Abstract
As urbanization progresses and city populations grow, river-crossing tunnels assume a crucial role in transportation networks, with the maximum scour depth constituting a critical parameter influencing tunnel safety. Using Line 6 of the Nanning Metro in Guangxi, China as a case study, a two-dimensional hydrosediment mathematical model was employed to investigate variations in maximum bedrock scouring. This study introduces the concept of critical frequency floods and compares it with urban flood control standards to determine the appropriate flood frequency for calculating maximum bedrock scour depth. The impact of bed sediment particle size on maximum scour depth is quantified, revealing a decrease in scour depth of 0.3 to 0.6 m for every 1 mm increase in particle size. The relationship between bed sedimentation and the Froude number demonstrates an upward-opening parabolic symmetry: lower Froude numbers correspond to relatively stable beds, while higher numbers correlate with an increased amplitude of bed erosion or deposition. The curve’s nadir identifies the critical threshold of the Froude number, facilitating calculation of the channel’s critical water depth. In practical engineering applications, a bed under conditions of critical water depth tends to be more stable, thereby favoring the selection of sites for river-crossing tunnels.
1. Introduction
River-crossing tunnels are essential components of urban transportation infrastructure, crucial for mitigating traffic congestion, fostering economic growth, and enhancing city stature [1,2,3]. With urbanization accelerating and populations growing, the demand for these tunnels continues to rise, underscoring their increasing significance in urban transport systems. In the design and construction of cross-river tunnels, engineers face a series of challenges, including predicting construction schedule risks, ensuring the efficiency of the air supply in emergency situations, and dealing with the issue of sedimentation in drainage channels. Li et al.’s research introduces a new perspective to risk assessment by considering emotional factors and has been confirmed in practice, thereby enhancing the predictive ability of construction schedule risks. The work of Wei et al. provides design guidance for air supply issues in tunnel emergencies, ensuring the safety of evacuation. The findings of Di et al. revealed the nonlinear hydraulic transport characteristics of sedimentation in drainage channels, offering technical guidance for cleaning and flood control within tunnels [4,5,6]. Safety is paramount in tunnel construction, with efforts focused on minimizing costs while ensuring safety standards are upheld. Deeper tunnels entail more complex geological conditions, heightened ground pressure, and increased construction costs due to elevated technical requirements, greater support and lining expenses, groundwater control challenges, and intensified safety measures. Therefore, tunnel design should meticulously determine a burial depth below the scouring limit to avoid excessive depth, which would escalate construction complexity and costs. Balancing depth with economic viability is crucial, ensuring tunnel safety while managing construction expenses effectively [7,8]. Nevertheless, in designing and constructing river-crossing tunnels, one encounters numerous challenges, with determining the maximum tunnel depth standing out as a critical concern [9,10].
Previous studies have extensively examined the maximum scour depth of river-crossing tunnels, yielding notable findings. Chen et al. [11] employed a two-dimensional tidal current and sediment model to compute the maximum scour depth of the Ningbo Metro Line 1 tunnel beneath the Fenghua River. Shi et al. [12] developed a predictive model to determine the maximum scour depth of the Qianjiang Tunnel at the Qiantang River estuary. Huang et al. [13] utilized a local physical model and a two-dimensional tidal sediment mathematical model to simulate riverbed erosion and deposition under extreme conditions in the MaliuZhou waterway. Zhang et al. [14] calculated the maximum scour depth of the Wuhan Light Rail Transit Line 8, passing beneath the Yangtze River, using a river engineering model. Suntoyo et al. [15] computed the maximum scour depth of the South Sumatra–West Java Submarine Pipeline based on principles of time-scale propagation.
Currently, empirical methods are predominantly used to calculate the maximum scour depth of riverbeds. Pandey et al. [16] introduced three new relationships for estimating maximum scour depth under conditions of balanced scouring for noncohesive sediments. Abdelaziz, AA et al. [17] proposed empirical equations to predict maximum scour depth locations in compound channels with wide bench foundations. Mostaani et al. [18] refined these equations, enhancing their accuracy in predicting maximum scour depths. Khosronejad et al. [19] further developed empirical relationships for estimating overall maximum scour depths near large-scale meandering streams and rivers through extensive experimentation. Lai, JS et al. [20] proposed a method to estimate the maximum scour depth of uniform sediments by analyzing the evolution characteristics of pier scour depths. Empirical formula methods, while offering simple and quick calculations, often consider only one operating condition and may lack accuracy under complex flow conditions, particularly nonlinear or extreme conditions, complicating the determination of required flood frequencies for calculating critical scour depths. In contrast, numerical simulation methods have largely overcome these limitations. They not only expand the model’s scope but also comprehensively simulate various physical processes such as friction, erosion, and deposition, dynamically portraying changes in riverbed morphology and providing visual outputs. Therefore, they possess broad applicability and high utility [21,22]. Nevertheless, accurately identifying severely scoured riverbed areas in complex terrains with rapidly fluctuating floods and varying flow patterns remains a significant challenge for numerical simulation methods, posing difficulties in siting tunnel projects and assessing their safety.
Research on determining the required flood frequency for calculating the limit of scour depth is limited. Rifo, C et al. [23] proposed a standard for selecting design scour depths based on frequency analysis. Burge, LM et al. [24] directly computed scour depths for specific return periods. Saha, R et al. [25] applied a bridge design standard for a 100-year period to estimate riverbed scour depth. However, these studies often select flood frequencies for calculating maximum scour depth somewhat arbitrarily, lacking comprehensive discussion on practical engineering applications.
Research on identifying severely scoured areas remains limited. Melville, BW et al. [26] have employed a method based on geometric characteristics of nonuniform pier geometries to delineate scour areas. Yu Tongshun et al. [12] used scaled models to delineate the maximum scour area around composite pier foundations in practical engineering. Wu, P et al. [27] discovered that maximum scour depth occurs at a 75-degree angle to tank walls through flume experiments. However, these studies still have limitations, hindering the accurate capture and quantification of complex factors influencing the limit of the scour depth of riverbeds, such as water flow velocity, direction, level, sediment particle size, and channel morphology. Consequently, identifying unstable riverbeds and determining suitable engineering project locations remains challenging.
