Characterization of Groundwater Geochemistry in an Esker Aquifer in Western Finland Based on Three Years of Monitoring Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Groundwater Studies in Finland
1.2. Objective of the Study
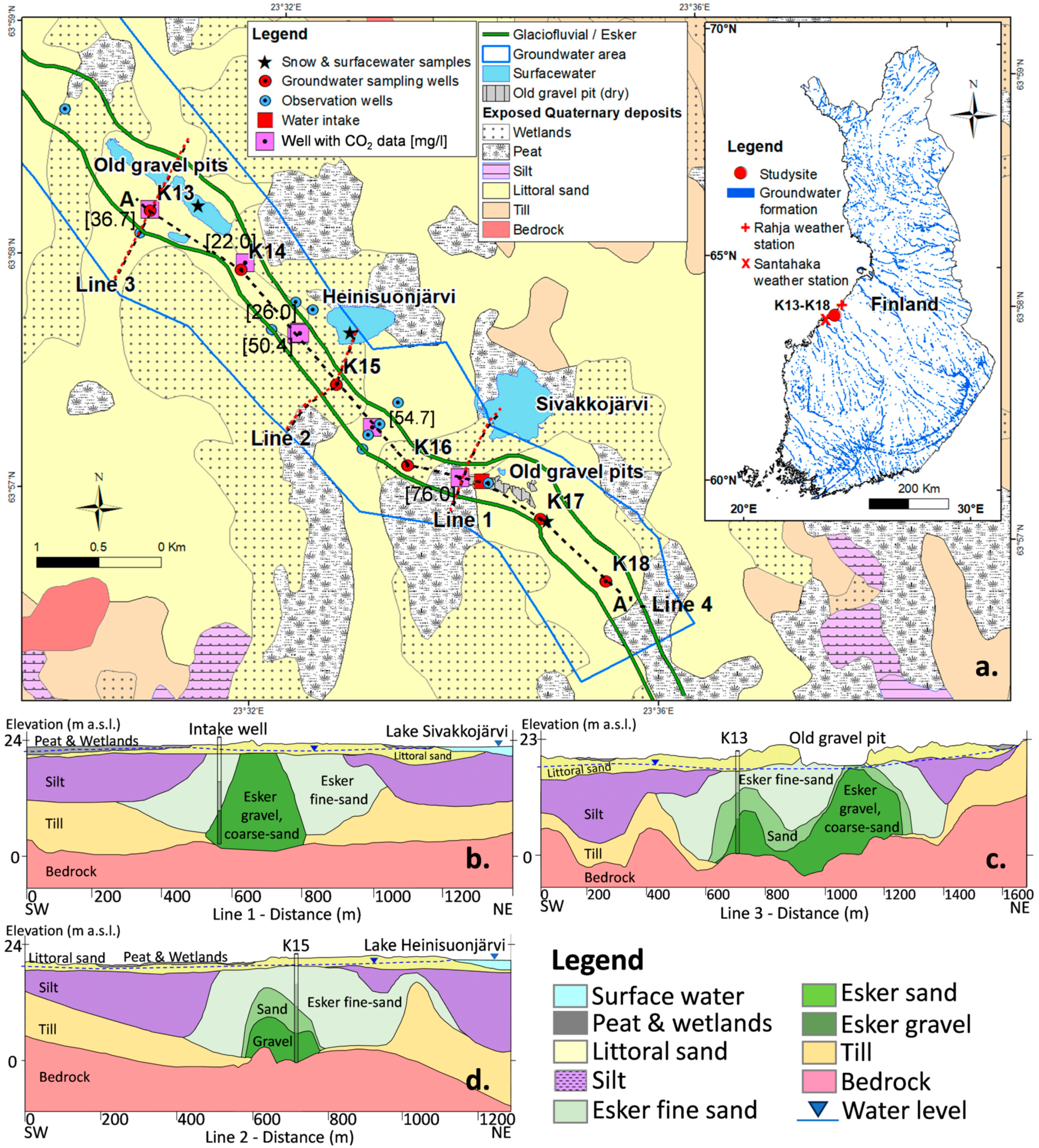
2. Study Area
2.1. General Setting
2.2. Geological and Hydrogeological Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Groundwater and Snow Sampling and Analysis
3.2. Stable Isotopic Composition of Oxygen and Hydrogen
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
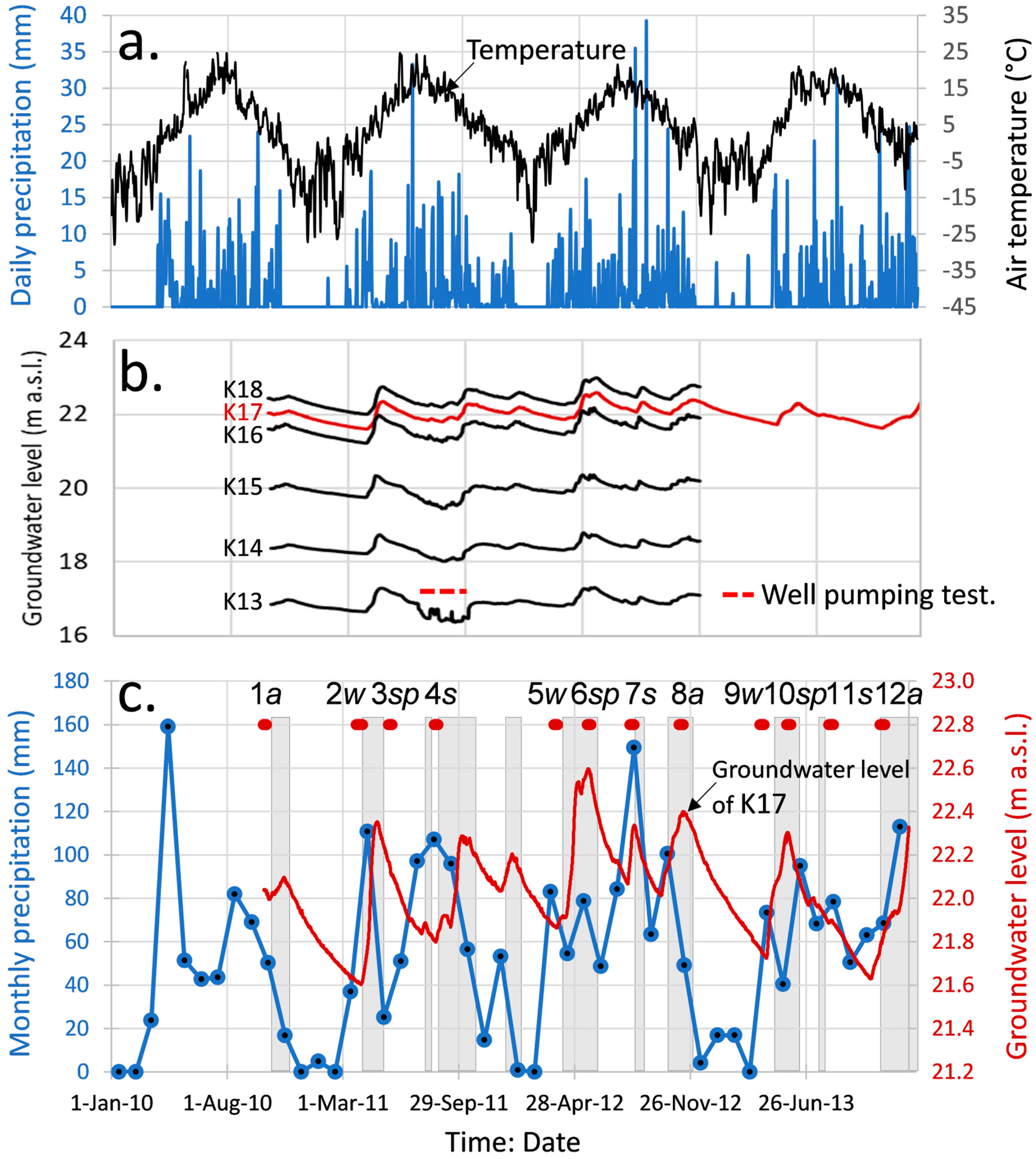
4.1. Groundwater Level
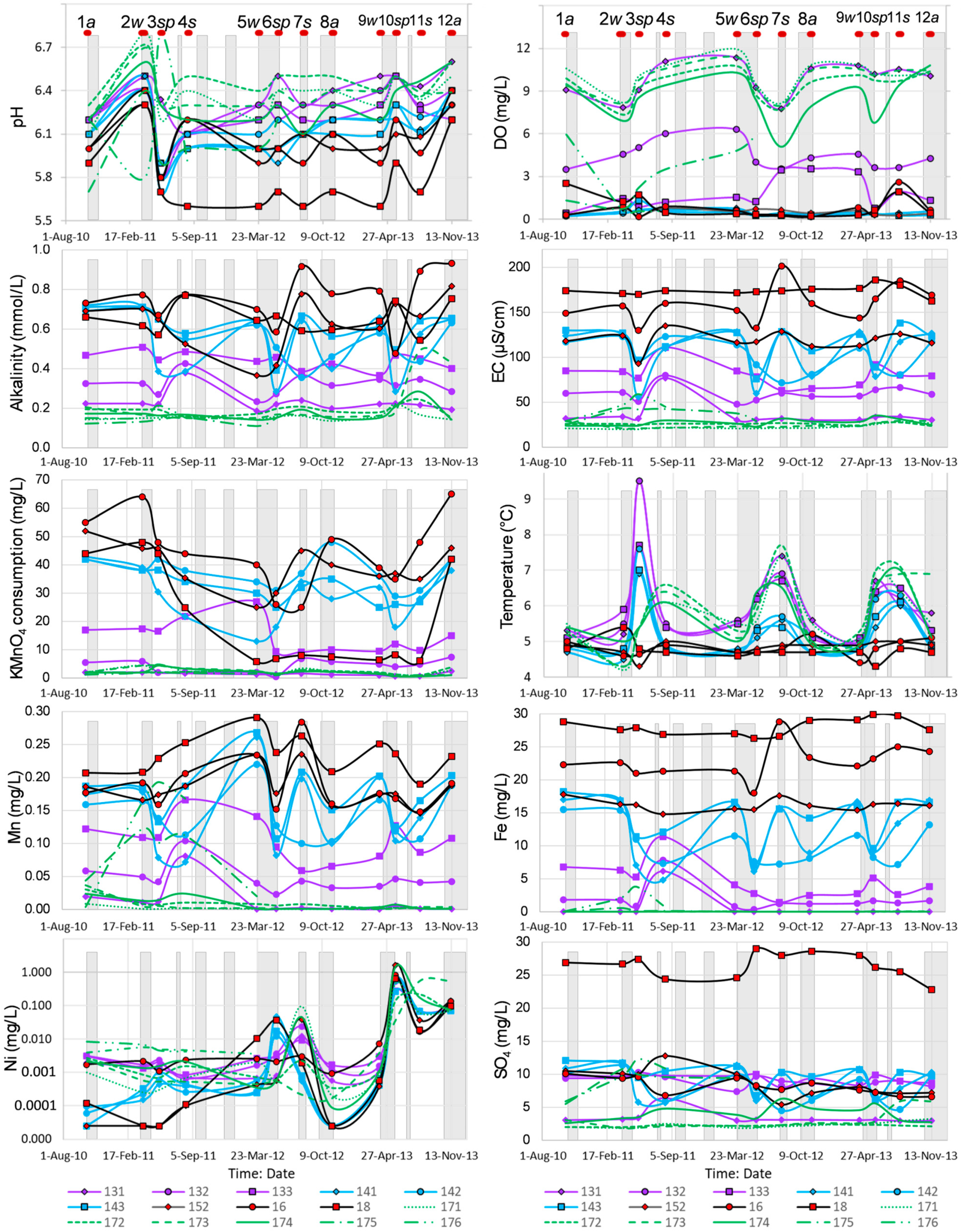
4.2. Hydrogeochemistry
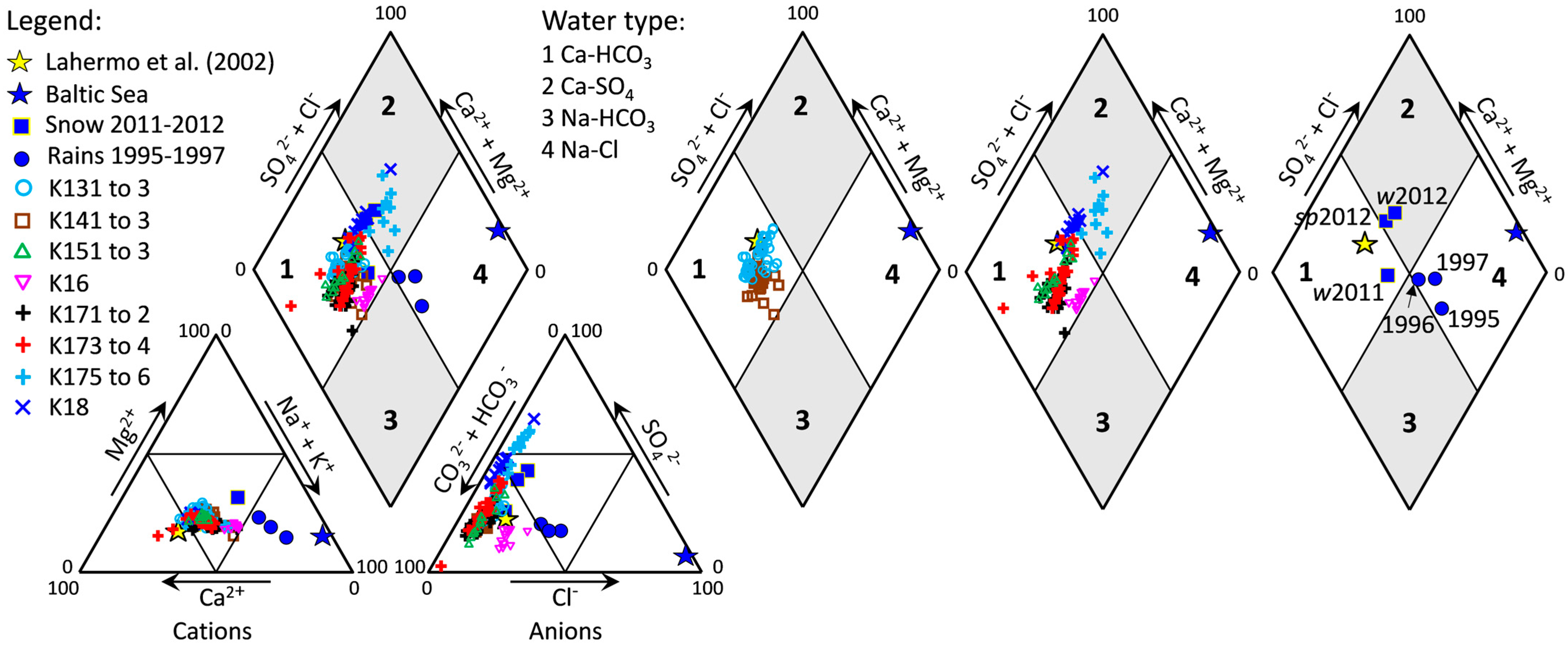
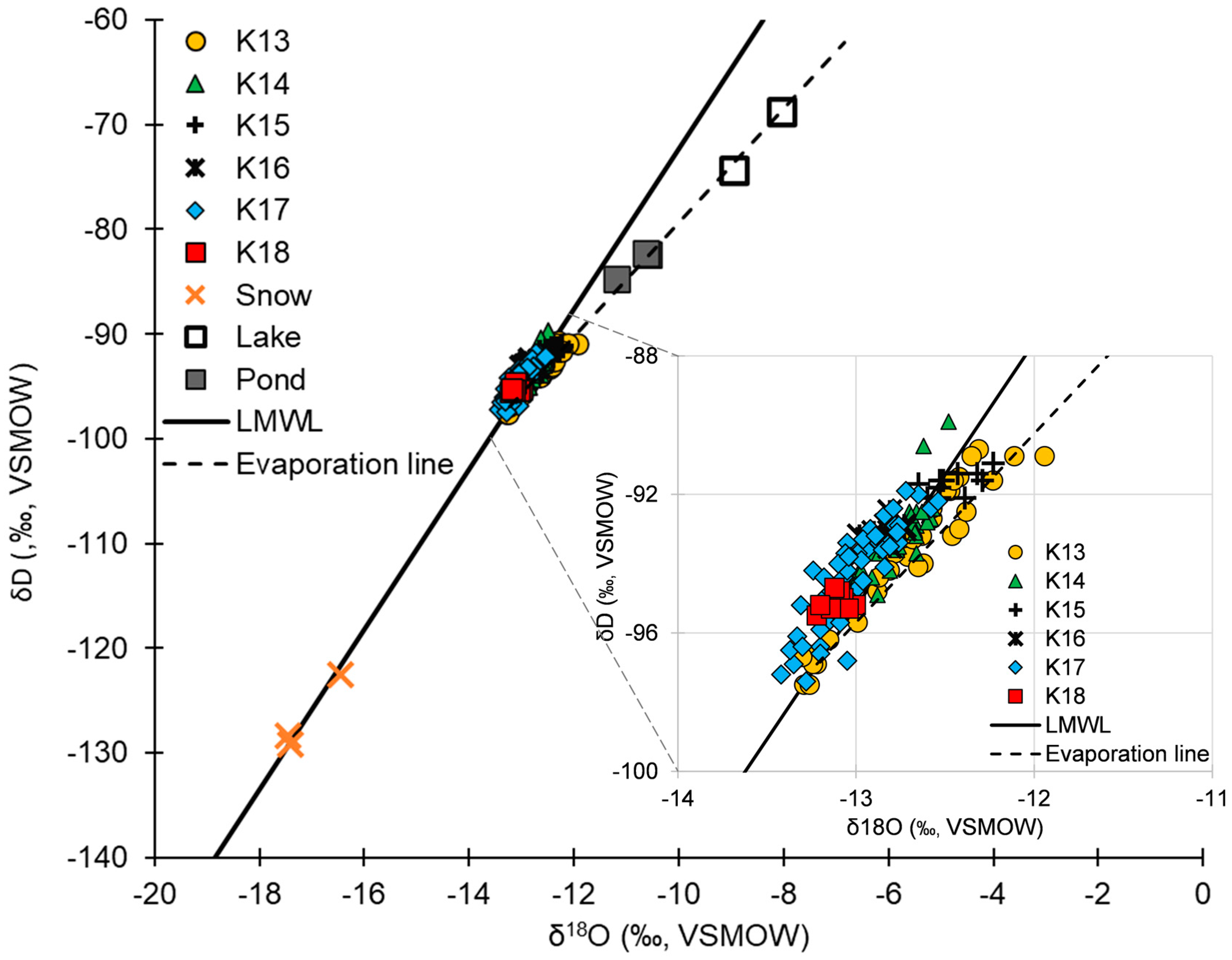
4.3. Stable Isotopes of Oxygen and Hydrogen
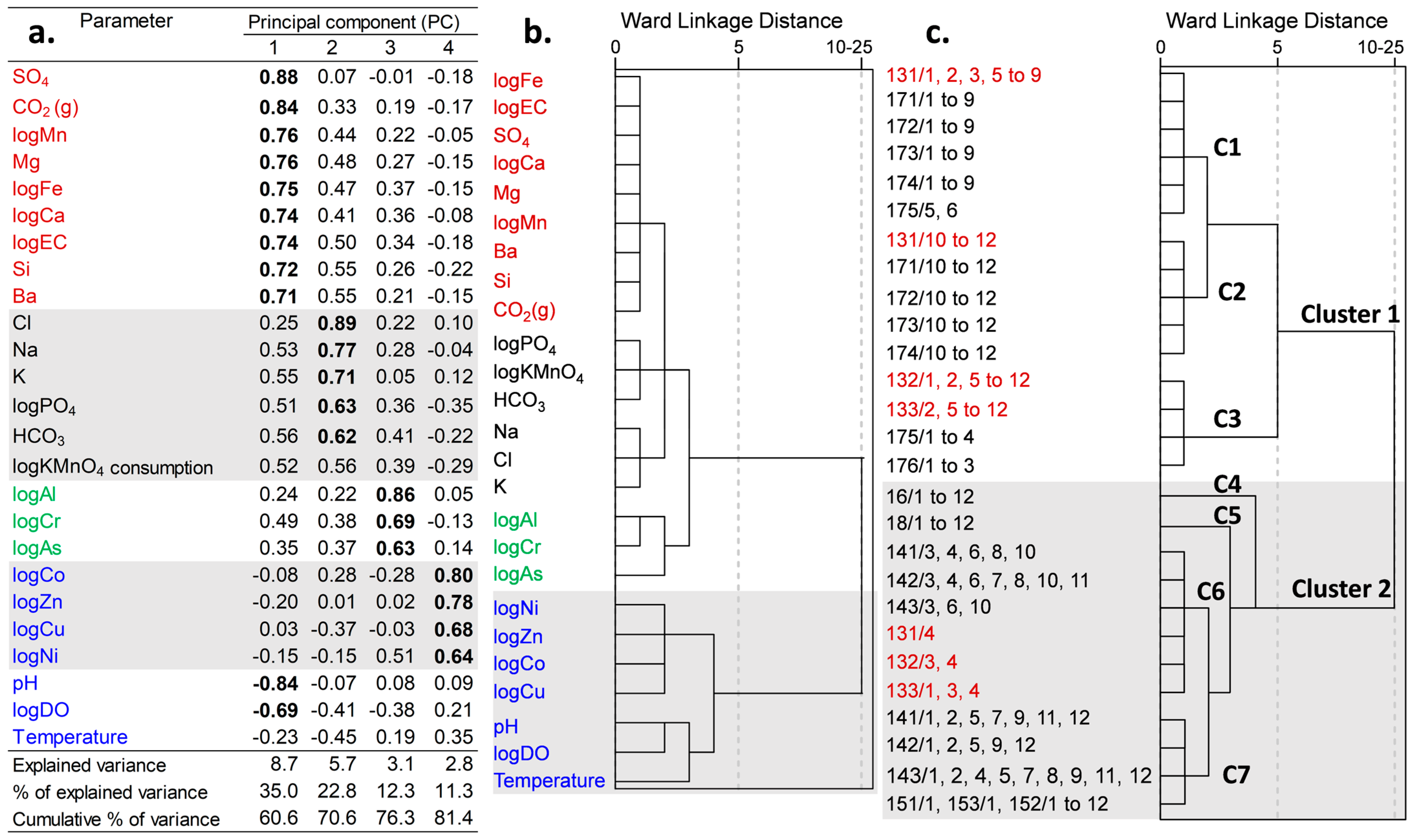
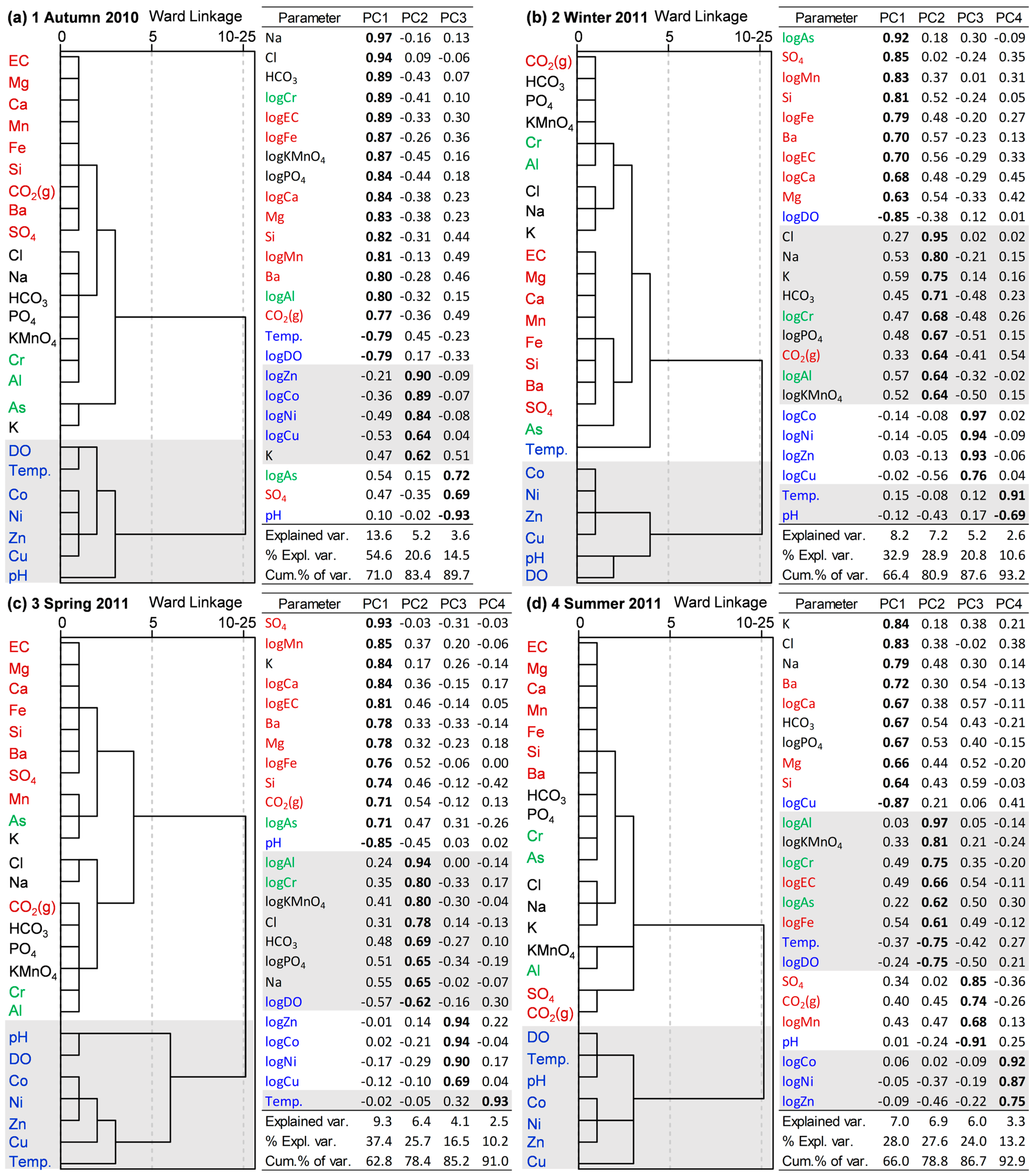
4.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
5. Discussion
5.1. Redox Conditions
5.2. pH of Groundwater
5.3. Groundwater and Surface Water Interactions
5.4. Spatial and Temporal Variability in Groundwater Geochemistry
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Punkari, M. Glacial and glaciofluvial deposits in the interlobate areas of the Scandinavian ice sheet. Quaternary Sci. Rev. 1997, 16, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahokangas, E.; Mäkinen, J. Sedimentology of an ice lobe margin esker with implications for the deglacial dynamics of the Finnish Lake District lobe trunk. Boreas 2014, 43, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maries, G.; Ahokangas, E.; Mäkinen, J.; Pasanen, A.; Malehmir, A. Interlobate esker architecture and related hydrogeological features derived from a combination of high-resolution reflection seismic and refraction tomography, Virttaankangas, southwest Finland. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.I.; Gorrell, G.; Guilbault, J.-P.; Hunter, J.A.; Logan, C.; Ponomarenko, D.; Pugin, A.J.-M.; Pullan, S.E.; Russell, H.A.J.; Sharpe, D.R. Sequence stratigraphy of a glaciated basin fill, with a focus on esker sedimentation. GSA Bull. 2011, 123, 1478–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, R.M.; Kauffman, L.J.; Soller, D.R.; Haj, A.E.; Heisig, P.M.; Buchwald, C.A.; Westenbroek, S.M.; Reddy, J.E. Characterization and Occurrence of Confined and Unconfined Aquifers in Quaternary Sediments in the Glaciated Conterminous United States (Ver. 1.1, February 2019); U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2018—5091; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Artimo, A.; Mäkinen, J.; Berg, R.C.; Abert, C.C.; Salonen, V.-P. Three-dimensional geologic modeling and visualization of the Virttaankangas aquifer, southwestern Finland. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, A.; Korkka-Niemi, K. Characterization of groundwater-lake water interactions at Pyhäjärvi, a lake in SW Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2011, 16, 363–380. Available online: https://www.borenv.net/BER/archive/pdfs/ber16/ber16-363.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Okkonen, J.; Kløve, B. Assessment of temporal and spatial variation in chemical composition of groundwater in an unconfined esker aquifer in the cold temperate climate of Northern Finland. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2012, 71, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britschgi, R.; Rintala, J.; Puharinen, S.T. Groundwater areas—A guide for their designation and classification and preparation of protection plans. In Environmental Administration Guidelines 3/2018 (In Finnish with English Summary); Ministry of the Environment: Helsinki, Finland, 2018. Available online: https://julkaisut.valtioneuvosto.fi/handle/10024/161164 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Erickson, M.L.; Yager, R.M.; Kauffman, L.J.; Wilson, J.T. Drinking water quality in the glacial aquifer system, northern USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paalijärvi, M.; Okkonen, J. Water Supply Research and Groundwater Flow Modeling of the Karhinkangas and Sivakkokangas Groundwater Areas During 2011–2014; Investigation Report 64/2014; Geological Survey of Finland: Kokkola, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ala-Aho, P.; Rossi, P.M.; Kløve, B. Interaction of esker groundwater with headwater lakes and streams. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.; Okkonen, J.; Korkka-Niemi, K.; Hendriksson, N.; Backman, B. Confronting vicinity of the surface water and seashore in a shallow glaciogenic aquifer in southern Finland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1353–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kløve, B.; Ala-Aho, P.; Bertrand, G.; Gurdak, J.J.; Kupfersberger, H.; Kværner, J.; Muotka, T.; Mykrä, H.; Preda, E.; Rossi, P.; et al. Climate change impacts on groundwater and dependent ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2014, 518, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, B.; Lahermo, P.; Väisänen, U.; Paukola, T.; Juntunen, R.; Karhu, J.; Pullinen, A.; Rainio, H.; Tanskanen, H. The Effect of Geological Environment and Human Activities on Groundwater in Finland—The Results of Monitoring in 1969–1996; Report of Investigation 147; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Korkka-Niemi, K. Cumulative Geological, Regional and Site-Specific Factors Affecting Groundwater Quality in Domestic Wells in Finland; Monographs of the Boreal Environment Research, 20; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2001; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10138/39327 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Lahermo, P.; Tarvainen, T.; Hatakka, T.; Backman, B.; Juntunen, R.; Kortelainen, N.; Lakomaa, T.; Nikkarinen, M.; Vesterbacka, P.; Väisänen, U.; et al. One Thousand Wells-the Physical-Chemical Quality of Finnish Well Waters in 1999; Report of Investigation 155; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2002; Available online: http://tupa.gtk.fi/julkaisu/tutkimusraportti/tr_155.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Rossi, P.M.; Ala-Aho, P.; Doherty, J.; Kløve, B. Impact of peatland drainage and restoration on esker groundwater resources: Modeling future scenarios for management. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Chapelle, F.H. Redox Processes and Water Quality of Selected Principal Aquifer Systems. Groundwater 2008, 46, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, E.H.; Fessenden, J.; Kanjorski, N.; Koning, D.J.; Pawar, R. The impact of CO2 on shallow groundwater chemistry: Observations at a natural analog site and implications for carbon sequestration. Environ Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.; Okkonen, J. Impacts of Future Climate Change and Baltic Sea Level Rise on Groundwater Recharge, Groundwater Levels, and Surface Leakage in the Hanko Aquifer in Southern Finland. Water 2014, 6, 3671–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, D.; Boesen, C.; Kristiansen, H.; Larsen, F. Nitrate reduction in an unconfined sandy aquifer: Water chemistry, reduction processes, and geochemical modeling. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayotte, J.D.; Szabo, Z.; Focazio, M.J.; Eberts, S.M. Effects of human-induced alteration of groundwater flow on concentrations of naturally occurring trace elements at water-supply wells. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Böhlke, J.K.; Kauffman, L.J.; Kipp, K.L.; Landon, M.K.; Crandall, C.A.; Burow, K.R.; Brown, C.J. Source and transport controls on the movement of nitrate to public supply wells in selected principal aquifers of the United States. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.; de Vet, W. Modeling in situ iron removal from groundwater with trace elements such as As. In Arsenic in Ground Water; Welch, A.H., Stollenwerk, K.G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britschgi, R.; Antikainen, M.; Ekholm-Peltonen, M.; Hyvärinen, V.; Nylander, E.; Siiro, P.; Suomela, T. Mapping and Classification of Groundwater Areas; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2009; Available online: https://helda.helsinki.fi/bitstream/handle/10138/38830/yo_2009_pohjavesi_11_5_09.