Degradation of Diclofenac by Bisulfite Coupled with Iron and Manganous Ions: Dual Mechanism, DFT-Assisted Pathway Studies, and Toxicity Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Computational Analysis
2.5. Toxicity Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of DCF Degradation
3.2. Dual Mechanism
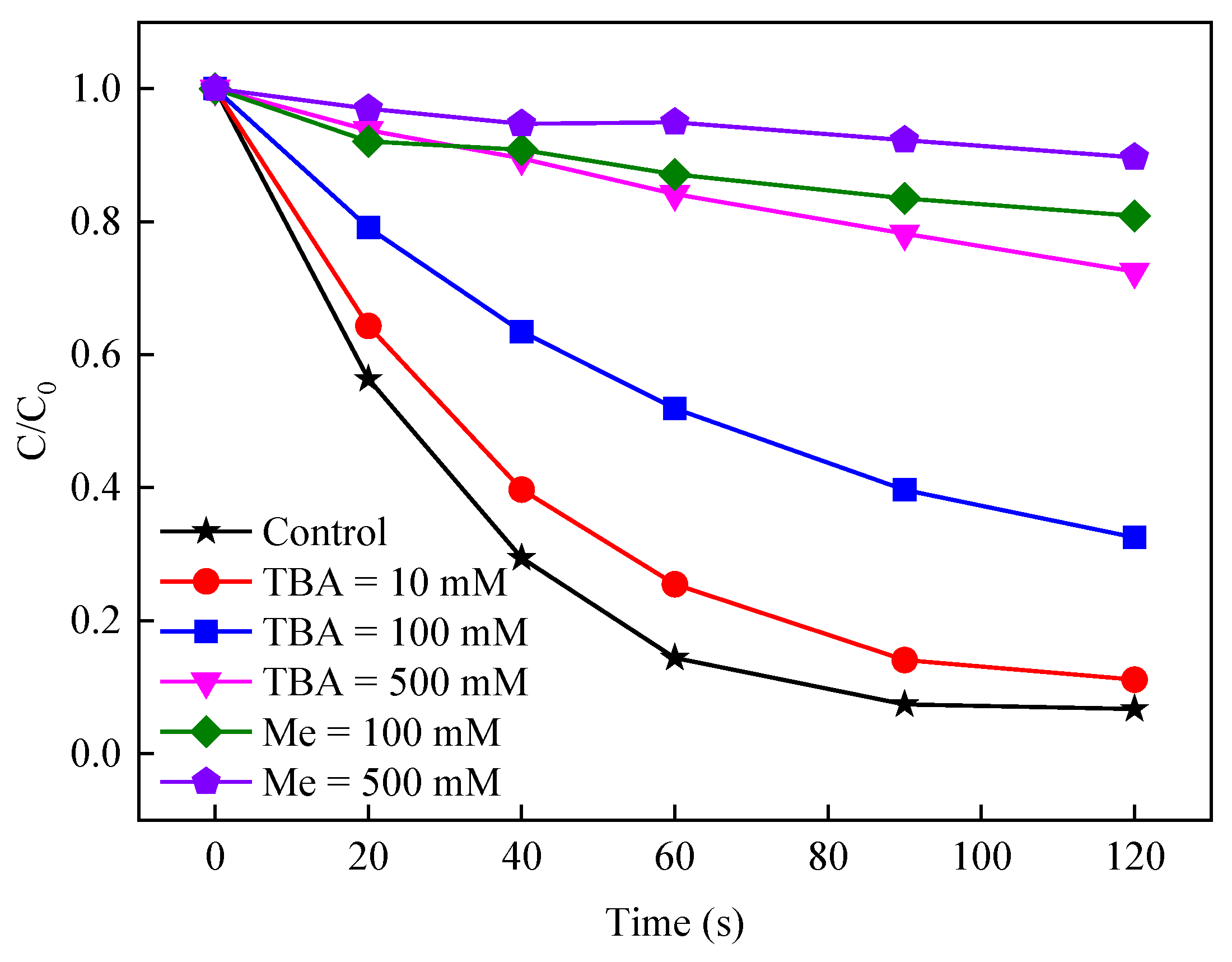
3.2.1. Kinetics Analysis of Different BS Concentrations
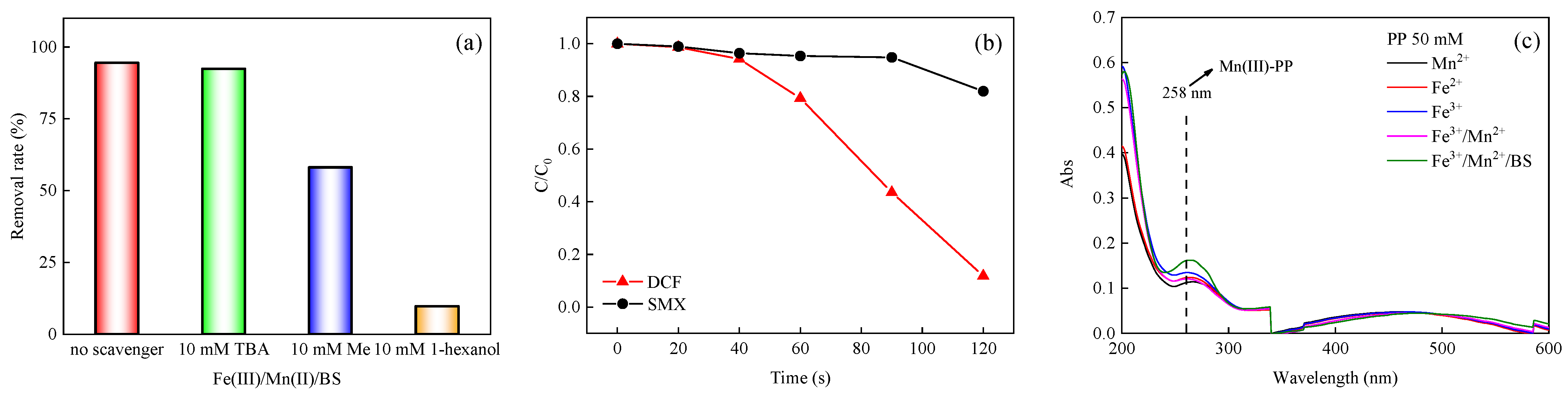
3.2.2. Identification of SO4•−
3.2.3. Identification of Mn(III)
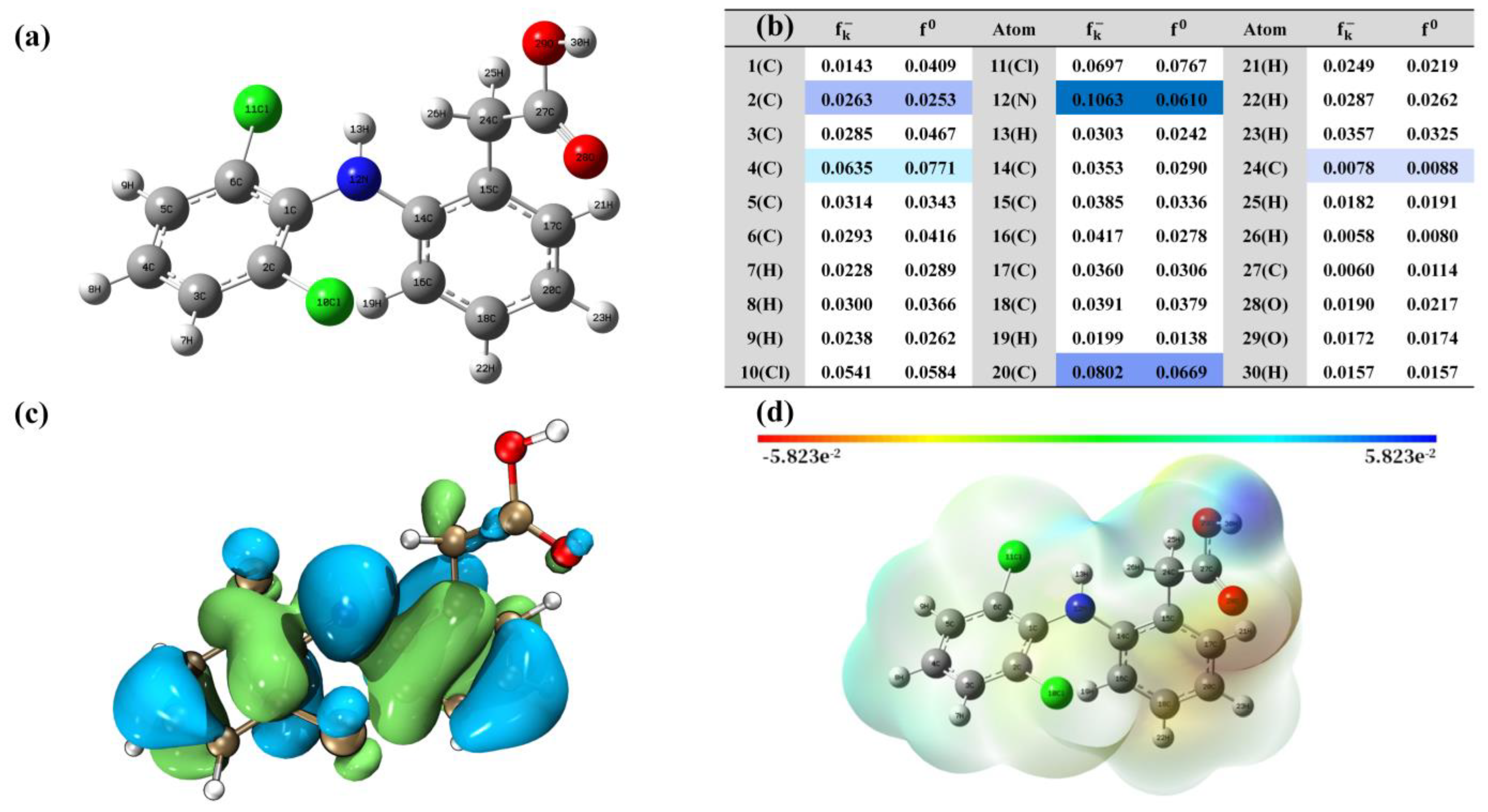
3.3. Attack Points Prediction by DFT
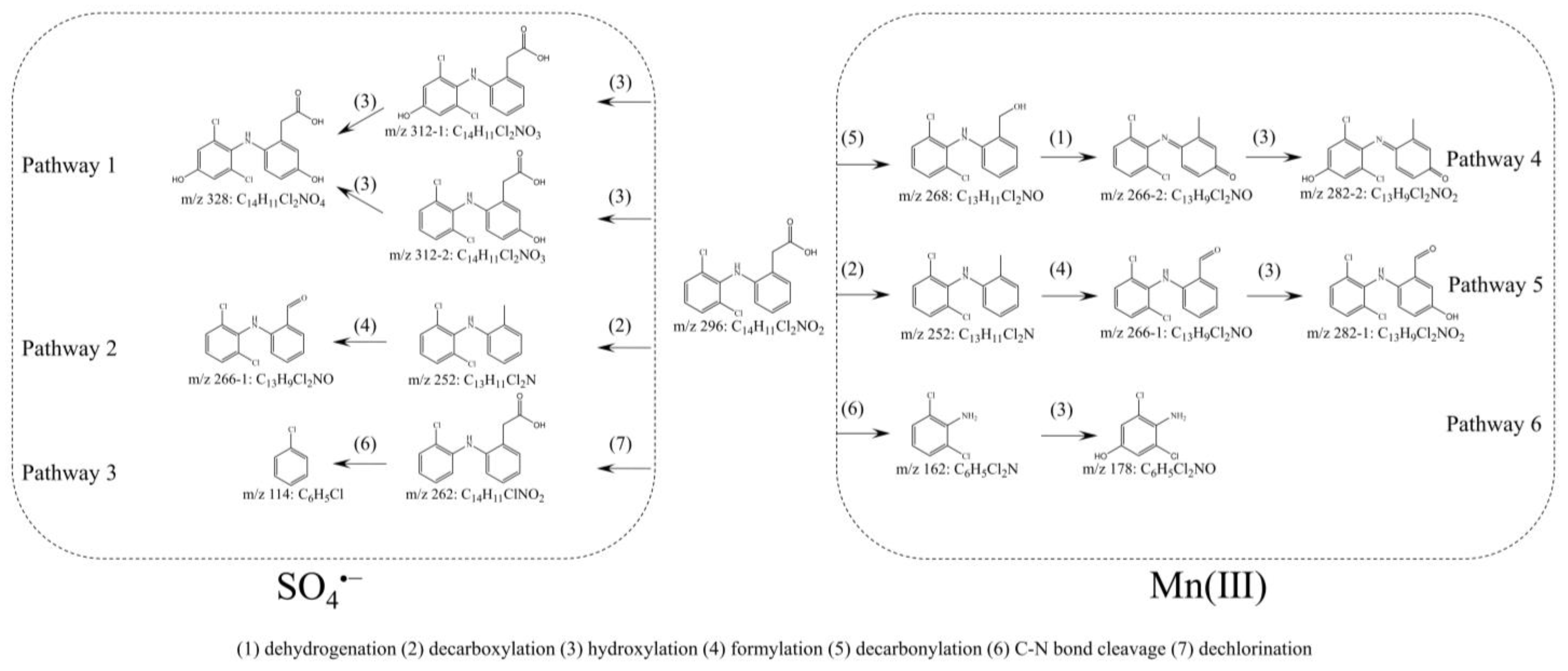
3.4. DCF Degradation Pathways
3.5. Toxicity Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, W.; Lv, W.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, W.; Li, T.; Dong, B. Effects of Long-Term Exposure of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products on Algogenic Organic Matter Characteristics. Water 2023, 15, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Leng, C.; Wang, H. Pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) degradation and microbial characteristics of low-temperature operation combined with constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, L.; Tang, L.; Mei, J.; Fu, J. Unveiling combined ecotoxicity: Interactions and impacts of engineered nanoparticles and PPCPs. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 170746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, R.; Tian, D.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Ren, K.; Gao, L.; et al. Occurrences, Seasonal Variations, and Potential Risks of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products in Lianjiang River, South of China. Water 2023, 15, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, M.S.; Azha, S.F.; Ismail, S. A review of diclofenac occurrences, toxicology, and potential adsorption of clay-based materials with surfactant modifier. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, C.; Hădade, N.; Pesek, S.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, R.; Moț, A.C. Removal and degradation of sodium diclofenac via radical-based mechanisms using S. sclerotiorum laccase. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2023, 249, 112400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñafiel, M.E.; Jara-Cobos, L.; Flores, D.; Jerves, C.; Menendez, M. Enhancing adsorptive removal of diclofenac from aqueous solution: Evaluating organic and inorganic acid treatment of zeolite. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stülten, D.; Zühlke, S.; Lamshöft, M.; Spiteller, M. Occurrence of diclofenac and selected metabolites in sewage effluents. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, A.B.; Kolpin, D.W.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Tolls, J. Peer reviewed: Are veterinary medicines causing environmental risks? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 286A–294A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Meisenheimer, M.; McDowell, D.; Sacher, F.; Brauch, H.-J.; Haist-Gulde, B.; Preuss, G.; Wilme, U.; Zulei-Seibert, N. Removal of pharmaceuticals during drinking water treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3855–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Snyder, S.A.; Wert, E.C.; Yoon, J. Removal of endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceuticals by nanofiltration and ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2007, 202, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, J.B.; Weiss, S.; Reemtsma, T. Routes and metabolites of microbial degradation of selected acidic pharmaceutical and their occurrence in municipal wastewater treated by a membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, T.; You, L.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, W. Degradation of Atrazine by Flow-Through UV-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: Roles of Light Source and Chlorine Addition. Water 2024, 16, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Pang, S.; Jiang, J. Degradation of metoprolol by UV/sulfite as an advanced oxidation or reduction process: The significant role of oxygen. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 128, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, L.D.S.; Hoffmann, M.T.; dos Santos, D.V.; Daniel, L.A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Algal Organic Matter Using TiO2/UV and Persulfate/UV. Water 2024, 16, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by base: Implications for the degradation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Fu, Y. Enhanced removal of sulfamethoxazole by Mn (II)/bisulfite in presence of nitrilotriacetic acid: Role of Mn (III). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, F.; Li, J. Sulfite activation by a low-leaching silica-supported copper catalyst for oxidation of As (III) in water at circumneutral pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Jin, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhou, R.; Yin, A.; Sun, J.; Zhu, L. Enhanced degradation of atrazine through UV/bisulfite: Mechanism, reaction routes and toxicological analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fu, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by UV/sulfite in presence of oxygen: Efficiency, influence factors