To address these challenges, this paper uses the Nanning Metro Line 6 river-crossing tunnel project as a case study and introduces the concept of critical flood frequency for determining riverbed limit scouring. A calculation method based on a two-dimensional hydrosediment model is proposed, overcoming limitations of empirical formulas that often consider only specific conditions. By employing this riverbed limit scouring model, the study aims to accurately pinpoint severely scoured areas of the riverbed, offering technical insights to optimize the siting of river-crossing tunnel projects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Basic Information of the River Channel
The Yu River, the primary tributary of the Xi River system within the Pearl River Basin, originates in Weishan County, Yunnan Province, China. As it flows through Nanning city, this segment is referred to as the Yong River. The levees flanking the Yong River in Nanning city adhere to a 50-year flood protection standard. Through coordinated management with upstream flood control reservoirs, the urban flood protection level in Nanning can be extended to 200 years. According to data from the Nanning Hydrological Station (III), the Yong River has an average annual natural runoff of 41.8 billion m3 per year, with an average sediment content of 0.24 kg/m3, making it one of Guangxi’s rivers with the lowest sediment load. The flow rate of the Yong River fluctuates significantly between wet and dry seasons. The largest recorded flood on record occurred in 1881, peaking at 23,100 m3/s with a recurrence interval of 300 years, marking the highest flow ever recorded. In contrast, the lowest extreme flow was a mere 95.6 m3/s.
Nanning Metro Line 6 spans the Yong River with an underwater tunnel located 35.3 km downstream of the Laokou Hydropower Station and 41.7 km upstream of the Yongning Hydropower Station. The project site covers a catchment area of 72,754 km2, with a normal water level at 67.14 m, characterized by a deep U-shaped river channel. Upstream of the project, key landmarks include the Nanning Hydrological Station (III) at 10.5 km, followed by the Yong River North Bridge at 1.66 km, the Taoyuan Bridge at 0.1 km, and downstream at 0.92 km, the Lingtie Bridge. The left bank near the project features the Beicheng East Levee, while the right bank is secured by the Henan East Levee. The river’s main channel near the project predominantly follows the left bank, passing under the Taoyuan Bridge and constrained by the Beicheng East Levee. As it nears the Taoyuan Bridge, the channel gradually shifts towards the right bank, further constrained by the Henan East Levee, causing a gradual centralization of the mainstream. The river width in this project section ranges from 280–400 m, with a composite section lacking distinct narrowing points that dictate the overall course of the river channel. Figure 1 illustrates the detailed project layout plan.
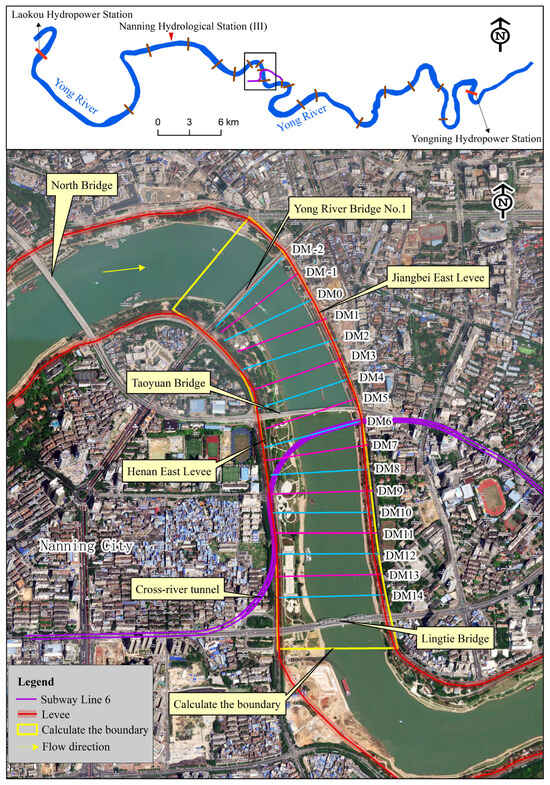
Figure 1.
Project layout plan.
2.1.2. The Composition of the Riverbed
(1) Strata and Rock Layers
The riverbed consists of active layers and an anti-erosion layer. Based on geological survey data, the active layers are categorized into four distinct layers: the fill layer, ranging in thickness from 1.2–7.8 m; the cohesive soil layer, varying in thickness from 1.3–3.0 m; the sandy soil layer, with a thickness ranging from 3.7–9.3 m; and the gravel (cobble) layer, varying from 9.0–13.3 m in thickness. The anti-erosion layer primarily consists of muddy siltstone and silty mudstone, located at the riverbed’s bottom, with elevations below 44.75 m. Due to the robust erosion resistance of the bedrock, the proposed project is planned to traverse beneath the Yong River, starting from below the bedrock level. It is preliminarily inferred that the erodible layers are positioned above the 44.75-m elevation mark.
(2) Particle Size
In the river section where the project is situated, the suspended sediment particle size ranges from 0.002 to 0.05 mm. Among these, suspended silt particles smaller than 0.02 mm constitute 81%, with an average median particle size of 0.008 mm. The bed sediment particle size ranges from greater than 0.002 mm, where particles sized between 0.002 and 20 mm account for about 75% of the total mass. The median particle size for bed sediment is 0.287 mm.
2.2. Mathematical Equations
This study employs a moving-bed mathematical model to calculate hydrosedimentological processes in rivers, widely used in river management, construction projects in riverine areas, and engineering safety assessments [28,29]. The mathematical model for a moving bed encompasses fundamental equations such as the continuity equation for flow, momentum equation for flow, conservation equation for suspended solids, and equation for bed deformation [30,31], structured as follows:
(1) Cartesian coordinate system fundamental equations:
The continuity equation for flow is as follows:
Momentum equation for flow is as follows:
The conservation equation for suspended solids is as follows:
Equation for bed deformation is as follows:
—time, s; —water depth, m; —flow velocity in x, y directions, m/s; —water level, m; —acceleration due to gravity, m/s2; —turbulent viscosity coefficient of flow, m2/s; —Chezy coefficient, where n is the roughness; —sediment content, kg/m3; —sediment carrying capacity, kg/m3; —settling velocity of sediment particles, m/s; —dry density of sediment, kg/m3; —recovery saturation coefficient; —sediment diffusion coefficient; —settling velocity, sediment content, and sediment carrying capacity of grouped sediment particles; —bed load transport rate in the x and y directions.
