AMY | Amylase |
| INV | Invertase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| SEM | Structural equation modeling |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| AL | Alkalinity |
| C cycling | Carbon cycling |
References
- Holmén, K. 11—The Global Carbon Cycle. In International Geophysics; Jacobson, M.C., Charlson, R.J., Rodhe, H., Orians, G.H., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 282–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVries, T.; Holzer, M.; Primeau, F. Recent Increase in Oceanic Carbon Uptake Driven by Weaker Upper-Ocean Overturning. Nature 2017, 5427640, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Bakker, D.C.E.; Hauck, J.; Landschützer, P.; Le Quéré, C.; Luijkx, I.T.; Peters, G.P.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2023. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 5301–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and Climate Change: Forcings, Feedbacks, and the Climate Benefits of Forests. Science 2008, 3205882, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, N.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, M.; Dai, M.; Zhai, W.; Gao, K.; et al. Carbon pools and fluxes in the China Seas and adjacent oceans. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 1535–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Wang, H.; Xu, G.; Aricò, S. Blue Carbon on the Rise: Challenges and Opportunities. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 54, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Strategic Approach for Mariculture to Practice “Ocean Negative Carbon Emission. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 3603, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Thielen, P.; Salzberg, S.L. Bracken: Estimating Species Abundance in Metagenomics Data. Peej Comput. Sci. 2017, 3, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatenh, E.; Gizaw, B.; Tsegaye, Z.; Tefera, G. Microbial Function on Climate Change—A Review. Open J. Environ. Biol. 2018, 3, 001–007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Amelung, W.; Lehmann, J.; Kästner, M. Quantitative Assessment of Microbial Necromass Contribution to Soil Organic Matter. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 2511, 3578–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, K.