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- FMI. Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI): Download Observations. Available online: https://en.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/download-observations#!/ (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Neuvonen, K.J. The Bedrock Map of Kannus Area (Map Sheet Number 2324); Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen, T. The Quaternary Geological Map of the Lohtaja Area (Map Sheet Numbers 2413 01 and -04); Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Am. Geophys. Union Trans. 1944, 25, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.B. Graphical User Interface for MODFLOW, Version 4; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 00-315. 2000. Available online: http://water.usgs.gov/nrp/gwsoftware/GW_Chart/GW_Chart.html (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Envineer. EIA Report for the Application of Water Intake in Karhinkangas, Kokkola (Kokkolan Karhinkankaan vedenoton YVA-selostus, in Finnish); Kokkola Vesi: Kokkola, Finland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsberg, E. Groundwater Protection plan in Kokkola Area (Kokkolan Pohjavesialueiden Suojelusuunnitelma, in Finnish); Investigation report; Geological Survey of Finland: Kokkola, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of Input and Examples for PHREEQC Version 3—A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; Techniques and Methods, Book 6, Chap. A43; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2013. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a43/ (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Ball, J.W.; Nordstrom, D.K. WATEQ4F-User’Smanual with Revised Thermodynamic Data Base and Test Cases for Calculating Speciation of Major, Trace and Redox Elements in Natural Waters; U. S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 91-183; U. S. Geological Survey: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1991. [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; A.A. Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Drever, J.I. The Geochemistry of Natural Waters, Surface and Groundwater Environments, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Harbison, J.E. Groundwater Chemistry and Hydrological Processes within a Quaternary Coastal Plain, Pimpama, Southeast Queensland. Ph.D. Thesis, Queensland University of Technology, Queensland, Australia, 2007. Available online: https://eprints.qut.edu.au/16647 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Rautio, A.; Kivimäki, A.-L.; Korkka-Niemi, K.; Nygård, M.; Salonen, V.