Evaluating Uncertainties in an SM-Based Inversion Algorithm for Irrigation Estimation in a Subtropical Humid Climate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Datasets
2.2. SM2RAIN Implementation
Evaluation Metrics
2.3. Sources of Uncertainty
2.3.1. Sensitivity Analysis
2.3.2. Impact of Satellite Overpass Times
3. Results and Discussion
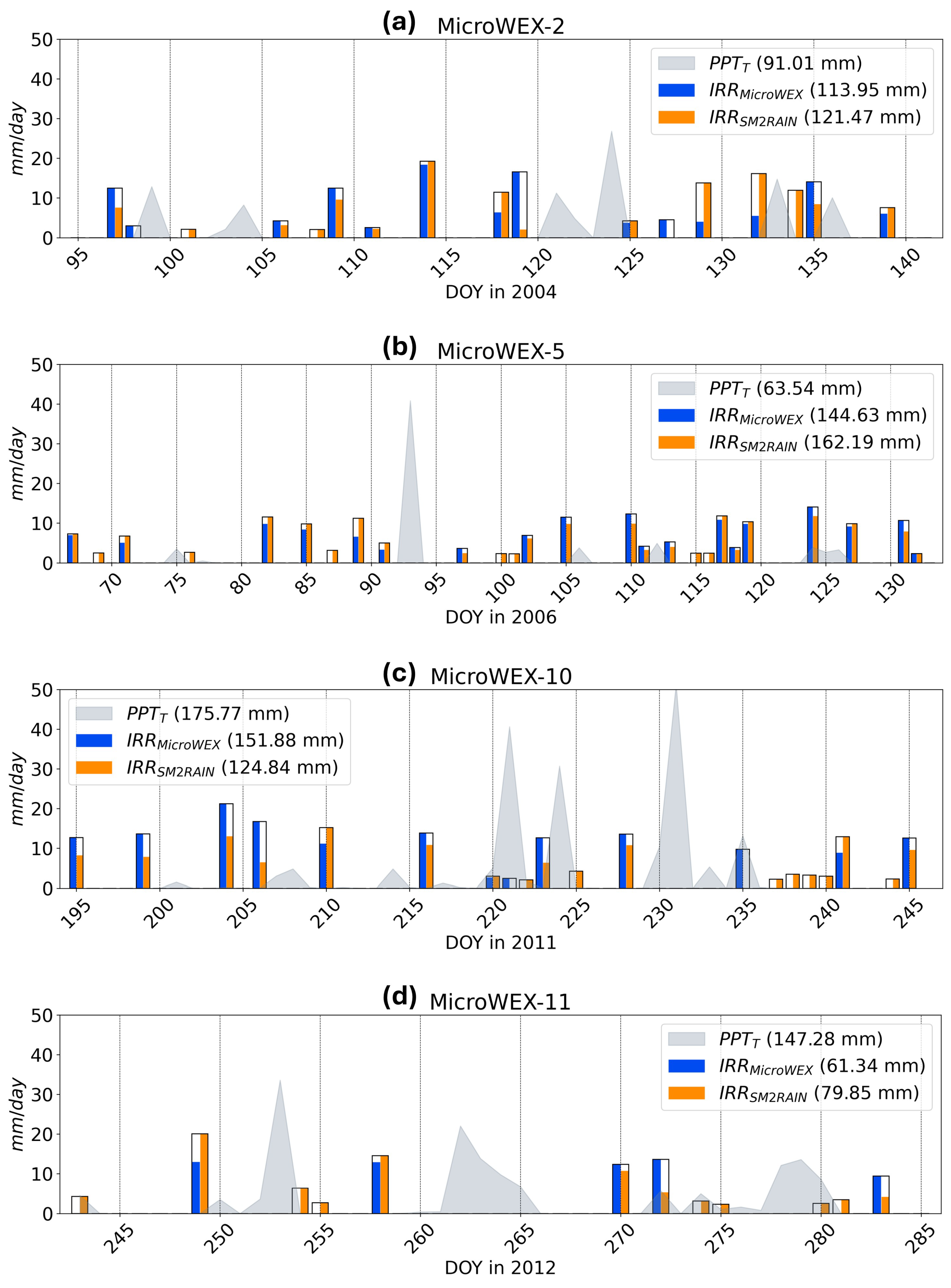
3.1. Irrigation Estimates
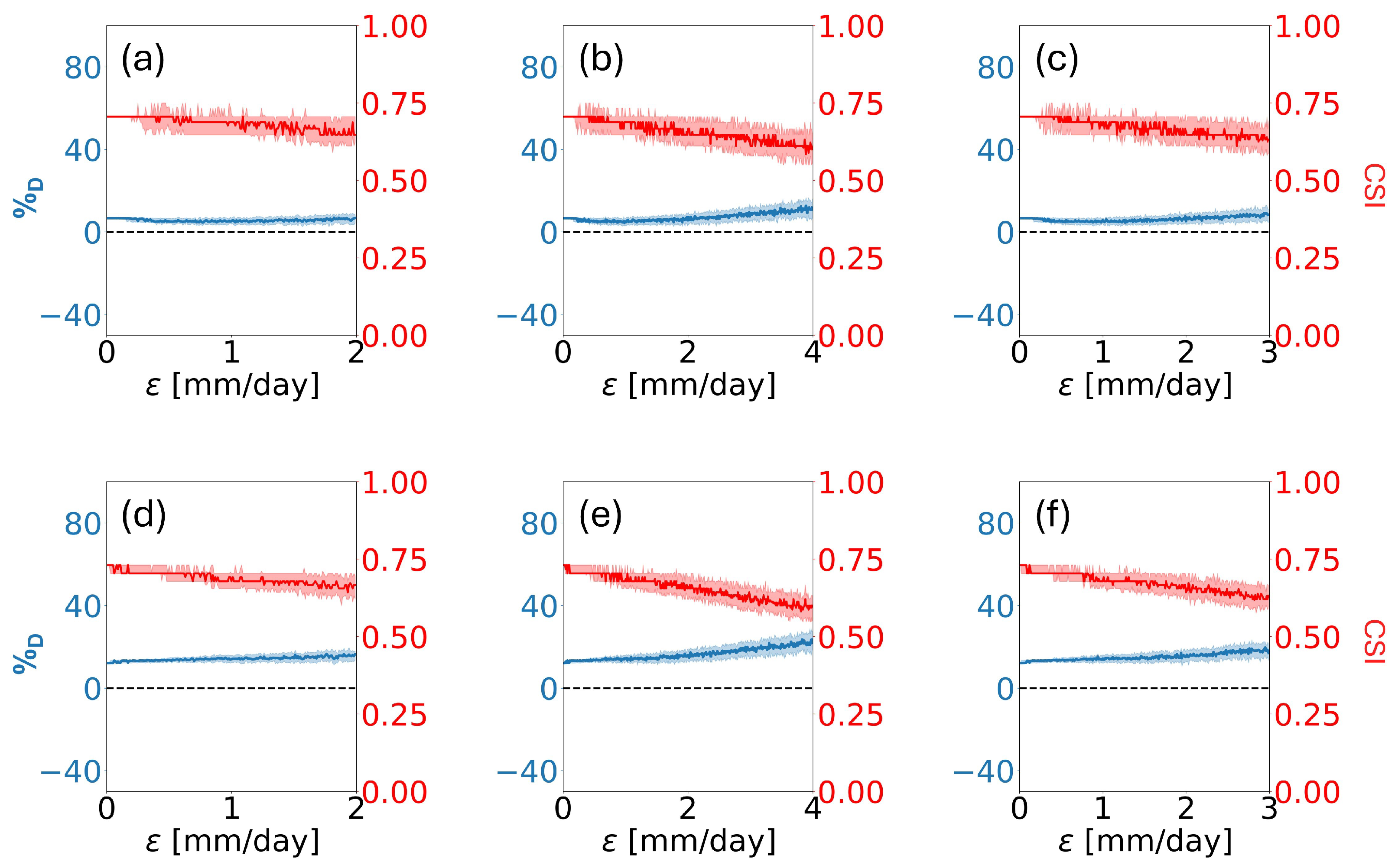
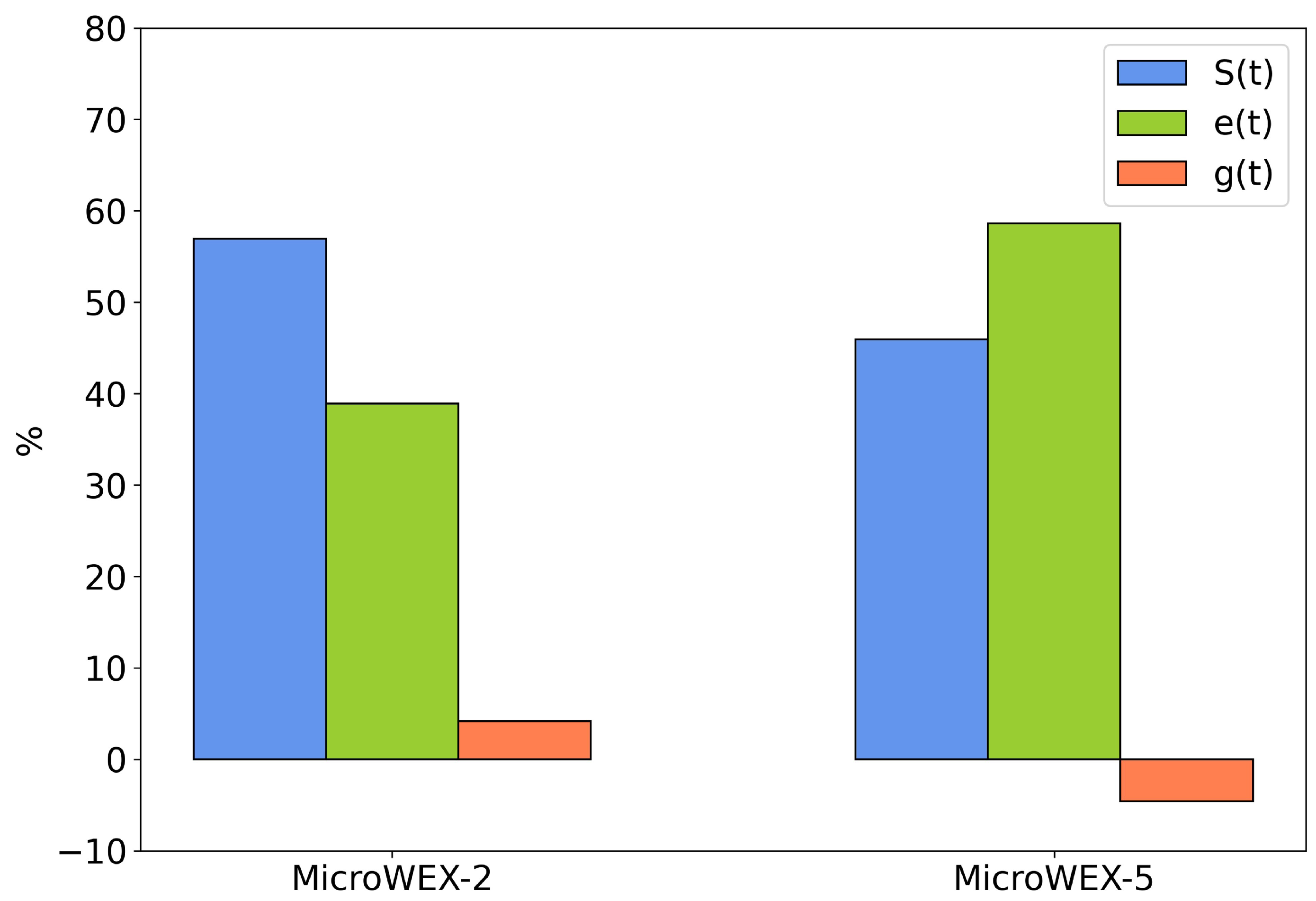
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
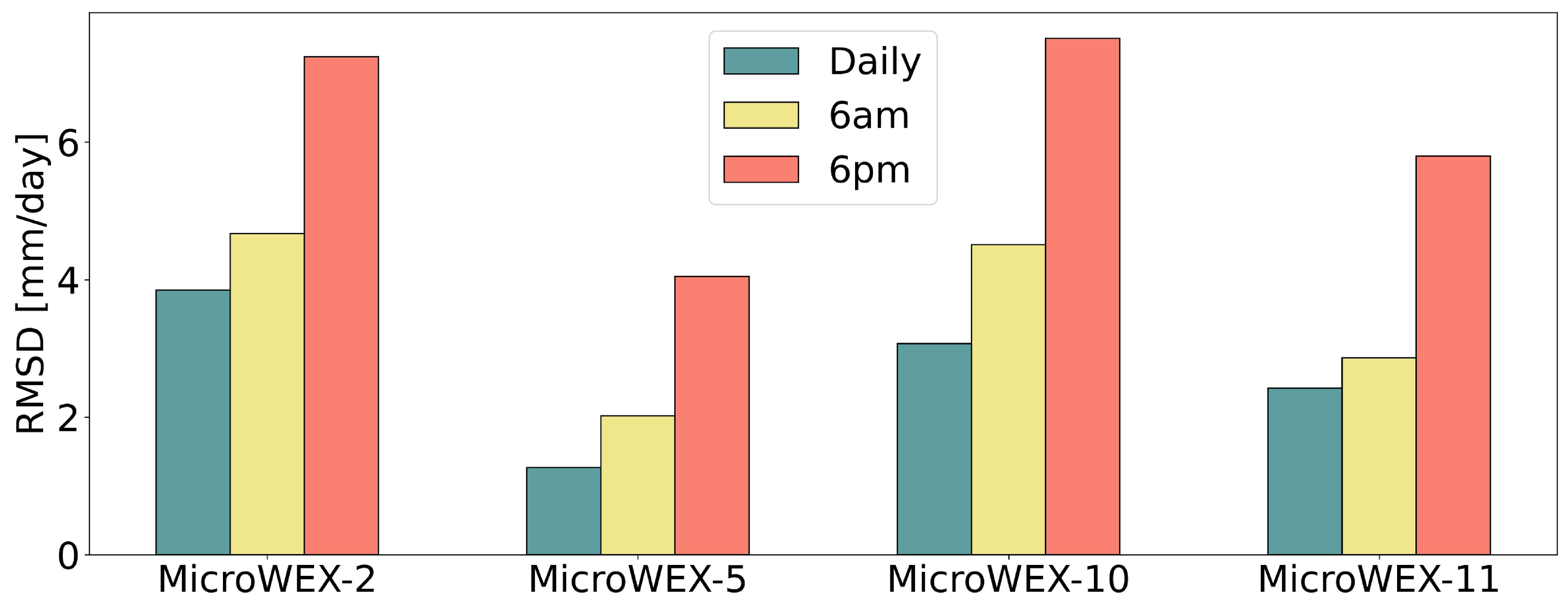
3.3. Impact of Satellite Overpass Time
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture—Systems at Breaking Point (SOLAW 2021); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, R.E.; Im, E.S.; Eltahir, E.A. Rainfall consistently enhanced around the Gezira Scheme in East Africa due to irrigation. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.M.; Beltrán-Przekurat, A.; Niyogi, D.; Pielke, R.A.; Vörösmarty, C.J. The impact of agricultural intensification and irrigation on land–atmosphere interactions and Indian monsoon precipitation—A mesoscale modeling perspective. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 67, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.W.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Purdy, A.J.; Adams, K.H.; McEvoy, A.L.; Reager, J.T.; Bindlish, R.; Wiese, D.N.; David, C.H.; Rodell, M. Groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley accelerates during megadrought. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Harter, T.; Hirono, Y.; Horino, H.; Mitsuno, T. Assessment of Root Zone Nitrogen Leaching as Affected by Irrigation and Nutrient Management Practices. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermid, S.; Nocco, M.; Lawston-Parker, P.; Keune, J.; Pokhrel, Y.; Jain, M.; Jägermeyr, J.; Brocca, L.; Massari, C.; Jones, A.D.; et al. Irrigation in the Earth system. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, C.; Modanesi, S.; Dari, J.; Gruber, A.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Girotto, M.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Le Page, M.; Jarlan, L.; Zribi, M.; et al. A Review of Irrigation Information Retrievals from Space and Their Utility for Users. