The Impact of Cobalt Species on the Hazardous Characteristics of Cobalt-Leaching Residue: A Case Study from Guangdong Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
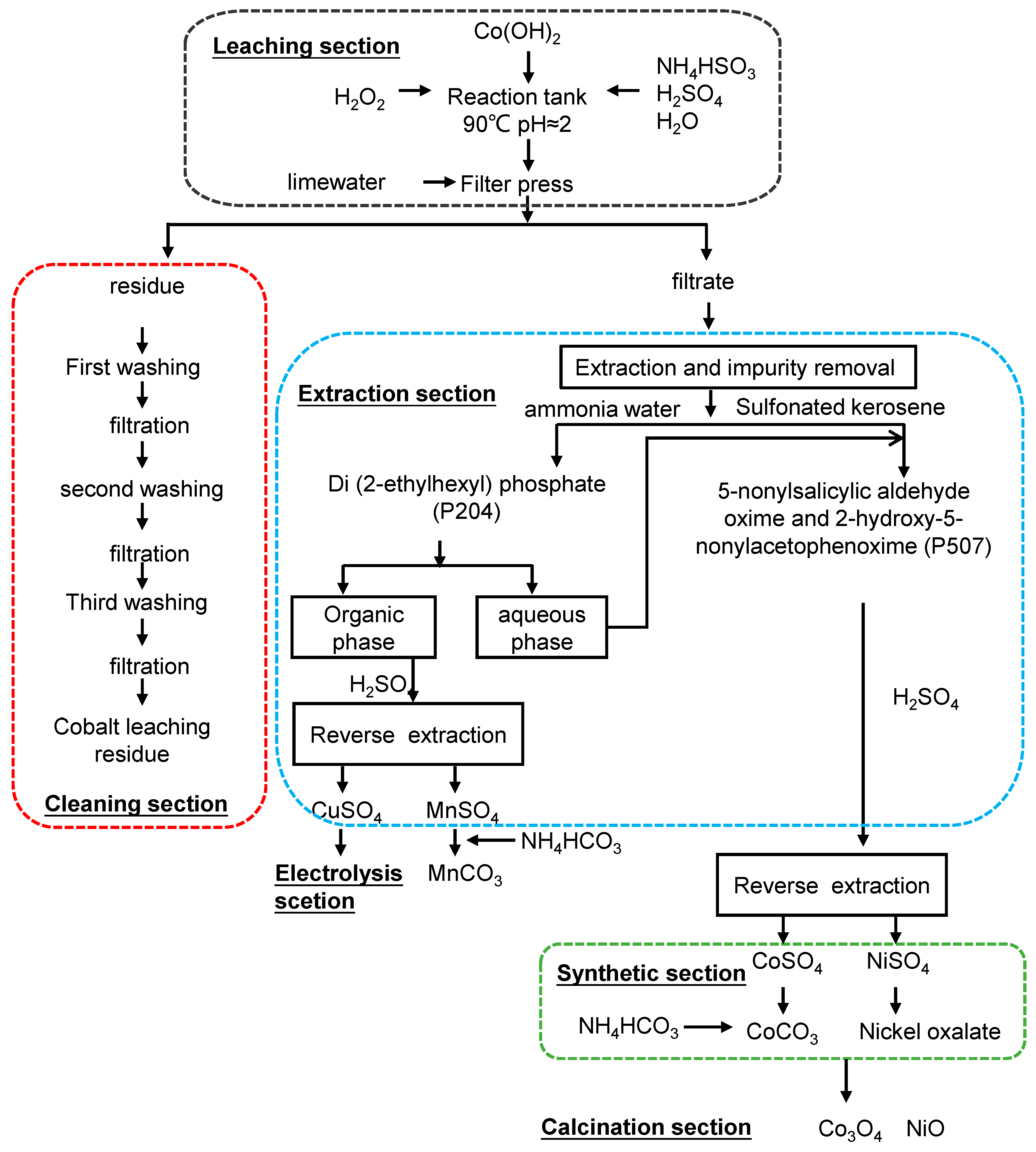
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.2.1. Preliminary Screening of Hazardous Characteristics
2.2.2. Sequential Extraction Analysis of Cobalt
2.2.3. Other Analyses
2.2.4. Calculation of Cumulative Toxic Content
3. Results and Discussion
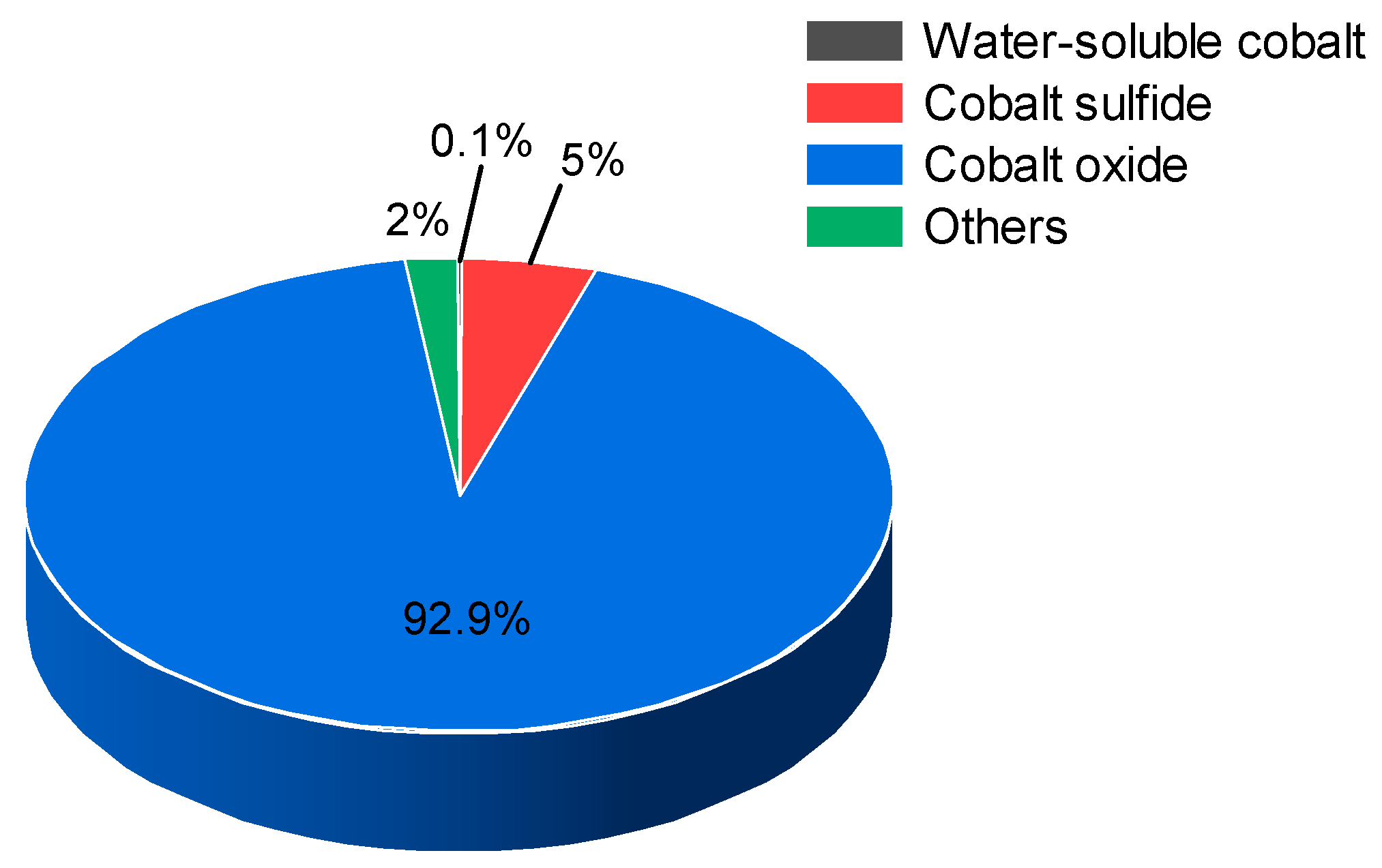
3.1. Speciation Analysis of Cobalt
3.2. Cumulative Toxicity of Cobalt
3.3. Leaching Toxicity and Toxic Substance Concentrations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Co | Cobalt |
| CoCl2 | Cobalt chloride |
| CoSO4 | Cobalt sulfate |
| LT+ | The standard value of highly toxic substances in solid waste |
| LT | The standard value of toxic substances in solid waste |
| LCarc | The standard value of carcinogenic substances in solid waste |
| LMuta | The standard value of mutagenic substances in solid waste |
| LTera | The standard value of reproductive toxic substances in solid waste |
| PT+ | Content of highly toxic substances in solid waste |
| PT | Content of toxic substances in solid waste |
| PCarc | Content of carcinogenic substances in solid waste |
| PMuta | Content of mutagenic substances in solid waste |
| PTera | Content of reproductive toxic substances in solid waste |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Yousefi, S.; Doulati Ardejani, F.; Ziaii, M.; Karamoozian, M. The Speciation of Cobalt and Nickel at Mine Waste Dump Using Improved Correlation Analysis: A Case Study of Sarcheshmeh Copper Mine. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 1065–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruland, K.W.; Donat, J.R.; Hutchins, D.A. Interactive Influences of Bioactive Trace Metals on Biological Production in Oceanic Waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1555–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barałkiewicz, D.; Siepak, J. Chromium, Nickel and Cobalt in Environmental Samples and Existing Legal Norms. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 8, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Barceloux, D.G. Cobalt. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, D.F.; Darvishi, D.; Shabestari, Z.M.H.; Alamdari, E.K.; Sadrnezhaad, S.K. Leaching Recovery of Zinc, Cobalt and Manganese from Zinc Purification Residue. Int. J. Eng. Trans. B Appl. 2007, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Han, G.; Peng, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, T.-A.; Dou, Z. Overview of Cobalt Resources and Comprehensive Analysis of Cobalt Recovery from Zinc Plant Purification Residue—A Review. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 193, 105327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, J.; Gray, M.; Mullick, F.; Tchounwou, P.; Tseng, C. Metal Contaminants in New Zealand: Sources, Treatments, and Effects on Ecology and Human Health; Resolution Press: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bartacek, J.; Fermoso, F.G.; Baldó-Urrutia, A.M.; Hullebusch, E.D.V.; Lens, P.N.L. Cobalt Toxicity in Anaerobic Granular Sludge: Influence of Chemical Speciation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantoura, R.F.C.; Dickson, A.; Riley, J.P. The Complexation of Metals with Humic Materials in Natural Waters. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 1978, 6, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paustenbach, D.J.; Tvermoes, B.E.; Unice, K.M.; Finley, B.L.; Kerger, B.D. A Review of the Health Hazards Posed by Cobalt. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 316–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyssens, L.; Vinck, B.; Van Der Straeten, C.; Wuyts, F.; Maes, L. Cobalt Toxicity in Humans—A Review of the Potential Sources and Systemic Health Effects. Toxicology 2017, 387, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5085.6-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Toxic Substance Content. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Chiang, K.Y.; Tsai, C.C.; Wang, K.S. Comparison of Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Apc Residue from an Msw Incinerator Using Various Extraction Methods. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5085.3-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Extraction Toxicity. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB/T 15555.4-1995; Solid Waste. Determination of Chromium (VI). 