-P.; Lahti, K.; Vahtera, H. Vulnerability of groundwater resources to interaction with river water in a boreal catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3015–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, S.C.; Korkka-Niemi, K.; Rautio, A.; Salonen, V.-P.; Åberg, A. Groundwater recharge/discharge patterns and groundwater–surface water interactions in a sedimentary aquifer along the River Kitinen in Sodankylä, northern Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2019, 24, 155–187. Available online: https://www.borenv.net/BER/archive/pdfs/ber24/ber24-155-187.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Dansgaard, W. Stable Isotope in Precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM SPSS Statistics. Data and Statistical Analysis Software System Version 28. 2018. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/spss-statistics/28.0.0 (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G.; Dutter, R. Statistical Data Analysis Explained: Applied Environmental Statistics with R; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, V.; Lefebvre, R.; Therrien, R.; Savard, M.M. Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 353, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, C.; Thyne, G.D.; McCray, J.E.; Turner, A.K. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templ, M.; Filzmoser, P.; Reimann, C. Cluster analysis applied to regional geochemical data: Problems and possibilities. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2198–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnham, I.M.; Singh, A.K.; Stetzenbach, K.J.; Johannesson, K.H. Treatment of nondetects in multivariate analysis of groundwater geochemistry data. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2002, 60, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, O.; Vänni, T. Rainwater Quality and Bulk Deposition in Finland in 1994; The Finnish Environment 13; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen, O.; Vänni, T. Rainwater Quality and Bulk Deposition in Finland in 1995; The Finnish Environment 78; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen, O.; Vänni, T. Rainwater Quality and Bulk Deposition in Finland in 1996; The Finnish Environment 120; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- EU Drinking Water Directive. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. 2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2020/2184/oj (accessed on 24 July 2022).