(2) Cartesian coordinate system fundamental equations:
The water flow continuity equation is as follows:
Water flow motion equation is as follows:
The mass conservation equation for suspended solids is as follows:
Bed deformation equation is as follows:
(3) Sediment transport calculation formula
The sediment transport calculation in the model follows the van Rijn sand transport formula, expressed as [32]:
(4) The calculation method used in the discrete model
The model discretizes equations using the finite volume method with grid alignment. Derived from this approach, the basic equations of the general curvilinear coordinate system model are uniformly discretized as follows:
In the discretization process, the convection term is implemented using Patankar’s power law scheme. To maintain the coupling of pressure and velocity within the grid system, the calculation of interfacial flow velocity employs the momentum interpolation method. The coupling solution for pressure and velocity is then computed using the SIMPLEC algorithm.
Boundary conditions:
Boundary conditions in planar two-dimensional water flow and sediment mathematical models generally involve river mouth and outlet boundaries, riverbank constraints, and dynamic boundary treatments. In this model specifically they are as follows:
Inlet boundary: The known total cross-sectional flow rate at the inlet determines the distribution of in-flow discharge across the section. For dynamic bed simulations, the sediment content at each grid point of the inlet section must also be specified.
Outlet boundary: generally, the water level of the outlet section is specified.
Riverbank boundary: it acts as a no-slip boundary, where the velocity is set to zero at this boundary.
Dynamic boundary: This model employs the “freezing” method for dynamic boundary treatment. It determines whether a grid cell is exposed above the water surface based on the riverbed elevation at the water level nodes. If the cell is not exposed, normal roughness values are applied; if exposed, a very large positive number close to infinity is used. Additionally, to prevent interference with the solution of water flow control equations, a thin water layer of about 0.1 cm thickness is assigned to nodes exposed to the water surface.
Parameter handling:
The accuracy of the moving-bed mathematical model hinges significantly on parameter selection and the management of related factors. Key considerations include determining values for roughness and turbulent viscosity coefficients, calculating sediment carrying capacity in water flow, handling bed sediment gradation patterns, and establishing calculation grids [33].
The river roughness is calibrated using measured hydrological data, and the turbulent viscosity coefficient is calculated as , with α taken as 0.5.
The sediment carrying capacity of the flow is determined using Zhang Ruijin’s formula:
where are the coefficients and exponents of the sediment carrying capacity; is the average section flow velocity, m/s; and is the representative settling velocity of the sediment, m/s.
The riverbed is divided into three layers: the surface layer, which facilitates sediment exchange; the middle layer, serving as a transition zone; and the bottom layer, which limits sediment scouring. Throughout each calculation period, the interfaces between these layers are kept constant, allowing sediment exchange solely within the surface layer, while the middle and bottom layers remain undisturbed temporarily.
The proposed project is situated 100 m upstream of the existing Nanning Taoyuan Bridge. To accurately replicate real flow conditions, a grid matching the dimensions of the bridge piers is created, and roughness parameters for these bridge pier grids are adjusted accordingly. The bridge piers are treated as fixed structures without flow interaction. The river section modeled by this study spans 2 km, covering 1 km upstream and 1 km downstream of the project site. The total computational area is 969,504 square meters, with an average river width of 485 m. It is divided into 6300 quadrilateral grids, arranged with 63 grids in the x-direction (transverse) and 100 grids in the y-direction (longitudinal). Grid spacing in the flow direction ranges from 20 to 50 m, while in the width direction, it ranges from 7 to 15 m.
The model computes both the grid topography and the interpolated grid topography, and Figure 2 presents specific details.
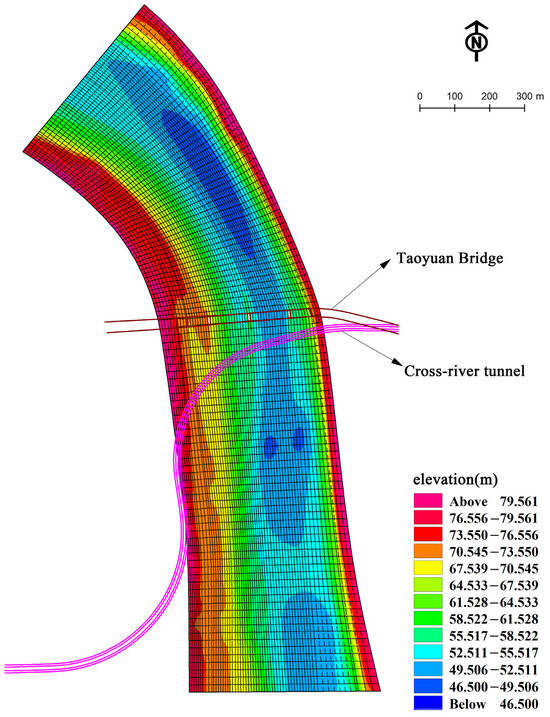
Figure 2.
Calculated grid and initial topographic map.
2.3. Data Source
The topographic and geological data for the engineering river section in this study were obtained through on-site surveys conducted by the Guangxi Nanning Survey & Design Institute Co., Ltd., under the Pearl River Water Resources Commission. These surveys spanned from early August 2021 to late December 2021. Hydrological and sediment transport data for the same period were sourced from the Nanning Hydrological Center.
3. Results
3.1. Model Validation
3.1.1. Model Debugging
During model debugging, the focus is on refining both the fixed-bed and mobile-bed models. The fixed-bed model primarily fine-tunes roughness parameters across the engineering river section. This involves setting parameters for the main channel and shoals, and through iterative testing, calibrating the main channel roughness to range between 0.019 and 0.023, and shoal roughness between 0.028 and 0.036. Once the fixed-bed model is optimized, attention shifts to calibrating the sediment transport coefficient and exponent in the mobile-bed model. Iterative adjustments are made to set the suspended sediment transport coefficient k between 0.10 and 0.15 for the modeled river section, with an exponent m of 0.92.
3.1.2. Steady-Bed Model Validation
The fixed-bed model is validated by examining the water surface profiles along the stream and the flow velocities across the cross-sections.
