Biological Treatment of Nitroaromatics in Wastewater
Abstract
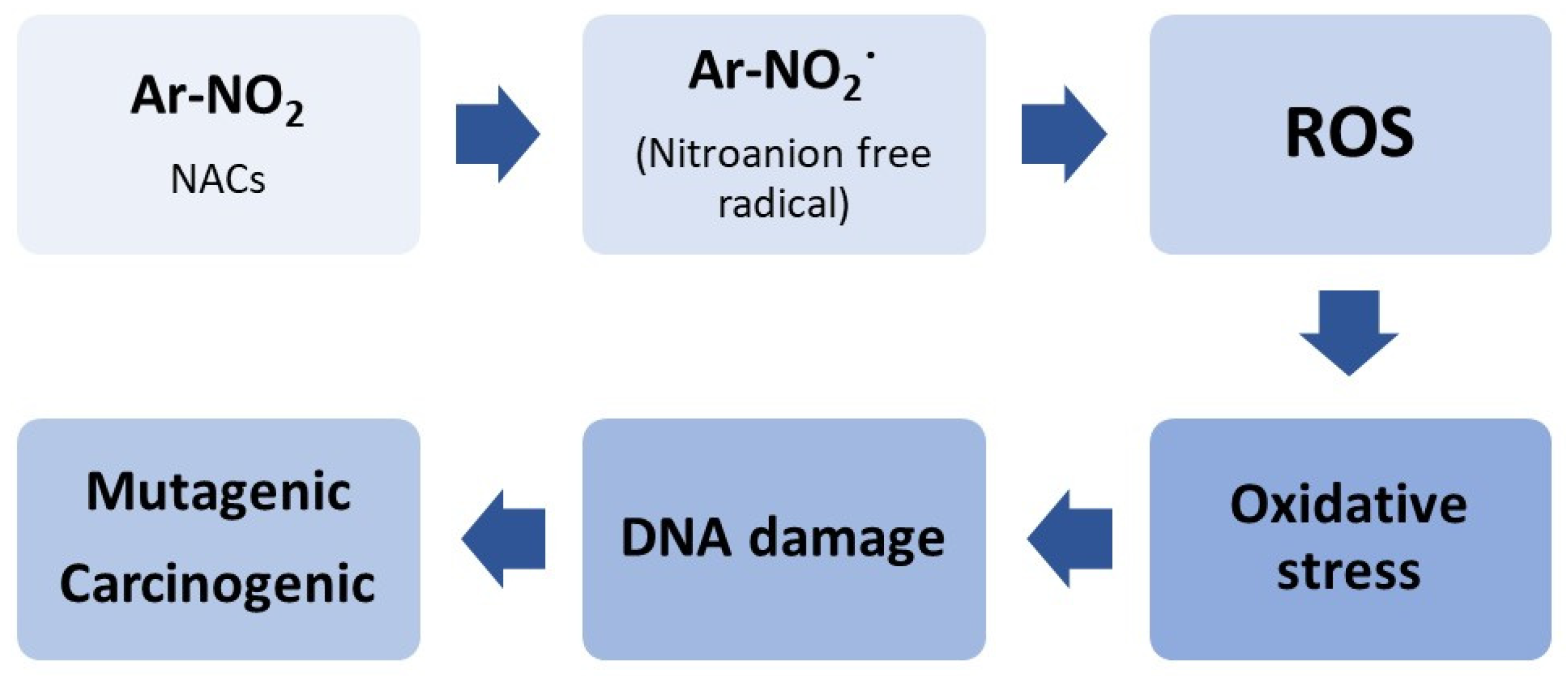
1. Introduction
2. Bioremediation of NACs
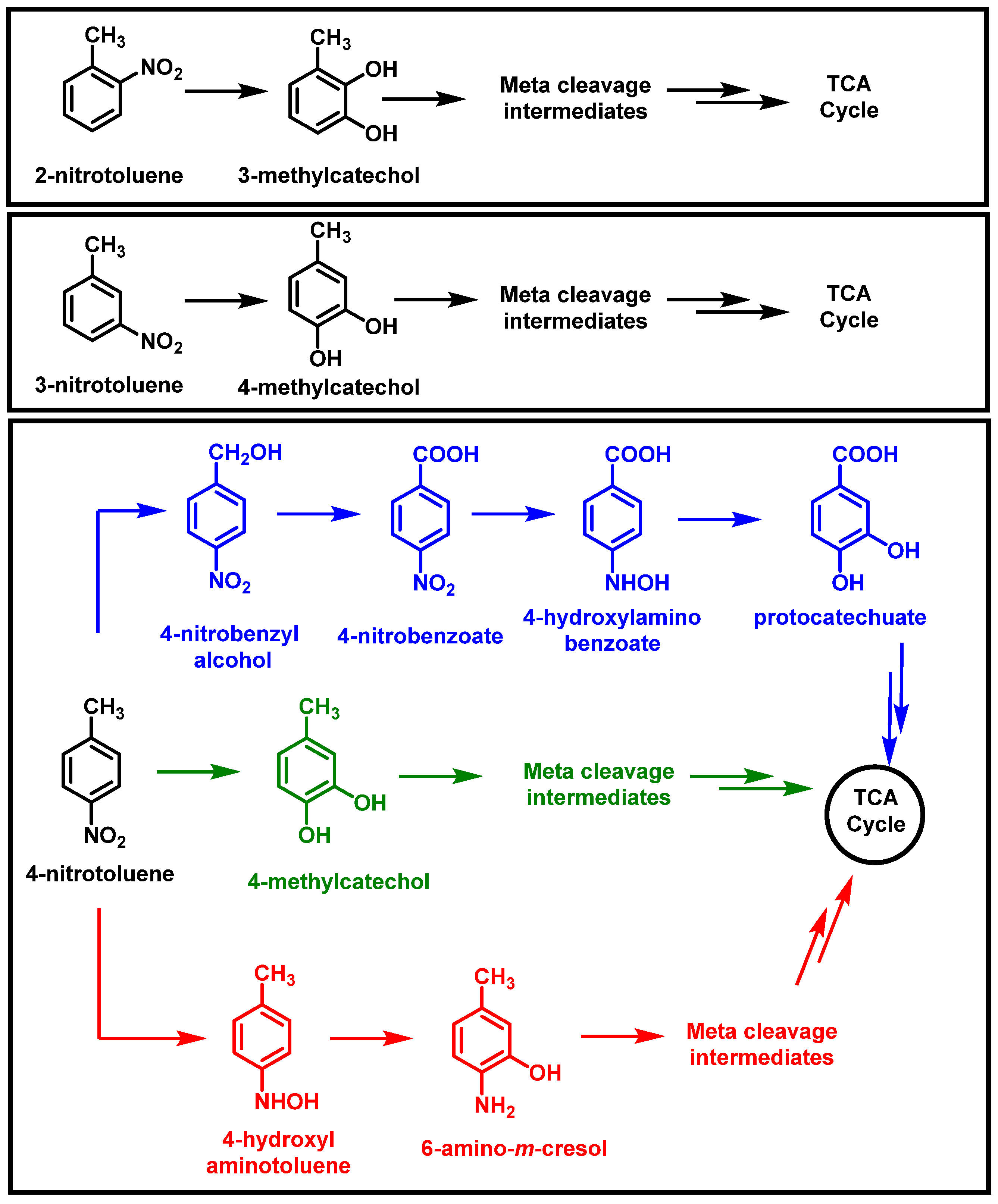
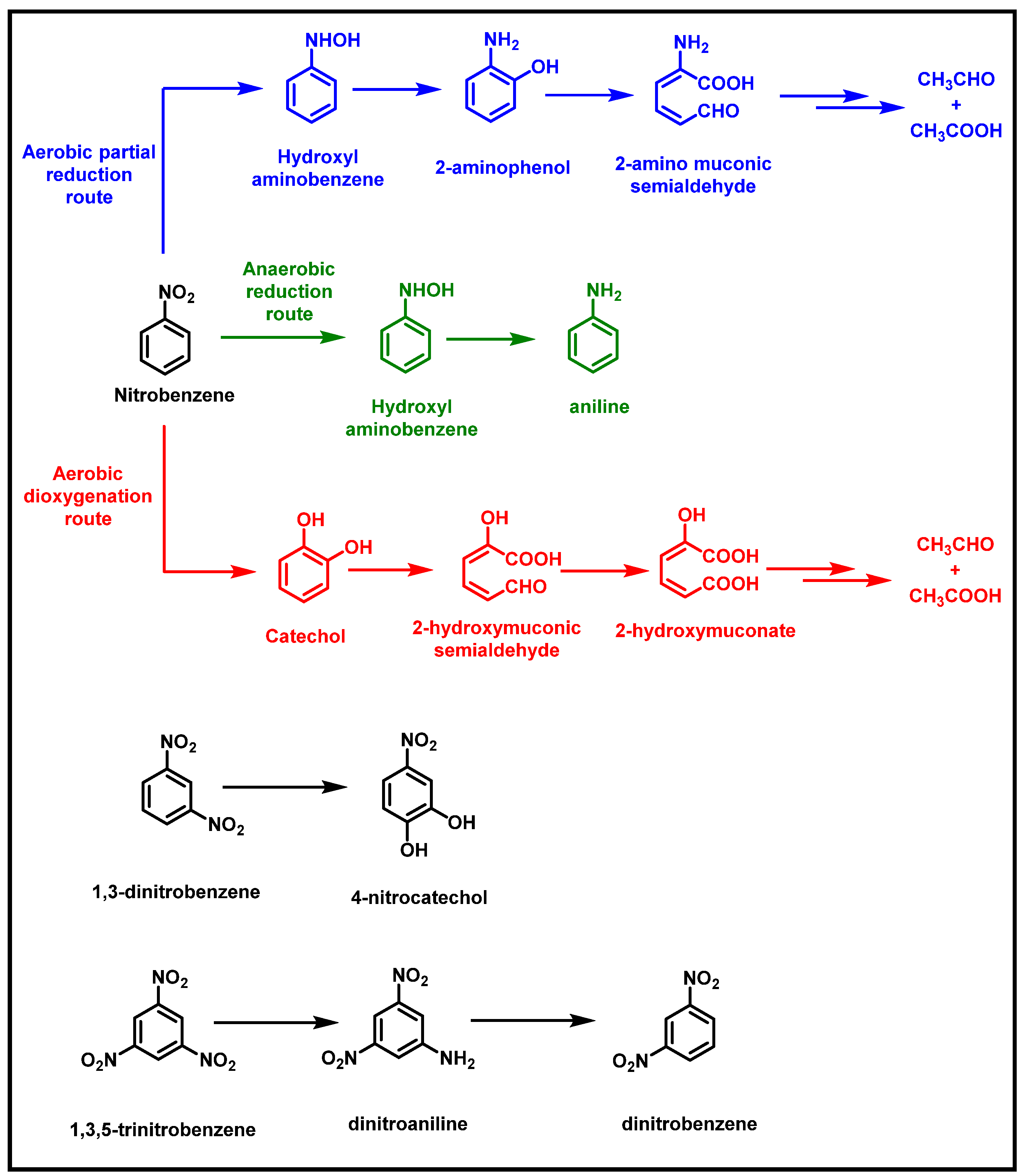
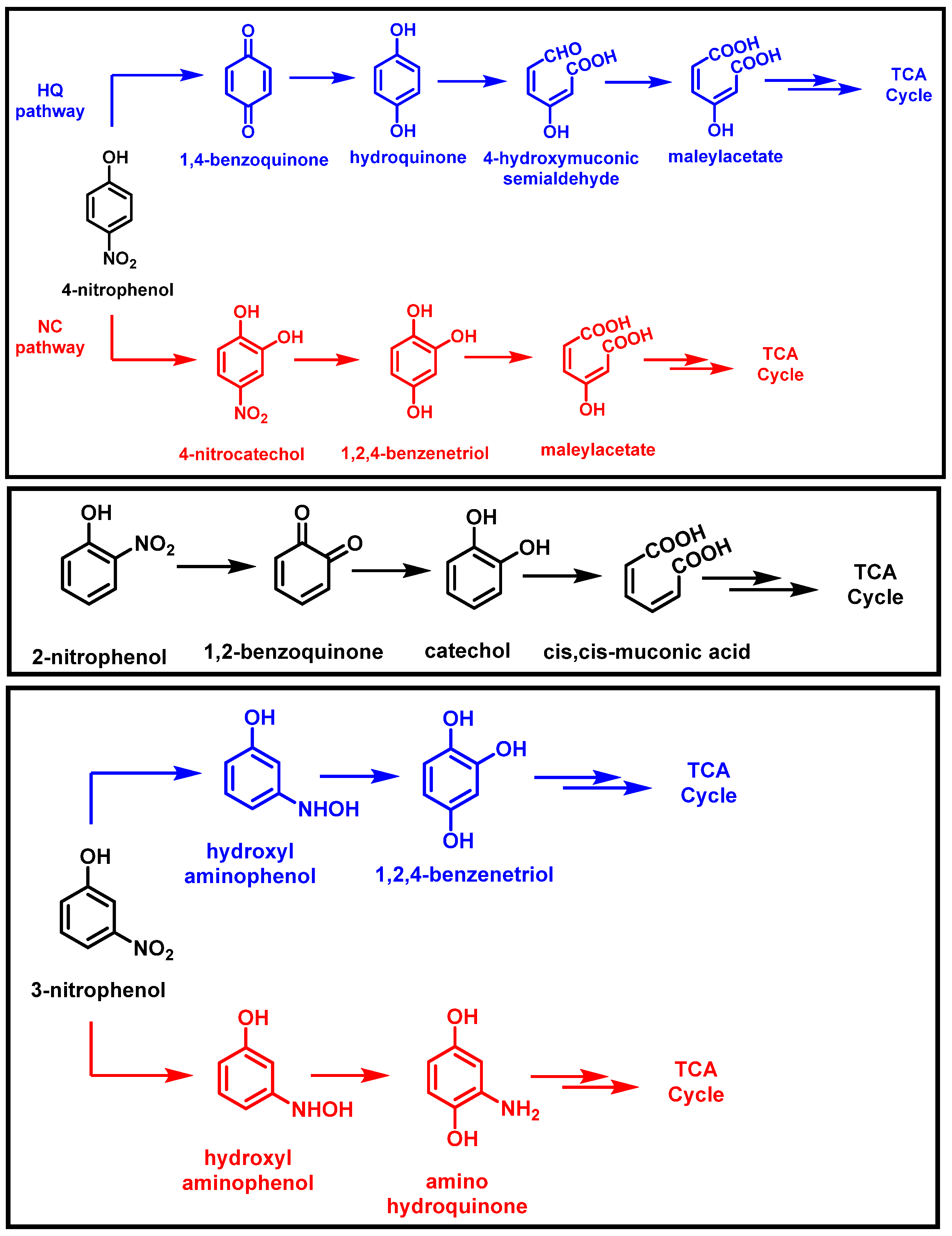
2.1. Bacterial Degradation of NACs under Aerobic Conditions
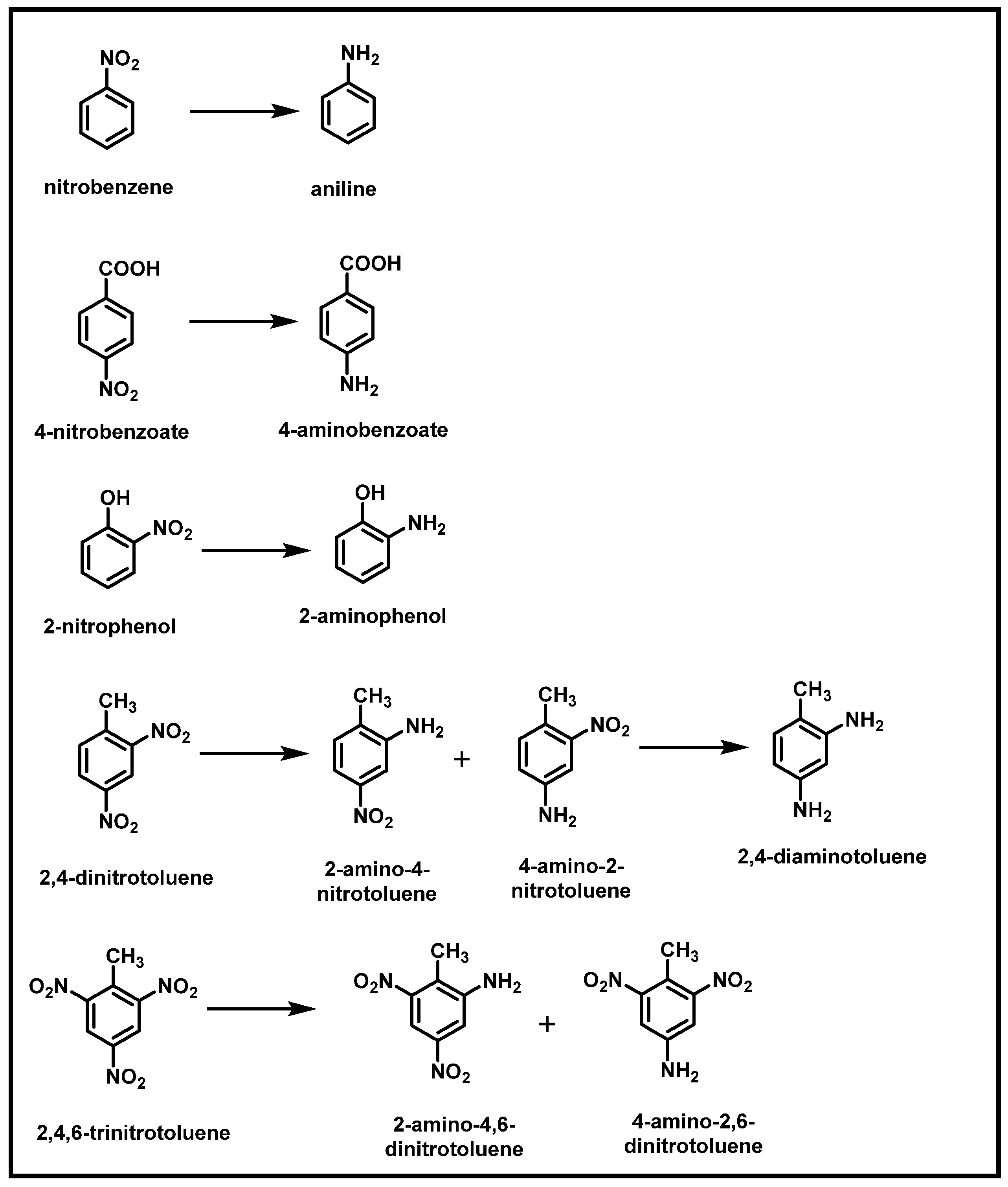
2.2. Bacterial Degradation of NACs under Anaerobic Conditions
2.3. Degradation of NACs by Fungi, Yeast, and Algae
3. Biological Treatment Methods for NAC Removal from Wastewater
3.1. Activated Sludge Process
3.2. Sequencing Batch Reactor
3.3. Biofilm-Based Reactor
3.4. Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor
3.5. Membrane Bioreactor
3.6. Microbial Fuel Cells
3.7. Constructed Wetlands
| Bioreactor | Biomass | NACs | Condition | Carbon Source | NAC Removal Efficiency (%) | Degradation Products | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slurry bubble column | Activated sludge | 4-NP | Aerobic | None | 100% | - | [90] |
| SBR | Granular sludge | NB | Aerobic | None | 100% | CO2 | [91] |
| SBR | Activated sludge | 4-NP | Aerobic | Glucose | 100% | CO2 | [95,134] |
| SBR | Granular sludge | 4-NP | Aerobic | Acetate | 100% | CO2 | [96] |
| SBR | Rhodococcus opacus strain JW01 | TNP | Aerobic | Glucose | >99.9% | CO2 | [135] |
| SBR | Nitrifying sludge | 4-NP | Aerobic | Glucose | 99.9% | - | [93] |
| UASB | Anaerobic sludge | 4-NP | Anaerobic | Sodium acetate | 96–100 | 4-AP | [110] |
| UASB | Granular sludge | 2,6-DNP | Anaerobic | Glucose, sodium acetate | >98% | - | [111] |
| UASB | Anaerobic granular sludge | 2-NP, 4-NP, 2,4-DNP | Anaerobic | Sodium acetate | >99% | 2-AP, 4-AP, 2-A,4-NP | [112] |
| UASB | Anaerobic sludge | 3-NP | Anaerobic | Sodium acetate | >95% | 3-AP | [113] |
| ABR | Anaerobic granular sludge | 4-NP | Anaerobic | Glucose | 99% | 4-AP, phenol, ammonia | [136] |
| AMBR | Anaerobic granular sludge | 4-NP | Anaerobic | Glucose | 94% | 4-AP | [116] |
| Packed bed biofilm reactor | Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6 | 4-NP | Aerobic | None | 100% | CO2 | [137] |
| Biological aerated filter (BAF) reactor | Rhodococcus sp. NJUST16 | TNP | Aerobic | None | 98% | CO2 | [107] |
| BAF and anaerobic filter (AF) | B925 | TNT | Anaerobic–aerobic | Ethanol | 100% | CO2 | [108] |
| Aerobic biological fluidized bed (ABFB) reactor | Activated sludge | 4-NP | Aerobic | None | 99% | CO2 | [100] |
| Membrane-aerated biofilm reactor (MBR) | Activated sludge | 4-NP | Aerobic | None | 94.40% | CO2 | [101] |
| Anaerobic semi-fixed bed biofilm reactor | Anaerobic digestion sludge | 4-NP | Anaerobic | Glucose | 98% | 4-AP | [138] |
| MBR | Activated sludge | 4-NP | Anoxic–aerobic | None | 95.86% | CO2 | [119] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ju, K.-S.; Parales, R.E. Nitroaromatic Compounds, from Synthesis to Biodegradation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Bagheri, A.R.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Environmental Occurrence, Toxicity Concerns, and Remediation of Recalcitrant Nitroaromatic Compounds. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 291, 112685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soojhawon, I.; Lokhande, P.D.; Kodam, K.M.; Gawai, K.R. Biotransformation of Nitroaromatics and Their Effects on Mixed Function Oxidase System. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2005, 37, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Hirata, Y.; Kishida, M.; Mori, Y.; Kondo, A.; Noda, S.; Tanaka, T. P-Nitrobenzoate Production from Glucose by Utilizing p-Aminobenzoate N-Oxygenase: AurF. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 171, 110321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.; Chaudhari, A. Microbial Remediation of Nitro-Aromatic Compounds: An Overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 496–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacic, P.; Somanathan, R. Nitroaromatic Compounds: Environmental Toxicity, Carcinogenicity, Mutagenicity, Therapy and Mechanism. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, J.; Tarale, P.; Sivanesan, S.; Bafana, A. Environmental Persistence, Hazard, and Mitigation Challenges of Nitroaromatic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 28650–28667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.; Shang, J.; Khazi, M.I.; Kumar, N.; Lisak, G. Metal-Organic Framework for Sorptive/Catalytic Removal and Sensing Applications against Nitroaromatic Compounds. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 84, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.K.; Sasikala, C.; Ramana, C.V. Degradation of Chlorinated Nitroaromatic Compounds. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2265–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.Z.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhu, L. Catalytic Ozonation-Biological Coupled Processes for the Treatment of Industrial Wastewater Containing Refractory Chlorinated Nitroaromatic Compounds. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Jia, R.; Xie, K.; Xu, X. Bioreduction of Para-Chloronitrobenzene in Drinking Water Using a Continuous Stirred Hydrogen-Based Hollow Fiber Membrane Biofilm Reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Pan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, P.; Qiu, G.; Shan, K.; Chu, X. Accelerated Removal of High Concentration P-Chloronitrobenzene Using Bioelectrocatalysis Process and Its Microbial Communities Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Deng, Y.D.; Chen, Z.F.; Zuo, Z.H.; Tian, Y.S.; Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.J.; Han, H.J.; Li, Z.J.; et al. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for 2,4-Dinitrotoluene Degradation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ning, G.; Li, F.; Sheng, G.D. Biotransformation of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene by Obligate Marine Shewanella marisflavi EP1 under Anaerobic Conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 180, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Goel, S.S.; Ramanathan, G.; Ronen, Z. Biotransformation of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene by Diaphorobacter Sp. Strain DS2. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 120749–120762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Robota, I.V.; Mazur, D.M.; Lebedev, A.T.; Golovleva, L.A. Application of Bacillus Sp. Strain VT-8 for Decontamination of TNT-Polluted Sites. Microbiology 2014, 83, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.K.; Sharma, A. New Metabolic Pathway for Degradation of 2-Nitrobenzoate by Arthrobacter Sp. SPG. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhang, F.J.; Deng, Y.D.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.J.; Tian, Y.S.; Peng, R.H.; Yao, Q.H. Biodegradation of P-Nitrophenol by Engineered Strain. AMB Express 2021, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.A.; Khaled, H.E.; Elsayed, A.K. Long-Term Exposure to p-Nitrophenol Induces Hepatotoxicity via Accelerating Apoptosis and Glycogen Accumulation in Male Japanese Quails. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44420–44431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Z.; Xie, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, G.; Huang, J. Study on the Aerobic Biodegradability and Degradation Kinetics of 3-NP; 2,4-DNP and 2,6-DNP. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241–242, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.S.; Copello, G.J.; Rao, A.L.J. HPLC-UV Platform for Trace Analysis of Three Isomeric Mononitrophenols in Water with Chitin Based Solid Phase Extraction. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4143–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, A.; Elend, M.; Gerling, S.; Berger-Preiss, E.; Steinbach, K. Identification of Highly Polar Nitroaromatic Compounds in Leachate and Ground Water Samples from a TNT-Contaminated Waste Site by LC-MS, LC-NMR, and off-Line NMR and MS Investigations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.K.; Bae, H. Toxicity and Microbial Degradation of Nitrobenzene, Monochloronitrobenzenes, Polynitrobenzenes, and Pentachloronitrobenzene. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 265140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma-Takeda, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Ohkuma, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Murata, M.; Ogawa, K.; Iwamuro, T.; Li, S.; Sun, G.F.; Kumagai, Y.; et al. 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene-Induced Reproductive Toxicity via Oxidative DNA Damage by Its Metabolite. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Varshney, A.; Mohan, S.; Dahiya, P. An Innovative Approach of Bioremediation in Enzymatic Degradation of Xenobiotics. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2022, 38, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Singh, A.; Ward, O.P. Biodegradation of Nitroaromatics and Other Nitrogen-Containing Xenobiotics. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 20, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y. Recent Advances in Biological Removal of Nitroaromatics from Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.K.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, V.P. Bacterial Degradation of Nitrophenols and Their Derivatives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; He, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, C.; Zhou, Z. Biodegradation of Nitrobenzene in a Lysogeny Broth Medium by a Novel Halophilic Bacterium Bacillus licheniformis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.H.; Khan, N.A.; Ahmed, S.; Dhingra, A.; Singh, C.P.; Khan, S.U.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Changani, F.; Yousefi, M.; Alam, S.; et al. Application of Advanced Oxidation Processes Followed by Different Treatment Technologies for Hospital Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, B. Macroscopic and Spectroscopic Investigations of the Adsorption of Nitroaromatic Compounds on Graphene Oxide, Reduced Graphene Oxide, and Graphene Nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6181–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.D.; Bunce, N.J. Treatment Methods for the Remediation of Nitroaromatic Explosives. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.; Gandhi, D.; Sivanesan, S.; Naoghare, P.; Bafana, A. Remediation of Different Nitroaromatic Pollutants by a Promising Agent of Cupriavidus Sp. Strain A3. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, Z.C.; Bruce, N.C. Bacterial Pathways for Degradation of Nitroaromatics. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.L.; Zhao, S.P.; Lai, J.L.; Yang, X.; Dong, B.; Zhu, Y.B.; Zhang, Y. Oxygen-Insensitive Nitroreductase Bacteria-Mediated Degradation of TNT and Proteomic Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 116227–116238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Goel, S.S.; Siebner, H.; Ronen, Z.; Ramanathan, G. Transformation of 2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene by Stenotrophomonas Strain SG1 under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Siebner, H.; Ramanathan, G.; Ronen, Z. Inhibition Effect of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) on RDX Degradation by Rhodococcus Strains Isolated from Contaminated Soil and Water. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 120018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Mishra, K.; Ramanthan, G. Bioremediation of Nitroaromatic Compounds. In Wastewater Treatment Engineering; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friemann, R.; Ivkovic-Jensen, M.M.; Lessner, D.J.; Yu, C.L.; Gibson, D.T.; Parales, R.E.; Eklund, H.; Ramaswamy, S. Structural Insight into the Dioxygenation of Nitroarene Compounds: The Crystal Structure of Nitrobenzene Dioxygenase. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Kumari, A.; Ramaswamy, S.; Ramanathan, G. Expression, Purification and Substrate Specificities of 3-Nitrotoluene Dioxygenase from Diaphorobacter Sp. Strain DS2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessner, D.J.; Johnson, G.R.; Parales, R.E.; Spain, J.C.; Gibson, D.T. Molecular Characterization and Substrate Specificity of Nitrobenzene Dioxygenase from Comamonas Sp. Strain JS765. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.F.; Hu, H.; Liu, D.F.; Ding, H.T.; Jia, X.M.; Zhao, Y.H. Optimization of a Bacterial Consortium for Nitrobenzene Degradation. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Su, Y.M.; Liu, N.; Hong, M. Effects of Temperature, PH, and Salinity on the Growth Kinetics of Pseudomonas Sp. NB-1, a Newly Isolated Cold-Tolerant, Alkali-Resistant, and High-Efficiency Nitrobenzene-Degrading Bacterium. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 2171–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Pandey, G.; Sharma, N.K.; Paul, D.; Pandey, J.; Jain, R.K. P-Nitrophenol Degradation via 4-Nitrocatechol in Burkholderia Sp. SJ98 and Cloning of Some of the Lower Pathway Genes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3435–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ren, L.; Jia, Y.; Ruth, N.; Shi, Y.; Qiao, C.; Yan, Y. Degradation Characteristics and Metabolic Pathway of 4-Nitrophenol by a Halotolerant Bacterium Arthrobacter Sp. CN2. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2016, 98, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.S.; Sivaramakrishna, A.; Mehta, A. Bioremediation of P-Nitrophenol by Pseudomonas putida 1274 Strain. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, N.Y. Molecular Characterization of a Novel Ortho-Nitrophenol Catabolic Gene Cluster in Alcaligenes Sp. Strain NyZ215. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 6587–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, H.Z.; Hao, F.; Rayner, S.; Tang, H.; Zhou, N.Y. Characterization of Catabolic Meta-Nitrophenol Nitroreductase from Cupriavidus necator JMP134. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, H.; Abe, K.; Hasegawa, Y. Isolation and Characterization of a New 2,4-Dinitrophenol-Degrading Bacterium Burkholderia sp. Strain KU-46 and Its Degradation Pathway. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 274, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirooka, T.; Nagase, H.; Hirata, K.; Miyamoto, K. Degradation of 2,4-Dinitrophenol by a Mixed Culture of Photoautotrophic Microorganisms. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Kapley, A.; Purohit, H.J. Degradation of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) by Arthrobacter Sp. HPC1223 Isolated from Effluent Treatment Plant. Indian J. Microbiol. 2012, 52, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; He, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Han, W. Biodegradation Kinetics of Picric Acid by Rhodococcus sp. NJUST16 in Batch Reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, S.; Fischer, P.; Knackmuss, H.J. Converging Catabolism of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (Picric Acid) and 2,4-Dinitrophenol by Nocardioides simplex FJ2-1A. Biodegradation 2001, 12, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okozide, O.E.; Adebusoye, S.A.; Obayori, O.S.; Rodrigues, D.F. Aerobic Degradation of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol by Proteus Sp. Strain OSES2 Obtained from an Explosive Contaminated Tropical Soil. Biodegradation 2021, 32, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Han, W.; He, R. Biodegradation of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol by Rhodococcus sp. Isolated from a Picric Acid-Contaminated Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Ramanathan, G. Biomineralization of 3-Nitrotoluene by Diaphorobacter Species. Biodegradation 2013, 24, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, N.Y. Biodegradation of 3-Nitrotoluene by Rhodococcus Sp. Strain ZWL3NT. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9217–9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, S.I.; Hoskeri, R.S.; Shouche, Y.S.; Ninnekar, H.Z. Biodegradation of 2-Nitrotoluene by Micrococcus Sp. Strain SMN-1. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.S.; Parales, R.E. Evolution of a New Bacterial Pathway for 4-Nitrotoluene Degradation. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 82, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küce, P.; Coral, G.; Kantar, Ç. Biodegradation of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene (DNT) by Arthrobacter Sp. K1 Isolated from a Crude Oil Contaminated Soil. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, S.F.; Paoli, G.C.; Spain, J.C. Aerobic Degradation of Dinitrotoluenes and Pathway for Bacterial Degradation of 2,6-Dinitrotoluene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, M.Á.; Márquez, S.L.; Quezada, C.P.; Osorio, M.I.; Castro-Nallar, E.; González-Nilo, F.D.; Pérez-Donoso, J.M. Biotransformation of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene by Pseudomonas Sp. TNT3 Isolated from Deception Island, Antarctica. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, K.; Van Landuyt, J.; Mattelin, V.; Martin, B.; Neyts, M.; Parmentier, K.; Boon, N. Enhanced Removal of Warfare Agent Tri-Nitro-Toluene by a Methylophaga-Dominated Microbiome. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, J.; Anand, S.; Dutta, J.; Rai, P.K. 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) Degradation by Indiicoccus Explosivorum (S5-TSA-19). Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi-Ben Moshe, S.; Ronen, Z.; Dahan, O.; Weisbrod, N.; Groisman, L.; Adar, E.; Nativ, R. Sequential Biodegradation of TNT, RDX and HMX in a Mixture. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulla, S.I.; Manjunatha, T.P.; Hoskeri, R.S.; Tallur, P.N.; Ninnekar, H.Z. Biodegradation of 3-Nitrobenzoate by Bacillus flexus Strain XJU-4. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Chowdhury, P.P.; Deb, S.; Dutta, T.K. Degradation Pathways of 2- and 4-Nitrobenzoates in Cupriavidus Sp. Strain ST-14 and Construction of a Recombinant Strain, ST-14::3NBA, Capable of Degrading 3-Nitrobenzoate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4253–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Peres, C.M.; Russ, R.; Lenke, H.; Agathos, S.N. Biodegradation of 4-Nitrobenzoate, 4-Aminobenzoate and Their Mixtures: New Strains, Unusual Metabolites and Insights into Pathway Regulation. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 37, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, H.; Hasegawa, Y. Degradation of 2-Nitrobenzoate by Burkholderia terrae Strain KU-15. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Ye, Z.F.; Zhang, M.H. Bioremediation of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT) in Immobilized Micro-Organism Biological Filter. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, N.G.; Feeherry, F.E.; Levinson, H.S. Microbial Transformation of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene and Other Nitroaromatic Compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 31, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.F.; Min, D.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.B.; Xiao, X.; Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q. Anaerobic Reduction of 2,6-Dinitrotoluene by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1: Roles of Mtr Respiratory Pathway and NfnB. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathy, R. Anaerobic Metabolism and Bioremediation of Explosives-Contaminated Soil. In Advances in Applied Bioremediation; Singh, A., Kuhad, R.C., Ward, O.P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 151–172. ISBN 978-3-540-89621-0. [Google Scholar]
- Razo-Flores, E.; Lettinga, G.; Field, J.A. Biotransformation and Biodegradation of Selected Nitroaromatics under Anaerobic Conditions. Biotechnol. Prog. 1999, 15, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, H.; Tanaka, H.; Wariishi, H. Fungal Cytochrome P450s Catalyzing Hydroxylation of Substituted Toluenes to Form Their Hydroxymethyl Derivatives. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 234, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Teramoto, H.; Tanaka, H.; Wariishi, H. Degradation of 4-Nitrophenol by the Lignin-Degrading Basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 66, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.; Carabajal, M.; Hofrichter, M.; Ullrich, R. Degradation of 4-Nitrophenol by the White-Rot Polypore Trametes versicolor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 107, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasonye, F.; Winquist, E.; Räsänen, M.; Kontro, J.; Björklöf, K.; Vasilyeva, G.; Jørgensen, K.S.; Steffen, K.T.; Tuomela, M. Bioremediation of TNT Contaminated Soil with Fungi under Laboratory and Pilot Scale Conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 105, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-González, M.Y.; Chandra, R.; Castillo-Zacarias, C.; Robledo-Padilla, F.; Rostro-Alanis, M.D.J.; Parra-Saldivar, R. Biotransformation and Degradation of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene by Microbial Metabolism and Their Interaction. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziganshin, A.M.; Naumova, R.P.; Pannier, A.J.; Gerlach, R. Influence of PH on 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene Degradation by Yarrowia lipolytica. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Qu, B.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Zhao, H. Aerobic Degradation of Nitrobenzene by Immobilization of Rhodotorula Mucilaginosa in Polyurethane Foam. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khromykh, N.O.; Marenkov, O.M.; Sharamok, T.S.; Anishchenko, A.O.; Yesipova, N.B.; Nesterenko, O.S.; Kurchenko, V.O.; Mylostyvyi, R.V. Simulating 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) Elimination in a Pond Inhabited by Freshwater Algae of the Rhizoclonium Genus. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2023, 14, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, F.; Ma, H.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, Z.; Liu, D. Bio-Reaction of Nitrobenzene with Microcystis aeruginosa: Characteristics, Kinetics and Application. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.F.; Cheng, P.; Choi, M.M.F.; Poon, K. Stress Response of Chlorella Pyrenoidosa to Nitro-Aromatic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3784–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Hasanan, K.; Abdullah, M.; Badr, O.A.; Awad, H.M.; Elsamadony, M.; El-Dissouky, A.; Qyyum, M.A.; Nizami, A.S. Graphene Enhanced Detoxification of Wastewater Rich 4-Nitrophenol in Multistage Anaerobic Reactor Followed by Baffled High-Rate Algal Pond. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Uribe, O.; Cheney, D.P.; Rorrer, G.L. Comparison of TNT Removal from Seawater by Three Marine Macroalgae. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinharoy, A.; Lens, P.N.L. Biological Removal of Selenate and Selenite from Wastewater: Options for Selenium Recovery as Nanoparticles. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Tang, Q.; Wu, M.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Qu, Y. Performance and Microbial Community Analysis of Bioaugmented Activated Sludge for Nitrogen-Containing Organic Pollutants Removal. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineta, R.; Salehi, Z.; Yoshikawa, H.; Kawase, Y. Oxygen Transfer during Aerobic Biodegradation of Pollutants in a Dense Activated Sludge Slurry Bubble Column: Actual Volumetric Oxygen Transfer Coefficient and Oxygen Uptake Rate in p-Nitrophenol Degradation by Acclimated Waste Activated Sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 53, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, Z.; Yoshikawa, H.; Mineta, R.; Kawase, Y. Aerobic Biodegradation of P-Nitrophenol by Acclimated Waste Activated Sludge in a Slurry Bubble Column. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q. Biodegradation of Nitrobenzene by Aerobic Granular Sludge in a Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR). Desalination 2011, 281, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.H.; Silverstein, J.A. Acclimation of Activated Sludge to Degrade Toxic Levels of 2,4-Dinitrophenol. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, D.; Yan, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Du, B.; Wang, Q.; Hou, H. Aerobic Biodegradation of P-Nitrophenol in a Nitrifying Sludge Bioreactor: System Performance, Sludge Property and Microbial Community Shift. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.; González, D.; Estival, A.; Buitrón, G. Comparison of Two Types of Inocula during Acclimation and Stable Operation for Nitrophenol Biodegradation in an Anaerobic-Aerobic SBR. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Hernández, M.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E.; Carrera, J. Bioaugmentation for Treating Transient or Continuous P-Nitrophenol Shock Loads in an Aerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suja, E.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Venugopalan, V.P. P-Nitrophenol Biodegradation by Aerobic Microbial Granules. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-H.; Yan, X.-L. Biodegradation of 2,4-Dinitrophenol under Denitrification Conditions. Technology 2010, 7, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Ye, Z. Insight into the Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Denitrifying Biofilms under Nitrobenzene Exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Ji, M.; Nghiem, L.D.; Trinh, Q.T.; Tran, N.H. Insights into Biofilm Carriers for Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes: Current State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Yuan, Y.; Lai, B. Microbial Community Dynamics in Aerated Biological Fluidized Bed (ABFB) with Continuously Increased p-Nitrophenol Loads. Process Biochem. 2017, 63, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Assessing the Performance and Microbial Structure of Biofilms in Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor for High P-Nitrophenol Concentration Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.J.; Fortunato, M.S.; Papalia, M.; Radice, M.; Gutkind, G.; Magdaleno, A.; Gallego, A.; Korol, S.E. Selection and Identification of a Bacterial Community Able to Degrade and Detoxify M-Nitrophenol in Continuous Biofilm Reactors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhu, G.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y. Iron Carriers Promote Biofilm Formation and P-Nitrophenol Degradation. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Ge, R.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Xia, X.; Zhang, F. Simultaneous Removal of Nitrate, Nitrobenzene and Aniline from Groundwater in a Vertical Baffled Biofilm Reactor. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, M.; Guo, Z.; et al. A Novel Membrane-Aerated Biofilter for the Enhanced Treatment of Nitroaniline Wastewater: Nitroaniline Biodegradation Performance and Its Influencing Factors. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Zhao, Z.W.; Gao, W.; Cui, F.Y. Study on the Factors Affecting Simultaneous Removal of Ammonia and Manganese by Pilot-Scale Biological Aerated Filter (BAF) for Drinking Water Pre-Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; He, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Xu, L. Biodegradation of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (Picric Acid) in a Biological Aerated Filter (BAF). Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bai, X. Degradation of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) by Immobilized Microorganism-Biological Filter. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Davies, C.; Ikumi, D.S. Performance of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactor and Other Anaerobic Reactor Configurations for Wastewater Treatment: A Comparative Review and Critical Updates. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-AQUA 2018, 67, 858–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Hua, C.X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.B.; Shen, J.Y. P-Nitrophenol (PNP) Removal in an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactor. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 864–867, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Z.; Shi, E.; Fu, X.; Wu, J.; Jiang, L.; Guo, L. Acclimation of Anaerobic Granular Sludge and 2,6-DNP Removal in the Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactors. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 183–185, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, K.; Gupta, S.K. Continuous Biotransformation and Removal of Nitrophenols under Denitrifying Conditions. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2953–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, T.; Jiang, L.; Gao, M. Degradation of 3-Nitrophenol with Sodium Acetate as Co-Substrate in an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 393–395, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Han, X.; Lu, H.; Zhou, J. Study of Archaea Community Structure during the Biodegradation Process of Nitrobenzene Wastewater in an Anaerobic Baffled Reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angenent, L.T.; Sung, S. Development of Anaerobic Migrating Blanket Reactor (AMBR), a Novel Anaerobic Treatment System. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuşçu, Ö.S.; Sponza, D.T. Kinetics of Para-Nitrophenol and Chemical Oxygen Demand Removal from Synthetic Wastewater in an Anaerobic Migrating Blanket Reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gede Wenten, I.; Friatnasary, D.L.; Khoiruddin, K.; Setiadi, T.; Boopathy, R. Extractive Membrane Bioreactor (EMBR): Recent Advances and Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Hu, Z. Biodegradation of Nitrophenol Compounds and the Membrane Fouling Trends in Different Submerged Membrane Bioreactors. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, P.; Bi, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shen, W.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Simultaneous P-Nitrophenol and Nitrogen Removal in PNP Wastewater Treatment: Comparison of Two Integrated Membrane-Aerated Bioreactor Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 363, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, F.Y.; Dong, W.Y. Nitrobenzene Removal from Micro-Polluted Water Resource by a Submerged MBR and the Importance of Activated Sludge. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11300–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.; Verma, P. Microbial Fuel Cell: A Green Approach for the Utilization of Waste for the Generation of Bioelectricity. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2016, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaie, M.; Farhadian, M.; Jeihanipour, A.; Biria, D. Effective Factors on the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cells in Wastewater Treatment—A Review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2015, 4, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Rozendal, R.A.; Rabaey, K.; Keller, J. Nitrobenzene Removal in Bioelectrochemical Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8690–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Geng, M.; Song, H.; Sun, J. Removal of Chloramphenicol and Simultaneous Electricity Generation by Using Microbial Fuel Cell Technology. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 5128–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kong, C.H. Enhanced Removal of P-Nitrophenol in a Microbial Fuel Cell after Long-Term Operation and the Catabolic Versatility of Its Microbial Community. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, F.; Zhai, W.; Scott, K.; Wang, X.; Diao, G. Efficient Removal of Nitrobenzene and Concomitant Electricity Production by Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells with Activated Carbon Air-Cathode. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, S.; Ni, H.; Pei, Y.; Xu, R.; Ling, Z.; Salama, E.S.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Micro-Aeration in Anode Chamber Promotes p-Nitrophenol Degradation and Electricity Generation in Microbial Fuel Cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Hu, J.; Qu, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Hu, J.; Zeng, C. Efficient Reduction of Nitrobenzene by Sulfate-Reducer Enriched Biocathode in Microbial Electrolysis Cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vymaza, J. The Historical Development of Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment. Land 2022, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirui, W.K.; Wu, S.; Lei, M.; Dong, R. Nitrobenzene Degradation Pathways and Their Interaction with Sulfur and Nitrogen Transformations in Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lu, Z.; Tan, S.; Ciren, J.; Tan, C. Effects of Glucose and Starch on the Toxicity of Nitrobenzene to Plants and Microbes in Constructed Wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Jing, Z.; Hu, J.; Yuan, P.; Liu, Y.; Cao, S. Degradation of Nitrobenzene-Containing Wastewater by a Microbial-Fuel-Cell-Coupled Constructed Wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 112, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Li, Y.; Nie, L.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Influence of Plant Radial Oxygen Loss in Constructed Wetland Combined with Microbial Fuel Cell on Nitrobenzene Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Hernández, M.; Carrera, J.; Pérez, J.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E. Enrichment of a K-Strategist Microbial Population Able to Biodegrade p-Nitrophenol in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3871–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidhaas, J.L.; Schroeder, E.D.; Chang, D.P. An Aerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor for 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (Picric Acid) Biodegradation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuşçu, Ö.S.; Sponza, D.T. Performance of Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR) Treating Synthetic Wastewater Containing p-Nitrophenol. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2005, 36, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.K.; Pakshirajan, K.; Ghosh, P.K. Biodegradation of P-Nitrophenol Using Arthrobacter Chlorophenolicus A6 in a Novel Upflow Packed Bed Reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Yu, N.; Chen, Y.; Tong, Q.; Guo, Y. Anaerobic Semi-Fixed Bed Biofilm Reactor (An-SFB-BR) for Treatment of High Concentration p-Nitrophenol Wastewater under Shock Loading Conditions. Biodegradation 2021, 32, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, S.; Ronen, Z. Biological Treatment of Nitroaromatics in Wastewater. Water 2024, 16, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060901
Gupta S, Ronen Z. Biological Treatment of Nitroaromatics in Wastewater. Water. 2024; 16(6):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060901
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Swati, and Zeev Ronen. 2024. "Biological Treatment of Nitroaromatics in Wastewater" Water 16, no. 6: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060901
APA StyleGupta, S., & Ronen, Z. (2024). Biological Treatment of Nitroaromatics in Wastewater. Water, 16(6), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060901