- Kortelainen, N. Isotopic Fingerprints in Surficial Waters: Stable Isotope Methods Applied in Hydrogeological Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2007. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10138/21197 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Salminen, R., (Chief-editor); Batista, M.J.; Bidovec, M.; Demetriades, A.; De Vivo, B.; De Vos, W.; Duris, M.; Gilucis, A.; Gregorauskiene, V.; Halamic, J.; et al. Geochemical Atlas of Europe. In Part 1—Background Information, Methodology and Maps; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2005; Available online: http://www.gtk.fi/publ/foregsatlas/index.php (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Edmunds, W.M.; Kinniburgh, D.G.; Moss, P.D. Trace metals in interstitial waters from sandstones: Acidic inputs to shallow groundwaters. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 77, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, B. Groundwater Quality, Acidification, and Recovery Trends between 1969 and 2002 in South Finland, Geological Survey of Finland Bulletin 401; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2004; Available online: https://tupa.gtk.fi/julkaisu/bulletin/bt_401.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2024).
- Jakobsen, R.; Postma, D.J. Redox zoning, rates of sulfate reduction and interactions with Fe-reduction and methanogenesis in a shallow sandy aquifer, Rømø, Denmark. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.B.; Jensen, D.L.; Christensen, T. Effect of dissolved organic carbon on the mobility of cadmium, nickel and zinc in leachate polluted groundwater. War. Res. 1996, 30, 3037–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, C.G.E.M.; Cirkel, D.G.; de Jonge, M.J.; Hartog, N. Concentration of Iron (II) in Fresh Groundwater Controlled by Siderite, Field Evidence. Aquat. Geochem. 2021, 27, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.R.; Wigington, P.J., Jr.; Phillips, D.L.; Comeleo, R.; Coulombe, R. Willamette River Basin surface water isoscape (δ18O and δ2H): Temporal changes of source water within the river. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlatte, M.; Quillet, A.; Larocque, M.; Cloutier, V.; Pellerin, S.; Paniconi, C. Aquifer–peatland connectivity in southern Quebec (Canada). Hydrol. Process 2015, 29, 2600–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, R.G.; Wilkin, R.T.; Puls, R.W. Monitored Attenuation of Inorganic Contaminants in Ground Water Volume 2—Assessment for Non-Radionuclides Including Arsenic, Cadmium, Chromium, Copper, Lead, Nickel, Nitrate, Perchlorate, and Selenium; EPA/600/R-07/140; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Klaus, M. Decadal increase in groundwater inorganic carbon concentrations across Sweden. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttila, V.; Granholm, H.; Laanikari, J.; Yrjölä, T.; Aalto, A.; Heikinheimo, P.; Honkatuki, J.; Järvinen, H.; Liski, J.; Merivirta, R.; et al. Finland’s National Strategy for Adaptation to Climate Change; Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry of Finland: Vammala, Finland, 2005.