In 2021, this model validates using the maximum peak flow observed in the engineering river section on 13 October 2021, which reached 3560 m3/s. At that time, the downstream water level was 67.63 m, and the sediment content was 0.067 kg/m3. Topographic changes were based on a 1:1000 topographic map surveyed in August 2021. Initial conditions assume a normal water level of 67 m in the river. The initial suspended sediment conditions are derived from a statistical analysis of 65 years (1954–2018) of sediment transport data from the Nanning Hydrology (III) Station, located 10.5 km upstream of the project. Over these years, the average suspended sediment load was calculated at 9.36 million tons per year, equivalent to 0.212 kg/m3.
- Water level validation
Table 1 presents the validation results for water levels, demonstrating that the calculated values exhibit minimal discrepancies compared to the measured data, with differences consistently within 2 cm.

Table 1.
Water level calibration and validation results.
- Velocity verification
Figure 3 illustrates the verification of velocity distribution at various sections, indicating that the calculated velocities align closely with observed conditions. The position of the main channel flow lines also corresponds well to the actual positions. Regarding velocity magnitude, the discrepancies between simulated and observed velocities are predominantly within 0.2 m/s, with quantitative results generally agreeing well.
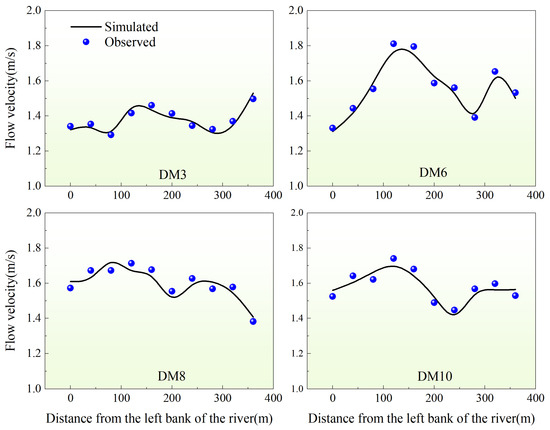
Figure 3.
Section velocity verification diagram.
Based on the validation outcomes for water levels and sectional velocities, it is clear that this model demonstrates excellent accuracy and reliability in hydrodynamics. This positions it as a robust tool for simulating and calculating engineering river sections based on these findings.
3.1.3. Riverbed Operation Model Verification
To enhance the precision and efficiency of river dynamics models, this study optimizes the roughness distribution field parameters (including longitudinal segmentation and lateral beach channel roughness settings). It simulates channel characteristics by incorporating median particle size distribution field parameters derived from detailed geological survey data. Additionally, it applies advanced grid technology to navigate complex terrains and obstacles, alongside parallel computing across multiple systems to adjust parameters and boost computational efficiency.
- Verification of sedimentation and scouring distribution
Figure 4a displays the surveyed riverbed topography as of December 2021, while Figure 4b shows the modeled riverbed topography from August to December 2021. Comparing the two reveals consistent features in riverbanks and sandbars, with slight variations noted in deeper channels. Overall, the models exhibit a high level of agreement, affirming the model’s accuracy in predicting changes in riverbed topography.
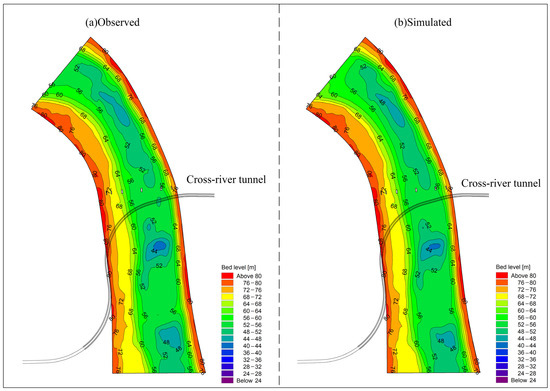
Figure 4.
Comparison of calculated and measured topographies at the end of 2021.
- Verification of cross-sectional sedimentation and scouring
Figure 5 compares the calculated topography of characteristic cross-sections at the project site as of December 2021 against the actual measured topography. The results show a high level of agreement with measured topographic data, typically exhibiting errors within 0.2 m. The model effectively simulates changes in cross-sectional scouring and silting, highlighting its capability in accurately depicting these dynamics.
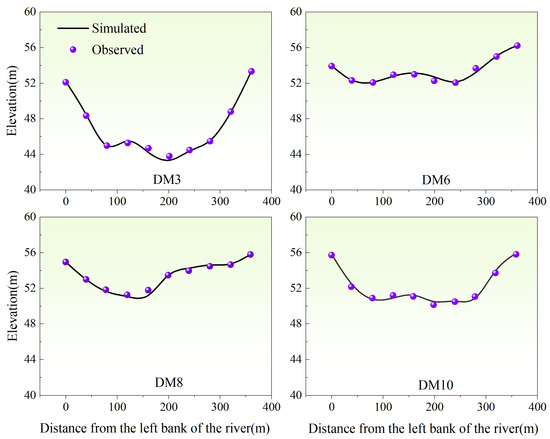
Figure 5.
Comparison of calculated and measured scouring and silting changes at the end of December 2021.
Overall, the two-dimensional planar mathematical model developed in this study demonstrates a high level of agreement between its calculated results and actual measured data after validation with water and sediment data. It effectively simulates the flow and sediment transport characteristics of the engineering river section, indicating its capability to provide accurate predictions for such hydrodynamic processes.
3.2. Test Conditions
This study aimed to analyze the scouring conditions of engineering river sections under three flood scenarios: high, medium, and low. The upper boundary conditions for the model included historical maximum flood, urban flood control design flood, and a large flood recorded in 2018, with flow rates of 23,100 m3/s, 19,100 m3/s, and 7540 m3/s, respectively. It is noted that the Nanning flood control system is designed to handle peak flows of the Yong River expected once every 50 to 200 years, matching the urban flood control design flood.
From 9 to 24 August 1968, a basin-wide flood occurred on the Yong River due to the influence of a southwest vortex and a typhoon, resulting in a peak flow of 13,300 m3/s, which corresponds to an event with a return period of about once in 8 years. This flood persisted for 15 days. Given its duration and significance, this study selects this flood event as a representative case and scales it up to simulate events with return periods of once in 300 years and once in 50 years. The details are shown in Figure 6.