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Nitrogen Fertilization Raises CO2 Efflux from Inorganic Carbon: A Global Assessment. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 247, 2810–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Jin, H.; Dong, Y. Increased Enzyme Activities and Fungal Degraders by Gloeophyllum Trabeum Inoculation Improve Lignocellulose Degradation Efficiency During Manure-Straw Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Liu, M.; Xi, M. Divergent Response of Blue Carbon Components to Wetland Types and Hydrological Effects in Typical Estuarine Wetlands of Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Bian, Q.; Jiang, Y.J.; Zhu, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.T.; Sun, B. Organic Amendments Drive Shifts in Microbial Community Structure and Keystone Taxa Which Increase C Mineralization across Aggregate Size Classes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 153, 108062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaquias, M.A.E. Systematics, Phylogeny, and Natural History of Bullacta Exarata (Philippi, 1849): An Endemic Cephalaspidean Gastropod from the China Sea. J. Nat. Hist. 2010, 44, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmi, M.F.A.; Simarani, K. Effect of Two Contrasting Biochars on Soil Microbiota in the Humid Tropics of Peninsular Malaysia. Geoderma 2021, 395, 115088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Yang, Y.; Fu, S.; Jiang, P.; Luo, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Hu, S.; et al. Biochar reduces soil heterotrophic respiration in a subtropical plantation through increasing soil organic carbon recalcitrancy and decreasing carbon-degrading microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shi, L.; Fu, Q.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Huang, Q. Influence Mechanisms of Long-Term Fertilizations on the Mineralization of Organic Matter in Ultisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 201, 104594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Tyler, H.L.; Millar, J.J. Determination of Microbial Extracellular Enzyme Activity in Waters, Soils, and Sediments Using High Throughput Microplate Assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 80, 50399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.A.; Morris, S.J.; Bohm, S. The Determination of Soil C Pool Sizes and Turnover Rates: Biophysical Fractionation and Tracers. In Assessment Methods for Soil Carbon, 1st ed.; Kimble, J.M., Follett, R.