and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 268, 118709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, M.; Chen, C.; Chen, M.; Luo, K.; Xu, J.; Zhou, D.; Wu, F. Efficient bacterial inactivation by transition metal catalyzed auto-oxidation of sulfite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12663–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Hou, P.; Yuan, X.; Stanić, M.H.; Qiang, Z.; Dong, H. Homogeneous activation of bisulfite by transition metals for micro-pollutant degradation: Mn (VII) versus Cr (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Chen, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X.; Strathmann, T.J. Degradation of organic contaminants through activating bisulfite by cerium (IV): A sulfate radical-predominant oxidation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhang, T.; Song, S. Synthetic Fe-rich nontronite as a novel activator of bisulfite for the efficient removal of tetracycline. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rao, D.; Liu, H.; Hao, T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, B. The promoting effect of bisulfite on pollutant abatement by Fe (II)/peroxydisulfate: Dual roles of bisulfite as the accelerator of FeII-(FeIII/FeIV) recycling and radical precursor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, J. Mn (II)-enhanced oxidation of benzoic acid by Fe (III)/H2O2 system. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Cui, K.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, D.; Xi, S.; Wu, Z.; Wu, F. Remediating thiacloprid-contaminated soil utilizing straw biochar-loaded iron and manganese oxides activated persulfate: Removal effects and soil environment changes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Luo, T.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Brigante, M.; Mailhot, G. Enhanced oxidation of aniline using Fe (III)-S (IV) system: Role of different oxysulfur radicals. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zheng, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, W. Activation of MnFe2O4 by sulfite for fast and efficient removal of arsenic (III) at circumneutral pH: Involvement of Mn (III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhou, G. Degradation of diclofenac by Fe (II)-activated bisulfite: Kinetics, mechanism and transformation products. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.E.A. Gaussian 09, Revision 9.0; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Huang, W.; Liang, C.; Gao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Meng, L.; Zhong, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, J. Sulfamethazine degradation and copper transformation in Cu (II)/PMS system: In-depth investigation of the interaction between intermediates and copper. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, K.; Zhong, X.; Ning, H. Electro-Assisted Fe3+/Persulfate System for the Degradation of Bezafibrate in Water: Kinetics, Degradation Mechanism, and Toxicity. Water 2024, 16, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, J.; Fronaeus, S.; Elding, L.I. Kinetics and mechanism for manganese-catalyzed oxidation of sulfur (IV) by oxygen in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 4527–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronaeus, S.; Berglund, J.; Elding, L.I. Iron−manganese redox processes and synergism in the mechanism for manganese-catalyzed Autoxidation of hydrogen sulfite. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 4939–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameton, R.A.; Muller, J.G.; Burrows, C.J. Oxidative DNA damage from sulfite autoxidation catalyzed by manganese (III). Comptes Rendus Chim. 2002, 5, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiangwei, L.; Lidong, W.; Yi, Z.; Yongliang, M.; Shuai, C.; Shuang, L.; Peiyao, X.; Jiming, H. Oxidation rate of magnesium sulfite catalyzed by cobalt ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4145–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, J.E.; Luther, G.W., III; Nealson, K.H. Chemical and biological reduction of Mn (III)-pyrophosphate complexes: Potential importance of dissolved Mn (III) as an environmental oxidant. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 885–894. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Deng, J.; Lu, X.; Wan, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. Rapid and continuous degradation of diclofenac by Fe (II)-activated persulfate combined with bisulfite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 262, 118335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huie, R.E.; Neta, P. Rate constants for some oxidations of S (IV) by radicals in aqueous solutions. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1987, 21, 1743–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huie, R.E.; Clifton, C.L.; Altstein, N. A pulse radiolysis and flash photolysis study of the radicals SO-2, SO-3, SO-4 and SO-5. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part C. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1989, 33, 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, N.; Lai, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Li, J. A critical review of environmental remediation via iron-mediated sulfite advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, F.; Ge, L. Enhanced decolorization of orange II solutions by the Fe (II)–sulfite system under xenon lamp irradiation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10089–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Song, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, T. Organic contaminants degradation from the S (IV) autoxidation process catalyzed by ferrous-manganous ions: A noticeable Mn (III) oxidation process. Water Res. 2018, 133, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestovsky, O.; Bakac, A. Reactivity of aqueous Fe (IV) in hydride and hydrogen atom transfer reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13757–13764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, P.; Huie, R.E.; Ross, A.B. Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 1027–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.J.; Sarasa, J.; Loge, F.J.; Teel, A.L. Oxidative and reductive pathways in manganese-catalyzed Fenton’s reactions. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, C.L.; Huie, R.E. Rate constants for hydrogen abstraction reactions of the sulfate radical, SO4−. Alcohols. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1989, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Barbati, S.; Doumenq, P.; Chiron, S. Sulfate radical anion oxidation of diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole for water decontamination. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, J.; Liang, L.; He, F. Role of dissolved Mn (III) in transformation of organic contaminants: Non-oxidative versus oxidative mechanisms. Water Res. 2017, 111, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, X.; Song, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Y.F.; Jiao, N. Mn-catalyzed highly efficient aerobic oxidative hydroxyazidation of olefins: A direct approach to β-azido alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6059–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalkiewicz, S.; Malyszko, J. Study on the stability of Co (III), Mn (III) and Tl (III) ions in acetic acid solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 403, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ji, H.; Du, P.; Huang, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, W. Insights into catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate for carbamazepine degradation by MnO2 nanoparticles in-situ anchored titanate nanotubes: Mechanism, ecotoxicity and DFT study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. HCO3–/CO32–enhanced degradation of diclofenac by Cu (II)-activated peracetic acid: Efficiency and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Estrada, L.A.; Malato, S.; Gernjak, W.; Agüera, A.; Thurman, E.M.; Ferrer, I.