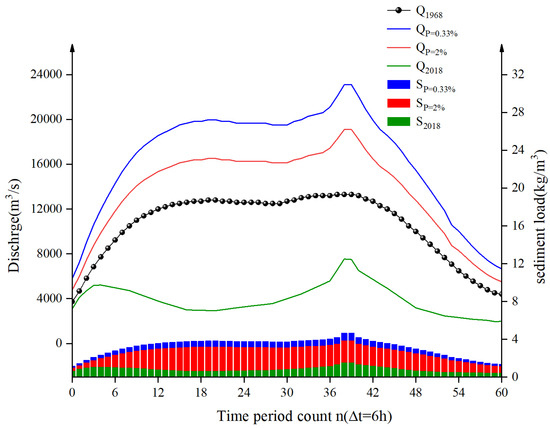
Figure 6.
Model boundary conditions.
The sediment transport at the upper boundary of the model is calculated using the relationship between water and sediment at Nanning Hydrological Station (III), with corresponding peak sediment concentrations of 4.65 kg/m3, 3.86 kg/m3, and 1.52 kg/m3. The particle size of the bed sediment is determined based on the median particle size of the riverbed from geological exploration data of engineering river sections, which is 0.287 mm. The model’s boundary conditions are depicted in Figure 5, and the characteristic values of the model experiments are outlined in Table 2.

Table 2.
Characteristic Values of Model Experiments.
3.3. Prediction of the Maximum Scouring Depth at the Tunnel Site Section
Figure 7 illustrates the erosion and deposition outcomes in the engineering section under three hydrological conditions modeled in this study. The cross-river tunnel riverbed section exhibits a pronounced U-shape, with a gentle slope on the right bank and a steeper slope on the left bank. Overall, the section experiences erosion, particularly in the deep channel area where the maximum erosion depth occurs. Relative to the initial topography, the sections under historical maximum flood, urban flood control design flood, and the 2018 measured large flood saw maximum erosion depths of 2.17 m, 5.01 m, and 6.12 m, respectively. Following erosion, the lowest elevations recorded were 50.55 m, 46.88 m, and 45.50 m, respectively.
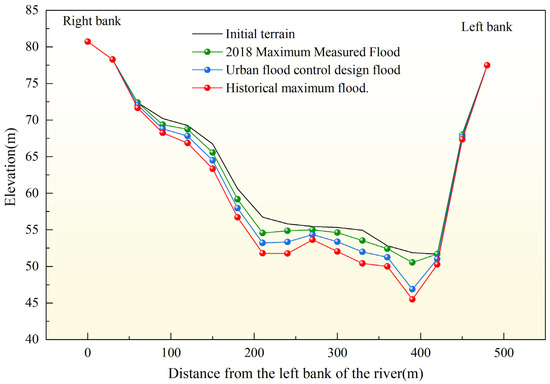
Figure 7.
Morphological changes in the engineered section riverbed.
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Extreme Flood Frequency
River-crossing tunnels play a critical role as control points for determining the burial depth of entire subway lines, a crucial aspect of engineering design [34,35]. Therefore, careful consideration of flood frequency is paramount. If the flood frequency is too low, the tunnel may not be buried deep enough, leaving the riverbed vulnerable to scouring during floods, thereby jeopardizing the project’s safety. Conversely, setting the burial depth too deep in response to a high flood frequency significantly escalates construction costs and complexity. This approach can lead to uneven slope gradients on either side of the tunnel, impacting the project’s overall design coherence. Rifo, C et al. [23] conducted similar research on bridge scouring, using flood frequency statistics to calculate the limit scour depth, which can vary widely. The design flood could range from a once-in-100-year event to an even rarer once-in-10,000-year flood. Given that subways are typically constructed in densely populated, economically developed urban areas [36], urban flood control standards serve as a benchmark for defining extreme flood frequencies. This ensures that tunnel designs are both safe and cost-effective, considering worst-case scenarios. To ensure safety and functionality, it is crucial to select a flood frequency with a longer recurrence period, such as an extreme flood event. This approach minimizes the risk of compromising either the city or the tunnel’s safety standards.
In this study, an extensive analysis was conducted on flood-induced scouring in the river section where the Nanning Metro Line 6 river-crossing tunnel is situated. We simulated and computed scouring intensity at eight different flood frequencies: = 50% (8700 m3/s), = 20% (11,800 m3/s), = 10% (14,100 m3/s), = 5% (16,100 m3/s), = 2% (19,100 m3/s), = 0.33% (23,000 m3/s), = 0.25% (25,000 m3/s), and = 0.2% (27,500 m3/s). Statistical analysis was performed on average flow velocity and maximum scouring depth over an 800 m stretch upstream and downstream of the engineering section (refer to Figure 1 DM-2~DM14 for section layout, with sampling intervals of 100 m). Detailed findings are presented in Figure 8.
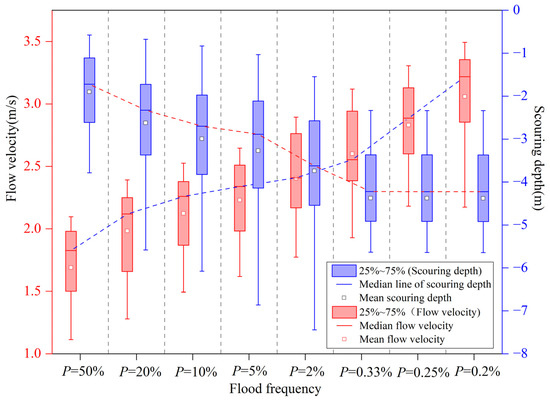
Figure 8.
Channel flow velocity vs. boxplot of flood scouring at different frequencies.
Figure 8 demonstrates that flow velocity directly impacts scouring intensity. As flood frequency increases from a 2-year to a 300-year recurrence interval, flow velocity gradually rises, leading to increased scouring depth. However, once flow velocity reaches or exceeds that of a 300-year flood, sediment transport capacity becomes saturated, causing scouring depth to stabilize or decrease. This saturation occurs because higher velocities do not further enhance erosion or sediment transport beyond a certain point. Elevated flow velocities can also alter riverbed morphology, creating shoals and deep channels that dissipate water energy and mitigate erosion. Moreover, these conditions may alter the riverbed strata, leaving behind larger, more erosion-resistant sand grains that reduce scouring depth.