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Wu, J.; Brookes, P.C. Measuring Soil Microbial Biomass Using an Automated Procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 435, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality Control and Preprocessing of Metagenomic Datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Salzberg, S.L. Kraken: Ultrafast Metagenomic Sequence Classification Using Exact Alignments. Genome Biol. 2014, 153, R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Ahn, J.W. Model Setting and Interpretation of Results in Research Using Structural Equation Modeling: A Checklist with Guiding Questions for Reporting. Asian Nurs. Res. 2021, 153, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.-X. Wekemo Bioincloud: A User-Friendly Platform for Meta-Omics Data Analyses. iMeta 2024, 31, e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aller, R.C. Bioturbation and Remineralization of Sedimentary Organic Matter: Effects of Redox Oscillation. Chem. Geol. 1994, 114, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Filgueira, R.; Sun, Y.; Han, M.; Tang, Q.; Sun, Y. Intensive oyster farming enhances carbon storage in sediments over decades. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ling, Y.; Xiao, H. Dynamics Variation of Soil Labile Organic Carbon Fractions in Different Wetland Types of Dongting Lake under Seasonal Water Level Fluctuation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Bertilsson, S. Contrasting Effects of Solar UV Radiation on Dissolved Organic Sources for Bacterial Growth. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Q. Carbon Dynamics in Seawater and Sediment: A Case Study of Shellfish and Seaweed Mariculture Systems. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 204, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Thrush, S.F.; Wan, X.