1,5-Diphenylcarbohydrazide Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- HJ 702-2014; Solid Waste-Determination of Mercury, Arsenic, Selenium, Bismuth, Antimony. MicrowaveDissolution/AtomicFluorescence Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- HJ 781-2016; Solid Waste. Determination of 22 Metal Elements. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Particulate Trace Metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violante, A.; Huang, P.M.; Gadd, G.M. Biophysico-Chemical Processes of Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Soil Environments; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, R.N.; Kinsela, A.S. The Aqueous Phase Speciation and Chemistry of Cobalt in Terrestrial Environments. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Acutely Toxic Substance | Toxic Substances | Carcinogenic Substances | Reproductive Toxic Substance | Mutagenic Substance | Cumulative Toxicity (Dimensionless) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chromate | Mercuric Chloride | Silver Cyanide | White Spirit | Lead Fluoride | Manganese | Antimony Pentoxide | Cadmium Sulfate | Nickel Sulfide | Cobalt Sulfate | Beryllium Oxide | Lead Phosphate | Sodium Chromate | ||
| Considering Co species | 0.0034 | 5.32 × 10−5 | 5.15 × 10−5 | 0.16 | 0.0064 | 0.0136 | 5.46 × 10−4 | 2 × 10−5 | 0.0287 | 0.0002 | 0.0050 | 2.21 × 10−4 | 1.46 × 10−3 | 0.4507 |
| Not considering Co species | 0.0034 | 5.31 × 10−5 | 5.15 × 10−5 | 0.162 | 0.0064 | 0.0136 | 5.46 × 10−4 | 2 × 10−5 | 0.0287 | 0.1490 | 0.0050 | 2.21 × 10−4 | 1.46 × 10−3 | 1.9383 |
| Sampling Date | Sample Number | Cr6+ | As | Se | Fluoride | Ni | Co | Total Chromium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 December 2019 | 1 | ND | 0.00396 | 0.00322 | 0.318 | 0.03 | 0.05 | ND |
| 6 December 2019 | 2 | ND | 0.00586 | 0.00348 | 0.226 | 0.03 | 0.10 | ND |
| 10 December 2019 | 3 | ND | 0.00754 | 0.00238 | 0.417 | 0.03 | 0.08 | ND |
| 14 December 2019 | 4 | ND | 0.00153 | 0.0044 | 0.430 | 0.04 | 0.05 | ND |
| 18 December 2019 | 5 | ND | 0.00355 | 0.00551 | 0.306 | 0.04 | 0.05 | ND |
| 22 December 2019 | 6 | ND | 0.00155 | 0.0071 | 0.616 | 0.04 | 0.08 | ND |
| 26 December 2019 | 7 | ND | 0.00246 | 0.00376 | 1.070 | 0.03 | 0.08 | ND |
| 30 December 2019 | 8 | ND | 0.00306 | 0.00314 | 1.420 | 0.04 | 0.05 | ND |