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Photo-Fenton degradation of diclofenac: Identification of main intermediates and degradation pathway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8300–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Mu, W.; Chang, C. In-situ construct CuInS2/Bi/Bi2MoO6 S-scheme/Schottky dual heterojunctions catalyst for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac sodium. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 351, 124077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Rao, Y.Y.; Ning, H.; Chen, J.X.; Zeng, Q.; Tian, F.X.; Gao, N.Y. Comparative investigation of diclofenac degradation by Fe2+/chlorine and Fe2+/PMS processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. Degradation kinetics and mechanism of diclofenac by UV/peracetic acid. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9907–9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, D.; Liang, J. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac by carbon quantum dots modified porous g-C3N4: Mechanisms, degradation pathway and DFT calculation. Water Res. 2019, 151, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculewicz, J.; Kowalska, D.; Świacka, K.; Toński, M.; Stepnowski, P.; Białk-Bielińska, A.; Dołżonek, J. Transformation products of pharmaceuticals in the environment: Their fate,(eco) toxicity and bioaccumulation potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Kuang, S.; Su, Y.; Ren, X.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y. Degradation of Diclofenac by Bisulfite Coupled with Iron and Manganous Ions: Dual Mechanism, DFT-Assisted Pathway Studies, and Toxicity Assessment. Water 2024, 16, 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141994
Wang H, Kuang S, Su Y, Ren X, Yang B, Sun Y. Degradation of Diclofenac by Bisulfite Coupled with Iron and Manganous Ions: Dual Mechanism, DFT-Assisted Pathway Studies, and Toxicity Assessment. Water. 2024; 16(14):1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141994
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hongbin, Shijie Kuang, Youlun Su, Xu Ren, Bowen Yang, and Yongliang Sun. 2024. "Degradation of Diclofenac by Bisulfite Coupled with Iron and Manganous Ions: Dual Mechanism, DFT-Assisted Pathway Studies, and Toxicity Assessment" Water 16, no. 14: 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141994
APA StyleWang, H., Kuang, S., Su, Y., Ren, X., Yang, B., & Sun, Y. (2024). Degradation of Diclofenac by Bisulfite Coupled with Iron and Manganous Ions: Dual Mechanism, DFT-Assisted Pathway Studies, and Toxicity Assessment. Water, 16(14), 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141994