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y.; Jiang, G.; Sun, R.; Wang, L.; He, P. Optimization of Hard Clams, Polychaetes, Physical Disturbance and Denitrifying Bacteria of Removing Nutrients in Marine Sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 1101, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, E.; Bouillon, S.; Dittmar, T.; Marchand, C. What Is Bioturbation? The Need for a Precise Definition for Fauna in Biogeochemical Studies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stief, P. Stimulation of Microbial Nitrogen Cycling in Aquatic Ecosystems by Benthic Macrofauna: Mechanisms and Environmental Implications. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7829–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J. Reviews and Syntheses: To the Bottom of Carbon Processing at the Seafloor. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babur, E.; Uslu, Ö.S.; Battaglia, M.L.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Danish, S.; Fahad, S.; Diatta, A.A.; Datta, R.; Ozlu, E. Nitrogen Fertilizer Effects on Microbial Respiration, Microbial Biomass, and Carbon Sequestration in a Mediterranean Grassland Ecosystem. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 154, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giorgio, P.A.; Cole, J.J. Bacterial Growth Efficiency in Natural Aquatic Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 503–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wachenfeldt, E.; Bastviken, D.; Tranvik, L.J. Microbially Induced Flocculation of Allochthonous Dissolved Organic Carbon in Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 545, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baćmaga, M.; Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J. Bioaugmentation of Soil Contaminated with Azoxystrobin. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 2281, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y. Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Metabolic Function Diversity in Soda Saline–Alkali Rice Paddy Fields of Northeast China. Sustainability 2020, 1223, 10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, A.M.; Mattei, E.; Messina, A.; Tarola, A.M. Inhibition of Polyphenol Oxidases Activity by Various Dipeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 5210, 2741–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Responses of Extracellular Enzymes to Simple and Complex Nutrient Inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil Enzymes in a Changing Environment: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L. Phenol