- Seneviratne, S.; Zhang, X.; Adnan, M.; Badi, W.; Dereczynski, C.; Luca, A.D.; Ghosh, S.; Iskandar, I.; Kossin, J.; Lewis, S.; et al. Weather and Climate Extreme Events in a Changing Climate. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1513–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variable | Unit | Min. | Median | Mean | Max. | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Drinking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 181 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 47 | Water | ||||
| Temp. | °C | 4.20 | 5.30 | 5.52 | 9.50 | 4.90 | 6.10 | 6.10 | 5.10 | |
| DO | mg/L | 0.17 | 2.21 | 4.53 | 13.01 | 3.31 | 2.21 | 2.06 | 2.50 | 5.00 |
| pH | 5.60 | 6.28 | 6.23 | 6.80 | 6.30 | 6.20 | 6.20 | 6.20 | 6.50–9.50 | |
| EC | µS/cm | 20.00 | 59.90 | 73.92 | 201.40 | 57.00 | 52.40 | 69.05 | 60.00 | 2500.00 |
| TDS | mg/L | 28.47 | 57.75 | 78.79 | 193.14 | 57.05 | 50.81 | 67.27 | 57.71 | |
| CO2 | mg/L | 3.36 | 23.40 | 29.90 | 82.43 | 18.77 | 22.90 | 28.15 | 23.00 | |
| Alkalinity | mmol/L | 0.11 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.92 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.33 | |
| K | mg/L | 0.58 | 1.23 | 1.24 | 2.44 | 1.34 | 1.18 | 1.23 | 1.21 | |
| Ca | mg/L | 1.43 | 3.99 | 4.06 | 8.16 | 4.03 | 3.16 | 4.32 | 4.31 | |
| Mg | mg/L | 0.43 | 1.26 | 1.29 | 2.70 | 1.57 | 0.96 | 1.23 | 1.50 | |
| Na | mg/L | 0.88 | 2.77 | 3.17 | 11.00 | 2.76 | 2.56 | 3.17 | 3.04 | 200.00 |
| Cl | mg/L | 0.41 | 1.60 | 2.13 | 12.00 | 1.50 | 1.40 | 1.78 | 1.73 | 250.00 |
| Si | mg/L | 4.61 | 6.92 | 7.11 | 11.30 | 7.08 | 6.79 | 6.97 | 6.59 | |
| SO4 | mg/L | 0.59 | 6.80 | 7.58 | 29.00 | 8.33 | 6.20 | 6.10 | 7.15 | 250.00 |
| Fe | mg/L | <0.03 | 1.75 | 7.59 | 29.90 | 1.75 | 0.97 | 2.03 | 2.07 | 0.20 |
| NO3 | mg/L | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | 1.30 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | 50.00 |
| NH4 | mg/L | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.43 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.50 |
| PO4 | mg/L | <0.02 | <0.02 | 0.09 | 0.47 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | |
| KMnO4 | mg/L | 0.44 | 5.50 | 16.18 | 65.00 | 4.90 | 4.40 | 5.45 | 7.40 | 20.00 |
| Mn | µg/L | 0.38 | 78.50 | 90.76 | 291.00 | 80.90 | 78.50 | 76.45 | 65.60 | 50.00 |
| Ba | µg/L | 3.01 | 17.10 | 23.86 | 91.10 | 17.70 | 15.80 | 17.25 | 16.20 | |
| Al | µg/L | 1.60 | 34.50 | 76.98 | 1280.00 | 16.00 | 43.70 | 41.15 | 45.20 | 200.00 |
| As | µg/L | <0.05 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 1.57 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 10.00 |
| Co | µg/L | <0.02 | 0.20 | 0.51 | 3.63 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.14 | |
| Cr | µg/L | <0.20 | 1.25 | 2.30 | 11.60 | 0.63 | 2.17 | 1.65 | 1.12 | 25.00 |
| Cu | µg/L | <0.10 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 3.84 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 2000.00 |
| Ni | µg/L | <0.05 | 1.72 | 66.53 | 1660.00 | 0.87 | 3.64 | 7.03 | 1.74 | 20.00 |
| Zn | µg/L | <0.20 | 2.36 | 2.86 | 12.10 | 2.02 | 2.90 | 2.19 | 2.21 | |
| Variable | Unit | GW | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Finland | Snow | Rain | Sivakjv. | Heinisjv. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 181 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 47 | 739 | 3 | 31 | 2 | 3 | |
| Temp. | °C | 5.30 | 4.90 | 6.10 | 6.10 | 5.10 | 6.80 | ||||
| DO | mg/L | 2.21 | 3.31 | 2.21 | 2.06 | 2.50 | 7.40 | 8.57 | 9.83 | ||
| pH | 6.28 | 6.30 | 6.20 | 6.20 | 6.20 | 6.40 | 5.00 | 4.92 | 6.24 | 7.24 | |
| EC | µS/cm | 59.90 | 57.00 | 52.40 | 69.05 | 60.00 | 125.00 | 17.45 | 22.70 | 33.00 | |
| TDS | mg/L | 57.75 | 57.05 | 50.81 | 67.27 | 57.71 | 20.67 | ||||
| CO2 | mg/L | 23.40 | 18.77 | 22.90 | 28.15 | 23.00 | 34.00 | ||||
| Alkalinity | mmol/L | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.55 | 0.07 | 0.03 | ||
| K | mg/L | 1.23 | 1.34 | 1.18 | 1.23 | 1.21 | 2.78 | 0.93 | 0.44 | ||
| Ca | mg/L | 3.99 | 4.03 | 3.16 | 4.32 | 4.31 | 11.40 | 2.74 | 0.24 | ||
| Mg | mg/L | 1.26 | 1.57 | 0.96 | 1.23 | 1.50 | 2.38 | 0.71 | 0.13 | ||
| Na | mg/L | 2.77 | 2.76 | 2.56 | 3.17 | 3.04 | 4.18 | 0.71 | 0.44 | ||
| Cl | mg/L | 1.60 | 1.50 | 1.40 | 1.78 | 1.73 | 4.46 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 1.10 | |
| Si | mg/L | 6.92 | 7.08 | 6.79 | 6.97 | 6.59 | 12.90 | 5.23 | |||
| SO4 | mg/L | 6.80 | 8.33 | 6.20 | 6.10 | 7.15 | 10.40 | 3.00 | 0.60 | 3.20 | |
| Fe | mg/L | 1.75 | 1.75 | 0.97 | 2.03 | 2.07 | <0.03 | <0.03 | 1.48 | ||
| NO3 | mg/L | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | 3.19 | 1.10 | 0.32 | <2.00 | <2.00 |
| NH4 | mg/L | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.14 | 0.32 | <0.03 | <0.03 | |
| PO4 | mg/L | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
| KMnO4 | mg/L | 5.50 | 4.90 | 4.40 | 5.45 | 7.40 | 4.50 | ||||