This indicates that there is a threshold flow velocity beyond which the sensitivity of maximum scouring depth to changes in flow velocity decreases. The flood frequency associated with this critical flow velocity is termed the critical flood frequency. In this study, the critical flood frequency is a once-in-300-year event, which exceeds Nanning city’s urban flood control standard of once-in-200 years. Therefore, selecting a 300-year flood as the flow condition for calculating maximum scour is appropriate because it meets the requirements for the maximum scour calculation without compromising the implementation of the urban flood control standard.
4.2. Analysis of the Influence of Riverbed Particle Size on the Maximum Scour Depth
The variability in riverbed particle composition influences scouring depth significantly: coarse-grained riverbeds, characterized by high friction forces and shear strength but low sediment-carrying capacity, exhibit shallower scour depths. In contrast, fine-grained riverbeds, with low friction and shear strength but high sediment-carrying capacity, experience deeper scouring [33,37,38]. In this study, scouring conditions of riverbed sections were simulated under six flood frequencies: = 50%, = 20%, = 10%, = 5%, = 2%, and = 0.33%, corresponding to median particle sizes of 0.287 mm, 0.5 mm, 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm, and 5 mm. Average flow velocities and maximum scouring depths were statistically analyzed at 17 stations within 800 m upstream and downstream of the engineering section (see Figure 1 DM-2 to DM14 for layout, with 100 m intervals). Detailed results are presented in Figure 9. Maximum scouring depths for each median particle size under the six flood frequencies range as follows: 1.90–4.30 m, 1.67–3.89 m, 1.43–3.47 m, 1.15–2.98 m, 0.77–2.31 m, 0.58–1.98 m, and 0.39–1.65 m. Average scouring depths are −3.14 m, −2.81 m, −2.47 m, −2.07 m, −1.54 m, −1.28 m, and −1.01 m, respectively. These values indicate that particle size strongly influences the riverbed’s maximum scouring depth, with larger particles leading to shallower scouring depths. For every 1 mm increase in particle size, scouring depth decreases by 0.3–0.6 m. In practical engineering applications, understanding the relationship between riverbed particle size and scouring depth helps quantify scouring risks and optimize design strategies. For instance, in a fine sand riverbed with a median particle size of 0.5 mm, a 300-year flood could result in a maximum average scouring depth of 3.89 m across the riverbed. Therefore, appropriate protective measures, such as reinforcing the riverbed or installing anti-scouring measures, should be based on detailed scouring calculations.
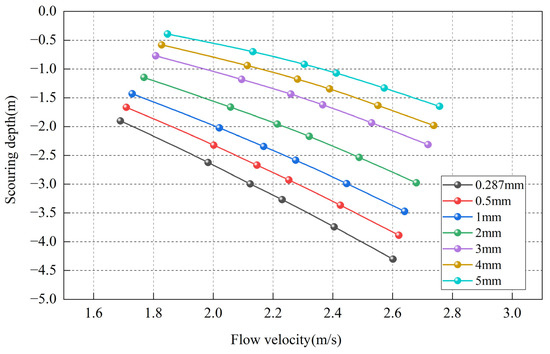
Figure 9.
Variation in scouring depth under different riverbed particle compositions and flow velocities.
4.3. The Analysis of the Impact of Flow Conditions on the Riverbed’s Maximum Scour
The Froude number (Fr), a dimensionless parameter characterizing the relative magnitude of fluid inertial force and gravity [39], is calculated by the following formula:
During the flood season in the Yong River, water depths typically exceed 15 m in average sectional measurements, while average flow velocities generally remain below 3.0 m/s. According to the Froude number calculation formula, the computed Froude numbers are typically less than 1, indicating slow flow conditions in the Yong River during floods. This signifies that gravitational forces exert a predominant influence over inertial forces, with fluid motion resistance primarily attributed to riverbed friction [40,41,42]. Despite the significant increase in flow volume during the flood season, flow velocities are constrained by riverbed friction, preventing further acceleration and thereby maintaining the Froude number at a relatively low level [39,43].
Figure 10 illustrates the correlation between the Froude number (Fr) and the amplitude of riverbed scouring and silting across six flood frequencies: = 50%, = 20%, = 10%, = 5%, = 2%, and = 0.33%. The x-axis represents changes in riverbed elevation, while the y-axis represents Fr. The scatter plot reveals an upward-opening skewed symmetric curve, expanding gradually with higher flood intensities. Under flood conditions of = 50%, = 20%, = 10%, = 5%, = 2%, and = 0.33%, the amplitude of riverbed elevation changes ranges as follows: −3.311.97 m, −4.052.39 m, −4.613.06 m, −5.193.50 m, −5.484.24 m, and −6.535.36 m, respectively. This indicates that at lower Froude numbers, riverbed scouring and silting exhibit minimal changes, suggesting stability. As the Fr increases, the amplitude of these changes also increases, indicating heightened susceptibility to erosion or siltation at higher flow velocities. The curve’s symmetry suggests a critical Froude number threshold, identified as the curve’s lowest point and y-axis intercept. Below this threshold, the riverbed tends to remain stable.
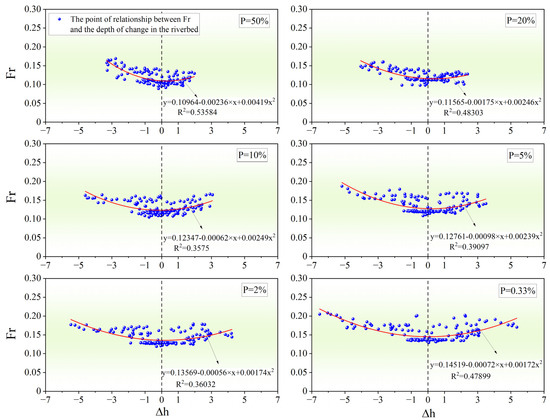
Figure 10.
The relationship between riverbed erosion and deposition and Fr (where positive values represent deposition and negative values represent erosion).