Oxidase, Peroxidase and Organic Matter Dynamics of Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Yin, J.J.; Wu, J.P.; Christakos, G. Accurate Carbon Storage Estimation for the Salt Marsh Ecosystem Based on Bayesian Maximum Entropy Approach—A Case Study for the Spartina Alterniflora Ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.Y.; Zhu, W.J.; Neori, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Chang, Z.Q. Benthic Suspension-Feeding Clams Affect Sedimentary Microbial Communities and Nitrogen Cycling in Seawater Pond Imta. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Xing, B.; Chan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, G. Impacts of Eutrophication on Microbial Community Structure in Sediment, Seawater, and Phyllosphere of Seagrass Ecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1449545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, J.D. Book Review: Ecology of Marine Bivalves: An Ecosystem Approach. Ecology 1998, 791, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.I.E. Ecosystem Influences of Natural and Cultivated Populations of Suspension-Feeding Bivalve Molluscs: A Review. J. Shellfish. Res. 2004, 23, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Prins, T.C. A Review of the Feedbacks between Bivalve Grazingand Ecosystem Processes. Aquat. Ecol. 1997, 31, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.L.; Jones, C.G.; Strayer, D.L.; Iribarne, O.O. Mollusks as Ecosystem Engineers: The Role of Shell Production in Aquatic Habitats. Oikos 2003, 1011, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, A.; Souza, A.T.; Ilarri, M.; Pascoal, C.; Sousa, R. Effects of the Invasive Clam Corbicula Fluminea (Müller, 1774) on an Estuarine Microbial Community. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Li, C.L.; Wang, M.X.; Zheng, P. Stable Isotope Signatures and Nutritional Sources of Some Dominant Species from the Pacmanus Hydrothermal Area and the Desmos Caldera. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Dou, Y.; Yang, X.; An, S. Soil Microbial Community and Their Functional Genes During Grassland Restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 13, e0208887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Lin, Q.; Yuan, M.