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawston, P.M.; Santanello, J.A.; Kumar, S.V. Irrigation Signals Detected From SMAP Soil Moisture Retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11860–11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, S.J.; Fensholt, R.; Stisen, S.; Koch, J. The precision of satellite-based net irrigation quantification in the Indus and Ganges basins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 2463–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, S.J.; Dari, J.; Modanesi, S.; Massari, C.; Brocca, L.; Fensholt, R.; Stisen, S.; Koch, J. An inter-comparison of approaches and frameworks to quantify irrigation from satellite data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaussinger, F.; Dorigo, W.; Gruber, A.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Brocca, L. Estimating irrigation water use over the contiguous United States by combining satellite and reanalysis soil moisture data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 897–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohaib, M.; Choi, M. Satellite-based global-scale irrigation water use and its contemporary trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, E.; Abolafia-Rosenzweig, R.; Tajrishy, M.; Kumar, S.V.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Das, N.N. Is It Possible to Quantify Irrigation Water-Use by Assimilating a High-Resolution Satellite Soil Moisture Product? Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolafia-Rosenzweig, R.; Livneh, B.; Small, E.E.; Kumar, S.V. Soil Moisture Data Assimilation to Estimate Irrigation Water Use. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 3670–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modanesi, S.; Massari, C.; Bechtold, M.; Lievens, H.; Tarpanelli, A.; Brocca, L.; Zappa, L.; De Lannoy, G.J.M. Challenges and benefits of quantifying irrigation through the assimilation of Sentinel-1 backscatter observations into Noah-MP. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 4685–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laluet, P.; Olivera-Guerra, L.E.; Altés, V.; Paolini, G.; Ouaadi, N.; Rivalland, V.; Jarlan, L.; Villar, J.M.; Merlin, O. Retrieving the irrigation actually applied at district scale: Assimilating high-resolution Sentinel-1-derived soil moisture data into a FAO-56-based model. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 293, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaadi, N.; Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Ezzahar, J.; Le Page, M.; Merlin, O. Irrigation Amounts and Timing Retrieval through Data Assimilation of Surface Soil Moisture into the FAO-56 Approach in the South Mediterranean Region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Dorigo, W.; Zaussinger, F.; Gruber, A.; Fernández-Prieto, D. How much water is used for irrigation? A new approach exploiting coarse resolution satellite soil moisture products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, J.; Brocca, L.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Morbidelli, R. Exploiting high-resolution remote sensing soil moisture to estimate irrigation water amounts over a Mediterranean region. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, J.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Giugliarelli, E.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Brocca, L. Irrigation estimates from space: Implementation of different approaches to model the evapotranspiration contribution within a soil-moisture-based inversion algorithm. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 265, 107537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G. Estimation of Global Irrigation Water Use by the Integration of Multiple Satellite Observations. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, E.; Tajrishy, M.; Ghazi Zadeh Hashemi, S.A.; Brocca, L. Quantification of irrigation water using remote sensing of soil moisture in a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, J.; Brocca, L.; Modanesi, S.; Massari, C.; Tarpanelli, A.; Barbetta, S.; Quast, R.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Freeman, V.; Barella-Ortiz, A.; et al. Regional data sets of high-resolution (1 and 6 km) irrigation estimates from space. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 1555–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippucci, P.; Tarpanelli, A.; Massari, C.; Serafini, A.; Strati, V.; Alberi, M.; Raptis, K.G.C.; Mantovani, F.; Brocca, L. Soil moisture as a potential variable for tracking and quantifying irrigation: A case study with proximal gamma-ray spectroscopy data. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 136, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clothier, B.E.; Green, S.R. Rootzone processes and the efficient use of irrigation water. Agric. Water Manag. 