| Detection limit | 0.004 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0148 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| Detection maximum | ND | 0.00754 | 0.0071 | 1.420 | 0.04 | 0.10 | ND | |
| Standard limits | 5 | 5 | 1 | 100 | 5 | - | 15 | |
| Sampling Date | Sample Number | White Spirit | Mg | Ni | Co | As | Cumulative Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | mg/kg | ||||||
| 2 December 2019 | 1 | 0.195 | 105 | 180 | 468 | 28.8 | 0.410 |
| 6 December 2019 | 2 | 0.212 | 149 | 171 | 510 | 36.5 | 0.420 |
| 10 December 2019 | 3 | 0.072 | 188 | 227 | 576 | 19.4 | 0.424 |
| 14 December 2019 | 4 | 0.05 | 120 | 116 | 333 | 31.4 | 0.269 |
| 18 December 2019 | 5 | 0.104 | 146 | 156 | 486 | 34.5 | 0.356 |
| 22 December 2019 | 6 | 0.041 | 205 | 252 | 635 | 24.9 | 0.465 |
| 26 December 2019 | 7 | 0.078 | 215 | 276 | 732 | 17.8 | 0.499 |
| 30 December 2019 | 8 | 0.072 | 161 | 172 | 468 | 21.4 | 0.342 |
| Detection limit | 0.02 | 3.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.01 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, C.; Xu, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H. The Impact of Cobalt Species on the Hazardous Characteristics of Cobalt-Leaching Residue: A Case Study from Guangdong Province, China. Water 2024, 16, 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202953
Lv Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Wu C, Xu X, Xiao K, Zhao Z, Zhang H. The Impact of Cobalt Species on the Hazardous Characteristics of Cobalt-Leaching Residue: A Case Study from Guangdong Province, China. Water. 2024; 16(20):2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202953
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yang, Yi Wang, Cheng Zhang, Chaoyue Wu, Xiaowei Xu, Keke Xiao, Zehua Zhao, and Houhu Zhang. 2024. "The Impact of Cobalt Species on the Hazardous Characteristics of Cobalt-Leaching Residue: A Case Study from Guangdong Province, China" Water 16, no. 20: 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202953
APA StyleLv, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, C., Wu, C., Xu, X., Xiao, K., Zhao, Z., & Zhang, H. (2024). The Impact of Cobalt Species on the Hazardous Characteristics of Cobalt-Leaching Residue: A Case Study from Guangdong Province, China. Water, 16(20), 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202953