By combining curve fitting formulas, yx=0 is calculated, and then the river depth is reverse-calculated using the Froude number formula. This depth is referred to as the “critical depth.” The critical depth varies with different flood frequencies. Above the Froude number threshold, the riverbed is less influenced by flow conditions, and erosion and siltation processes reach a dynamic equilibrium, maintaining relative stability. For floods with probabilities of = 50%, = 20%, = 10%, = 5%, = 2%, and = 0.33%, yx=0 are 0.110, 0.116, 0.123, 0.128, 0.137, and 0.145, respectively. The average river flow velocities are 1.34 m/s, 1.54 m/s, 1.71 m/s, 1.82 m/s, 2.01 m/s, and 2.27 m/s, respectively. Using the Froude number equation, the critical depths are calculated as 15.13 m, 17.97 m, 19.70 m, 20.61 m, 21.94 m, and 24.98 m. At the engineering site, the average depth of water under the condition of = 0.33% is 25.03 m, which is close to the critical depth, with a low Froude number, indicating that the riverbed is relatively stable with a small range of erosion and siltation. The fluid inertial force is small and insufficient to overcome the friction force of the riverbed, making it difficult for riverbed materials to be eroded and carried away. In addition, due to the slow flow velocity, the carrying capacity of the sediment is low, and the particle deposition is weak, resulting in a small range of riverbed deformation, further confirming the stability of the riverbed.
Based on the above analysis, when a tunnel is constructed under a river without altering the riverbed and facing extreme flood events, the critical depth provides a reliable criterion for evaluating the tunnel’s location. If the water depth at the tunnel site closely matches the critical depth, it suggests that the riverbed is less affected by varying flow conditions. This condition reduces the risk of deformation and erosion, thereby enhancing engineering safety. On the other hand, the significant difference between the water depth at the river crossing the tunnel site and the critical depth implies that the riverbed may be more prone to excessive erosion or siltation, leading to a greater amplitude of riverbed deformation. For instance, if the actual water depth is much lower than the critical depth, the cross-sectional flow area is small, the river channel flow velocity is relatively high, and the inertial force of the fluid relative to gravity is relatively large, the riverbed is more susceptible to erosion (similar to the negative x-axis situation in Figure 10), which will adversely affect the site selection for the tunnel project.
In limit scour simulations, two-dimensional models simplify three-dimensional flow dynamics, notably by omitting eddies, and they struggle to account for obstacles like vegetation that influence flow patterns. This limitation affects the model’s reliability in assessing riverbed protection measures. Therefore, future research should aim to accurately simulate three-dimensional flow, fully incorporate the effects of riverine vegetation and obstacles on riverbed limit scour, enhance model precision, and improve predictions of riverbed erosion. This approach will establish a more robust scientific foundation for riverbed protection strategies.
5. Conclusions
This study employed a two-dimensional hydrologic–sediment mathematical model to compute the ultimate scour depth of the Nanning Metro Line 6. It investigated the effects of flood frequency, riverbed characteristics, and flow conditions on ultimate scouring, yielding the following conclusions:
The ultimate scour depth for the Nanning Metro Line 6 is designed for a frequency of 300 years, with the maximum scour depth reaching 6.12 m. This frequency selection considers the thickness of the erosion-resistant layer of the riverbed and exceeds standard urban flood control requirements. The aim is to ensure the safety of the tunnel project while balancing economic considerations and construction challenges.
Accurately identifying the particle size of the riverbed has a substantial impact on the ultimate scour depth. The research findings indicate that as the particle size increases by 1 mm, the scour depth decreases by about 0.3 to 0.6 m. This discovery is instrumental in formulating effective strategies for protecting riverbeds and improving the stability of tunnel projects.
This study utilized the Froude number to evaluate the suitability of the project site, offering insights into riverbed stability for the chosen river section. The findings reveal an upward-opening parabolic symmetric relationship between changes in riverbed erosion and siltation and the Froude number. The water depth corresponding to the lowest point of the Froude number represents the critical depth, indicating relative stability of the riverbed, which is advantageous for selecting sites for river-crossing tunnels. In practical engineering site selection, considerations extend beyond riverbed stability to encompass factors like urban development plans, lithological stratigraphy, and existing surrounding projects. Therefore, using the critical depth as a criterion for assessing project site suitability can provide decision-makers with prompt and accurate technical guidance. While this approach has limitations in engineering applications, it remains a crucial technical reference for decision-making processes.
Author Contributions
M.Y. initiated the study. L.F., F.X. and M.Y. designed and supervised the study. L.F. and F.X. compiled the data, performed the analyses, and drafted the manuscript with help from M.Y. All authors contributed to the results discussion and the review and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Guangxi Science and Technology Major Project: Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Science and Technology Department (Grant No. 2023AA14011).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Meiqing Yang, Luojie Feng, Bingqing Xu, Yuan Lv, and Yongjun Huang were employed by the company Guangxi Nanning Survey & Design Institute Co., Ltd. of the Pearl River Water Resources Commission. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Qiu, H. Discrete Element Modeling of a Cross-River Tunnel under Subway Train Operation during Peak and off-Peak Periods. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.D.; Xiong, X.H.; Wang, K.W.; Jiao, Q.Z.; Li, X.B.; Dong, T.Y.; Wang, J.Y. Influence of Variable Cross-Section on Pressure Transients and Unsteady Slipstream in a Long Tunnel When High-Speed Train Passes Through. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Xin, Z.; Deng, L.Y. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Bearing Behaviour of Confined Concrete Arch for a Traffic Tunnel. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 22, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, D.; Li, T.; Fang, H.; Xiao, L.; Du, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Li, B. A CFD-DEM Investigation into Hydraulic Transport and Retardation Response Characteristics of Drainage Pipeline Siltation Using Intelligent Model. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 152, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Gong, J.; Deng, J.; Xu, W. Effects of Air Vent Size and Location Design on Air Supply Efficiency in Flood Discharge Tunnel Operations. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2023, 149, 04023050. Available online: https://ascelibrary.org/doi/10.1061/JHEND8.HYENG-13305 (accessed on 19 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, W.; Fu, H.; Bu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zang, D.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. Schedule Risk Model of Water Intake Tunnel Construction Considering Mood Factors and Its Application. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Cao, C.; Lei, M. Construction Technology for a Shallow-Buried Underwater Interchange Tunnel with a Large Span. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 70, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, H.; Liu, N.; Dai, F. The Long-Term Safety of a Deeply Buried Soft Rock Tunnel Lining under inside-to-Outside Seepage Conditions. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 67, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, Y. Viscoelastic-Plastic Stability Analysis of Large-Section Quasi-Rectangular Pipe-Jacking Tunnel under-Passing Box Culvert. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, F.; Zhang, L.; Qian, B.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M. Three-Dimensional Characteristics of Pressure Waves Induced by High-Speed Trains Passing through Tunnels. Acta Mech. Sin. 2024, 40, 323261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, A.F.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.T. Numerical simulation of maximum scour depth of the riverbed above a subway tunnel crossing the tidal river. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 256, 2548–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y. Study of Scour Depth in River Reach of Qianjiang Tunnel across Qiantang Estuary. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 4, 51–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Wang, H.; Wu, T. Study on Limit Scouring of Maliuzhou Waterway: A Case Study of the Cross Gate TunnelProject. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 330, p. 022123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, L. Experimental Study on the River Engineering Model of Tunnel across Yangtze River about Line No.8 of Track Traffic in Wuhan. In Proceedings of the Materials, Transportation and Environmental Engineering, PTS 1 and 2; Kao, J.C.M., Sung, W.P., Chen, R., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd: Dürnten, Switzerland; Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 779–780, pp. 572–577. [Google Scholar]
- Suntoyo; Perkasa, B.; Atikasari, T.J.; Wisudawan, A. Longitudinal Pipeline Scour Propagation Induced by Wave-Current Interaction For the South Sumatra-West Java Submarine Pipeline. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 135, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Sharma, P.K.; Ahmad, Z.; Karna, N. Maximum Scour Depth around Bridge Pier in Gravel Bed Streams. Nat. Hazards 2018, 91, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.A.; Lim, S.-Y. Migration of Maximum Scour Location around Wide Setback Bridge Abutments in Floodplains. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaani, A.; Azimi, A.H. Analytical Approach for Predicting Local Scour Downstream of Submerged Sluice Gate with an Apron. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosronejad, A.; Diplas, P.; Angelidis, D.; Zhang, Z.; Heydari, N.; Sotiropoulos, F. Scour Depth Prediction at the Base of Longitudinal Walls: A Combined Experimental, Numerical, and Field Study. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2020, 20, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-S.; Chang, W.-Y.; Yen, C.-L. Maximum Local Scour Depth at Bridge Piers under Unsteady Flow. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 135, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.H.; Cox, M.L. Enhancing Maximum Scour Depth Determination for Spur Dikes Using a Validated Two-Dimensional Model. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2020: Hydraulics, Waterways, and Water Distribution Systems Analysis; Ahmad, S., Murray, R., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 84–98. [Google Scholar]
- Stella, J.M. Modeling Alex Hurricane: Flood Map Simulation Applying Multisensor Grid Precipitation, Monterrey, Mexico. Rev. Ambiente Água 2023, 18, e2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifo, C.; Arriagada, P.; Ettmer, B.; Link, O. Frequency Analysis of Extreme Scour Depths at Bridge Piers and Their Contribution to Bridge Collapse Risk. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 2029–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, L.M.; Chaput-Desrochers, L.; Guthrie, R. Practical Applications of Bed Scour Calculations: Two Case Studies. In International Pipeline Conference; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, R.; Lee, S.O.; Hong, S.H. A Comprehensive Method of Calculating Maximum Bridge Scour Depth. Water 2018, 10, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, B.W.; Raudkivi, A.J. Effects of Foundation Geometry on Bridge Pier Scour. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1996, 122, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Hirshfield, F.; Sui, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, P. Impacts of Ice Cover on Local Scour around Semi-Circular Bridge Abutment. J. Hydrodyn. 2014, 26, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physics of Flow, Sediment Transport, Hydraulic Geometry, and Channel Geomorphic Adjustment during Flash Floods in an Ephemeral River, the Paria River, Utah and Arizona-All Databases. Available online: https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/wos/alldb/full-record/PQDT:64484515 (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- Bressan, F.; Mantilla, R.; Schilling, K.E.; Palmer, J.A.; Weber, L. Hydrologic-Hydraulic Modeling of Sediment Transport along the Main Stem of a Watershed: Role of Tributaries and Channel Geometry. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Dai, M.; Zhang, D. Impoundment Impact of the Three Gorge Reservoir on the Hydrological Regime in the Lower Han River, China. Water 2018, 10, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Dai, M.; Xu, W.; Yan, T. Water Compensation and Its Implication of the Three Gorges Reservoir for the River-Lake System in the Middle Yangtze River, China. Water 2018, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelvink, D.; Reniers, A. A Guide to Modeling Coastal Morphology; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, T.; Kawahara, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tateishi, A. Eulerian Deposition Model for Sediment Mixture in Gravel-Bed Rivers with Broad Particle Size Distributions. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, M.; Zhong, Z.; Du, X. Optimum Intensity Measures for Probabilistic Seismic Demand Model of Subway Stations with Different Burial Depths. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 154, 107138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Influence of Subway Burial Depth on Dynamic Response of Train-All Databases. Available online: https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ200603013.htm (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Rahim, A.; Xia, F.; Tolba, A.; Al-Makhadmeh, Z. IS2Fun: Identification of Subway Station Functions Using Massive Urban Data. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 27103–27113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakabe, T. Study on the Measurement and Indication Method of Sediment Discharge Taking Account of Particle Size. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on River Sedimentation, Vols 1-4; Hu, C., Tan, Y., Zhou, Z., Shao, X., Liu, C., Eds.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 2583–2590. [Google Scholar]
- Numerical Study on the Influence of Riverbed Median Particle Size onScour Pit Evolution Process around Bridge Pier-All Databases. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/42.1171.TV.20210805.0913.006 (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- Choi, G.W.; Ahn, S.J. Maximum Local Scour Depth Variation at Bridge Piers. In Proceedings of the Hydraulics of Rivers Water Works and Machinery, Vol II, Theme D, Proceedings: 21st Century: The New Era for Hydraulic Research And Its Applications; Li, G., Ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Kokpinar, M.A.; Kucukali, S. Effect of Particle Size on Flip Bucket Scour. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 43, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Experimental Study on the Hydraulic Characteristics of the Two-Stage Energy Dissipation in Low Froude Number Flow-All Databases. Available online: https://iahrapd2020.xsrv.jp/proceedings/pdf/1-1-20.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- River Patterns Based on Area Type Froude Number and Channel Scale of Maximum Sediment Transport Flow in the Yellow River-All Databases. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2019.02.002 (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- Park, S.W.; Hwang, J.H.; Ahn, J. Physical Modeling of Spatial and Temporal Development of Local Scour at the Downstream of Bed Protection for Low Froude Number. Water 2019, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).