1994, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Girvetz, E.H. Two Challenges for U.S. Irrigation Due to Climate Change: Increasing Irrigated Area in Wet States and Increasing Irrigation Rates in Dry States. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, C.A.; Maupin, M.A.; Caldwell, R.R.; Harris, M.A.; Ivahnenko, T.I.; Lovelace, J.K.; Barber, N.L.; Linsey, K.S. Estimated use of water in the United States in 2015. Circular 2018, 1441, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Her, Y.G.; Zhang, G.; Lusher, W. What Does Florida Weather during the Past 20 Years Look Like? Florida Weather Represented by the Florida Automated Weather Network (FAWN): AE537, 1/2020. EDIS 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, P.; Singh, G.; Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Lohman, R.; Colliander, A.; Pandey, D.K.; Setia, R.K. A multi-scale algorithm for the NISAR mission high-resolution soil moisture product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, J.; Casanova, J.; Lin, T.Y.; Tien, K.J.C.; Jang, M.Y.; Lanni, O.; Miller, L. Field Observations During the Second Microwave Water and Energy Balance Experiment (MicroWEX-2): From March 17 through June 3, 2004. EDIS 2005, CIR1480, 1–47. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/AE360 (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Casanova, J.; Yan, F.; Jang, M.y.; Fernandez, J.; Judge, J.; Slatton, C.; Calvin Tien, K.J.; Lin, T.y.; Lanni, O.; Miller, L.; et al. Field Observations During the Fifth Microwave Water and Energy Balance Experiment (MicroWEX-5): From March 9 through May 26, 2006. EDIS Circular 2007, 1514, 1–45. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/AE407 (accessed on 26 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Liu, P.W.; Nagarajan, K.; Preston, D.; Rush, P.; Duan, X.; Chen, G.; Terwilleger, R.; Monsivais-Huertero, A.; Judge, J.; et al. Field Observations during the Tenth Microwave Water and Energy Balance Experiment (MicroWEX-10): From March 1, 2011, through January 5, 2012. EDIS 2015, AE512, 1–97. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/AE512 (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Bongiovanni, T.; Liu, P.W.; Nagarajan, K.; Preston, D.; Rush, P.; Van Emmerik, T.H.M.; Steele-Dunne, S.; Terwilleger, R.; Baar, E.; Wallace, M.; et al. Field Observations during the Eleventh Microwave Water and Energy Balance Experiment (MicroWEX-11): From April 25, 2012, through December 6, 2012. EDIS 2015, AE514, 1–86. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/AE514 (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- USDA. National Agricultural Statistics Service 2023 Florida State Agriculture Overview. 2024. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Quick_Stats/Ag_Overview/stateOverview.php?state=FLORIDA (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Wright, D.L.; Rowland, D.; Sidhu, S. Water Use and Irrigation Management of Agronomic Crops. EDIS. 2022, Volume SS-AGR-15, pp. 1–5. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/AA131 (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Dewitz, J. National Land Cover Database (NLCD) 2021 Products; U.S. Geological Survey, Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2023.
- Wilson, K.B.; Hanson, P.J.; Mulholland, P.J.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Wullschleger, S.D. A comparison of methods for determining forest evapotranspiration and its components: Sap-flow, soil water budget, eddy covariance and catchment water balance. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 106, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarezi, R.S.; Nogueira, T.A.R.; Zepeda, S.G.C. Performance of Soil Moisture Sensors in Florida Sandy Soils. Water 2020, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, W.; Jackson, J.L.; Morgan, K. The Florida Automated Weather Network: Ten Years of Providing Weather Information to Florida Growers. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 2008, 121, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, J.A.; Judge, J.; Misra, V.; Jayasankar, C.B.; Lusher, W.R. Gap-free 16-year (2005–2020) sub-diurnal surface meteorological observations across Florida. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, R.H.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Gálvez, J.; Simmonds, L.P.; Barahona, E. Estimating detailed soil water profile records from point measurements. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.F.; Short Gianotti, D.J.; Dong, J.; Akbar, R.; Crow, W.T.; McColl, K.A.; Konings, A.G.; Nippert, J.B.; Tumber-Dávila, S.J.; Holbrook, N.M.; et al. Remotely Sensed Soil Moisture Can Capture Dynamics Relevant to Plant Water Uptake. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, J.J.; Judge, J. Estimation of energy and moisture fluxes for dynamic vegetation using coupled SVAT and crop-growth models. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W07415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsivais-Huertero, A.; Judge, J.; Steele-Dunne, S.; Liu, P.W. Impact of Bias Correction Methods on Estimation of Soil Moisture When Assimilating Active and Passive Microwave Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Pereira, L.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and Environment. The state and movement of water in living organism. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1965, 19, 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, D.; Manfreda, S.; Keller, K.; Smithwick, E.A. Predicting root zone soil moisture with soil properties and satellite near-surface moisture data across the conterminous United States. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Tian, J.; Kang, W.; Gao, C.; Hong, W.; He, C. Rainfall estimation from surface soil moisture using SM2RAIN in cold mountainous areas. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, F.; Saltelli, A.; Tarantola, S. Trends in sensitivity analysis practice in the last decade. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, E.P.; Huete, A.R.; Nagler, P.L.; Hirschboeck, K.K.; Brown, P. Integrating Remote Sensing and Ground Methods to Estimate Evapotranspiration. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2007, 26, 139–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Jia, G.; Liu, Z.; Sun, L.; Zheng, P.; Zhu, X. Grassland soil moisture fluctuation and its relationship with evapotranspiration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Das, N.; Kim, S.B.; Cosh, M.H.; Dunbar, R.S.; Dang, L.; Pashaian, L.; et al. Validation of SMAP surface soil moisture products with core validation sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, H.E.; Pan, M.; Miralles, D.G.; Reichle, R.H.; Dorigo, W.A.; Hahn, S.; Sheffield, J.; Karthikeyan, L.; Balsamo, G.; Parinussa, R.M.; et al. Evaluation of 18 satellite- and model-based soil moisture products using in situ measurements from 826 sensors. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| MicroWEX-2 | MicroWEX-5 | MicroWEX-10 | MicroWEX-11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2004 | 2006 | 2011 | 2012 |