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Hu, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, X.; He, Z.; et al. Responses of the Functional Structure of Soil Microbial Community to Livestock Grazing in the Tibetan Alpine Grassland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 192, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, C.Q.; Gao, C.; Xu, P. Efficient Utilization of Hemicellulose Hydrolysate for Propionic Acid Production Using Propionibacterium Acidipropionici. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
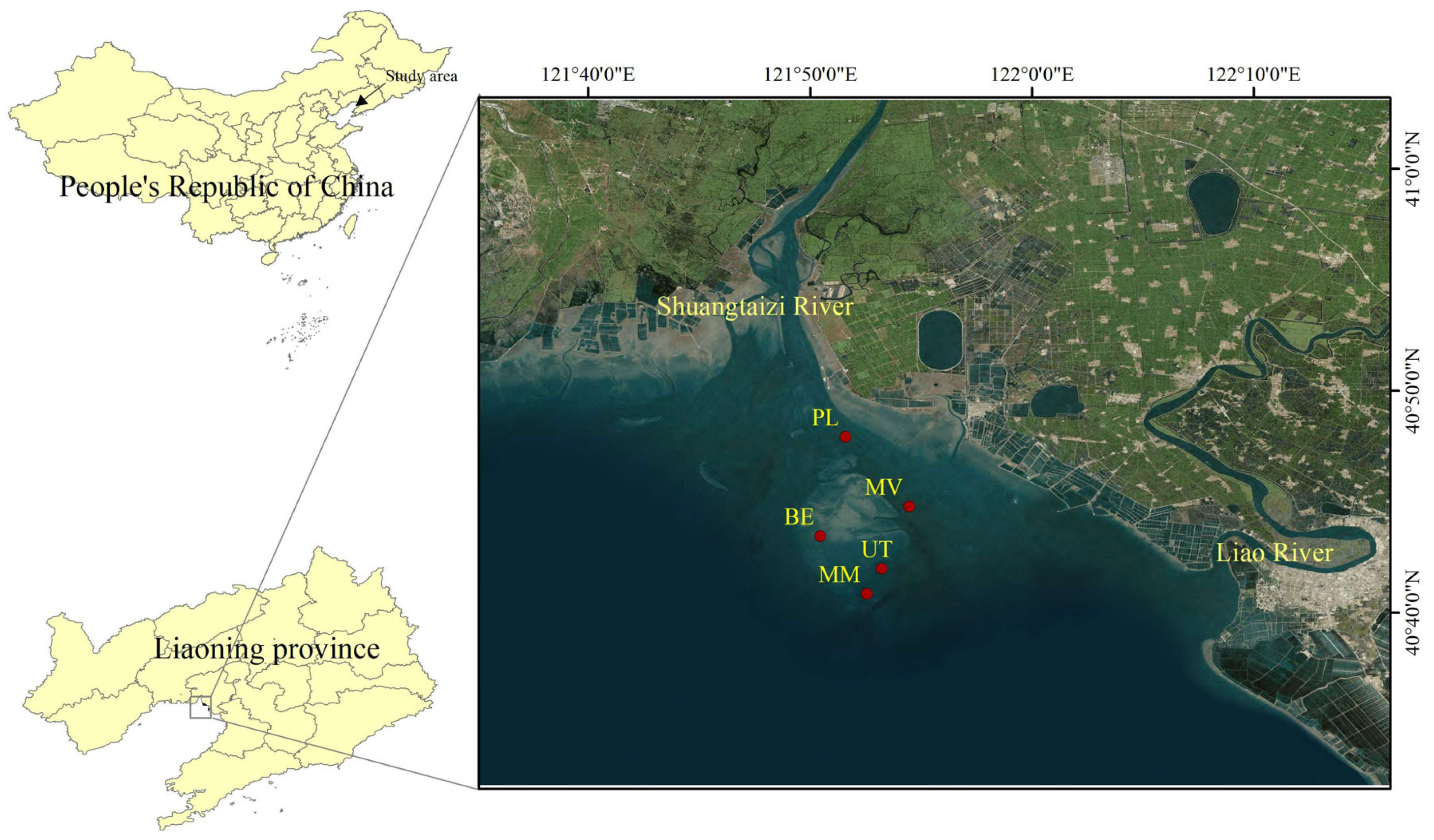
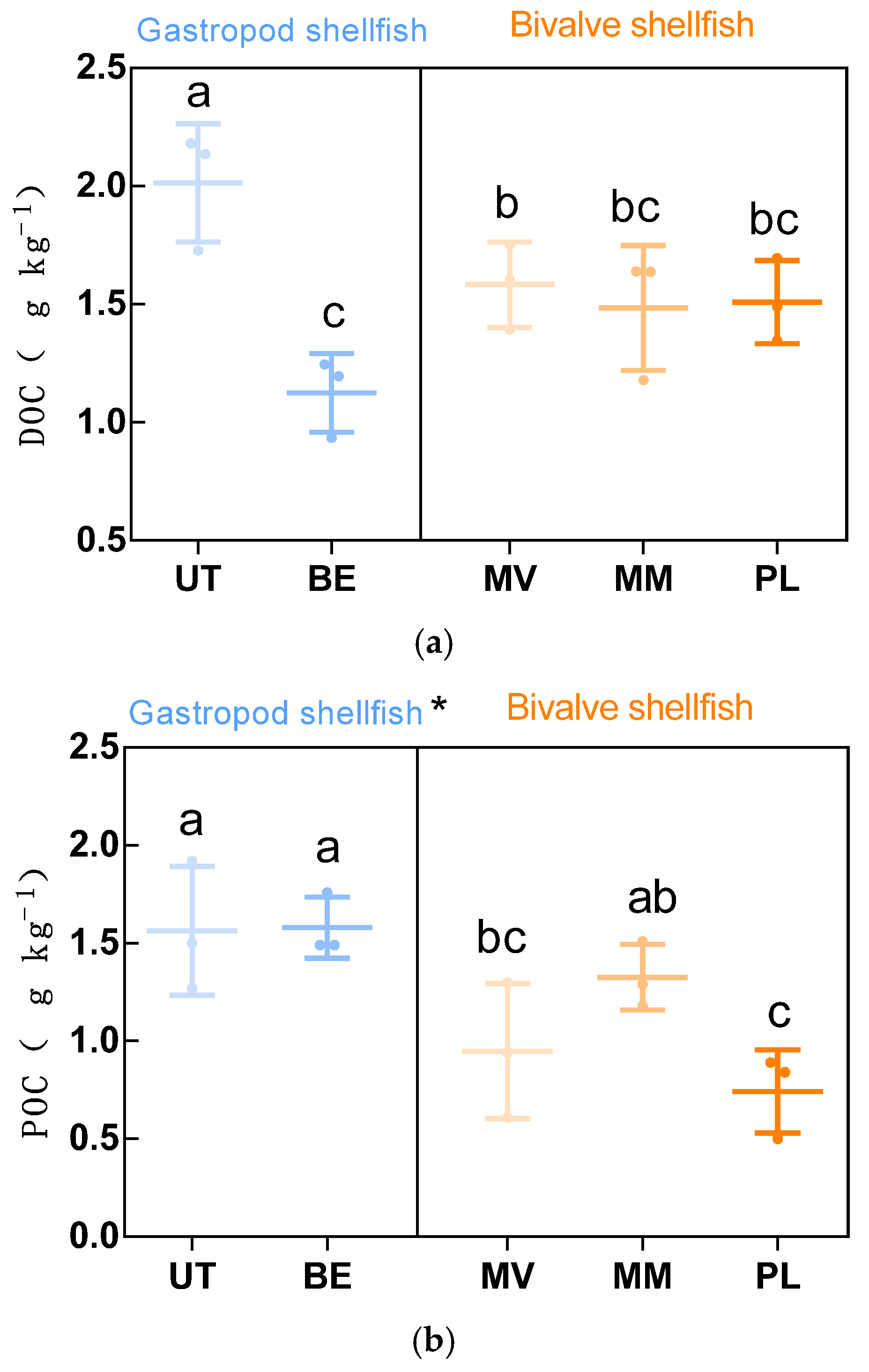
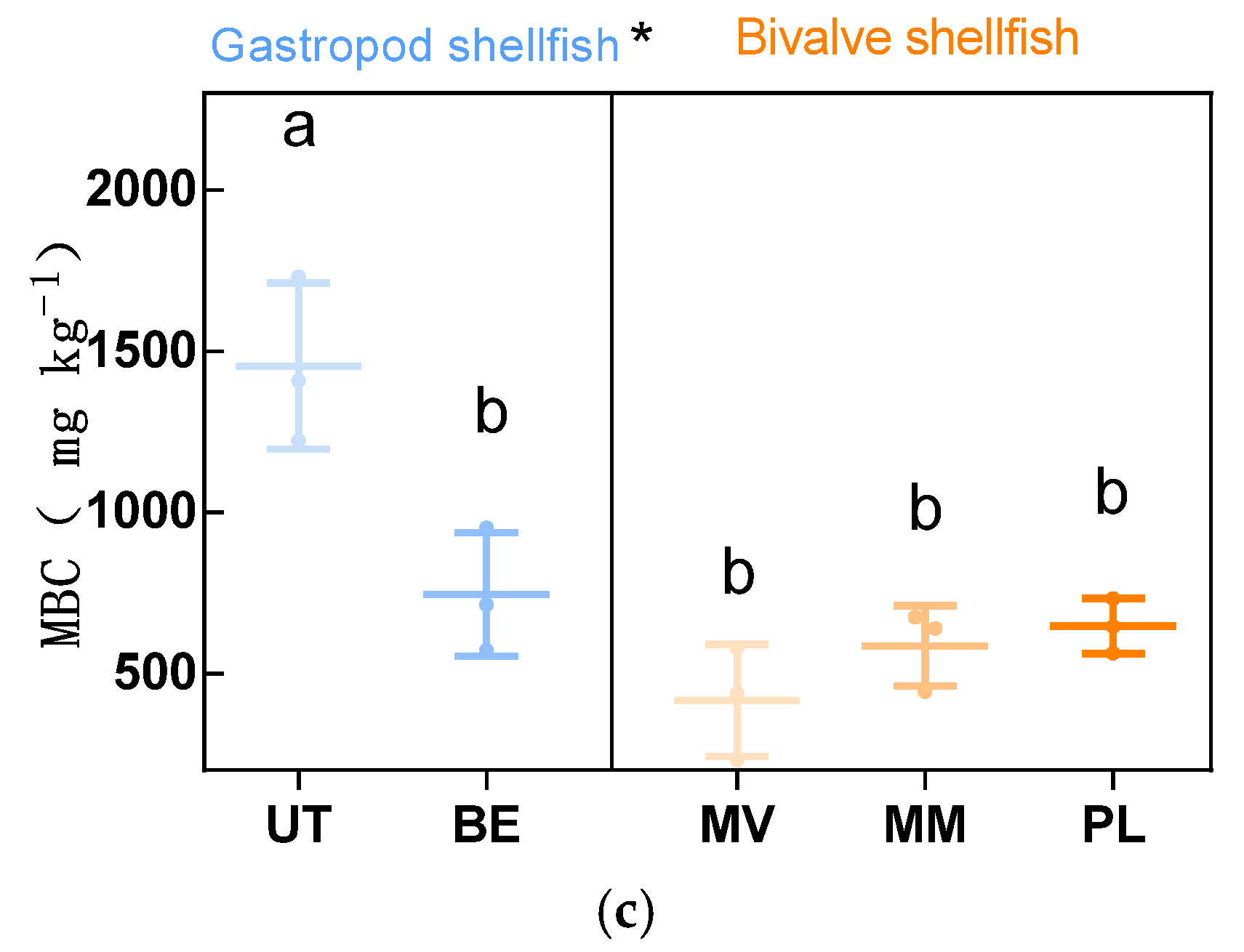


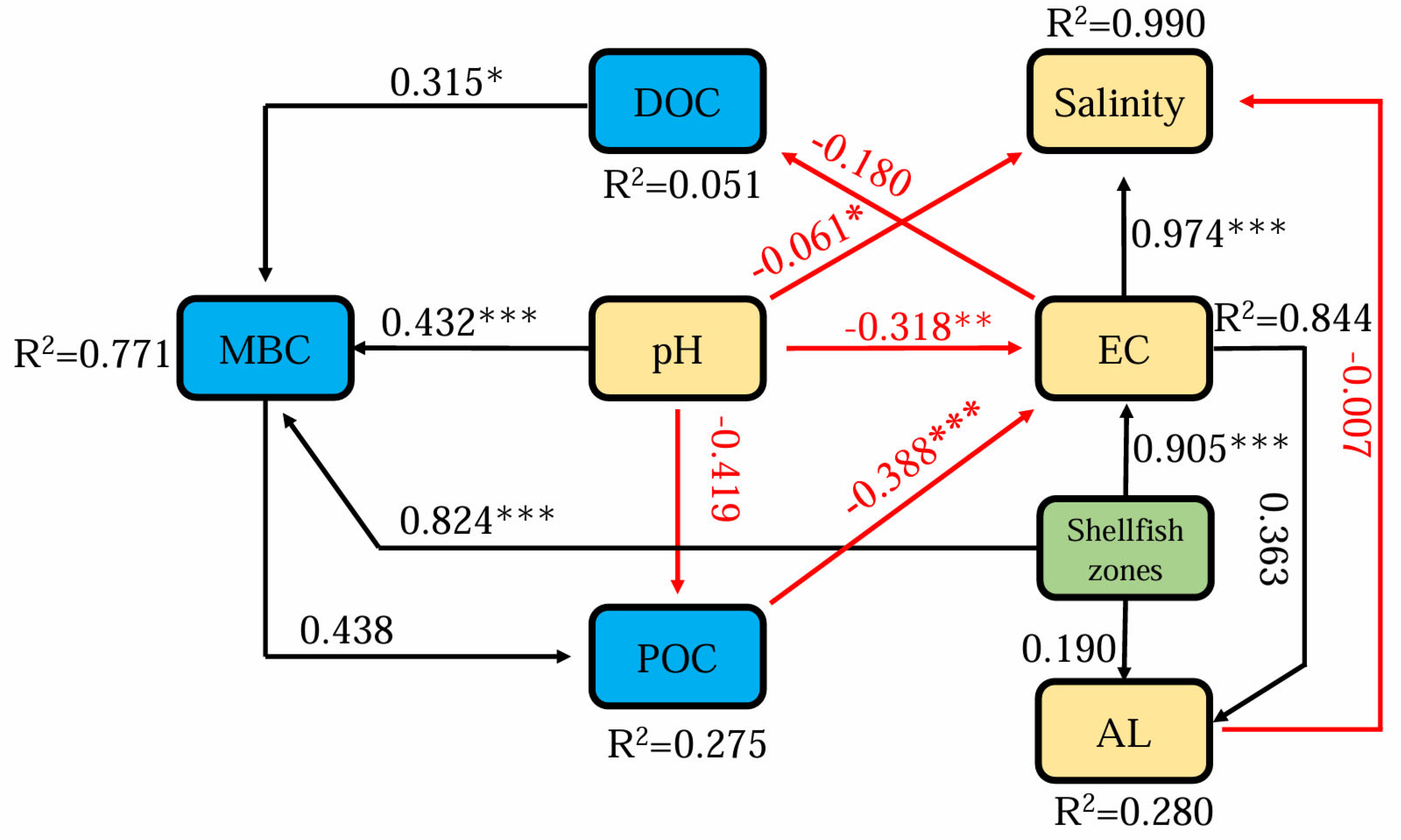



| Site | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|
| BE area | 121.83814598 | 40.70742592 |
| UT area | 121.88582885 | 40.68225399 |
| MV area | 121.90727995 | 40.73062954 |
| MM area | 121.87419763 | 40.66285293 |
| PL area | 121.85773738 | 40.78455639 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Q.; Li, B.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Sun, M.; Zeng, R.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, C. Divergent Response of Blue Carbon Components and Microbial Communities in Sediments to Different Shellfish Zones of Geligang, Liaodong Bay, China. Water 2025, 17, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121728
Hu Q, Li B, Bai Y, Zheng F, Sun M, Zeng R, Wang X, Li X, Zhu C. Divergent Response of Blue Carbon Components and Microbial Communities in Sediments to Different Shellfish Zones of Geligang, Liaodong Bay, China. Water. 2025; 17(12):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121728
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Qingbiao, Bingyu Li, Yongan Bai, Fangliang Zheng, Muzhan Sun, Ruiqi Zeng, Xuetong Wang, Xiaodong Li, and Chunyu Zhu. 2025. "Divergent Response of Blue Carbon Components and Microbial Communities in Sediments to Different Shellfish Zones of Geligang, Liaodong Bay, China" Water 17, no. 12: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121728
APA StyleHu, Q., Li, B., Bai, Y., Zheng, F., Sun, M., Zeng, R., Wang, X., Li, X., & Zhu, C. (2025). Divergent Response of Blue Carbon Components and Microbial Communities in Sediments to Different Shellfish Zones of Geligang, Liaodong Bay, China. Water, 17(12), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121728