| Mn | µg/L | 78.50 | 80.90 | 78.50 | 76.45 | 65.60 | 4.36 | 2.45 | 3.00 | ||
| Ba | µg/L | 17.10 | 17.70 | 15.80 | 17.25 | 16.20 | 18.10 | 5.43 | |||
| Al | µg/L | 34.50 | 16.00 | 43.70 | 41.15 | 45.20 | 101.00 | 4.94 | 150.00 | ||
| As | µg/L | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.11 | <1.00 | <1.00 | |
| Co | µg/L | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.22 | <0.50 | <0.50 | |
| Cr | µg/L | 1.25 | 0.63 | 2.17 | 1.65 | 1.12 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.83 | 0.63 | |
| Cu | µg/L | 0.23 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 2.49 | 0.24 | <1.00 | <1.00 | |
| Ni | µg/L | 1.72 | 0.87 | 3.64 | 7.03 | 1.74 | 0.84 | 1.06 | <3.00 | <3.00 | |
| Zn | µg/L | 2.36 | 2.02 | 2.90 | 2.19 | 2.21 | 10.40 | 3.13 | 27.60 | 18.30 |
| Variable | Min. | Median | Mean | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface water (lakes and pond), (n = 4) | ||||
| δD | −84.70 | −71.50 | −78.48 | −68.70 |
| δ18O | −11.18 | −8.50 | −9.88 | −8.05 |
| d-excess | −4.30 | −3.50 | 0.56 | 4.74 |
| Snow (n = 3) | ||||
| δD | −129.20 | −128.40 | −126.70 | −122.50 |
| δ18O | −17.44 | −17.41 | −17.10 | −16.46 |
| d-excess | 9.18 | 10.08 | 10.13 | 11.12 |
| Groundwater (n = 124) | ||||
| δD | −97.50 | −93.50 | −93.71 | −89.90 |
| δ18O | −13.31 | −12.81 | −12.82 | −11.94 |
| d-excess | 4.60 | 9.00 | 8.85 | 11.70 |
| HCA Cluster | 1 (Oxidizing Zone) | 2 (Reducing Zone) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Number of samples (n) | 54 | 21 | 26 | 12 | 12 | 22 | 34 |
| Temperature (°C) | 5.45 | 6.40 | 5.50 | 4.80 | 4.70 | 5.45 | 4.80 |
| DO (mg/L) | 9.46 | 10.20 | 3.37 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.42 |
| pH | 6.37 | 6.50 | 6.30 | 6.00 | 5.70 | 6.10 | 6.10 |
| EC (µS/cm) | 26.00 | 27.70 | 60.05 | 158.40 | 173.35 | 80.80 | 123.65 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 35.85 | 39.04 | 57.34 | 160.92 | 135.32 | 88.57 | 126.82 |
| CO2 (mg/L) | 9.99 | 7.16 | 20.69 | 57.85 | 51.67 | 39.57 | 53.93 |
| Alkalinity (mmol/L) | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.65 |
| K (mg/L) | 0.89 | 0.91 | 1.38 | 2.13 | 1.56 | 1.19 | 1.50 |
| Ca (mg/L) | 1.94 | 2.49 | 4.37 | 5.70 | 7.47 | 4.37 | 6.03 |
| Mg (mg/L) | 0.58 | 0.59 | 1.58 | 2.04 | 2.35 | 1.49 | 1.95 |
| Na (mg/L) | 1.41 | 1.38 | 2.75 | 8.02 | 4.71 | 3.82 | 4.58 |
| Cl (mg/L) | 0.75 | 0.71 | 1.69 | 8.28 | 1.81 | 2.18 | 3.18 |
| Si (mg/L) | 5.38 | 5.20 | 6.70 | 9.81 | 9.78 | 7.68 | 8.95 |
| SO4 (mg/L) | 2.58 | 2.90 | 9.39 | 8.00 | 26.80 | 6.57 | 10.15 |
| Fe (mg/L) | <0.03 | <0.03 | 1.67 | 22.45 | 27.75 | 7.47 | 16.15 |
| NO3 (mg/L) | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 | <0.20 |
| NH4 (mg/L) | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.15 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.08 |
| PO4 (mg/L) | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | 0.39 | <0.02 | <0.02 | 0.20 |
| KMnO4 (mg/L) | 2.00 | 1.00 | 5.65 | 46.00 | 8.10 | 27.00 | 36.50 |
| Mn (µg/L) | 2.20 | 1.59 | 73.25 | 176.50 | 234.00 | 107.00 | 185.00 |
| Ba (µg/L) | 4.61 | 6.19 | 16.10 | 65.10 | 72.15 | 23.25 | 39.75 |
| Al (µg/L) | 10.00 | 50.70 | 21.25 | 85.60 | 25.65 | 143.00 | 91.60 |
| As (µg/L) | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.64 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.29 |
| Co (µg/L) | 0.19 | 0.20 | 1.03 | 1.83 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.04 |
| Cr (µg/L) | 0.15 | 0.62 | 0.91 | 5.28 | 3.55 | 3.48 | 4.11 |
| Cu (µg/L) | 0.22 | 0.24 | 1.09 | <0.10 | <0.10 | 0.40 | 0.05 |
| Ni (µg/L) | 0.90 | 75.40 | 4.43 | 2.45 | 1.25 | 0.96 | 0.42 |
| Zn (µg/L) | 2.18 | 4.27 | 3.38 | 4.35 | 0.94 | 2.01 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luoma, S.; Okkonen, J.; Korkka-Niemi, K.; Hendriksson, N.; Paalijärvi, M. Characterization of Groundwater Geochemistry in an Esker Aquifer in Western Finland Based on Three Years of Monitoring Data. Water 2024, 16, 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223301
Luoma S, Okkonen J, Korkka-Niemi K, Hendriksson N, Paalijärvi M. Characterization of Groundwater Geochemistry in an Esker Aquifer in Western Finland Based on Three Years of Monitoring Data. Water. 2024; 16(22):3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223301
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuoma, Samrit, Jarkko Okkonen, Kirsti Korkka-Niemi, Nina Hendriksson, and Miikka Paalijärvi. 2024. "Characterization of Groundwater Geochemistry in an Esker Aquifer in Western Finland Based on Three Years of Monitoring Data" Water 16, no. 22: 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223301
APA StyleLuoma, S., Okkonen, J., Korkka-Niemi, K., Hendriksson, N., & Paalijärvi, M. (2024). Characterization of Groundwater Geochemistry in an Esker Aquifer in Western Finland Based on Three Years of Monitoring Data. Water, 16(22), 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223301