| Period | Apr–May | March–May | July–Sep | Aug–Oct |
| Total rainfall (mm) [No. events (days)] | 91.01 [8] | 63.54 [8] | 175.77 [20] | 147.28 [18] |
| Total irrigation (mm) [No. events (days)] | 115.33 [15] | 144.63 [19] | 151.88 [13] | 61.34 [5] |
| Minimum–maximum temperatures (°C) | 13.57–28.06 | 13.84–27.93 | 23.15–34.22 | 21.01–31.20 |
| Average PET (mm/day) | 4.83 | 5.19 | 4.51 | 3.58 |
| Parameter | Unit | Baseline | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity (n) | [-] | 0.34 | 0.2–0.6 |
| Saturated moisture content () | 0.34 | 0.2–0.6 | |
| Soil thickness (Z) | mm | 160 | 40–300 |
| FAR | POD | CSI | RMSD | NSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MicroWEX-2 | 0.09 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 6.59 | 3.84 | 0.33 |
| MicroWEX-5 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.73 | 12.14 | 1.26 | 0.89 |
| MicroWEX-10 | 0.18 | 0.85 | 0.55 | −17.80 | 3.07 | 0.70 |
| MicroWEX-11 | 0.18 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 30.19 | 2.42 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almendra-Martín, L.; Judge, J.; Monsivaís-Huertero, A.; Liu, P.-W. Evaluating Uncertainties in an SM-Based Inversion Algorithm for Irrigation Estimation in a Subtropical Humid Climate. Water 2024, 16, 2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172445
Almendra-Martín L, Judge J, Monsivaís-Huertero A, Liu P-W. Evaluating Uncertainties in an SM-Based Inversion Algorithm for Irrigation Estimation in a Subtropical Humid Climate. Water. 2024; 16(17):2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172445
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmendra-Martín, Laura, Jasmeet Judge, Alejandro Monsivaís-Huertero, and Pang-Wei Liu. 2024. "Evaluating Uncertainties in an SM-Based Inversion Algorithm for Irrigation Estimation in a Subtropical Humid Climate" Water 16, no. 17: 2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172445
APA StyleAlmendra-Martín, L., Judge, J., Monsivaís-Huertero, A., & Liu, P.-W. (2024). Evaluating Uncertainties in an SM-Based Inversion Algorithm for Irrigation Estimation in a Subtropical Humid Climate. Water, 16(17), 2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172445






